Adventitious Root Culture—An Alternative Strategy for Secondary Metabolite Production: A Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Adventitious Root Culture
2.1. Formation of Adventitious Roots in Plants
- The root pre-emergence: this phase includes alterations in the molecular and biochemical process prior to cytological development until the occurrence of root primordia;
- Root development;
- Root growth;
- Root configuration.
2.2. Media Properties and Culture Conditions
2.3. Effect of Auxins on Adventitious Root Formation
2.4. Effect of Sucrose on Adventitious Root Cultures
2.5. Effect of Abiotic Elicitors on Adventitious Root Cultures
2.6. Effect of Biotic Elicitors on Adventitious Root Cultures
3. Adventitious Root Culture in Bioreactors
4. Advantages of Adventitious Root Cultures
5. Challenges to Use Adventitious Root Culture
6. Future Prospects
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Reed, B.M.; Sarasan, V.; Kane, M.; Bunn, E.; Pence, V.C. Biodiversity conservation and conservation biotechnology tools. In Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol.-Plant 2011, 47, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.L.; Yu, H.; Luo, H.M.; Wu, Q.; Li, C.F.; Steinmetz, A. Conservation and sustainable use of medicinal plants: Problems, progress, and prospects. Chin. Med. 2016, 11, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pathak, M.R.; Abido, M.S. The role of biotechnology in the conservation of biodiversity. J. Exp. Biol. 2014, 2, 352–363. [Google Scholar]
- Newman, D.J.; Cragg, G.M. Natural Products as Sources of New Drugs over the Nearly Four Decades from 01/1981 to 09/2019. J. Nat. Prod. 2020, 83, 770–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ataei-Azimi, A.; Hashemloian, B.D.; Ebrahimzadeh, H.; Majd, A. High in vitro production of ant-canceric indole alkaloids from periwinkle (Catharanthus roseus) tissue culture. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2008, 7, 2834–2839. [Google Scholar]
- Hasan, S.Z.; Misra, V.; Singh, S.; Arora, G.; Sharma, S.; Sharma, S. Current status of herbal drugs and their future perspectives. Biol. Forum Int. J. 2009, 1, 12–17. [Google Scholar]
- Madhusudanan, K.P.; Banerjee, S.; Khanuja, S.P.; Chattopadhyay, S.K. Analysis of hairy root culture of Rauvolfia serpentina using direct analysis in real time mass spectrometric technique. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2008, 22, 596–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangeetha, S.; Manjunatha, N.; Samanta, M.K.; Malik, M. Pharmacokinetic evaluation of quinine in tablet formulation from herbal extract. Int. J. Biopharm. 2011, 2, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, R.; Khan, M.M.A.; Singh, M.; Nasir, S.; Naeem, M.; Siddiqui, M.H.; Mohammad, F. Gibberellic acid and triacontanol can ameliorate the opium yield and morphine production in opium poppy (Papaver somniferum L.). Acta Agric. Scand. Sect. B Soil Plant Sci. 2007, 57, 307–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashtiania, F.; Sefidkonb, F. Tropane alkaloids of Atropa belladonna L. and Atropa acuminata Royle ex Miers plants. J. Med. Plants Res. 2011, 5, 6515–6522. [Google Scholar]
- George, J.; Bais, H.P.; Ravishankar, G.A. Biotechnological production of plant-based insecticides. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2000, 20, 49–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dias, D.A.; Urban, S.; Roessner, U. A historical overview of natural products in drug discovery. Metabolites 2012, 2, 303–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Razdan, M.K. Introduction to Plant Tissue Culture; Science Publishers: Enfield, NH, USA; Plymouth, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Erb, M.; Kliebenstein, D.J. Plant secondary metabolites as defenses, regulators, and primary metabolites: The blurred functional trichotomy. Plant Physiol. 2020, 184, 39–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giri, C.C.; Shyamkumar, B.; Anjaneyulu, C. Progress in tissue culture, genetic transformation and applications of biotechnology to trees: An overview. Trees 2004, 18, 115–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skoog, F.; Miller, C. Chemical regulation of growth and organ formation in plant tissues cultured. Symp. Soc. Exp. Biol. 1957, 11, 118–130. [Google Scholar]
- Vanisree, M.; Lee, C.Y.; Lo, S.F.; Nalawade, S.M.; Lin, C.Y.; Tsay, H.S. Studies on the production of some important secondary metabolites from medicinal plants by plant tissue cultures. Bot. Bull. Acad. Sinca Taipie 2004, 45, 1–22. [Google Scholar]
- Karuppusamy, S. A review on trends in production of secondary metabolites from higher plants by in vitro tissue, organ and cell cultures. J. Med. Plants Res. 2009, 3, 1222–1239. [Google Scholar]
- Mehrotra, S.; Goel, M.K.; Kukreja, A.K.; Mishra, B.N. Efficiency of liquid culture systems over conventional micropropagation: A progress towards commercialization. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2007, 6, 1484–1492. [Google Scholar]
- Filova, A. Production of secondary metabolities in plant tissue cultures. Res. J. Agric. Sci. 2014, 46, 236–245. [Google Scholar]
- Rao, S.R.; Ravishankar, G.A. Plant cell cultures: Chemical factories of secondary metabolites. Biotechnol. Adv. 2002, 20, 101–153. [Google Scholar]
