Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Profiling Reveal the Potential Functions of the SWEET Gene Family during the Sink Organ Development Period in Apple (Malus × domestica Borkh.)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Identification and Characterization of SWEET Family Genes from the Apple Plant
2.2. Multi-Sequence Alignment and Evolutionary Tree Construction of SWEETs
2.3. Prediction of the Secondary and 3D Model Structure of MdSWEET Proteins
2.4. Gene Structure, Conserved Motif, Chromosomal Location, and Duplication Analysis
2.5. Promoter Cis-Element Analysis of MdSWEETs
2.6. Plant Materials and Experimental Treatments
2.7. Measurement of Sugar Content
2.8. RNA Extraction and Quantitative Real-Time PCR
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Identification and Characterization of SWEET Gene Family Members in Apple
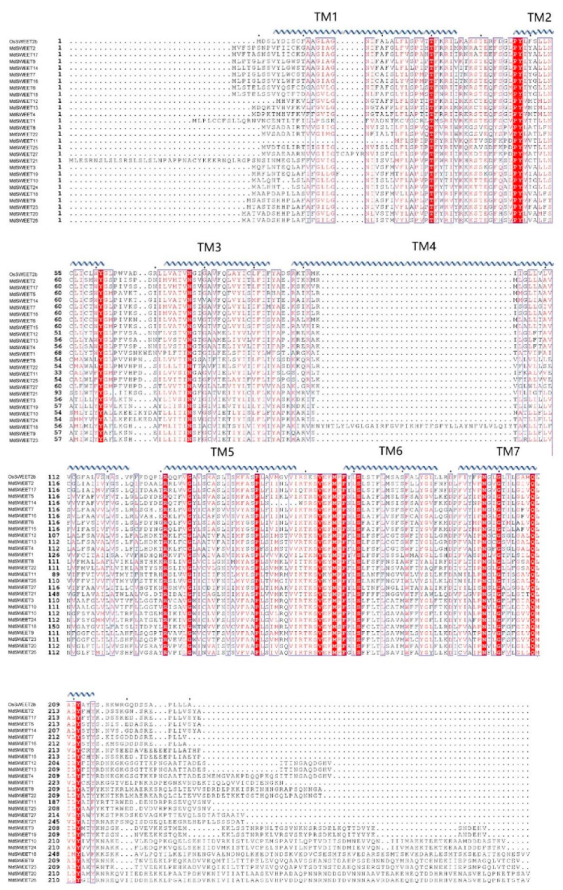
3.2. Multi-Sequence Alignment and Phylogenetic Analysis of the SWEET Proteins
3.3. Secondary and 3D Model Structure of MdSWEET Proteins
3.4. Gene Structural and Conservative Motif Analyses of the MdSWEET Gene Family in Apple
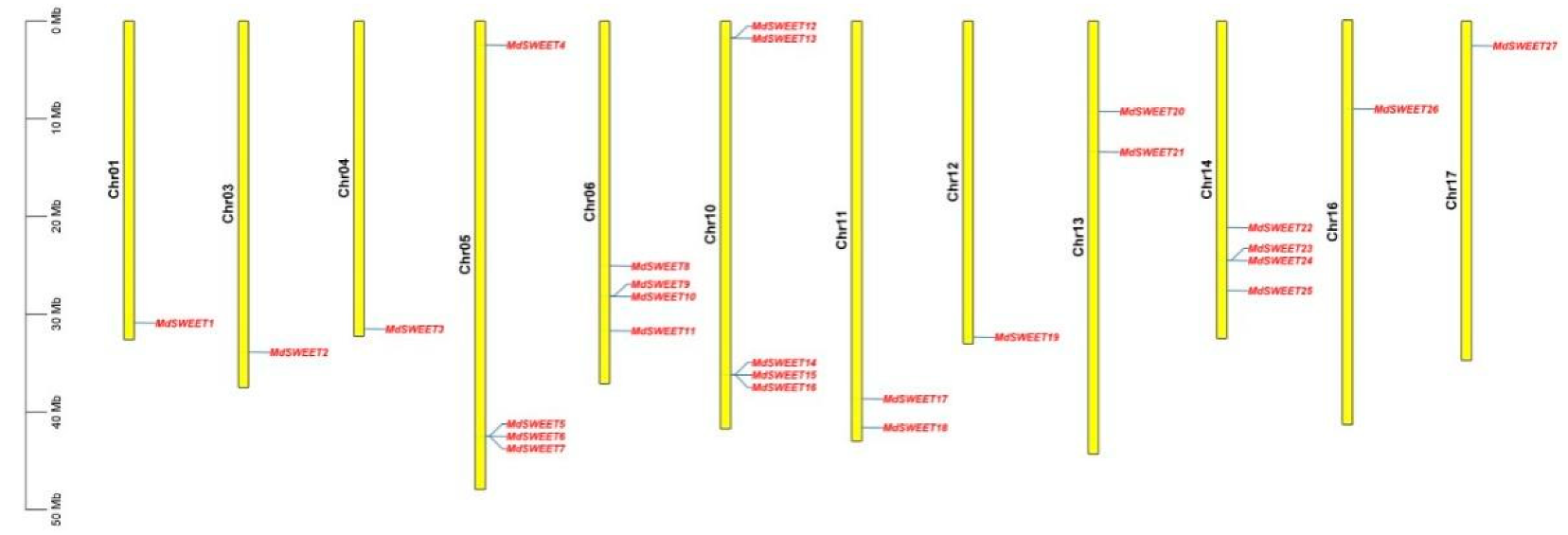
3.5. Chromosome Localization and Gene Duplication Analysis of MdSWEET Genes
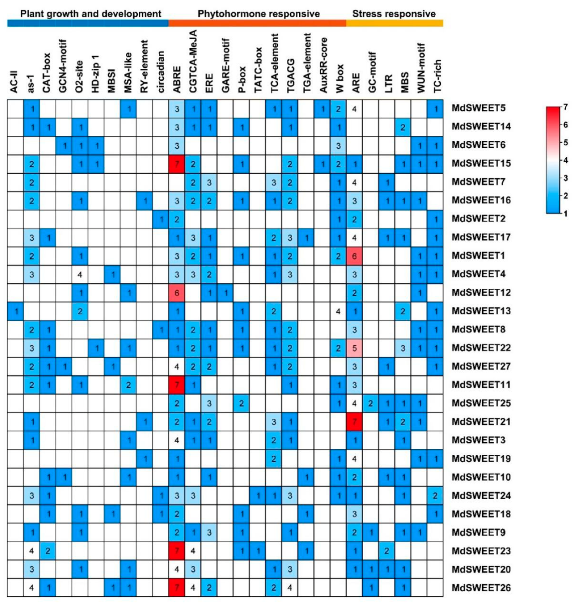
3.6. Cis-Acting Elements in the Promoter Regions of MdSWEET Genes
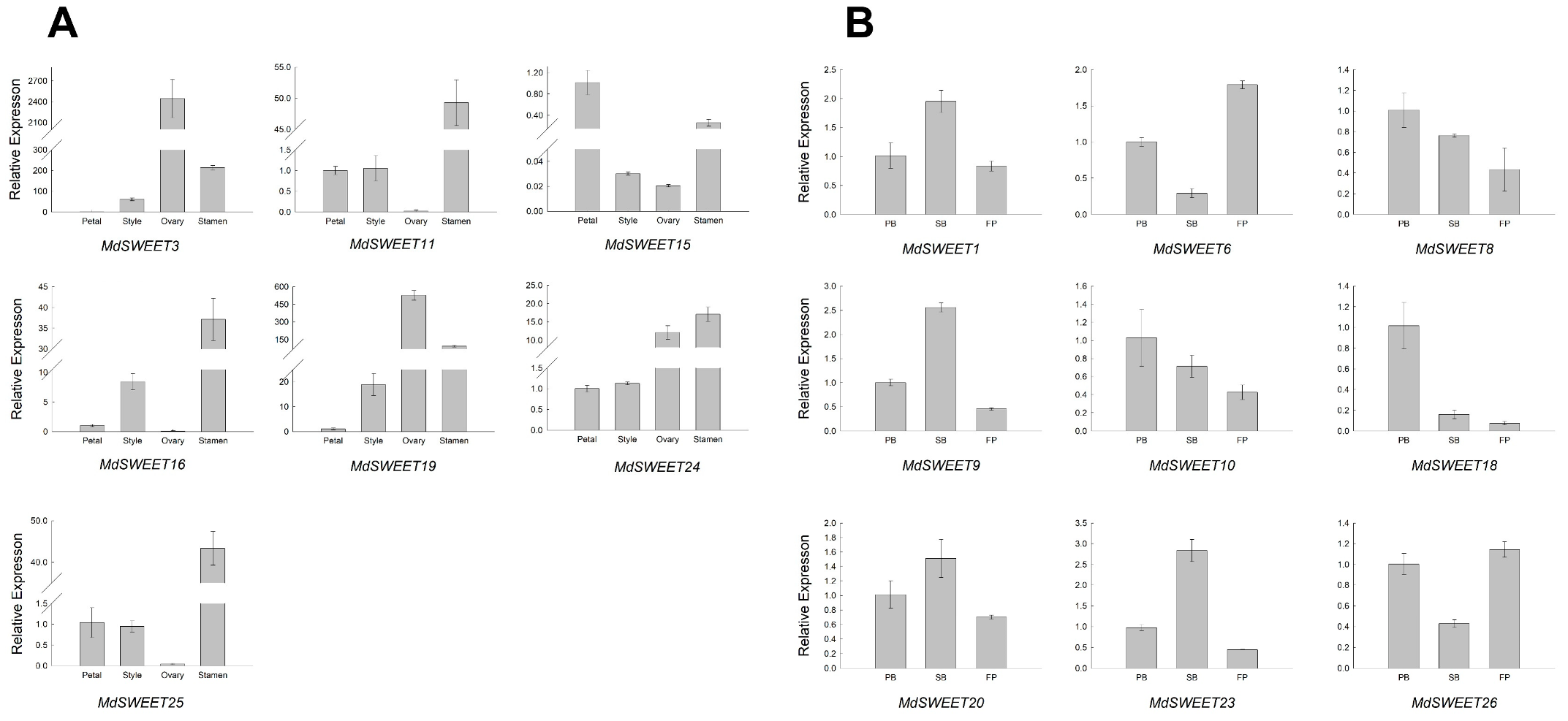
3.7. Expression Patterns of MdSWEET Genes in Different Apple Tissues/Organs and Developmental Stages
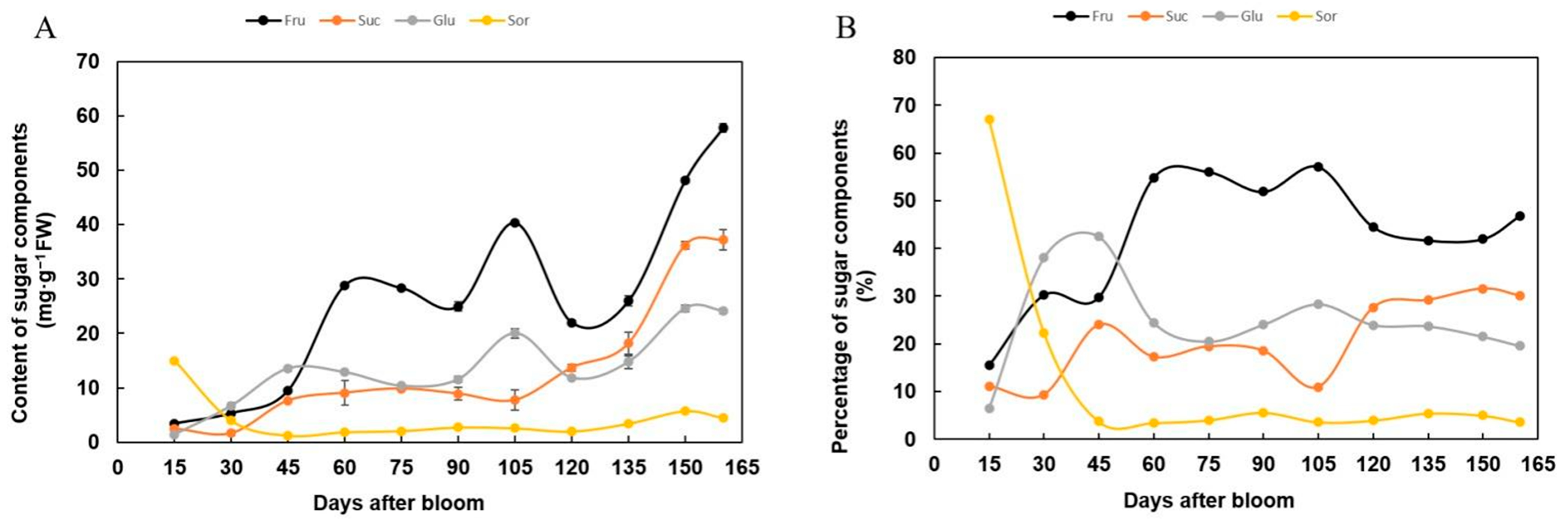
3.8. Relationship between the Expression of MdSWEET Genes and the Concentration of Major Sugars during Fruit Development of the “Hanfu” Apple
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ruan, Y.L. Sucrose metabolism: Gateway to diverse carbon use and sugar signaling. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. 2014, 65, 33–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slewinski, T.L. Diverse functional roles of monosaccharide transporters and their homologs in vascular plants: A physiological perspective. Mol. Plant 2011, 4, 641–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.Q.; Qu, X.Q.; Hou, B.H.; Sosso, D.; Osorio, S.; Fernie, A.R.; Frommer, W.B. Sucrose efflux mediated by SWEET proteins as a key step for phloem transport. Science 2012, 335, 207–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.Q.; Hou, B.H.; Lalonde, S.; Takanaga, H.; Hartung, M.L.; Qu, X.Q.; Guo, W.J.; Kim, J.G.; Underwood, W.; Chaudhuri, B.; et al. Sugar transporters for intercellular exchange and nutrition of pathogens. Nature 2010, 468, 527–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, L.Q. SWEET sugar transporters for phloem transport and pathogen nutrition. New Phytol. 2014, 201, 1150–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breia, R.; Conde, A.; Badim, H.; Fortes, A.M.; Gerós, H.; Granell, A. Plant SWEETs: From sugar transport to plant–pathogen interaction and more unexpected physiological roles. Plant Physiol. 