Abstract
The use of glyphosate-based herbicides (GBHs) in industrial agriculture has intensified in the past decades, causing a growing concern about the occurrence and spatial distribution of glyphosate and its principal metabolite, aminomethylphosphonic acid (AMPA), in the environment. In 2014, glyphosate and AMPA content was measured in 45 soils from the St. Lawrence Lowlands (Quebec, Canada) before seeding and at harvest in soybean field crops using various weed management practices with or without GBH applications. At the same time, a recent history of agricultural practices and soil conditions was compiled for the sampled sites. The results of the study show that 91% of the samples contained detectable amount of either glyphosate or AMPA, with maximum values of 0.47 mg·kg−1 and 1.16 mg·kg−1 for glyphosate and AMPA, respectively. Surprisingly, detectable amounts of AMPA were measured in fields not treated with GBHs in 2014, whereas traces of both glyphosate and AMPA were detected in organic field crops, highlighting the potential spreading and/or persistence of both compounds in the environment. Glyphosate content was significantly higher in clay soils rich in exchangeable cations, such as Mg2+, K+ and Ca2+, which can contribute to the retention of glyphosate in soil via complexation processes.
1. Introduction
The use of herbicides, and in particular, glyphosate-based ones (GBHs), in agricultural weed management practices has intensified over the past decades. Based on their affordability and their efficiency to control weeds [1], GBHs were rapidly adopted in field crop agricultural practices following the emergence of Roundup Ready (RR) soybean cultivar in 1996 [2]. Most agricultural farms use an RR and non-RR crop rotation to maintain high yields and stay competitive on the grain market in comparison with a solely non-RR field crop system [3]. In order to control the rise of glyphosate-resistant weeds worldwide [4], both the number of GBH applications and the doses of active ingredients increased over the last decades [5]. Whereas glyphosate is either relatively quickly degraded [6] or adsorbed in soil [7], not much is known about the impact of repeated GBH applications regarding agricultural soil health and functions [8,9,10]. The glyphosate half-life in soil is generally short, ranging from a few days to a few weeks [8,11,12,13,14], whereas the half-life of its main metabolite, aminomethylphosphonic acid (AMPA), is estimated to be up to six times longer [8,14,15,16,17]. However, numerous studies report much longer residence time for glyphosate and AMPA in soil, with amounts of both compounds measured more than a year after the last GBH application [16,18,19,20], highlighting the pluriannual persistence of glyphosate and AMPA in agricultural soils [21]. Longer residence time seems to be linked to the type of soil and its composition [16]. Indeed, clay, oxides and organic matter appear to promote glyphosate and AMPA retention in soil [7,22,23,24,25]. The presence of exchangeable cations also seems to affect the dynamics of glyphosate and AMPA in soil by the formation of complexes, which are then able to be adsorb onto mineral surfaces [26,27]. Most studies reporting a persistence of glyphosate and AMPA in agricultural soils following GBH applications have been conducted in South America [21,28] and more recently in Europe [29,30]. In North America, studies are scarce, somewhat outdated and have been performed in non-agricultural soils [31,32]. However, recent glyphosate studies in water bodies report the dispersion of both glyphosate and AMPA in the environment [19,33,34], emphasizing the need for a better knowledge of the variables influencing the persistence and the dispersion of these compounds in the environment.
In this study, we aim to determine glyphosate and AMPA content in the surface horizon (0–20 cm) of field crop soils cultivated with soybean at the year of sampling under three distinct cropping systems: RR, Identity Preserved (IP) and organic farming (OF), in the St. Lawrence Lowlands (Quebec, Canada). The study also aims at evaluating the variables influencing the persistence of glyphosate and AMPA in agricultural soils. The ultimate goal is to estimate the effects of agricultural practices using GBHs as a weed management practice and the role of soil texture and exchangeable cations on glyphosate and AMPA persistence in soils. In the context of soil preservation, this study provides much needed data, which should help to better understand glyphosate and AMPA dynamics in agricultural ecosystems in order to identify risk areas and to optimize agricultural practices in soya field crops.
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Study Sites and Soil Sampling
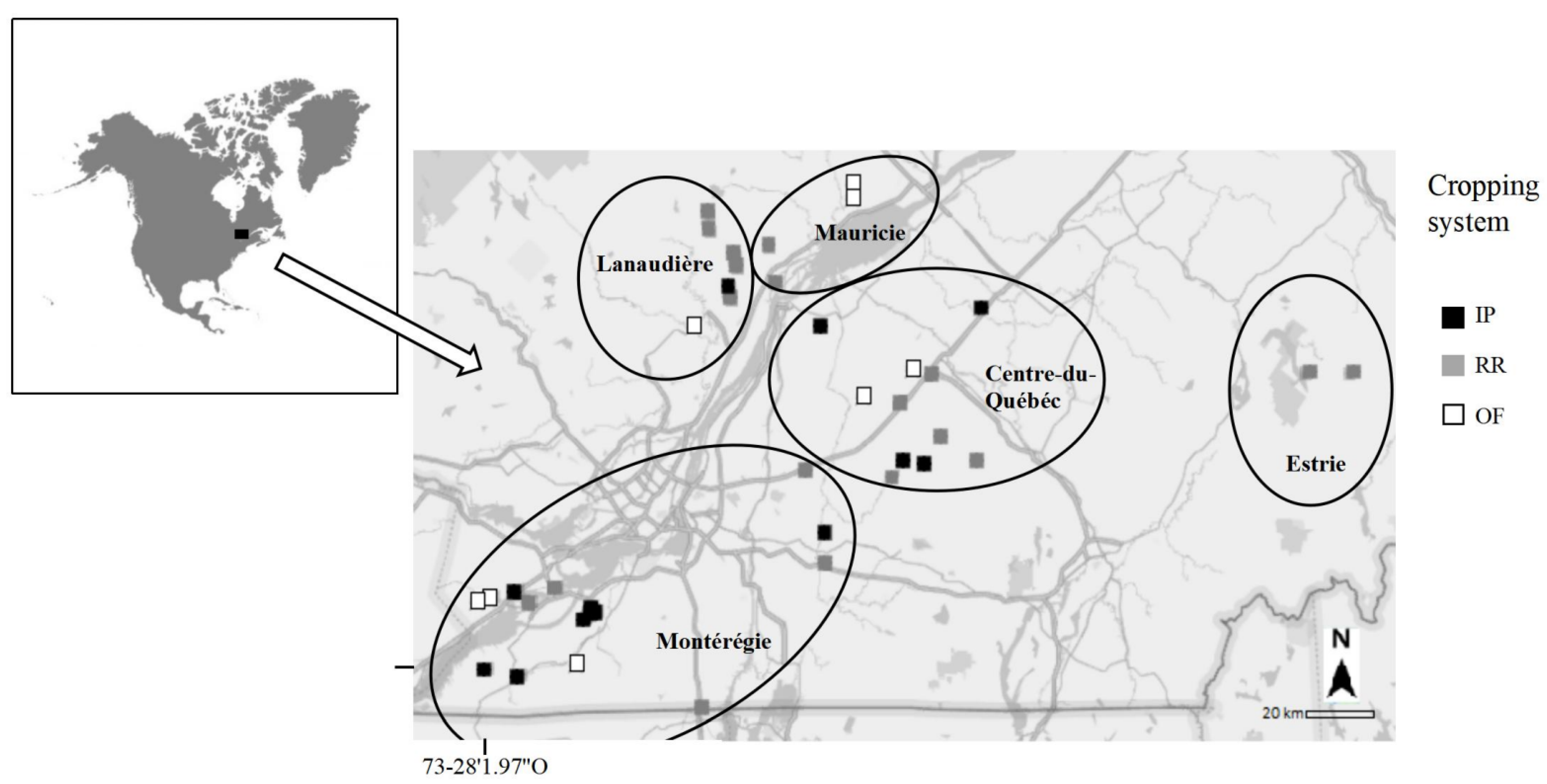
Soil samples were collected in 2014 in 45 soybean field crops from the St. Lawrence Lowlands (Quebec, Canada) (Figure 1). Sites covered five regions: Montérégie (1), Lanaudière (2), Mauricie (3), Centre-du-Québec (4) and Estrie (5). Sites were subdivided regarding the type of cropping systems: (i) RR, with one or more GBH applications (n = 21), (ii) IP, which is not genetically modified to resist glyphosate but where GBH applications can be used pre-sowing (n = 16) and (iii) OF, where GBH applications are prohibited (n = 8). The maximum distance as the crow flies between all sites was 270 km.
