Decisive Climatic Factors for Production of Bioactive Saponarin-Rich Barley Sprouts: A Study of Seasonal Effect
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Material and Cultivation
2.2. Soil and Plant Sampling
2.3. Analytical
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Property of Field Soil
3.2. Growth of Barley Sprouts
3.3. Determination of Saponarin Content in Barley Sprouts
3.4. Relationship between Saponarin Contents and Environmental Parameters
3.5. Analysis of PCA through Sprout Growth
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Daferera, D.J.; Ziogas, B.N.; Polissiou, M.G. GC-MS Analysis of Essential Oils from Some Greek Aromatic Plants and Their Fungitoxicity on Penicillium digitatum. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2000, 48, 2576–2581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.V.; Luo, Y. Studies on Molecular Mechanisms of Ginkgo biloba Extract. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2004, 64, 465–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shu, Z.; Hussain Sh, A.; Shahen, M.; Wang, H.; Alagawany, M.; Abd El-Hac, M.E.; Ali Kalhor, S.; Rashid, M.; Ali Shar, P. Pharmacological Uses of Ginkgo biloba Extracts for Cardiovascular Disease and Coronary Heart Diseases. Int. J. Pharmacol. 2018, 15, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aborus, N.E.; Čanadanović-Brunet, J.; Ćetković, G.; Šaponjac, V.T.; Vulić, J.; Ilić, N. Powdered Barley Sprouts: Composition, Functionality and Polyphenol Digestibility. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 52, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Gioia, F.; Renna, M.; Santamaria, P. Sprouts, Micogreens and “Baby Leaf” Vegetables. In Minimally Processed Refrigerated Fruits and Vegetables; Yildiz, F., Wiley, R.C., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; pp. 723–745. ISBN 978-1-4939-7016-2. [Google Scholar]
- Meyerowitz, S. Sprouts, the Miracle Food: The Complete Guide to Sprouting, 8th ed.; Sproutman Publication: Great Barrington, MA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, W.Y.; Emmy, H.K.I.; Abbe, M.M.J.; Amin, I. Antioxidant Capacity and Phenolic Content of Selected Commercially Available Cruciferous Vegetables. Malays. J. Nutr. 2007, 13, 71–80. [Google Scholar]
- Abdallah, M.M.F. Seed Sprouts, a Pharaoh’S Heritage to Improve Food Quality. Arab Univ. J. Agric. Sci. 2008, 16, 469–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebert, A. Sprouts, Microgreens, and Edible Flowers: The Potential for High Value Specialty Produce in Asia. In Proceedings of the SEAVEG 2012: High Value Vegetables in Southeast Asia: Production, Supply and Demand, Chiang Mai, Thailand, 24–26 January 2012; pp. 216–227. [Google Scholar]
