Figure 1.
Influence of calcium superphosphate (CSP) levels on leaf iron (Fe, mg kg−1) contents of CaCO3-stressed sweet potato plants in 2019 and 2020 seasons. Bars with a different letter indicate significant difference between treatments at p ≤ 0.05. CSP20, CSP40, CSP60, CSP80, and CSP100 represent CSP added as a soil application at 69, 138, 207, 276, and 345 kg ha−1, respectively.
Figure 1.
Influence of calcium superphosphate (CSP) levels on leaf iron (Fe, mg kg−1) contents of CaCO3-stressed sweet potato plants in 2019 and 2020 seasons. Bars with a different letter indicate significant difference between treatments at p ≤ 0.05. CSP20, CSP40, CSP60, CSP80, and CSP100 represent CSP added as a soil application at 69, 138, 207, 276, and 345 kg ha−1, respectively.
Figure 2.
Influence of calcium superphosphate (CSP) levels on leaf manganese (Mn, mg kg−1) contents of CaCO3-stressed sweet potato plants in 2019 and 2020 seasons. Bars with a different letter indicate significant difference between treatments at p ≤ 0.05. CSP20, CSP40, CSP60, CSP80, and CSP100 represent CSP added as a soil application at 69, 138, 207, 276, and 345 kg ha−1, respectively.
Figure 2.
Influence of calcium superphosphate (CSP) levels on leaf manganese (Mn, mg kg−1) contents of CaCO3-stressed sweet potato plants in 2019 and 2020 seasons. Bars with a different letter indicate significant difference between treatments at p ≤ 0.05. CSP20, CSP40, CSP60, CSP80, and CSP100 represent CSP added as a soil application at 69, 138, 207, 276, and 345 kg ha−1, respectively.
Figure 3.
Influence of calcium superphosphate (CSP) levels on leaf zinc (Zn, mg kg−1) contents of CaCO3-stressed sweet potato plants in 2019 and 2020 seasons. Bars with a different letter indicate significant difference between treatments at p ≤ 0.05. CSP20, CSP40, CSP60, CSP80, and CSP100 represent CSP added as a soil application at 69, 138, 207, 276, and 345 kg ha−1, respectively.
Figure 3.
Influence of calcium superphosphate (CSP) levels on leaf zinc (Zn, mg kg−1) contents of CaCO3-stressed sweet potato plants in 2019 and 2020 seasons. Bars with a different letter indicate significant difference between treatments at p ≤ 0.05. CSP20, CSP40, CSP60, CSP80, and CSP100 represent CSP added as a soil application at 69, 138, 207, 276, and 345 kg ha−1, respectively.
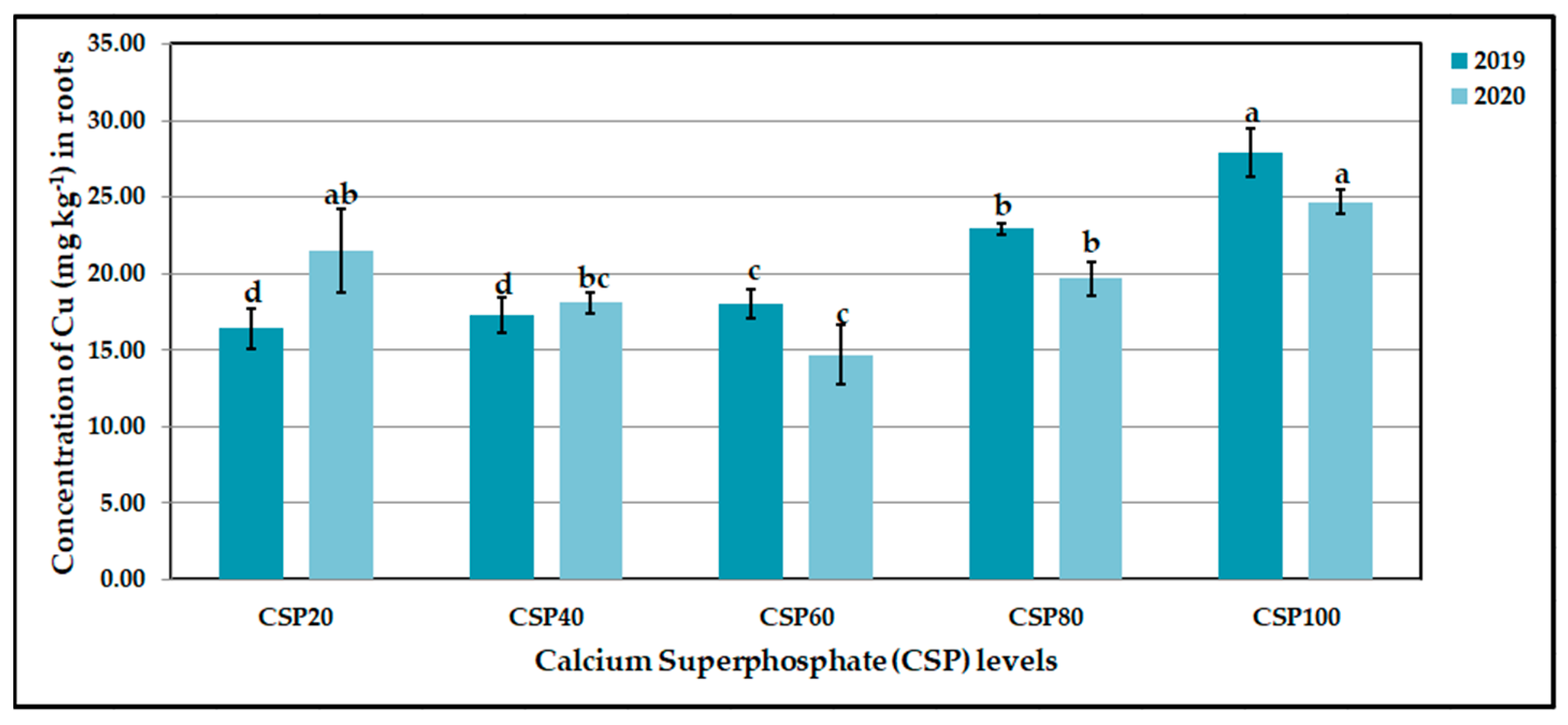
Figure 4.
