Foliar Applications of ZnO and Its Nanoparticles Increase Safflower (Carthamus tinctorius L.) Growth and Yield under Water Stress
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Design
2.2. Irrigation of the Field
2.3. Determination of Growth and Yield Parameters
2.4. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Effect of Zn Application on Plant Growth (First-Year Data)
3.2. Effect of Nano Zn Particles Application on Plant Growth under Different Irrigation Regimes (Second Year)
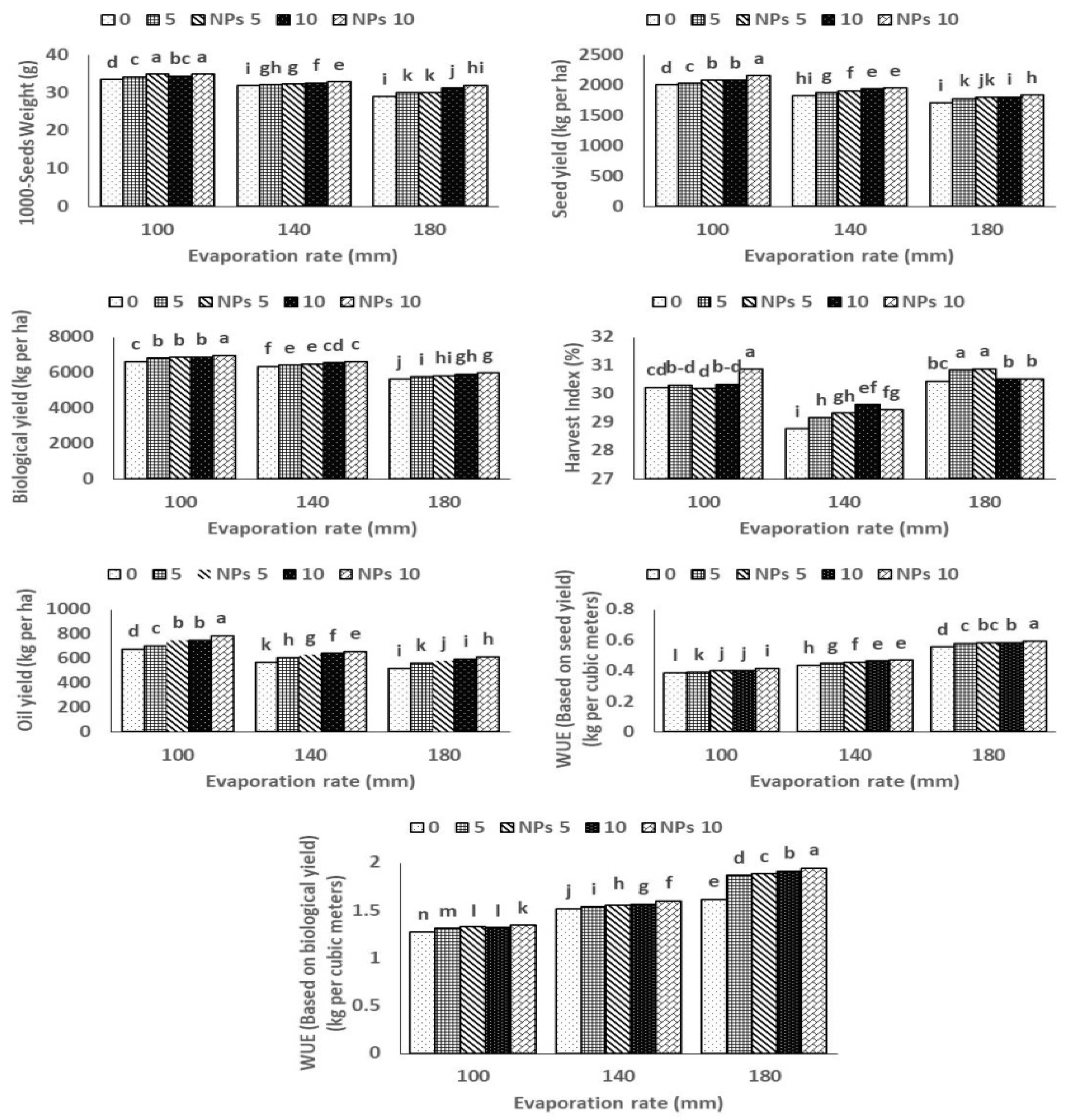
3.3. Effect of ZnO and ZnO-NP in Alleviating Water Stress
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yeilaghi, H.; Arzani, A.; Ghaderian, M.; Fotovat, R.; Feizi, M.; Pourdad, S.S. Effect of salinity on seed oil content and fatty acid composition of safflower (Carthamus tinctorius L.) genotypes. Food Chem. 2012, 130, 618–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delshad, E.; Yousefi, M.; Sasannezhad, P.; Rakhshandeh, H.; Ayati, Z. Medical uses of Carthamus tinctorius L. (Safflower): A comprehensive review from Traditional Medicine to Modern Medicine. Electron. Physician 2018, 10, 6672–6681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Turgumbayeva, A.; Ustenova, G.; Rakhimov, K.; Ross, S. Phytochemistry And Pharmacological Activities Of Safflower Carthamus tinctorius L. Planta Medica 2016, 82, PC80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turgut, B. Comparison of wheat and safflower cultivation areas in terms of total carbon and some soil properties under semi-arid climate conditions. Solid Earth 2015, 6, 719–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chavoushi, M.; Najafi, F.; Salimi, A.; Angaji, S.A. Effect of salicylic acid and sodium nitroprusside on growth parameters, photosynthetic pigments and secondary metabolites of safflower under drought stress. Sci. Hortic. 2019, 259, 108823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tunçtürk, M.; Tunçtürk, R.; Yildirim, B.; Çiftçi, V. Changes of micronutrients, dry weight and plant development in canola (Brassica napus L.) cultivars under salt stress. African J. Biotechnol 2013, 10, 3726–3730. [Google Scholar]
- Sein-Echaluce, V.C.; Mulet, J.M.; Barja, M.V.; Peleato, M.L.; Fillat, M.F. Exploring the Ability of Cyanobacterial Ferric Uptake Regulator (FUR) Proteins to Increase Yeast Tolerance to Abiotic Stresses. In Cyanobacterial Lifestyle and Its Applications in Biotechnology; Academic Press: London, UK, 2021; pp. 179–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sisakht, S.N.E.; KordLaghari, K.P.; Keshavarz, K. Influence of Zn and ferrous sulfate on yield and yield component of Phaseolus vulgaris. Int. J. Biosci. 2015, 6, 123–129. [Google Scholar]
