Design, Synthesis, Mode of Action and Herbicidal Evaluation of Quinazolin-4(3H)-one Derivatives Based on Aryloxyphenoxypropionate Motif
Abstract
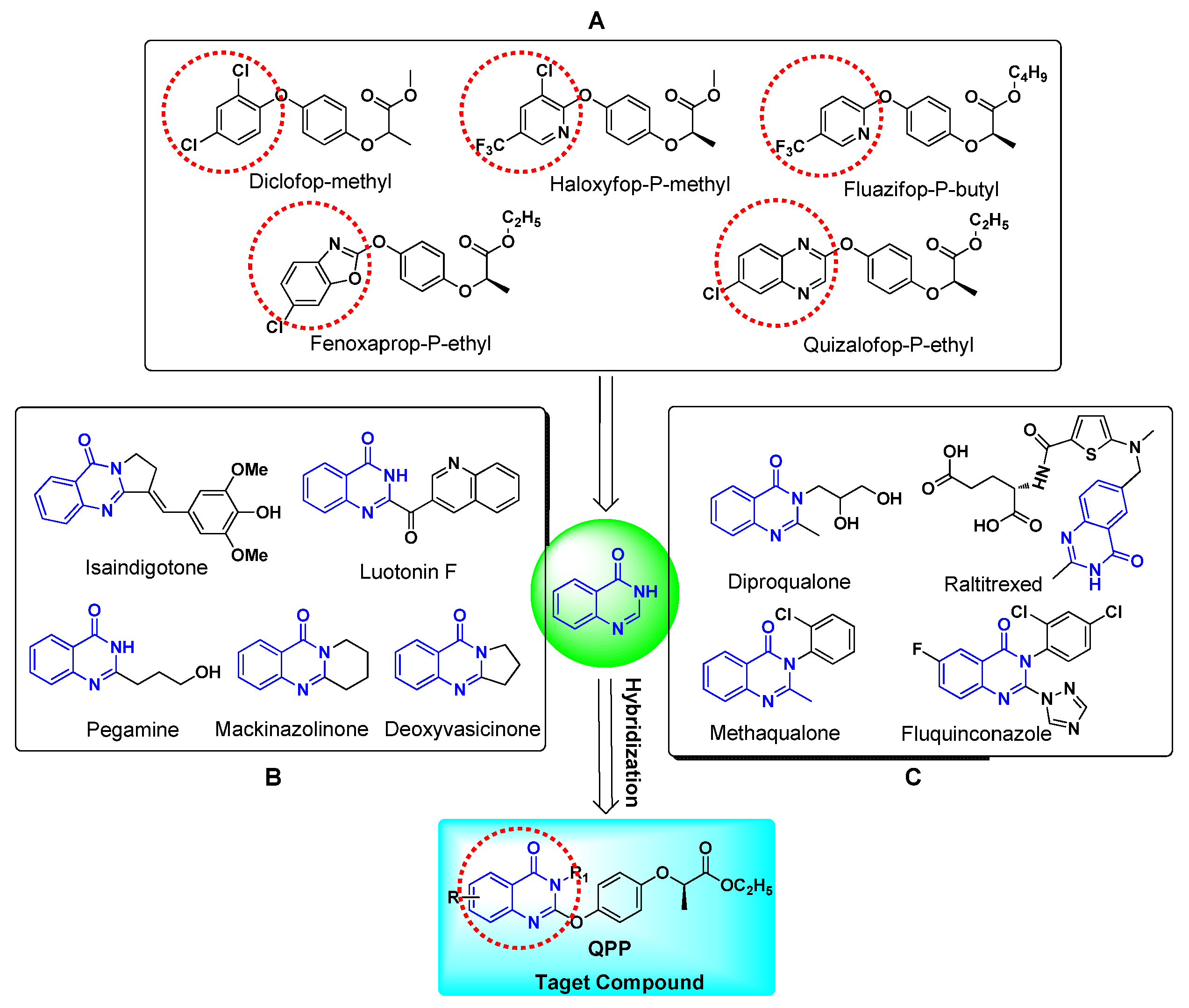
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. General Information
2.2. Chemical Synthesis Procedures
2.2.1. General Procedure for the Synthesis of Intermediates 2a–2o and 5a–5n
2.2.2. General Procedure for the Synthesis of Intermediates 3a–3o and 6a–6n
2.2.3. General Procedure for the Synthesis of Target Compounds QPP-1 to QPP-29
2.3. X-ray Diffraction Analysis of Target Compound QPP-7
2.4. Evaluation of Herbicidal Activity
2.5. Crop Selectivity
2.6. Molecular Docking Study
2.7. ACCase Extraction and Inhibition Activity Assay
3. Results and Discussion
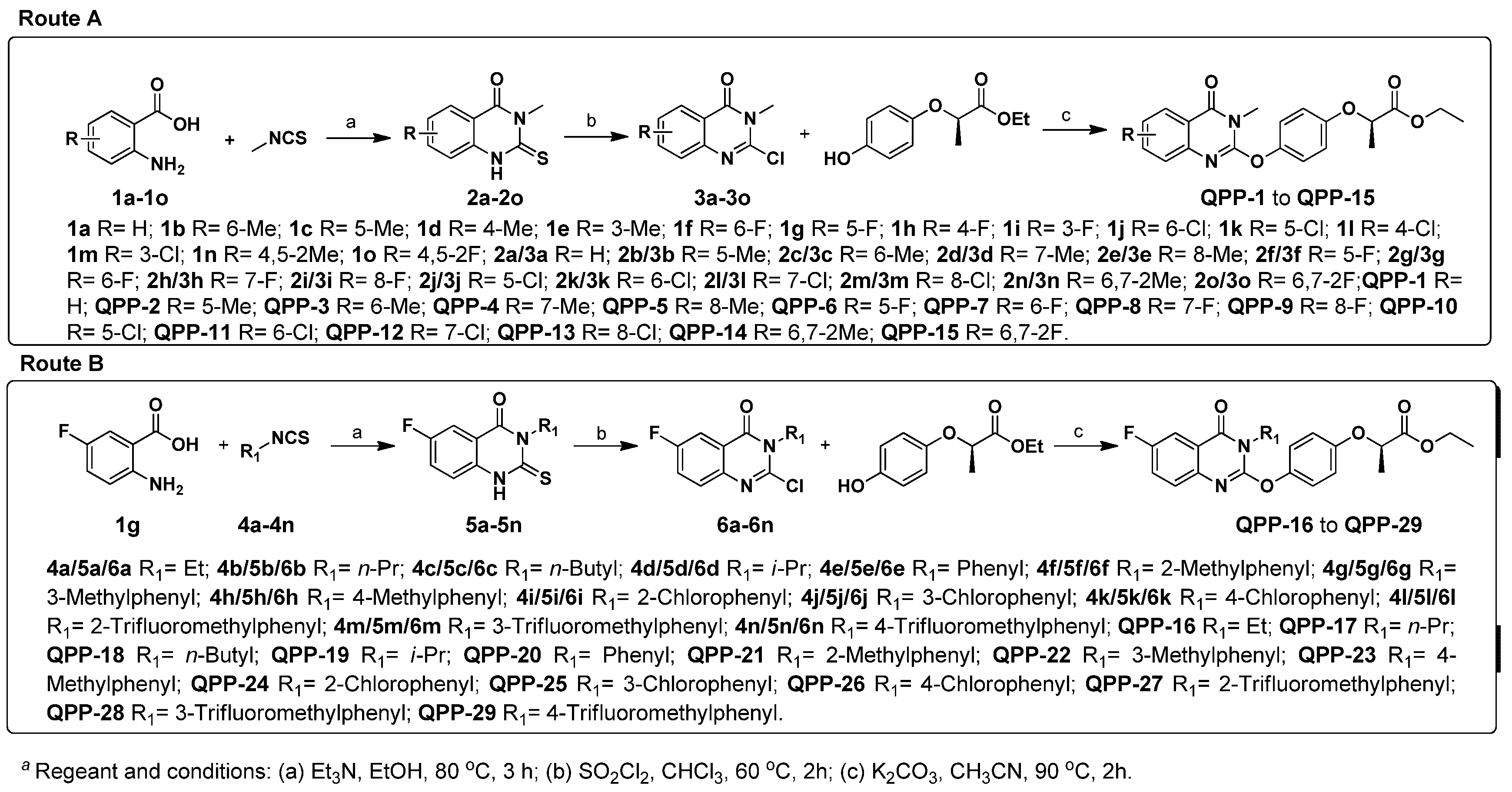
3.1. Synthetic Chemistry
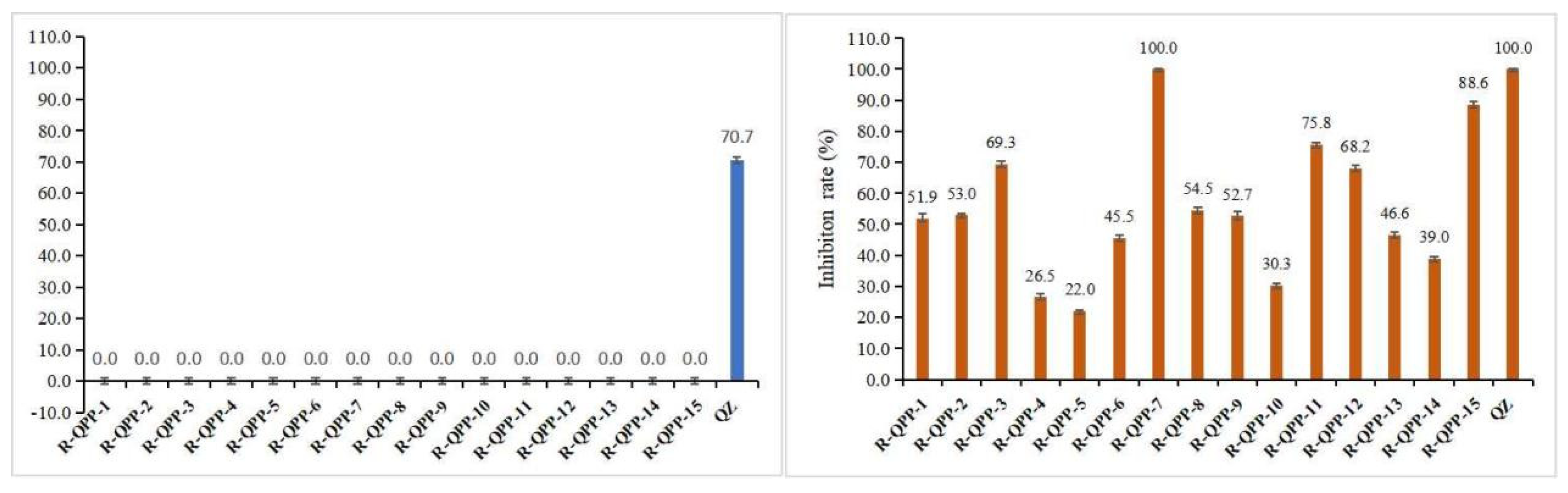
3.2. In Vitro Herbicidal Activity of Target Compounds QPP-1 to QPP-15
3.3. Herbicidal Activity of Target Compounds QPP-1 to QPP-29 in Greenhouse Tests and SAR Study
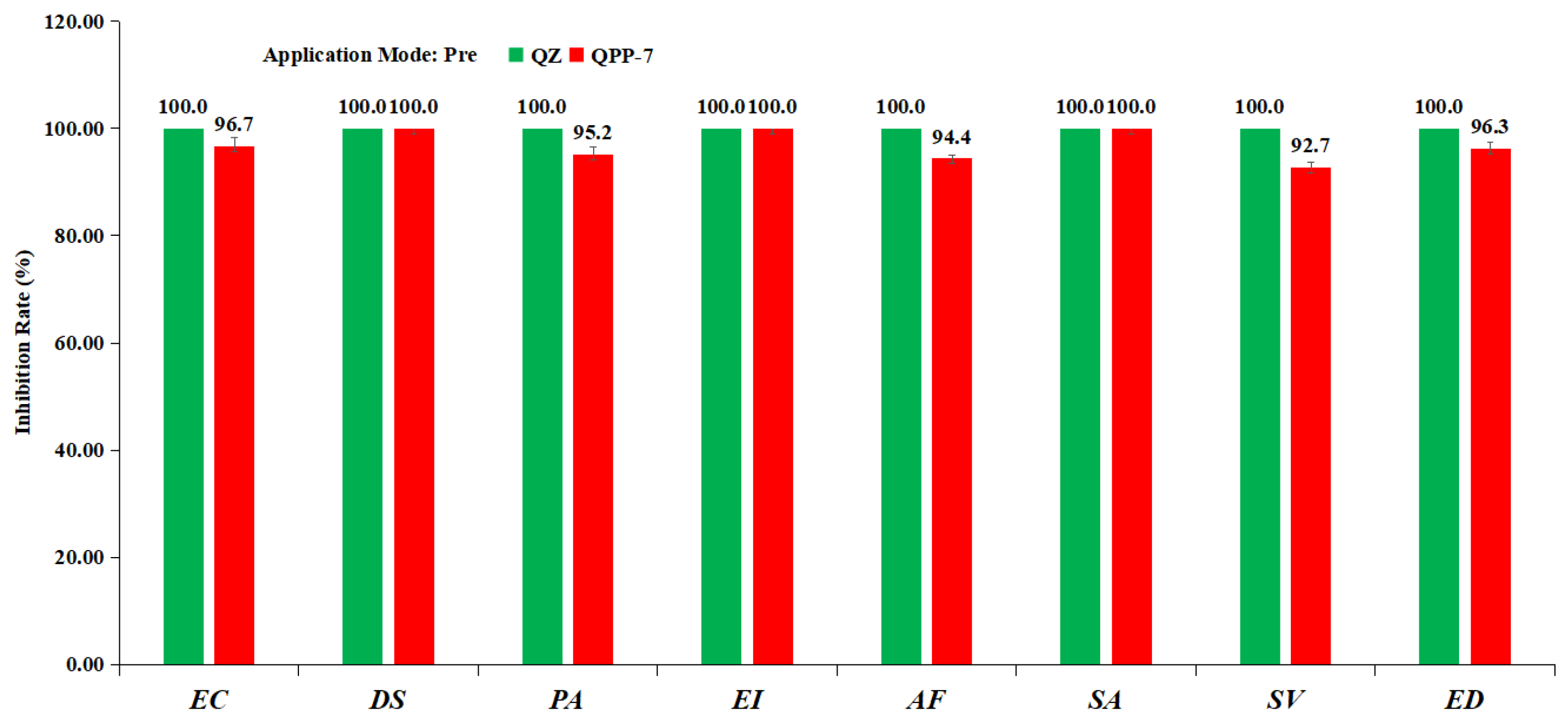
3.4. Herbicidal Spectrum and Crop Safety of Compound QPP-7
3.5. Molecular Mode of Action of the Target Compound QPP-7
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tong, L. Acetyl-coenzyme A carboxylase: Crucial metabolic enzyme and attractive target for drug discovery. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2005, 62, 1784–1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zagnitko, O.; Jelenska, J.; Tevzadze, G.; Haselkorn, R.; Gornicki, P. An isoleuciney leucine residue in the carboxyltransferase domain of acetyl-CoA carboxylase is critical for interaction with aryloxyphenoxypropionate and cyclohexanedione inhibitors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 6617–6622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, H.L.; Yang, Z.R.; Shen, Y.; Tong, L. Crystal Structure of the Carboxyltransferase Domain of Acetyl-Coenzyme A Carboxylase. Science 2003, 299, 2064–2067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Délye, C. Weed resistance to acetyl coenzyme A carboxylase inhibitors: An update. Weed Sci. 2005, 53, 728–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leach, G.E.; Devine, M.D.; Kirkwood, R.C.; Marshall, G. Target enzyme-based resistance to acetyl-coenzyme A carboxylase inhibitors in Eleusine indica. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 1995, 51, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoltenberg, D.E.; Wiederholt, R.J. Giant foxtail (Setaria faberi) resistance to aryloxyphenoxypropionate and cyclohexanedione herbicides. Weed Res. 1995, 43, 527–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heap, I.M.; Morrison, I.N. Resistance to aryloxyphenoxypropionate and cyclohexanedione herbicides in green foxtail (Setaria viridis). Weed Sci. 1996, 44, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preston, C.; Tardif, F.J.; Christoffer, J.T.; Powles, S.B. Multiple resistance to dissimilar herbicide chemistries in a biotype of Lolium rigidum due to enhanced activity of several herbicide degrading enzymes. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 1996, 54, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Harrison, D.K.; Chalupska, D.; Gornicki, P.; O’Donnell, C.C.; Adkins, S.W.; Haselkorn, R.; Williams, R.R. Single-site mutations in the carboxyltransferase domain of plastid acetyl-CoA carboxylase confer resistance to grass-specific herbicides. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 3627–3632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.Q.; Powles, S.B. Six amino acid substitutions in the carboxyltransferase domain of the plastidic acetyl-CoA carboxylase gene are linked with resistance to herbicides in a Lolium rigidum population. New Phytol. 2006, 172, 636–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sparks, T.C.; Duke, S.O. Structure simplification of natural products as a lead generation approach in agrochemical discovery. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 8324–8346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newman, D.J.; Cragg, G.M. Natural products as sources of new drugs over the nearly four decades from 01/1981 to 09/2019. J. Nat. Prod. 2020, 83, 770–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sparks, T.C.; Hahn, D.R.; Garizi, N.V. Natural