Influence of calcium superphosphate (CSP) levels on leaf copper (Cu, mg kg−1) contents of CaCO3-stressed sweet potato plants in 2019 and 2020 seasons. Bars with a different letter indicate significant difference between treatments at p ≤ 0.05. CSP20, CSP40, CSP60, CSP80, and CSP100 represent CSP added as a soil application at 69, 138, 207, 276, and 345 kg ha−1, respectively.
Figure 4.
Influence of calcium superphosphate (CSP) levels on leaf copper (Cu, mg kg−1) contents of CaCO3-stressed sweet potato plants in 2019 and 2020 seasons. Bars with a different letter indicate significant difference between treatments at p ≤ 0.05. CSP20, CSP40, CSP60, CSP80, and CSP100 represent CSP added as a soil application at 69, 138, 207, 276, and 345 kg ha−1, respectively.
Figure 5.
Influence of Bacillus megaterium DSM 2894 var. on leaf iron (Fe, mg kg−1) contents of CaCO3-stressed sweet potato plants in 2019 and 2020 seasons. Bars with a different letter indicate significant difference between treatments at p ≤ 0.05. DSM0 = non-inoculated with Bacillus megaterium DSM 2894 var., DSM1 = inoculated with Bacillus megaterium DSM 2894 var.
Figure 5.
Influence of Bacillus megaterium DSM 2894 var. on leaf iron (Fe, mg kg−1) contents of CaCO3-stressed sweet potato plants in 2019 and 2020 seasons. Bars with a different letter indicate significant difference between treatments at p ≤ 0.05. DSM0 = non-inoculated with Bacillus megaterium DSM 2894 var., DSM1 = inoculated with Bacillus megaterium DSM 2894 var.
Figure 6.
Influence of Bacillus megaterium DSM 2894 var. on leaf manganese (Mn, mg kg−1) contents of CaCO3-stressed sweet potato plants in 2019 and 2020 seasons. Bars with a different letter indicate significant difference between treatments at p ≤ 0.05. DSM0 = non-inoculated with Bacillus megaterium DSM 2894 var., DSM1 = inoculated with Bacillus megaterium DSM 2894 var.
Figure 6.
Influence of Bacillus megaterium DSM 2894 var. on leaf manganese (Mn, mg kg−1) contents of CaCO3-stressed sweet potato plants in 2019 and 2020 seasons. Bars with a different letter indicate significant difference between treatments at p ≤ 0.05. DSM0 = non-inoculated with Bacillus megaterium DSM 2894 var., DSM1 = inoculated with Bacillus megaterium DSM 2894 var.
Figure 7.
Influence of Bacillus megaterium DSM 2894 var. on leaf zinc (Zn, mg kg−1) contents of CaCO3-stressed sweet potato plants in 2019 and 2020 seasons. Bars with a different letter indicate significant difference between treatments at p ≤ 0.05. DSM0 = non-inoculated with Bacillus megaterium DSM 2894 var., DSM1 = inoculated with Bacillus megaterium DSM 2894 var.
Figure 7.
Influence of Bacillus megaterium DSM 2894 var. on leaf zinc (Zn, mg kg−1) contents of CaCO3-stressed sweet potato plants in 2019 and 2020 seasons. Bars with a different letter indicate significant difference between treatments at p ≤ 0.05. DSM0 = non-inoculated with Bacillus megaterium DSM 2894 var., DSM1 = inoculated with Bacillus megaterium DSM 2894 var.
Figure 8.
Influence of Bacillus megaterium DSM 2894 var. on leaf copper (Cu, mg kg−1) contents of CaCO3-stressed sweet potato plants in 2019 and 2020 seasons. Bars with a different letter indicate significant difference between treatments at p ≤ 0.05. DSM0 = non-inoculated with Bacillus megaterium DSM 2894 var., DSM1 = inoculated with Bacillus megaterium DSM 2894 var.
Figure 8.
Influence of Bacillus megaterium DSM 2894 var. on leaf copper (Cu, mg kg−1) contents of CaCO3-stressed sweet potato plants in 2019 and 2020 seasons. Bars with a different letter indicate significant difference between treatments at p ≤ 0.05. DSM0 = non-inoculated with Bacillus megaterium DSM 2894 var., DSM1 = inoculated with Bacillus megaterium DSM 2894 var.
Figure 9.
Influence of calcium superphosphate (CSP) levels on root iron (Fe, mg kg−1) contents of CaCO3-stressed sweet potato plants in 2019 and 2020 seasons. Bars with a different letter indicate significant difference between treatments at p ≤ 0.05. CSP20, CSP40, CSP60, CSP80, and CSP100 represent CSP added as a soil application at 69, 138, 207, 276, and 345 kg ha−1, respectively.
Figure 9.
Influence of calcium superphosphate (CSP) levels on root iron (Fe, mg kg−1) contents of CaCO3-stressed sweet potato plants in 2019 and 2020 seasons. Bars with a different letter indicate significant difference between treatments at p ≤ 0.05. CSP20, CSP40, CSP60, CSP80, and CSP100 represent CSP added as a soil application at 69, 138, 207, 276, and 345 kg ha−1, respectively.
Figure 10.
Influence of calcium superphosphate (CSP) levels on root manganese (Mn, mg kg−1) contents of CaCO3-stressed sweet potato plants in 2019 and 2020 seasons. Bars with a different letter indicate significant difference between treatments at p ≤ 0.05. CSP20, CSP40, CSP60, CSP80, and CSP100 represent CSP added as a soil application at 69, 138, 207, 276, and 345 kg ha−1, respectively.