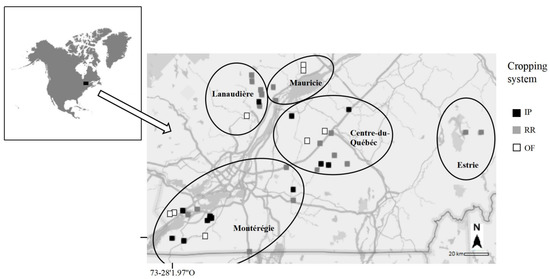
Figure 1.
Location of the study sites (n = 45) on the St. Lawrence Lowlands during the sampling campaign in 2014 before sowing (May 2014) and at harvest (October 2014) for the three cropping systems RR (Roundup Ready); IP (Identity Preserved) and OF (Organic Farming).
Farmers’ self-administered questionnaires were used to collect data about the agricultural practices specific to each site (i.e., soil tillage and number of GBH applications) (Table 1). Unfortunately, GBH application rates were not specified by the majority of the farmers.

Table 1.
Weeding and soil preparation practices at the sites of the study. The number of applications could not be determined at seven sites.
Environmental variables (i.e., soil texture, principal soil limitations, total precipitations and field area) for each sampled field were gathered using the Info-Sols database (www.info-sols.ca (accessed on 23 March 2022)), a geographic information system for the agricultural landscape in Quebec (Canada), and data from Environment and Climate Change Canada (www.canada.ca/en/environment-climate-change (accessed on 1 September 2015)). Based on these data, each sampling site was assigned to a specific texture class (Table 2).

Table 2.
Site distribution by soil textural class in the five study regions.
Each site was sampled twice. The first sampling mission took place in May 2014 before soybean seeding, whereas the second one was performed in October 2014 before harvest. On each site, three soil cores (0–20 cm) spaced 100 m apart were collected and georeferenced in order to accurately sample the same spots during the second campaign. Soil samples were frozen and stored at −20 °C upon analyses.
2.2. Exchangeable Cations Analyses
Soil samples were dried in an oven at 55 °C and sieved using a two-millimeter sieve prior to analysis. The Mehlich III method of the CEAEQ (2010) with a soil/solution ratio of 1:10 was used to extract the exchangeable phosphorus and the exchangeable cations of the following elements: K, Fe, Mn, Mg, Ca, Cu, Zn and Al. Exchangeable cations were measured by atomic absorption spectrometry (ARL 906AA, GBC Scientific Equipment, Melbourne, Australia), whereas phosphorus was analyzed by UV-visible spectrometry at wavelength 875 nm, using the Harwood et al. method (1969) slightly modified by Lucotte and Anglejan [35]. In brief, 10 mL of sample solution was added to 10 mL of reactive Harwood, then supplemented with 50 mL of milli-Q water. The mixture was stirred vigorously and conserved for 30 min, before analysis within 90 min. Harwood’s reagent was prepared as follows: in a 500 mL balloon, 250 mL of 4N sulphuric acid was added with 75 mL of ammonium molybdate, 25 mL of antimony potassium tartrate and 100 mL of 10% ascorbic acid (p/v), then supplemented with milli-Q water.
2.3. Glyphosate and AMPA Content Measurements
Soil samples were freeze-dried, crushed and sieved using a two-millimeter sieve, and 5 g of soil was directly weighed into a 50 mL falcon. Then, glyphosate and AMPA were extracted using a slightly modified version of the method described by Alferness and Iwata [36]. Briefly, an extraction solution was prepared by mixing 34.5 mL of NH4OH (28–30%) with 13.6 g of KH2PO4 and adjusting the final volume to 1 L. The extraction solution was diluted 1:2 and a volume of 40 mL was transferred to the falcon containing the soil sample. The falcon was mixed using a vortex mixer for 30 sec before being placed on a rotating wheel at 200 rpm for 30 min. Afterwards, samples were centrifuged at 3500 rpm for 20 min before being filtered at 0.2 µm (InnoSepTM SF25 nylon filter). An amount of 40 µL of the extract was transferred to an injection vial and evaporated to dryness under a stream of nitrogen. Then, the extract was derivatized, following the protocol described by Deyrup et al. [37], by adding 500 µL of trifluoroethanol (TFE) and 1000 µL of trifluoroacetic anhydride (TFAA) and heating at 100 °C for one hour. After cooling down to room temperature, the extract was once again evaporated to dryness under a stream of nitrogen. Prior to GC-ECD injection, samples were dissolved in 1000 µL of isopropyl acetate where 1 µL of 1-bromopentadecane was finally added in order to monitor injection reproducibility. A Varian GC 3800 gas chromatograph equipped with a Restek RXI-5SIL MS capillary column (30 m × 0.25 mm ID, 0.25 µm) was used to analyze samples. The chromatographic conditions used for glyphosate detection were as follows: injector temperature, 250 °C; detector temperature, 300 °C and oven temperature program, 60 °C (hold for 0.50 min, 6 °C·min−1 to 170, 60 °C·mn−1 to 250 °C, hold 10.0 min, for a total run of 30.17 min). High purity hydrogen was used as a carrier gas (at a flow of 1.4 mL·min−1), and the injection volume was 1 µL.
To minimize uncertainty of chromatographic measurements, GC-ECD performance parameters were checked on a daily basis to verify their suitability for the purpose of glyphosate/AMPA analysis. The limit of detection (LOD) and limit of quantification (LOQ) were determined based on the method described in Mocak et al. [38]. The calculated LOD and LOQ were 0.02 mg·kg−1 and 0.05 mg·kg−1, and 0.03 mg·kg−1 and 0.09 mg·kg−1 for glyphosate and AMPA, respectively. Calibration curves of six points showed good linearity for both analytes (r2 = 0.96; p < 0.0001 and r2 = 0.99; p < 0.0001 for glyphosate and AMPA, respectively) in the domain of expected samples concentration.
Regarding sample quantification, each sample batch included a standard curve made of five standards (0, 0.2, 0.4, 0.6, 0.8 mg·kg−1 for AMPA and 0, 0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4 mg·kg−1 for glyphosate) ran in the same matrix as the unknown sample.
2.4. Statistical Analyses
In order to use samples with glyphosate or AMPA content below the LOD or between the LOD and the LOQ in the statistical analyses, we arbitrarily assigned values. Specifically, content below the LOD was assigned with a value of LOD/2 (i.e., 0.01 mg·kg−1 and 0.02 mg·kg−1 for glyphosate and AMPA, respectively), whereas samples with content between the LOD and LOQ were given a value of LOQ/2 (i.e., 0.03 mg·kg−1 and 0.05 mg·kg−1 for glyphosate and AMPA, respectively).
Samples were compared using a rank test for matched Wilcoxon samples, used to compare glyphosate and AMPA levels of the soil samples taken at the time of planting (May 2014) and those collected at harvest (October 2014), with a serving threshold of 0.05. For the other parameters studied, namely crop management, the number of GBH applications, tillage and soil texture, a non-parametric variance analysis was used to compare glyphosate and AMPA content, since distribution was not normal and variance not homogenous for both compounds obtained with a Kruskal–Wallis row test with a meaning threshold of 0.05. The distribution of the content was represented by a box plot and the frequencies measured by histograms. For the comparison of the different soil textures, only the clay (CT), loam (LT) and sandy-loam (SLT) soils were selected, as the number of the other classes was too low to be representative. Glyphosate and AMPA levels and the presence of cations available in soils for the harvest campaign (October 2014) were combined with a multivariate analysis and a main component analysis (PCA) including 10 variables (i.e., glyphosate, AMPA, P, Mn, K, Cu, Al, Ca, Fe and Mg content) after focusing and reducing the data. For this analysis, 22 of 45 samples covering the entire study area, with the exception of the Estrie region, were used due to the limit of the exchangeable cations and phosphorus analyses. Soil textures for which the number of samples was insufficient were also not counted in this analysis. Five axes were chosen, achieving an inertia of 80.5%. The data analysis used soil texture as an additional variable and was completed with the correlation matrix and the square cosinus table of variables. All tests were carried out with the JMP Pro 14 software from SAS Institute (Cary, NC, USA).
3. Results
3.1. Glyphosate and AMPA Content in Surface Soils
In the collected soils, glyphosate content ranged from below the LOD to 0.47 mg·kg−1 and AMPA content from below the LOD to 1.16 mg·kg−1 (Table 3). At least one of the two compounds was detected in 91% of the samples, whereas both glyphosate and AMPA were measured in 39% of the samples. However, AMPA was more widespread with 70% of the samples containing AMPA in comparison to 42% for glyphosate. Surprisingly, both glyphosate and AMPA were detected in some OF soil samples with maximum values of 0.15 mg·kg−1 and 0.24 mg·kg−1, respectively. In RR systems, 48% of the total sample, spring and harvest samples merged, presented detectable amounts of glyphosate, AMPA or both whereas, in IP systems, glyphosate and AMPA were measured at every sample site with the exception of two (80%). On the other hand, only one OF site had measurable amounts of AMPA and glyphosate simultaneously.

