Abstract
It is well known that soil fertility is poor in most newly reclaimed land, which has been developed as an effective way to compensate farmland occupation. In order to ameliorate the soil quality of the newly reclaimed land, this study investigated the effect of commercial organic fertilizer (COF) (0.45, 0.90, 1.35 and 1.80 kg/m2), sheep manure (SM) (0.45, 0.75, 1.05 and 1.35 kg/m2), mushroom residue (MR) (1.50, 2.25, 3.00 and 3.75 kg/m2), and chemical compound fertilizer (CCF) (0.075 kg/m2) on the growth of sweet potato, soil pH, organic matter content (OMC), available phosphate, total nitrogen, available potassium, exchangeable Ca and Mg, as well as bacterial and fungal microbial composition during 2019–2021. The results from this study indicated that the COF, SM, MR, and CCF did not significantly change the soil pH, but significantly increased the OMC, which has been regarded as the most significant soil quality parameter. This suggests that the soil amendments used in this study have great potential to improve the soil quality in newly reclaimed land. However, these soil amendments exhibited a differential effect on sweet potato biomass, nutrient elements and the microbial community of the newly reclaimed soil, which depend on the kind and concentration of organic/chemical fertilizer, the application time, as well as the plant and soil parameters. The change was also observed on the bacterial and fungal soil microbial community, which provides us with a microbial basis to understand why organic fertilizer has a great effect on soil improvement. Overall, our results suggest that soil amended with organic fertilizers has great potential for the production of sweet potato in immature soil from the new reclamation land.
1. Introduction
Sweet potato (Ipomoea batatas) is a carbohydrate-rich root crop with a potentially rich protein, lipid, calcium, and carotene source. These qualities make the crop a valuable source of food, animal feed, and industrial raw material [1]. The crop is ranked seventh in global food crop production and is the third most important root crop after potato and cassava [2,3]. In recent years, sweet potato has been cultivated in mountainous areas in Zhejiang Province, China due to the decrease in available cultivated land resources with the rapid development of urbanization over the last several decades [2,4].
However, the immature soil in the barren mountain land is not very suitable for plant growth. Indeed, compared to the normal yield (about 27,600 kg/ha) of sweet potato, the yield of sweet potato is only about 15,000 kg/ha in mature soil. The low yield may be mainly attributed to the acidic soil, high gravel content, poor nutrient content, and very low content of organic matter [2,5], which also resulted in the decrease in the number and diversity of soil microorganisms. Therefore, in order to develop the production of mountainous sweet potato, it is very necessary to find effective measures to improve the quality of the immature soil in mountainous areas in Zhejiang Province, China.
It is well known that soil health is highly associated with the community of soil microorganisms [6,7], which has often been determined using culture techniques through the growth on selective or non-selective media. The culture method provides a good strategy for the analyzing of the soil bacterial profiles over the past few decades by isolating the live bacteria and then focusing on the number of total bacteria. This has led to the discovery of previously unknown organisms, but it also has the disadvantage of being unable to know whether these soil bacteria are alive or dead. In contrast, high-throughput genomic sequencing techniques, especially amplicon sequencing, have provided a comprehensive analysis in the community composition of soil bacteria and fungi without having to culture them. Furthermore, compared with the traditional plate culture method, the non-culture method has the advantage of quicker results, less samples, and being less expensive [6,7,8].
The objective of the study was to evaluate the effect of organic and inorganic amendments with various application amounts on the biomass of sweet potato and the fertility of immature soil in newly reclaimed land. Furthermore, the underlying mechanism of organic amendments was determined by investigating the change in microbial soil communities.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Sites Description
This experiment was carried out on newly reclaimed land after reclamation of the mountains in Shangyuan Village (29°25′39″ N; 119°28′54″ E) of Jiande county, Hangzhou city (Meteorological data as shown in Supplementary file Table S1), Zhejiang Province, China. The soil type was acidic red with gravel, based on the soil classification system of the FAO-UNESCO [9], while its fertility grade (1–10, with one being the best) is grade 3 and class 6 based on the nutrient classification standard of the second soil survey in China [10].
2.2. Collection of Organic/Chemical Fertilizer
Commercial organic fertilizer (COF), sheep manure (SM) and mushroom residue (MR) were selected for application in this study due to their massive consumption in agriculture production. The three kinds of organic fertilizers (COF, SM and MR) were provided by Chuan’an Shicheng Soil Fertilizer Co., Ltd. (Hangzhou, China), Hangzhou Nanwuzhuang Soil Fertilizer Co., Ltd. (Hangzhou, China) and Hangzhou Academy of Agriculture Sciences (Hangzhou, China), respectively. The chemical compound fertilizer (CCF, N-P-K, 16-16-16) was purchased from Shenzhen Batian Ecological Engineering Co., Ltd. (Shenzhen, China). The pH, composition, and price of each organic/chemical material used in this study are listed in Table 1.

Table 1.
The pH, composition and price of each soil amendment used in this study.
2.3. Experimental Design and Data Collection
The field plot experiment was completely randomly designed in this study, which was continuously conducted in 10 April–10 August of each year during 2019–2021. The area of each plot was 20 m2, while the width and depth of the plot were 60 cm and 25 cm, respectively. As shown in Table 2, the field plot experiment consisted of 14 treatments: COF at the concentrations of 0.45, 0.90, 1.35 and 1.80 kg/m2; SM at the concentrations of 0.45, 0.75, 1.05, 1.35 kg/m2; MR at the concentrations of 1.50, 2.25, 3.00 and 3.75 kg/m2; and CCF at 0.075 kg/m2. The treatment without organic/chemical fertilizer was used as the control. Following the mixture of the fertilizer with the top 0–20 cm soil, the newly reclaimed land was planted with the seedlings of sweet potato (cultivar ‘xinxiang’), which were provided by Hangzhou Academy of Agriculture Sciences, Hangzhou, China. The sweet potato was managed regularly. About 10 August each year, sweet potatoes (both the above- and below-ground part) and soil samples were collected for further study. Using a shovel, about 1.5 kg of fresh soil samples were collected from the mixed rhizosphere soil (5–20 cm) of each plot according to the quartering method. After passing through a 0.45 mm sieve to remove fine roots and debris, 20 g of each sample was kept in a refrigerator at −80 °C for DNA extraction, while the other samples were air-dried at room temperature for soil properties measurement. The experiment was repeated for three years, and each treatment had three replicates.

Table 2.
The 14 treatments used in this study.
2.4. Measurement of Soil and Plant Parameters
2.4.1. Measurement of Plant Parameters
After four months of planting, the above- and below-ground sweet potato was dug up using hoes from the soil. The above-ground part was cut from the below-ground part of the sweet potato. After removing the soil from the below-ground part of the sweet potato, the effect of different organic/chemical fertilizers on the biomass of sweet potato was determined by measuring the above- and below-ground and total fresh weight of sweet potato by using a digital scale (TCS-50, Shanghai hento Industrial Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China).
2.4.2. Measurement of Soil Physical and Chemical Property
After natural air drying, the physical and chemical properties of the collected rhizosphere soil in Section 2.3 were examined according to the methods of [11,12,13,14,15,16]. Briefly, the pH of the soil was measured at a soil/distilled water suspension ratio of 1:5 (g/mL) with a pH meter (FE28, MettlerToledo, Zurich, Switzerland); the content of organic matter was determined by the K2Cr2O7 oxidation external heating method; the content of total N was determined using an automatic Kjeldahl distillation–titration unit; the content of available P was determined by hydrochloric acid–ammonium fluoride extraction molybdenum–antimony anti-colorimetry; the available K was extracted by using ammonium acetate, and the contents were determined by using a flame photometer; the exchangeable Ca and Mg were extracted by using ammonium acetate, and the contents were determined by using an ice3500 atomic absorption spectrophotometer.
2.5. Soil Metagenome Sequencing and Analysis
Genomic DNA was extracted from the collected rhizosphere soil in Section 2.3 by using the E.Z.N.ATM Mag–Bind Soil DNA Kit (OMEGA, Norcross, GA, USA) according to the manufacturer’s recommendations. The quantity and quality of the extracted DNA were detected using a NanoDrop ND-1000 spectrophotometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) and agarose gel electrophoresis, respectively. Bacterial diversity was determined as described by Wu et al. [17] by amplifying the 16S rRNA V3–V4 region of the bacterial 16S rRNA genes using the specified forward primer 341F (5′–CCTACGGGNGGCWGCAG–3′) and reverse primer 805R (5′–GACTACHVGGGTATCTAATCC–3′) primers. Fungal diversity was determined as described by Ren et al. [13] by amplifying the ITS1 and ITS2 regions using ITS1F (5′–CTTGGTCATTTAGGAAGTAA–3′) and ITS2 (5′–GCTGCGTTCTTCATTCGA TGC–3′) primers. The prepared amplicons were sequenced on Illumina MiSeqTM/HiseqTM platform with two paired-end read cycles of 300 bases each from Sangon Biotech (Shanghai) Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China).
