Assessment of Soil Contamination Using GIS and Multi-Variate Analysis: A Case Study in El-Minia Governorate, Egypt
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
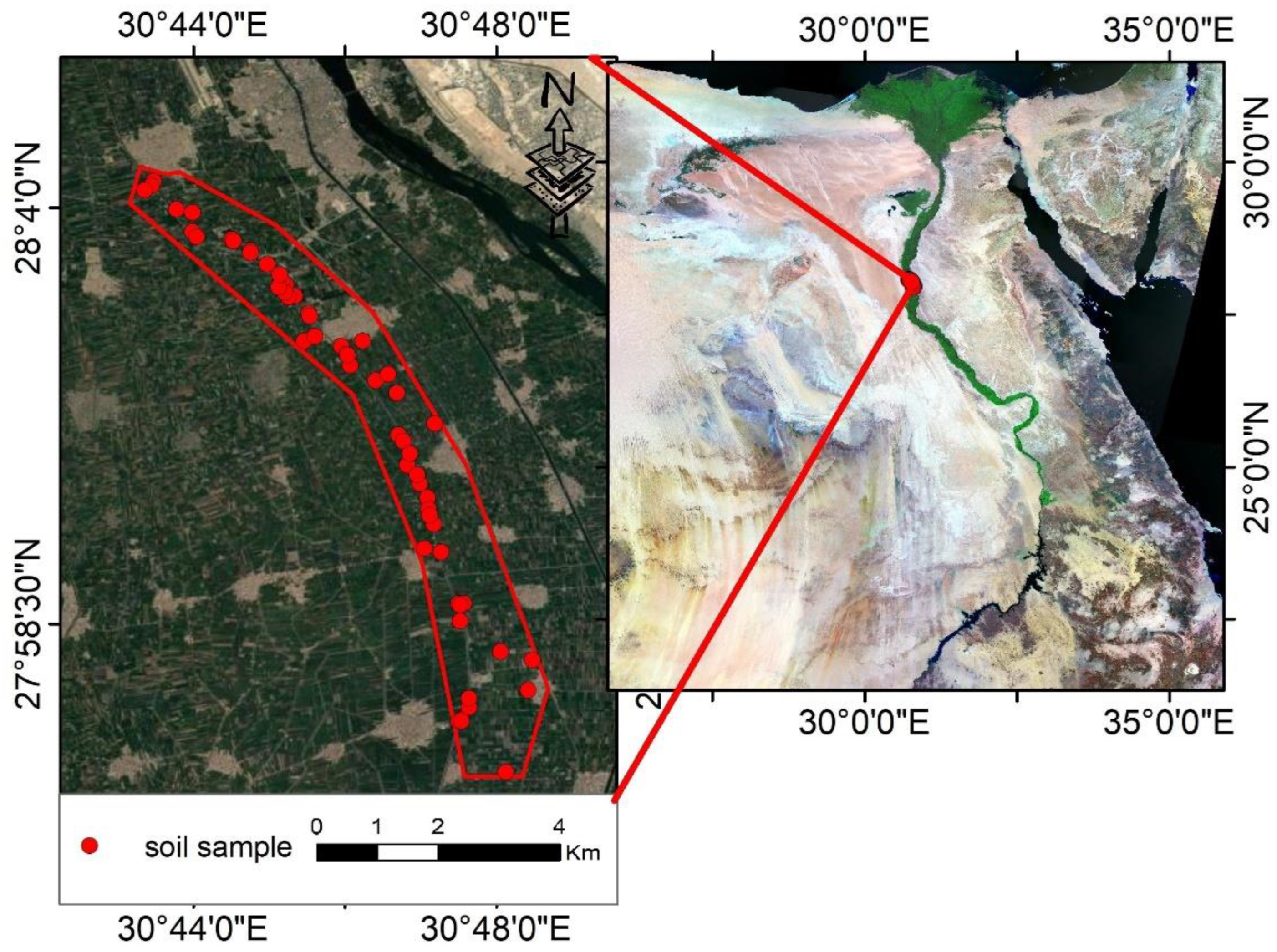
2.1. Discerption of the Study Area
2.2. Anthropogenic Activities in the Study Area
2.3. Field Study and Soil Analysis
2.4. Contamination Indices
2.5. Spatial Variability Maps of Some Soil Properties and Heavy Metals
2.6. Statistical and Principal Component Analysis
2.7. Remote Sensing and Image Processing
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Soil Properties and Heavy Metals of the Study Area
3.2. Geostatistical Analysis and Mapping
3.3. Principal Component Analysis (PCA)
3.4. Cluster Analysis Based on PCA
3.5. Land Use of the Study Area
3.6. Contamination Factor (CF) and the Degree of Contamination (DC)
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- El-Zeiny, A.M.; El-Hamid, H.T.A. Environmental and human risk assessment of heavy metals at northern Nile Delta region using geostatistical analyses. Egypt. J. Remote Sens. Space Sci. 2022, 25, 21–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nascimento, A.R.V.J.D.; Cunha, G.K.G.; Nascimento, C.W.A.D.; da Cunha, K.P.V. Assessing Soil Quality and Heavy Metal Contamination on Scheelite Mining Sites in a Tropical Semi-arid Setting. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2021, 232, 375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayode, A.A.; Akram, M.; Laila, U.; Al-Khashman, O.A.; Omowumi, T.; Elbossaty, W.F.M. Biological implications of atmospheric and pedospheric levels of heavy metals. Adv. Toxicol. Toxic Effects 2021, 5, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- AbdelRahman, M.A.E.; Shalaby, A.; Mohamed, E.S. Comparison of two soil quality indices using two methods based on geographic information system. Egypt. J. Remote Sens. Space Sci. 2019, 22, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baroudy, A.A.E.; Ali, A.M.; Mohamed, E.S.; Moghanm, F.S.; Shokr, M.S.; Savin, I.; Poddubsky, A.; Ding, Z.; Kheir, A.M.S.; Aldosari, A.A.; et al. Modeling Land Suitability for Rice Crop Using Remote Sensing and Soil Quality Indicators: The Case Study of the Nile Delta. Sustainability 2020, 12, 9653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, A.; Haghnia, G.H.; Ayoubi, S.; Safari, T. Impacts of geology and land use on magnetic susceptibility and selected heavy metals in surface soils of Mashhad plain, northeastern Iran. J. Appl. Geophys. 2017, 138, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd-Elmabod, S.; Bakr, N.; Muñoz-Rojas, M.; Pereira, P.; Zhang, Z.; Cerdà, A.; Jordán, A.; Mansour, H.; De La Rosa, D.; Jones, L. Assessment of Soil Suitability for Improvement of Soil Factors and Agricultural Management. Sustainability 2019, 11, 1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Elbehiry, F.; Elbasiouny, H.; Cappuyns, V.; Brevik, E.C. Available concentrations of some potentially toxic and emerging contaminants in different soil orders in Egypt and assessment of soil