2021, 186, 836–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.Q.; Cheung, L.S.; Feng, L.; Tanner, W.; Frommer, W.B. Transport of sugars. Ann. Rev. Biochem. 2015, 848, 865–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, J.L.; Piron, M.C.; Meyer, S.; Merdinoglu, D.; Bertsch, C.; Mestre, P. The SWEET family of sugar transporters in grapevine: VvSWEET4 is involved in the interaction with Botrytis cinerea. J. Exp. Bot. 2014, 65, 6589–6601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Feng, C.Y.; Han, J.X.; Han, X.X.; Jiang, J. Genome-wide identification, phylogeny, and expression analysis of the SWEET gene family in tomato. Gene 2015, 573, 261–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Wang, Z.Y.; Kumar, V.; Xu, X.F.; Yuan, P.; Zhu, X.F.; Li, T.Y.; Jia, B.; Xuan, Y.H. Genome-wide identification of the SWEET gene family in wheat. Gene 2018, 642, 284–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.P.; Zhang, F.; Song, S.H.; Tang, X.W.; Xu, H.; Liu, G.M.; Wang, Y.Q.; He, H.J. Genome-wide identification, characterization, and expression analysis of the SWEET gene family in cucumber. J. Integr. Agric. 2017, 16, 1486–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ho, L.H.; Klemens, P.A.W.; Neuhaus, H.E.; Ko, H.-Y.; Hsieh, S.-Y.; Guo, W.-J. SlSWEET1a is involved in glucose import to young leaves in tomato plants. J. Exp. Bot. 2019, 70, 3241–3254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, I.W.; Sosso, D.; Chen, L.Q.; Gase, K.; Kim, S.G.; Kessler, D.; Klinkenberg, P.M.; Gorder, M.K.; Hou, B.H.; Qu, X.Q.; et al. Nectar secretion requires sucrose phosphate synthases and the sugar transporter SWEET9. Nature 2014, 508, 546–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.Y.; Liu, F.L.; Chen, C.; Ma, F.W.; Li, M.J. The Malus domestica sugar transporter gene family: Identifications based on genome and expression profiling related to the accumulation of fruit sugars. Front. Plant Sci. 2014, 5, 569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhen, Q.L.; Fang, T.; Peng, Q.; Liao, L.; Zhao, L.; Owiti, A.; Han, Y.P. Developing gene-tagged molecular markers for evaluation of genetic association of apple SWEET genes with fruit sugar accumulation. Hortic. Res. 2018, 5, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, C.Y.; Li, H.Y.; Xia, X.Y.; Liu, X.Y.; Yang, L. Functional and evolution characterization of SWEET sugar transporters in Ananas comosus. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 496, 407–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.M.; Qin, M.F.; Qiao, X.; Cheng, Y.S.; Li, X.L.; Zhang, H.P.; Wu, J. A new insight into the evolution and functional divergence of SWEET transporters in chinese white pear (Pyrus bretschneideri). Plant Cell Physiol. 