2.6. Statistical Analysis
Statistical analysis was performed using SPSS software version 16 (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA). The levels of significance (p < 0.05) of the main treatments and their interactions were calculated through one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) after testing for normality and variance homogeneity.
The sequence data analysis of 16S rRNA and ITS gene amplicons was carried out as described in previous studies [12,13] with minor modifications. In brief, paired-end reads were preprocessed using Cutadapt V1.18 software [18,19]. Following primer sequence removal, clean reads were subjected to clustering to generate operational taxonomic units (OTUs) using VSEARCH software with a 97% similarity cutoff [20]. After selection of the representative read of each OTU using the QIIME package (version 2020.06) [21], all 16S rDNA and ITS representative reads were annotated and blasted against the Silva database (Version 123) using the RDP classifier (confidence threshold was 70%) [22], and the Unite database (ITSs rDNA) using BLAST [23], respectively. Alpha diversity was estimated using the Chao1 index [24] and Shannon index [25]. The unweighted unifrac distance matrix obtained by QIIME was used for principal coordinate analysis (PCoA) and phylogenetic tree construction.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Effects of Different Amendments on Biomass of Sweet Potato
The result from this study indicated that organic/chemical fertilizers exhibited a significant increase (4.7–40.5%) in the above-ground fresh weight of sweet potato, a significant increase (5.1–33.3%) in the below-ground fresh weight of sweet potato, and a significant increase (11.5–30.8%) in the total fresh weight of sweet potato compared to the corresponding control in 2019, 2020 and 2021, respectively (Table 3, Supplementary file Table S2). Although the above- and below-ground parts and total fresh weight of sweet potato in new reclamation soil were significantly increased by all of the tested organic/chemical fertilizers from 2019 to 2021, the increased effect was dependent on the kind and concentration of organic/chemical fertilizers as well as plant parameters. The various effects of biological fertilizers on the biomass of sweet potato may be mainly attributed to the difference in their composition.

Table 3.
Effect of different organic and chemical fertilizers on sweet potato fresh weight, soil pH, and organic matter content compared to the control.
In agreement with the result of this study, some previous studies have also reported the use of soil amendments in the production of sweet potato. For example, Nedunchezhiyan et al. [26] reported that the application of rice straw and farmyard manure increased sweet potato growth and root yield under lowland conditions. Zhao et al. [27] revealed the mechanisms underlying the reduction in aluminum toxicity and improvements in the yield of sweet potato after organic and inorganic amendment of an acidic ultisol. Liu et al. [28] reported the effects of biochar amendment on rapeseed and sweet potato yields and water stable aggregate in upland red soil. Wang et al. [29] revealed that the application of the activated humic acid-nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium compound fertilizer in sweet potato production could be used effectively to increase the soil quality, facilitate the growth of sweet potato, and increase its yield under similar conditions to this work.
3.2. Effects of Different Organic/Chemical Amendments on Soil pH and Organic Matters Contents
The results indicated that there was no significant difference in soil pH between organic/chemical fertilizers and the control during 2019–2021. This result is somewhat different with the data from our previous studies [6,12,13], which indicated that the pH of soil was able to be significantly changed by biological organic fertilizers. This conflicting result may be mainly attributed to the difference in the soil in the two experiments (Table 3; Supplementary File Table S3). However, in agreement with our previous studies [6], the soil OMC was generally improved by three kinds of biological organic fertilizers at different concentrations. The increased effect was dependent on the kind and concentration of biological organic fertilizers as well as the application time (Table 3; Supplementary file Table S3). On the other hand, the soil OMC was unaffected by CCF at 2020 and 2021 but was significantly changed by CCF at 2019 with a 7.47% reduction. This may be due to the repeated application of chemical fertilizer reducing the proportion of microaggregates (<0.25 mm) [30].
To our surprise, the result of this study clearly revealed that the effects of organic amendments in OMC improvement are generally better than that of commercial chemical fertilizer. There was a differential effect among COF, SM and MR in the improvement of OMC, which may be mainly due to the difference in the rich organic content of the three organic amendments. On the other hand, this result also reveals that the effect of organic fertilizers in OMC is closely related to its concentration, which may be because those organic fertilizers at a high concentration may have a weak or harmful effect on soil quality. It revealed the complexity of the interaction between organic fertilizer and soil (or soil microbe). Therefore, it can be inferred that organic fertilizers have great potential to improve soil quality of the newly reclaimed soil.
A similar observation on the increase in OMC was reported by Li et al. [6], who found that different organic fertilizers could comprehensively enhance the soil OMC of newly reclaimed lands, resulting in the improvement of soil fertility. Furthermore, other studies have also shown that the soil OMC and the quality of newly reclaimed land could be effectively improved by increasing the use of organic fertilizers. The measures include planting winter legume crops, returning crop stems and stalks to the field, promoting the use of commercial organic fertilizer, comprehensively utilizing agricultural and animal husbandry wastes, and making compost by using rural litter, other plant residues, and gully soil [31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38].
The main obstacle to high crop yield in the newly reclaimed land may be attributed to a low pH and OMC, which have been regarded as the basis for soil fertility and quality. Indeed, due to the long-term application of chemical fertilizer and the lack of application of organic fertilizer in recent years, the newly cultivated land is generally acidic with decreased soil fertility in Zhejiang Province, China [8]. Obviously, the result of this study indicated that the application of organic fertilizer could improve the fertility and quality of the immature soil by adjusting the pH value and OMC of soil, resulting in the plant growth promotion in the immature soil. However, we did not observe the correlation between the composition of these soil amendments and their effect on the soil pH, OMC and other physiochemical parameters. Therefore, it can be inferred that some other factors such as the soil microbes may be also involved in the improvement of soil quality.
3.3. Effects of Different Amendments on the Selected Nutrient Concentrations
3.3.1. Change in the Total N
The result from this study indicated that the total N content of the soil was not significantly affected by chemical fertilizer compared to the corresponding control during 2019–2021. This may be due to the fact that chemical fertilizer has a slight effect on organic nitrogen, which is the main component of the soil total N. Take note that N applied as chemical fertilizer is subject to various soil transformations, including leaching by rainfall. Therefore, N could have been leached below the rooting zone. However, the content of total N was differentially changed by three kinds of biological organic fertilizers. The change in soil total N could have been caused by the decomposition of applied biological organic fertilizers. The effect was dependent on the kind and concentration of biological organic fertilizers as well as the application time. Indeed, the content of total N was significantly improved by COF at 1.80 kg/m2, SM at 1.05 kg/m2, MR at 2.25 and 3.00 kg/m2 with a 28.3–29.5% increase, but unaffected by all of the other organic fertilizer treatments in 2019. The content of the total N was significantly improved by COF at 1.80 kg/m2, SM at 1.05 and 1.35 kg/m2, and MR at 2.25, 3.00 and 3.75 kg/m2 with a 34.1–52.4% increase, but unaffected by all of the other organic fertilizer treatments in 2020. The content of total N was significantly changed by all of the organic fertilizer treatments with a 36.5–71.2% increase in 2021 (Table 4; Supplementary file Table S4).

Table 4.
Effect of different organic and chemical fertilizers on soil total N, available P, available K, exchangeable Ca and exchangeable Mg compared to the control.
3.3.2. Change in Available P
The result from this study indicated that compared to the control, the available P of the soil was significantly changed by all of the chemical/biological fertilizer treatments, with a 29.7–77.2% increase in 2019, a 118.7–188.6% increase in 2020 and a 163.6–191.0% increase in 2021, respectively (Table 4; Supplementary file Table S4). Similar observations were found in previous studies, for example, Criquet and Braud [39] determined the effects of organic and mineral amendments on available P and phosphatase activities in a degraded Mediterranean soil under a short-term incubation experiment. In contrast, Yuan et al. [40] found that seven years of biochar amendment has a negligible effect on soil available P and a progressive effect on organic C in paddy soils.