pollution. J. Soils Sediments 2021, 21, 3645–3662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, E.; Abu-Hashim, M.; AbdelRahman, M.; Schütt, B.; Lasaponara, R. Evaluating the Effects of Human Activity over the Last Decades on the Soil Organic Carbon Pool Using Satellite Imagery and GIS Techniques in the Nile Delta Area, Egypt. Sustainability 2019, 11, 2644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- El-Zeiny, A.M.; Effat, H.A. Environmental analysis of soil characteristics in El-Fayoum Governorate using geomatics approach. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2019, 191, 463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alengebawy, A.; Abdelkhalek, S.; Qureshi, S.; Wang, M.-Q. Heavy Metals and Pesticides Toxicity in Agricultural Soil and Plants: Ecological Risks and Human Health Implications. Toxics 2021, 9, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammam, A.A.; Mohamed, E. Mapping soil salinity in the East Nile Delta using several methodological approaches of salinity assessment. Egypt. J. Remote Sens. Space Sci. 2020, 23, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Effat, H.A.; El-Zeiny, A.M. Integration of satellite data and spatial decision models for zoning new urban communities in El-Fayoum Desert. Arab. J. Geosci. 2020, 13, 1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, E.S.; Ali, A.M.; El Shirbeny, M.A.; El Razek, A.A.A.; Savin, I.Y. Near infrared spectroscopy techniques for soil contamination assessment in the Nile Delta. Eurasian Soil Sci. 2016, 49, 632–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shokr, M.S.; El Baroudy, A.A.; Fullen, M.A.; El-Beshbeshy, T.R.; Ali, R.R.; Elhalim, A.; Guerra, A.J.T.; Jorge, M.C.O. Mapping of heavy metal contamination in alluvial soils of the Middle Nile Delta of Egypt. J. Environ. Eng. Landsc. Manag. 2016, 24, 218–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Behairy, R.A.; El Baroudy, A.A.; Ibrahim, M.M.; Kheir, A.M.S.; Shokr, M.S. Modelling and Assessment of Irrigation Water Quality Index Using GIS in Semi-arid Region for Sustainable Agriculture. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2021, 232, 352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, E.S.; Belal, A.; Shalaby, A. Impacts of soil sealing on potential agriculture in Egypt using remote sensing and GIS techniques. Eurasian Soil Sci. 2015, 48, 1159–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Nahry, A.H.; Mohamed, E.S. Potentiality of land and water resources in African Sahara: A case study of south Egypt. Environ. Earth Sci. 2010, 63, 1263–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heuvelink, G.B.M.R.; Webster, M.A. Oliver: Geostatistics for Environmental Scientists. Math. Geosci. 