Table 3.
Measured glyphosate and AMPA content in agricultural soils of the study for Roundup Ready (RR), Identity Preserved (IP) and Organic Farming (OF) cropping systems.
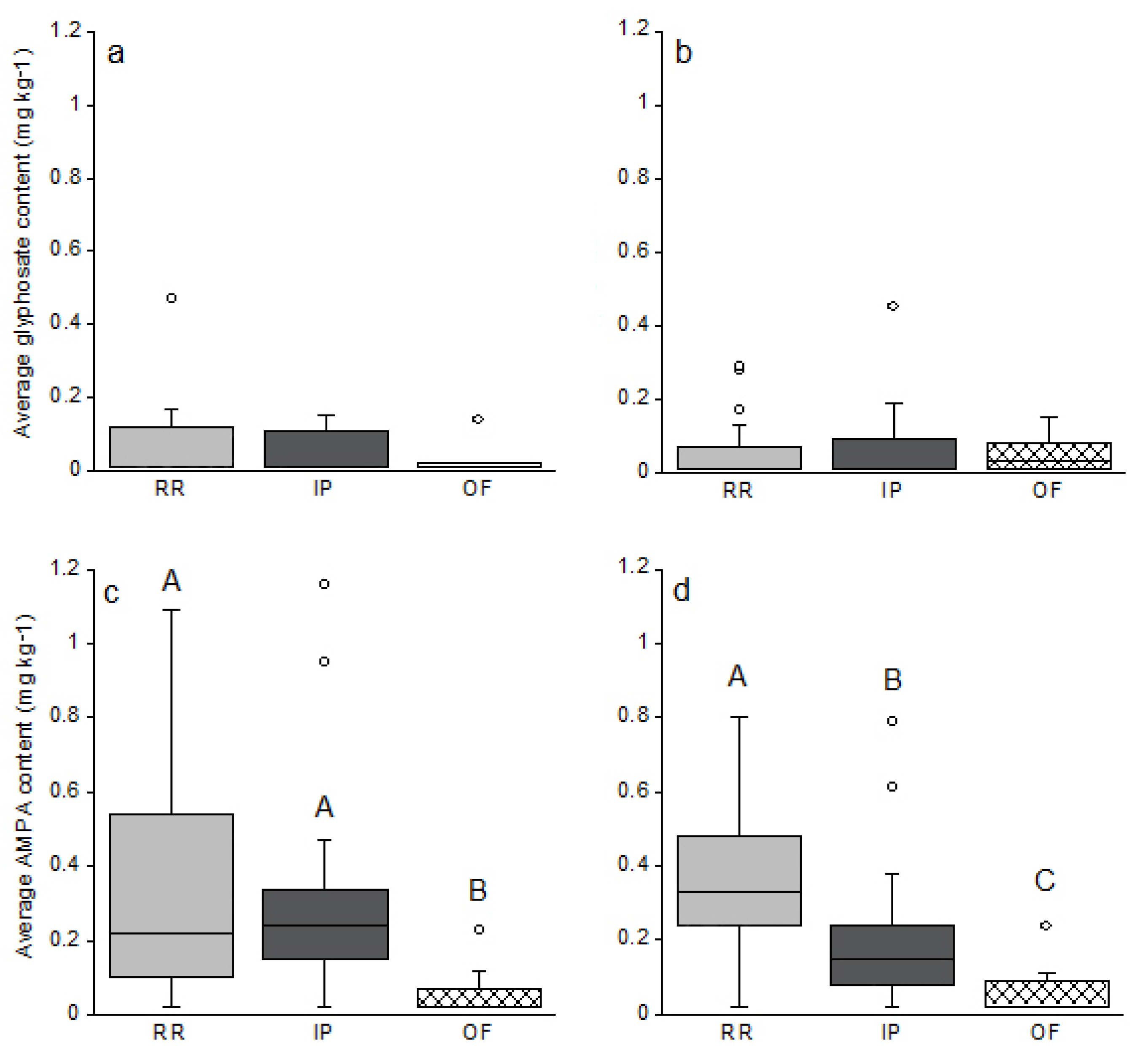
No significant difference was observed between glyphosate or AMPA content measured during spring or at harvest time (p > 0.05, Wilcoxon test on paired samples), whatever the soybean culture management (Figure 2a–d). However, within a single sample campaign, significant differences were observed for AMPA content in soil (Figure 2c,d). Indeed, in May before seeding, AMPA content in OF systems were inferior to the ones measured in RR and IP systems. RR and IP systems displayed similar AMPA content at the same period (Figure 2c). At harvest time, AMPA content was significantly different between all three agrosystems as follows: RR > IP > OF (Figure 2d). Regarding glyphosate, no difference was observed at either spring or harvest between the three agrosystems (Figure 2a,b).
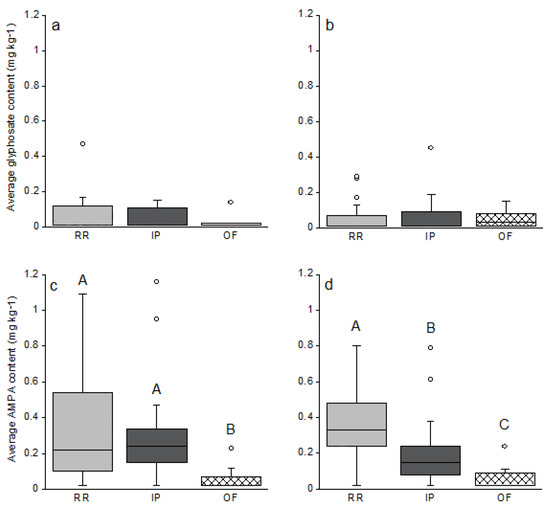
Figure 2.
Glyphosate (a,b) and AMPA (c,d) content according to the agricultural system used in May 2014 before sowing (a,c) and in October 2014 (b,d) at harvest time for the three cropping systems RR (Roundup Ready); IP (Identity Preserved) and OF (Organic Farming). For RR, n = 21; IP n = 16 and OF n = 8. Boxplots represent the median, and the 25 and 75 % quantiles. Circles ° represent potential outliers. Significant differences were tested using the non-parametric Kruskal–Wallis test, with a significant threshold set at 0.05 and annotated on the graph with letters A, B and C corresponding to the different significant groups. When there is no letter, it means that no significant differences were observed between the three groups.