3.3.3. Change in Available K
This study indicated that, compared to the control, the available K content of the soil was reduced by SM at 1.35 kg/m2 and MR at 2.25 and 3.00 kg/m2, and unaffected by COF at 1.80 kg/m2, and SM at 0.45 and 0.75 kg/m2, but was significantly increased (range from 2.6% to 11.2%) by all the other chemical/biological fertilizer treatments in 2019. The various effects may be mainly attributed to the difference in composition of chemical/organic fertilizers. Furthermore, the content of available K was significantly changed (with a 2.1–11.0% increase) by all of the chemical/biological fertilizer treatments compared to the control in 2020. In addition, the content of available K was significantly changed (with a 7.2–17.3% increase) by all of the chemical/biological fertilizer treatments compared to the control in 2021 (Table 4; Supplementary file Table S4).
3.3.4. Change in Exchangeable Ca and Mg Contents
Similar to the other soil parameters, an irregular change was also found in the content of exchangeable Ca and Mg in new reclamation soil (Table 4; Supplementary file Table S5). In detail, compared to the control, the exchangeable Ca was significantly increased by MR at 1.50 kg/m2, but unaffected by all of the other chemical/biological fertilizer treatments in 2019. Furthermore, the exchangeable Ca was unaffected by COF at 0.45 and 0.90 kg/m2, MR at 1.50 kg/m2 and chemical fertilizer treatment, but was significantly increased by all of the other biological fertilizer treatments in 2020. In addition, the exchangeable Ca was unaffected by COF at 0.45 kg/m2 and chemical fertilizer treatment, but was significantly increased by all of the other biological fertilizer treatments in 2021. Compared to the control, the content of exchangeable Mg in new reclamation soil was significantly increased by COF at 1.80 kg/m2, was significantly reduced SM at 0.45 kg/m2, and MR at 2.25 and 3.00 kg/m2, but was unaffected by all of other biological fertilizer treatments in 2019. Furthermore, the content of exchangeable Mg was unaffected by all of chemical/biological fertilizer treatments compared to the control in 2020. In addition, the content of exchangeable Mg was significantly increased by COF at 1.35 and 1.80 kg/m2, SM at 0.45 and 1.35 kg/m2, but was unaffected by all of the other chemical/biological fertilizer treatments compared to the control in 2021 (Table 4; Supplementary file Table S5). The differential effect of organic/chemical fertilizers in exchangeable Ca and Mg may be related with their composition.
The nutrients N, P, and K have been regarded as the most indispensable primary macronutrients for the growth and development of crops [41]. However, the results of these nutrients were low in our experimental site on newly reclaimed land, which may be the main reason that most of the newly reclaimed land is not suitable for plant growth. Indeed, the soils in this study have an initial pH of 4.60, with 0.95 g/kg of total N, 10.15 g/kg of organic matter contents, 14.80 mg/kg of available P, and 415.02 mg/kg of available K. Secondary macronutrients such as Ca and Mg were also observed to be low: the initial value of exchangeable Ca and Mg is 3.86 cmol/kg and 0.84 cmol/kg, respectively. Therefore, to improve the N, P, K, Ca, Mg, soil pH, and OM content in the soil, biological organic fertilizers were used in the current study on newly reclaimed land in Zhejiang Province. Previous studies [8] have reported that biological organic fertilizers were able to effectively improve the content of these nutrient elements in newly reclaimed land. However, the results from this study indicated that the effect of biological organic fertilizers was dependent on the kind and concentration of biological organic fertilizers as well as the nutrient elements.
3.4. Effects of Different Organic/Chemical Amendments in Microbial Community Diversity
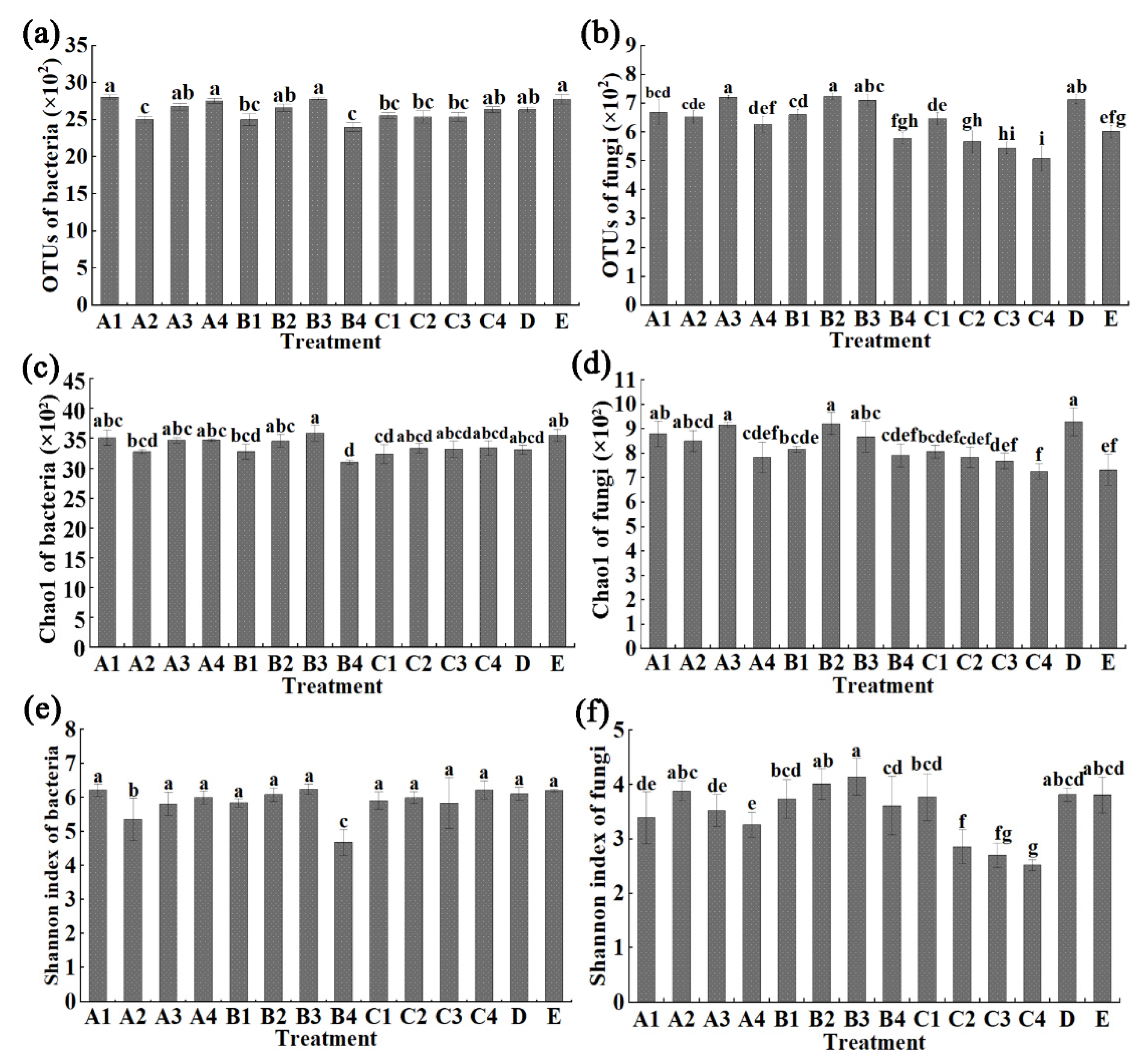
The results from this study indicated that the average bacterial OTUs number of COF at 0.45, 0.90, 1.35 and 1.80 kg/m2, SM at 0.45, 0.75, 1.05 and 1.35 kg/m2, MR at 1.50, 2.25, 3.00 and 3.75 kg/m2, CCF at 0.075 kg/m2 and control is 2808.33, 2439.33, 2644.00, 2756.67, 2503.67, 2664.00, 2780.67, 2403.00, 2553.33, 2539.00, 2537.00, 2637.67, 2639.33, and 2779.67, respectively. In general, the bacterial OTUs number was unaffected by COF at 0.45, 1.35 and 1.80 kg/m2, SM at 0.75 and 1.05 kg/m2, MR at 3.75 kg/m2 and chemical fertilizer, but was significantly reduced by all of other biological fertilizer treatments (Figure 1a). Furthermore, the bacterial Chao1 index was significantly changed by SM at 1.35 kg/m2 and MR at 1.50 kg/m2 with 12.6% and 8.8% reduction compared with the untreated control, respectively, but was unaffected by all of other chemical/biological fertilizer treatments (Figure 1c). In addition, the Shannon index was significantly changed by COF at 0.90 and SM at 1.35 kg/m2 with 13.5% and 24.5% reduction compared with the untreated control, respectively, but was unaffected by all of other chemical/biological fertilizer treatments (Figure 1e). This may be due to the nutrients of biological fertilizers being more suitable for bacterial growth than fungal growth.