2009, 41, 487–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jolliffe, I. Principal component analysis. Encyclopedia of Statistics in Behavioral Science; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Abdel-Fattah, M.K.; Mohamed, E.S.; Wagdi, E.M.; Shahin, S.A.; Aldosari, A.A.; Lasaponara, R.; Alnaimy, M.A. Quantitative Evaluation of Soil Quality Using Principal Component Analysis: The Case Study of El-Fayoum Depression Egypt. Sustainability 2021, 13, 1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irpino, A.; Verde, R. A New Wasserstein Based Distance for the Hierarchical Clustering of Histogram Symbolic Data. In Data Science and Classification; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006; pp. 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Fattah, M.K.; Abd-Elmabod, S.K.; Aldosari, A.A.; Elrys, A.S.; Mohamed, E.S. Multivariate Analysis for Assessing Irrigation Water Quality: A Case Study of the Bahr Mouise Canal, Eastern Nile Delta. Water 2020, 12, 2537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Christakos, G.; Guo, M.; Xiao, L.; Huang, W. Space-time quantitative source apportionment of soil heavy metal concentration increments. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 223, 560–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Yang, X.; He, M.; Christakos, G. Beyond mere pollution source identification: Determination of land covers emitting soil heavy metals by combining PCA/APCS, GeoDetector and GIS analysis. CATENA 2020, 185, 104297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin-Zhong, W.; Guo-Shun, L.; Hong-Chao, H.; Zhen-Hai, W.; Qing-Hua, L.; Xu-Feng, L.; Wei-Hong, H.; Yan-Tao, L. Determination of management zones for a tobacco field based on soil fertility. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2009, 65, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Rawy, M.; Abdalla, F.; El Alfy, M. Water Resources in Egypt. In The Geology of Egypt; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 687–711. [Google Scholar]
- Masoud, A.M.; Moneim, A.A.; Redwan, M. Environmental Impact of Wastewater Inflow on Groundwater Quality, West Girga, Sohag, Egypt. Sohag Eng. J. 2022, 2, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayhoub, A.; Azzam, A. A survey on the assessment of wind energy potential in Egypt. Renew. Energy 1997, 11, 235–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shelbaya, M.M.A.; El-Azeim, M.M.A.; Menesi, A.M.; El-Mageed, M.M.A. Heavy Metals and Microbial Activity in Alluvial Soils Affected by Different Land-Uses. J. Soil Sci. Agric. Eng. 2021, 12, 165–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakarya, Y.M.; Metwaly, M.M.; AbdelRahman, M.A.E.; Metwalli, M.R.; Koubouris, G. Optimized Land Use through Integrated Land Suitability and GIS Approach in West El-Minia Governorate, Upper Egypt. Sustainability 2021, 13, 12236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gee, G.W.; Bauder, J.W. Particle-size Analysis. In Methods of Soil Analysis; Soil Science Society of America: Madison, WI, USA, 1986; pp. 383–411. [Google Scholar]