3.2. Impact of the Number of GBH Applications
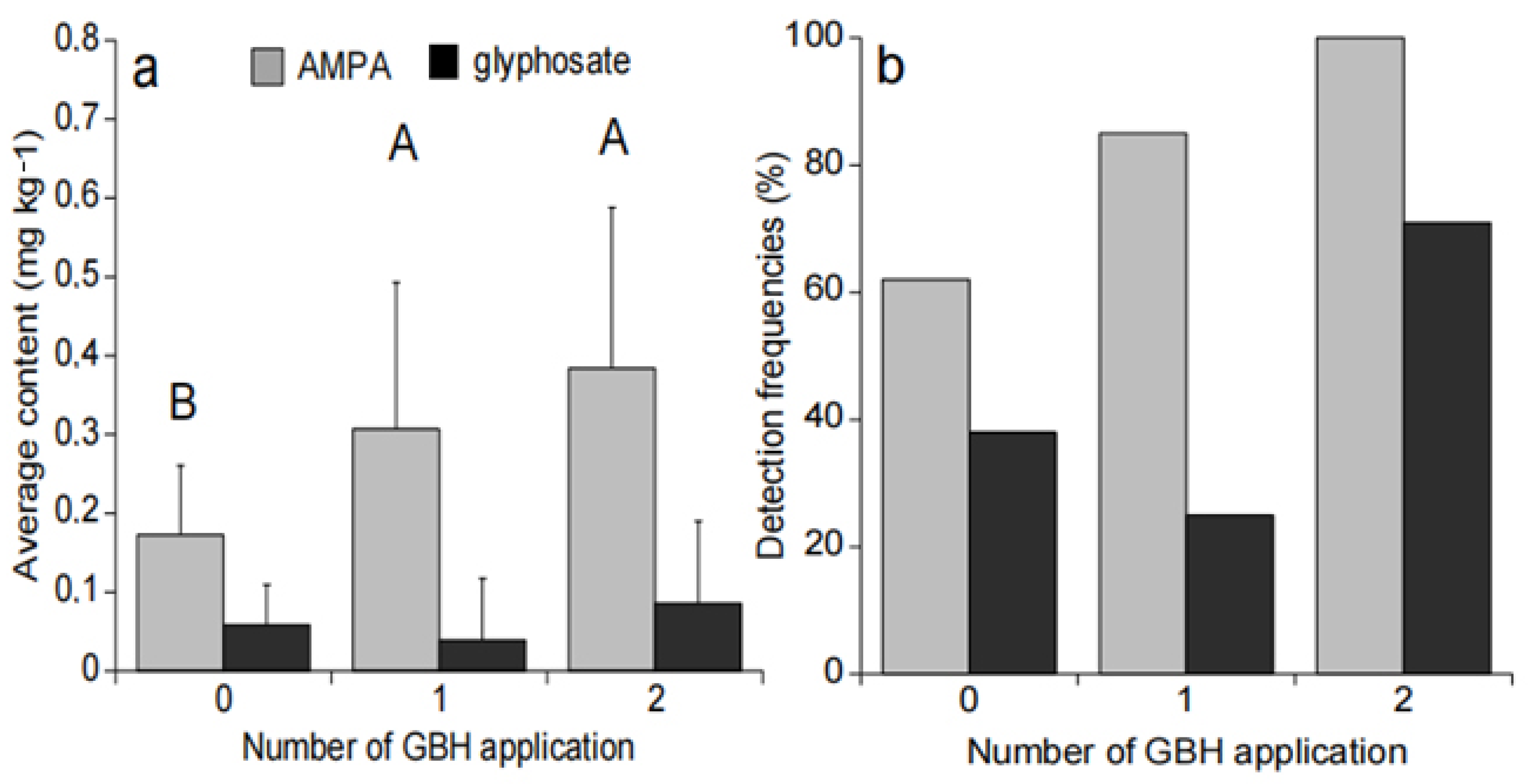
Glyphosate content was not significantly different between sample sites no matter the number of GBH applications (Figure 3a). However, the glyphosate detection frequency was higher in soil that received two GBH applications in comparison with the ones with one or no GBH application (Figure 3b).
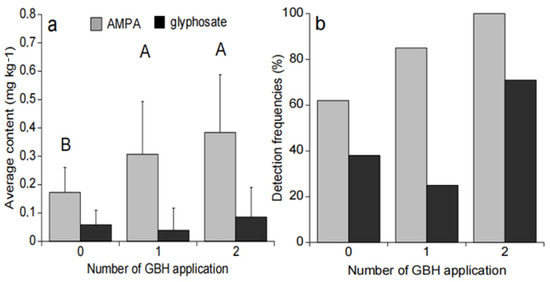
Figure 3.
Average glyphosate and AMPA content and associated standard deviation (a). Glyphosate and AMPA detection frequencies in soils (b) at harvest time according to the number of GBH applications. The letters A and B represent the different significant groups.
AMPA content were significantly different between sites without GBH applications and with one GBH application (p = 0.002), as well as between sites without GBH applications or with two GBH applications (p = 0.003) (Figure 3a). The number of GBH applications did not seem to affect the average AMPA content measured in soil samples (p > 0.05) (Figure 3a), but the AMPA detection frequency in soil was higher along with the number of GBH applications (Figure 3b).
3.3. Impact of Tillage
Regarding tillage, a comparison between glyphosate and AMPA content measured in soils with direct seeding and soils with tillage did not show significant difference (p > 0.05).
3.4. Impact of Soil Texture and Composition
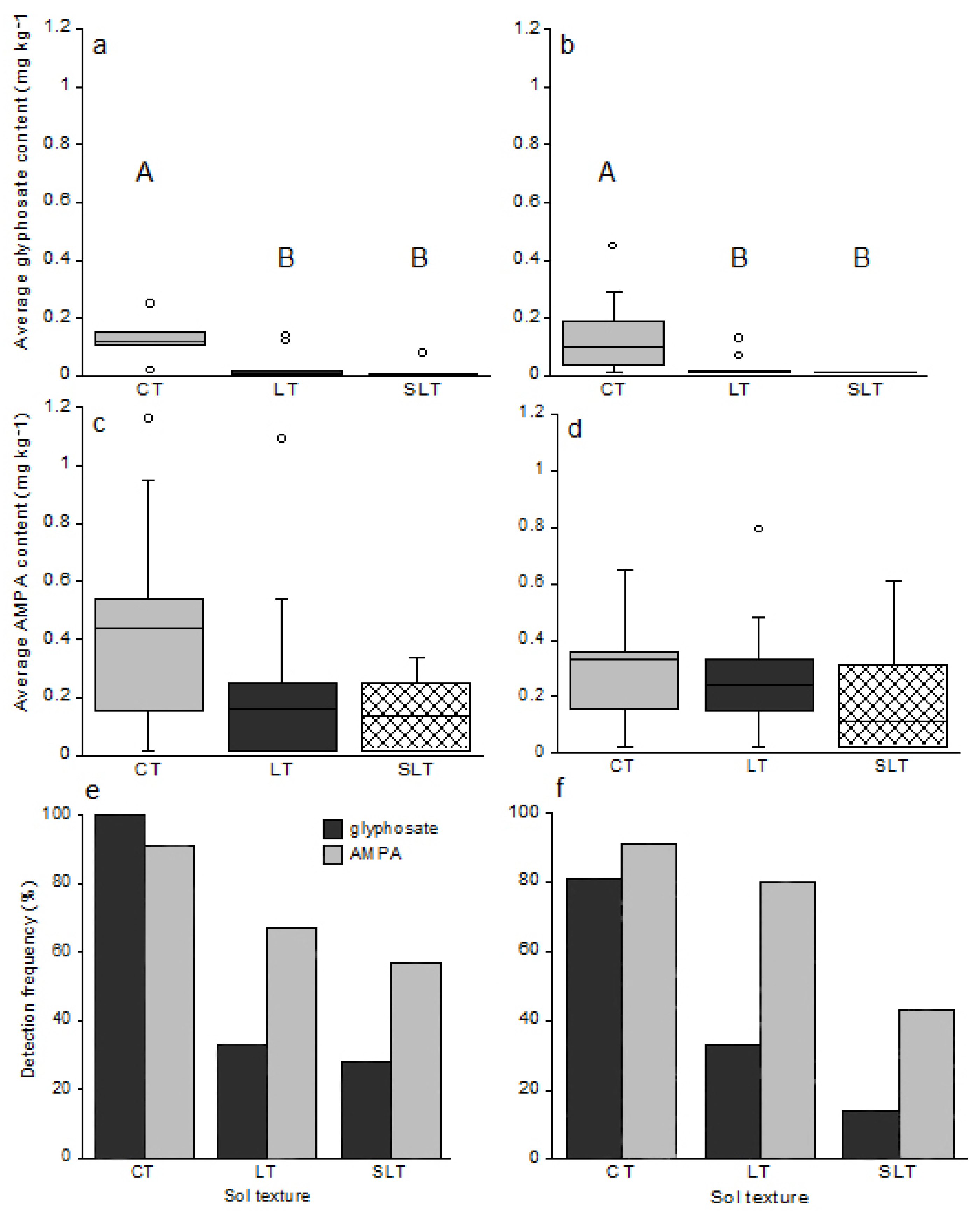
Glyphosate content was significantly higher in CT soils (n = 10) in comparison with LT soils (n = 15) and SLT soils (n = 6), either during spring (CT vs. LT p = 0.0018; CT vs. SLT p = 0.0003; Figure 4) or at harvest time (CT vs. LT p = 0.0049; CT vs. SLT p = 0.0026; Figure 4a,b). Glyphosate was detected in all CT soil samples, whereas it was present in 13% and 17% of LT soils and SLT soils, respectively (Figure 4). Regarding AMPA content, no significant difference was observed depending on soil texture, but the compound was more often detected in CT soils (91%) in comparison with LT soils (67%) and SLT soils (50%) (Figure 4e,f).
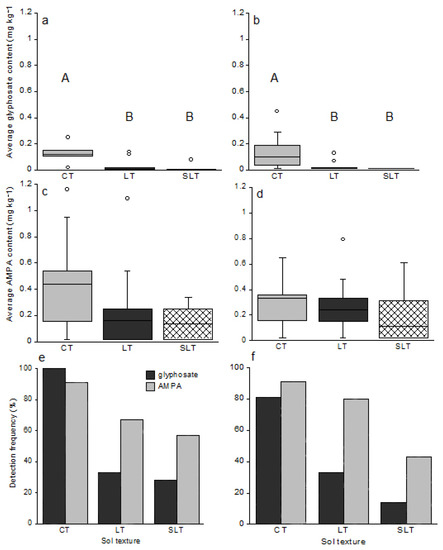
Figure 4.