2017, 58, 839–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, X.Y.; Guo, W.; Li, J.C.; Yue, P.T.; Bu, H.D.; Jiang, J.; Liu, W.T.; Xu, Y.X.; Yuan, H.; Li, T.; et al. Histone acetylation at the promoter for the transcription factor PuWRKY31 affects sucrose accumulation in pear fruit. Plant Physiol. 2020, 182, 2035–2046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.S.; Feng, C.Y.; Wang, M.N.; Li, T.L.; Liu, X.; Jiang, J. Plasma membrane-localized SlSWEET7a and SlSWEET14 regulate sugar transport and storage in tomato fruits. Hortic. Res. 2021, 8, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Li, M.; Guo, S.G.; Sun, H.H.; Zhao, J.Y.; Zhang, J.; Liu, G.M.; He, H.J.; Tian, S.W.; Yu, Y.T.; et al. Evolutionary gain of oligosaccharide hydrolysis and sugar transport enhanced carbohydrate partitioning in sweet watermelon fruits. Plant Cell 2021, 33, 1554–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daccord, N.; Celton, J.-M.; Linsmith, G.; Becker, C.; Choisne, N.; Schijlen, E.; van de Geest, H.; Bianco, L.; Micheletti, D.; Velasco, R.; et al. High-quality de novo assembly of the apple genome and methylome dynamics of early fruit development. Nat. Genet. 2017, 49, 1099–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, S.L.; Yi, K.; Liu, G.C.; Han, Z.H.; Xu, X.F.; Wang, D.M.; Li, T.Z. The Self-fruitfulness of “Hanfu” apple and identification of S-genotypes. Acta Hortic. Sin. 2008, 35, 475–480. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.J.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Thomas, H.R.; Frank, M.H.; He, Y.H.; Xia, R. Tbtools: An integrative toolkit developed for interactive analyses of big biological data. Mol. Plant 2020, 13, 1194–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Y.Y.; Cheung, L.S.; Li, S.; Eom, J.-S.; Chen, L.-Q.; Xu, Y.; Perry, K.; Frommer, W.B.; Feng, L. Structure of a eukaryotic SWEET transporter in a homotrimeric complex. Nature 2015, 527, 259–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Li, M.; Knyaz, C.; Tamura, K. MEGA X: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis across computing platforms. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 1547–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelley, L.A.; Mezulis, S.; Yates, C.M.; Wass, M.N.; Sternberg, M.J.E. The Phyre2 web portal for protein modeling, prediction and analysis. Nat. Protoc. 2015, 10, 845–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.P.; Tang, H.B.; DeBarry, J.D.; Tan, X.; Li, J.P.; Wang, X.Y.; Lee, T.; Jin, H.Z.; Marler, B.; Guo, H.; et al. MCScanX: A toolkit for detection and evolutionary analysis of gene synteny and collinearity. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, e49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nie, P.X.; Wang, X.Y.; Hu, L.P.; Zhang, H.Y.; Zhang, J.X.; Zhang, Z.X.; Zhang, L.Y. The predominance of the apoplasmic phloem-unloading pathway is interrupted by a symplasmic pathway during Chinese jujube fruit development. Plant Cell Physiol. 