- Schumacher, B. Methods for the Determination of Total Organic Carbon (TOC) In Soils and Sediments; Ecological Risk Assessment Support Center Office of Research and Development: Washington, DC, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Page, A.L.; Keeney, D. Methods of Soil Analysis; American Society of Agronomy: Madison, WI, USA, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, S.R.; McLennan, S. The geochemical evolution of the continental crust. Rev. Geophys. 1995, 33, 241–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Håkanson, L. An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control. A sedimentological approach. Water Res. 1980, 14, 975–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isaaks, E.H.; Srivastava, M.R. Applied Geostatistics; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Cambardella, C.A.; Moorman, T.B.; Novak, J.M.; Parkin, T.B.; Karlen, D.L.; Turco, R.F.; Konopka, A.E. Field-Scale Variability of Soil Properties in Central Iowa Soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1994, 58, 1501–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, K.; Ver Hoef, J.M.; Krivoruchko, K.; Lucas, N. Using ArcGIS Geostatistical Analyst; ESRI: Redlands, CA, USA, 2001; Volume 380. [Google Scholar]
- Gundogdu, K.S.; Guney, I. Spatial analyses of groundwater levels using universal kriging. J. Earth Syst. Sci. 2007, 116, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Massart, D.L.; Vandeginste, B.G.; Buydens, L.M.C.; De Jong, S.; Lewi, P.J.; Smeyers-Verbeke, J. Handbook of Chemometrics and Qualimetrics: Part B. Applied Spectroscopy; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1998; Volume 52, p. 302. [Google Scholar]
- Lillesand, T.M.; Kiefer, R.W. Remote Sensing and Image Interpretation; WIley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Richards, L. Diagnosis and improvement of saline and alkali soils. Soil Sci. 1954, 78, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Rawy, M.; AbdelRahman, M.; Ismail, E. Integrated Use of Pollution Indices and Geomatics to Assess Soil Contamination and Identify Soil Pollution Source in El-Minia Governorate, Upper Egypt. J. Eng. Sci. Technol. 2020, 15, 2223–2238. [Google Scholar]
- Bradl, H.B. Source and Origins of Heavy Metals. In Interface Science and Technology; Bradl, H.B., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2005; pp. 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Azeim, M.A.; Mohamed, W.; Hammam, A. Soil Physiochemical Properties in Relation to Heavy Metals Status of Agricultural Soils in El-Minia Governorate, Egypt. J. Soil Sci. Agric. Eng. 2016, 7, 423–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, S.; Yadav, K.K.; Kumar, S.; Gupta, N.; Cabral-Pinto, M.M.; Rezania, S.; Radwan, N.; Alam, J. Chromium contamination and effect on environmental health and its remediation: A sustainable approaches. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 285, 112174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahey, S.; Kumar, R.; Sharma, M.; Kumar, V.; Bhardwaj, R. A critical review on toxicity of cobalt and its bioremediation strategies. SN Appl. Sci. 2020, 2, 1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaborowska, M.; Kucharski, J.; Wyszkowska, J. Biological activity of soil contaminated with cobalt, tin, and molybdenum. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2016, 188, 398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wuana, R.A.; Okieimen, F.E. Heavy Metals in Contaminated Soils: A Review of Sources, Chemistry, Risks and Best Available Strategies for Remediation. ISRN Ecol. 2011, 2011, 402647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- AbdelRahman, M.A.E.; Zakarya, Y.M.; Metwaly, M.M.; Koubouris, G. Deciphering Soil Spatial Variability through Geostatistics and Interpolation Techniques. Sustainability 2020, 13, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jolliffe, I.T.; Cadima, J. Cadima, Principal component analysis: A review and recent developments. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2016, 374, 20150202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdi, H.; Williams, L.J. Principal component analysis. WIREs Comput. Stat. 2010, 2, 433–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhiyuan, W.; Dengfeng, W.; Huiping, Z.; Zhiping, Q. Assessment of Soil Heavy Metal Pollution with Principal Component Analysis and Geoaccumulation Index. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2011, 10, 1946–1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gergen, I.; Harmanescu, M. Application of principal component analysis in the pollution assessment with heavy metals of vegetable food chain in the old mining areas. Chem. Central J. 2012, 6, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peres-Neto, P.R.; Jackson, D.A.; Somers, K.M. How many principal components? Stopping rules for determining the number of non-trivial axes revisited. Comput. Stat. Data Anal. 2005, 49, 974–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaiser, H.F. The Application of Electronic Computers to Factor Analysis. Educ. Psychol. Meas. 1960, 20, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, A.; Cullis, B.; Thompson, R. Exploring variety-environment data using random effects AMMI models with adjustments for spatial field trend: Part 1: Theory. In Quantitative Genetics, Genomics and Plant Breeding; CABI: Wallingford, UK, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Suárez, M.H.; Pérez, D.M.; Rodríguez-Rodríguez, E.M.; Romero, C.D.; Borreguero, F.E.; Galindo-Villardón, P. The Compositional HJ-Biplot—A New Approach to Identifying the Links among Bioactive Compounds of Tomatoes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Skrbic, B.; Durisic-Mladenovic, N. Principal component analysis for soil contamination with organochlorine compounds. Chemosphere 2007, 68, 2144–2152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, A.K.; Dubes, R.C. Algorithms for Clustering Data; Prentice-Hall, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Penkova, T. Principal component analysis and cluster analysis for evaluating the natural and anthropogenic territory safety. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2017, 112, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Anwar, A.; Mekky, H.S.; Salman, S.A.; Elnazer, A.A.; Abdel Wahab, W.; Asmoay, A.S. Mineralogical and petrographical studies of agricultural soil, Assiut Governorate, Egypt. Bull. Natl. Res. Cent. 2019, 43, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Ramady, H.; Alshaal, T.; Bakr, N.; Elbana, T.; Mohamed, E.; Belal, A.A. (Eds.) The Soils of Egypt; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Stockmann, U.; Padarian, J.; McBratney, A.; Minasny, B.; de Brogniez, D.; Montanarella, L.; Hong, S.Y.; Rawlins, B.G.; Field, D.J. Global soil organic carbon assessment. Glob. Food Secur. 2015, 6, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abuzaid, A.S.; AbdelRahman, M.A.E.; Fadl, M.E.; Scopa, A. Land Degradation Vulnerability Mapping in a Newly-Reclaimed Desert Oasis in a Hyper-Arid Agro-Ecosystem Using AHP and Geospatial Techniques. Agronomy 2021, 11, 1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Sharma, A.; Kaur, P.; Sidhu, G.P.S.; Bali, A.S.; Bhardwaj, R.; Thukral, A.; Cerda, A. Pollution assessment of heavy metals in soils of India and ecological risk assessment: A state-of-the-art. Chemosphere 2019, 216, 449–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heleika, M.A.; Ismail, E.; Ahmed, M. Delineation of contamination zone using geophysical and hydrogeochemical methods around the El Moheet drain in the El Minia district, Upper Egypt. Arab. J. Geosci. 2018, 11, 625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, V.; Vajpayee, P.; Singh, S.N.; Mehrotra, S. Effect of chromium accumulation on photosynthetic pigments, oxidative stress defense system, nitrate reduction, proline level and eugenol content of Ocimum tenuiflorum L. Plant Sci. 2004, 167, 1159–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashed, M. Monitoring of contaminated toxic and heavy metals, from mine tailings through age accumulation, in soil and some wild plants at Southeast Egypt. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 178, 739–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abuzaid, A.S.; Jahin, H.S.; Asaad, A.A.; Fadl, M.E.; AbdelRahman, M.A.E.; Scopa, A. Accumulation of Potentially Toxic Metals in Egyptian Alluvial Soils, Berseem Clover (Trifolium alexandrinum L.), and Groundwater after Long-Term Wastewater Irrigation. Agriculture 2021, 11, 713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd-Elmabod, S.K.; Mansour, H.; Hussein, A.A.E.F.; Mohamed, E.S.; Zhang, Z. Influence of irrigation water quantity on the land capability classification. Plant Arch. 2019, 2, 2253–2561. [Google Scholar]
- Elgharably, A.; Abdel Mageed, A.; Elgharably, G. Status of heavy metals in soils of Assiut as affected by the long-term use of sewage water in crop irrigation: Case study. Egypt. J. Soil Sci. 2014, 54, 289–304. [Google Scholar]









| Statistic | pH 1:2.5 | ECe dS m−1 | OC g kg−1 | mg kg−1 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cr | Co | Cu | Cd | Pb | Zn | ||||
| Nbr. of observations | 60 | 60 | 60 | 60 | 60 | 60 | 60 | 60 | 60 |
| Minimum | 7.79 | 1.76 | 7.52 | 53.09 | 19.97 | 34.61 | 0.29 | 15.59 | 66.28 |
