Effect of Integrated Organic–Inorganic Amendments on Leaf Physiological and Grain Starch Viscosity (Rapid Visco-Analyzer Profile) Characteristics of Rice and Ultisols Soil Quality
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Site Description
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Sampling and Analysis
2.3.1. Chemical Properties of Soil
2.3.2. Rice Leaf Physiological Attributes
2.3.3. Rice Grain Nutritional and Cooking Attributes
2.3.4. Rapid Visco-Analyzer (RAV) Profile Characteristics of the Rice Grains
2.3.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Soil Chemical Properties
3.2. Leaf Physiological Traits
3.3. Rice Grain Nutritional and Cooking Qualities
3.4. Starch Viscosity Profile Characteristics
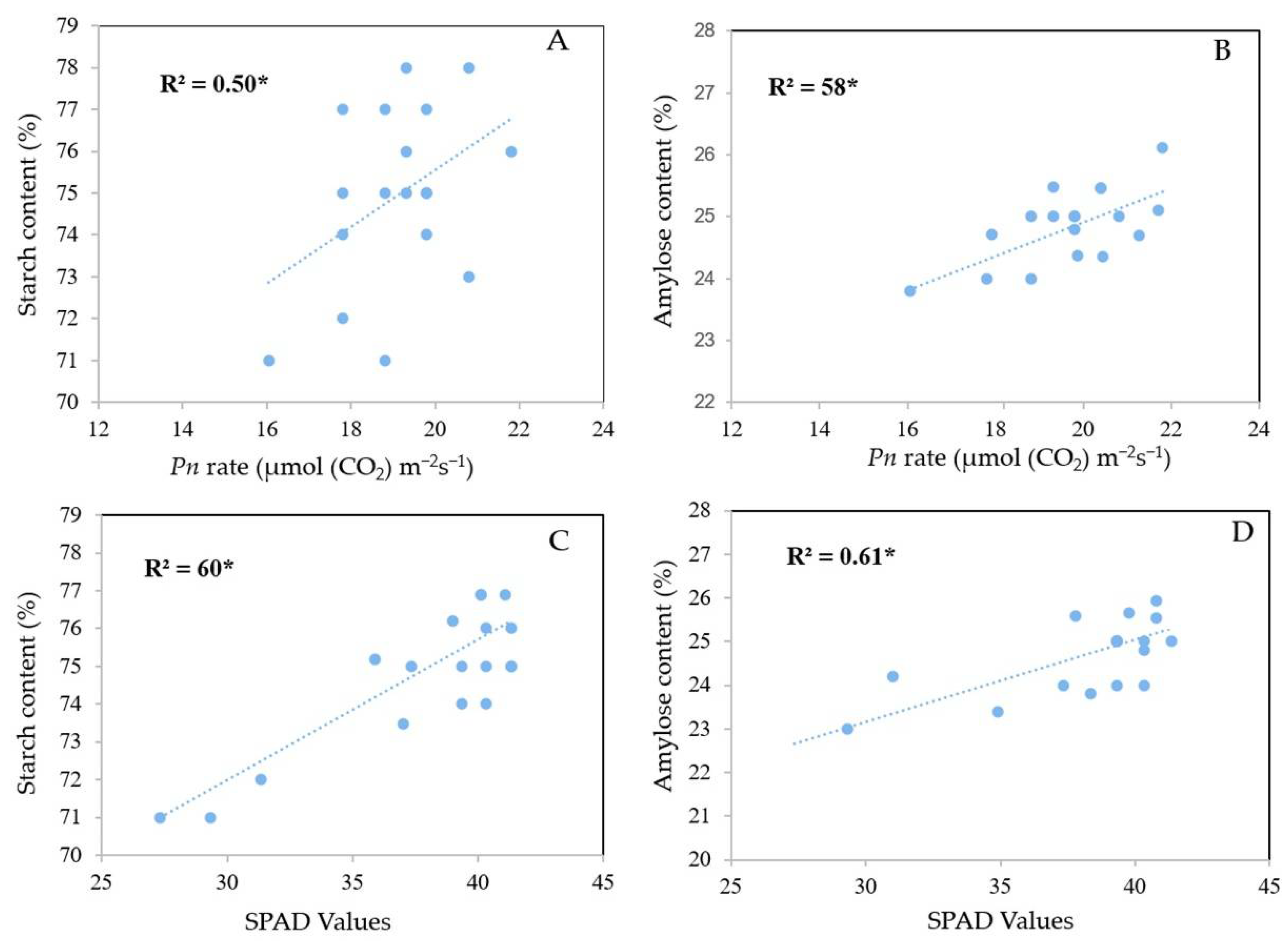
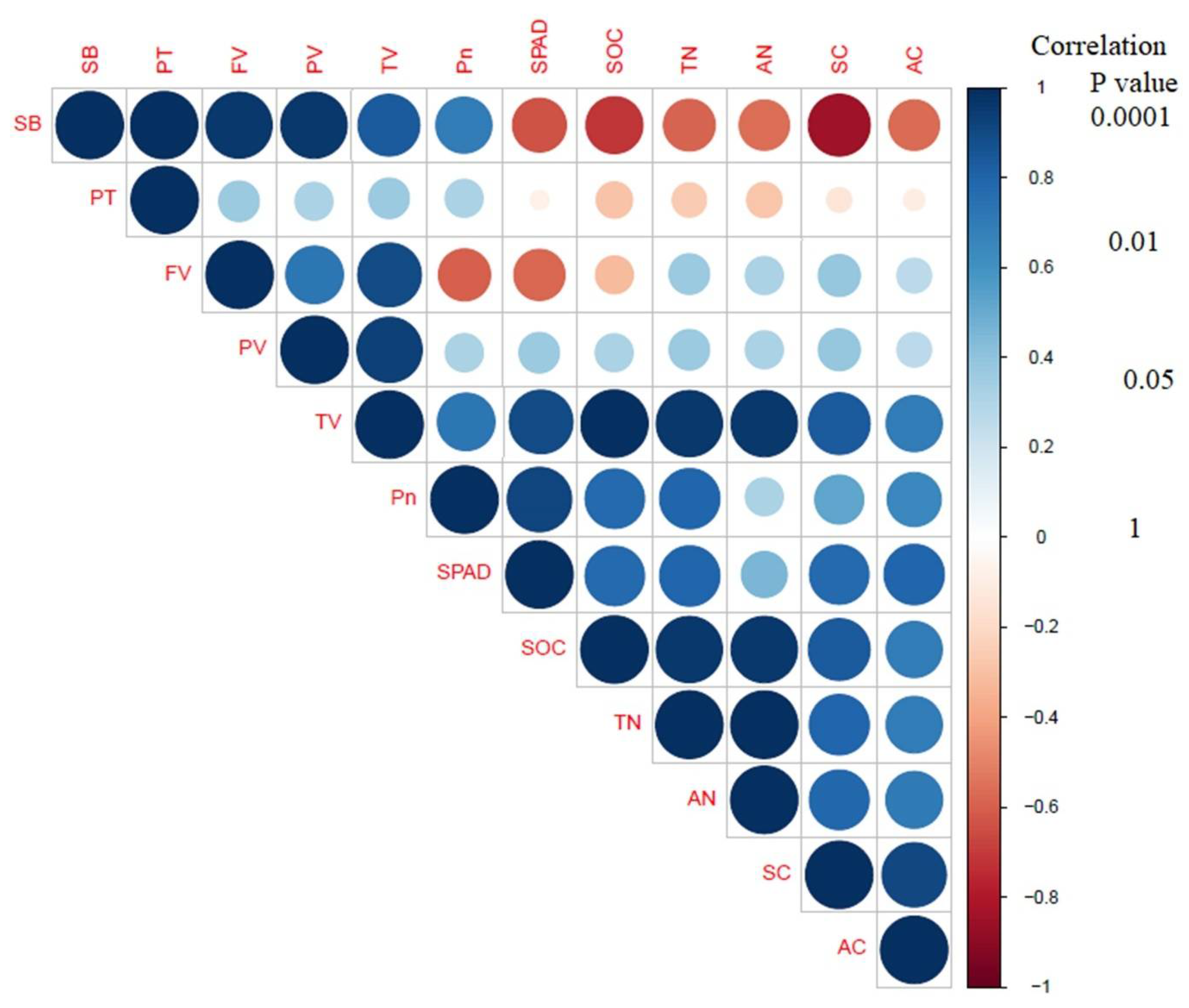
3.5. Relationship between Soil Chemical Traits, Leaf Physiological Activities, Grain Nutritional Attributes, and the RVA Profile
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Fischer, R.A.; Byerlee, D.; Edmeades, G.L. Crop yields and global food security: Will yield increase continue to feed the world? Eur. Rev. Agric. Econ. 2014, 43, 191–192. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.; Ding, W.; Luo, Y.; Yu, H.; Xu, Y.; Müller, C.; Xu, X.; Zhu, T. Nitrous oxide emissions from cultivated black soil: A case study in Northeast China and global estimates using empirical model. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2014, 28, 1311–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, C.; Wang, Y.; Hu, Y.; Christie, P.; Zhang, J.; Li, X. Maize yield and soil fertility with combined use of compost and inorganic fertilizers on a calcareous soil on the North China Plain. Soil Tillage Res. 2016, 155, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarma, B.; Borkotoki, B.; Narzari, R.; Kataki, R.; Gogoi, N. Organic amendments: Effect on carbon mineralization and crop productivity in acidic soil. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 152, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agegnehu, G.; Lakew, B.; Nelson, P.N. Cropping sequence and nitrogen fertilizer effects on the productivity and quality of malting barley and soil fertility in the Ethiopian highlands. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2014, 60, 1261–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, P.; Fan, C.; Zhang, Q.; Xiong, Z. Overdose fertilization induced ammoniaoxidizing archaea producing nitrous oxide in intensive vegetable fields. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 650, 1787–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.H.; Sun, R.B.; Xu, L.; Liang, J.N.; Wu, T.Y.; Zhou, J. Effects of micro-/nano-hydroxyapatite and phytoremediation on fungal community structure in copper contaminated soil. Eco. Envi. Saf. 2019, 174, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ju, X.T.; Xing, G.X.; Chen, X.P.; Zhang, S.L.; Zhang, L.J.; Liu, X.J.; Cui, Z.L.; Yin, B.; Christie, P.; Zhu, Z.L.; et al. Reducing environmental risk by improving N management in intensive Chinese agricultural systems. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 3041–3046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, X.; Wang, D.J.; Zhang, H.L.; Zhang, G.; Wei, Z.Q. Organic amendments affect phosphorus sorption characteristics in a paddy soil. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2013, 175, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, J.; Yang, L.Z.; Yan, T.M.; Xue, F.; Zhao, D. Nitrogen fertilizer reduction in rice production for two consecutive years in the Taihu Lake area. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2012, 146, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.F.; Chen, X.P.; Zhang, F.S.; Zhang, H.; Schroder, J.; Römheld, V. Fertilization and nitrogen balance in a wheat–maize rotation system in North China. Agron. J. 2006, 98, 938–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Z.; Zhang, F.; Miao, Y.; Sun, Q.; Li, F.; Chen, X.; Li, J.; Ye, Y.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, Q.; et al. Soil nitrate-N levels required for high yield maize production in the North China Plain. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2008, 82, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, A.; He, L.; Ali, I.; Ullah, S.; Khan, A.; Khan, A.; Akhtar, K.; Wei, S.; Zhao, Q.; Zhang, J.; et al. Manure combined with chemical fertilizer increases rice productivity by improving soil health, post-anthesis biomass yield, and nitrogen metabolism. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, 238–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; Li, J.; Zhu, P.; Peng, C.; Wang, J.; He, H.; Zhang, X. Long-term manure amendments enhance neutral sugar accumulation in bulk soil and particulate organic matter in a mollisol. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2014, 78, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seufert, V.; Ramankutty, N.; Foley, J.A. Comparing the yields of organic and conventional agriculture. Nature 2012, 485, 229–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mangalassery, S.; Kalaivanan, D.; Philip, P.S. Effect of inorganic fertilisers and organic amendments on soil aggregation and biochemical characteristics in a weathered tropical soil. Soil Tillage Res. 2019, 187, 144–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, U.; Shahid, M.; Tripathi, R.; Mohanty, S.; Kumar, A.; Bhattacharyya, P.; Lal, B.; Gautam, P.; Raja, R.; Panda, B.B.; et al. Variation of functional diversity of soil microbial community in sub-humid tropical rice-rice cropping system under long-term organic and inorganic fertilization. Ecol. Indic. 2017, 73, 536–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandyopadhyay, K.; Misra, A.; Ghosh, P.; Hati, K.E. ect of integrated use of farmyard manure and chemical fertilizers on soil physical properties and productivity of soybean. Soil Tillage Res. 2010, 110, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rome, I. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations; Duke University: Durham, NC, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, Z.; Zhai, L. Current Status and Forecast of Rice Consumption in Asian Countries. Consumer Econ. 2013, 29, 18–23. [Google Scholar]