- Amoo, S.O.; Aremu, A.O.; Van Staden, J. Shoot proliferation and rooting treatments influence secondary metabolite production and antioxidant activity in tissue culture-derived Aloe arborescens grown ex vitro. Plant Growth Regul. 2013, 70, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jirakiattikul, Y.; Rithichai, P.; Songsri, O.; Ruangnoo, S.; Itharat, A. In vitro propagation and bioactive compound accumulation in regenerated shoots of Dioscorea birmanica Prain & Burkill. Acta Physiol. Plant. 2016, 38, 249–257. [Google Scholar]
- Jirakiattikul, Y.; Rithichai, P.; Boonyuen, T.; Ruangnoo, S.; Itharat, A. Effect of elicitors on bioactive compound accumulation in shoot culture of Dioscorea membranacea. Planta Med. 2016, 82, 518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kupchan, S.M.; Dessertine, A.L.; Blaylock, B.T.; Bryan, R.F. Isolation and structural elucidation of allamandin, and antileukemic iridoid lactone from Allamanda cathartica. J. Org. Chem. 1974, 39, 2477–2482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Essiett, A.U.; Udo, E.S. Comparative phytochemical screening and nutritional potentials of the stems, leaves and flowers of Allamanda cathartica (Apocynaceae). Int. J. Sci. Technol. 2015, 4, 248–253. [Google Scholar]
- Fartyal, M.; Kumar, P. Evaluation of antimicrobial efficacy of alkaloids, flavonoids and steroids of Allamanda cathartica Linn. against some pathogenic bacteria. Int. J. Adv. Pharm. Biol. Chem. 2016, 5, 303–313. [Google Scholar]
- Abirami, H.; Kumar, P.S. In vitro regeneration and extraction of secondary metabolites in Aegle marmelos (L.) Correa. Asian J. Plant Sci. Res. 2013, 3, 99–106. [Google Scholar]
- da Silva, B.O.; Amaral, A.C.F.; Ferreira, J.L.P.; Santiago, L.J.M.; Louro, R.P. Micropropagation and in vitro production of secondary metabolites of Croton floribundus Spreng. Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol.-Plant 2013, 49, 366–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thangavel, K.; Ravichandran, P.; Ebbie, M.G.; Manimekalai, V. In vitro microrhizome production in Decalepis hamiltonii. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2014, 13, 1308–1313. [Google Scholar]
- Mishra, S.; Srivastava, N.; Sundaresan, V.; Shanker, K. Amruthapala (Decalepis arayalpathra (J. Joseph and V. Chandras.) Venter): A Comprehensive Review on Diversity, Therapeutic Uses, and Valorization of Bioactive Constituents. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2019, 20, 376–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.M.; Son, S.H.; Yun, S.R.; Kwon, O.W.; Seon, J.H.; Paek, K.Y. Pilot-scale culture of adventitious roots of ginseng in a bioreactor system. Plant Cell Tiss. Org. Cult. 2000, 62, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paek, K.Y.; Murthy, H.N.; Hahn, E.J.; Zhong, J.J. Large Scale Culture of Ginseng Adventitious Roots for Production of Ginsenosides. In Biotechnology in China I; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; Volume 113, pp. 151–176. [Google Scholar]
- Baque, M.A.; Elgirban, A.; Lee, E.J.; Paek, K.Y. Sucrose regulated enhanced induction of anthraquinone, phenolics, flavonoids biosynthesis and activities of antioxidant enzymes in adventitious root suspension cultures of Morinda citrifolia (L.). Acta Physiol. Plant. 2012, 34, 405–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bais, H.P.; Loyola-Vargas, V.M.; Flores, H.E.; Vivanco, J.M. Root-specific metabolism: The biology and biochemistry of underground organs. Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol.-Plant 2001, 37, 730–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fulzele, T.B.; Satdive, R.K.; Pol, B.B. Untransformed root cultures of Nothapodytes foetida and production of camptothecin. Plant Cell Tiss. Org. Cult. 2002, 69, 285–288. [Google Scholar]
- Gangopadhyay, M.; Dewanjee, S.; Bhattacharya, S. Enhanced plumbagin production in elicited Plumbago indica hairy root cultures. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2011, 111, 706–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillai, D.B.; Jose, B.; Satheeshkumar, K.; Krishnan, P.N. Optimization of inoculum density in hairy root culture of Plumbago rosea L. for enhanced growth and plumbagin production towards scaling-up in bioreactor. Indian J. Biotechnol. 2015, 14, 264–269. [Google Scholar]
- Gaosheng, H.; Jingming, J. Production of Useful Secondary Metabolites through Regulation of Biosynthetic Pathway in Cell and Tissue Suspension Culture of Medicinal Plants. In Recent Advances in Plant In Vitro Culture; InTech Open: Rijeka, Croatia, 2012; Volume 11, pp. 197–210. [Google Scholar]
- Sorin, C.; Bussell, J.D.; Camus, I. Auxin and light control of adventitious rooting in Arabidopsis required ARGONAUTE1. Plant Cell 2005, 17, 1343–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rahmat, E.; Kang, Y. Adventitious root culture for secondary metabolite production in medicinal plants: A review. J. Plant Biotechnol. 2019, 46, 143–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Fan, J.; Tan, Q.; Zhao, M.; Zhou, T.; Cao, F. The effects of exogenous hormones on rooting process and the activities of key enzymes of Malus hupehensis stem cuttings. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0172320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Praveen, N.; Manohar, S.H.; Naik, P.M.; Nayeem, A.; Jeong, J.H.; Murthy, H.N. Production of androghrapholide from adventitious root cultures of Andrographis paniculata. Curr. Sci. 2009, 96, 5–10. [Google Scholar]