products, their derivatives, mimics and synthetic equivalents: Role in agrochemical discovery. Pest Manag. Sci. 2017, 73, 700–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerwick, B.C.; Sparks, T.C. Natural products for pest control: An analysis of their role, value and future. Pest Manag. Sci. 2014, 70, 1169–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahrens, H.; Lange, G.; Müller, T.; Rosinger, C.; Willms, L.; van Almsick, V. 4-Hydroxyphenylpyruvate dioxygenase inhibitors in combination with safeners: Solutions for modern and sustainable agriculture. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 9388–9398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marrone, P.G. Pesticidal natural products-status and future potential. Pest Manag. Sci. 2019, 75, 2325–2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, D.; Wang, M.L.; Zhao, S.Y.; Shu, Y.S.; Zeng, H.L.; Xiao, C.; Lu, C.; Liu, Y.Y. Pharmaceutical prospects of naturally occurring quinazolinone and its derivatives. Fitoterapia 2017, 119, 136–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Fu, H.; Zhong, H.; Hong, K.; Zhu, W. Antifungal quinazolinones from marine-derived Bacillus cereus and their preparation. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2011, 21, 4005–4007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, N.; Li, Z.L.; Li, D.H.; Sun, Y.T.; Shan, D.T.; Bai, J.; Pei, Y.H.; Jing, Y.K.; Hua, H.M. Quinolone and indole alkaloids from the fruits of Euodia rutaecarpa and their cytotoxicity against two human cancer cell lines. Phytochemistry 2015, 109, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Li, Y.; Niu, S.; Zhang, H.; Liu, X.; Che, Y. N-Hydroxypyridones, phenylhydrazones, and a quinazolinone from Isaria farinosa. J. Nat. Prod. 2011, 74, 32–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, J.; Lin, T.; Wang, W.; Xin, Z.; Zhu, T.; Gu, Q.; Li, D. Antiviral alkaloids produced by the mangrove-derived fungus Cladosporium sp. PJX-41. J. Nat. Prod. 2013, 76, 1133–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, C.M.; Li, X.M.; Li, C.S.; Sun, H.F.; Gao, S.S.; Wang, B.G. Benzodiazepine