Low-Cost Smart Farm Irrigation Systems in Kherson Province: Feasibility Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- To investigate climate conditions.
- To study water-use productivity.
- To estimate the payback period of a retrofitted irrigation system.
2. Materials and Methods
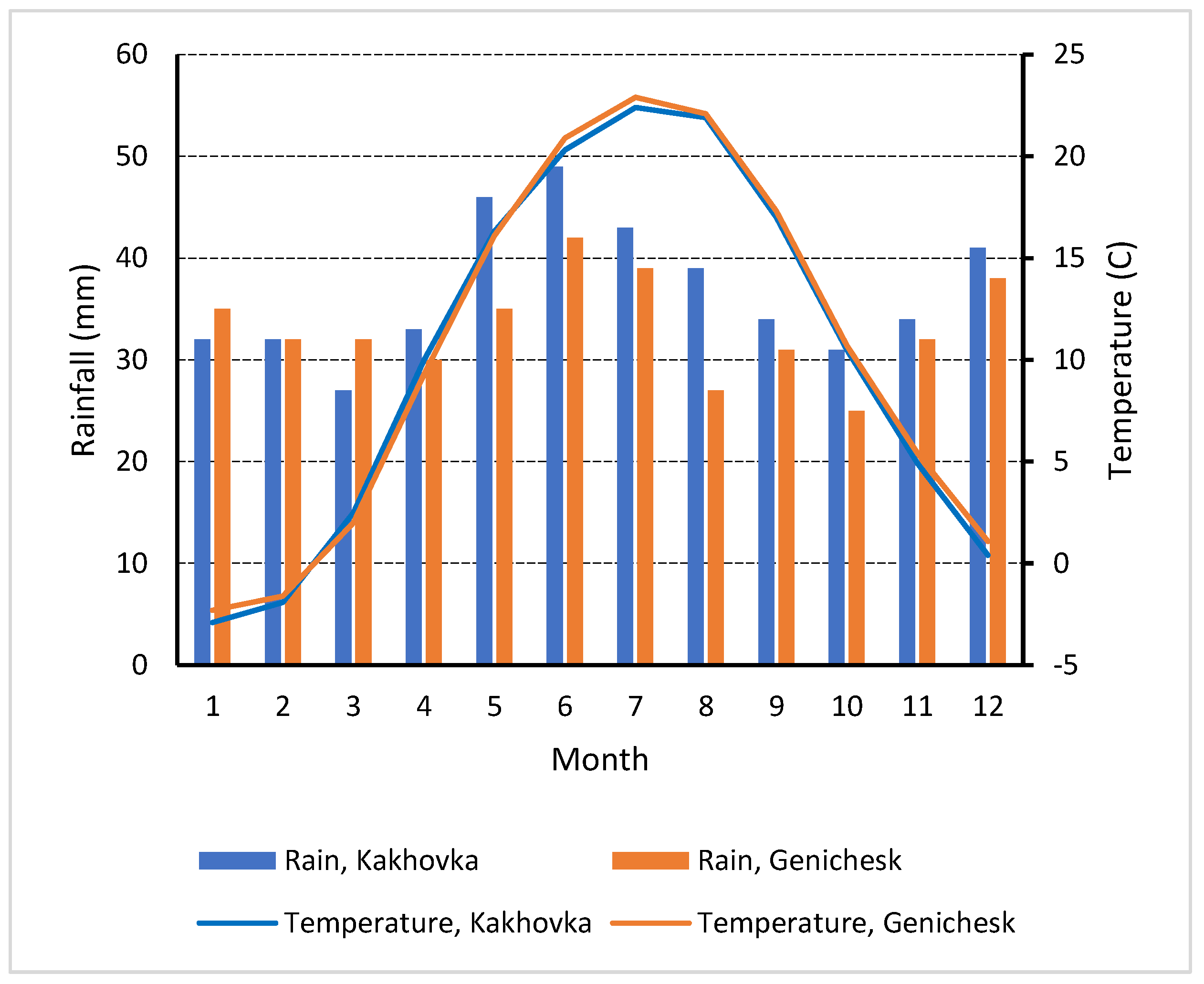