- Hahn, E.J.; Kim, Y.S.; Yu, K.W.; Jeong, C.S.; Paek, K.Y. Adventitious root cultures of Panax ginseng C.A. Meyer and ginsenoside production through large-scale bioreactor system. J. Plant Biotech. 2003, 5, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Khanam, M.N.; Anis, M.; Ahmad, S. Establishment of adventitious root cultures of Allamanda cathartica L. for the production of iridoid glycosides and its identification using HPTLC MS. Ind. Crops Prod. 2018, 125, 198–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murthy, H.N.; Hahn, E.J.; Paek, K.Y. Adventitious roots and secondary metabolism. Chin. J. Biotechnol. 2008, 24, 711–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivakumar, G. Bioreactor technology: A novel industrial tool for high-tech production of bioactive molecules and biopharmaceuticals from plant root. Biotechnol. J. 2006, 12, 1419–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusuf, N.A.; Rahim, N.S.M.; Azhar, S.Z.A.; Ghani, K.A.; Sommano, S.; Khalid, N. Adventitious root cultures of Boesenbergia rotunda as a source of Pinostrobin. Int. J. Adv. Sci. Eng. Inf. Technol. 2018, 8, 377–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalafalla, M.M.; Daffalla, H.M.; El-Shemy, H.A.; Abdellatef, E. Establishment of in vitro fast-growing normal root culture of Vernonia amygdalina—A potent African medicinal plant. Afric. J. Biotechnol. 2009, 8, 5952–5957. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Y.D.; Kim, H.G.; Sim, S.J.; Kim, J.C.; Min, J.Y.; Hwang, J.G.; Kang, S.M.; Moon, H.S.; Kim, J.K.; Choi, M.S. Effects of culture media on catechins and caffeine production in adventitious roots of tea tree (Camellia sinensis L.). J. Agric. Life Sci. 2013, 47, 11–20. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, C.H.; Murthy, H.N.; Hahn, E.J.; Paek, K.Y. Large-scale cultivation of adventitious roots of Echinacea purpurea in airlift bioreactors for the production of chichoric acid, chlorogenic acid and caftaric acid. Biotechnol. Lett. 2007, 29, 1179–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.S.; Yang, T.J.; Park, S.U.; Baek, J.H.; Wu, S.Q.; Lim, K.B. Induction and proliferation of adventitious roots from Aloe vera leaf tissues for in vitro production of aloe-emodin. Plant Omics 2011, 4, 190–194. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, Y.S.; Ju, H.K.; Kim, Y.J.; Lim, T.G.; Uddin, M.R.; Kim, Y.B.; Baek, J.H.; Kwon, S.W.; Lee, K.W.; Seo, H.S.; et al. Enhancement of anti-inflammatory activity of Aloe vera adventitious root extracts through the alteration of primary and secondary metabolites via salicylic acid elicitation. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e82479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiesman, Z.; Riov, J.; Epstein, E. Comparison of movement and metabolism of indole-3-acetic acid and indole-3-butyric acid in mung bean cuttings. Physiol. Plant. 1988, 74, 556–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrido, G.; Ramón Guerrero, J.; Angel Cano, E.; Acosta, M.; Sánchez-Bravo, J. Origin and basipetal transport of the IAA responsible for rooting of carnation cuttings. Physiol. Plant. 2002, 114, 303–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubery, P.H.; Sheldrake, A.R. Carrier-mediated auxin transport. Planta 1974, 118, 101–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delbarre, A.; Muller, P.; Imhoff, V.; Guern, J. Comparison of mechanisms controlling uptake and accumulation of 2, 4-dichlorophenoxy acetic acid, naphthalene-1-acetic acid, and indole-3-acetic acid in suspension-cultured tobacco cells. Planta 1996, 198, 532–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heloir, M.C.; Kevers, C.; Hausman, J.F.; Gaspar, T. Changes in the concentrations of auxins and polyamines during rooting of in vitro propagated walnut shoots. Tree Physiol. 1996, 16, 515–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vesperinas, E.S. In vitro root induction in hypocotyls and plumule explants of Helianthus annus. Environ. Exp. Bot. 1998, 39, 217–227. [Google Scholar]
- Baskaran, P.; Jayabalan, N. Psoralen production in hairy roots and adventitious roots cultures of Psoralea corylifolia. Biotechnol. Lett. 2009, 31, 1073–10777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Klerk, G.J.; Van Der Krieken, W.; de Jong, J.C. Review the formation of adventitious roots: New concepts, new possibilities. Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol.-Plant 1999, 35, 189–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanam, M.N. Studies on Interactive Effects of Different Plant Growth Regulators on In Vitro Regeneration and Biochemical Yield in Allamanda cathartica L. Ph.D. Thesis, Aligarh Muslim University, Aligarh, India, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Sujatha, G.; Ranjitha Kumari, B.D. Establishment of fast growing in vitro root culture system in Artemisia vulgaris. J. Agric. Technol. 2012, 8, 1779–1790. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, S.Q.; Lian, M.L.; Gao, R.; Park, S.Y.; Piao, X.C. Bioreactor application on adventitious root culture of Astragalus membranaceus. Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol.-Plant 2011, 47, 719–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenifer, U.; Francina Cecilia, K.; Ravindhran, R. In vitro adventitious root and hairy root cultures in Boerhaavia diffusa L. Int. J. Curr. Res. 2012, 4, 65–67. [Google Scholar]