- Kamiyama, M.; Shibamoto, T. Flavonoids with Potent Antioxidant Activity Found in Young Green Barley Leaves. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 6260–6267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.S.; Lee, M.J.; Ra, J.E.; Lee, K.S.; Eom, S.; Ham, H.M.; Kim, H.Y.; Kim, S.B.; Lim, J. Growth and Bioactive Phytochemicals in Barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) Sprouts Affected by Atmospheric Pressure Plasma during Seed Germination. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2020, 53, 314002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byun, A.R.; Chun, H.; Lee, J.; Lee, S.W.; Lee, H.S.; Shim, K.W. Effects of a Dietary Supplement with Barley Sprout Extract on Blood Cholesterol Metabolism. Evidence-based Complement. Altern. Med. 2015, 2015, 473056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Lee, S.Y.; Kim, B.; Seo, W.D.; Jia, Y.; Wu, C.; Jun, H.J.; Lee, S.J. Barley Sprout Extract Containing Policosanols and Polyphenols Regulate AMPK, SREBP2 and ACAT2 Activity and Cholesterol and Glucose Metabolism In Vitro and In Vivo. Food Res. Int. 2015, 72, 174–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.S.; Jeong, E.; Jo, S.M.; Park, J.; Kim, J.Y. Comparative Study of the Effects of Light Controlled Germination Conditions on Saponarin Content in Barley Sprouts and Lipid Accumulation Suppression in HepG2 Hepatocyte and 3T3-L1 Adipocyte Cells Using Barley Sprout Extracts. Molecules 2020, 25, 5349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frangne, N.; Eggmann, T.; Koblischke, C.; Weissenböck, G.; Martinoia, E.; Klein, M. Flavone Glucoside Uptake into Barley Mesophyll and Arabidopsis Cell Culture Vacuoles. Energization Occurs by H+-Antiport and ATP-binding Cassette-type Mechanisms. Plant Physiol. 2002, 128, 726–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, K.H.; Park, M.J.; Ra, J.E.; Han, S.I.; Nam, M.H.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, J.H.; Seo, W.D. Saponarin from Barley Sprouts Inhibits NF-κB and MAPK on LPS-induced RAW 264.7 Cells. Food Funct. 2014, 5, 3005–3013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.; Woo, S.-Y.; Ra, J.-E.; Lee, K.-S.; Seo, W.D.; Lee, J.H. Saponarin Content and Biosynthesis-related Gene Expression in Young Barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) seedlings. J. Plant Biotechnol. 2019, 46, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouphael, Y.; Cardarelli, M.; Bassal, A.; Leonardi, C.; Giuffrida, F.; Colla, G. Vegetable Quality as Affected by Genetic Agronomic and Environmental Factors. J. Food Agric. Environ. 2012, 10, 680–688. [Google Scholar]
- Yoon, Y.-E. Establishment of Optimal Growing Condition for Production of Saponarin-Enriched Barley Sprouts (Hordeum vulgare L.). Ph.D. Thesis, Gyeongsang National University, Jinju, Korea, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Seo, W.D.; Yuk, H.J.; Curtis-Long, M.J.; Jang, K.C.; Lee, J.H.; Han, S.I.; Kang, H.W.; Nam, M.H.; Lee, S.J. Effect of the Growth Stage and Cultivar on Policosanol Profiles of Barley Sprouts and Their Adenosine 5′-monophosphate-activated Protein Kinase Activation. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 1117–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, D.W.; Sommers, L.E. Total Carbon, Organic Carbon, and Organic Matter. In Methods of Soil Analysis: Part 3 Chemical Methods; Sparks, D.L., Page, A.L., Helmke, P.A., Loeppert, R.H., Soltanpour, P.N., Tabatabai, M.A., Johnston, C.T., Summer, M.E., Eds.; Soil Science Society of America-American Society of Agronomy: Madison, WI, USA, 1996; Chapter 34; pp. 961–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kjeldahl, J.A. New Method for the Determination of Nitrogen in Organic Matter. Z. Anal. Chem. 1883, 22, 366–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NIAST. Method of Soil and Plant Analysis; National Institute of Agriculture Science and Technology: Suwon, Korea, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, Y.; Fang, S.; Fu, X.; Shang, X.; Yang, W. Seasonal Variation in Phenolic Compounds and Antioxidant Activity in Leaves of Cyclocarya paliurus (Batal.) Iljinskaja. Forests 2019, 10, 624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.; Xu, F.; Li, L.; Cheng, H.; Zhang, W. Seasonal Pattern of Flavonoid Content and Related Enzyme Activities in Leaves of Ginkgo biloba L. Not. Bot. Horti Agrobot. Cluj-Napoca 2012, 40, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, D.A.; Camilo, C.J.; de Fátima Alves Nonato, C.; Rodrigues, F.F.G.; Menezes, I.R.A.; Ribeiro-Filho, J.; Xiao, J.; de Almeida Souza, M.M.; da Costa, J.G.M. Influence of Seasonal Variation on Phenolic Content and In Vitro Antioxidant Activity of Secondatia floribunda A. DC. (Apocynaceae). Food Chem. 2020, 315, 126277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Deng, G.; Cheng, S.; Zhang, W.; Huang, X.; Li, L.; Cheng, H.; Rong, X.; Li, J. Molecular Cloning, Characterization and Expression of the Phenylalanine Ammonia-lyase Gene from Juglans regia. Molecules 2012, 17, 7810–7823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chung, N.J.; Kim, J.Y.; Lee, Y.; Shin, S.H.; Song, J.S.; Shin, S.C.; Kim, B.T. Variations of Saponarin Content in Young Barley Leaves Illuminated with Different Light-Emitting Diodes (LEDs). J. Crop Sci. Biotechnol. 2019, 22, 317–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Wang, P.; Wu, W.; Zhao, Y.; Idehen, E.; Sang, S. Steroidal Saponins in Oat Bran. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 1549–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brauch, D.; Porzel, A.; Schumann, E.; Pillen, K.; Mock, H.P. Changes in Isovitexin-O-glycosylation during the Development of Young Barley Plants. Phytochemistry 2018, 148, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sager, J.C.; McFarlane, J.C. Radiation. In Plant Growth Chamber Handbook. In Growth Chamber Handbook; North Central Regional Research Publication No. 340; Iowa State University: Ames, IA, USA, 1997; pp. 1–29. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, L.N.; Feng, G.N.; Gao, Y.; Shen, Y.X.; Li, H.S.; Gu, Y.; Luan, H.Y. Phytochemical Constituents and Antioxidant Enzyme Activity Profiles of Different Barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) Cultivars at Different Developmental Stages. Agronomy 2020, 10, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]



| Parameter | 2019 | 2020 | Optimal Range † |
|---|---|---|---|