2.1. Climate
2.2. Irrigation Water Supply
2.3. Field Experiments
2.4. Component and Functions of a Smart Irrigation System
- vegetation index
- normalized difference vegetation index
- heterogeneity of plants
- humidity index
- heterogeneity of moisture
2.5. Water-Use Efficiency
2.6. Economic Indicators
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
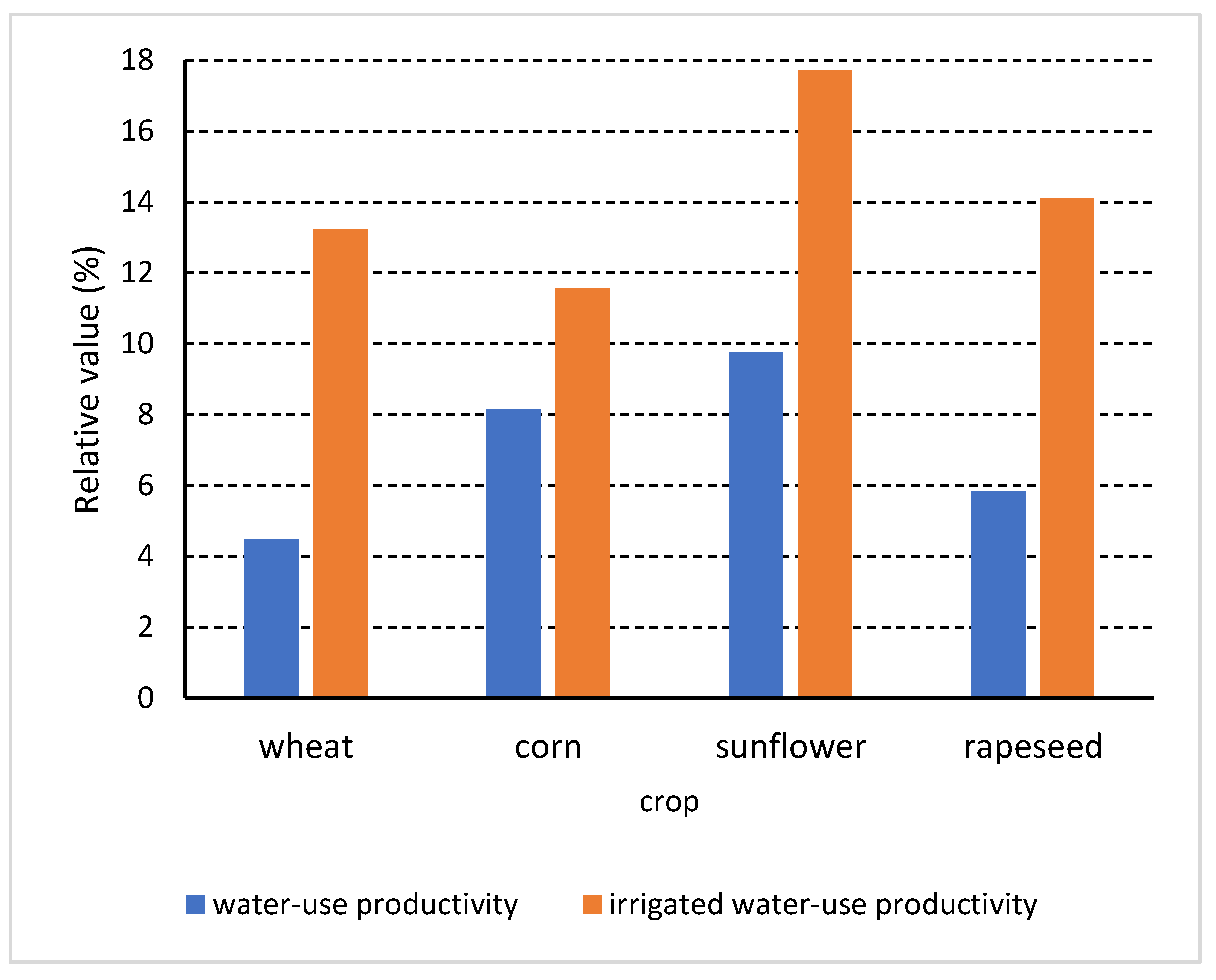
3.1. Water-Use Productivity
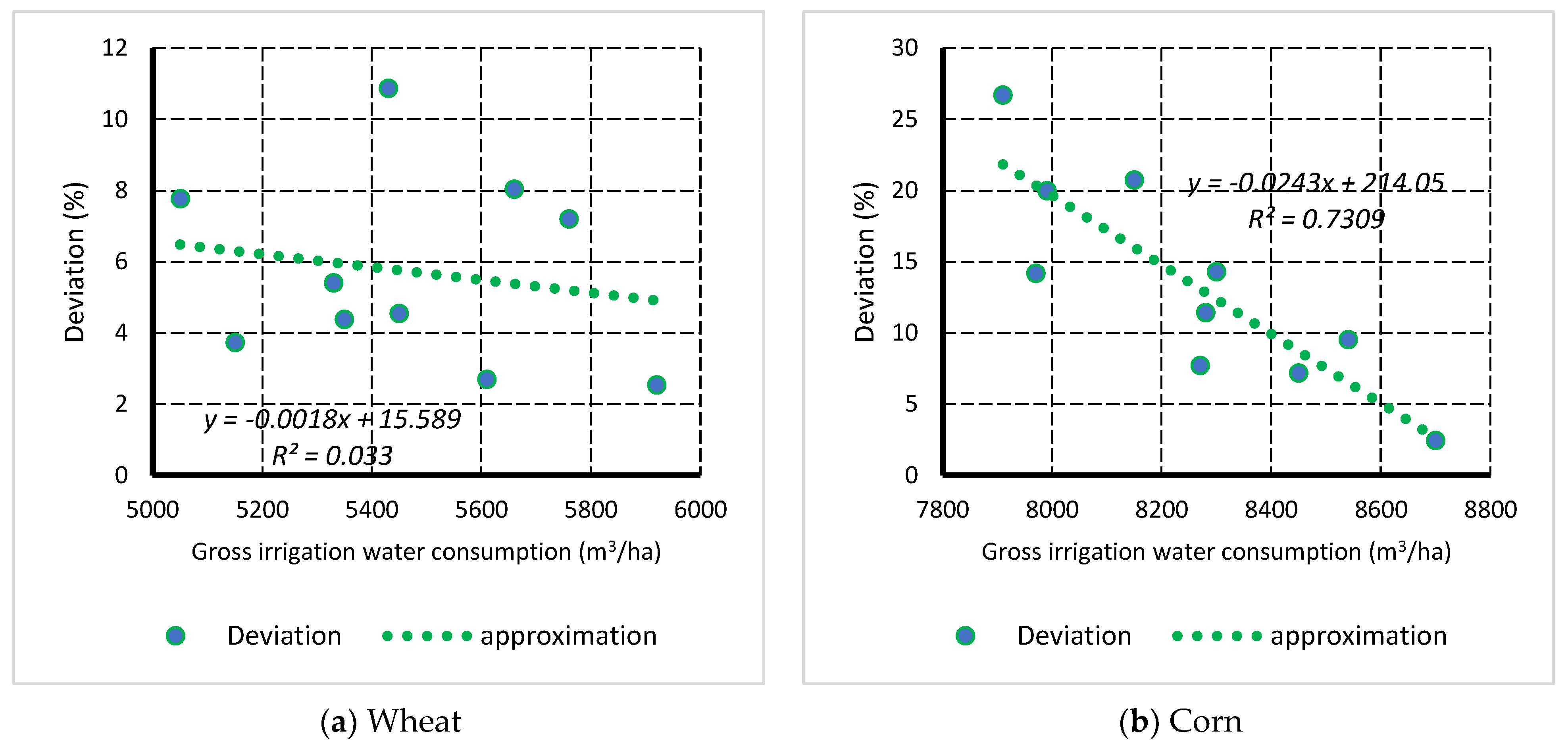
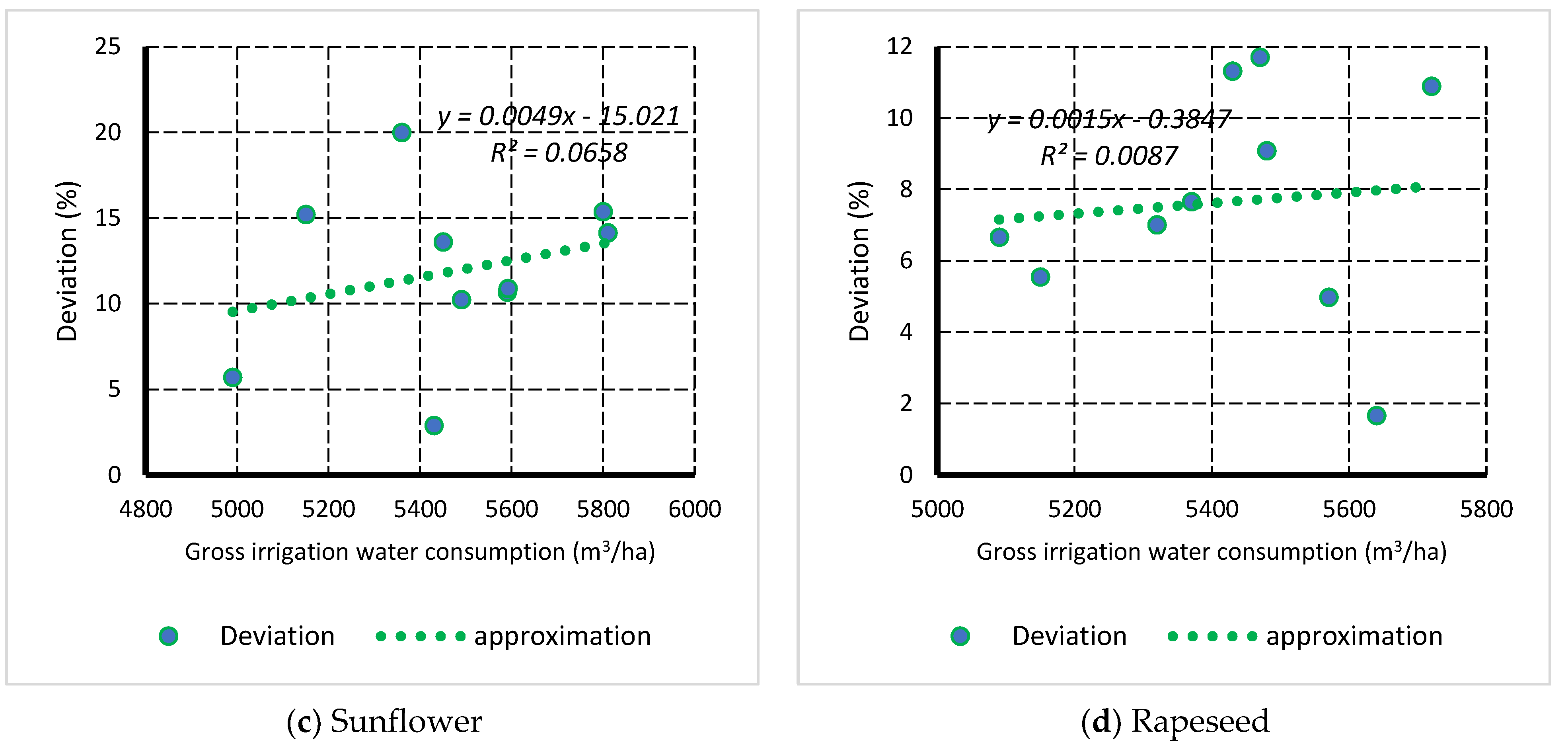
3.2. Relationship between Deviation of Yield and Gross Water Consumption
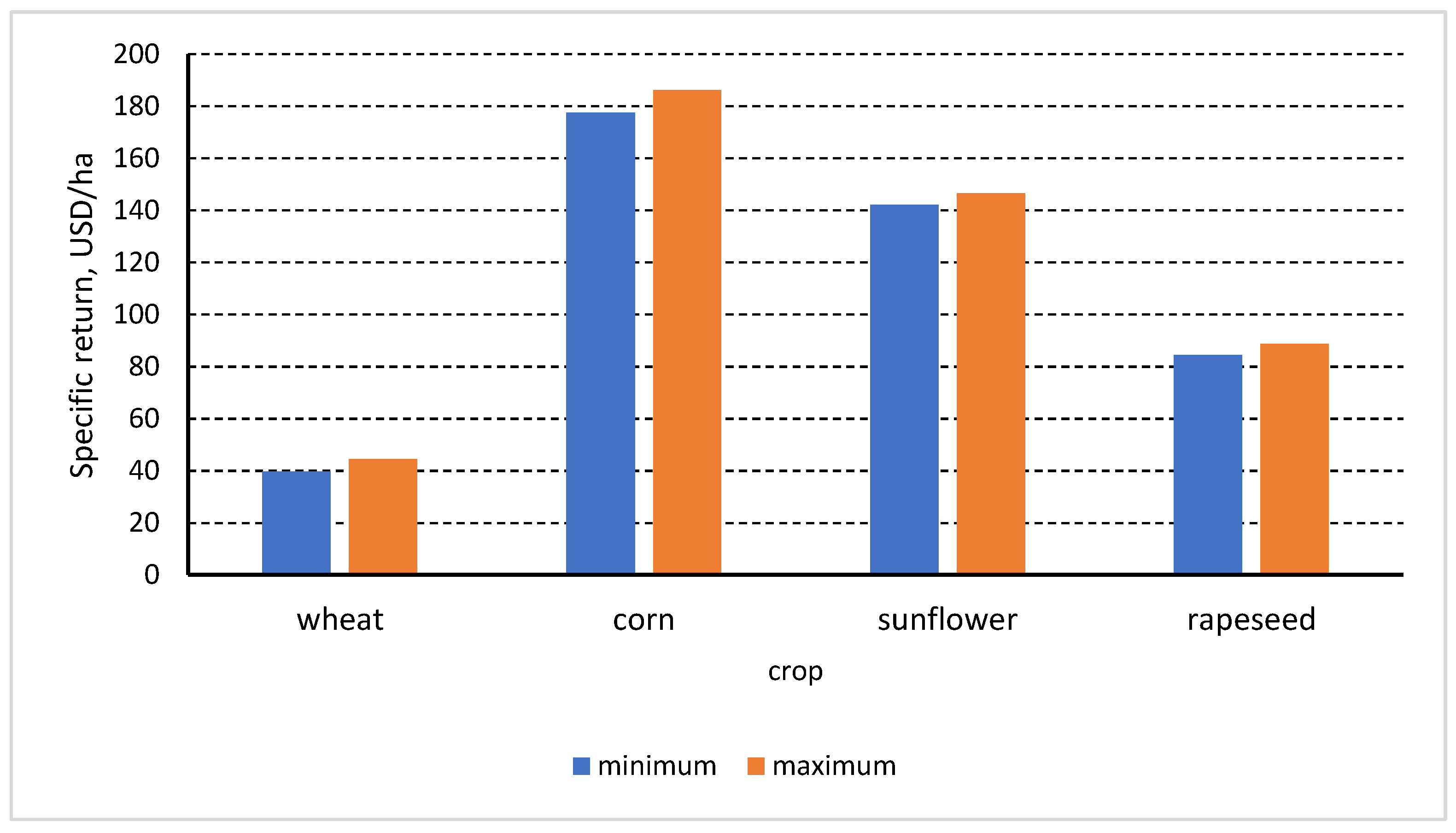
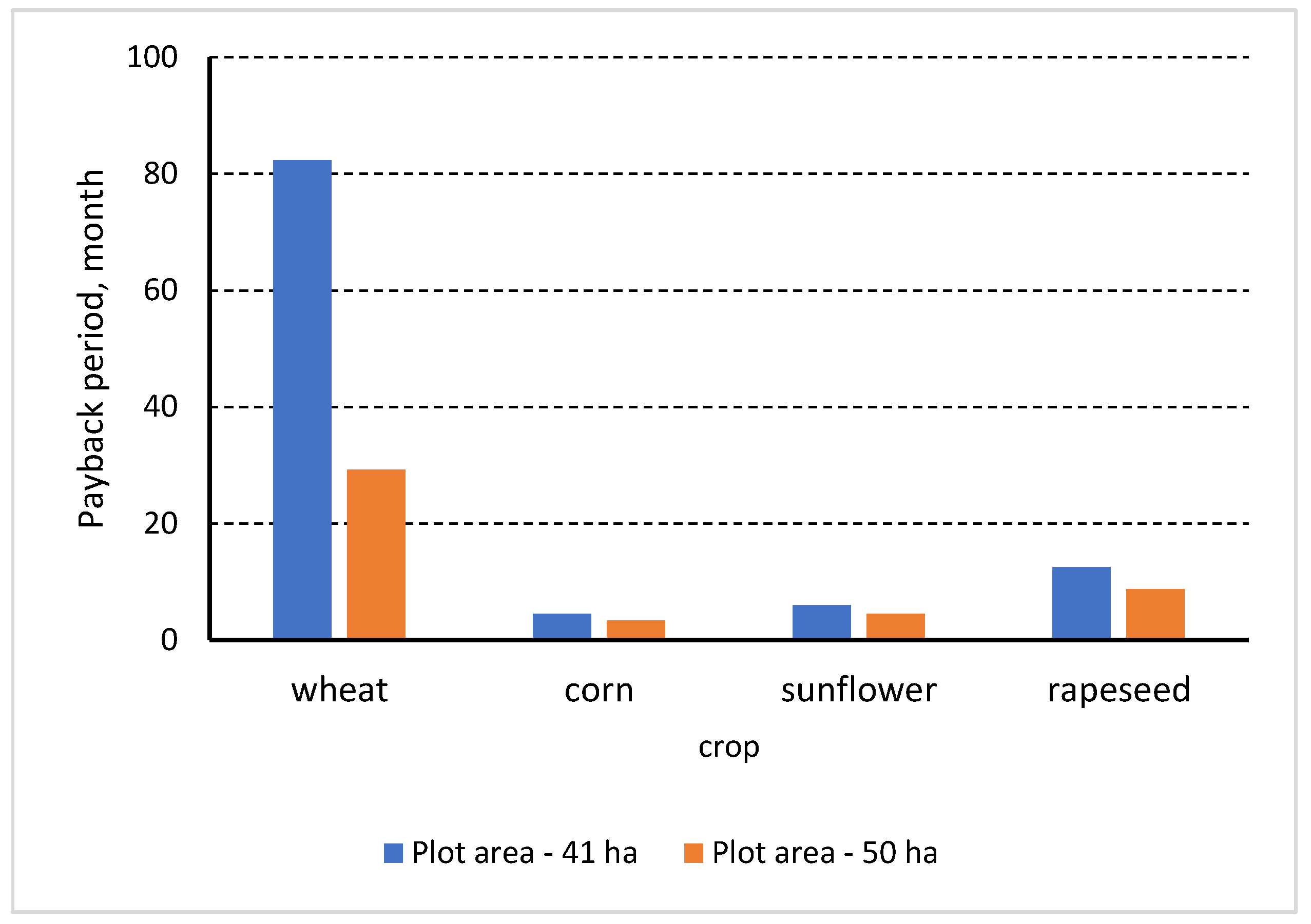
3.3. Economic Efficiency
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alexandratos, N.; Bruinsma, J. World Agriculture Towards 2030/2050: The 2012 Revision; ESA Work. Pap. No.12–03; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2012; p. 153. Available online: http://www.fao.org/3/ap106e/ap106e.pdf (accessed on 2 October 2021).
