Using Nitrogen Stable Isotopes to Authenticate Organically and Conventionally Grown Vegetables: A New Tracking Framework
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Samples
2.2. Determination of 15N/14N Isotope Ratio by EA-IRMS and Statistical Analyses
3. Results & Discussion
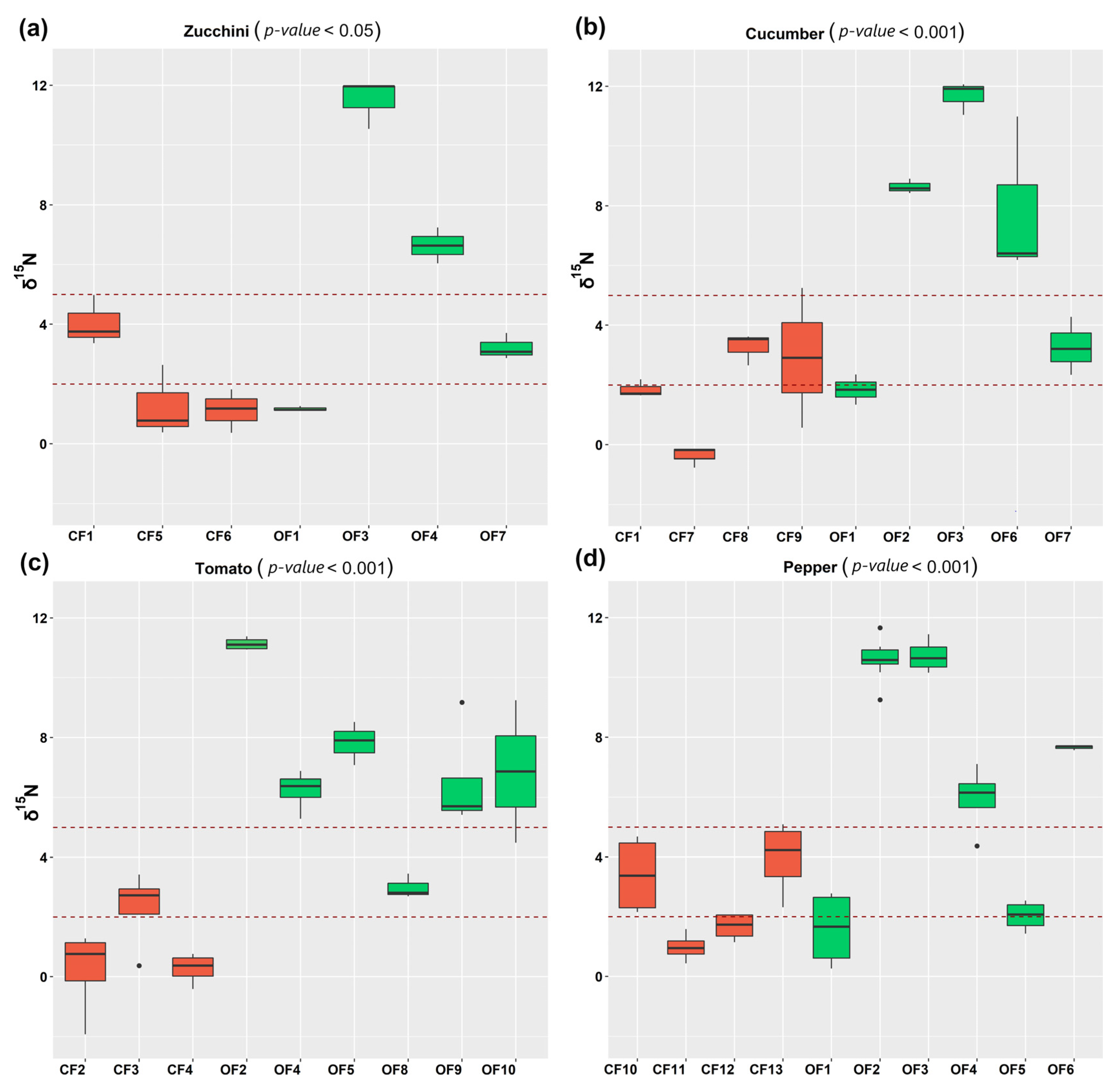
3.1. Effect of Fertilization Regime on the Nitrogen Isotope Composition of Vegetables
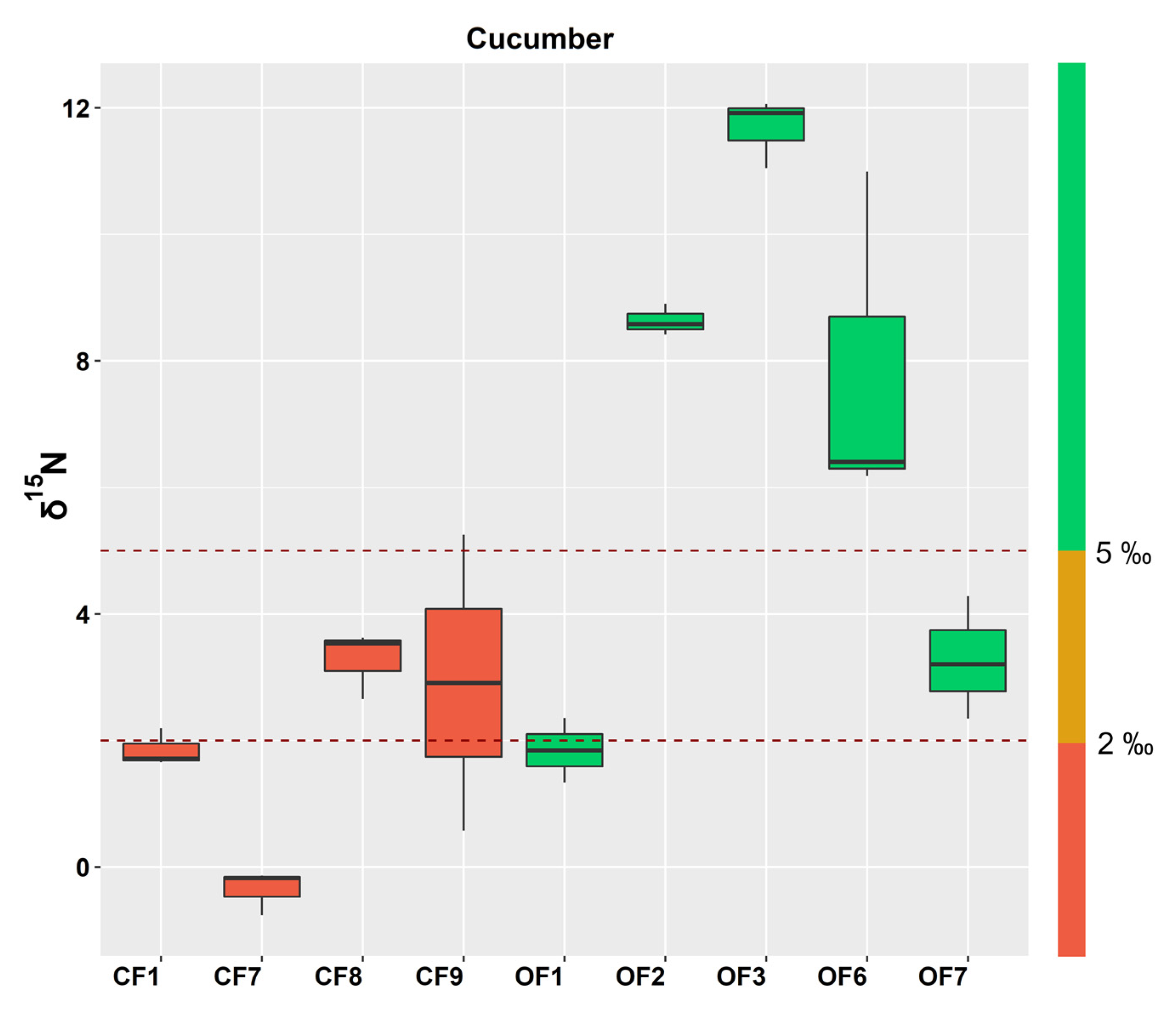
3.1.1. Cucurbitaceae
3.1.2. Solanaceae
3.2. δ15N Decision Limits for the Dynamic Tracking of Organic Horticultural Crops: A “Traffic Light” Framework
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Baron, J.; Jay-Russell, M.T. Assessment of Current Practices of Organic Farmers Regarding Biological Soil Amendments of Animal Origin in a Multi-Regional US Study. Food Prot. Trends 2018, 38, 347–362. [Google Scholar]
- Hoefkens, C.; Vandekinderen, I.; De Meulenaer, B.; Devlieghere, F.; Baert, K.; Sioen, I.; De Henauw, S.; Verbeke, W.; Van Camp, J. A Literature-Based Comparison of Nutrient and Contaminant Contents between Organic and Conventional Vegetables and Potatoes. Br. Food J. 2009, 111, 1078–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mihailova, A.; Kelly, S.D.; Chevallier, O.P.; Elliott, C.T.; Maestroni, B.M.; Cannavan, A. High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry-Based Metabolomics for the Discrimination between Organic and Conventional Crops: A Review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 110, 142–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willer, H.; Trávnícek, J.; Meier, C.; Schlatter, B. The World of Organic Agriculture. Statistics and Emerging Trends. IFOAM 2021, 340. [Google Scholar]
- Reganold, J.P.; Wachter, J.M. Organic Agriculture in the Twenty-First Century. Nat. Plants 2016, 2, 15221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dangour, A.D.; Dodhia, S.K.; Hayter, A.; Allen, E.; Lock, K.; Uauy, R. Nutritional Quality of Organic Foods: A Systematic Review. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2009, 90, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cubero-Leon, E.; De Rudder, O.; Maquet, A. Metabolomics for Organic Food Authentication: Results from a Long-Term Field Study in Carrots. Food Chem. 2018, 239, 760–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Lima, M.D.; Barbosa, R. Methods of Authentication of Food Grown in Organic and Conventional Systems Using Chemometrics and Data Mining Algorithms: A Review. Food Anal. Methods 2019, 12, 887–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danezis, G.P.; Tsagkaris, A.S.; Camin, F.; Brusic, V.; Georgiou, C.A. Food Authentication: Techniques, Trends & Emerging Approaches. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2016, 85, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hohmann, M.; Monakhova, Y.; Erich, S.; Christoph, N.; Wachter, H.; Holzgrabe, U. Differentiation of Organically and Conventionally Grown Tomatoes by Chemometric Analysis of Combined Data from Proton Nuclear Magnetic Resonance and Mid-Infrared Spectroscopy and Stable Isotope Analysis. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 9666–9675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laursen, K.H.; Schjoerring, J.K.; Kelly, S.D.; Husted, S. Authentication of Organically Grown Plants–Advantages and Limitations of Atomic Spectroscopy for Multi-Element and Stable Isotope Analysis. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2014, 59, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Zhong, P.; Jiang, A.; Shen, X.; Li, X.; Xu, Z.; Shen, Y.; Sun, Y.; Lei, H. Raman Spectroscopy Coupled with Chemometrics for Food Authentication: A Review. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2020, 131, 116017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bateman, A.S.; Kelly, S.D.; Woolfe, M. Nitrogen Isotope Composition of Organically and Conventionally Grown Crops. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 2664–2670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camin, F.; Perini, M.; Bontempo, L.; Fabroni, S.; Faedi, W.; Magnani, S.; Baruzzi, G.; Bonoli, M.; Tabilio, M.R.; Musmeci, S.; et al. Potential Isotopic and Chemical Markers for Characterising Organic Fruits. Food Chem. 2011, 125, 1072–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capuano, E.; Boerrigter-Eenling, R.; van der Veer, G.; van Ruth, S.M. Analytical Authentication of Organic Products: An Overview of Markers. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2013, 93, 12–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novak, V.; Adler, J.; Husted, S.; Fromberg, A.; Laursen, K.H. Authenticity Testing of Organically Grown Vegetables by Stable Isotope Ratio Analysis of Oxygen in Plant-Derived Sulphate. Food Chem. 2019, 291, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Novotná, H.; Kmiecik, O.; Gałązka, M.; Krtková, V.; Hurajová, A.; Schulzová, V.; Hallmann, E.; Rembiałkowska, E.; Hajšlová, J. Metabolomic Fingerprinting Employing DART-TOFMS for Authentication of Tomatoes and Peppers from Organic and Conventional Farming. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2012, 29, 1335–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carter, J.F.; Chesson, L.A. Food Forensics: Stable Isotopes as a Guide to Authenticity and Origin; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017; pp. 273–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, K.M. Nitrogen Isotopes as a Screening Tool To Determine the Growing Regimen of Some Organic and Nonorganic Supermarket Produce from New Zealand. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 4078–4083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verenitch, S.; Mazumder, A. Isotopic Characterization as a Screening Tool in Authentication of Organic Produce Commercially Available in Western North America. Isotopes Environ. Health Stud. 2015, 51, 332–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šturm, M.; Lojen, S. Nitrogen Isotopic Signature of Vegetables from the Slovenian Market and Its Suitability as an Indicator of Organic Production. Isotopes Environ. Health Stud. 2011, 47, 214–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brand, W.A.; Coplen, T.B.; Vogl, J.; Rosner, M.; Prohaska, T. Assessment of International Reference Materials for Isotope-Ratio Analysis (IUPAC Technical Report). Pure Appl. Chem. 2014, 86, 425–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Flores, P.; Fenoll, J.; Hellín, P. The Feasibility of Using Δ15N and Δ13C Values for Discriminating between Conventionally and Organically Fertilized Pepper (Capsicum annuum L.). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 5740–5745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bateman, A.S.; Kelly, S.D.; Jickells, T.D. Nitrogen Isotope Relationships between Crops and Fertilizer: Implications for Using Nitrogen Isotope Analysis as an Indicator of Agricultural Regime. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 5760–5765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, H.; Roßmann, A.; Voerkelius, S.; Schnitzler, W.H.; Georgi, M.; Graßmann, J.; Zimmermann, G.; Winkler, R. Isotope Characteristics of Vegetables and Wheat from Conventional and Organic Production. Isotopes Environ. Health Stud. 2005, 41, 223–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Crop | Regime | Nfarmers | Nsamples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Zucchini | Organic | 4 | 27 |
| Conventional | 3 | 33 | |
| Cucumber | Organic | 5 | 42 |
| Conventional | 4 | 33 | |
| Tomato | Organic | 6 | 60 |
| Conventional | 3 | 36 | |
| Pepper | Organic | 6 | 81 |
| Conventional | 4 | 48 |
| Crop | Regime | δ15N | Min | Max |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zucchini | Organic | 5.54 ± 1.10 | 1.10 | 11.97 |
| Conventional | 2.14 ± 1.64 | 0.37 | 4.98 | |
| Cucumber | Organic | 7.00 ± 3.81 | 1.34 | 12.06 |
| Conventional | 1.83 ± 1.87 | −0.76 | 5.25 | |
| Tomato | Organic | 7.08 ± 2.77 | 2.69 | 11.39 |
| Conventional | 0.94 ± 1.48 | −1.92 | 3.42 | |
| Pepper | Organic | 6.99 ± 3.89 | 0.26 | 11.66 |
| Conventional | 2.51 ± 1.53 | 0.44 | 5.10 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Muñoz-Redondo, J.M.; Montenegro, J.C.; Moreno-Rojas, J.M. Using Nitrogen Stable Isotopes to Authenticate Organically and Conventionally Grown Vegetables: A New Tracking Framework. Agronomy 2023, 13, 131. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13010131
Muñoz-Redondo JM, Montenegro JC, Moreno-Rojas JM. Using Nitrogen Stable Isotopes to Authenticate Organically and Conventionally Grown Vegetables: A New Tracking Framework. Agronomy. 2023; 13(1):131. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13010131
Chicago/Turabian StyleMuñoz-Redondo, José Manuel, José Carlos Montenegro, and José Manuel Moreno-Rojas. 2023. "Using Nitrogen Stable Isotopes to Authenticate Organically and Conventionally Grown Vegetables: A New Tracking Framework" Agronomy 13, no. 1: 131. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13010131
APA StyleMuñoz-Redondo, J. M., Montenegro, J. C., & Moreno-Rojas, J. M. (2023). Using Nitrogen Stable Isotopes to Authenticate Organically and Conventionally Grown Vegetables: A New Tracking Framework. Agronomy, 13(1), 131. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13010131