| pH1:5W | 6.35 | 6.42 | 6.5–7.0 |
| EC (ds m−1) | 1.11 | 0.94 | 0–2.0 |
| Organic matter (g kg−1) | 17.6 | 17.3 | 20–30 |
| Total nitrogen (g kg−1) | 1.52 | 0.90 | - |
| Available P2O5 (mg kg−1) | 260 | 249 | 150–250 |
| Cation exchange capacity (cmolc kg−1) | 15.8 | 14.1 | - |
| Exchangeable K (cmolc kg−1) | 0.62 | 0.51 | 0.45–0.55 |
| Exchangeable Ca (cmolc kg−1) | 8.13 | 7.89 | 6.0–7.0 |
| Exchangeable Mg (cmolc kg−1) | 1.74 | 1.84 | 2.0–2.5 |
| Sowing time | Length of Leaves (cm) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2019 | 2020 | |||||
| 10 | 15 | 18 | 10 | 15 | 18 | |
| Mar | 0.096 | 0.147 | 0.197 | 0.095 | 0.157 | 0.193 |
| Apr | 0.088 | 0.145 | 0.206 | - | - | - |
| May | 0.097 | 0.164 | 0.209 | 0.100 | 0.159 | 0.205 |
| Jun | 0.093 | 0.156 | 0.192 | - | - | - |
| Jul | 0.099 | 0.154 | 0.196 | - | - | - |
| Aug | 0.097 | 0.151 | 0.205 | - | - | - |
| Sep | 0.088 | 0.158 | 0.201 | 0.106 | 0.160 | 0.207 |
| Oct | 0.095 | 0.158 | 0.203 | 0.090 | 0.159 | 0.201 |
| Mean | 0.094 | 0.154 | 0.201 | 0.098 | 0.159 | 0.202 |
| Two-way ANOVA | 2019 | 2020 | ||||
| Sowing time | 0.572 | 0.231 | ||||
| Length of leaves | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||||
| Interaction | 0.770 | 0.838 | ||||
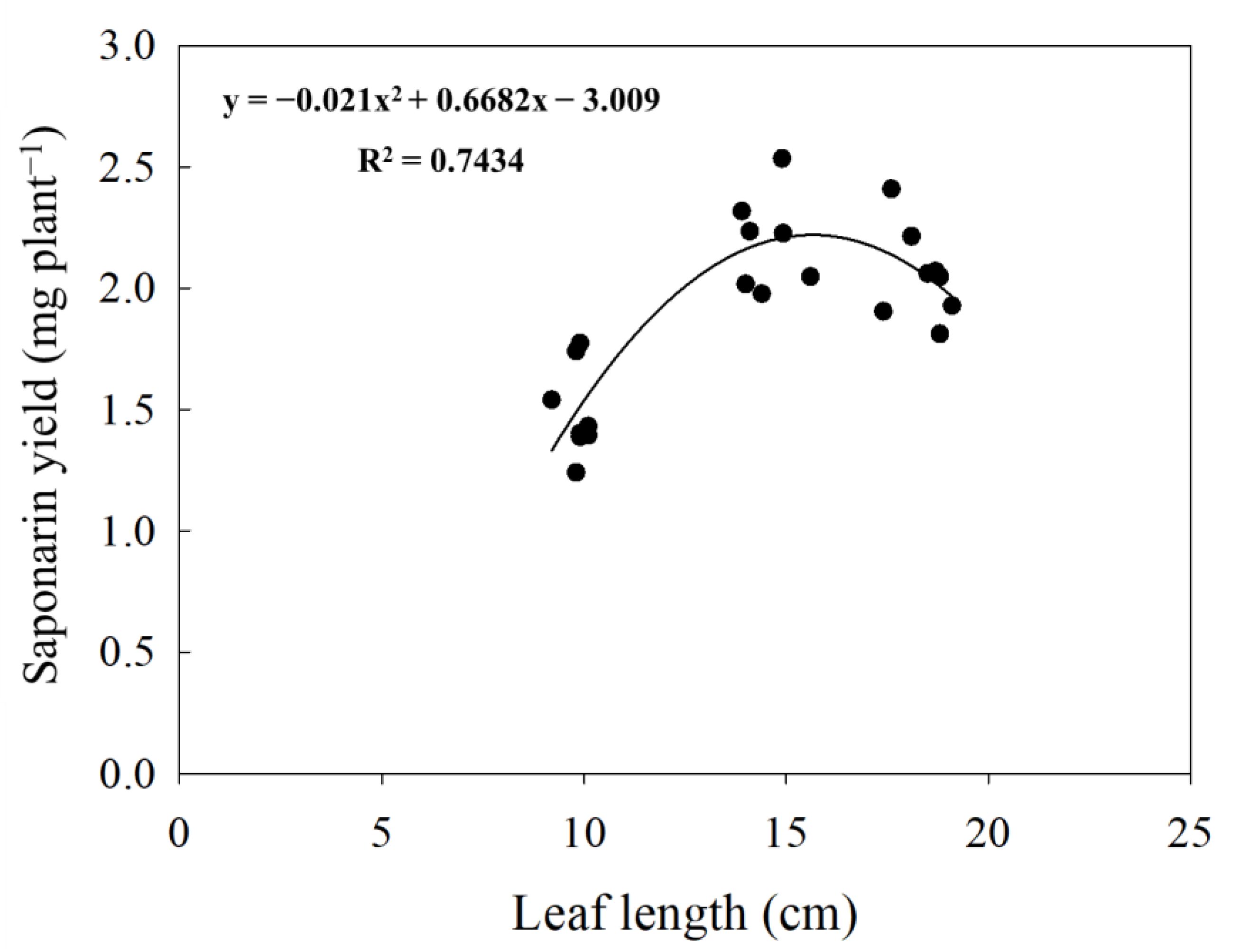
| Leaf Length (cm) | Yield (mg plant−1) |
|---|---|
| 10 | 1.43 b |
| 15 | 2.18 a |
| 18 | 2.06 a |
| Parameter | R | p Value |
|---|---|---|
| FW | −0.700 | <0.001 |
| Leaf length | −0.704 | <0.001 |
| GI | −0.395 | 0.017 |
| GP | −0.120 | 0.484 |
| ADT | −0.435 | 0.008 |
| DTR | 0.535 | 0.001 |
| ACT | −0.597 | <0.001 |
| ALP | 0.446 | 0.006 |
| ADP | 0.095 | 0.584 |
| ACP | −0.122 | 0.479 |
| RH | −0.461 | 0.005 |
| Rainfall | −0.553 | <0.001 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yoon, Y.-E.; Choe, H.; Kantharaj, V.; Seo, W.D.; Lee, J.H.; Cheong, M.S.; Lee, K.-A.; Kim, Y.-N.; Lee, Y.B. Decisive Climatic Factors for Production of Bioactive Saponarin-Rich Barley Sprouts: A Study of Seasonal Effect. Agronomy 2022, 12, 2056. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12092056
Yoon Y-E, Choe H, Kantharaj V, Seo WD, Lee JH, Cheong MS, Lee K-A, Kim Y-N, Lee YB. Decisive Climatic Factors for Production of Bioactive Saponarin-Rich Barley Sprouts: A Study of Seasonal Effect. Agronomy. 2022; 12(9):2056. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12092056
Chicago/Turabian StyleYoon, Young-Eun, Hyeonji Choe, Vimalraj Kantharaj, Woo Duck Seo, Jin Hwan Lee, Mi Sun Cheong, Keum-Ah Lee, Young-Nam Kim, and Yong Bok Lee. 2022. "Decisive Climatic Factors for Production of Bioactive Saponarin-Rich Barley Sprouts: A Study of Seasonal Effect" Agronomy 12, no. 9: 2056. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12092056
APA StyleYoon, Y.-E., Choe, H., Kantharaj, V., Seo, W. D., Lee, J. H., Cheong, M. S., Lee, K.-A., Kim, Y.-N., & Lee, Y. B. (2022). Decisive Climatic Factors for Production of Bioactive Saponarin-Rich Barley Sprouts: A Study of Seasonal Effect. Agronomy, 12(9), 2056. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12092056