| Maximum | 8.56 | 10.10 | 16.90 | 165.96 | 43.52 | 91.40 | 2.07 | 79.41 | 235.44 |
| Mean | 8.12 | 4.04 | 12.64 | 82.63 | 28.62 | 51.57 | 0.88 | 31.54 | 93.91 |
| Standard deviation | 0.14 | 1.80 | 2.63 | 22.29 | 5.59 | 11.43 | 0.46 | 16.44 | 32.40 |
| Skewness (Pearson) | 0.27 | 1.57 | −0.07 | 1.14 | 0.40 | 1.42 | 0.82 | 1.70 | 2.84 |
| Chemical composition of the upper continental crust (Taylor and Mclennan,1995) | 35 | 10 | 25 | 0.1 | 20 | 71 | |||
| Average natural concentration of heavy metals in rocks (values in mg kg−1) (Bradl, 2005) | 15–70 | 1.3–10 | 9.9–39 | 0.1–0.13 | 2.6–27 | 37–68 | |||
| Variable | Model | Nugget (C0) | Partial sill | Sill (C0 + C) | Nugget/Sill | Major Range | SDC | RMSE | ASE | RMSSE | ASE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | Gaussiang | 0.090 | 0.22 | 0.31 | 0.29 | 270 | Moderate | 0.57 | 0.024 | 0.95 | 0.48 |
| EC | Exponential | 0.006 | 0.26 | 0.27 | 0.02 | 560 | strong | 0.65 | 0.010 | 0.97 | 0.40 |
| OC | Stable | 0.000 | 0.24 | 0.24 | 0.00 | 270 | strong | 0.65 | 0.020 | 0.92 | 0.43 |
| Cr | spherical | 0.020 | 0.34 | 0.36 | 0.05 | 270 | strong | 0.91 | 0.020 | 0.91 | 0.40 |
| Co | Stable | 0.610 | 0.29 | 0.90 | 0.67 | 270 | Moderate | 0.50 | 0.001 | 0.97 | 0.40 |
| Cu | Stable | 0.120 | 0.20 | 0.32 | 0.37 | 292 | Moderate | 0.50 | 0.030 | 0.96 | 0.42 |
| Cd | Stable | 0.000 | 0.34 | 0.34 | 0.00 | 270 | strong | 0.68 | 0.030 | 0.88 | 0.52 |
| Pb | Gaussiang | 0.150 | 0.07 | 0.22 | 0.68 | 1615 | Moderate | 0.51 | 0.002 | 0.98 | 0.42 |
| Zn | spherical | 0.000 | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.00 | 362 | strong | 0.72 | 0.070 | 1.01 | 0.59 |
| Variables | pH (1:2.5) | ECe dS m−1 | OC g kg−1 | Cr mg kg−1 | Co mg kg−1 | Cu mg kg−1 | Cd mg kg−1 | Pb mg kg−1 | Zn mg kg−1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH (1:2.5) | 1 | ||||||||
| ECe dS m−1 | −0.402 ** | 1 | |||||||
| OC g kg−1 | −0.068 | 0.165 | 1 | ||||||
| Cr mg kg−1 | −0.391 ** | 0.160 | 0.211 | 1 | |||||
| Co mg kg−1 | −0.231 | −0.038 | 0.447 *** | 0.272 * | 1 | ||||
| Cu mg kg−1 | −0.282 | 0.071 | 0.445 *** | 0.616 *** | 0.417 ** | 1 | |||
| Cd mg kg−1 | −0.437 *** | 0.113 | 0.084 | 0.839 *** | 0.161 | 0.535 *** | 1 | ||
| Pb mg kg−1 | −0.320 * | 0.173 | 0.004 | 0.526 *** | 0.027 | 0.464 *** | 0.585 *** | 1 | |
| Zn mg kg−1 | −0.354 ** | 0.323 * | 0.285 * | 0.414 ** | 0.218 | 0.539 *** | 0.470 *** | 0.589 *** | 1 |
| F1 | F2 | F3 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Eigenvalue | 3.801 | 1.456 | 1.168 | |
| Variability (%) | 42.228 | 16.178 | 12.983 | |
| Cumulative % | 42.228 | 58.405 | 71.388 | |
| pH (1:2.5) | Factor loadings or Correlations between variables and factors | −0.588 | 0.204 | −0.409 |
| ECe dS m−1 | 0.331 | −0.215 | 0.835 | |
| OC g kg−1 | 0.389 | 0.737 | 0.231 | |
| Cr mg kg−1 | 0.830 | −0.097 | −0.264 | |
| Co mg kg−1 | 0.416 | 0.704 | −0.015 | |
| Cu mg kg−1 | 0.789 | 0.291 | −0.196 | |
| Cd mg kg−1 | 0.812 | −0.267 | −0.296 | |
| Pb mg kg−1 | 0.705 | −0.402 | −0.160 | |
| Zn mg kg−1 | 0.744 | −0.051 | 0.169 |