Figure 10.
Influence of calcium superphosphate (CSP) levels on root manganese (Mn, mg kg−1) contents of CaCO3-stressed sweet potato plants in 2019 and 2020 seasons. Bars with a different letter indicate significant difference between treatments at p ≤ 0.05. CSP20, CSP40, CSP60, CSP80, and CSP100 represent CSP added as a soil application at 69, 138, 207, 276, and 345 kg ha−1, respectively.
Figure 11.
Influence of calcium superphosphate (CSP) levels on root zinc (Zn, mg kg−1) contents of CaCO3-stressed sweet potato plants in 2019 and 2020 seasons. Bars with a different letter indicate significant difference between treatments at p ≤ 0.05. CSP20, CSP40, CSP60, CSP80, and CSP100 represent CSP added as a soil application at 69, 138, 207, 276, and 345 kg ha−1, respectively.
Figure 11.
Influence of calcium superphosphate (CSP) levels on root zinc (Zn, mg kg−1) contents of CaCO3-stressed sweet potato plants in 2019 and 2020 seasons. Bars with a different letter indicate significant difference between treatments at p ≤ 0.05. CSP20, CSP40, CSP60, CSP80, and CSP100 represent CSP added as a soil application at 69, 138, 207, 276, and 345 kg ha−1, respectively.
Figure 12.
Influence of calcium superphosphate (CSP) levels on root copper (Cu, mg kg−1) contents of CaCO3-stressed sweet potato plants in 2019 and 2020 seasons. Bars with a different letter indicate significant difference between treatments at p ≤ 0.05. CSP20, CSP40, CSP60, CSP80, and CSP100 represent CSP added as a soil application at 69, 138, 207, 276, and 345 kg ha−1, respectively.
Figure 12.
Influence of calcium superphosphate (CSP) levels on root copper (Cu, mg kg−1) contents of CaCO3-stressed sweet potato plants in 2019 and 2020 seasons. Bars with a different letter indicate significant difference between treatments at p ≤ 0.05. CSP20, CSP40, CSP60, CSP80, and CSP100 represent CSP added as a soil application at 69, 138, 207, 276, and 345 kg ha−1, respectively.
Figure 13.
Influence of Bacillus megaterium DSM 2894 var. on root iron (Fe, mg kg−1) contents of CaCO3-stressed sweet potato plants in 2019 and 2020 seasons. Bars with a different letter indicate significant difference between treatments at p ≤ 0.05. DSM0 = non-inoculated with Bacillus megaterium DSM 2894 var., DSM1 = inoculated with Bacillus megaterium DSM 2894 var.
Figure 13.
Influence of Bacillus megaterium DSM 2894 var. on root iron (Fe, mg kg−1) contents of CaCO3-stressed sweet potato plants in 2019 and 2020 seasons. Bars with a different letter indicate significant difference between treatments at p ≤ 0.05. DSM0 = non-inoculated with Bacillus megaterium DSM 2894 var., DSM1 = inoculated with Bacillus megaterium DSM 2894 var.
Figure 14.
Influence of Bacillus megaterium DSM 2894 var. on root manganese (Mn, mg kg−1) contents of CaCO3-stressed sweet potato plants in 2019 and 2020 seasons. Bars with a different letter indicate significant difference between treatments at p ≤ 0.05. DSM0 = non-inoculated with Bacillus megaterium DSM 2894 var., DSM1 = inoculated with Bacillus megaterium DSM 2894 var.
Figure 14.
Influence of Bacillus megaterium DSM 2894 var. on root manganese (Mn, mg kg−1) contents of CaCO3-stressed sweet potato plants in 2019 and 2020 seasons. Bars with a different letter indicate significant difference between treatments at p ≤ 0.05. DSM0 = non-inoculated with Bacillus megaterium DSM 2894 var., DSM1 = inoculated with Bacillus megaterium DSM 2894 var.
Figure 15.
Influence of Bacillus megaterium DSM 2894 var. on root zinc (Zn, mg kg−1) contents of CaCO3-stressed sweet potato plants in 2019 and 2020 seasons. Bars with a different letter indicate significant difference between treatments at p ≤ 0.05. DSM0 = non-inoculated with Bacillus megaterium DSM 2894 var., DSM1 = inoculated with Bacillus megaterium DSM 2894 var.
Figure 15.
Influence of Bacillus megaterium DSM 2894 var. on root zinc (Zn, mg kg−1) contents of CaCO3-stressed sweet potato plants in 2019 and 2020 seasons. Bars with a different letter indicate significant difference between treatments at p ≤ 0.05. DSM0 = non-inoculated with Bacillus megaterium DSM 2894 var., DSM1 = inoculated with Bacillus megaterium DSM 2894 var.
Figure 16.
Influence of Bacillus megaterium DSM 2894 var. on root copper (Cu, mg kg−1) contents of CaCO3-stressed sweet potato plants in 2019 and 2020 seasons. Bars with a different letter indicate significant difference between treatments at p ≤ 0.05. DSM0 = non-inoculated with Bacillus megaterium DSM 2894 var., DSM1 = inoculated with Bacillus megaterium DSM 2894 var.
Figure 16.
Influence of Bacillus megaterium DSM 2894 var. on root copper (Cu, mg kg−1) contents of CaCO3-stressed sweet potato plants in 2019 and 2020 seasons. Bars with a different letter indicate significant difference between treatments at p ≤ 0.05. DSM0 = non-inoculated with Bacillus megaterium DSM 2894 var., DSM1 = inoculated with Bacillus megaterium DSM 2894 var.
Figure 17.