- Adu-Kwarteng, E.; Ellis, W.; Oduro, I.; Manful, J. Rice grain quality: A comparison of local varieties with new varieties under study in Ghana. Food Control 2003, 14, 507–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.; Okadome, H.; Toyoshima, H.; Isobe, S.; Ohtsubo, K.I. Thermal and physicochemical properties of rice grain, flour and starch. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2000, 48, 2639–2647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derycke, V.; Veraverbeke, W.S.; Vandeputte, G.E.; De Man, W.; Hoseney, R.C.; Delcour, J.A. Impact of proteins on pasting and cooking properties of nonparboiled and parboiled rice. Cereal Chem. 2005, 82, 468–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robyt, J.F. Starch: Structure, properties, chemistry, and enzymology. In Glycoscience; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; p. 1437. [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura, Y.; Sakurai, A.; Inaba, Y. The fine structure of amylopectin in endosperm from Asian cultivated rice can be largely classified into two classes. Starch 2002, 54, 117–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Chen, M.; Lin, G.; Yang, Y.; Yu, X.; Wu, Y.; Xiong, F. Structural development and physicochemical properties of starch in caryopsis of super rice with different types of panicle. BMC Plant Biol. 2019, 19, 482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kesarwani, A.; Chiang, P.Y.; Chen, S.S. Rapid visco analyzer measurements of japonica rice cultivars to study interrelationship between pasting properties and farming system. Int. J. Agron. 2016, 2016, 3595326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peisong, H.; Huqu, Z.; Shaoqing, T.; Jianmin, W. Rapid evaluation of rice cooking and palatability quality by RVA profile. Zuo Wu Xue Bao 2004, 30, 519–524. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.F.; Zhang, Y.D.; Zhen, Z.H.U.; Ling, Z.H.A.O.; Zhao, Q.Y.; Ling, X.U.; Wang, C.L. Inheritance analysis and QTL mapping of rice starch viscosity (rapid visco analyzer profile) characteristics. Rice Sci. 2008, 15, 186–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckles, D.M.; Thitisaksakul, M. How environmental stress affects starch composition and functionality in cereal endosperm. Starch-Starke 2014, 66, 58–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plett, D.C.; Ranathunge, K.; Melino, V.J.; Kuya, N.; Uga, Y.; Kronzucker, H.J. The intersection of nitrogen nutrition and water use in plants: New paths toward improved crop productivity. J. Exp. Bot. 2020, 71, 4452–4468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Zhou, Q.; Li, E.; Yuan, L.; Wang, W.; Zhang, H.; Gu, J. Effects of nitrogen fertilizer on structure and physicochemical properties of ‘super’rice starch. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 239, 116237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.; Haixiang, Z.; Wenzhe, L.; Zhi, D.; Qinyang, Z.; Wenzhu, C.; Shaohua, W.; Yanfeng, D. Nitrogen fertilizer at heading stage effectively compensates for the deterioration of rice quality by affecting the starch-related properties under elevated temperatures. Food Chem. 2019, 277, 455–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Victoria, R.; Banwart, S.; Black, H.; Ingram, J.; Joosten, H.; Milne, E.; Noellemeyer, E. The Benefits of Soil Carbon. In UNEP Year Book 2012: Emerging Issues in Our Global Environment; United Nations Environment Programme: Nairobi, Kenya, 2012; pp. 19–32. [Google Scholar]
- Ramesh, T.; Bolan, N.S.; Kirkham, M.B.; Wijesekara, H.; Kanchikerimath, M.; Rao, C.S.; Sandeep, S.; Rinklebe, J.; Ok, Y.S.; Choudhury, B.U.; et al. Soil organic carbon dynamics: Impact of land use changes and management practices: A review. Adv. Agron. 2019, 156, 1–107. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, K.; Zhao, Y.; Xu, X.; Hai, N.; Huang, B.; Deng, W. Effects of long-term fertilization and residue management on soil organic carbon changes in paddy soils of China: A meta-analysis. Agric. Eco. Environ. 2015, 204, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Mesquita Alves, J.; de Lima, A.S.; de Mesquita, E.F.; Junior, S.D.O.M.; de Sousa Ferreira, R.; da Silva, F.L.; da Mota Santos, J. Gas exchange and chlorophyll content in tomato grown under different organic fertilizers and biofertilizer doses. Afr. J. Agric. Res. 2018, 13, 2256–2262. [Google Scholar]
- Nkcukankcuka, M.; Jimoh, M.O.; Griesel, G.; Laubscher, C.P. Growth characteristics, chlorophyll content and nutrients uptake in Tetragonia decumbens Mill. cultivated under different fertigation regimes in hydroponics. Crop Pasture Sci. 2021, 73, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Liang, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Hao, W.; Lin, X.; Wu, X.; Luo, A. The interactive effects of water and fertilizer on photosynthetic capacity and yield in tomato plants. Aust. J. Crop Sci. 2012, 6, 200–209. [Google Scholar]
- Li, R.; Li, M.; Ashraf, U.; Liu, S.; Zhang, J. Yield Analysis of Early Indica Rice Zhenguiai 1 in South China. China Rice 2006, 1, 17. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Tian, H.; Liu, J.; Pan, S. Pattern and change of soil organic carbon storage in China: 1960s–1980s. Tellus B Chem. Phys. Meteorol. 2003, 55, 416–427. [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan, D.M.; Moore, A.D.; Brewer, L.J. Soil Organic Matter as a Soil Health Indicator: Sampling, Testing, and Interpretation; Oregon State University Extension Service; Oregon State University: Corvallis, OR, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Ohyama, T.; Ito, M.; Kobayashi, K.; Araki, S.; Yasuyoshi, S.; Sasaki, O.; Yamazaki, T.; Soyama, K.; Tanemura, R.; Mizuno, Y. Analytical procedures of N, P, K contents in plant and manure materials using H2SO4-H2O2 Kjeldahl digestion method. Bull. Fac. Agric. Niigata Univ. 1991, 43, 110–120. [Google Scholar]