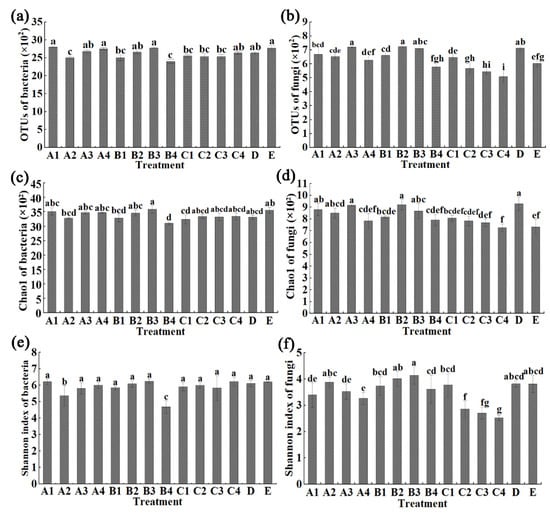
Figure 1.
Effect of different fertilizers at different concentrations on © distribution of bacteria (a) and fungi (b), Chao1 diversity index of bacteria (c) and fungi (d), Shannon’s diversity index of bacter©(e) and fungi (f) in sweet potato rhizosphere soil. A1–4: Commercial organic fertilizer at 0.45, 0.90, 1.35 and 1.80 kg/m2; B1–4: sheep manure at 0.45, 0.75, 1.05 and 1.35 kg/m2; C1–4: mushroom residue at 1.50, 2.25, 3.00 and 3.75 kg/m2; D: chemical compound fertilizer (0.075 kg/m2); E: control. Different lower case letters above columns indicate statistical differences (p < 0.05).
The average fungal OTUs number of COF at 0.45, 0.90, 1.35 and 1.80 kg/m2, SM at 0.45, 0.75, 1.05 and 1.35 kg/m2, MR at 1.50, 2.25, 3.00 and 3.75 kg/m2, CCF at 0.075 kg/m2 and the control is 669.00, 653.00, 722.00, 627.00, 661.33, 724.67, 711.33, 578.33, 646.67, 567.33, 545.67, 508.33, 714.67, and 602.33, respectively (Figure 1b). In general, the average fungal OTUs number was significantly increased (9.8% to 20.3%) by COF at 0.45 and 1.35 kg/m2, SM at 0.45, 0.75 and 1.05 kg/m2 and chemical fertilizer, was significantly reduced (9.4% to 15.6%) by MR at 3.00 and 3.75 kg/m2, and was unaffected by all of the other biological fertilizer treatments compared to the control (Figure 1d). The fungal Chao1 indexes were unaffected by COF at 1.80 kg/m2, SM at 0.45 and 1.35 kg/m2, MR at 1.50, 2.25, 3.00 and 3.75 kg/m2, but were significantly increased by all of the other chemical/biological fertilizer treatments compared to the control, respectively. Furthermore, the fungal Shannon indexes were significantly reduced by COF at 1.80 kg/m2, MR at 2.25, 3.00 and 3.75 kg/m2, but were unaffected by all of the other chemical/biological fertilizer treatments compared to the control (Figure 1f).
Obviously, the fungal and bacterial diversity were differentially affected by various chemical/biological fertilizers. On the other hand, it is well known that soil fertility is associated with the richness of the soil microbes, which has been reported to be involved in a variety of soil biological processes such as N fixation and P solubilization [6,7,8,12,13]. Furthermore, amplicon sequencing of bacterial 16S rRNA and fungal ITS gives a comprehensive analysis in the community composition of the soil microbes. Indeed, the three fertilizers (COF, SM, MR) at different concentrations caused changes in the number of operational taxonomic units (OTUs), Chao1 and Shannon index in microbial community structure compared with the untreated control, while previous studies have found that organic fertilizers can cause a greater ratio of bacterial and f©al OTU distribution and diversity indexes in immature soil [8]. Therefore, the improvement of the soil quality by various organic amendment may be partially attributed to the enrichment of specific microbes. Further study should be carried out to elucidate the role of specific soil microbe in soil amendment of organic fertilizers in new reclamation land.
3.5. Effects of Different Organic/Chemical Amendments in Soil Microbial Community Structure
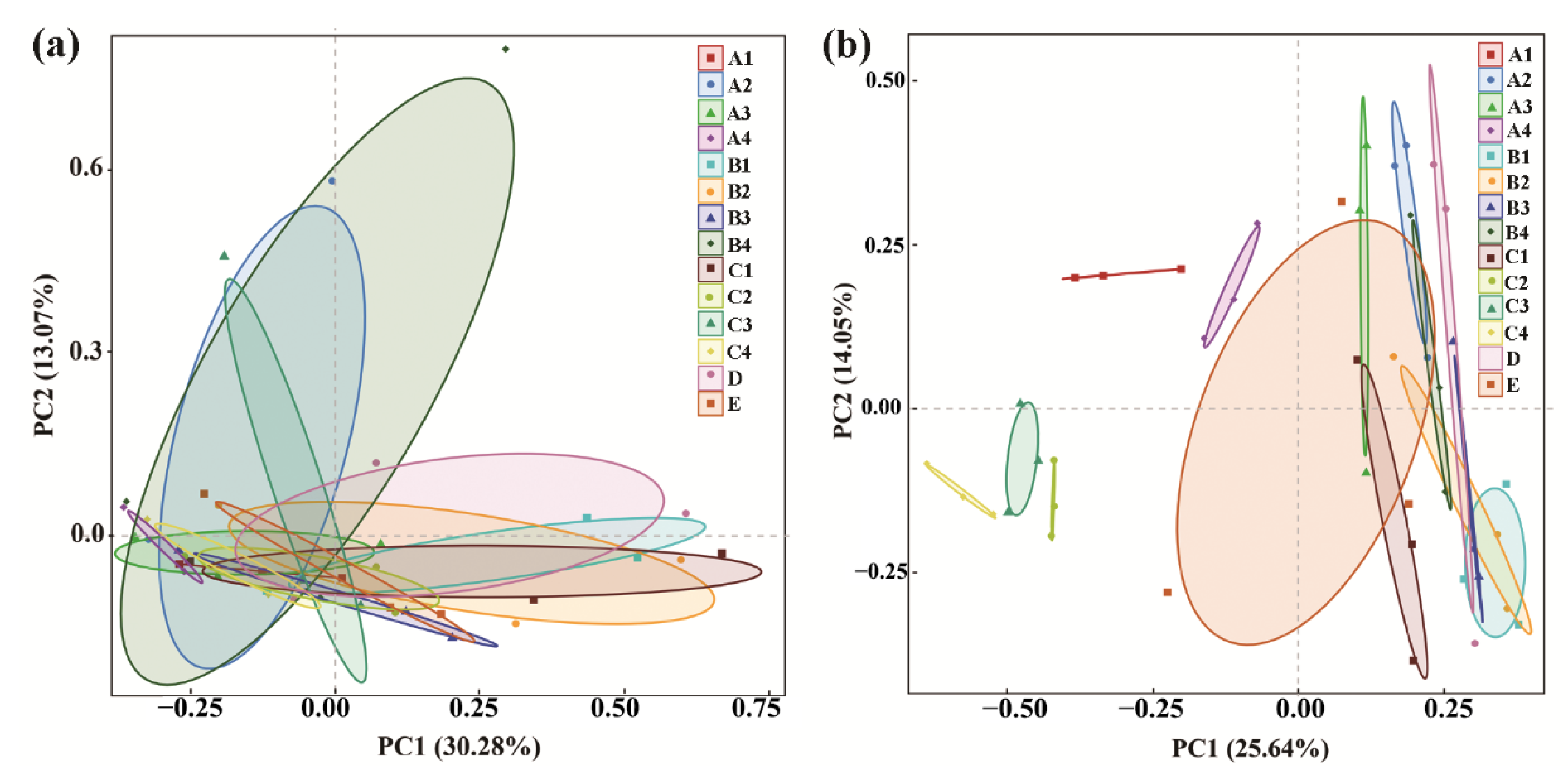
PCoA analysis of the bacterial community indicated that the three replicates of each treatment were clustered into one group; however, the control was overlapped by all of the chemical/organic fertilizer treatments except COF at 1.80 kg/m2 and MR at 3.75 kg/m2, which were well separated from the control. Meanwhile, the treatment COF at 1.80 kg/m2 was also well separated from CCF, indicating that the bacterial community structure of the rhizosphere soil was significantly changed by both COF at 1.80 kg/m2 and MR at 3.75 kg/m2, especially COF at 1.80 kg/m2 (Figure 2a). Similarly, PCoA analysis of the fungal community structure indicated that the three replicates of each treatment were clustered into one group, while the control was overlapped by all of the chemical/organic fertilizer treatments except COF (0.45, 1.80 kg/m2), SM (0.45, 1.05 kg/m2), MR (3.00, 3.75 kg/m2) and CCF, which were well separated from the control. This indicates that the fungal community structure of rhizosphere soil was significantly changed by these chemical/organic fertilizer treatments (Figure 2b). In agreement with the results of this study, continuous application of COF or MR fertilizer in immature soil caused a significant change in bacterial and fungal communities in barberry and cotton soil [13,42].