Influence of calcium superphosphate (CSP) levels on anti-radical power (ARP) of tubers of CaCO3-stressed sweet potato plants grown in 2019 and 2020 seasons. Bars with a different letter indicate significant different between treatments at p ≤ 0.05. CSP20, CSP40, CSP60, CSP80, and CSP100 represent CSP added as a soil application at 69, 138, 207, 276, and 345 kg ha−1, respectively.
Figure 17.
Influence of calcium superphosphate (CSP) levels on anti-radical power (ARP) of tubers of CaCO3-stressed sweet potato plants grown in 2019 and 2020 seasons. Bars with a different letter indicate significant different between treatments at p ≤ 0.05. CSP20, CSP40, CSP60, CSP80, and CSP100 represent CSP added as a soil application at 69, 138, 207, 276, and 345 kg ha−1, respectively.
Figure 18.
Influence of calcium superphosphate levels (CSP) on protein content of CaCO3-stressed sweet potato plants grown in 2019 and 2020 seasons. Bars with a different letter indicate significant different between treatments at p ≤ 0.05. CSP20, CSP40, CSP60, CSP80, and CSP100 represent CSP added as a soil application at 69, 138, 207, 276, and 345 kg ha−1, respectively.
Figure 18.
Influence of calcium superphosphate levels (CSP) on protein content of CaCO3-stressed sweet potato plants grown in 2019 and 2020 seasons. Bars with a different letter indicate significant different between treatments at p ≤ 0.05. CSP20, CSP40, CSP60, CSP80, and CSP100 represent CSP added as a soil application at 69, 138, 207, 276, and 345 kg ha−1, respectively.
Figure 19.
Influence of Bacillus megaterium DSM 2894 var. on anti-radical power (ARP) of tubers of CaCO3-stressed sweet potato plants grown in 2019 and 2020 seasons. Bars with a different letter indicate significant different between treatments at p ≤ 0.05. DSM0 = non-inoculated with Bacillus megaterium DSM 2894 var., DSM1 = inoculated with Bacillus megaterium DSM 2894 var.
Figure 19.
Influence of Bacillus megaterium DSM 2894 var. on anti-radical power (ARP) of tubers of CaCO3-stressed sweet potato plants grown in 2019 and 2020 seasons. Bars with a different letter indicate significant different between treatments at p ≤ 0.05. DSM0 = non-inoculated with Bacillus megaterium DSM 2894 var., DSM1 = inoculated with Bacillus megaterium DSM 2894 var.
Figure 20.
Influence of Bacillus megaterium DSM 2894 var. on protein content (%) of tubers of CaCO3-stressed sweet potato plants grown in 2019 and 2020 seasons. Bars with a different letter indicate significant different between treatments at p ≤ 0.05. DSM0 = non-inoculated with Bacillus megaterium DSM 2894 var., DSM1 = inoculated with Bacillus megaterium DSM 2894 var.
Figure 20.
Influence of Bacillus megaterium DSM 2894 var. on protein content (%) of tubers of CaCO3-stressed sweet potato plants grown in 2019 and 2020 seasons. Bars with a different letter indicate significant different between treatments at p ≤ 0.05. DSM0 = non-inoculated with Bacillus megaterium DSM 2894 var., DSM1 = inoculated with Bacillus megaterium DSM 2894 var.
Figure 21.
Influence of calcium superphosphate (CSP) levels on total roots yield of CaCO3-stressed sweet potato plants grown in 2019 and 2020 seasons. Bars with a different letter indicate significant different between treatments at p ≤ 0.05. DSM0 = non-inoculated with Bacillus megaterium DSM 2894 var., DSM1 = inoculated with Bacillus megaterium DSM 2894 var.
Figure 21.
Influence of calcium superphosphate (CSP) levels on total roots yield of CaCO3-stressed sweet potato plants grown in 2019 and 2020 seasons. Bars with a different letter indicate significant different between treatments at p ≤ 0.05. DSM0 = non-inoculated with Bacillus megaterium DSM 2894 var., DSM1 = inoculated with Bacillus megaterium DSM 2894 var.
Figure 22.
Influence of Bacillus megaterium DSM 2894 var. on total root yield of CaCO3-stressed sweet potato plants grown in 2019 and 2020 seasons. Bars with a different letter indicate significant different between treatments at p ≤ 0.05. DSM0 = non-inoculated with Bacillus megaterium DSM 2894 var., DSM1 = inoculated with Bacillus megaterium DSM 2894 var.
Figure 22.
Influence of Bacillus megaterium DSM 2894 var. on total root yield of CaCO3-stressed sweet potato plants grown in 2019 and 2020 seasons. Bars with a different letter indicate significant different between treatments at p ≤ 0.05. DSM0 = non-inoculated with Bacillus megaterium DSM 2894 var., DSM1 = inoculated with Bacillus megaterium DSM 2894 var.
Table 1.
Weather data for the study region in Egypt over the sweet potato growing seasons.
Table 1.
Weather data for the study region in Egypt over the sweet potato growing seasons.
| Month | Day °C | Night °C | RH (%) | AWS (ms−1) | AM-PEC-A (mm d−1) | AP (mm d−1) |
|---|
| 2019 Season |
| April | 34.46 | 9.34 | 49.19 | 2.92 | 5.32 | 0.05 |
| May | 44.23 | 12.04 | 39.88 | 3.58 | 6.67 | 0.00 |
| June | 42.86 | 17.34 | 35.00 | 3.59 | 7.41 | 0.00 |
| July | 41.38 | 18.58 | 37.75 | 3.28 | 6.75 | 0.00 |
| August | 42.52 | 20.69 | 39.56 | 3.63 | 6.72 | 0.00 |
| 2020 Season |
| April | 36.30 | 7.54 | 39.56 | 3.07 | 5.84 | 0.01 |
| May | 45.16 | 12.71 | 27.00 | 3.22 | 7.07 | 0.00 |
| June | 42.45 | 19.41 | 34.50 | 3.76 | 7.71 | 0.00 |
| July | 44.13 | 20.97 | 36.62 | 3.50 | 7.01 | 0.00 |
| August | 42.75 | 21.19 | 38.06 | 3.07 | 6.84 | 0.00 |
Table 2.