- Jeong, J.A.; Wu, C.H.; Murthy, H.N.; Hahn, E.J.; Paek, K.Y. Application of an airlift bioreactor system for the production of adventitious root biomass and caffeic acid derivatives of Echinacea purpurea. Biotechnol. Bioprocess. Eng. 2009, 14, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, S.; Ling, A.P.K.; Ng, T.H.; Ibrahim, R.; Paek, K.Y. Adventitious roots induction of recalcitrant tropical woody plant, Eurycoma longifolia. Rom. Biotechnol. Lett. 2012, 17, 7026–7035. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, S.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, W.; Wang, J.; Man, S.; Liu, H. Effects of nitrogen source and phosphate concentration on biomass and metabolites accumulation in adventitious root culture of Glycyrrhiza uralensis Fisch. Acta Physiol. Plant. 2014, 36, 915–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saiman, M.Z.; Mustafa, N.R.; Schulte, A.E.; Verpoorte, R.; Choi, Y.H. Induction, characterization, and NMR-based metabolic profiling of adventitious root cultures from leaf explants of Gynura procumbens. Plant Cell Tiss. Org. Cult. 2012, 109, 465–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ciu, X.H.; Chakrabarty, D.; Lee, E.J.; Paek, K.Y. Production of adventitious roots and secondary metabolites by Hypericum perforatum L. in a bioreactor. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 4708–4716. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, S.Q.; Yu, X.K.; Lian, M.L.; Park, S.Y.; Piao, X.C. Several factors affecting hypericin production of Hypericum perforatum during adventitious root culture in airlift bioreactors. Acta Physiol. Plant. 2014, 36, 975–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baque, M.A.; Shiragi, M.H.K.; Lee, E.J.; Paek, K.Y. Elicitor effect of chitosan and pectin on the biosynthesis of anthraquinones, phenolics and flavonoids in adventitious root suspension cultures of Morinda citrifolia (L.). Aust. J. Crop Sci. 2012, 6, 1349–1355. [Google Scholar]
- Baque, M.A.; Shiragi, M.H.K.; Moh, S.H.; Lee, E.J.; Paek, K. Production of biomass and bioactive compounds by adventitious root suspension cultures of Morinda citrifolia (L.) in a liquid-phase airlift balloon-type bioreactor. Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol.-Plant 2013, 49, 737–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, A.P.K.; Kok, K.M.; Hussein, S.; Ong, S.L. Effects of plant growth regulators on adventitious roots induction from different explants of Orthosiphon stamineus. Am. Eurasian J. Sustain. Agric. 2009, 3, 493–501. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Y.S.; Hahn, E.J.; Murthy, H.N.; Paek, K.Y. Adventitious root growth and ginsenoside accumulation in Panax ginseng cultures as affected by methyl jasmonate. Biotechnol. Lett. 2004, 26, 1619–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.S.; Yeung, E.C.; Hahn, E.J.; Paek, K.Y. Combined effects of phytohormone, indole-3-butyric acid, and methyl jasmonate on root growth and ginsenoside production in adventitious root cultures of Panax ginseng CA Meyer. Biotechnol. Lett. 2007, 29, 1789–1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murthy, H.N.; Paek, K.Y. Panax ginseng Adventitious Root Suspension Culture: Protocol for Biomass Production and Analysis of Ginsenosides by High Pressure Liquid Chromatography. In Protocols for In Vitro Cultures and Secondary Metabolite Analysis of Aromatic and Medicinal Plants, 2nd ed.; Jain, S., Ed.; Methods in Molecular Biology Series; Humana Press: New York, NY, USA, 2016; Volume 1391. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, X.; Zhu, C.; Jia, W.; Gao, W.; Qiu, M.; Zhang, Y.; Xiao, P. Induction and characterization of adventitious roots directly from the explants of Panax notoginseng. Biotechnol. Lett. 2005, 27, 1771–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silja, P.K.; Satheeshkumar, K. Establishment of adventitious root cultures from leaf explants of Plumbago rosea and enhanced plumbagin production through elicitation. Ind. Crops Prod. 2015, 76, 479–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajesh, M.; Sivanandhan, G.; Arun, M.; Vasudevan, V.; Theboral, J.; Girija, S.; Manickavasagam, M.; Selvaraj, N.; Ganapathi, A. Factors influencing podophyllotoxin production in adventitious root culture of Podophyllum hexandrum Royle. Acta Physiol. Plant. 2014, 36, 1009–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, T.T.; Lee, J.D.; Jeong, C.S.; Paek, K.Y.; Park, S.Y. Improvement of biosynthesis and accumulation of bioactive compounds by elicitation in adventitious root cultures of Polygonum multiflorum. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 102, 199–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fazal, H.; Abbasi, B.; Ahmad, N. Optimization of adventitious root culture for production of biomass and secondary metabolites in Prunella vulgaris L. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2014, 174, 2086–2095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betsui, F.; Tanaka-Nishikawa, N.; Shimomura, K. Anthocyanin production in adventitious root cultures of Raphanus sativus L. cv. Peking Koushin. Plant Biotechnol. 2004, 21, 387–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Taniguchi, S.; Yazaki, K.; Yabu-Uchi, R.; Kawakami, K.Y.; Ito, H.; Hatano, T.; Yoshida, T. Galloylglucoses and riccionidin A in Rhus javanica adventitious root cultures. Phytochemistry 2000, 53, 357–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdieh, M.; Noori, M.; Hoseinkhani, S. Establishment of In vitro Adventitious Root Cultures and Analysis of Flavonoids in Rumex crispus. Plant Tiss. Cult. Biotechnol. 2015, 25, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mahdieh, M.; Noori, M.; Hoseinkhani, S. Studies of in vitro adventitious root induction and flavonoid profiles in Rumex crispus. Adv. Life Sci. 2015, 5, 53–57. [Google Scholar]