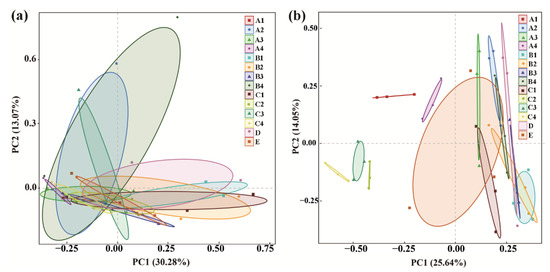
Figure 2.
PCoA results of soil bacteria (a) and fungi (b) based on OUT abundance. A1–4: commercial organic fertilizer at 0.45, 0.90, 1.35 and 1.80 kg/m2; B1–4: sheep manure at 0.45, 0.75, 1.05 and 1.35 kg/m2; C1–4: mushroom residue at 1.50, 2.25, 3.00 and 3.75 kg/m2; D: chemical compound fertilizer (0.075 kg/m2); E: control. Effect of organic/chemical fertilizer on soil microbial community composition.
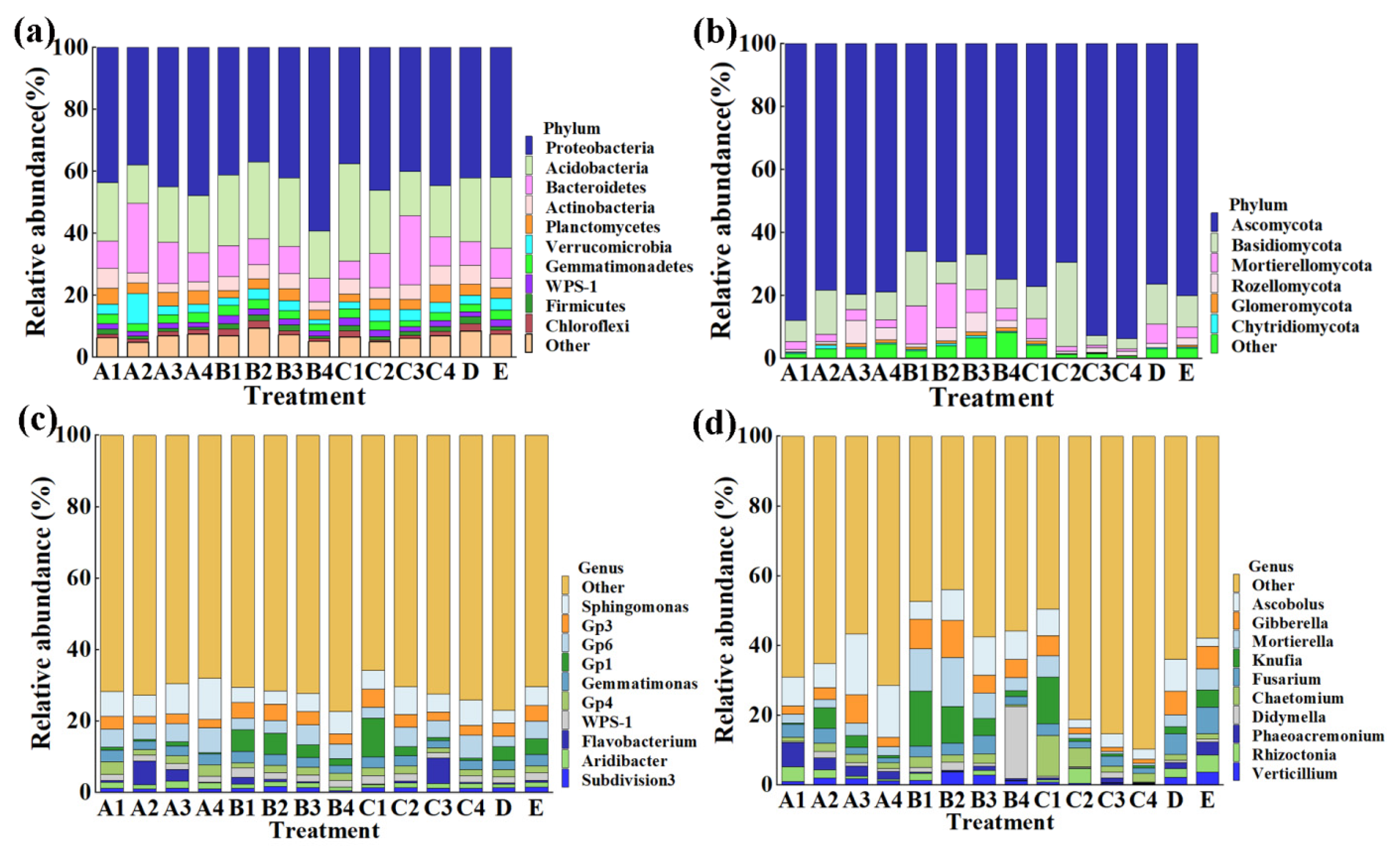
This result indicated that the composition of soil bacterial and fungal community was changed by all of the 14 chemical/biological fertilizer treatments at the levels of phylum (Figure 3a,b) and genus (Figure 3c,d) compared to the control. In general, the variation in soil microbial community structure was dependent on the kind and concentration of chemical/biological fertilizers. Indeed, the top 10 phyla in the rhizosphere soil of sweet potato were selected to generate a relative abundance histogram, in which Proteobacteria, Acidobacteria, Bacteroidetes, Actinobacteria, and Planctomycetes were the main bacterial phyla, with a relative abundance of 36.9–59.2%, 12.4–31.4%, 7.5–22.5% and 2.8–6.3%, respectively (Figure 3a). Furthermore, the relative abundance histogram based on the top 10 species showed that Sphingomonas, Gp3, Gp6, Gemmatimonas, Gp4, and WPS-1 were the main bacterial genera (average relative abundance > 1%). In addition, we found that the COF and MR treatments caused a 56.1% and 18.6% increase in the relative abundance of Sphingomonas, and 10.3% and 18.3% reduction in Gemmatimonas, respectively, in rhizosphere soil of sweet potato compared with the control (Figure 3c). The change in the number of specific bacteria may be mainly due to the different nutrients between chemical/biological fertilizers. Interestingly, recent studies have also shown that some Sphingomonas species were able to improve plant growth by producing plant growth hormones, e.g., gibberellins and indole acetic acid during stress conditions such as drought, salinity, and heavy metals in agricultural soil [43]. Therefore, more attention should be paid to the potential role of Sphingomonas in improvement of the soil quality.
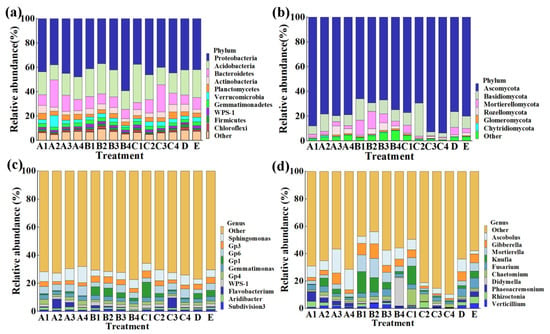
Figure 3.
Effect of the different fertilizers at different concentration on the relative microbial abundance of sweet potato rhizosphere soil at the phylum and genus level. (a) Bacteria at phylum level; (b) fungi at phylum level; (c) bacteria at genus level; (d) fungi at genus level. A1–4: commercial organic fertilizer at 0.45, 0.90, 1.35 and 1.80 kg/m2; B1–4: sheep manure at 0.45, 0.75, 1.05 and 1.35 kg/m2; C1–4: mushroom residue at 1.50, 2.25, 3.00 and 3.75 kg/m2; D: chemical compound fertilizer (0.075 kg/m2); E: control.