Some physical and chemical soil characters of the experimental sites before transplanting in seasons 2019 and 2020.
Table 2.
Some physical and chemical soil characters of the experimental sites before transplanting in seasons 2019 and 2020.
| Soil Property | 2019 Season | 2020 Season |
|---|
| Particles size distribution |
| Sand % | 63.6 | 66.8 |
| Silt % | 7.8 | 16.5 |
| Clay % | 28.6 | 16.7 |
| Soil texture class | Sandy loam | Sandy Clay loam |
| pH in soil paste | 7.19 | 7.77 |
| ECe (dSm−1) in soil paste extracted | 3.95 | 4.24 |
| Soluble ions mmol L−1 |
| CO3−− | - | - |
| HCO3− | 2.03 | 2.70 |
| Cl− | 21.1 | 25.6 |
| SO4−− | 20.3 | 18.3 |
| Na+ | 31.6 | 31.3 |
| K+ | 0.65 | 0.88 |
| Ca++ | 7.11 | 7.47 |
| Mg++ | 4.03 | 6.98 |
| Organic matter (OM) % | 0.90 | 1.03 |
| CaCO3 (%) | 10.8 | 11.3 |
| Total N (mg kg−1) | 450 | 515 |
| Available-P, mg kg−1 (Extractable with NaHCO3(pH = 8.5) | 3424 | 4013 |
| Available K mg kg−1 (Extractable with NH4AOC) | 1816 | 1237 |
| Fe, mg kg−1 (Extractable with DPTA) | 6.03 | 4.15 |
| Mn, mg kg−1 (Extractable with DPTA) | 18.2 | 10.7 |
| Zn, mg kg−1 (Extractable with DPTA) | 0.07 | 0.04 |
| Cu, mg kg−1 (Extractable with DPTA) | 0.68 | 0.40 |
Table 3.
The tested treatment in the study.
Table 3.
The tested treatment in the study.
| Treatment | Description |
|---|
| CSP20 × DSM0 | 69 kg ha−1 of calcium superphosphate (20% of RPF) with non-inoculated plants by Bacillus megaterium DSM 2894 var. |
| CSP20 × DSM1 | 69 kg ha−1 of calcium super phosphate (20% of RPF) with inoculated plants by Bacillus megaterium DSM 2894 var. |
| CSP40 × DSM0 | 138 kg ha−1 of calcium super phosphate (40% of RPF) with non-inoculated plants by Bacillus megaterium DSM 2894 var. |
| CSP40 × DSM1 | 138 kg ha−1 of calcium super phosphate (40% of RPF) with inoculated plants by Bacillus megatherium DSM 2894 var. |
| CSP60 × DSM0 | 207 kg ha−1 of calcium super phosphate (60% of RPF) with non-inoculated plants by Bacillus megaterium DSM 2894 var. |
| CSP60 × DSM1 | 207 kg ha−1 of calcium super phosphate (60% of RPF) with inoculated plants by Bacillus megaterium DSM 2894 var. |
| CSP80 × DSM0 | 276 kg ha−1 of calcium super phosphate (80% of RPF) with non-inoculated plants by Bacillus megaterium DSM 2894 var. |
| CSP80 × DSM1 | 276 kg ha−1 of calcium super phosphate (80% of RPF) with inocutated plants by Bacillus megaterium DSM 2894 var. |
| CSP100 × DSM0 | 345 kg ha−1 of calcium super phosphate (100% of RPF) with non-inoculated plants by Bacillus megaterium DSM 2894 var. |
| CSP100 × DSM1 | 345 kg ha−1 of calcium super phosphate (100% of RPF) with inoculated plants by Bacillus megaterium DSM 2894 var. |
Table 4.
Influence of calcium superphosphate (CSP) levels, Bacillus megaterium DSM 2894 var. and their interactions on some leaf nutrients content of CaCO3-stressed sweet potato plants in 2019 and 2020.
Table 4.
Influence of calcium superphosphate (CSP) levels, Bacillus megaterium DSM 2894 var. and their interactions on some leaf nutrients content of CaCO3-stressed sweet potato plants in 2019 and 2020.
