Comparison of Field Performance of Different Driving Systems and Forward Speed Measuring Methods for a Wet Direct Seeder of Rice
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
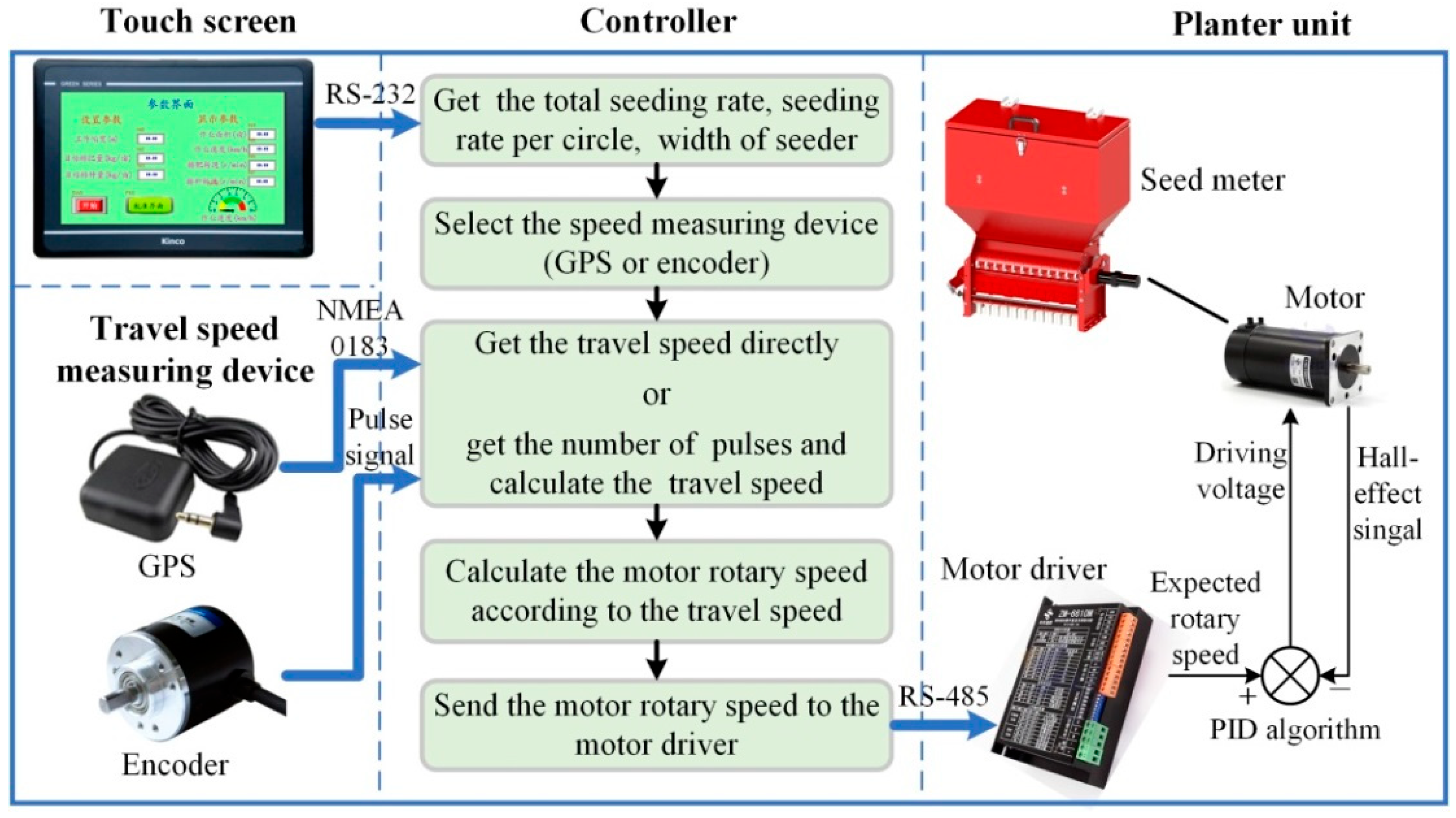
2.1. Description of the Rice Direct Seeder and the Drive System
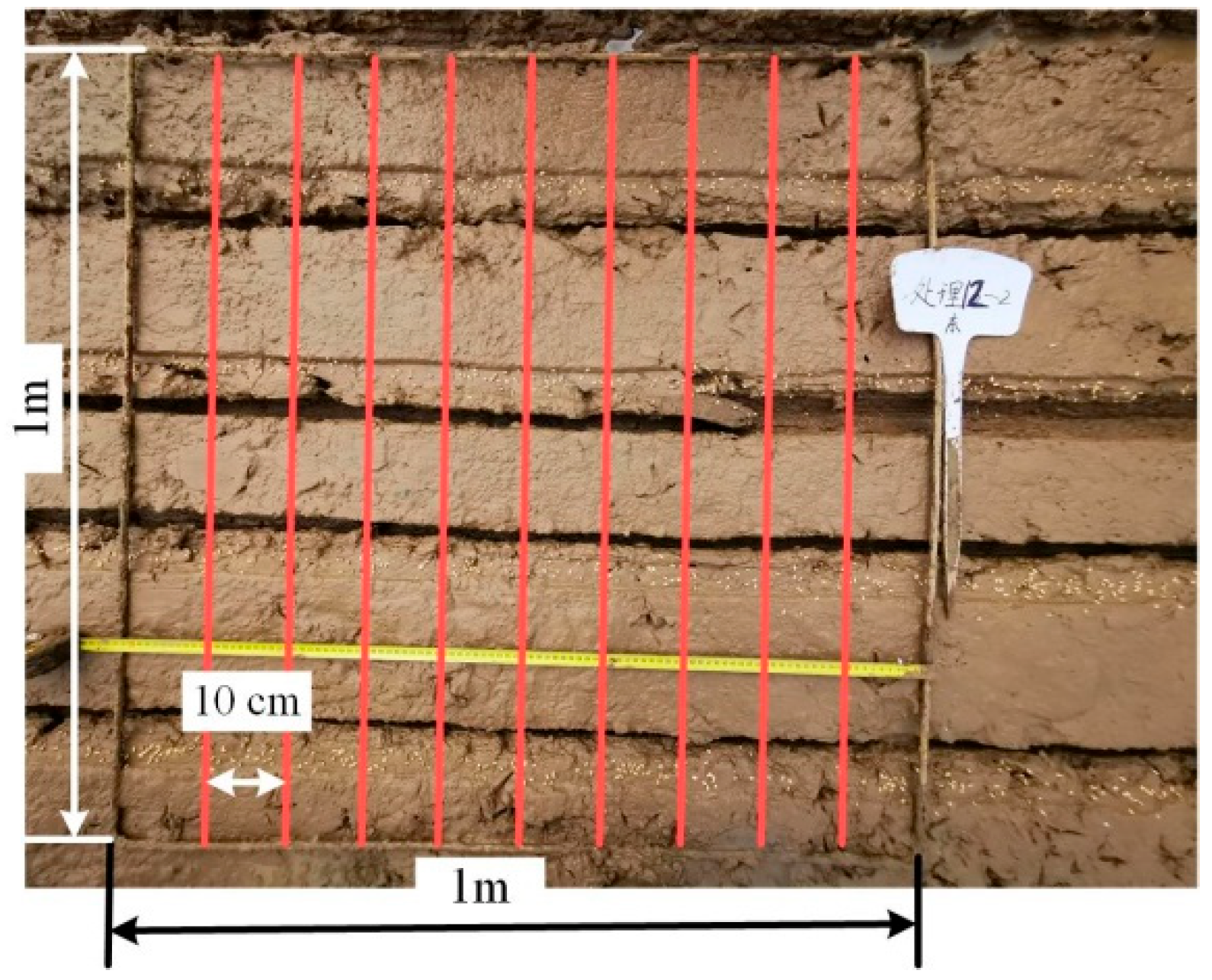
2.2. Field Test
2.3. Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
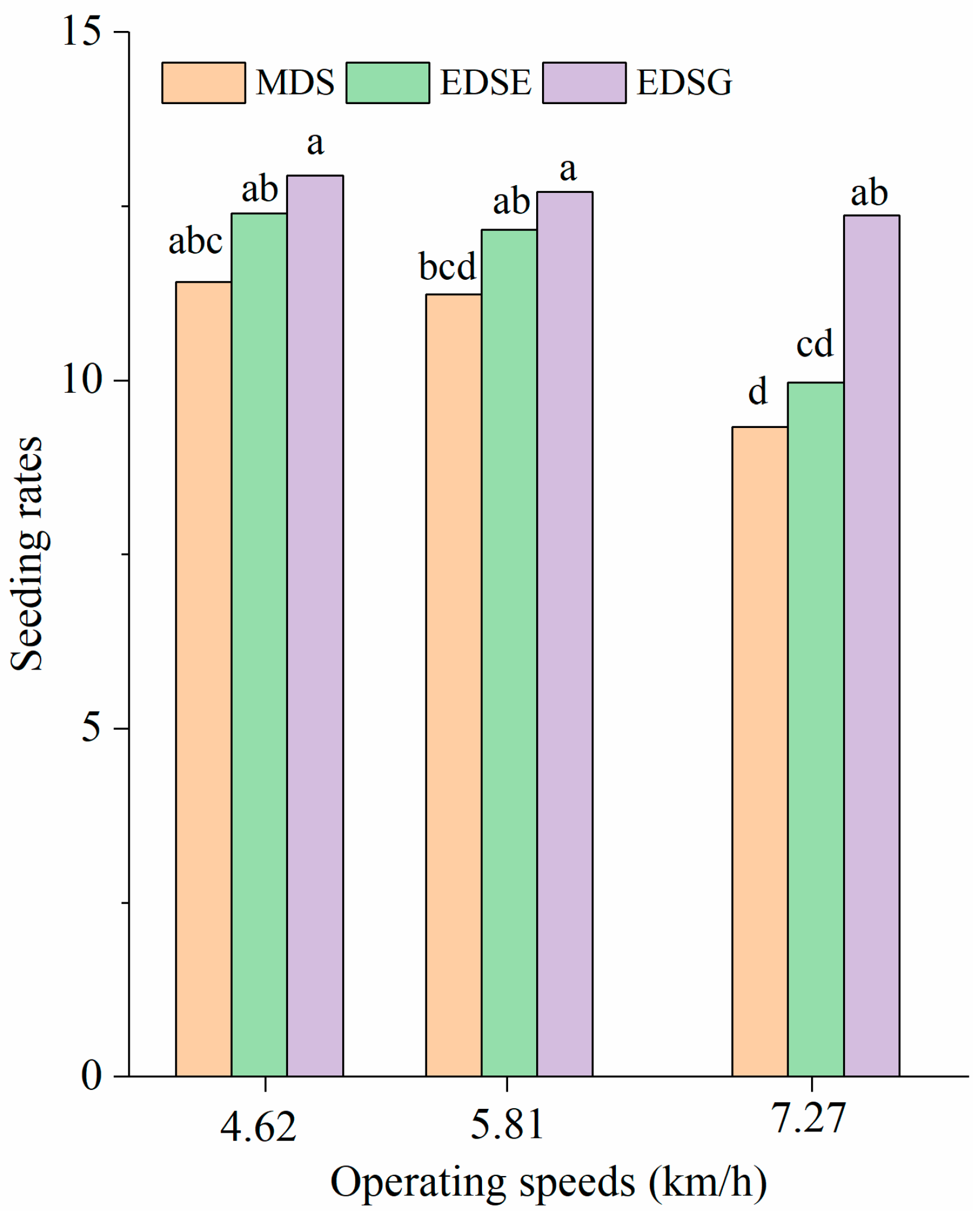
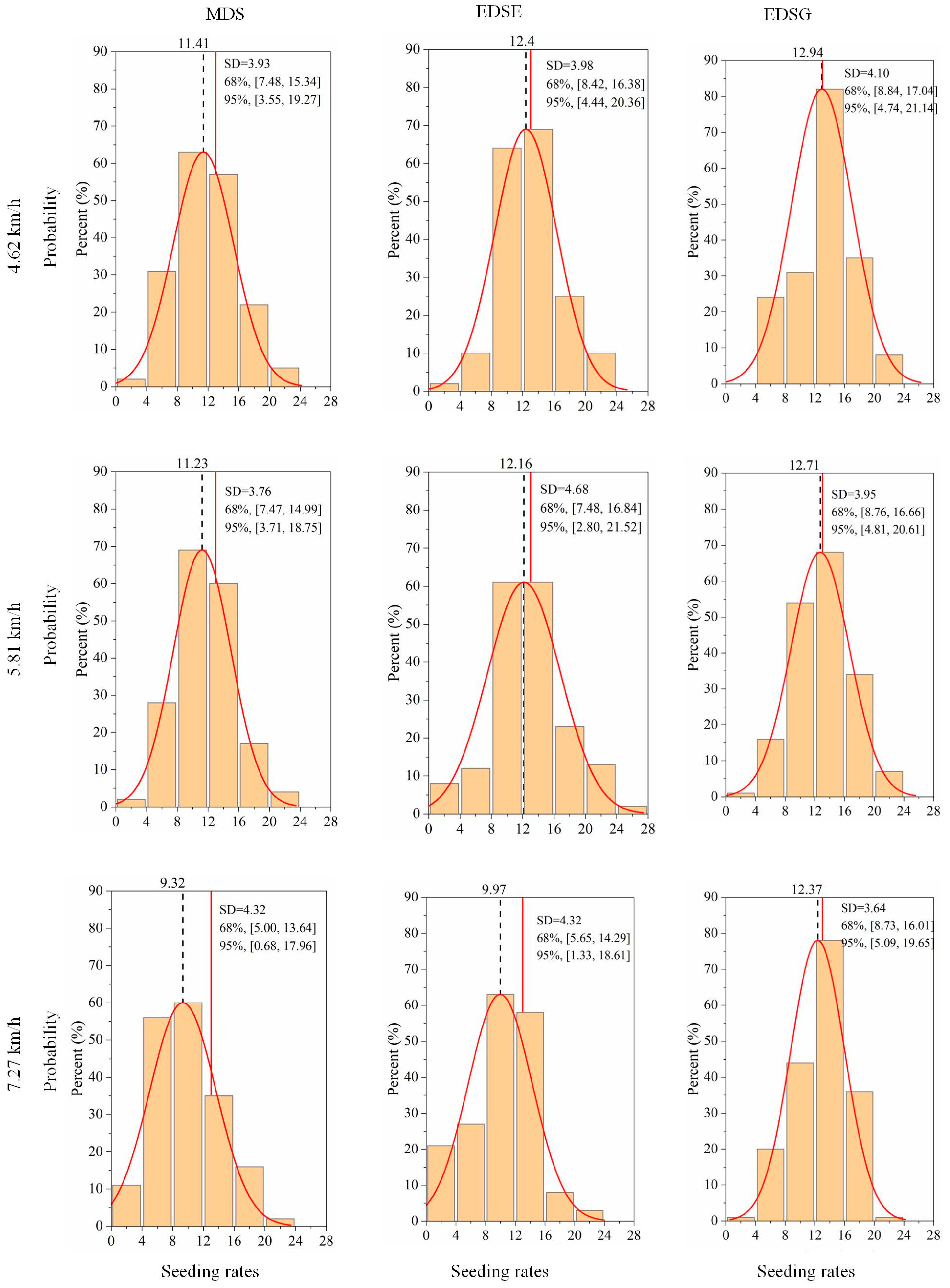
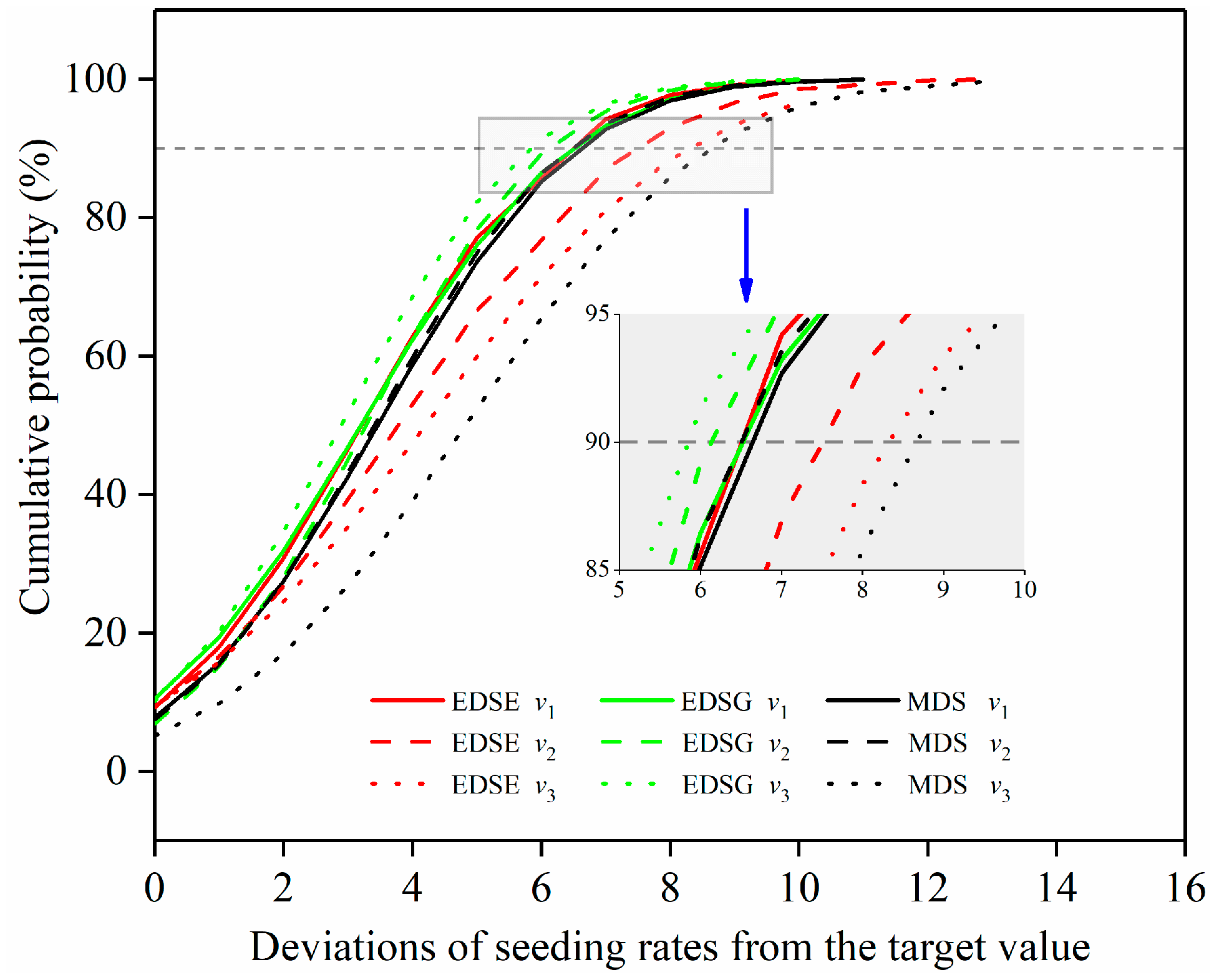
3.1. Seeding Uniformity
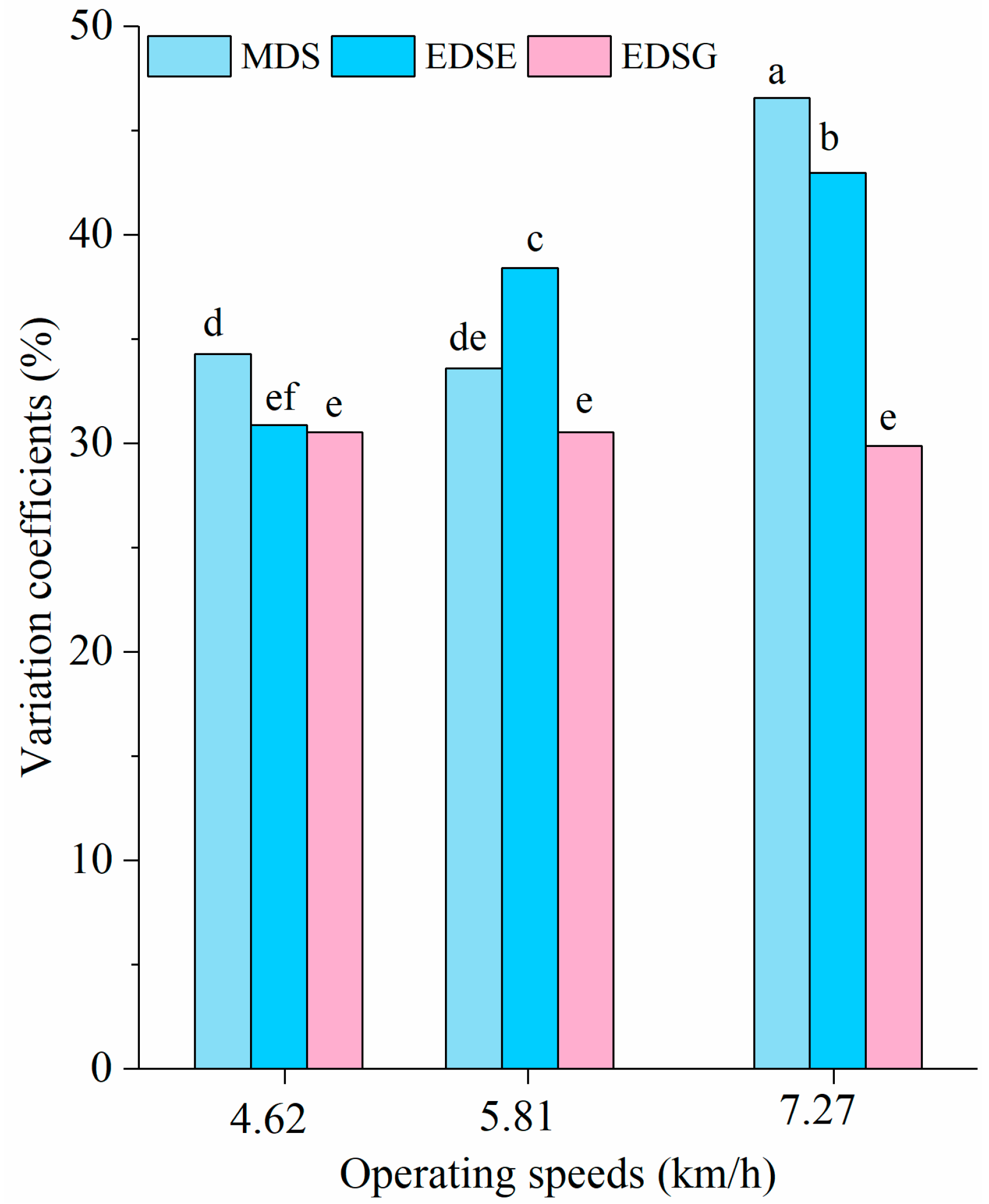
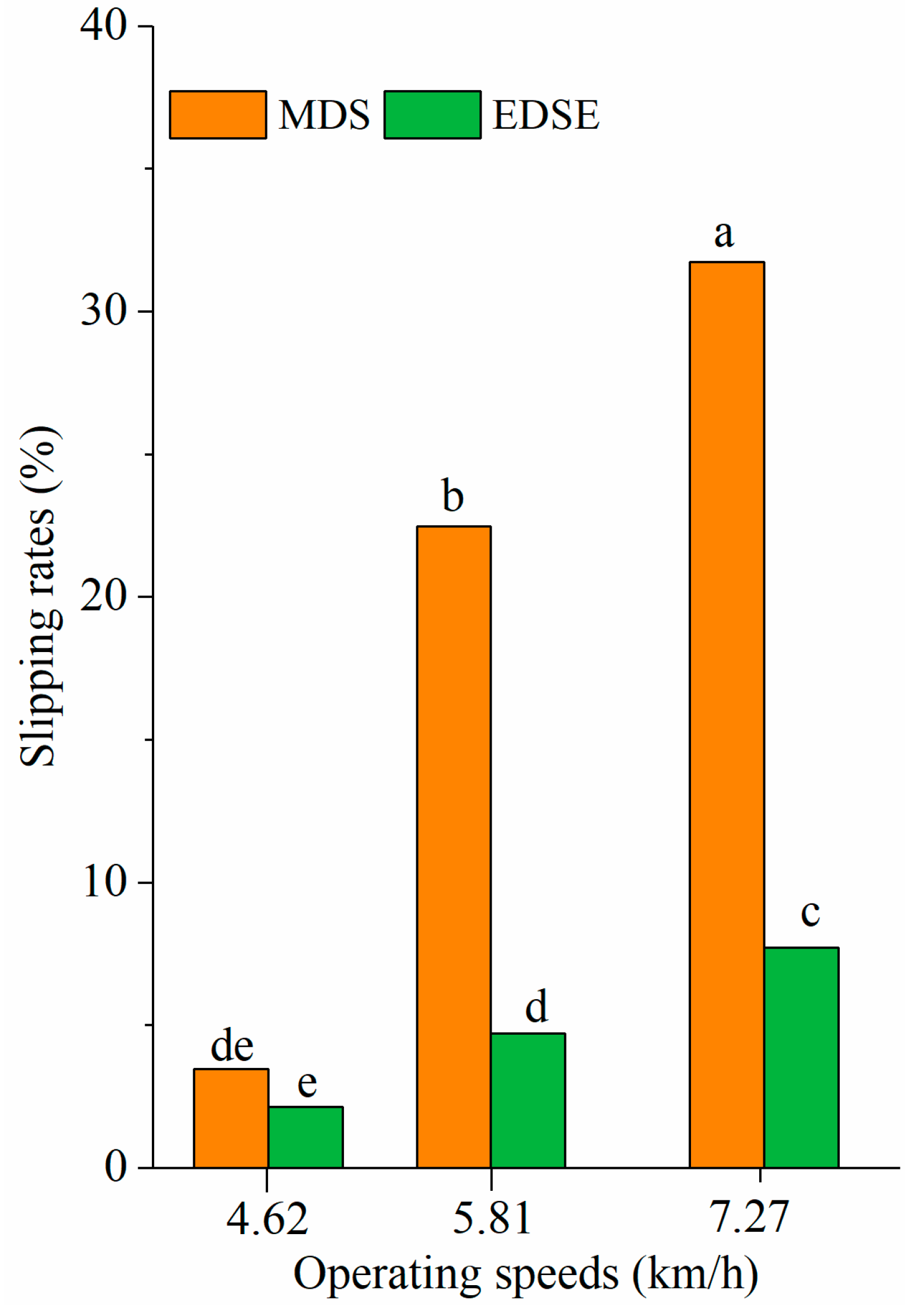
3.2. Slippage
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Khush, G.S.; Gupta, P. Strategies for increasing the yield potential of cereals: Case of rice as an example. Plant Breed. 2013, 132, 433–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.Q.; Fan, D.J.; Zhang, X.X.; Chen, J.; Li, C.F.; Cao, C.G. Deep placement of nitrogen fertilizer reduces ammonia volatilization