2010, 51, 1007–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Ayaz, A.; Zheng, M.; Yang, X.; Zaman, W.; Zhao, H.; Lü, S. Arabidopsis KCS5 and KCS6 play redundant roles in wax synthesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bezrutczyk, M.; Hartwig, T.; Marc, H.; Char, S.N.; Yang, J.; Yang, B.; Frommer, W.B.; Sosso, D. Impaired phloem loading in zmsweet13a,b,c sucrose transporter triple knock-out mutants in Zea mays. New Phytol. 2018, 218, 594–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Geng, Y.Q.; Wu, M.J.; Zhang, C.M. Sugar transporter ZjSWEET2.2 mediates sugar loading in leaves of Ziziphus jujuba Mill. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, L.; Zhang, D.; Miao, Q.; Yang, J.; Xuan, Y.; Hu, Y. Essential role of sugar transporter OsSWEET11 during the early stage of rice grain filling. Plant Cell Physiol. 2017, 58, 863–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, J.; Luo, D.P.; Yang, B.; Frommer, W.B.; Eom, J.-S. SWEET11 and 15 as key players in seed filling in rice. New Phytol. 2018, 218, 604–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yuan, M.; Wang, S.P. Rice MtN3/Saliva/SWEET family genes and their homologs in cellular organisms. Mol. Plant 2013, 6, 665–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Patil, G.; Valliyodan, B.; Deshmukh, R.; Prince, S.; Nicander, B.; Zhao, M.Z.; Sonah, H.; Song, L.; Lin, L.; Chaudhary, J.; et al. Soybean (Glycine max) SWEET gene family: Insights through comparative genomics, transcriptome profiling and whole genome re-sequence analysis. BMC Genom. 2015, 16, 520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, L.J.; Yao, J.B.; Chen, W.; Li, Y.; LÜ, Y.J.; Guo, Y.; Wang, J.Y.; Yuan, L.; Liu, Z.Y.; Zhang, Y.S. A genome-wide analysis of SWEET gene family in cotton and their expressions under different stresses. J. Cotton Res. 2018, 1, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chardon, F.; Bedu, M.; Calenge, F.; Klemens, P.A.; Spinner, L.; Clement, G.; Chietera, G.; Leran, S.; Ferrand, M.; Lacombe, B.; et al. Leaf fructose content is controlled by the vacuolar transporter SWEET17 in Arabidopsis. Curr. Biol. 2013, 23, 697–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klemens, P.A.W.; Patzke, K.; Deitmer, J.; Spinner, L.; Hir, R.L.; Bellini, C.; Bedu, M.; Chardon, F.; Krapp, A.; Neuhaus, H.E. Overexpression of the vacuolar sugar carrier AtSWEET16 modifies germination, growth, and stress tolerance in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2013, 163, 1338–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cannon, S.B.; Mitra, A.; Baumgarten, A.; Young, N.D.; May, G. The roles of segmental and tandem gene duplication in the evolution of large gene families in Arabidopsis thaliana. BMC Plant Biol. 2004, 4, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.Z. Evolution by gene duplication: An update. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2003, 18, 292–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abelenda, J.; Bergonzi, S.; Oortwijn, M.; Sonnewald, S.; Du, M.; Visser, R.; Sonnewald, U.; Bachem, C. Source-sink regulation is mediated by interaction of an FT Homolog with a SWEET protein in potato. Curr. Biol. 2019, 29, 1178–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moriyama, E.N.; Strope, P.K.; Opiyo, S.O.; Chen, Z.; Jones, A.M. Mining the Arabidopsis thaliana genome for highly-divergent seven transmembrane receptors. Genome Biol. 2006, 7, R96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, P.P.; Wei, P.N.; Niu, F.F.; Liu, X.F.; Zhang, H.L.; Lyu, M.L.; Yuan, Y.; Wu, B.H. Cloning and functional assessments of floral-expressed SWEET transporter genes from Jasminum sambac. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Engel, M.L.; Holmes-Davis, R.; McCormick, S. Green sperm. Identification of male gamete promoters in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2005, 138, 2124–2133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guan, Y.F.; Huang, X.Y.; Zhu, J.; Gao, J.F.; Zhang, H.X.; Yang, Z.N. RUPTURED POLLEN GRAIN 1 (RPG1), a member of MtN3 /Saliva gene family, is crucial for exine pattern formation and cell integrity of microspores in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Physiol. 2008, 147, 852–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.; Yu, Y.C.; Li, Y.; Chen, L.Q. Hexose transporter SWEET5 confers galactose sensitivity to Arabidopsis pollen germination via a galactokinase. Plant Physiol. 2022, 189, 388–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Y.; Angenent, G.; Dahlhaus, E.; Franken, J.; Peters, J.; Wullems, G.; Creemers-Molenaar, J. Partial silencing of the NEC1 gene results in early opening of anthers in Petunia hybrida. Mol. Genet. Genom. 2001, 265, 414–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Y.; Angenent, G.; Wittich, P.; Peters, J.; Franken, J.; Busscher, M.; Zhang, L.; Dahlhaus, E.; Kater, M.; Wullems, G. NEC1, a novel gene, highly expressed in nectary tissue of Petunia hybrida. Plant J. 2000, 24, 725–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Chen, D.; Jiang, G.; Song, H.; Tu, M.; Sun, S. Molecular cloning and expression analysis of EjSWEET15, encoding for a sugar transporter from loquat. Sci. Hortic. 2020, 272, 109552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.Y.; Peng, Y.B.; Pelleschi-Travier, S.; Fan, Y.; Lu, Y.F.; Lu, Y.M.; Gao, X.P.; Shen, Y.Y.; Delrot, S.; Zhang, D.P. Evidence for apoplasmic phloem unloading in developing apple fruit. Plant Physiol. 2004, 135, 574–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Berüter, J.; Studer Feusi, M.E. Comparison of sorbitol transport in excised tissue discs and cortex tissue of intact apple fruit. J. Plant Physiol. 