- Reis, R.V.; Borges, A.P.P.L.; Chierrito, T.P.C.; de Souto, E.R.; de Souza, L.M.; Iacomini, M.; de Oliveira, A.J.B.; Gonçalves, R.A.C. Establishment of adventitious root culture of Stevia rebaudiana Bertoni in a roller bottle system. Plant Cell Tiss. Org. Cult. 2011, 106, 329–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, M.; Bhattacharya, S.; Khosla, P.K.; Puri, S. Improving production of plant secondary metabolites through biotic and abiotic elicitation. J. Appl. Res. Med. Aromat. Plants 2019, 12, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivanandhan, G.; Arun, M.; Mayavan, S.; Rajesh, M.; Mariashibu, T.S.; Manickavasagam, M.; Selvaraj, N.; Ganapathi, A. Chitosan enhances withanolides production in adventitious root cultures of Withania somnifera (L.) Dunal. Ind. Crop Prod. 2012, 37, 124–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wadegaonkar, P.A.; Bhagwat, K.A.; Rai, M.K. Direct rhizogenesis and establishment of fast growing normal root organ culture of Withania somnifera Dunal. Plant Cell Tiss. Org. Cult. 2006, 84, 223–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Praveen, N.; Murthy, H.N. Production of withanolide-A from adventitious root cultures of Withania somnifera. Acta Physiol. Plant. 2010, 32, 1017–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, S.I. Plant sugar-response pathways. Part of a complex regulatory web. Plant Physiol. 2000, 124, 1532–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smeekens, S. Sugar-induced signal transduction in plants. Ann. Rev. Plant Biol. 2000, 51, 49–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zimmermann, M.H.; Ziegler, H. List of Sugar and Sugar Alcohols in Sieve-Tube Exudates. In Encyclopedia of Plant Physiology, Volume I, Transport in Plants I; Zimmermann, M.H., Milburn, J.A., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1975; pp. 480–503. [Google Scholar]
- George, E.F. Plant Propagation by Tissue Culture. Part 1: The Technology, 2nd ed.; Exegetics Limited: Herefordshire, UK, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- de Klerk, G.M.; Gerrits, M.M. Development of Dormancy in Tissue-Cultured Lily Bulblets and Apple Shoots. In Plant Dormancy: Physiology, Biochemistry, and Molecular Biology; CAB International: Wallingford, UK, 1996; pp. 115–131. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, J.L.S.; Van Staden, J. The effect of nitrogen and sucrose concentrations on the growth of Eucomis autumnalis (Mill.) Chitt. plantlets in vitro, and on subsequent anti-inflammatory activity in extracts prepared from the plantlets. Plant Growth Regul. 2001, 34, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altman, A.; Wareing, P.F. The effect of IAA on sugar accumulation and basipetal transport of 14C-labelled assimilates in relation to root formation in Phaseolus vulgaris cuttings. Physiol. Plant. 1975, 33, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veierskov, B.; Skytt Andersen, A.; Eriksen, E.N. Dynamics of extractable carbohydrates in Pisum sativum. I. Carbohydrate and nitrogen content in pea plants and cuttings grown at two different irradiances. Physiol. Plant. 1982, 55, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haissig, B.E. Metabolic Processes in Adventitious Rooting of Cuttings. In New Root Formation in Plants and Cuttings; Jackson, M.B., Ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1986; pp. 141–189. [Google Scholar]
- Lazzeri, P.A.; Hildebrand, D.F.; Sunega, J.; Williams, E.G.; Collins, G.B. Soybean somatic embryogenesis: Interactions between sucrose and auxin. Plant Cell Rep. 1988, 7, 517–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ling, A.P.K.; Chin, M.F.; Hussein, S. Adventitious root production of Centella asiatica in response to plant growth regulators and sucrose concentration. Med. Aromat. Plant Sci. Biotechnol. 2009, 3, 36–41. [Google Scholar]
- Calamar, A.; De Klerk, G.J. Effect of sucrose on adventitious root regeneration in apple. Plant Cell Tiss. Org. Cult. 2002, 70, 207–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, J.W.; Roberts, L.W.; Wilson, P.W.; Gresshoff, P.M. Stimulatory and inhibitory effects of sucrose concentration on xylogenesis in lettuce pith explants; possible mediation by ethylene biosynthesis. Ann. Bot. 1994, 73, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, Z.H.; Mujib, A.; Aslam, J.; Hakeem, K.R.; Parween, T. In Vitro Production of Secondary Metabolites Using Elicitor in Catharanthus roseus: A Case Study. In Crop Improvement; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2013; pp. 401–419. [Google Scholar]
- Naik, P.M.; Al-Khayri, J.M. Impact of abiotic elicitors on in vitro production of plant secondary metabolites: A review. J. Adv. Res. Biotech. 2016, 1, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Munns, R.; Tester, T. Mechanisms of salinity tolerance. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2008, 59, 651–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bernstein, N. Effects of Salinity on Root Growth. In Plant Roots: The Hidden Half, 4th ed.; Eshel, A., Beeckman, T., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2013; p. 784. [Google Scholar]