alkaloids from marine-derived endophytic fungus Aspergillus ochraceus. Helv. Chim. Acta 2009, 92, 1366–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, Y.; Teng, X.; Wang, Y.; Liu, P.; Li, G.; Zhu, W. New quinazolinone alkaloids within rare amino acid residue from coralassociated fungus, Aspergillus versicolor LCJ-5-4. Org. Lett. 2011, 13, 1130–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cagir, A.; Jones, S.H.; Gao, R.; Eisenhauer, B.M.; Hecht, S.M. Luotonin A. A naturally occurring human DNA topoisomerase I poison. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 13628–13629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molina, P.; Tárraga, A.; Gonzalez-Tejero, A.; Rioja, I.; Ubeda, A.; Terencio, M.C.; Alcaraz, M.J. Inhibition of leukocyte functions by the alkaloid isaindigotone from Isatis indigotica and some new synthetic derivatives. J. Nat. Prod. 2001, 64, 1297–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sen, D.; Chatterjee, T.K. Pharmacophore modeling and 3D quantitative structureactivity relationship analysis of febrifugine analogues as potent antimalarial agent. J. Adv. Pharm. Technol. Res. 2013, 4, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kshirsagar, U.A. Recent developments in the chemistry of quinazolinone alkaloids. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2015, 13, 9336–9352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatadi, S.; Lakshmi, T.V.; Nanduri, S. 4(3H)-Quinazolinone derivatives: Promising antibacterial drug leads. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 170, 157–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amrutkar, R.D.; Amrutkar, S.V.; Ranawat, M.S. Quinazolin-4-one: A varsatile molecule. Curr. Bioact. Compd. 2020, 16, 370–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Z.M.; Wu, W.H.; Miao, Y.X.; Tang, Y.Q.; Zhou, Y.K.; Zheng, L.F.; Fu, Y.; Song, Z.B.; Peng, Y.Y. Recent advances in quinazolinones as an emerging molecular platform for luminescent materials and bioimaging. Org. Chem. Front. 