- Pereira, L.S. Water, Agriculture and Food: Challenges and Issues. Water Resour. Manag. 2017, 31, 2985–2999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, W.; Kamran, F. A hybrid PV/utility powered irrigation water pumping system for rural agricultural areas. Cogent Eng. 2018, 5, 1466383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassas, M. Aridity, drought and desertification. In Arab Environment Future Challenges; Arab Forum for Environment and Development: Beirut, Lebanon, 2008; pp. 95–110. Available online: https://research.fit.edu/media/site-specific/researchfitedu/coast-climate-adaptation-library/middle-east/regional---middle-east/Tolba--Saab.-2008.-Middle-East-Arab-Environments-Future-Challenges.pdf (accessed on 22 September 2021).
- Arable Land By Country. 2021. Available online: https://worldpopulationreview.com/country-rankings/arable-land-by-country (accessed on 22 September 2021).
- Agricultural Irrigated Land (% of Total Agricultural Land)-Country Ranking. Available online: https://www.indexmundi.com/facts/indicators/AG.LND.IRIG.AG.ZS/rankings (accessed on 22 September 2021).
- Lykhovyd, P. Irrigation Needs in Ukraine According to Current Aridity Level. J. Ecol. Eng. 2021, 22, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Review of World Water Resources by Country; Food and Agriculture Organization of The United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2003; Available online: https://www.fao.org/3/y4473e/y4473e00.htm (accessed on 22 November 2021).
- Ladychuk, D.; Shaporynska, N.; Lavrenko, S.; Lavrenko, N. The methods for determining agrolandscape typicality for projects of water supply construction. AgroLife Sci. J. 2021, 10, 121–129. [Google Scholar]
- García, I.F.; Montesinos, P.; Poyato, E.C.; Díaz, J.R. Optimal design of pressurized irrigation networks to minimize the operational cost under different management scenarios. Water Resour. Manag. 2017, 31, 1995–2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission. Communication from the Commission to the European Parliament, the European Council, the Council, the European Economic and Social Committee and the Committee of the Regions; The European Green Deal. COM/2019/640 Final; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2019; Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=CELEX%3A52019DC0640 (accessed on 20 October 2021).
- Chukurna, O.; Nitsenko, V.; Kralia, V.; Sahachko, Y.; Morkunas, M.; Volkov, A. Modelling and Managing the Effect of Transferring the Dynamics of Exchange Rates on Prices of Machine-Building Enterprises in Ukraine. Pol. J. Manag. Stud. 2019, 19, 117–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnatyuk, V.A. Mechanism of laser damage of transparent semiconductors. Phys. B Condens. Matter 2001, 308–310, 935–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, L.; Parra, L.; Jimenez, J.M.; Lloret, J.; Pascal Lorenz, P. IoT-Based Smart Irrigation Systems: An Overview on the Recent Trends on Sensors and IoT Systems for Irrigation in Precision Agriculture. Sensors 2020, 20, 1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Havrysh, V.; Hruban, V.; Sadovoy, O.; Batsurovska, I.; Fedorchuk, V.; Yablunovskaya, K. Energy Saving Technologies for Automatical Move Irrigation Equipment. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE Problems of Automated Electrodrive. Theory and Practice (PAEP), Kremenchuk, Ukraine, 21–25 September 2020; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavrenko, S.O.; Lavrenko, N.M.; Maksymov, D.O.; Maksymov, M.V.; Didenko, N.O.; Islam, K.R. Variable tillage depth and chemical fertilization impact on irrigated common beans and soil physical properties. Soil Tillage Res. 2021, 212, 105024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamula, I.; Tanasiieva, M.; Travin, V.; Nitsenko, V.; Balezentis, T.; Streimikiene, D. Assessment of the Profitability of Environmental Activities in Forestry. Sustainability 2020, 12, 2998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Canaj, K.; Parente, A.; D’Imperio, M.; Boari, F.; Buono, V.; Toriello, M.; Mehmeti, A.; Montesano, F.F. Can Precise Irrigation Support the Sustainability of Protected Cultivation? A Life-Cycle Assessment and Life-Cycle Cost Analysis. Water 2022, 14, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Incrocci, L.; Thompson, R.B.; Fernandez-Fernandez, M.D.; De Pascale, S.; Pardossi, A.; Stanghellini, C.; Rouphael, Y.; Gallardo, M. Irrigation management of European greenhouse vegetable crops. Agric. Water Manag. 2020, 242, 106393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domínguez-Niño, J.M.; Oliver-Manera, J.; Girona, J.; Casadesús, J. Differential irrigation scheduling by an automated algorithm of water balance tuned by capacitance-type soil moisture sensors. Agric. Water Manag. 2020, 228, 105880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cáceres, G.; Millán, P.; Pereira, M.; Lozano, D. Smart Farm Irrigation: Model Predictive Control for Economic Optimal Irrigation in Agriculture. Agronomy 2021, 11, 1810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostapenko, R.; Herasymenko, Y.; Nitsenko, V.; Koliadenko, S.; Balezentis, T.; Streimikiene, D. Analysis of Production and Sales of Organic Products in Ukrainian Agricultural Enterprises. Sustainability 2020, 12, 3416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bazaluk, O.; Yatsenko, O.; Zakharchuk, O.; Ovcharenko, A.; Khrystenko, O.; Nitsenko, V. Dynamic Development of the Global Organic Food Market and Opportunities for Ukraine. Sustainability 2020, 12, 6963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shvets, V.Y.; Rozdobudko, E.V.; Solomina, G.V. Aggregated methodology of multicriterion economic and ecological examination of the ecologically oriented investment projects. Nauk. Visnyk Natsionalnoho Hirnychoho Universytetu 2013, 3, 139–144. [Google Scholar]
- Koval, V.; Mikhno, I.; Udovychenko, I.; Gordiichuk, Y.; Kalina, I. Sustainable natural resource management to ensure strategic environmental development. TEM J. 2021, 10, 1022–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, W.; Dechmi, F. DSSAT modelling for best irrigation management practices assessment under mediterranean conditions. Agric. Water Manag. 2019, 216, 27–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrishambaf, O.; Faria, P.; Gomes, L.; Vale, Z. Agricultural irrigation scheduling for a crop management system considering water and energy use optimization. Energy Rep. 2020, 6, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Vuran, M.C.; Irmak, S. Autonomous precision agriculture through integration of wireless underground sensor networks with center pivot irrigation systems. Ad Hoc Netw. 2013, 11, 1975–1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boobalan, J.; Jacintha, V.; Nagarajan, J.; Thangayogesh, K.; Tamilarasu, S. An IOT based agriculture monitoring system. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on Communication and Signal Processing, Tamilnadu, India, 3–5 April 2018; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 0594–0598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pernapati, K. IoT based low cost smart irrigation system. In Proceedings of the 2018 Second International Conference on Inventive Communication and Computational Technologies, Coimbatore, India, 20–21 April 2018; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 1312–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brajovic, M.; Vujovic, S.; Dukanovic, S. An overview of smart irrigation software. In Proceedings of the 2015 4th Mediterranean Conference on Embedded Computing, Budva, Montenegro, 14–18 June 2015; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2015; pp. 353–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munir, M.S.; Bajwa, I.S.; Ashraf, A.; Anwar, W.; Rashid, R. Intelligent and Smart Irrigation System Using Edge Computing and IoT. Complexity 2021, 2021, 6691571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monthly and Annual Precipitation in Kherson. 2021. Available online: http://www.pogodaiklimat.ru/history/33902_2.htm (accessed on 14 October 2021).