Average glyphosate and AMPA content based on the texture of clay (CT n = 10), loam (LT n = 15) and sandy loam (SLT n = 6) soils in May 2014 before sowing (a,c) and in October 2014, at harvest time (b,d). Boxplots represent the median, and the 25 and 75% quantiles. Circles ° represent potentially outliers. The detection frequencies of both compounds according to soil texture were represented by bar histograms before sowing (e) and at harvest time (f). The letters A and B represent the different significant groups.
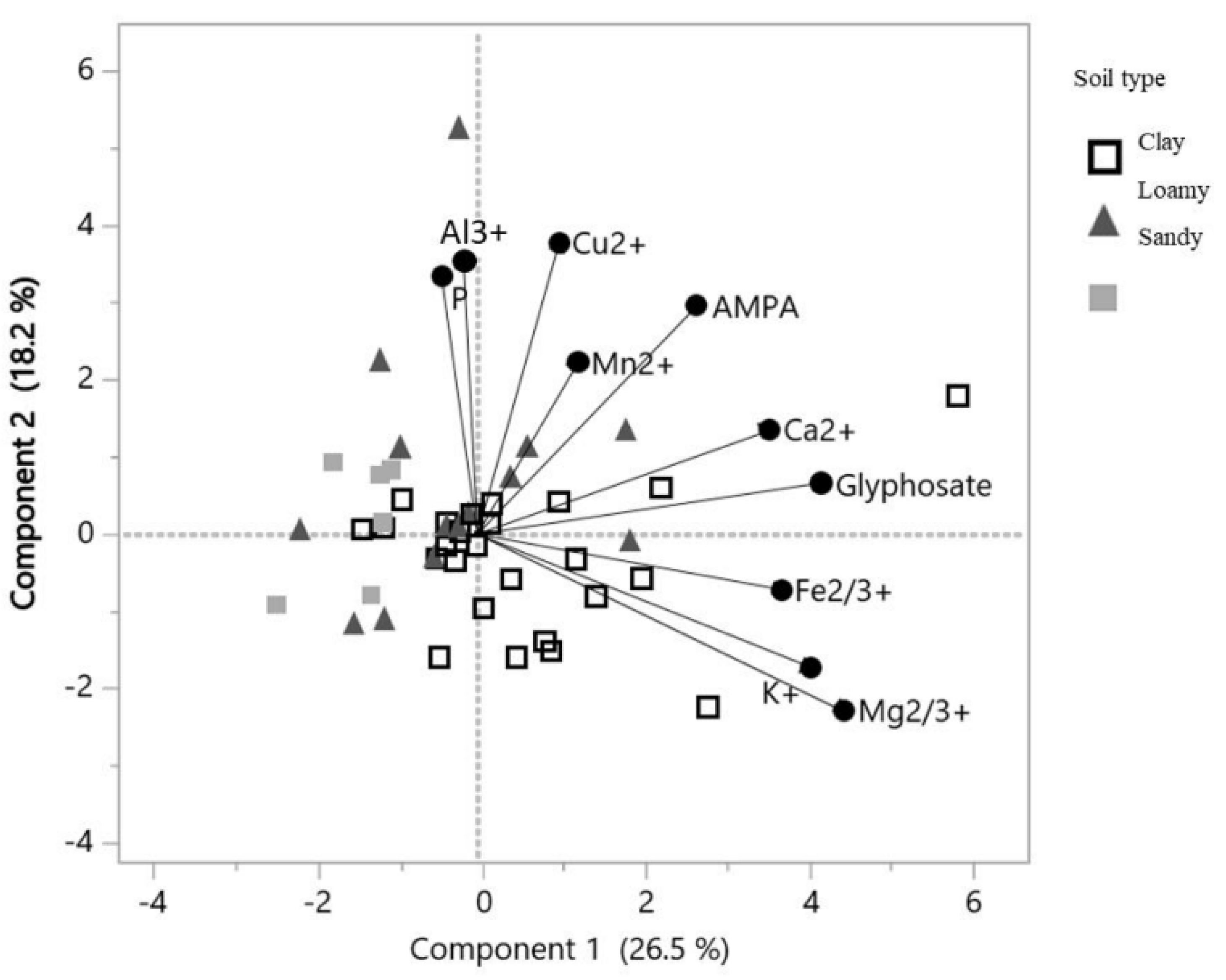
A principal component analysis based on 22 samples and 10 variables was run in order to evaluate a potential link between glyphosate or AMPA content and the exchangeable cation content in soils (Figure 5, Table 4). The PC1 was best explained with the following gradient: Mg2+ content > glyphosate content > K+ content > Fe2+/3+ content > Ca2+ content (Table 4). The multivariate analysis also highlighted a positive correlation between glyphosate content and Ca2+ content (r2 = 0.59, p = 0.032). The first component largely explained the content of these elements in SLT soils and CT soils (cos2 = 0.83 and 0.62, respectively) (Figure 5). The component 2 was best explained with the following gradient: Cu2+ content > Al3+ content > phosphorus content > AMPA content (Table 4). The PC2 explained the content of these elements in SL soils (cos2 = 0.46) (Figure 4).
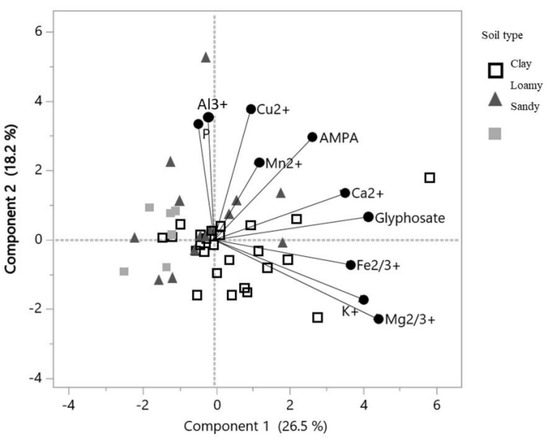
Figure 5.
Graphic representation of the PCA based on components 1 and 2, incorporating the additional variable of the three major textural classes (clay, loamy and sandy), according to the three soybean crop management systems (RR, IP and OF).

Table 4.
Partial contribution of variables as %, representing the composition of soils derived from the PCA, according to the 5 axes chosen and representing 80.45% of total inertia.
4. Discussion
4.1. Persistence and Accumulation of Glyphosate and AMPA in Soil
With 91% of the collected soil samples containing glyphosate and/or AMPA, our results highlight the ubiquity of these compounds in field crop soils cultivated with soybean under three distinct cropping systems (i.e., RR, IP and OF). As expected, AMPA is present more often than glyphosate, with 70% of the samples having detectable amounts of AMPA and 42% of glyphosate. In the literature, lower percentages of detection were generally reported, with 62.5% in studies performed in Argentina [28], 50 to 66% in the USA [19] and 45% in a large variety of crops in Western Europe [29,39]. However, these studies were not exclusively related to field crop soils. A higher frequency of glyphosate and AMPA detection in the studied soils seems to indicate that field crop systems with soybean and maize rotation could potentially promote the persistence of these compounds in agricultural soil. Primost et al. [21] reported the presence of at least one of these two compounds in all the soil samples from 17 fields in Argentina where farmers were applying GBHs. The authors explained the ubiquity of glyphosate and AMPA in their study by the fact that they sampled soils directly in fields treated with GBH applications, in opposition to other studies in which analyses have been made in various compartments at the watershed scale, and thus, the fields were not necessarily systematically exposed to GBH applications.
Glyphosate content measured in soils was in agreement with the ones reported in the literature worldwide for field crops, whereas AMPA content was higher [29,34,40]. However, Primost et al. [21] reported much higher glyphosate and AMPA content than the ones measured in this study. Considering that the glyphosate degradation rate is slower at lower temperatures [41], the cold winter experienced in the Quebec region could in part explain these differences. Indeed, in cold climate, both compounds were detected several years after the last GBH applications [8,42,43] and the glyphosate half-life can be as long as 460 days [7]. Laitinen and collaborators [20] evaluated that 19% and 48% of the initially applied quantities of glyphosate and AMPA, respectively, remained 20 months after the last application in a climate similar to what is encountered in the Quebec region. The fact that, in the present study, glyphosate and AMPA are detectable in field crop soils treated with GBHs as well as in field crop soils which did not receive any GBH applications in 2014 seems to indicate that these compounds can be persistent for more than one year in soils and have the potential to accumulate through time. This observation is in agreement with other studies reporting an accumulation of glyphosate in soils through time [8,10,44,45,46,47]. Andrea et al. [48] suggested that glyphosate mineralization depended on the crop history and decreased with repeated applications. Recently, Primost et al. [21] estimated that glyphosate content could increase by 1 mg per kg of soil every five GBH applications, due to an application rate superior to the dissipation rate contributing to a non-linear accumulation of glyphosate and AMPA in soils. Glyphosate and AMPA content in Argentine soils being 2 to 5 times higher than those measured in Quebec soils [21,28] highlights the impact of crop history in glyphosate and AMPA persistence and accumulation in soil. In Argentina, soils receive an average of 3.3 GBH applications per year, whereas in Quebec, glyphosate-resistant field crops generally do not receive more than two GBH applications. However, as previously mentioned, the relation between glyphosate accumulation in soil and the number of GBH applications does not seem linear. This agrees with our results since: (i) regarding glyphosate and AMPA content in soil, no difference was observed between spring and harvest for both compounds, (ii) the number of GBH applications (0, 1 or 2) did not seem to impact the glyphosate content in soils and/or its detection frequency and (iii) the ranges of glyphosate and AMPA content in soils are the same for RR and IP agrosystems.