2021, 8, 1867–1889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.J.; Shi, J.; Luo, N.; Ding, M.H.; Bao, X.P. Synthesis, crystal structure, and agricultural antimicrobial evaluation of novel quinazoline thioether derivatives incorporating the 1,2,4-triazolo[4,3-a]pyridine moiety. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 11598–11606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.W.; Yin, X.D.; Li, H.; Ma, K.Y.; Zhang, Z.J.; Zhou, R.; Wang, Y.L.; Hu, G.F.; Liu, Y.Q. Design, synthesis, and structure-activity relationship of quinazolinone derivatives as potential fungicides. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 4604–4614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Li, P.; Li, Z.N.; Yin, J.; He, M.; Xue, W.; Chen, Z.W.; Song, B.A. Synthesis and bioactivity evaluation of novel arylimines containing a 3-aminoethyl-2-[(p-trifluoromethoxy)anilino]-4(3H)-quinazolinone moiety. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 9575–9582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, K.; Li, P.; Yang, X.F.; Wang, S.B.; Wang, X.K.; Hua, X.W.; Sun, B.; Ji, L.S.; Xu, X.H. Design and synthesis of novel 4-hydroxyl-3-(2-phenoxyacetyl)-pyran-2-one derivatives for use as herbicides and evaluation of their mode of action. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 10489–10497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, K.; Liu, Y.; Wang, S.B.; Sun, B.; Hua, X.W.; Xu, X.H. Synthesis and herbicidal activity of 3-Acetyl-4-hydroxy-2,1-benzothiazine derivatives. Chem. Res. Chin. Univ. 2019, 35, 609–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, K.; Li, P.; Zhou, X.Y.; Wang, S.B.; Wang, X.K.; Ji, L.S.; Liu, R.M.; Xu, X.H. Design, synthesis and herbicidal activity of 5-acylbarbituric acid derivatives and study of molecular mode of action. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2020, 40, 2788–2797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, K.; Hua, X.W.; Tao, Y.-Y.; Liu, Y.; Liu, N.; Ma, Y.; Li, Y.H.; Xu, X.H.; Kong, C.H. Discovery of (2-benzoylethen-1-ol)-containing 1,2-benzothiazine derivatives as novel 4-hydroxyphenylpyruvate dioxygenase (HPPD) inhibiting-based herbicide lead compounds. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2016, 24, 92–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, G.; Zekarias, B.L.; Li, X.Y.; Jaffett, V.A.; Guzei, I.A.; Golden, J.E. Divergent 2-chloroquinazolin-4(3H)-one rearrangement: Twistedcyclic guanidine formation or ring-fused N-acylguanidines via a domino process. Chem. Eur. J. 2020, 26, 2486–2492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Tweel, B.; Tong, L. Molecular basis for the inhibition of the carboxyltransferase domain of acetyl-coenzyme-A carboxylase by haloxyfop and diclofop. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 5910–5915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cocker, K.M.; Moss, S.R.; Coleman, J.O.D. Multiple mechanisms of resistance to fenoxaprop-P-ethyl in United Kingdom and other European populations of herbicideresistant Alopecurus myosuroides (black-grass). Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 1999, 65, 169–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Comp. | Rate (g ha−1) | B. campestris | A. retroflexus | E. crusgalli | D. sanguinalis | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pre | Post | Pre | Post | Pre | Post | Pre | Post | ||
| QPP-3 | 750 | 8.3 ± 1.7 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 94.5 ± 1.3 | 24.7 ± 1.6 | 88.9 ± 0.2 | 1.9 ± 0.4 |
| 375 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 60.4 ± 1.4 | 5.0 ± 1.0 | 76.7 ± 1.3 | 0 | |
| 187.5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 45.0 ± 2.1 | 0 | 48.9 ± 1.8 | 0 | |
| QPP-7 | 750 | 7.8 ± 0.9 | 0 | 4.8 ± 0.2 | 0 | 100 | 42.1 ± 0.6 | 100 | 61.6 ± 1.9 |
| 375 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 96.7 ± 1.6 | 24.0 ± 0.6 | 100 | 21.3 ± 1.2 | |
| 187.5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 64.8 ± 3.1 | 0 | 55.6 ± 1.4 | 0 | |
| QPP-11 | 750 | 4.2 ± 0.3 | 6.6 ± 0.4 | 0 | 0 | 91.2 ± 1.5 | 15.7 ± 1.3 | 84.4 ± 0.8 | 13.2 ± 0.4 |
| 375 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 75.8 ± 0.4 | 10.2 ± 1.0 | 72.2 ± 1.1 | 6.6 ± 0.1 | |
| 187.5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 60.4 ± 0.8 | 0 | 53.3 ± 2.0 | 0 | |