Meanwhile, according to the distribution and relative abundances of fungi in sweet potato rhizosphere soil at the phylum level, Ascomycota and Basidiomycota were the main phylum, with a relative abundance of 66.0–92.8% and 3.0–26.7%, respectively (Figure 3b). Furthermore, at the genus level, Ascobolus, Gibberella, and Fusarium were the main fungal genera (average relative abundance > 1%) (Figure 3b). Compared with the control, the COF, SM, and MR treatments caused a 399.0%, 249.9%, and 75.8% increase in the relative abundance of Ascobolus and 63.2%, 54.1%, and 68.7% reduction in Fusarium, respectively (Figure 3d). Interestingly, the relative abundance of Gibberella was reduced by 34.9% and 61.8% under COF and MR treatment, respectively, but was increased by 14.8% under SM treatment (Figure 3d). The role of the saprophytic fungi Ascobolus in soil is still unclear. However, the fungi from the genus Gibberella and Fusarium have been reported to be the pathogen of many leaf- and soil-borne diseases [44]. The conflict effect on the relative abundance of Gibberella revealed the complexity of the soil fungal community.
This study revealed a change in the composition of soil microbial community structure among the samples. In general, the change may depend on the kind and concentration of chemical/biological fertilizers, while it seems that no similar bacterial species were enriched by all of the treatments. Furthermore, no similar change in soil bacterial communities was observed for all of the treatments. However, this result also found that some specific bacteria may be associated with soil amendment. In agreement with the result of this study, our previous studies [8] also showed that organic fertilizers at three different concentrations significantly increased the ratio of Rhizobiales and Alphaproteo bacteria in the community structure compared with the control. Therefore, it can be inferred that the improvement of organic fertilizers in the soil quality may be mainly due to the change in the genera abundance distribution by enriching specific soil microbe in the newly cultivated land.
3.6. Effects of Different Organic/Chemical Amendments in Rhizosphere Microbiome and Biomarker
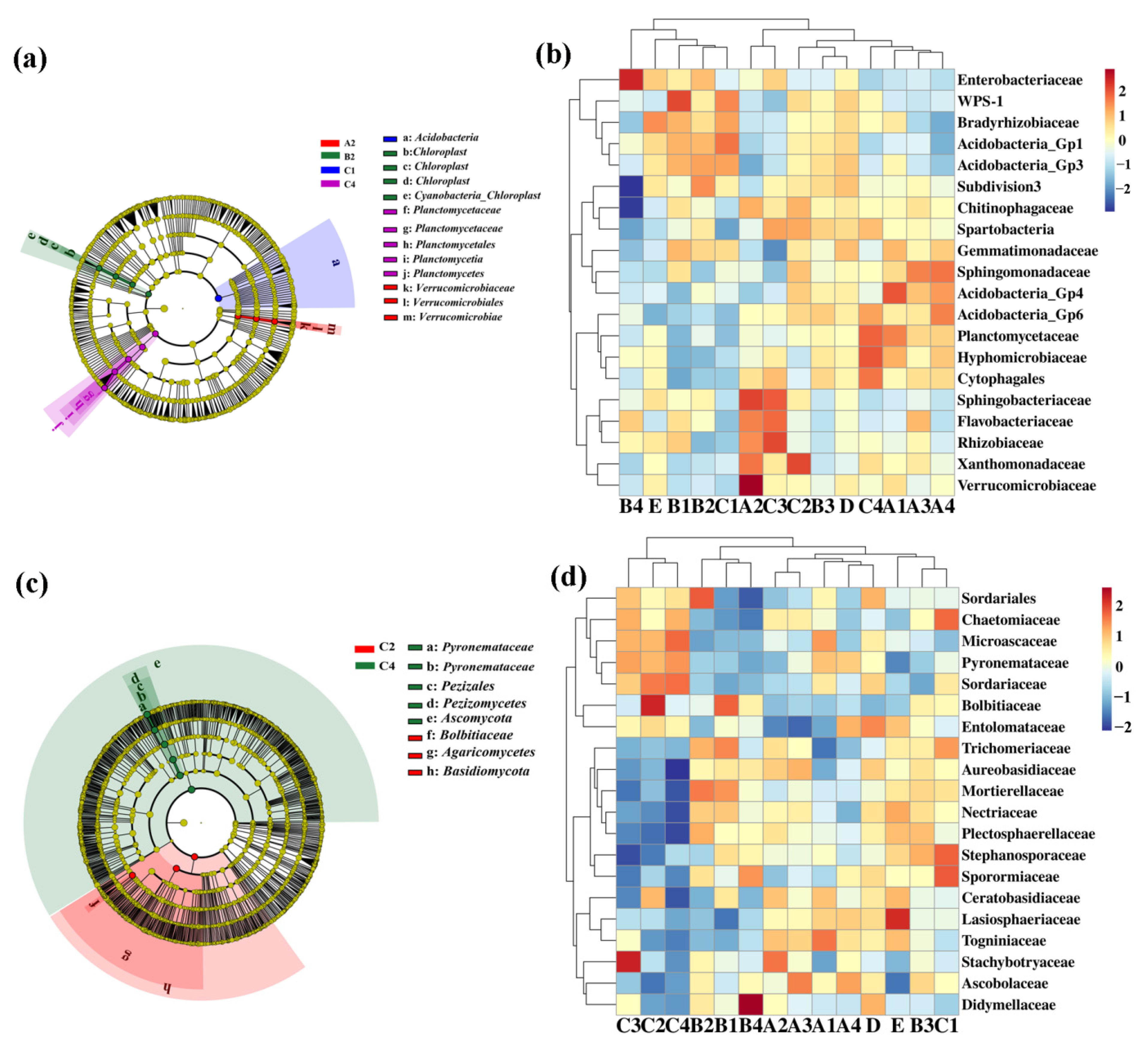
The linear discriminant analysis of effect size (LEfSe) (LDA > 4, p < 0.05) was used to reveal the biomarker with the largest difference in rhizosphere soil bacterial communities under different treatment conditions (Figure 4a). A total of 13 biomarkers were found in the COF, SM and MR treatments. In detail, COF at 0.90 kg/m2 is enriched with Verrucomicrobiaceae, Verrucomicrobiales and Verrucomicrobiae, SM at 0.75 kg/m2 is enriched with Cyanobacteria, Chloroplast and three kinds of Chloroplast, and MR at 3.75 kg/m2 is enriched with Planctomycetia, Planctomycetes and two types Planctomycetaceae (Figure 4a). Furthermore, the difference in relative abundance composition (family level) of the rhizosphere bacterial community under different organic fertilizer treatments was visually explained through heat maps (Figure 4b). The COF treatment was enriched with Acidobacteria_GP4, Sphingobacteriaceae and Verrucomicrobiaceae, but was reduced with Acidobacteria_GP1 and WPS-1. The SM treatment was enriched with WPS-1 and Enterobacteriaceae, but was reduced with Verrucomicrobiaceae. The MR treatment was enriched with Acidobacteria_GP1, Xanthomondaceae, Rhizobiaceae, Flavobacteriaceae, Cytophagales, Hyphomicrobiaceae, and Planctomycetaceae.
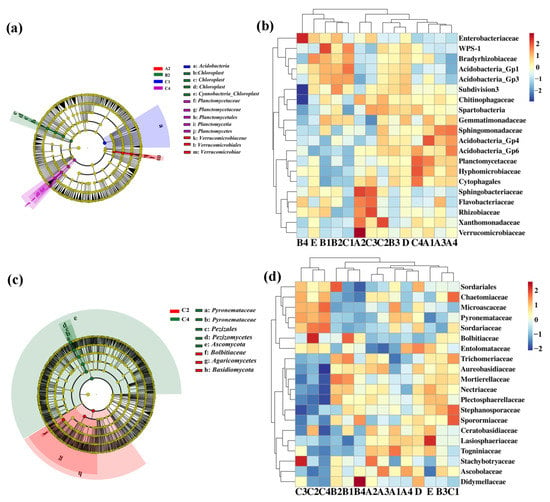
Figure 4.
Linear discriminant analysis (LDA) effect size (LEfSe) of the (a) bacterial and (c) fungal taxa, which identifies the different taxa among the different treatment. Only taxa are shown with LDA values greater than 4 and 5 in bacteria and fungi, respectively (p < 0.05). Hierarchical clustering analysis and heat map of bacteria (b) and fungi (d) at the family level. The tree plot represents a clustering analysis of the top 20 bacteria or fungi at family levels according to their Pearson correlation coefficient matrix and relative abundance, the upper tree plot represents a clustering analysis of soil samples according to the Euclidean distance of data. A1–4: commercial organic fertilizer at 0.45, 0.90, 1.35 and 1.80 kg/m2; B1–4: sheep manure at 0.45, 0.75, 1.05 and 1.35 kg/m2; C1–4: mushroom residue at 1.50, 2.25, 3.00 and 3.75 kg/m2; D: chemical compound fertilizer (0.075 kg/m2); E: control.