- Joyce, S.M.; Cassells, A.C.; Jain, S.M. Stress and aberrant phenotypes in vitro culture. Plant Cell Tiss. Org. Cult. 2003, 74, 103–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghighi, Z.; Karimi, N.; Modarresi, M.; Mollayi, S. Enhancement of compatible solute and secondary metabolites production in Plantago ovata Forsk. by salinity stress. J. Med. Plants Res. 2012, 6, 3495–3500. [Google Scholar]
- Brachet, J.; Cosson, L. Changes in the total alkaloid content of Datura innoxia Mill. subjected to salt stress. J. Exp. Bot. 1986, 37, 650–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnamurthy, R.; Bhagwat, K.A. Polyamines as modulators of salt tolerance in rice cultivars. Plant Physiol. 1989, 91, 500–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Varshney, K.A.; Gangwar, L.P.; Goel, N. Choline and betaine accumulation in Trifolium alexandrinum L. during salt stress. Egypt. J. Bot. 1988, 31, 81–86. [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy, B.; De Filippis, L.F. Physiological and oxidative response to NaCl of the salt tolerant Grevillea ilicifolia and the salt sensitive Grevillea arenaria. J. Plant Physiol. 1999, 155, 746–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, A.; Malpathak, N. Green hairy root cultures of Solanum khasianum Clarke—A new route to in vitro solasodine production. Curr. Sci. 2004, 87, 1442–1447. [Google Scholar]
- Jacob, A.; Malpathak, N. Plantlet regeneration enhances solasodine productivity in hairy root cultures of Solanum khasianum clarke. Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol.-Plant. 2005, 41, 291–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misra, N.; Gupta, A.K. Effect of salinity and different nitrogen sources on the activity of antioxidant enzymes and indole alkaloid content in Catharanthus roseus seedlings. J. Plant Physiol. 2006, 163, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, G.; Wang, X.; Guo, R.; Wang, Q. Effect of salt stress on phenolic compounds, glucosinolates, myrosinase and antioxidant activity in radish sprouts. Food Chem. 2010, 121, 1014–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valifard, M.; Mohsenzadeh, S.; Kholdebarin, B.; Rowshan, V. Effects of salt stress on volatile compounds, total phenolic content and antioxidant activities of Salvia mirzayanii. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2014, 93, 92–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fatima, S.; Mujib, A.; Tonk, D. NaCl amendment improves vinblastine and vincristine synthesis in Catharanthus roseus: A case of stress signalling as evidenced by antioxidant enzymes activities. Plant Cell Tiss. Org. Cult. 2015, 121, 445–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chhatoi, N.; Pradhan, B.; Deo, B. Effect of NaCl on root proliferation of Musa species through tissue culture. J. Plant Sci. Res. 2016, 3, 163–169. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, K.W.; Murthy, H.N.; Jeong, C.S.; Hahn, E.J.; Paek, K.Y. Organic germanium stimulates the growth of ginseng adventitious roots and ginsenoside production. Process Biochem. 2005, 40, 2959–2961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.M.; Jung, H.Y.; Kang, Y.M.; Yun, D.J.; Bahk, J.D.; Yang, J.K.; Choi, M.S. Effects of methyl jasmonate and salicylic acid on the production of tropane alkaloids and the expression of PMT and H6H in adventitious root cultures of Scopolia parviflora. Plant Sci. 2004, 166, 745–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, K.; Kubota, H.; Goda, Y.; Yamada, T.; Maitani, T. Glutathione enhanced anthraquinone production in adventitious root cultures of Rubia tinctorum L. Plant Biotech. 1997, 14, 63–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivanandhan, G.; Arun, M.; Mayavan, S.; Rajesh, M.; Jeyaraj, M.; Dev, G.K.; Manickavasagam, M.; Selvaraj, N.; Ganapathi, A. Optimization of elicitation conditions with methyl jasmonate and salicylic acid to improve the productivity of withanolides in the adventitious root culture of Withania somnifera (L.) Dunal. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2012, 16, 681–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saeed, S.; Ali, H.; Khan, T.; Kayani, W.; Khan, M.A. Impacts of methyl jasmonate and phenyl acetic acid on biomass accumulation and antioxidant potential in adventitious roots of Ajuga bracteosa Wall ex Benth., a high valued endangered medicinal plant. Physiol. Mol. Biol. Plants 2017, 23, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khan, T.; Abbasi, B.H.; Khan, M.A.; Azeem, M. Production of biomass and useful compounds through elicitation in adventitious root cultures of Fagonia indica. Ind. Crops Prod. 2017, 108, 451–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faizah, H.; Tanjung, M.; Purnobasuki, H.; Manuhara, Y.S. Biomass and flavonoid production of Gynura procumbens (L.). Merr adventitious root culture in Baloon-type Bubble- Bioreactor (BTBB) influenced by elicitation. Asian J. Plant Sci. 2018, 17, 107–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.H.; Murthy, H.N.; Wu, C.H.; Paek, K.Y. Sucrose-induced osmotic stress affects biomass, metabolite, and antioxidant levels in root suspension cultures of Hypericum perforatum L. Plant Cell Tiss. Org. Cult. 2010, 103, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, S.S.; Siril, E.A. Elicitor mediated adventitious root culture for the large-scale production of anthraquinones from Oldenlandia umbellata L. Ind. Crops Prod. 2018, 114, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.H.; Murthy, H.N.; Hahn, E.J.; Paek, K.Y. Establishment of adventitious root co-culture of Ginseng and Echinacea for the production of secondary metabolites. Acta Physiol. Plant. 2008, 30, 891–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Le, K.C.; Im, W.T.; Paek, K.Y.; Park, S.Y. Biotic elicitation of ginsenoside metabolism of mutant adventitious root culture in Panax ginseng. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 102, 1687–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Li, J.; Li, J.; Liu, S.; Wu, X.; Li, J.; Gao, W. Transcriptome profiling shows gene regulation patterns in ginsenoside pathway in response to methyl jasmonate in Panax Quinquefolium adventitious root. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 37263. [Google Scholar]