1995, 146, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaki, S. Isolation of vacuoles from immature apple fruit flesh and compartmentation of sugar, organic acid, phenolic compounds and amino acids. Palnt Cell Physiol. 1984, 25, 151–166. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, R.C.; Peng, C.C.; Xu, Y.H.; Wang, X.F.; Li, Y.; Shang, Y.; Du, S.Y.; Zhao, R.; Zhang, X.Y.; Zhang, L.Y.; et al. Apple sucrose transporter SUT1 and sorbitol transporter SOT6 interact with cytochrome b5 to regulate their affinity for substrate sugars. Plant Physiol. 2009, 150, 1880–1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ni, J.P.; Li, J.M.; Zhu, R.X.; Zhang, M.Y.; Qi, K.J.; Zhang, S.L.; Wu, J. Overexpression of sugar transporter gene PbSWEET4 of pear causes sugar reduce and early senescence in leaves. Gene 2020, 743, 144582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Gene | Accession Number | Number of Amino Acids (aa) | Molecular Weight (Da) | Theoretical pI | Instability Index | Aliphatic Index | Grand Average of Hydropathicity | Transmembrane Domain |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MdSWEET1 | MD01G1215700 | 267 | 29,800.19 | 8.97 | 41.01 | 112.28 | 0.490 | 6 |
| MdSWEET2 | MD03G1250600 | 235 | 26,042.15 | 9.34 | 45.93 | 121.96 | 0.863 | 7 |
| MdSWEET3 | MD04G1236000 | 267 | 29,846.5 | 9.34 | 28.59 | 117.49 | 0.642 | 7 |
| MdSWEET4 | MD05G1012200 | 263 | 28,799.01 | 9.68 | 34.91 | 100.11 | 0.511 | 7 |
| MdSWEET5 | MD05G1293100 | 235 | 25,952.91 | 9.02 | 35.46 | 123.62 | 0.911 | 7 |
| MdSWEET6 | MD05G1293200 | 239 | 26,752.73 | 5.42 | 44.92 | 116.57 | 0.776 | 7 |
| MdSWEET7 | MD05G1293300 | 232 | 25,370.24 | 8.71 | 34.52 | 129.78 | 0.959 | 7 |
| MdSWEET8 | MD06G1112000 | 261 | 29,363.14 | 9.90 | 40.37 | 126.21 | 0.613 | 7 |
| MdSWEET9 | MD06G1136500 | 298 | 33,191.83 | 8.21 | 43.04 | 103.05 | 0.462 | 7 |
| MdSWEET10 | MD06G1136600 | 295 | 33,115.42 | 5.80 | 44.98 | 124.2 | 0.681 | 7 |
| MdSWEET11 | MD06G1176800 | 215 | 24,637.52 | 9.23 | 43.46 | 130.33 | 0.823 | 6 |
| MdSWEET12 | MD10G1012200 | 243 | 26,504.45 | 9.54 | 21.66 | 105.14 | 0.692 | 7 |
| MdSWEET13 | MD10G1013100 | 248 | 27,134.18 | 9.54 | 20.71 | 104.19 | 0.664 | 7 |
| MdSWEET14 | MD10G1269100 | 229 | 25,204.89 | 8.81 | 28.44 | 122.97 | 0.913 | 7 |
| MdSWEET15 | MD10G1269300 | 238 | 26,746.47 | 5.13 | 43.03 | 111.76 | 0.728 | 7 |
| MdSWEET16 | MD10G1269400 | 232 | 25,374.17 | 8.55 | 36.2 | 127.28 | 0.934 | 7 |
| MdSWEET17 | MD11G1270800 | 235 | 25,969.73 | 7.59 | 47.41 | 121.53 | 0.845 | 7 |
| MdSWEET18 | MD11G1299200 | 340 | 38,117 | 7.56 | 40.54 | 109.53 | 0.533 | 9 |
| MdSWEET19 | MD12G1255000 | 268 | 30,385.11 | 9.47 | 30.74 | 117.84 | 0.627 | 7 |
| MdSWEET20 | MD13G1124300 | 305 | 34,116.92 | 8.52 | 34.31 | 108.66 | 0.381 | 7 |
| MdSWEET21 | MD13G1166800 | 281 | 31,083.4 | 6.73 | 47.41 | 112.38 | 0.484 | 7 |
| MdSWEET22 | MD14G1133400 | 261 | 29,467.11 | 9.63 | 34.66 | 118.35 | 0.588 | 7 |
| MdSWEET23 | MD14G1151300 | 298 | 33,491.47 | 8.82 | 32.7 | 108.52 | 0.497 | 7 |