| Cluster | Statistic | pH (1:2.5) | ECe dS m−1 | OC g kg−1 | mg kg−1 | DC | DC Level | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cr | Co | Cu | Cd | Pb | Zn | |||||||
| 1 | No. of observations | 38 | 38 | 38 | 38 | 38 | 38 | 38 | 38 | 38 | 38 | Moderate |
| Minimum | 7.96 | 1.76 | 7.52 | 53.09 | 19.97 | 34.61 | 0.29 | 16.98 | 66.28 | 10.64 | ||
| Maximum | 8.56 | 6.23 | 16.90 | 90.90 | 43.52 | 91.40 | 1.07 | 48.60 | 131.13 | 19.85 | ||
| Mean | 8.17 a | 3.38 b | 12.13 a | 69.88 b | 27.63 a | 47.00 b | 0.61 b | 24.80 b | 82.12 b | 15.14 b | ||
| SD | 0.12 | 0.94 | 2.65 | 9.41 | 6.08 | 9.11 | 0.17 | 7.33 | 11.81 | 1.88 | ||
| Skewness | 1.35 | 0.81 | 0.16 | −0.07 | 0.58 | 2.96 | 0.38 | 1.65 | 1.72 | −0.25 | ||
| 2 | No. of observations | 22 | 22 | 22 | 22 | 22 | 22 | 22 | 22 | 22 | 22 | Considerable |
| Minimum | 7.79 | 2.39 | 9.37 | 63.51 | 22.72 | 43.00 | 0.41 | 15.59 | 79.28 | 13.12 | ||
| Maximum | 8.22 | 10.10 | 16.80 | 165.96 | 42.56 | 81.33 | 2.07 | 79.41 | 235.44 | 33.57 | ||
| Mean | 8.02 b | 5.17 a | 13.52 a | 104.64 a | 30.33 a | 59.45 a | 1.35 a | 43.19 a | 114.30 a | 25.70 a | ||
| SD | 0.12 | 2.31 | 2.34 | 20.90 | 4.09 | 10.72 | 0.42 | 20.75 | 44.34 | 5.68 | ||
| Skewness | −0.31 | 0.63 | −0.40 | 0.50 | 0.92 | 0.67 | −0.79 | 0.59 | 1.62 | −0.93 | ||
| DC | mg kg−1 | Area, h (%) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Level | Value | Cr | Co | Cu | Cd | Pb | Zn | |
| Moderate | 14.16 ± 1.4 | 68.84 ± 9.4 | 27.09 ± 5.4 | 47.15 ± 10.0 | 0.53 ± 0.1 | 23.80 ± 7.9 | 80.27 ± 8.0 | 830.9 (28.73%) |
| Considerable | 22.16 ± 4.8 | 91.23 ± 19.5 | 29.44 ± 5.2 | 53.83 ± 10.2 | 1.12 ± 0.3 | 36.04 ± 18.0 | 101.29 ± 35 | 2045.0 (70.7%) |
| very high | 32.85 ± 0.5 | 124.53 ± 24.8 | 34.14 ± 5.4 | 68.32 ± 8.7 | 1.83 ± 0.2 | 57.28 ± 13.7 | 143.09 ± 53.7 | 16.4 (0.57) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hammam, A.A.; Mohamed, W.S.; Sayed, S.E.-E.; Kucher, D.E.; Mohamed, E.S. Assessment of Soil Contamination Using GIS and Multi-Variate Analysis: A Case Study in El-Minia Governorate, Egypt. Agronomy 2022, 12, 1197. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12051197
Hammam AA, Mohamed WS, Sayed SE-E, Kucher DE, Mohamed ES. Assessment of Soil Contamination Using GIS and Multi-Variate Analysis: A Case Study in El-Minia Governorate, Egypt. Agronomy. 2022; 12(5):1197. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12051197
Chicago/Turabian StyleHammam, Amr A., Wagih S. Mohamed, Safa Essam-Eldeen Sayed, Dmitry E. Kucher, and Elsayed Said Mohamed. 2022. "Assessment of Soil Contamination Using GIS and Multi-Variate Analysis: A Case Study in El-Minia Governorate, Egypt" Agronomy 12, no. 5: 1197. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12051197
APA StyleHammam, A. A., Mohamed, W. S., Sayed, S. E.-E., Kucher, D. E., & Mohamed, E. S. (2022). Assessment of Soil Contamination Using GIS and Multi-Variate Analysis: A Case Study in El-Minia Governorate, Egypt. Agronomy, 12(5), 1197. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12051197