The increase in AMPA content and detection frequency with the number of GBH applications in 2014 could be due to the history of each site, regarding the number of GBH applications they received the previous years.
Soil tillage does not seem to be a major factor influencing glyphosate and AMPA persistence in Quebec soils since no difference is observed between sites with soil tillage vs. direct seeding crop system sites. This observation agrees with previous studies [24,47,49]. Soracco et al. [50] also reported an accumulation of glyphosate and AMPA in soils under conventional and no-till systems during a soybean growing season. However, they observed a higher variation in glyphosate and AMPA content in soils under tillage. Other studies noticed an increase of glyphosate and AMPA content in no-till soils after GBH applications [46,51]. It seems that tillage could potentially increase glyphosate and AMPA leaching [52] since pore size and their connectivity could be affected and increase solute transport [47,53]. Nevertheless, the effects of soil tillage are difficult to evaluate in field conditions because agricultural practices depend on other factors, such as the GBH application method, crop history or soil type.
4.2. Impact of Soil Texture on Glyphosate and AMPA Dynamics
Based on our results, glyphosate seems to be more persistent in CT soils than in LT and SLT soils (Figure 4a,b), but AMPA content in soils is similar no matter the soil type (Figure 4c,d). AMPA is known to have a superior retention capacity in comparison with glyphosate, likely due to a different type of fixation site [45]. Indeed, due to its chemical configuration, soils have a higher adsorption capacity for AMPA than for glyphosate, which could explain AMPA’s lesser sensitivity to crop and soil variables, and thus, its ubiquity and generally higher content in soils. Since aluminum oxides have a strong adsorption capacity for AMPA [24,45], the principal way for AMPA adsorption could be via ligand exchange and thus would be dependent on oxide content rather than soil texture.
Numerous studies highlighted glyphosate adsorption on clay silicates and oxides [54,55,56]. Clay soils seem to promote glyphosate accumulation by delaying its degradation. Indeed, Bergström et al. [16] showed a 6.5 higher glyphosate persistence in clay soils than in sandy soils; additionally, the fact that glyphosate is more persistent in soils with a higher clay content seems to be a consensus [45,47,57]. It seems to be due to a stronger glyphosate adsorption on clay [40,58,59,60]. Contrary to the AMPA, glyphosate adsorption could be achieved via complexation mechanisms, thus explaining the link between glyphosate content and soil texture in the present study (Figure 4a,b). Glyphosate adsorption in soil is influenced by clay content and the soil cations exchange capacity (CEC) [47]. The CEC is the amount of exchangeable cations in the soil that can attach to the soil organic matter and clays, promoting cations-glyphosate complexation [26,61]. A decrease in glyphosate availability can be observed following the formation of these chemical complexes [62], and thus potentially affect glyphosate degradation in soils. In a study by Nguyen et al. [63], glyphosate mineralization ranged from 7 to 71% of the initially applied amount in 21 agricultural soils with various textures. In this case, the calcium and potassium exchangeable cations seemed to largely influence glyphosate mineralization (i.e., a positive correlation). However, the formation of calcium–glyphosate complexes have been also linked to a decrease in glyphosate bioavailability for degradation [64]. In the clay soils of our study, the multivariate analysis seems to indicate that the exchangeable cations promoting the most glyphosate persistence in soils are Mg2+, K+, Ca2+ and Fe2+/3+. Major cations such as Mg2+, K+ and Ca2+ are known to increase the glyphosate sorption coefficient in sandy loam soils [65]. Moreover, soils with higher clay, calcium and magnesium content and a stronger CEC were also linked to a greater glyphosate adsorption [47]. These cations can form insoluble complexes with glyphosate over a long period of time [26,27], thus stabilizing glyphosate in agricultural soils.
4.3. Glyphosate and AMPA Diffusion Potential in the Environment
Our results highlight the ubiquity of both glyphosate and AMPA in agricultural soils of the St. Lawrence Lowlands. It is of concern to detect these compounds in sites where GBH applications are not performed (i.e., organic farming systems), but not surprising since studies reported the presence of both glyphosate and AMPA in soils never exposed to GBHs [28,66]. In Quebec, certified organic field crop farmers are required to not apply herbicides for at least three years in a row.
The presence of glyphosate and AMPA in these soils could be explained by two mechanisms: (i) The long-term persistence in soils of glyphosate and AMPA that originated from GBH applications before the process of application for the organic certification. It is unlikely since only two samples had superior content in spring in comparison with harvest. (ii) The proximity of the OF sites to field crops using GBH applications and the diffusion of glyphosate with the wind [67,68,69,70] and with surface waters (Zheng et al., 2018). Indeed, glyphosate and AMPA that originated from GBH applications or from wind eroded sediment were detected in air samples from agricultural areas in the United States [70]. The amount of glyphosate measured during diffusion by pulverization and by run-off can be similar, with 6.9% and 3.9% of the applied quantity, respectively [71]. An important part of glyphosate is that it is leachable for a few weeks after GBH application. Glyphosate is generally detected more often in spring during the GBH applications period [72] and up to 47% of the applied glyphosate can be washed away with run-off [14,73], although AMPA is also leachable [74,75]. Moreover, a fraction of both glyphosate and AMPA adsorbed in soil can also be leached long after the last GBH application [8]. A history of repeated GBH applications over years could also increase glyphosate and AMPA leaching from agricultural soils with a positive correlation between the number of years a site has been exposed to GBHs and the degree of leaching [76]. This information highlights the issue of GBHs extensive use and how glyphosate and AMPA have the potential to impact agricultural soils for years due to their persistence. Glyphosate and AMPA are not to be only considered as a problem in glyphosate-resistant crops since their diffusion in the environment can be non-negligible [19,33,34]. This persistence and diffusion of both compounds also raise concerns on soil health and sustainability for the long term and on the impact of non-glyphosate-resistant crops.
5. Conclusions
A residual fraction of glyphosate and AMPA persist in soils, which may raise concerns for the sustainability of the cropping system. In addition, both compounds have also been detected in organically managed soils with no recent application of pesticides, showing widespread diffusion of these compounds in agricultural areas. Persistence appears to be more important in clay soils with a higher content of exchangeable cations, such as potassium and calcium, which play a large role in the fertility of agricultural soils. The cations’ competition or interaction with other organic molecules, such as anions and exudates, can affect the herbicide behavior in soil and needs to be studied in fields with farmers. These results highlight the high persistence of glyphosate and AMPA in soils on the St. Lawrence Lowlands. Monitoring available cations, glyphosate and AMPA in different soils and cultures is a new approach that provides a better understanding of the retention mechanisms of these compounds in soils and a solid basis for the advancement of knowledge in field conditions.