| Treatment | N | P | Ca |
|---|
| Ca(H2PO4)2 | Leaves (%) |
|---|
| DSM0 | DSM1 | Mean | DSM0 | DSM1 | Mean | DSM0 | DSM1 | Mean |
|---|
| 2019 Season |
| CSP20 | 3.48 de ± 0.15 | 3.85 bc ± 0.03 | 3.66 b ± 0.09 | 1.83 e ± 0.06 | 2.74 b ± 0.02 | 2.29 d ± 0.04 | 0.99 b ± 0.01 | 1.03 a ± 0.02 | 1.01 a ± 0.02 |
| CSP40 | 3.40 de ± 0.06 | 4.09 b ± 0.05 | 3.75 ab ± 0.06 | 2.10 d ± 0.04 | 2.75 b ± 0.03 | 2.42 cd ± 0.04 | 0.89 c ± 0.02 | 0.91 c ± 0.02 | 0.90 b ± 0.02 |
| CSP60 | 3.34 e ± 0.04 | 4.60 a ± 0.22 | 3.97 a ± 0.13 | 2.37 c ± 0.01 | 2.75 b ± 0.06 | 2.56 bc ± 0.04 | 0.80 d ± 0.02 | 0.79 d ± 0.02 | 0.79 c ± 0.02 |
| CSP80 | 3.50 de ± 0.03 | 3.95 bc ± 0.03 | 3.73 b ± 0.03 | 2.36 c ± 0.01 | 2.81 b ± 0.20 | 2.58 b ± 0.02 | 0.79 d ± 0.03 | 0.75 e ± 0.01 | 0.77 cd ± 0.02 |
| CSP100 | 3.67 cd ± 0.04 | 3.68 cd ± 0.06 | 3.68 b ± 0.05 | 2.35 c ± 0.01 | 3.58 a ± 0.07 | 2.96 a ± 0.04 | 0.79 d ± 0.04 | 0.71 f ± 0.03 | 0.75 d ± 0.04 |
| Mean | 3.48 b ± 0.04 | 4.04 a ± 0.08 | 3.76 ± 0.71 | 2.20 b ± 0.02 | 2.93 a ± 0.02 | 2.56 ± 0.05 | 0.85 a ± 0.06 | 0.84 a ± 0.02 | 0.85 ± 0.04 |
| 2020 Season |
| CSP20 | 3.37 g ± 0.11 | 3.97 c ± 0.06 | 3.67 d ± 0.09 | 1.91 i ± 0.01 | 2.72 e ± 0.01 | 2.31 e ± 0.01 | 0.99 b ± 0.03 | 1.02 a ± 0.01 | 1.01 a ± 0.02 |
| CSP40 | 3.38 fg ± 0.07 | 4.23 b ± 0.09 | 3.81 c ± 0.08 | 2.12 h ± 0.01 | 2.73 d ± 0.02 | 2.43 d ± 0.02 | 0.89 d ± 0.02 | 0.91 c ± 0.01 | 0.90 b ± 0.02 |
| CSP60 | 3.51 f ± 0.09 | 4.46 a ± 0.08 | 3.98 a ± 0.09 | 2.33 f ± 0.01 | 2.75 c ± 0.03 | 2.54 c ± 0.02 | 0.79 g ± 0.02 | 0.80 g ± 0.03 | 0.80 e ± 0.03 |
| CSP80 | 3.65 e ± 0.08 | 4.11 b ± 0.08 | 3.88 b ± 0.08 | 2.32 f ± 0.01 | 3.16 b ± 0.01 | 2.74 b ± 0.01 | 0.79 h ± 0.02 | 0.83 f ± 0.02 | 0.81 d ± 0.02 |
| CSP100 | 3.80 d ± 0.06 | 3.79 d ± 0.07 | 3.80 c ± 0.07 | 2.31 g ± 0.01 | 3.57 a ± 0.01 | 2.94 a ± 0.01 | 0.78 i ± 0.01 | 0.86 e ± 0.02 | 0.82 c ± 0.02 |
| Mean | 3.54 b ± 0.08 | 4.11 a ± 0.08 | 3.83 ± 0.08 | 2.20 b ± 0.01 | 2.99 a ± 0.02 | 2.59 ± 0.02 | 0.85 b ± 0.02 | 0.88 a ± 0.02 | 0.87 ± 0.02 |
Table 5.
Influence of interaction between phosphorus fertilizer and Bacillus megaterium DSM 2894 var. on some leaf micronutrients content of sweet potato plants grown on calcareous saline soil in 2019 and 2020 seasons.
Table 5.
Influence of interaction between phosphorus fertilizer and Bacillus megaterium DSM 2894 var. on some leaf micronutrients content of sweet potato plants grown on calcareous saline soil in 2019 and 2020 seasons.
| Treatment | Fe | Mn | Zn | Cu |
|---|
| Ca(H2PO4)2 | Leaves (mg kg−1) |
|---|
| DSM0 | DSM1 | DSM0 | DSM1 | DSM0 | DSM1 | DSM0 | DSM1 |
|---|
| 2019 Season |
| CSP20 | 531.80 a ± 9.12 | 430.05 b ± 2.51 | 74.40 bc ± 0.22 | 100.02 a ± 0.22 | 20.77 e ± 1.24 | 26.46 ab ± 0.01 | 15.99 cd ± 2.71 | 30.22 a ± 0.27 |
| CSP40 | 406.90 b ± 47.40 | 383.39 b-d ± 1.99 | 95.40 a ± 0.19 | 88.49 ab ± 0.65 | 24.95 bc ± 0.21 | 24.95 bc ± 0.02 | 21.68 bc ± 0.45 | 21.82 bc ± 1.42 |
| CSP60 | 506.80 a ± 24.19 | 336.74 d ± 1.47 | 103.58 a ± 11.16 | 76.96 bc ± 1.09 | 28.70 a ± 1.79 | 23.44 cd ± 0.02 | 24.35 ab ± 1.97 | 13.42 d ± 2.57 |
| CSP80 | 507.20 a ± 13.18 | 362.03 cd ± 7.60 | 87.89 ab ± 4.84 | 87.23 ab ± 0.37 | 25.95 b ± 0.80 | 22.35 de ± 0.04 | 20.22 b–d ± 2.57 | 15.99 cd ± 0.44 |
| CSP100 | 504.30 a ± 1.56 | 405.40 bc ± 0.58 | 66.70 c ± 7.98 | 98.61 a ± 1.17 | 23.00 c–e ± 0.02 | 21.26 de ± 0.06 | 16.90 cd ± 3.14 | 18.56 b–d ± 1.69 |
| 2020 Season |
| CSP20 | 532.00 a ± 1.62 | 426.60 e ± 4.50 | 73.80 f ± 1.06 | 99.18 c ± 0.70 | 31.48 a ± 0.07 | 26.56 b ± 0.07 | 18.44 e ± 0.97 | 30.30 a ± 0.31 |
| CSP40 | 498.20 b ± 0.12 | 382.63 g ± 2.43 | 94.98 cd ± 0.06 | 88.68 d ± 0.54 | 25.27 c ± 0.03 | 24.97 c ± 0.03 | 23.30 cd ± 0.48 | 21.33 d ± 1.14 |
| CSP60 | 470.60 d ± 6.35 | 338.66 i ± 0.36 | 110.13 a ± 6.11 | 78.18 ef ± 0.38 | 19.65 g ± 0.59 | 23.38 d ± 0.01 | 27.58 b ± 0.58 | 12.36 f ± 1.96 |
| CSP80 | 483.60 c ± 1.04 | 369.95 h ± 1.09 | 98.61c ± 0.63 | 98.85 c ± 0.92 | 20.93 f ± 0.04 | 22.24 e ± 0.02 | 25.76 bc ± 0.38 | 17.54 e ± 1.34 |
| CSP100 | 502.80 b ± 0.69 | 401.24 f ± 1.82 | 81.06 d ± 0.31 | 119.51 a ± 2.22 | 22.80 de ± 0.09 | 21.10 f ± 0.03 | 23.36 cd ± 0.76 | 22.72 d ± 0.72 |
Table 6.