- Jackson, M.L. Soil Chemical Analysis—Advanced Course; University of Wisconsin: Madison, WI, USA, 1956; p. 991. [Google Scholar]
- Page, A.L.; Keeney, D.R. Methods of Soil Analysis; American Society of Agronomy: Madison, WI, USA, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Olsen, S.R. Estimation of available phosphorus in soils by extraction with sodium bicarbonate. Colo. Agric. Exp. Stn. Sci. J. Ser. 1954, 418, 18–19. [Google Scholar]
- Leaf, A.L. Determination of Available Potassium in Soils of Forest Plantations. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1958, 22, 458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z. Grain Quality and Its Analysis Technology; Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, T.; Jackson, D.S.; Wehling, R.L.; Geera, B. Comparison of amylose determination methods and the development of a dual wavelength iodine binding technique. Cereal Chem. 2008, 85, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujihara, S.; Sasaki, H.; Aoyagi, Y.; Sugahara, T. Nitrogen-to-protein conversion factors for some cereal products in Japan. J. Food Sci. 2008, 73, 204–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Zhang, Y.; Xiao, H.; Lin, W.; Li, H.; Qin, S. The relationship between characteristics of rice raw material and quality of rice noodle. Cereal Feed. Ind. 2005, 9, 21–24. [Google Scholar]
- Ruan, S.L.; Mao, G.Q. Study on rice cooking properties. Cereal Feed. Ind. 2004, 10, 25–26. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, L.L.; Zhou, X.Q.; Xiong, N.; Sun, T.L.; Liu, L.; Ni, S.S.; Meng, H.; Peng, Z.B. Research on Sensory Evaluation Methods for Pressed and Fresh Rice Noodles. Mod. Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 32, 253–261. [Google Scholar]
- American Association of Cereal Chemists. Approved Methods of Analysis, 10th ed.; American Association of Cereal Chemists (AACC): Saint Paul, MI, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Raina, C.S.; Singh, S.; Bawa, A.S.; Saxena, D.C. A comparative study of Indian rice starches using different modification model solutions. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2007, 40, 885–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adekiya, A.O.; Agbede, T.M.; Aboyeji, C.M.; Dunsin, O.; Simeon, V.T. Effects of biochar and poultry manure on soil characteristics and the yield of radish. Sci. Hortic. 2019, 243, 457–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bitew, Y.; Alemayehu, M. Impact of crop production inputs on soil health: A review. Asian J. Plant Sci. 2017, 16, 109–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purakayastha, T.J.; Huggins, D.R.; Smith, J.L. Carbon sequestration in native prairie, perennial grass, no-till, and cultivated Palouse silt loam. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2008, 72, 534–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murmu, K.; Swain, D.K.; Ghosh, B.C. Comparative assessment of conventional and organic nutrient management on crop growth and yield and soil fertility in tomato-sweet corn production system. Aust. J. Crop Sci. 2013, 7, 1617–1626. [Google Scholar]
- Wittmann, C.; Aschan, G.; Pfanz, H. Leaf and twig photosynthesis of young beech (Fagus sylvatica) and aspen (Populus tremula) trees grown under different light regime. Basic Appl. Ecol. 2001, 2, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Xiong, Z.; Wang, J.; Xu, X.; Huang, Q.; Shen, Q. Mitigating net global warming potential and greenhouse gas intensities by substituting chemical nitrogen fertilizers with organic fertilization strategies in rice–wheat annual rotation systems in China: A 3-year field experiment. Ecol. Eng. 2015, 81, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daszkowska-Golec, A.; Szarejko, I. Open or Close the Gate—Stomata Action under the Control of Phytohormones in Drought Stress Conditions. Front. Plant Sci. 2013, 4, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, M.; Fitzgerald, M.A. Proteins in rice grains influence cooking properties. J. Cereal Sci. 2002, 36, 285–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jun, J.; Dayong, X.; Yixia, C.; Shuyun, H.; Min, G.; Qingsen, Z. Effect of N-fertilizer on main quality characters of rice and RVA profile parameters. Zuo Wu Xue Bao 2004, 30, 154–158. [Google Scholar]
- Bryant, R.J.; Anders, M.; McClung, A. Impact of production practices on physicochemical properties of rice grain quality. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2012, 92, 564–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamaki, M.; Yoshimatsu, K.; Horino, T. Relationships between the duration of organic farming culture and amylographic characteristics and mineral contents of rice. Jpn. J. Crop Sci. 1995, 64, 677–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Champagne, E.T.; Bett-Garber, K.L.; Grimm, C.C.; McClung, A.M. Effects of organic fertility management on physicochemical properties and sensory quality of diverse rice cultivars. Cereal Chem. 2007, 84, 320–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Wang, Y.; Chen, T.; Zheng, J.; Sun, Y.; Chi, D. Soil nitrogen regulation using clinoptilolite for grain filling and grain quality improvements in rice. Soil Tillage Res. 2020, 199, 104547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuan, Y.; Yi, Y.; Liang, H.E.; Wei, S.; Chen, N.; Jiang, L.; Li, T. Amylose content and RVA profile characteristics of noodle rice under different conditions. Agron. J. 2020, 112, 117–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.; Pal, N.; Mahajan, G.; Singh, S.; Shevkani, K. Rice grain and starch properties: Effects of nitrogen fertilizer application. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 86, 219–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, I.; Iqbal, A.; Ullah, S.; Muhammad, I.; Yuan, P.; Zhao, Q.; Yang, M.; Zhang, H.; Huang, M.; Liang, H.; et al. Effects of Biochar Amendment and Nitrogen Fertilizer on RVA Profile and Rice Grain Quality Attributes. Foods 2022, 11, 625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

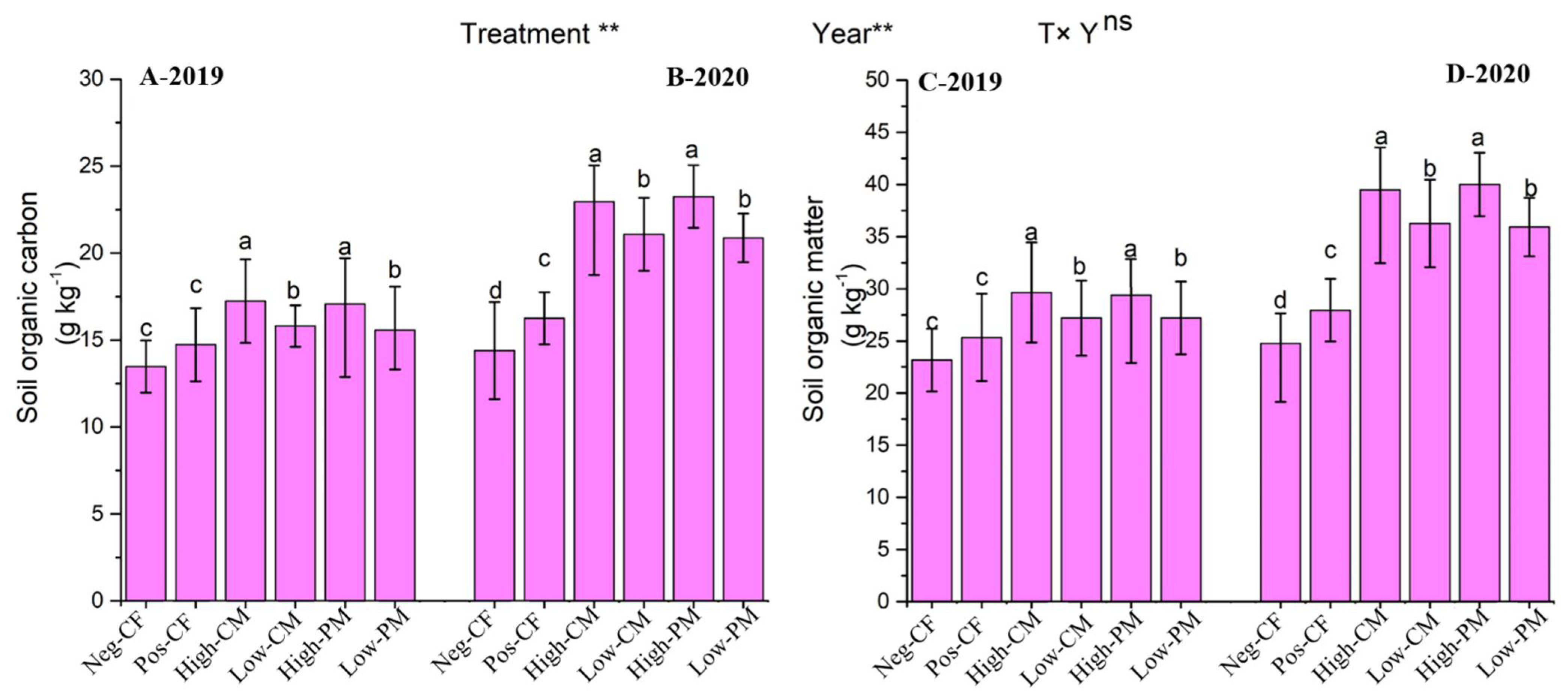
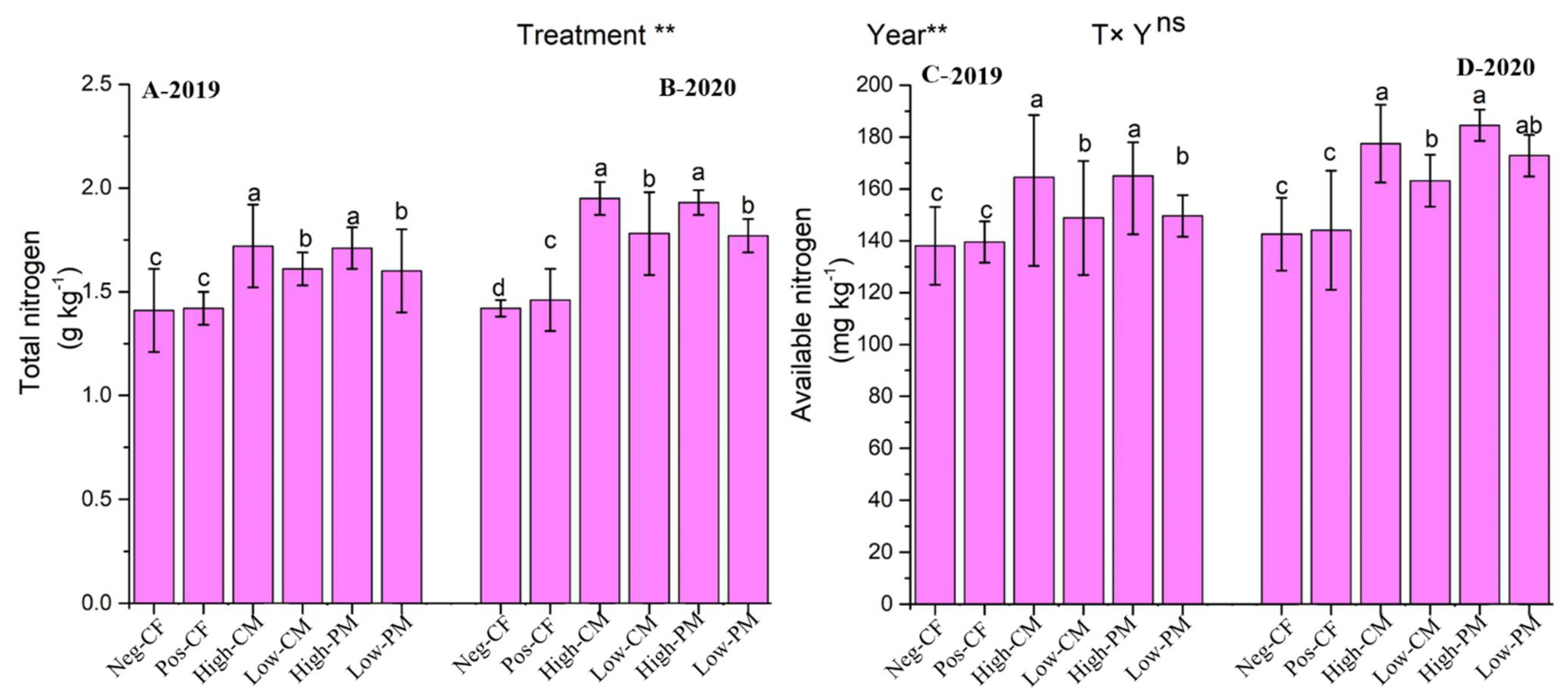
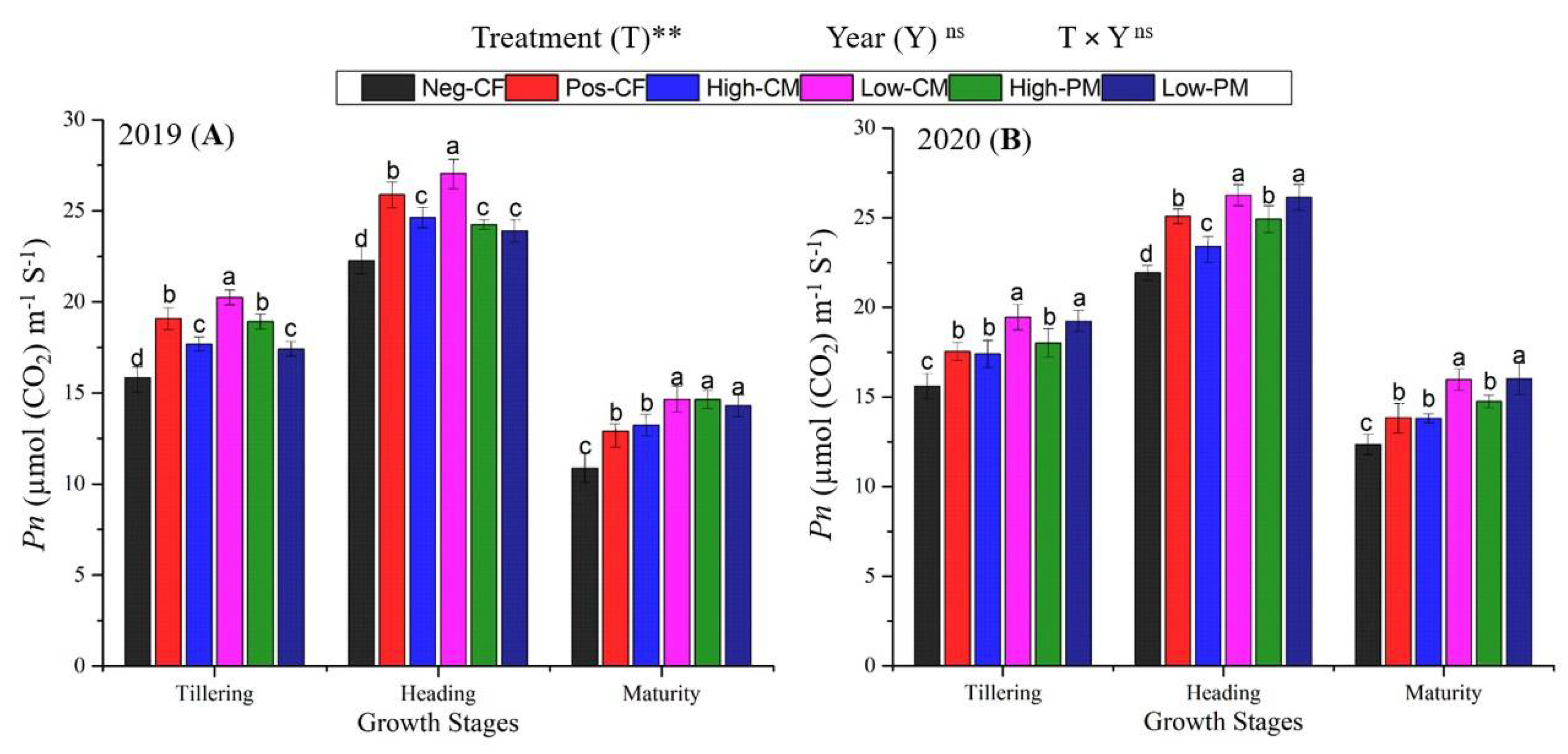
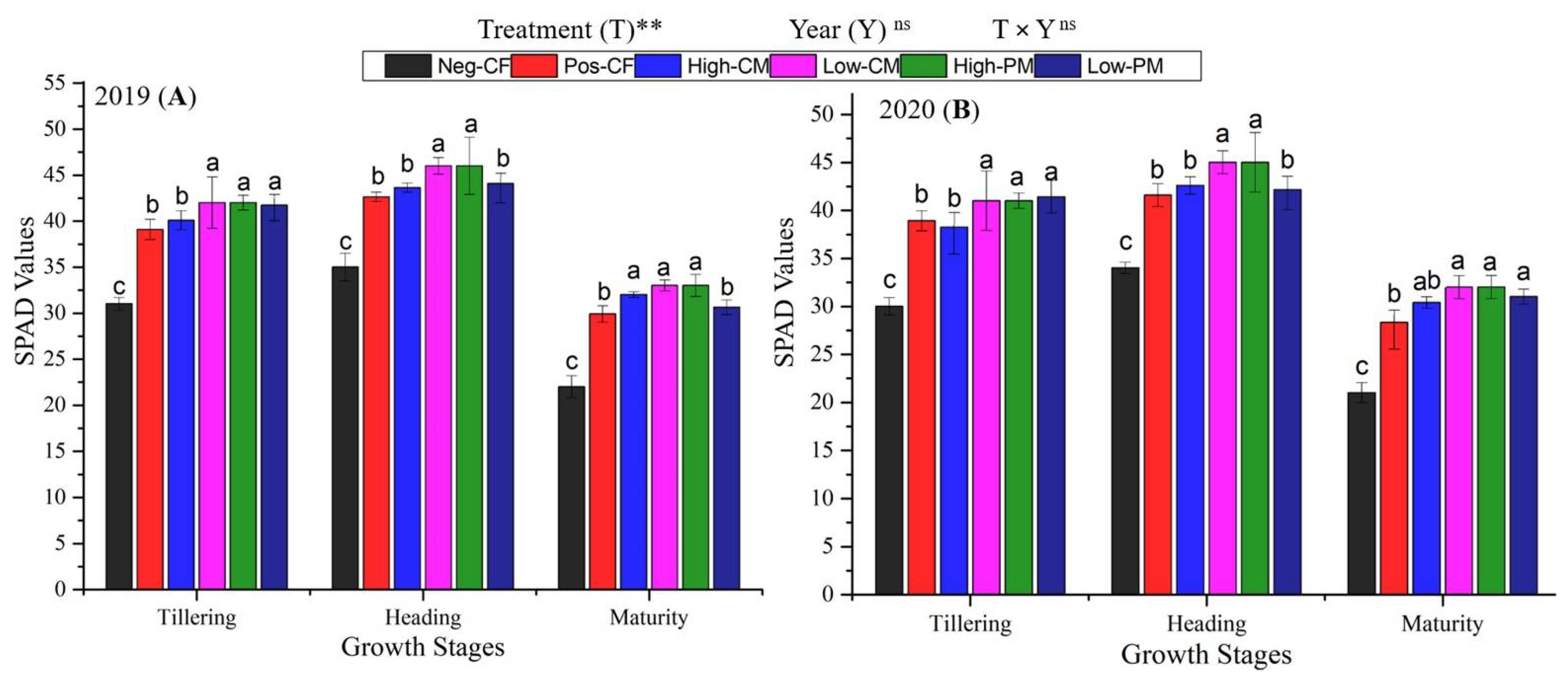

| Properties | Soil | CM | PM |
|---|---|---|---|
| pH (water) | 5.95 | 7.75 | 7.95 |
| SOC (g kg−1) | 15.74 | 146.33 | 164.22 |
| SOM (g kg−1) | 25.08 | 254.63 | 282.42 |
| Total N (g kg−1) | 1.41 | 9.76 | 13.58 |
| Total P (g kg−1) | 0.75 | 10.12 | 7.32 |
| Total K (g kg−1) | - | 14.22 | 9.76 |
| Available N (mg kg−1) | 134.7 | - | - |
| Available P (mg kg−1) | 23.12 | - | - |
| Available K (mg kg−1) | 233.3 | - | - |
| C:N ratio | 7.16 | 14.92 | 12.98 |
| Treatment | N (kg/ha) | Urea (kg/ha) | CM, PM, (kg/ha) | Basal Fertilization (kg/ha) | Tillering (kg/ha) | Panicle Initiation (kg/ha) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Neg-CF: | 0 | 0 | 0 | KCl: 128, P2O2: 397 | KCl: 128 | Urea: 00 |
| Pos-CF: | 150 | 322 | 0 | Urea: 192, KCl: 128, P2O2: 397 | KCl: 128, Urea: 65 | Urea: 65 |
| High-CM | 150 | 130 | 9188 | Urea: 0, CM: 9188, KCl: 128, P2O2: 397 | KCl: 128, Urea: 65 | Urea: 65 |
| Low-CM | 150 | 225 | 4572 | Urea: 94, CM: 4572, KCl: 128, P2O2: 397 | KCl: 128, Urea: 65 | Urea: 65 |
| High-PM | 150 | 128 | 6623 | Urea: 0, PM: 6623, KCl: 128, P2O2: 397 | KCl: 128, Urea: 65 | Urea: 65 |
| Low-PM | 150 | 225 | 3290 | Urea: 94, PM: 3290, KCl: 128, P2O2: 397 | KCl: 128, Urea: 65 | Urea: 65 |
| Year | Treatment | SDV | ER (%) | Eve (%) | PC (%) | SC (%) | AC (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2019 | Neg-CF | 6.27 a | 278 a | 92 a | 5.85 c | 71 d | 23.00 c |
| Pos-CF | 5.92 a | 273 a | 92 a | 6.55 b | 73 c | 24.00 b | |
| High-CM | 5.52 a | 285 a | 92 a | 6.41 b | 74 b | 24.00 b | |
| Low-CM | 5.44 a | 279 a | 93 a | 7.20 a | 76 a | 25.64 a | |
| High-PM | 5.53 a | 290 a | 91 a | 6.45 b | 74 b | 24.66 b | |
| Low-PM | 5.80 a | 280 a | 93 a | 7.35 a | 76 a | 26.68 a | |
| Average | 5.75 b | 280 a | 92 b | 6.64 a | 74 a | 24.66 a | |
| 2020 | Neg-CF | 6.89 a | 265 a | 93 a,b | 5.72 c | 70 c | 21.00 d |
| Pos-CF | 6.81 a | 258 a,b | 94 a | 6.54 b | 71 c | 23.00 c | |
| High-CM | 6.11 a | 260 a,b | 93 a,b | 6.58 b | 75 b | 24.07 b | |
| Low-CM | 6.34 a | 252 a,b | 94 a | 7.46 a | 76 a | 26.11 a | |
| High-PM | 6.84 a | 255 a,b | 93 a,b | 6.57 b | 75 b | 24.11 b | |
| Low-PM | 6.66 a | 258 a,b | 94 a | 7.40 a | 77 a | 26.18 a | |
| Average | 6.61 a | 258 b | 94 a | 6.71 a | 74 a | 24.08 a | |
| ANOVA | |||||||
| Treatment (T) | ns | ns | ns | * | ** | ** | |