and increases nitrogen utilization efficiency in no-tillage paddy fields in central China. Field Crops Res. 2015, 184, 80–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.B. Reflection on China’s rice production strategies during the transition period. Sci. Sin. 2014, 44, 845–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Hussain, S.; Liu, H.; Peng, S.; Huang, J.; Cui, K.; Nie, L. Implications of low sowing rate for hybrid rice varieties under dry direct-seeded rice system in Central China. Field Crops Res. 2015, 175, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.; Tang, Q.; Zou, Y. Current status and challenges of rice production in china. Plant Prod. Sci. 2019, 12, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liang, Z.; Zhang, D.; Yang, L.; Cui, T.; Hao, Y. Experimental study on motor driven pneumatic precision seed-metering device for maize. In Proceedings of the 2015 ASABE Annual International Meeting, New Orleans, LO, USA, 26–29 July 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, E.A.; Rascon, J.; Koller, A.; Porter, W.M.; Taylor, R.K.; Raun, W.R.; Kochenower, R. Evaluation of corn seed vacuum metering systems. In Proceedings of the 2015 ASABE Annual International Meeting, Dallas, Texas, 29 July–1 August 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, Z.; Yaoming, L.; Jin, C.; Lizhang, X. Numerical analysis and laboratory testing of seed spacing uniformity performance for vacuum-cylinder precision seeder. Biosyst. Eng. 2010, 106, 344–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanusan, S.; Polthanee, A.; Audebert, A.; Seripong, S.; Mouret, J.C. Growth and yield of rice (Oryza sativa) as affected by varieties, seeding depth and water deficits at vegetative stage. Asian J. Plant Sci. 2010, 9, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cay, A.; Kocabiyik, H.; May, S. Development of an electro-mechanic control system for seed-metering unit of single seed corn planters Part I: Design and laboratory simulation. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2018, 144, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Yan, B.; Cui, T.; Yu, Y.; He, X.; Liu, Q.; Liang, Z.; Yin, X.; Zhang, D. Global overview of research progress and development of precision maize planters. Int. Agric. Biol. Eng. 2016, 9, 9–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cay, A.; Kocabiyik, H.; May, S. Development of an electro-mechanic control system for seed-metering unit of single seed corn planters part II: Field performance. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2018, 145, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aykas, E.; Yalçin, H.; Yazgi, A. Balta Tipi Gömücü Ayağa Sahip Tek Dane Ekim Makinalarının Farklı Bölgelerde Mısır Ekiminde Ekim Performanslarının Karşılaştırılması. J. Agric. Mach. Sci. 2013, 9, 67–72. [Google Scholar]
- Kamgar, S.; Eslami, M.J.; Mehdi, M.M. Design, development and evaluation of a mechatronic transmission system to improve the performance of a conventional row crop planter. Int. J. Agron. Plant Prod. 2013, 4, 480–487. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.; He, X.; Cui, T.; Zhang, D.; Shi, S.; Rui, Z.; Mantao, W. Development of mechatronic driving system for seed meters equipped on conventional precision corn planter. Int. J. Agric. Biol. Eng. 2015, 8, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- He, X.; Cui, T.; Zhang, D.; Wei, J.; Wang, M.; Yu, Y.; Liu, Q.; Yan, B.; Zhao, D.; Yang, L. Development of an electric-driving control system for a precision planter based on a closed-loop PID algorithm. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2017, 136, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iacomi, C.; Popescu, O. A new concept for seed precision planting. Agric. Agric. Sci. Proc. 2015, 6, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Z.; Huang, Y.; Wang, B.; Zhang, M.; Ma, Y.; Ke, X.; Luo, X. Design and experiment of rice precision metering device with sowing amountstepless adjusting. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2018, 34, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Yu, H.; Hao, X.; He, L.; He, R.; Li, X.; Dou, X. Design and experiment of sowing control system for rice direct seeder based on PID algorithm. J. South China Agric. Univ. 2019, 40, 118–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Z.; Liu, H.; Fu, W.; Huang, W.; Wang, X. Evaluation of ground speed measurements for agricultural machinery. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2010, 26, 141–145. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, B.; Zhang, W.; Yu, S.; Ji, Y.; Li, K.; Zhang, S. Establishment of Seeding Amount Control Model for Centralized Pneumatic Metering System for Rice. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2018, 48, 125–131. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.; Ge, Q.; Chu, G.; Xu, C.; Yan, J.; Zhang, X.; Wang, D. Seasonal differences in the rice grain yield and nitrogen use efficiency response to seedling establishment methods in the middle and lower reaches of the yangtze river in China. Field Crops Res. 2017, 205, 157–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 9478-2005; General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the PR China: Testing Methods of Sowing in Line. Standardization Administration of the PR China: Beijing, China, 2005.
- JB/T 6274.1–2001; Specifications for Grain Drills. Ministry of Industry and Information Technology of PR China: Beijing, China, 2001.
- Ding, Y.; Yang, L.; Zhang, D.; Cui, T.; He, X.; Zhong, X. Control system of motor-driving maize precision planter based on GPS speed measurement. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mec. 2018, 49, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Forward Speed (km·h−1) | Drive System | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| MDS | EDSE | EDSG | |
| 4.62 | 7 | 5 | 5 |
| 5.81 | 13 | 8 | 5 |
| 7.27 | 16 | 12 | 3 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Qi, B.; Xia, Q. Comparison of Field Performance of Different Driving Systems and Forward Speed Measuring Methods for a Wet Direct Seeder of Rice. Agronomy 2022, 12, 1655. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12071655
Wang Y, Zhang W, Qi B, Xia Q. Comparison of Field Performance of Different Driving Systems and Forward Speed Measuring Methods for a Wet Direct Seeder of Rice. Agronomy. 2022; 12(7):1655. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12071655
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yunxia, Wenyi Zhang, Bing Qi, and Qianqian Xia. 2022. "Comparison of Field Performance of Different Driving Systems and Forward Speed Measuring Methods for a Wet Direct Seeder of Rice" Agronomy 12, no. 7: 1655. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12071655
APA StyleWang, Y., Zhang, W., Qi, B., & Xia, Q. (2022). Comparison of Field Performance of Different Driving Systems and Forward Speed Measuring Methods for a Wet Direct Seeder of Rice. Agronomy, 12(7), 1655. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12071655