Influence of phosphorus fertilizer, Bacillus megaterium DSM 2894 var. and their interactions on some tuber nutrients accumulation of CaCO3-stressed sweet potato plants in 2019 and 2020.
Table 6.
Influence of phosphorus fertilizer, Bacillus megaterium DSM 2894 var. and their interactions on some tuber nutrients accumulation of CaCO3-stressed sweet potato plants in 2019 and 2020.
| Treatment | N | P | Ca |
|---|
| Ca(H2PO4)2 | Tubers (%) |
|---|
| DSM0 | DSM1 | Mean | DSM0 | DSM1 | Mean | DSM0 | DSM1 | Mean |
|---|
| 2019 Season |
| CSP20 | 2.16 b ± 0.01 | 1.73 d ± 0.12 | 1.94 d ± 0.07 | 2.59 de ± 0.00 | 3.70 d ± 0.01 | 3.15 d ± 0.01 | 0.27 j ± 0.03 | 0.43 a ± 0.02 | 0.35 a ± 0.03 |
| CSP40 | 2.19 b ± 0.04 | 1.82 d ± 0.06 | 2.01 c ± 0.05 | 2.72 g ± 0.02 | 3.64 de ± 0.02 | 3.18 d ± 0.02 | 0.27 j ± 0.04 | 0.42 b ± 0.03 | 0.35 a ± 0.04 |
| CSP60 | 2.15 b ± 0.01 | 1.99 c ± 0.04 | 2.07 b ± 0.03 | 2.94 f ± 0.10 | 3.59 g ± 0.03 | 3.27 c ± 0.07 | 0.28 h ± 0.02 | 0.41 c ± 0.06 | 0.35 a ± 0.04 |
| CSP80 | 2.15 b ± 0.06 | 2.15 b ± 0.04 | 2.15 a ± 0.05 | 3.53 e ± 0.10 | 4.21 b ± 0.02 | 3.87 b ± 0.06 | 0.30 g ± 0.03 | 0.36 d ± 0.03 | 0.33 b ± 0.03 |
| CSP100 | 2.07 bc ± 0.07 | 2.32 a ± 0.04 | 2.19 a ± 0.06 | 4.03 c ± 0.01 | 4.83 a ± 0.01 | 4.43 a ± 0.01 | 0.31 e ± 0.03 | 0.30 f ± 0.03 | 0.31 c ± 0.03 |
| Mean | 2.14 a ± 0.04 | 2.00 b ± 0.06 | 2.07 ± 0.05 | 3.16 b ± 0.02 | 3.99 a ± 0.02 | 3.58 ± 0.04 | 0.29 b ± 0.06 | 0.39 a ± 0.02 | 0.85 ± 0.04 |
| 2020 Season |
| CSP20 | 2.39 a ± 0.11 | 2.13 bc ± 0.06 | 2.26 b ± 0.09 | 2.57 j ± 0.01 | 3.77 d ± 0.01 | 3.17 c ± 0.01 | 0.99 b ± 0.03 | 1.02 a ± 0.01 | 1.01 a ± 0.02 |
| CSP40 | 2.31 a–c ± 0.07 | 2.15 bc ± 0.09 | 2.23 b ± 0.08 | 2.69 i ± 0.01 | 3.68 e ± 0.02 | 3.18 c ± 0.02 | 0.89 d ± 0.02 | 0.91 c ± 0.01 | 0.90 b ± 0.02 |
| CSP60 | 2.38 ab ± 0.09 | 2.31 a–c ± 0.08 | 2.35 ab ± 0.09 | 2.80 h ± 0.01 | 3.58 f ± 0.03 | 3.19 c ± 0.02 | 0.79 g ± 0.02 | 0.80 g ± 0.03 | 0.80 e ± 0.03 |
| CSP80 | 2.44 a ± 0.08 | 2.43 a ± 0.08 | 2.44 a ± 0.08 | 3.41 g ± 0.01 | 4.21 b ± 0.01 | 3.81 b ± 0.01 | 0.79 h ± 0.02 | 0.83 f ± 0.02 | 0.81 d ± 0.02 |
| CSP100 | 2.28 a-c ± 0.06 | 2.48 a ± 0.07 | 2.38 ab ± 0.07 | 4.01 c ± 0.01 | 4.84 a ± 0.01 | 4.42 a ± 0.01 | 0.78 i ± 0.01 | 0.86 e ± 0.02 | 0.82 c ± 0.02 |
| Mean | 2.36 a ± 0.08 | 2.30 a ± 0.08 | 3.33 ± 0.08 | 3.10 b ± 0.01 | 4.01 a ± 0.02 | 3.56 ± 0.02 | 0.85 b ± 0.02 | 0.88 a ± 0.02 | 0.87 ± 0.02 |
Table 7.
Influence of interaction between phosphorus fertilizer and Bacillus megaterium DSM 2894 var. on some root micronutrients content of sweet potato plants grown on calcareous saline soil in 2019 and 2020 seasons.
Table 7.