- Zaker, A.; Sykora, C.; Gossnitzer, F.; Abrishamchi, C.; Asili, J.; Mousavi, S.H.; Wawrosh, C. Effects of some elicitors on tanshinone production in adventitiousroot cultures of Perovskia abrotanoides Karel. Ind. Crops Prod. 2015, 67, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zou, D.; Liu, M.; Cong, M.; Cheng, N.; Gao, H.; Wang, S.; Liu, Z.; Li, G. Induction of Psammosilene tunicoides adventitious roots and the accumulation of triterpenoid saponins as affected by culture conditions. Int. J. Agric. Biol. 2017, 19, 1535–1540. [Google Scholar]
- Bicer, P.O.; Demirci, T.; Asci, O.A.; Baydar, N.G. Effects of methyl jasmonate and caffeic acid applications on secondary metabolite production in madder (Rubia tinctorum) root cultures. Ind. J. Pharm. Educ. Res. 2017, 51, 508–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jung, H.Y.; Kang, S.M.; Kang, Y.M.; Kang, M.J.; Yun, D.J. Enhanced production of scopolamine by bacterial elicitors in adventitious hairy root cultures of Scopolia parviflora. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 2003, 33, 987–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazmi, A.; Khan, M.A.; Mohammad, S.; Ali, A.; Kamil, A.; Arif, M.; Ali, H. Elicitation directed growth and production of steviol glycosides in the adventitious roots of Stevia rebaudiana Bertoni. Ind. Crops Prod. 2019, 139, 111530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dörnenburg, H.; Knorr, D. Strategies for the improvement of secondary metabolite production in plant cell cultures. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 1995, 17, 674–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, M.Z.; An, X.L.; Cui, X.H.; Jiang, X.L.; Piao, X.C.; Jin, M.Y.; Lian, M.L. Production of eurycomanone and polysaccharides through adventitious root culture of Eurycoma longifolia in a bioreactor. Biochem. Eng. J. 2021, 171, 108013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manuhara, Y.S.W.; Kusuma, D.Y.; Sari, R.L.K.; Kristanti, A.N. Biomass production of Gynura procumbens adventitious roots in different type of liquid culture. Biosaintifika. J. Biol. Biol. Educ. 2017, 9, 523–529. [Google Scholar]
- Etienne, H.; Berthouly, M. Temporary immersion systems in plant micropropagation. Plant Cell Tiss. Org. Cult. 2002, 69, 215–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.H.; Murthy, H.N.; Paek, K.Y. Production of Adventitious Root Biomass and Bioactive Compounds from Hypericum perforatum L. through Large Scale Bioreactor Cultures. In Production of Biomass and Bioactive Compounds Using Bioreactor Technology; Paek, K.Y., Murthy, H.N., Zhong, J.J., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 251–284. [Google Scholar]
- Ho, T.T.; Lee, K.J.; Lee, J.D.; Bhushan, S.; Paek, K.Y.; Park, S.Y. Adventitious root culture of Polygonum multiflorum for phenolic compounds and its pilot-scale production in 500 L-tank. Plant Cell Tiss. Org. Cult. 2017, 130, 167–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gantet, P.; Imbanlt, N.; Thiersault, M.; Doireau, M. Necessary of a functional octadecanoic pathway for indole alkaloid synthesis by Catharanthus roseus cell suspensions cultured in an auxin starved medium. Plant Cell Physiol. 1998, 39, 220–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, E.; Curtis, W.R. Characterization of fluid-flow resistance in root cultures with a convective flow tubular bioreactor. Biotech. Bioeng. 1998, 60, 375–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kevers, C.; Jacques, P.; Thonart, P.; Gaspar, T. In vitro Root Culture of Panax ginseng and Panax quinquefolium. Plant Growth Regul. 1999, 27, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deepthi, S.; Satheeshkumar, K. Cell line selection combined with jasmonic acid elicitation enhance camptothecin production in cell suspension cultures of Ophiorrhiza mungos L. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 101, 545–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altman, J. People on country, healthy landscapes and sustainable Indigenous economic futures: The Arnhem Land case. Aust. Rev. Public Aff. 2003, 4, 65–82. [Google Scholar]
- Tandon, V.R.; Gupta, R.K. An experimental evaluation of anticonvulsant activity of Vitex negundo. Ind. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2005, 49, 199–205. [Google Scholar]
- Engelmann, F. Use of biotechnologies for the conservation of plant biodiversity. Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol.-Plant 2011, 47, 5–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
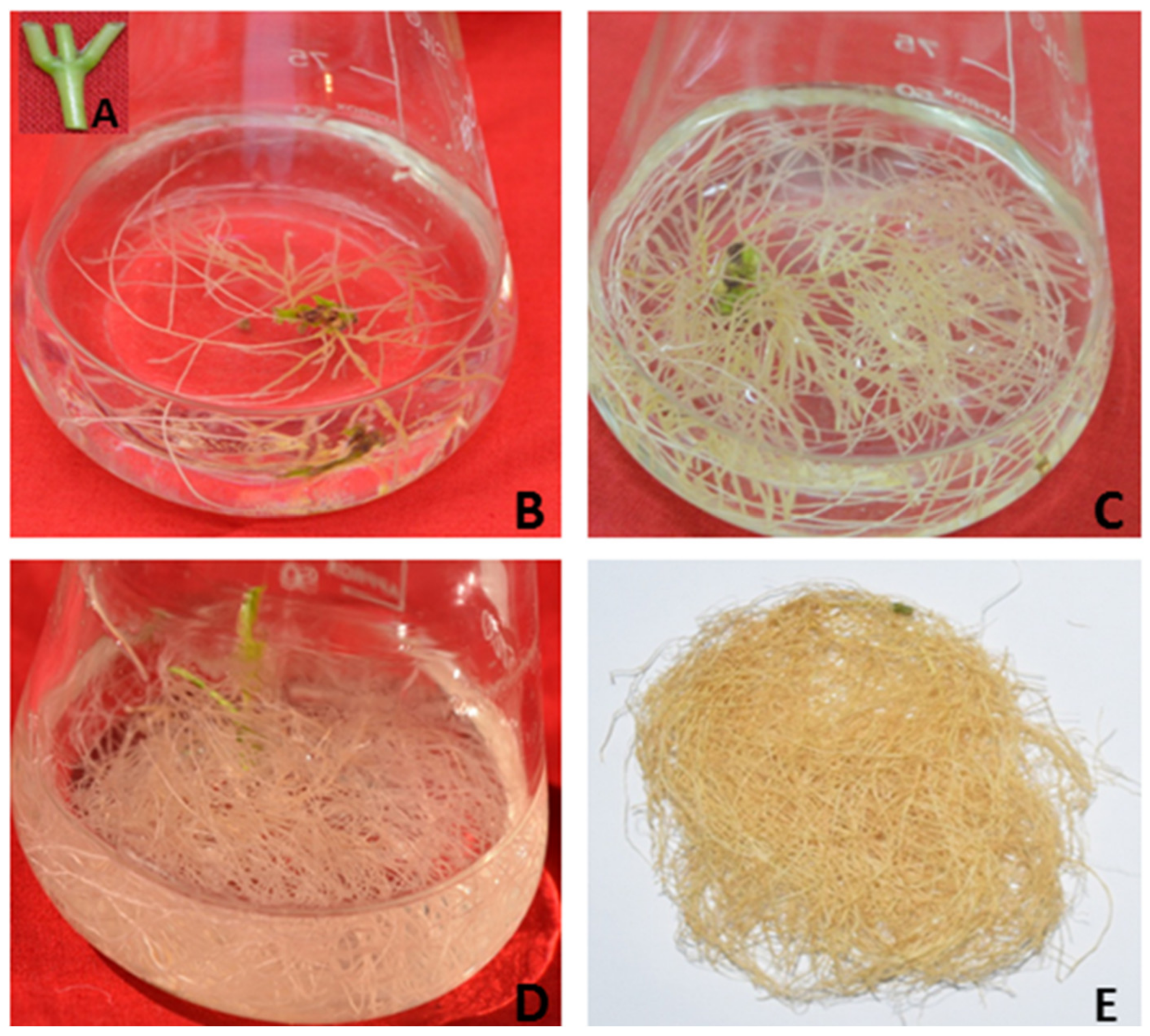

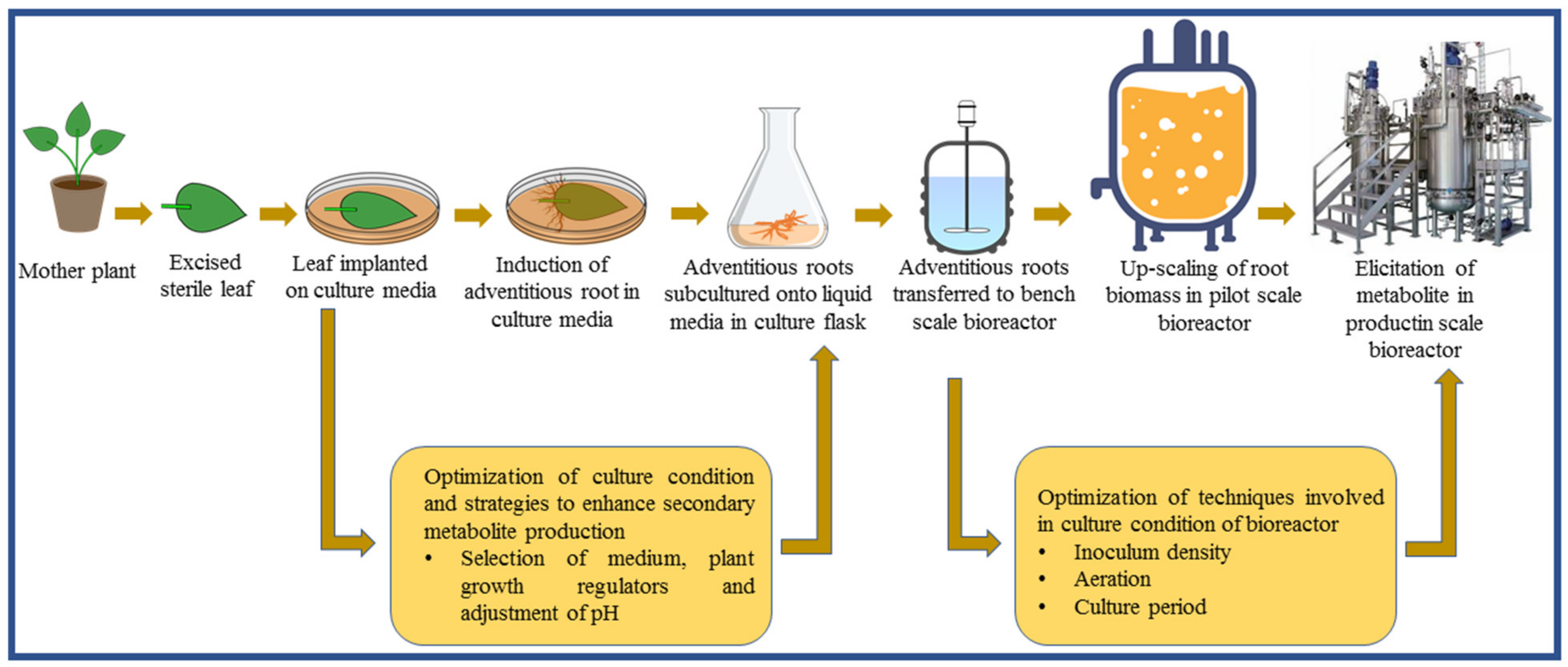
| Plant Species | Explants Used | Hormones Used | Metabolites | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Allamanda cathartica | Nodal segment | ½ MS + IBA (0.5 µM) | Iridoid glycosides | [45] |