- Ayers, R.S.; Westcot, D.W. Water Quality for Agriculture. In FAO Irrigation and Drainage; Paper 29 Rev. 1; FAO: Rome, Italy, 1985; Available online: http://www.fao.org/3/t0234e/t0234e.pdf (accessed on 22 October 2021).
- Likhovid, P.V. Analysis of the Ingulets irrigation water quality by agronomical criteria. Success Mod. Sci. Educ. 2015, 5, 10–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ali, M.H.; Talukder, M.S.U. Increasing water productivity in crop production–A synthesis. Agric. Water Manag. 2008, 95, 1201–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howell, T.A. Enhancing water use efficiency in irrigated agriculture. Agron. J. 2001, 93, 281–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- FAO. Soil Testing Methods–Global Soil Doctor Programme–A Farmer-to-farmer Training Programme; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2020. Available online: http://www.fao.org/3/ca2796en/CA2796EN.pdf (accessed on 7 October 2021).
- Foley, D.J.; Thenkabail, P.S.; Aneece, I.P.; Teluguntla, P.G.; Oliphant, A.J. A meta-analysis of global crop water productivity of three leading world crops (wheat, corn, and rice) in the irrigated areas over three decades. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2020, 13, 939–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vozhehova, R.A.; Maliarchuk, M.P.; Biliaieva, I.M.; Markovska, O.Y.; Maliarchuk, A.S.; Tomnytskyi, A.V.; Lykhovyd, P.V.; Kozyrev, V.V. The effect of tillage system and fertilization on corn yield and water use efficiency in irrigated conditions of the South of Ukraine. Biosyst. Divers. 2019, 27, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Djaman, K.; O’Neill, M.; Owen, C.; Smeal, D.; West, M.; Begay, D.; Angadi, S.V.; Koudahe, K.; Allen, S.; Lombard, K. Seed Yield andWater Productivity of Irrigated Winter Canola (Brassica napus L.) under Semiarid Climate and High Elevation. Agronomy 2018, 8, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saeed, A.A.Q.; Abdel-Nasser, G.; Gomaa, M.A. Growth, Productivity and Water Use of Sunflower Crop Under Drip Irrigation System. J. Adv. Agric. Res. 2015, 20, 420–437. [Google Scholar]
- Petrova, R.; Matev, A.; Kirchev, H.; Sevov, A. Productivity of sunflower grown in a periodic water deficit conditions. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2013, 5, 39–45. [Google Scholar]
- Albaji, M.; Nasab, S.B.; Behzad, M.; Naseri, A.A.; Shahnazari, A.; Meskarbashee, M.; Judy, F.; Jovzi, M.; Shokoohfar, A.R. Water productivity and water use efficiency of sunflower under conventional and limited irrigation. J. Food Agric. Environ. 2011, 9, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araya, A.; Prasad, P.V.V.; Ciampitti, I.A.; Jha, P.K. Using crop simulation model to evaluate influence of water management practices and multiple cropping systems on crop yields: A case study for Ethiopian highlands. Field Crops Res. 2021, 260, 108004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, P.K.; Kumar, S.N.; Ines, A.V.M. Responses of soybean to water stress and supplemental irrigation in upper Indo-Gangetic plain: Field experiment and modeling approach. Field Crops Res. 2018, 219, 76–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dispatching the Work of Sprinklers. Available online: http://products.vidcompro.net/dispetcherizatsiya-rabotyi-dozhdevalnyih-mashin/ (accessed on 9 March 2022).
- Agrotender. Available online: https://agrotender.com.ua/traders/region_ukraine/raps (accessed on 13 October 2021).