| MdSWEET24 | MD14G1151400 | 295 | 33,290.71 | 6.83 | 38.63 | 120.2 | 0.706 | 7 |
| MdSWEET25 | MD14G1183000 | 236 | 26,576.96 | 8.93 | 38.41 | 136.06 | 0.981 | 7 |
| MdSWEET26 | MD16G1125300 | 305 | 34,303.1 | 6.5 | 30.25 | 114.03 | 0.426 | 7 |
| MdSWEET27 | MD17G1035200 | 250 | 27,611.86 | 9.03 | 31.52 | 117.72 | 0.674 | 7 |
| Protein | Alpha Helix (%) | Extended Strand (%) | Beta Turn (%) | Random Coil (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MdSWEET1 | 40.07 | 18.73 | 3.75 | 37.45 |
| MdSWEET2 | 42.13 | 20.85 | 5.11 | 31.91 |
| MdSWEET3 | 44.57 | 17.60 | 1.50 | 36.33 |
| MdSWEET4 | 35.74 | 20.15 | 4.18 | 39.92 |
| MdSWEET5 | 41.70 | 22.98 | 3.40 | 31.91 |
| MdSWEET6 | 53.97 | 17.57 | 3.35 | 25.10 |
| MdSWEET7 | 43.1 | 22.84 | 3.45 | 30.6 |
| MdSWEET8 | 37.16 | 20.69 | 4.21 | 37.93 |
| MdSWEET9 | 36.91 | 18.46 | 2.01 | 42.62 |
| MdSWEET10 | 45.76 | 17.97 | 1.36 | 34.92 |
| MdSWEET11 | 41.40 | 22.79 | 4.19 | 31.63 |
| MdSWEET12 | 37.86 | 23.46 | 4.12 | 34.57 |
| MdSWEET13 | 39.52 | 21.37 | 6.45 | 32.66 |
| MdSWEET14 | 45.85 | 20.52 | 5.68 | 27.95 |
| MdSWEET15 | 47.06 | 20.17 | 2.10 | 30.67 |
| MdSWEET16 | 49.14 | 17.24 | 3.02 | 30.60 |
| MdSWEET17 | 41.70 | 22.55 | 3.83 | 31.91 |
| MdSWEET18 | 39.41 | 20.29 | 1.76 | 38.53 |
| MdSWEET19 | 43.66 | 16.04 | 2.99 | 37.31 |
| MdSWEET20 | 40.66 | 16.39 | 1.31 | 41.64 |
| MdSWEET21 | 45.20 | 18.86 | 1.42 | 34.52 |
| MdSWEET22 | 42.53 | 21.07 | 3.83 | 32.57 |
| MdSWEET23 | 44.63 | 15.10 | 2.68 | 37.58 |
| MdSWEET24 | 50.51 | 15.25 | 1.69 | 32.54 |
| MdSWEET25 | 40.25 | 23.31 | 5.08 | 31.36 |
| MdSWEET26 | 38.69 | 20.33 | 3.61 | 37.38 |
| MdSWEET27 | 36.80 | 21.20 | 3.60 | 38.40 |
| Duplication Type | Duplicated Gene Pairs | Chr | Clade |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tandem duplication | MdSWEET5/MdSWEET6 | Chr05/05 | I/I |
| MdSWEET9/MdSWEET10 | Chr06/06 | III/III | |
| MdSWEET15/MdSWEET16 | Chr10/10 | I/I | |
| MdSWEET23/MdSWEET24 | Chr14/14 | III/III | |
| Segmental duplication | MdSWEET15/MdSWEET17 | Chr10/11 | I/I |
| MdSWEET3/MdSWEET19 | Chr04/12 | III/III | |
| MdSWEET2/MdSWEET17 | Chr03/11 | I/I | |
| MdSWEET5/MdSWEET14 | Chr05/10 | I/I | |
| MdSWEET4/MdSWEET12 | Chr05/10 | I/I | |
| MdSWEET11/MdSWEET25 | Chr06/14 | II/II | |
| MdSWEET11/MdSWEET27 | Chr06/17 | II/II | |
| MdSWEET8/MdSWEET22 | Chr06/14 | II/II | |
| MdSWEET9/MdSWEET20 | Chr06/13 | III/III | |
| MdSWEET9/MdSWEET23 | Chr06/14 | III/III | |
| MdSWEET9/MdSWEET26 | Chr06/16 | III/III | |
| MdSWEET25/MdSWEET27 | Chr14/17 | II/II | |
| MdSWEET20/MdSWEET23 | Chr13/14 | III/III | |
| MdSWEET20/MdSWEET26 | Chr13/16 | III/III | |
| MdSWEET23/MdSWEET26 | Chr14/16 | III/III |
| Fru | Glu | Suc | Sor | Soluble Sugar | Fru | Glu | Suc | Sor | Soluble Sugar | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MdSWEET1 | −0.005 | −0.084 | −0.115 | −0.141 | −0.082 | MdSWEET15 | −0.599 | −0.387 | −0.489 | 0.036 | −0.720 * |