| Andrographis paniculata | Leaf | MS + NAA (2.7 µM) | Andrographolide and diterpenoids | [43] |
| Artemisia vulgaris | Leaf and roots | MS + IAA (11.4 µM) + IBA (4.9 µM) | Coumarins, sesquiterpene lactones, volatile oils and inulin | [63] |
| Astragalus membranaceus | Seedling-derived roots | B5 + IBA (2.0 mg/L) | Polysaccharides, saponins and flavonoids | [64] |
| Boerhaavia diffusa | Leaf | MS + (1.0 mg/L) NAA | Punarnavine | [65] |
| Echinacea purpurea | Root | MS + IBA (2.0 mg/L) | Chichoric acid, chlorogenic acid and caftaric acid | [51,66] |
| Eurycoma longifolia | Leaf | ½ MS + NAA (3.0 mg/L) | Quassinoids and cathine-6-one Alkaloids | [67] |
| Glycyrrhiza uralensis | In vitro root | ½ MS + IBA (6.5 g/L) | Glycyrrhetinic acid, flavonoids and polysaccharides | [68] |
| Gynura procumbens | Leaf | MS + NAA (3 mg/L) + IBA (1 mg/L) | Caffeic acid, chlorogenic acid and 3, 5-di-O-caffeoylquinic acid | [69] |
| Hypericum perforatum | Leaf and stem | ½ MS + Kn (0.1 mg/L) + IBA (1 mg/L) | Flavonols, napthodianthrones phloroglucinols and xanthones | [70] |
| Hypericum perforatum | Adventitious root | MS + IBA (1.25 mg/L) | Hypericin | [71] |
| Morinda citrifolia | Leaf | ¼ MS + IBA (5.00 mg/L) + 5% Sucrose; MS + IBA (5.00 mg/L) | Anthraquinones, phenolics and flavonoids | [34,72,73] |
| Orthosiphon stamineus | leaf, root and stem | MS + IAA (3.00 mg/L) | Rosmarinic acid, oxygenated diterpenes and sinensitin | [74] |
| Panax ginseng | Leaf and root calluses | MS without NH4NO3 + NAA (2 mg/L); MS without NH4NO3 + IBA (25 µM); MS+ 2,4-D (4.5 µM) | Ginsenosides | [75,76,77] |
| Panax notoginseng | Leaf stalk, leaves and lateral roots | ½ MS + IBA (3.0 mg/L) | Protopanaxatriol saponins | [78] |
| Plumbago rosea | Leaf | MS + IAA (1.50 mg/L) + IBA (1.00 mg/L) | Plumbagin | [79] |
| Podophyllum hexandrum | Root | ½ MS + IBA (3 mg/L) + sucrose (2%) | Podophyllotoxin | [80] |
| Polygonum multiflorum | Root | ½ MS + IBA (9.84 µM) + sucrose (50 g/L) | Anthraquinones, stilbenes, flavonoids, tannins and phospholipids | [81] |
| Prunella vulgaris | Leaf-derived callus | MS + NAA (1.00 mg/L) | Phenolics and flavonoids | [82] |
| Psoralea corylifolia | Hypocotyl | MS + IBA (3 μM) | Psoralen | [60] |
| Raphanus sativus | Seedling-derived roots | ½ MS + IBA (0.5 mg/L) | Anthocyanin | [83] |
| Rhus javanica | Root | LS + NH4+ (30 mM) + NO3− (30 mM) + IBA (10−6 M) | Galloylglucoses (gallotannins), anthocyanidin and riccionidin A | [84] |
| Rumex crispus | Leaf | MS + NAA (5.0 µM) + Kn (0.5 µM) | Flavonoids | [85,86] |
| Stevia rebaudiana | Root tip | MS + NAA (10.7 µM) | Stevioside and rebaudioside | [87] |
| Withania somnifera | Leaf, leaf callus, cotyledon and internode | ½ MS + IAA (2.85 μM) + IBA (9.85 μM); ½ MS + IBA (0.5 mg/L); ½ MS + IBA (0.5 mg/L) + IAA (0.1 mg/L) | Withanolides, withaferin A and withanone | [88,89,90,91] |
| S.No. | Plant Species | Secondary Metabolites | Elicitors Applied | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Aloe vera | Aloe-emodin and chrysophanol | SA, MJ, ethephon | [53] |
| 2 | Ajuga bracteosa | Flavonoids, phenolics | MJ, PAA | [126] |
| 3 | Fagonia indica | Apigenin, rutin | MJ, PAA | [127] |
| 4 | Gynura procumbens | kaempferol and quercetin | Saccharomyces cereviciae, CuSO4 | [128] |
| 5 | Hypericum perforatum | Phenolics | MJ, SA, lactabumin hydrolysate | [129] |
| 6 | Morinda citrifolia | Antrhaquinones, phenolics, flavonoids | Chitosan, pectin | [72] |
| 7 | Oldenlandia umbellata | Anthroquinones | Yeast extract, pectin, xylan, | [130] |
| 8 | Panax ginseng | Ginsenoside | MJ | [131] |
| 9 | Panax ginseng | Ginsenoside | Mesorhizobium amorphae | [132] |
| 10 | Panax quinquefolium | Ginsenoside | MJ | [133] |
| 11 | Perovskia abrotanoides | Tanshinone | MJ, AgNO3, sorbitol, yeast extract | [134] |
| 12 | Polygonum multiforum | Phenolics | MJ, SA, yeast extract, chitosan | [81] |
| 13 | Psammosilene tunicoides | Triterpenoid saponins | oxalic acid | [135] |
| 14 | Rubia tinctorum | Antrhaquinones | MJ and caffeic acid | [136] |
| 15 | Scopolia parviflora | Scopolamine | MJ, SA, Bacteria | [123,137] |
| 16 | Stevia rebaudiana | Steviol glycosides | MJ, PAA | [138] |
| 17 | Withania somnifera | Withanolide, withaferin | Aluminium chloride, chitosan | [89] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khanam, M.N.; Anis, M.; Javed, S.B.; Mottaghipisheh, J.; Csupor, D. Adventitious Root Culture—An Alternative Strategy for Secondary Metabolite Production: A Review. Agronomy 2022, 12, 1178. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12051178
Khanam MN, Anis M, Javed SB, Mottaghipisheh J, Csupor D. Adventitious Root Culture—An Alternative Strategy for Secondary Metabolite Production: A Review. Agronomy. 2022; 12(5):1178. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12051178
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhanam, Mehrun Nisha, Mohammad Anis, Saad Bin Javed, Javad Mottaghipisheh, and Dezső Csupor. 2022. "Adventitious Root Culture—An Alternative Strategy for Secondary Metabolite Production: A Review" Agronomy 12, no. 5: 1178. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12051178
APA StyleKhanam, M. N., Anis, M., Javed, S. B., Mottaghipisheh, J., & Csupor, D. (2022). Adventitious Root Culture—An Alternative Strategy for Secondary Metabolite Production: A Review. Agronomy, 12(5), 1178. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12051178