Author Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Funding acquisition as well as the provision of resources were provided by M.L. (Marc Lucotte). S.M. was supervised by M.L. (Marc Lucotte) and M.L. (Michel Labrecque). Material preparation, data collection and analyses were performed by S.M., M.M. and É.S.-B. Soil sampling was realized by S.M., É.S. and É.S.-B. The first draft of the manuscript was written by S.M. and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was made possible by financial support from the Natural Science and Engineering Research Council of Canada (NSERC) to the first (S.M., scholarship) and second authors (M.L., Discovery Grant).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available within the article or on request from Marc Lucotte.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Duke, S.; Powles, S.; Sammons, D. Glyphosate—How it Became a Once in a Hundred Year Herbicide and Its Future. Outlooks Pest Manag. 2018, 29, 247–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duke, S.O. Perspectives on transgenic, herbicide-resistant crops in the United States almost 20 years after introduction. Pest Manag. Sci. 2015, 71, 652–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hategekimana, B.; Trant, M. Adoption and Diffusion of New Technology in Agriculture: Genetically Modified Corn and Soybeans. Can. J. Agric. Econ.-Rev. Can. D Agroecon. 2002, 50, 357–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heap, I.; Duke, S.O. Overview of glyphosate-resistant weeds worldwide. Pest Manag. Sci. 2018, 74, 1040–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benbrook, C.M. Trends in glyphosate herbicide use in the United States and globally. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2016, 28, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hove-Jensen, B.; Zechel, D.; Jochimsen, B. Utilization of Glyphosate as Phosphate Source: Biochemistry and Genetics of Bacterial Carbon-Phosphorus Lyase. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. MMBR 2014, 78, 176–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Borggaard, O.; Gimsing, A. Fate of Glyphosate in Soil and the Possibility of Leaching to Ground and Surface Waters: A Review. Pest Manag. Sci. 2008, 64, 441–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonsen, L.; Fomsgaard, I.; Svensmark, B.; Spliid, N. Fate and availability of glyphosate and AMPA in agricultural soil. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part B 2008, 43, 365–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sviridov, A.; Shushkova, T.; Ermakova, I.; Ivanova, E.; Epiktetov, D.; Leont’evskii, A. Microbial Degradation of Glyphosate Herbicides (Review). Appl. Biochem. Microbiol. 2015, 51, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Travaglia, C.; Masciarelli, O.; Fortuna, J.; Marchetti, G.; Cardozo, P.; Lucero, M.; Zorza, E.; Luna, V.; Reinoso, H. Towards sustainable maize production: Glyphosate detoxification by Azospirillum sp. and Pseudomonas sp. Crop Prot. 2015, 77, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheah, U.-B.; Kirkwood, R.C.; Lum, K.-Y. Degradation of Four Commonly Used Pesticides in Malaysian Agricultural Soils. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1998, 46, 1217–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamy, L.; Barriuso, E.; Gabrielle, B. Environmental fate of herbicides trifluralin, metazachlor, metamitron and sulcotrione compared to that of glyphosate, a substitute broad spectrum herbicide for different glyphosate-resistant crops. Pest Manag. Sci. 2005, 61, 905–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Rajab, A.J.; Schiavon, M. Degradation of 14C-glyphosate and aminomethylphosphonic acid (AMPA) in three agricultural soils. J. Environ. Sci. 2010, 22, 1374–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Wang, F.; Bento, C.P.M.; Meng, L.; van Dam, R.; Mol, H.; Liu, G.; Ritsema, C.J.; Geissen, V. Decay characteristics and erosion-related transport of glyphosate in Chinese loess soil under field conditions. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 530–531, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shushkova, T.; Ermakova, I.; Leontievsky, A. Glyphosate bioavailability in soil. Biodegradation 2010, 21, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergström, L.; Börjesson, E.; Stenström, J. Laboratory and Lysimeter Studies of Glyphosate and Aminomethylphosphonic Acid in a Sand and a Clay Soil. J. Environ. Qual. 2011, 40, 98–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, B.; Singh, K. Microbial degradation of herbicides. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2014, 42, 245–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eberbach, P. Applying non-steady-state compartmental analysis to investigate the simultaneous degradation of soluble and sorbed glyphosate (N-(phosphonomethyl)glycine) in four soils. Pestic. Sci. 1998, 52, 229–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scribner, E.A.; Battaglin, W.A.; Gilliom, R.J.; Meyer, M.T. Concentrations of Glyphosate, Its Degradation Product, Aminomethylphosphonic Acid, and Glufosinate in Ground- and Surface-Water, Rainfall, and Soil Samples Collected in the United States, 2001–2006; U.S. Geological Survey Scientific Investigations Report 2007–5122; 111p. Available online: https://pubs.usgs.gov/sir/2007/5122/pdf/SIR2007-5122.pdf (accessed on 23 March 2022).
- Laitinen, P.; Rämö, S.; Nikunen, U.; Jauhiainen, L.; Siimes, K.; Turtola, E. Glyphosate and phosphorus leaching and residues in boreal sandy soil. Plant Soil 2009, 323, 267–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Primost, J.; Aparicio, V.; Costa, J.; Carriquiriborde, P. Glyphosate and AMPA, “pseudo-persistent” pollutants under real-world agricultural management practices in the Mesopotamic Pampas agroecosystem, Argentina. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 229, 771–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Rajab, A.J.; Amellal, S.; Schiavon, M. Sorption and leaching of 14 C-glyphosate in agricultural soils. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2008, 28, 419–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Albers, C.N.; Banta, G.T.; Hansen, P.E.; Jacobsen, O.S. The influence of organic matter on sorption and fate of glyphosate in soil —Comparing different soils and humic substances. Environ. Pollut. 2009, 157, 2865–2870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rampazzo, N.; Rampazzo Todorovic, G.; Mentler, A.; Blum, W. Adsorption of glyphosate and aminomethylphosphonic acid in soils. Int. Agrophys. 2013, 27, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gjettermann, B.; Styczen, M.; Bender Koch, C.; Hansen, S.; Petersen, C. Evaluation of Sampling Strategies for Pesticides in a Macroporous Sandy Loam Soil. Soil Sediment Contam. Int. J. 2011, 20, 986–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glass, R.L. Adsorption of glyphosate by soils and clay minerals. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1987, 35, 497–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eker, S.; Ozturk, L.; Yazici, A.; Erenoglu, B.; Romheld, V.; Cakmak, I. Foliar-Applied Glyphosate Substantially Reduced Uptake and Transport of Iron and Manganese in Sunflower (Helianthus annuus L.) Plants. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 10019–10025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aparicio, V.C.; De Gerónimo, E.; Marino, D.; Primost, J.; Carriquiriborde, P.; Costa, J.L. Environmental fate of glyphosate and aminomethylphosphonic acid in surface waters and soil of agricultural basins. Chemosphere 2013, 93, 1866–1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, V.; Montanarella, L.; Jones, A.; Fernández-Ugalde, O.; Mol, H.; Ritsema, C.; Geissen, V. Distribution of glyphosate and aminomethylphosphonic acid (AMPA) in Agricultural topsoils of the European Union. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 621, 1352–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karanasios, E.; Karasali, H.; Marousopoulou, A.; Akrivou, A.; Markellou, E. Monitoring of glyphosate and AMPA in soil samples from two olive cultivation areas in Greece: Aspects related to spray operators activities. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2018, 190, 361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.C.; Thompson, D.G.; Reynolds, P.E. Fate of glyphosate in a Canadian forest watershed. 1. Aquatic residues and off-target deposit assessment. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1990, 38, 1110–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, D.N.; Konar, S.K.; Banerjee, S.; Charles, D.A.; Thompson, D.G.; Prasad, R. Persistence, movement, and degradation of glyphosate in selected Canadian boreal forest soils. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1989, 37, 437–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glozier, N.E.; Struger, J.; Cessna, A.J.; Gledhill, M.; Rondeau, M.; Ernst, W.R.; Sekela, M.A.; Cagampan, S.J.; Sverko, E.; Murphy, C.; et al. Occurrence of glyphosate and acidic herbicides in select urban rivers and streams in Canada, 2007. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2012, 19, 821–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Battaglin, W.A.; Meyer, M.T.; Kuivila, K.M.; Dietze, J.E. Glyphosate and Its Degradation Product AMPA Occur Frequently and Widely in U.S. Soils, Surface Water, Groundwater, and Precipitation. JAWRA J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2014, 50, 275–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucotte, M.; D’anglejan, B. A comparison of several methods for the determination of iron hydroxides and associated orthophosphates in estuarine particulate matter. Chem. Geol. 1985, 48, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alferness, P.L.; Iwata, Y. Determination of Glyphosate and (Aminomethyl)phosphonic Acid in Soil, Plant and Animal Matrixes, and Water by Capillary Gas Chromatography with Mass-Selective Detection. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1994, 42, 2751–2759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deyrup, C.L.; Chang, S.M.; Weintraub, R.A.; Moye, H.A. Simultaneous esterification and acylation of pesticides for analysis by gas chromatography. 1. Derivatization of glyphosate and (aminomethyl) phosphonic acid with fluorinated alcohols-perfluorinated anhydrides. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1985, 33, 944–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mocak, J.; Bond, A.; Mitchell, S.; Scollary, G. A statistical overview of standard (IUPAC and ACS) and new procedures for determining the limits of detection and quantification: Application to voltammetric and stripping techniques (technical report). Pure Appl. Chem. 1997, 69, 297–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibáñez, M.; Pozo, O.; Sancho, J.; López, F.; Hernandez, F. Residue determination of glyphosate, glufosinate and aminomethylphosphonic acid in water and soil samples by liquid chromatography coupled to electrospray tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2005, 1081, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunarathna, S.; Gunawardana, B.; Jayaweera, M.; Manatunge, J.; Zoysa, E.K. Glyphosate and AMPA of agricultural soil, surface water, groundwater and sediments in areas prevalent with chronic kidney disease of unknown etiology, Sri Lanka. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part B 2018, 53, 729–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helander, M.; Saloniemi, I.; Saikkonen, K. Glyphosate in northern ecosystems. Trends Plant Sci. 2012, 17, 569–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bento, C.P.M.; Yang, X.; Gort, G.; Xue, S.; van Dam, R.; Zomer, P.; Mol, H.G.J.; Ritsema, C.J.; Geissen, V. Persistence of glyphosate and aminomethylphosphonic acid in loess soil under different combinations of temperature, soil moisture and light/darkness. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 572, 301–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kjær, J.; Olsen, P.; Ullum, M.; Grant, R. Leaching of Glyphosate and Amino-Methylphosphonic Acid from Danish Agricultural Field Sites. J. Environ. Qual. 2005, 34, 608–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banks, M.L.; Kennedy, A.C.; Kremer, R.J.; Eivazi, F. Soil microbial community response to surfactants and herbicides in two soils. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2014, 74, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidoli, P.; Baran, N.; Angulo-Jaramillo, R. Glyphosate and AMPA adsorption in soils: Laboratory experiments and pedotransfer rules. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 5733–5742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassigneul, A.; Benoit, P.; Bergheaud, V.; Dumeny, V.; Etiévant, V.; Goubard, Y.; Maylin, A.; Justes, E.; Alletto, L. Fate of glyphosate and degradates in cover crop residues and underlying soil: A laboratory study. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 545–546, 582–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okada, E.; Costa, J.L.; Bedmar, F. Adsorption and mobility of glyphosate in different soils under no-till and conventional tillage. Geoderma 2016, 263, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andréa, M.M.D.; Peres, T.B.; Luchini, L.C.; Bazarin, S.; Papini, S.; Matallo, M.B.; Savoy, V.L.T. Influence of repeated applications of glyphosate on its persistence and soil bioactivity. Pesqui. Agropecu. Bras. 2003, 38, 1329–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fomsgaard, I.S.; Spliid, N.H.H.; Felding, G. Leaching of Pesticides Through Normal-Tillage and Low-Tillage Soil—A Lysimeter Study. II. Glyphosate. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part B 2003, 38, 19–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soracco, C.G.; Villarreal, R.; Lozano, L.A.; Vittori, S.; Melani, E.M.; Marino, D.J.G. Glyphosate dynamics in a soil under conventional and no-till systems during a soybean growing season. Geoderma 2018, 323, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peruzzo, P.J.; Porta, A.A.; Ronco, A.E. Levels of glyphosate in surface waters, sediments and soils associated with direct sowing soybean cultivation in north pampasic region of Argentina. Environ. Pollut. 2008, 156, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gjettermann, B.; Petersen, C.T.; Hansen, S.; Bender Koch, C.; Styczen, M. Kinetics of Glyphosate Desorption from Mobilized Soil Particles. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2010, 75, 434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipiec, J.; Kus, J.; Nosalewicz, A.; Turski, M. Tillage system effects on stability and sorptivity of soil aggregates. Int. Agrophys. 2006, 20, 189–193. [Google Scholar]
- Sheals, J.; Sjöberg, S.; Persson, P. Adsorption of Glyphosate on Goethite: Molecular Characterization of Surface Complexes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2002, 36, 3090–3095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barja, B.; Dos Santos Afonso, M. Aminomethylphosphonic Acid and Glyphosate Adsorption onto Goethite: A Comparative Study. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 585–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gimsing, A.; Borggaard, O. Competitive adsorption and desorption of glyphosate on clay silicates and oxides. Clay Miner. 2002, 37, 509–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maqueda, C.; Undabeytia, T.; Villaverde, J.; Morillo, E. Behaviour of glyphosate in a reservoir and the surrounding agricultural soils. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 593–594, 787–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Báez, M.E.; Espinoza, J.; Silva, R.; Fuentes, E. Sorption-desorption behavior of pesticides and their degradation products in volcanic and nonvolcanic soils: Interpretation of interactions through two-way principal component analysis. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 8576–8585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gros, P.; Ahmed, A.; Kühn, O.; Leinweber, P. Glyphosate binding in soil as revealed by sorption experiments and quantum-chemical modeling. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 586, 527–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paradelo, M.; Norgaard, T.; Moldrup, P.; Ferré, T.P.A.; Kumari, K.G.I.D.; Arthur, E.; de Jonge, L.W. Prediction of the glyphosate sorption coefficient across two loamy agricultural fields. Geoderma 2015, 259–260, 224–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dollinger, J.; Dagès, C.; Voltz, M. Glyphosate sorption to soils and sediments predicted by pedotransfer functions. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2015, 13, 293–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsui, M.; Chu, L.M. Environmental fate and non-target impact of glyphosate-based herbicide (Roundup®) in a subtropical wetland. Chemosphere 2008, 71, 439–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, N.K.; Dörfler, U.; Welzl, G.; Munch, J.C.; Schroll, R.; Suhadolc, M. Large variation in glyphosate mineralization in 21 different agricultural soils explained by soil properties. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 627, 544–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caetano, M.; Ramalho, T.; Botrel, D.; Cunha, E.; Mello, W. Understanding the inactivation process of organophosphorus herbicides: A DFT study of glyphosate metallic complexes with Zn2+, Ca2+, Mg2+, Cu2+, Co3+, Fe3+, Cr3+, and Al3+. Int. J. Quantum Chem. 2012, 112, 2752–2762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonge, H.; de Jonge, L. Influence of pH and solution composition on the sorption of Glyphosate and Proch-loraz to a sandy loam soil. Chemosphere 1999, 39, 753–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lupi, L.; Miglioranza, K.S.B.; Aparicio, V.C.; Marino, D.; Bedmar, F.; Wunderlin, D.A. Occurrence of glyphosate and AMPA in an agricultural watershed from the southeastern region of Argentina. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 536, 687–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bento, C.; Goossens, D.; Rezaei, M.; Riksen, M.; Mol, H.; Ritsema, C.; Geissen, V. Glyphosate and AMPA distribution in wind-eroded sediment derived from loess soil. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 220, 1079–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farenhorst, A.; Andronak, L.; McQueen, R. Bulk Deposition of Pesticides in a Canadian City: Part 1. Glyphosate and Other Agricultural Pesticides. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2015, 226, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lamprea, K.; Ruban, V. Pollutant concentrations and fluxes in both stormwater and wastewater at the outlet of two urban watersheds in Nantes (France). Urban Water J. 2011, 8, 219–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, F.-C.; Simcik, M.; Capel, P. Occurrence and Fate of the Herbicide Glyphosate and Its Degradate Aminomethylphosphonic Acid in the Atmosphere. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. SETAC 2011, 30, 548–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lupi, L.; Bedmar, F.; Puricelli, M.; Marino, D.; Aparicio, V.C.; Wunderlin, D.; Miglioranza, K.S.B. Glyphosate runoff and its occurrence in rainwater and subsurface soil in the nearby area of agricultural fields in Argentina. Chemosphere 2019, 225, 906–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carles, L.; Gardon, H.; Joseph, L.; Sanchís, J.; Farré, M.; Artigas, J. Meta-analysis of glyphosate contamination in surface waters and dissipation by biofilms. Environ. Int. 2019, 124, 284–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rampazzo Todorovic, G.; Rampazzo, N.; Mentler, A.; Blum, W.; Eder, A.; Strauss, P. Influence of soil tillage and erosion on the dispersion of glyphosate and aminomethylphosphonic acid in agricultural soils. Int. Agrophys. 2014, 28, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Imfeld, G.; Lefrancq, M.; Maillard, E.; Payraudeau, S. Transport and attenuation of dissolved glyphosate and AMPA in a stormwater wetland. Chemosphere 2013, 90, 1333–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landry, D.; Dousset, S.; Fournier, J.-C.; Andreux, F. Leaching of glyphosate and AMPA under two soil management practices in Burgundy vineyards (Vosne-Romanée, 21-France). Environ. Pollut. 2005, 138, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norgaard, T.; Moldrup, P.; Ferré, T.; Olsen, P.; Rosenbom, A.; de Jonge, L. Leaching of Glyphosate and Aminomethylphosphonic Acid from an Agricultural Field over a Twelve-Year Period. Vadose Zone J. 2014, 13, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).