| QZ | 750 | 38.6 ± 2.3 | 7.0 ± 1.1 | 31.2 ± 0.7 | 0 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| 375 | 24.5 ± 1.7 | 0 | 20.6 ± 1.3 | 0 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | |
| 187.5 | 11.1 ± 0.6 | 0 | 10.5 ± 1.7 | 0 | 97.8 ± 1.7 | 100 | 100 | 100 | |
| Comp. | % Injury | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| O. sativa | Z. mays | T. aestivum | G. spp | G. max | A. hypogaea | |
| QPP-7 | 0 | 55.5 ± 1.4 | 0 | 10.9 ± 1.1 | 4.5 ± 0.4 | 0 |
| QZ | 98.7 ± 0.9 | 16.8 ± 1.7 | 59.3 ± 1.2 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Comp. | Regression Equation | IC50 (nM) | 95% Confidence Interval | r |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| QPP-7 | y = 0.4842x + 16.9 | 54.65 | 40.26 to 82.67 | 0.9751 |
| QZ | y = 0.4449x + 24.2 | 41.19 | 27.82 to 69.67 | 0.9585 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, C.; Chen, K.; Li, N.; Fu, S.; Li, P.; Ji, L.; Liu, G.; Wang, X.; Lei, K. Design, Synthesis, Mode of Action and Herbicidal Evaluation of Quinazolin-4(3H)-one Derivatives Based on Aryloxyphenoxypropionate Motif. Agronomy 2022, 12, 1840. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12081840
Wang C, Chen K, Li N, Fu S, Li P, Ji L, Liu G, Wang X, Lei K. Design, Synthesis, Mode of Action and Herbicidal Evaluation of Quinazolin-4(3H)-one Derivatives Based on Aryloxyphenoxypropionate Motif. Agronomy. 2022; 12(8):1840. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12081840
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Chaochao, Ke Chen, Na Li, Shuyue Fu, Pan Li, Lusha Ji, Guoyun Liu, Xuekun Wang, and Kang Lei. 2022. "Design, Synthesis, Mode of Action and Herbicidal Evaluation of Quinazolin-4(3H)-one Derivatives Based on Aryloxyphenoxypropionate Motif" Agronomy 12, no. 8: 1840. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12081840
APA StyleWang, C., Chen, K., Li, N., Fu, S., Li, P., Ji, L., Liu, G., Wang, X., & Lei, K. (2022). Design, Synthesis, Mode of Action and Herbicidal Evaluation of Quinazolin-4(3H)-one Derivatives Based on Aryloxyphenoxypropionate Motif. Agronomy, 12(8), 1840. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12081840