- Marshall, M.; Thenkabail, P. Developing In Situ Non-destructive Estimates of Crop Biomass to Address Issues of Scale in Remote Sensing. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 808–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vermeulen, S.J.; Challinor, A.J.; Thornton, P.K.; Campbell, B.M.; Eriyagama, N.; Vervoort, J.M.; Kinyangi, J.; Jarvis, A.; Läderach, P.; Ramirez-Villegas, J.; et al. Addressing Uncertainty in Adaptation Planning for Agriculture. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 8357–8362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kotenko, S.; Nitsenko, V.; Hanzhurenko, I.; Havrysh, V. The Mathematical Modeling Stages of Combining the Carriage of Goods for Indefinite, Fuzzy and Stochastic Parameters. Int. J. Integr. Eng. 2020, 12, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Havrysh, V.; Kalinichenko, A.; Mentel, G.; Mentel, U.; Vasbieva, D.G. Husk Energy Supply Systems for Sunflower Oil Mills. Energies 2020, 13, 361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bazaluk, O.; Havrysh, V.; Fedorchuk, M.; Nitsenko, V. Energy Assessment of Sorghum Cultivation in Southern Ukraine. Agriculture 2021, 11, 695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perea, R.G.; Poyato, E.C.; Díaz, J.R. Forecasting of applied irrigation depths at farm level for energy tariff periods using Coactive neuro-genetic fuzzy system. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 256, 107068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez Díaz, J.; Camacho Poyato, E.; Blanco Pérez, M. Evaluation of water and energy use in pressurized irrigation networks in Southern Spain. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2011, 137, 644–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


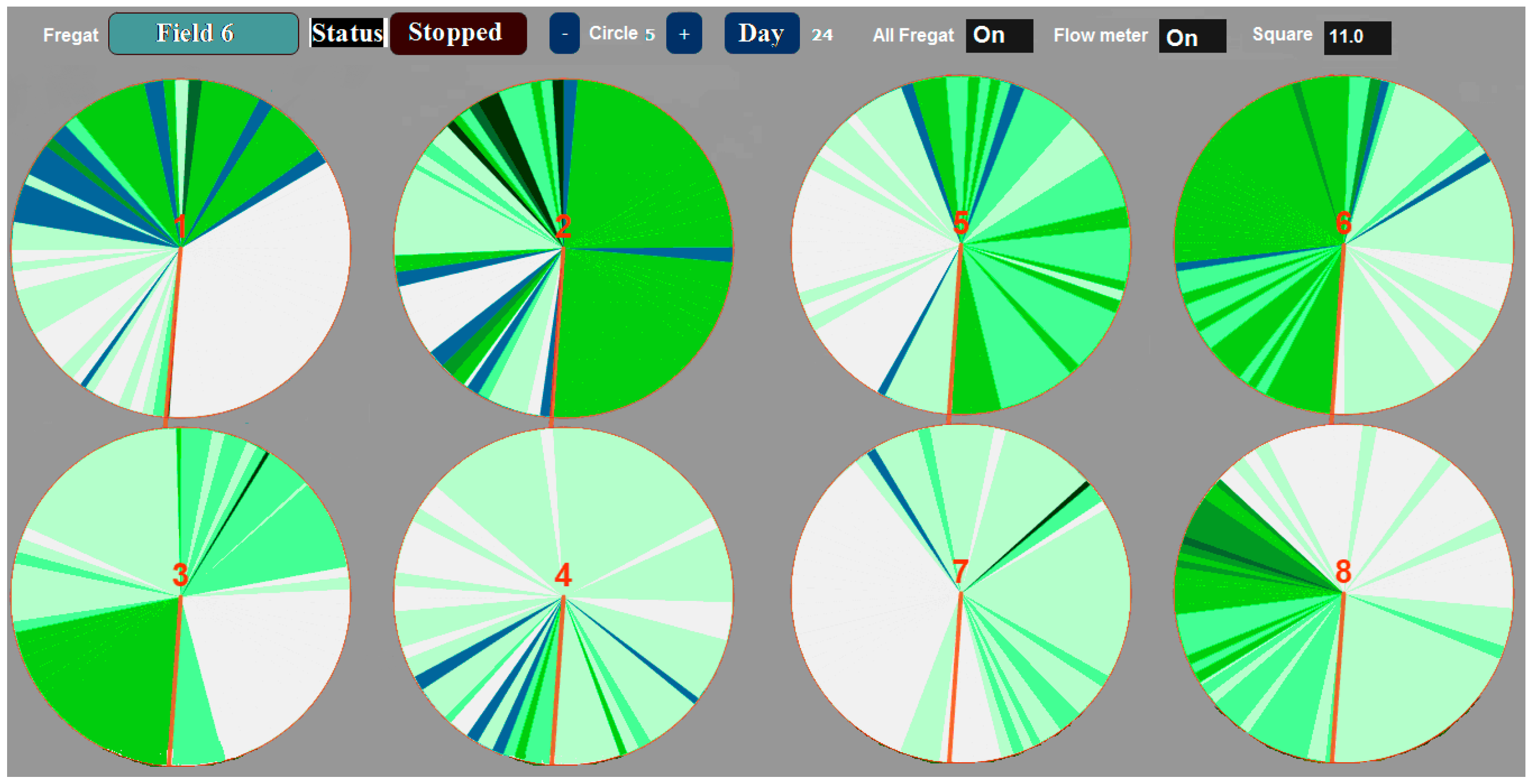
| Indicators | Unit | Farm | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | ||
| Soil organic carbon | g⋅kg−1 | 2.3 | 2.4 | 2.8 | 2.5 | 2.3 |
| pH | - | 8.1 | 8.1 | 6.8 | 7.1 | 5.0 |
| Nitrogen | mg⋅kg−1 | 35 | 25 | 24 | 34 | 31 |
| Phosphorus | mg⋅kg−1 | 32 | 31 | 34 | 30 | 37 |
| Potassium | mg⋅kg−1 | 298 | 310 | 500 | 412 | 546 |
| Bulk density | kg⋅m−3 | 1380 | 1390 | 1370 | 1365 | 1374 |
| Farming Operation | Crop | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wheat | Corn | Sunflower | Rapeseed | |
| Tillage | Skimming (8–10 cm) Ploughing (20–22 cm) Deep loosening (40 cm) Spring harrowing | Skimming (8–10 cm) Ploughing (25–27 cm) | Skimming (8–12 cm) Ploughing (25–27 cm) Harrowing | Skimming (8–10 cm) Ploughing (22–24 cm) Cultivation (5–7 cm) Harrowing |
| Sowing | Date: 20 September–5 October Pre-sowing cultivation (6–8 cm) Seeding rate: (40.0–50.0) × 105 seeds per hectare Rolling Harrowing | Date:1 May–10 May Pre-sowing cultivation (6–8 cm) Seeding rate: (0.8–1.0) × 105 seeds per hectare Rolling | Date: 10 April–1 May Pre-sowing cultivation (5–7 cm) Seeding rate: (0.4–0.6) × 105 seeds per hectare Rolling | Date: August Pre-sowing cultivation (3–4 cm) Seeding rate: 6.0 × 105 seeds per hectare |
| Irrigation | 1200–1500 m3/ha | 3900–4500 m3/ha | 1240–1500 m3/ha | 1030–1500 m3/ha |
| Fertilization | N40P10K10 | N60P60K60 | N50P50K50 | N95P50K30 |
| Weed control | Chemicals: 2.4-D–1.4 kg/ha; Sumi-Alfa–0.25 L/ha | Inter-row cultivation Chemicals: Harnesы–2.5 L/ha | Inter-row cultivation Chemicals: Reglon–1L/ha | Inter-row cultivation Chemicals: Cineb–2.4 kg/ha; Sumicidin–0.3 L/ha |
| Harvesting | July | October | September | July |