| Year (Y) | * | * | * | ns | ns | ns | |
| T × Y | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | |
| Treatment | Peak Viscosity | Tough Viscosity | Final Viscosity | Set Back | Peak Time | Pasting Temp | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2019 | Neg-CF | 2015 b | 2032 b | 4247 a | 2127 b | 6.69 b | 90.42 a |
| Pos-CF | 1928 b | 1858 c | 4080 b | 2221 a | 6.38 d | 90.70 a | |
| High-CM | 2625 a | 2333 a | 4468 a | 2134 b | 6.51 c | 87.72 b | |
| Low-CM | 1912 b | 1863 c | 3990 b | 2215 a | 6.49 c | 91.20 a | |
| High-PM | 2038 b | 1882 c | 4025 b | 2143 b | 6.60 b | 90.67 a | |
| Low-PM | 2347 a,b | 2148 b | 4305 a | 2157 b | 6.78 a | 85.02 b | |
| Mean | 2144 b | 2019 b | 4186 b | 2166 a | 6.57 a | 89.29 a | |
| 2020 | Neg-CF | 3829 a,b | 3024 a,b | 5047 b | 1967 c | 6.20 a,b | 82.10 a,b |
| Pos-CF | 3602 b | 3080 b | 4954 b | 2005 a | 6.09 b | 82.62 a,b | |
| High-CM | 3724 a,b | 3128 a,b | 4923 b | 1795 a | 6.16 a,b | 83.95 a | |
| Low-CM | 3846 a | 3168 a,b | 5031 b | 1864 b | 6.18 a,b | 82.62 a | |
| High-PM | 3774 a,b | 3143 a,b | 4949 b | 1924 b | 6.20 a,b | 83.67 a,b | |
| Low-PM | 3721 a | 3236 a | 5241 a | 1812 c | 6.22 a | 81.25 c | |
| Mean | 3749 a | 3130 a | 5024 a | 1895 b | 6.17 b | 82.70 b | |
| Treatment (T) | * | * | * | * | * | * | |
| Year (Y) | * | * | * | * | * | * | |
| T × Y | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Iqbal, A.; Ali, I.; Zhao, Q.; Yuan, P.; Huang, M.; Liang, H.; Zeeshan, M.; Muhammad, I.; Wei, S.; Jiang, L. Effect of Integrated Organic–Inorganic Amendments on Leaf Physiological and Grain Starch Viscosity (Rapid Visco-Analyzer Profile) Characteristics of Rice and Ultisols Soil Quality. Agronomy 2022, 12, 863. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12040863
Iqbal A, Ali I, Zhao Q, Yuan P, Huang M, Liang H, Zeeshan M, Muhammad I, Wei S, Jiang L. Effect of Integrated Organic–Inorganic Amendments on Leaf Physiological and Grain Starch Viscosity (Rapid Visco-Analyzer Profile) Characteristics of Rice and Ultisols Soil Quality. Agronomy. 2022; 12(4):863. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12040863
Chicago/Turabian StyleIqbal, Anas, Izhar Ali, Quan Zhao, Pengli Yuan, Min Huang, He Liang, Muhammad Zeeshan, Ihsan Muhammad, Shanqing Wei, and Ligeng Jiang. 2022. "Effect of Integrated Organic–Inorganic Amendments on Leaf Physiological and Grain Starch Viscosity (Rapid Visco-Analyzer Profile) Characteristics of Rice and Ultisols Soil Quality" Agronomy 12, no. 4: 863. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12040863
APA StyleIqbal, A., Ali, I., Zhao, Q., Yuan, P., Huang, M., Liang, H., Zeeshan, M., Muhammad, I., Wei, S., & Jiang, L. (2022). Effect of Integrated Organic–Inorganic Amendments on Leaf Physiological and Grain Starch Viscosity (Rapid Visco-Analyzer Profile) Characteristics of Rice and Ultisols Soil Quality. Agronomy, 12(4), 863. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12040863