Meanwhile, the LEfSe was executed at LDA > 5 (p < 0.05) in rhizosphere soil fungal communities under different treatments. A total of 8 biomarkers were found in the MR treatments. SM at 1.35 kg/m2 is enriched with Dothideomycetes and Ascomycota, and MR at 2.25 kg/m2 is enriched with Bolbitiaceae, Agaricomycetes and Basidiomycota, while MR at 3.75 kg/m2 is enriched with Pezizales, Ascomycetes, Pezizomycetes and two types of Pyronemataceae (Figure 4c). Furthermore, the difference in relative abundance composition (family level) of the rhizosphere fungal community under different organic fertilizer treatments was visually explained through heat maps (Figure 4d). The MR treatment was enriched with Stephanosporaceae, Sporormiaceae, Bolbitiaceae, Stachybotryaceae, Sordariaceae and Microascaceae, but was reduced with Nectriaceae, Plectosphaerellaceae, Aureobasidiaceae, Lasiosphaeriaceae, Togniniaceae and Entolomataceae.
The results demonstrate that different organic fertilizers can increase the existence of specific species, resulting in a change in the bacterial or fungal community structure in rhizosphere soil. In agreement with these results, a previous study [6] clearly showed that the four fungal isolates originating from wastelands may have greater potential to colonize in immature soil. Indeed, these fungal isolates from the different wastelands abandoned have great potential as a plant growth-promoting (PGP) fungus to develop the biofertilizer for the application in eggplant production in immature soil from the new reclamation land. These fungal isolates exhibited the great ability to solubilize P, increase the growth of eggplant, and produce siderophores and indole acetic acid [6]. In addition, the use of organic residues as amendments exerts a great influence on soil microbial communities [45,46,47,48], which not only increases the soil organic matter level and long-term soil fertility, but also improves the soil health and productivity.
Our recent studies have shown that soil microorganisms have played an important role in the soil reclamation due to the fact that many bacterial and fungal species can contribute to nutrient bioavailability and aggregate formation in soils as well as the formation and evolution of soil ecosystems [6,7,8]. For example, PGP fungi can improve plant biomass by altering soil chemistry and microbial communities [6], while PGP bacteria can influence plant growth through several important mechanisms, such as the suppression of plant pathogens, amelioration of abiotic stresses, biological nitrogen fixation, phosphate solubilization, and production of siderophores, extracellular enzymes, volatile organic compounds and phytohormones such as auxins, cytokinins, gibberellins, indoleacetic acid, abscisic acid, and ethylene [7]. Thus, the result of this study will provide a basis for the application of organic amendments in the production of mountainous sweet potato.
4. Conclusions
In summary, the result from this study indicated that the COF, SM, MR, and CCF did not significantly change the soil pH. However, the three organic fertilizers, in particular SM, significantly increased the OMC, which has been regarded as the most important soil quality parameter. This suggests that the soil amendments used in this study have great potential to improve the soil quality in newly reclaimed land. However, the effect of improvement differed among these soil amendments, which depend on the kind and concentration of chemical/organic fertilizers. Furthermore, the three organic fertilizers caused a differential change in the bacterial and fungal community of the new reclamation land. Interestingly, some specific microbes, such as Ascobolus species, have also been found to be closely related to the soil improvement of the three organic fertilizers, indicating the complexity of the interaction among immature soil–organic fertilizer–microbes. In conclusion, our results suggest that organic fertilizers can serve as suitable soil amendments for the production of sweet potato in immature soil from the new reclamation land.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/agronomy12071649/s1. Table S1. Meteorological data of Jiande County, Hangzhou, China during 2019–2021. Table S2. Effect of different organic and chemical fertilizers on sweet potato fresh weight. Table S3. Effect of different organic and chemical fertilizers on the soil pH and organic matter content. Table S4. Effect of different organic and chemical fertilizers on soil N, P and K nutrients. Table S5. Effect of different organic fertilizers on the soil exchangeable Ca and Mg.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, X.L., D.L., D.W., X.R., J.Y., T.A., Q.L. and B.L.; methodology, X.L., D.L., L.L. and T.A.; software, X.L., D.L., L.L. and T.A.; validation, X.L., D.L., D.W. and X.R.; formal analysis, X.L., D.L., L.L. and T.A.; investigation, X.L., D.L. and D.W.; resources, X.L., J.Y., X.R., Q.L. and B.L.; data curation, X.L. and J.Y.; writing—original draft preparation, X.L., D.L., J.Y., D.W., X.R., T.A., Q.L. and B.L.; writing—review and editing, J.Y., Q.L. and B.L.; visualization, X.L., J.Y., Q.L. and B.L.; supervision, J.Y., Q.L. and B.L.; project administration, J.Y. and Q.L.; funding acquisition, J.Y. and Q.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Key Research and Development Program of Zhejiang Province (2019C02035, 2017C02002, 2019C02006, and 2020C02006), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31872017 and 32072472), and the Shanghai Agriculture Applied Technology Development Program (2021-02-08-00-12-F00771).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
All the data supporting the conclusions of this article are included in this article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Neela, S.; Fanta, S.W. Review on nutritional composition of orange-fleshed sweet potato and its role in management of vitamin A deficiency. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 7, 1920–1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fan, W.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, P. Improved tolerance to various abiotic stresses in transgenic sweet potato (Ipomoea batatas) expressing spinach betaine aldehyde dehydrogenase. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e37344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hossain, A. Research on biogenic control of Dickeya dadantii causing stem and root rot of sweet potato through Bacillus and biosynthesized nanoparticles. Ph.D. Thesis, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Shi, H.; Lou, L.; Ma, W.; Shen, J.; Chen, W. Effect of Different Fertilization Methods on Fertility and Yield of Crop in Newly Reclaimed Red Soil. Chin. J. Soil Sci. 2019, 50, 1378–1383. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, H.; Tang, Z.; Zhang, A.; Li, H.; Liu, Q. Soil nutrient status and soil fertility evaluation of farmland in three main sweet potato regions in China. Soil Fert. Sci. China 2021, 5, 27–33. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.Q.; Li, D.Y.; Yan, J.L.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhang, J.Z.; Ahmed, T.; Li, B. Effect of Plant-Growth-Promoting Fungi on Eggplant (Solanum melongena L.) in New Reclamation Land. Agriculture 2021, 11, 1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.Q.; Yan, J.L.; Li, D.Y.; Jiang, Y.G.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhang, J.Z.; Ahmed, T.; Li, B. Isolation and Molecular Characterization of Plant-Growth-Promoting Bacteria and Their Effecton Eggplant (Solanummelongena) Growth. Agriculture 2021, 11, 1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.Q.; Su, Y.; Ahmed, T.; Ren, H.Y.; Javed, M.R.; Yao, Y.L.; An, Q.L.; Yan, J.L.; Li, B. Effects of different organic fertilizers on improving soil from newly reclaimed land to crop soil. Agriculture 2021, 11, 560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. FAO/Unesco Soil Map of the World, Revised Legend, with Corrections and Updates; World Soil Resources Report 60; Reprinted with Updates as Technical Paper 20; FAO: Rome, Italy; ISRIC: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, J.P.; Song, G. Soil type database of China: A nationwide soil dataset based on the second national soil survey. China Sci. Data 2016, 1, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Qu, B.P.; Liu, Y.X.; Sun, X.Y.; Li, S.Y.; Wang, S.Y.; Xiong, K.Y.; Yun, B.H.; Zhang, H. Effect of various mulches on soil physic-co-Chemical properties and tree growth (Sophora japonica) in urban tree pits. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0210777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ren, H.Y.; Wang, H.Y.; Qi, X.J.; Yu, Z.P.; Zheng, X.L.; Zhang, S.W.; Wang, Z.S.; Zhang, M.C.; Ahmed, T.; Li, B. The Damage Caused by Decline Disease in Bayberry Plants through Changes in Soil Properties, Rhizosphere Microbial Community Structure and Metabolites. Plants 2021, 10, 2083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.Y.; Wang, H.Y.; Yu, Z.P.; Zhang, S.W.; Qi, X.J.; Sun, L.; Wang, Z.S.; Zhang, M.C.; Ahmed, T.; Li, B. Effect of Two Kinds of Fertilizers on Growth and Rhizosphere Soil Properties of Bayberry with Decline Disease. Plants 2021, 10, 2386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baran, A.; Mierzwa-Hersztek, M.; Gondek, K.; Tarnawski, M.; Szara, M.; Gorczyca, O.; Koniarz, T. The influence of the quantity and quality of sediment organic matter on the potential mobility and toxicity of trace elements in bottom sediment. Environ. Geochem. Health 2019, 41, 2893–2910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lusiba, S.; Odhiambo, J.; Ogola, J. Effect of biochar and phosphorus fertilizer application on soil fertility: Soil physical and chemical properties. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2017, 63, 477–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Platt, B.F.; Kolb, D.J.; Kunhardt, C.G.; Milo, S.P.; New, L.G. Burrowing Through the Literature: The Impact of Soil-Disturbing Vertebrates on Physical and Chemical Properties of Soil. Soil Sci. 2016, 181, 175–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.Y.; Wen, C.Q.; Qin, Y.J.; Yin, H.Q.; Tu, Q.C.; Nostrand, J.D.V.; Yuan, T.; Yuan, M.T.; Deng, Y.; Zhou, J.Z. Phasing amplicon sequencing on Illumina Miseq for robust environmental microbial community analysis. BMC Microbiol. 2015, 15, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martin, M. Cutadapt removes adapter sequences from high-throughput sequencing reads. EMBnet. J. 2011, 17, 10–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyon, D.; Tsai, S.Q.; Khayter, C.; Foden, J.A.; Sander, J.D.; Joung, J.K. FLASH assembly of TALENs for high-throughput genome editing. Nat. Biotechnol. 2012, 30, 460–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rognes, T.; Flouri, T.; Nichols, B.; Quince, C.; Mahé, F. VSEARCH: A versatile open source tool for metagenomics. PeerJ. 2016, 4, e2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Kuczynski, J.; Stombaugh, J.; Bittinger, K.; Bushman, F.D.; Costello, E.K.; Fierer, N.; Peña, A.G.; Goodrich, J.K.; Gordon, J.I. QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat. Methods. 2010, 7, 335–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Q.; Garrity, G.M.; Tiedje, J.M.; Cole, J.R. Naive Bayesian classifier for rapid assignment of rRNA sequences into the new bacterial taxonomy. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 5261–5267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lobo, I. Basic Local Alignment Search Tool (BLAST). J. Mol. Biol. 2008, 215, 403–410. [Google Scholar]
- Chao, J.; Bunge, J. Estimatin the number of species in a stochastic abundance model. Biometrics 2002, 58, 531–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, T.C.; Walsh, K.A.; Harris, J.A.; Moffett, B.F. Using ecological diversity measures with bacterial communities. FEMS Micorbiol. Ecol. 2003, 43, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nedunchezhiyan, M.; Sinhababu, D.P.; Sahu, P.K. Effect of soil amendments and irrigation regimes on minimum tillage planted sweet potato (Ipomoea batatas) in rice (Oryza sativa) fallows under lowland conditions. Indian J. Agric. Sci. 2014, 84, 371–375. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, W.R.; Li, J.Y.; Jiang, J.; Lu, H.L.; Hong, Z.N.; Qian, W.; Xu, R.K.; Deng, K.Y.; Guan, P. The mechanisms underlying the reduction in aluminum toxicity and improvements in the yield of sweet potato (Ipomoea batatas L.) After organic and inorganic amendment of an acidic ultisol. Agric. Ecosys. Environ. 2020, 288, 106716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.X.; Chen, X.M.; Jing, Y.; Li, Q.X.; Zhang, J.B.; Huang, Q.R. Effects of biochar amendment on rapeseed and sweet potato yields and water stable aggregate in upland red soil. Catena 2014, 123, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.F.; Chen, X.G.; Tang, Z.H.; Liu, M.; Jin, R.; Zhang, A.J.; Zhao, P. Application of humic acid compound fertilizer for increasing sweet potato yield and improving the soil fertility. J. Plant Nutr. 2022, 45, 1933–1941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Wang, R.; Yang, X.; Sun, B.; Li, Q. Soil aggregation and aggregating agents as affected by long term contrasting management of an Anthrosol. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 39107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Asghar, W.; Kataoka, R. Green manure incorporation accelerates enzyme activity, plant growth, and changes in the fungal community of soil. Arch. Microbiol. 2022, 204, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, L.; Manzoor, N.; Li, X.; Naveed, M.; Nadeem, S.M.; Waqas, M.R.; Khalid, M.; Abbas, A.; Ahmed, T.; Li, B. Impact of Corn Cob-Derived Biochar in Altering Soil Quality, Biochemical Status and Improving Maize Growth under Drought Stress. Agronomy. 2021, 11, 2300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Still, S.M. Yield Comparison of Sweet Potatoes Grown in Four Commercial Organic Soils. Hortscience 2019, 54, S236. [Google Scholar]
- Bednik, M.; Medyńska-Juraszek, A.; Dudek, M.; Kloc, S.; Kręt, A.; Łabaz, B.; Waroszewski, J. Wheat straw biochar and NPK fertilization efficiency in sandy soil reclamation. Agronomy 2020, 10, 496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xie, X.; Xiang, Q.; Wu, T.; Zhu, M.; Xu, F.; Xu, Y.; Pu, L. Impacts of Agricultural Land Reclamation on Soil Nutrient Contents, Pools, Stoichiometry, and Their Relationship to Oat Growth on the East China Coast. Land 2021, 10, 355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merzlaya, G.E.; Afanasiev, R.A. Agrochemical Aspects of Using Sewage Sludge for Reclamation of Land for Various Purposes. Agrokhimiya 2020, 8, 70–77. [Google Scholar]
- Tenic, E.; Ghogare, R.; Dhingra, A. Biochar—a panacea for agriculture or just carbon? Horticulturae 2020, 6, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.-S.; Yang, H.I.; Park, H.-J.; Park, S.-I.; Seo, B.-S.; Lee, K.-S.; Lee, S.-H.; Lee, S.-M.; Kim, H.-Y.; Ryu, J.-H. Land-use management for sustainable rice production and carbon sequestration in reclaimed coastal tideland soils of South Korea: A review. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2020, 66, 60–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Criquet, S.; Braud, A. Effects of organic and mineral amendments on available P and phosphatase activities in a degraded Mediterranean soil under short-term incubation experiment. Soil Till. Res. 2008, 98, 164–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.H.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Chen, H.; Chen, G.L.; Wang, S.Q. Seven years of biochar amendment has a negligible effect on soil available P and a progressive effect on organic C in paddy soils. Biochar 2022, 4, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, A.M.; Ribeiro, N.P.; Assunção, N.S.; da Silva Nunes, J.G.; Sorroche, C.P.; Leonel, M. Impact of nitrogen and green manure on yield and quality of sweet potato in sandy soil: A Brazilian case study. J. Agric. Food Res. 2021, 4, 100131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.M.; Zhang, F.H.; Li, J.H.; Fan, H.; Cheng, Z.B.; Wang, K.Y. Effects of bio-organic fertilizer on soil microbiome against Verticillium dahliae. Int. J. Agric. Biol. 2016, 18, 923–931. [Google Scholar]
- Asaf, S.; Numan, M.; Khan, A.L.; Al-Harrasi, A. Sphingomonas: From diversity and genomics to functional role in environmental remediation and plant growth. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2020, 40, 138–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, E.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Hossain, A.; Qiu, W.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wu, W.; Sun, G.; Li, B. Green-synthesization of silver nanoparticles using endophytic bacteria isolated from garlic and its antifungal activity against wheat Fusarium head blight pathogen Fusarium graminearum. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Basanta, R.; de Varennes, A.; Diaz-Ravina, M. Microbial community structure and biomass of a mine soil with different organic and inorganic treatments and native plants. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2017, 17, 839–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, L.; Li, T.; Meng, H.; Xie, Y.; Zhang, J.; Hong, J. Effects of Seven-Year Fertilization Reclamation on Bacterial Community in a Coal Mining Subsidence Area in Shanxi, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health. 2021, 18, 12504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, J.Y.; Son, C.H.; Joung, K.H.; Kim, Y.G.; Chang, Y.H.; Choi, D.Y.; Cho, H.J.; Heo, J.Y.; Lee, Y.H. Soil microbial communities and growth of sweet potato (Ipomoea batatas L.) in paddy and upland soils. Korean J. Soil. Sci. Fert. 2020, 53, 140–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Hu, Y.; Han, M.; Xu, J.; Wang, X.; Liu, L.; Tang, Z.; Jiao, W.; Jin, R.; Liu, M. Effects of continuous cropping of sweet potatoes on the bacterial community structure in rhizospheric soil. BMC Microbiol. 2021, 21, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).