| Locatiom | Irrigation System | Yield, kg/ha | Rainfall, mm | Irrigation, mm | GIW, m3 | WUP, kg/m3 | IWUP, kg/m3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| wheat | |||||||
| Farm 1 | ICS | 6980 | 444 | 148 | 5920 | 1.18 | 4.72 |
| SIS | 6870 | 444 | 122 | 5660 | 1.21 | 5.63 | |
| Farm 2 | ICS | 6370 | 435 | 141 | 5760 | 1.11 | 4.52 |
| SIS | 6410 | 435 | 126 | 5610 | 1.14 | 5.09 | |
| Farm 3 | ICS | 5970 | 398 | 147 | 5450 | 1.10 | 4.06 |
| SIS | 6030 | 398 | 135 | 5330 | 1.13 | 4.47 | |
| Farm 4 | ICS | 5490 | 365 | 150 | 5150 | 1.07 | 3.66 |
| SIS | 5640 | 365 | 141 | 5060 | 1.11 | 4.00 | |
| Farm 5 | ICS | 5600 | 401 | 142 | 5430 | 1.03 | 3.94 |
| SIS | 5999 | 401 | 134 | 5350 | 1.12 | 4.48 | |
| corn | |||||||
| Farm 1 | ICS | 13000 | 444 | 410 | 8540 | 1.52 | 3.17 |
| SIS | 13900 | 444 | 401 | 8450 | 1.64 | 3.47 | |
| Farm 2 | ICS | 14240 | 435 | 435 | 8700 | 1.64 | 3.27 |
| SIS | 13970 | 435 | 395 | 8300 | 1.68 | 3.54 | |
| Farm 3 | ICS | 12280 | 398 | 430 | 8280 | 1.48 | 2.86 |
| SIS | 12950 | 398 | 401 | 7990 | 1.62 | 3.23 | |
| Farm 4 | ICS | 11040 | 365 | 450 | 8150 | 1.35 | 2.45 |
| SIS | 12180 | 365 | 432 | 7970 | 1.53 | 2.82 | |
| Farm 5 | ICS | 12650 | 401 | 426 | 8270 | 1.53 | 2.97 |
| SIS | 13160 | 401 | 390 | 7910 | 1.66 | 3.37 | |
| sunflower | |||||||
| Farm 1 | ICS | 3020 | 435 | 145 | 5800 | 0.52 | 2.08 |
| SIS | 3195 | 435 | 124 | 5590 | 0.57 | 2.58 | |
| Farm 2 | ICS | 3000 | 398 | 145 | 5430 | 0.55 | 2.07 |
| SIS | 3190 | 398 | 138 | 5360 | 0.60 | 2.31 | |
| Farm 3 | ICS | 2380 | 365 | 150 | 5150 | 0.46 | 1.59 |
| SIS | 2510 | 365 | 134 | 4990 | 0.50 | 1.87 | |
| Farm 4 | ICS | 2710 | 401 | 144 | 5450 | 0.50 | 1.88 |
| SIS | 3090 | 401 | 148 | 5490 | 0.56 | 2.09 | |
| Farm 5 | ICS | 3020 | 435 | 145 | 5800 | 0.52 | 2.08 |
| SIS | 3195 | 435 | 124 | 5590 | 0.57 | 2.58 | |
| rapeseed | |||||||
| Farm 1 | ICS | 3380 | 444 | 120 | 5640 | 0.60 | 2.82 |
| SIS | 3390 | 444 | 103 | 5470 | 0.62 | 3.29 | |
| Farm 2 | ICS | 3180 | 435 | 137 | 5720 | 0.56 | 2.32 |
| SIS | 3270 | 435 | 122 | 5570 | 0.59 | 2.68 | |
| Farm 3 | ICS | 2990 | 398 | 150 | 5480 | 0.55 | 1.99 |
| SIS | 3170 | 398 | 139 | 5370 | 0.59 | 2.28 | |
| Farm 4 | ICS | 2800 | 365 | 150 | 5150 | 0.54 | 1.87 |
| SIS | 2870 | 365 | 144 | 5090 | 0.56 | 1.99 | |
| Farm 5 | ICS | 2900 | 401 | 142 | 5430 | 0.53 | 2.04 |
| SIS | 3085 | 401 | 131 | 5320 | 0.58 | 2.35 | |
| Crop | Minimum | Maximum | Average |
|---|---|---|---|
| Wheat | 2.54 | 8.74 | 4.09 |
| Corn | 2.44 | 13.33 | 8.32 |
| Sunflower | 8.69 | 12.00 | 9.80 |
| Rapeseed | 3.33 | 9.43 | 5.82 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bazaluk, O.; Havrysh, V.; Nitsenko, V.; Mazur, Y.; Lavrenko, S. Low-Cost Smart Farm Irrigation Systems in Kherson Province: Feasibility Study. Agronomy 2022, 12, 1013. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12051013
Bazaluk O, Havrysh V, Nitsenko V, Mazur Y, Lavrenko S. Low-Cost Smart Farm Irrigation Systems in Kherson Province: Feasibility Study. Agronomy. 2022; 12(5):1013. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12051013
Chicago/Turabian StyleBazaluk, Oleg, Valerii Havrysh, Vitalii Nitsenko, Yuliia Mazur, and Sergiy Lavrenko. 2022. "Low-Cost Smart Farm Irrigation Systems in Kherson Province: Feasibility Study" Agronomy 12, no. 5: 1013. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12051013
APA StyleBazaluk, O., Havrysh, V., Nitsenko, V., Mazur, Y., & Lavrenko, S. (2022). Low-Cost Smart Farm Irrigation Systems in Kherson Province: Feasibility Study. Agronomy, 12(5), 1013. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12051013