| MdSWEET2 | −0.109 | −0.135 | −0.235 | 0.274 | −0.129 | MdSWEET16 | 0.343 | 0.237 | 0.259 | −0.236 | 0.157 |
| MdSWEET3 | −0.383 | −0.295 | −0.267 | −0.077 | −0.184 | MdSWEET17 | −0.264 | −0.262 | −0.295 | 0.440 | −0.205 |
| MdSWEET4 | 0.614 * | 0.470 | 0.635 * | 0.113 | 0.612 * | MdSWEET18 | 0.446 | 0.542 | 0.634 * | 0.130 | 0.472 |
| MdSWEET5 | −0.403 | −0.347 | −0.121 | 0.299 | −0.178 | MdSWEET19 | 0.658 * | 0.555 | 0.707 * | −0.131 | 0.627 * |
| MdSWEET6 | 0.663 * | 0.555 | 0.686 * | −0.032 | 0.653 * | MdSWEET20 | 0.683 * | 0.590 | 0.786 ** | 0.062 | 0.707 * |
| MdSWEET7 | 0.225 | 0.355 | 0.176 | −0.214 | 0.335 | MdSWEET21 | −0.491 | −645 * | −0.409 | 0.811 ** | −0.527 |
| MdSWEET8 | −0.474 | −0.576 | −0.326 | 0.932 ** | −0.396 | MdSWEET22 | −0.519 | −633 * | −0.386 | 0.914 ** | −0.470 |
| MdSWEET9 | 0.790 ** | 0.748 ** | 0.934 ** | 0.083 | 0.835 ** | MdSWEET23 | 0.765 ** | 0.726 * | 0.948 ** | 0.075 | 0.897 ** |
| MdSWEET10 | −0.532 | −0.300 | −0.361 | 0.303 | −0.513 | MdSWEET24 | −0.471 | −0.592 | −0.333 | 0.938 ** | −0.396 |
| MdSWEET11 | 0.408 | 0.308 | 0.224 | 0.127 | 0.480 | MdSWEET25 | 0.300 | 0.223 | −0.034 | −0.044 | −0.042 |
| MdSWEET12 | 0.773 ** | 0.775 ** | 0.921 ** | 0.007 | 0.821 ** | MdSWEET26 | 0.668 * | 0.575 | 0.751 ** | 0.017 | 0.684 * |
| MdSWEET13 | 0.660 * | 0.554 | 0.720 * | 0.021 | 0.674 * | MdSWEET27 | 0.047 | −0.099 | −0.084 | −0.075 | −0.166 |
| MdSWEET14 | 0.204 | −0.087 | −0.017 | −0.249 | −0.104 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nie, P.; Xu, G.; Yu, B.; Lyu, D.; Xue, X.; Qin, S. Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Profiling Reveal the Potential Functions of the SWEET Gene Family during the Sink Organ Development Period in Apple (Malus × domestica Borkh.). Agronomy 2022, 12, 1747. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12081747
Nie P, Xu G, Yu B, Lyu D, Xue X, Qin S. Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Profiling Reveal the Potential Functions of the SWEET Gene Family during the Sink Organ Development Period in Apple (Malus × domestica Borkh.). Agronomy. 2022; 12(8):1747. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12081747
Chicago/Turabian StyleNie, Peixian, Gongxun Xu, Bo Yu, Deguo Lyu, Xiaomin Xue, and Sijun Qin. 2022. "Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Profiling Reveal the Potential Functions of the SWEET Gene Family during the Sink Organ Development Period in Apple (Malus × domestica Borkh.)" Agronomy 12, no. 8: 1747. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12081747
APA StyleNie, P., Xu, G., Yu, B., Lyu, D., Xue, X., & Qin, S. (2022). Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Profiling Reveal the Potential Functions of the SWEET Gene Family during the Sink Organ Development Period in Apple (Malus × domestica Borkh.). Agronomy, 12(8), 1747. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12081747