Influence of interaction between phosphorus fertilizer and Bacillus megaterium DSM 2894 var. on some root micronutrients content of sweet potato plants grown on calcareous saline soil in 2019 and 2020 seasons.
| Treatment | ARP | Protein | TRY |
|---|
| Ca(H2PO4)2 | (%) | (Ton ha−1) |
|---|
| Tubers |
|---|
| | DSM0 | DSM1 | DSM0 | DSM1 | DSM0 | DSM1 |
|---|
| 2019 Season |
| CSP20 | 93.55 e ± 4.06 | 183.62 ab ± 9.63 | 13.47 b ± 1.99 | 19.78 d ± 0.74 | 9.03 f ± 1.29 | 12.31 d ± 1.17 |
| CSP40 | 170.16 bc ± 6.50 | 157.05 c ± 11.41 | 13.70 b ± 1.40 | 11.36 d ± 1.94 | 10.15 a ± 1.07 | 15.09 ef ± 0.85 |
| CSP60 | 147.84 c ± 3.12 | 199.74 a ± 16.89 | 13.41 b ± 1.64 | 12.41 c ± 2.04 | 11.03 de ± 1.16 | 18.86 a ± 1.97 |
| CSP80 | 159.17 c ± 4.33 | 169.74 bc ± 7.16 | 13.42 b ± 0.41 | 13.45 b ± 1.89 | 11.86 d ± 1.43 | 16.86 b ± 2.20 |
| CSP100 | 125.83 d ± 4.11 | 124.33 d ± 6.91 | 12.94 bc ± 1.98 | 14.47 a ± 1.61 | 12.51 d ± 1.47 | 17.24 b ± 2.03 |
| 2020 Season |
| CSP20 | 95.45 d ± 7.44 | 144.96 bc ± 11.07 | 14.93 a ± 0.86 | 13.32 a–c ± 1.51 | 8.90 d ± 0.53 | 12.57 c ± 2.06 |
| CSP40 | 164.15 a–c ± 4.20 | 144.95 bc ± 6.71 | 14.46 a–c ± 1.66 | 13.43 ab ± 1.10 | 11.51 c ± 1.07 | 15.96 b ± 2.41 |
| CSP60 | 183.34 ab ± 9.62 | 194.45 a ± 4.49 | 14.84 ab ± 2.32 | 14.41 a–c ± 1.07 | 12.24 a ± 1.40 | 19.32 a ± 1.60 |
| CSP80 | 156.25 a–c ± 6.01 | 191.37 a ± 8.51 | 15.27 a ± 2.64 | 15.19 a ± 2.02 | 11.38 c ± 0.57 | 17.38 b ± 2.63 |
| CSP100 | 129.17 cd ± 8.01 | 188.29 a ± 6.76 | 14.27 a–c ± 0.71 | 15.49 a ± 2.12 | 12.92 a ± 1.60 | 16.62 b ± 2.04 |
Table 8.
Influence of interaction between phosphorus fertilizer and Bacillus megaterium DSM 2894 var. on anti-radical power, protein content, and total roots yield of sweet potato plants grown on calcareous saline soil in 2019 and 2020 seasons.
Table 8.
Influence of interaction between phosphorus fertilizer and Bacillus megaterium DSM 2894 var. on anti-radical power, protein content, and total roots yield of sweet potato plants grown on calcareous saline soil in 2019 and 2020 seasons.
| Treatment | ARP | Protein | TRY |
|---|
| Ca(H2PO4)2 | (%) | (Ton ha−1) |
|---|
| 2019 Season |
| CSP20 | 93.55 e ± 4.06 | 183.62 ab ± 9.63 | 13.47 b ± 1.99 | 19.78 d ± 0.74 | 9.03 f ± 1.29 | 12.31 d ± 1.17 |
| CSP40 | 170.16 bc ± 6.50 | 157.05 c ± 11.41 | 13.70 b ± 1.40 | 11.36 d ± 1.94 | 10.15 a ± 1.07 | 15.09 ef ± 0.85 |
| CSP60 | 147.84 c ± 3.12 | 199.74 a ± 16.89 | 13.41 b ± 1.64 | 12.41 c ± 2.04 | 11.03 de ± 1.16 | 18.86 a ± 1.97 |
| CSP80 | 159.17 c ± 4.33 | 169.74 bc ± 7.16 | 13.42 b ± 0.41 | 13.45 b ± 1.89 | 11.86 d ± 1.43 | 16.86 b ± 2.20 |
| CSP100 | 125.83 d ± 4.11 | 124.33 d ± 6.91 | 12.94 bc ± 1.98 | 14.47 a ± 1.61 | 12.51 d ± 1.47 | 17.24 b ± 2.03 |
| 2020 Season |
| CSP20 | 95.45 d ± 7.44 | 144.96 bc ± 11.07 | 14.93 a ± 0.86 | 13.32 a–c ± 1.51 | 8.90 d ± 0.53 | 12.57 c ± 2.06 |
| CSP40 | 164.15 a–c ± 4.20 | 144.95 bc ± 6.71 | 14.46 a–c ± 1.66 | 13.43 ab ± 1.10 | 11.51 c ± 1.07 | 15.96 b ± 2.41 |
| CSP60 | 183.34 ab ± 9.62 | 194.45 a ± 4.49 | 14.84 ab ± 2.32 | 14.41 a–c ± 1.07 | 12.24 a ± 1.40 | 19.32 a ± 1.60 |
| CSP80 | 156.25 a–c ± 6.01 | 191.37 a ± 8.51 | 15.27 a ± 2.64 | 15.19 a ± 2.02 | 11.38 c ± 0.57 | 17.38 b ± 2.63 |
| CSP100 | 129.17 cd ± 8.01 | 188.29 a ± 6.76 | 14.27 a–c ± 0.71 | 15.49 a ± 2.12 | 12.92 a ± 1.60 | 16.62 b ± 2.04 |