- Saha, B.; Saha, S.; Saha, R.; Hazra, G.C.; Mandal, B. Influence of Zn, B and S on the yield and quality of groundnut (Arachis hypogea L.). Legum. Res. Int. J. 2015, 38, 832–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rengasamy, K.R.; Kulkarni, M.G.; Pendota, S.C.; Van Staden, J. Enhancing growth, phytochemical constituents and aphid resistance capacity in cabbage with foliar application of eckol—A biologically active phenolic molecule from brown seaweed. New Biotechnol. 2016, 33, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Movahhedy-Dehnavy, M.; Modarres-Sanavy, S.A.M.; Mokhtassi-Bidgoli, A. Foliar application of zinc and manganese im-proves seed yield and quality of safflower (Carthamus tinctorius L.) grown under water deficit stress. Ind. Crops Prod. 2009, 30, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehnavi, M.M.; Mohammad, S.A.; Sanavy, M. Effects of Withholding Irrigation and Foliar Application of Zinc and Manganese on Fatty Acid Composition and Seed Oil Content in Winter Safflower. In Proceedings of the 7th International Safflower Conference, Wagga Wagga, Australia, 3–6 November 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Mousa, G.T.; El-Sallami, I.H.; Ali, E.F. Response of Nigella sativa, L. to foliar application of gibberellic acid, benzyladenine, iron and zinc. Assiut J. Agric. Sci. 2003, 32, 141–156. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, Y.; Wang, L.; Xin, Z.; Zhao, L.; An, X.; Hu, Q. Effect of Foliar Application of Zinc, Selenium, and Iron Fertilizers on Nutrients Concentration and Yield of Rice Grain in China. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 2079–2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Gizawy, N.K.B.; Mehasen, S.A.S. Response of faba bean to bio, mineral phosphorus fertilizers and foliar application with zinc. World App. Sci. J. 2009, 6, 1359–1365. [Google Scholar]
- Potarzycki, J.; Grzebisz, W. Effect of zinc foliar application on grain yield of maize and its yielding compone. Plant Soil Environ. 2009, 55, 519–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bybordi, A.; Mamedov, G. Evaluation of Application Methods Efficiency of Zinc and Iron for Canola(Brassica napus L.). Not. Sci. Biol. 1970, 2, 94–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nasiri, Y.; Zehtab-Salmasi, S.; Nasrullahzadeh, S.; Najafi, N.; Ghassemi-Golezani, K. Effects of foliar application of micronu-trients (Fe and Zn) on flower yield and essential oil of chamomile (Matricaria chamomilla L.). J. Med. Plant Res. 2010, 4, 1733–1737. [Google Scholar]
- Heidarian, A.R.; Kord, H.; Mostafavi, K.; Mashhadi, F.A. Investigating Fe and Zn foliar application on yield and its com-ponents of soybean (Glycine max (L.) Merr.) at different growth stages. J. Agric. Biotechnol. Sustain. Dev. 2011, 3, 189–197. [Google Scholar]
- Duhan, J.S.; Kumar, R.; Kumar, N.; Kaur, P.; Nehra, K.; Duhan, S. Nanotechnology: The new perspective in precision agri-culture. Biotechnol. Rep. 2017, 15, 11–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rikabad, M.M.; Pourakbar, L.; Moghaddam, S.S.; Popović-Djordjević, J. Agrobiological, chemical and antioxidant properties of saffron (Crocus sativus L.) exposed to TiO2 nanoparticles and ultraviolet-B stress. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2019, 137, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panwar, J. Positive Effect of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles on Tomato Plants: A Step towards Developing Nano-Fertilizers. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Environmental Research and Technology (ICERT), Penang, Malaysia, 30 May–1 June 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Bozorgi, H.R. Study effects of nitrogen fertilizer management under nano iron chelate foliar spraying on yield and yield components of eggplant (Solanum melongena L.). J. Agric. Biol. Sci. 2012, 7, 233–237. [Google Scholar]
- Sheykhbaglou, R.; Sedghi, M.; Shishevan, M.T.; Sharifi, R.S. Effects of Nano-Iron Oxide Particles on Agronomic Traits of Soybean. Not. Sci. Biol. 2010, 2, 112–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Elfeky, S.A.; Mohammed, M.A.; Khater, M.S.; Osman, Y.A.; Elsherbini, E. Effect of magnetite nano-fertilizer on growth and yield of Ocimum basilicum L. Int. J. Indig. Med. Plants 2013, 46, 1286–11293. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.J.; Liu, Q.; Song, H.X. Effects of nano-preparation on growth and nitrogen fertilizer use efficiency on cabbage. J. Chin. Agric. Sci. Bul. 2011, 27, 264–267. [Google Scholar]
- Rajput, V.D.; Minkina, T.M.; Behal, A.; Sushkova, S.N.; Mandzhieva, S.; Singh, R.; Movsesyan, H.S. Effects of zinc-oxide na-noparticles on soil, plants, animals and soil organisms: A review. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monitor. Manag. 2018, 9, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Chung, H.; Kim, S.; Lee, I. The Genotoxic Effect of ZnO and CuO Nanoparticles on Early Growth of Buckwheat, Fagopyrum Esculentum. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2013, 224, 1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raskar, S.V.; Laware, S.L. Effect of zinc oxide nanoparticles on cytology and seed germination in onion. Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. App. Sci. 2014, 3, 467–473. [Google Scholar]
- Karimi, E.; Tadayyon, A. Effect of humic acid spraying on yield and some morphological characteristic of safflower (Car-thamus tinctorius L.) under drought stress conditions. Field Crops Res. 2018, 31, 19–38. [Google Scholar]
- Naserzadeh, Y.; Kartoolinejad, D.; Mahmoudi, N.; Zargar, M.; Pakina, E.; Heydari, M.; Astarkhanova, T.; Kavhiza, N.J. Nine strains of Pseudomonas fluorescens and P. putida: Effects on growth indices, seed and yield production of Carthamus tinc-torius L. Res. Crops 2018, 19, 622–632. [Google Scholar]
- Roche, J.; Mouloungui, Z.; Cerny, M.; Merah, O. Effect of Sowing Dates on Fatty Acids and Phytosterols Patterns of Carthamus tinctorius L. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 2839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khattak, S.G.; Dominy, P.J.; Ahmad, W. Effect of Zn as soil addition and foliar application on yield and protein content of wheat in alkaline soil. J. Natl. Sci. Found. Sri Lanka 2015, 43, 303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chevilly, S.; Dolz-Edo, L.; López-Nicolás, J.M.; Morcillo, L.; Vilagrosa, A.; Yenush, L.; Mulet, J.M. Physiological and molecular characterization of the differential response of broccoli (Brassica oleracea var. Italica) cultivars reveals limiting factors for broccoli tolerance to drought stress. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 10394–10404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadollahi, P.; Asgharipour, M.R.; Kheiri, N.; Ghaderi, A. Effects of drought stress and different types of organic fertilizers on the yield and yield components of safflower (Carthamus tinctorius L.). J. Oil Plant Prod. 2015, 1, 27–40. [Google Scholar]
- Mosupiemang, M.; Emongor, V.E.; Malambane, G. A Review of Drought Tolerance in Safflower. Int. J. Plant Soil Sci. 2022, 140–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, M.I.; Lyra, D.-A.; Farooq, M.; Nikoloudakis, N.; Khalid, N. Salt and drought stresses in safflower: A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2015, 36, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ashrafi, E.; Razmjoo, K. Effect of Irrigation Regimes on Oil Content and Composition of Safflower ( Carthamus tinctorius L.) Cultivars. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2010, 87, 499–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidari, M.; Tohidimoghadam, H.R.; Ghooshchi, F.; Modares Sanavi, S.A.M.; Kasraie, P. Effect of seed priming and foliar application of growth regulators on morphophysiological changes and safflower grain and oil yield under drought stress. Environ. Stresses Crop Sci. 2022, 15, 1073–1089. [Google Scholar]
- Ekiz, H.; Bagci, S.A.; Kiral, A.S.; Eker, S.; Gültekin, I.; Alkan, A.; Cakmak, I. Effects of zinc fertilization and irrigation on grain yield and zinc concentration of various cereals grown in zinc-deficient calcareous soils. J. Plant Nutr. 1998, 21, 2245–2256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, D.; Sun, D.; Wang, C.; Ding, H.; Qin, H.; Hou, J.; Huang, X.; Xie, Y.; Guo, T. Physiological Responses and Yield of Wheat Plants in Zinc-Mediated Alleviation of Drought Stress. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moghadam, H.R.T.; Zahedi, H.; Ashkiani, A. Effect of zinc foliar application on auxin and gibberellin hormones and catalase and superoxide dismutase enzyme activity of corn (Zea mays L) under water stress. Maydica 2013, 58, 218–223. [Google Scholar]
- Cakmak, I. Possible roles of zinc in protecting plant cells from damage by reactive oxygen species. New Phytol. 2000, 146, 185–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafeez, B.M.K.Y.; Khanif, Y.M.; Saleem, M. Role of zinc in plant nutrition-a review. Am. J. Experiment Agric. 2013, 3, 374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugano, S.; Kaminaka, H.; Rybka, Z.; Catala, R.; Salinas, J.; Matsui, K.; Ohme-Takagi, M.; Takatsuji, H. Stress-responsive zinc finger gene ZPT2-3 plays a role in drought tolerance in petunia. Plant J. 2003, 36, 830–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Al-Juthery, H.W.; Habeeb, K.H.; Altaee, F.J.K.; AL-Taey, D.K.; Al-Tawaha, A.R.M. Effect of foliar application of different sources of nano-fertilizers on growth and yield of wheat. Biosci. Res. 2018, 4, 3976–3985. [Google Scholar]
- Drostkar, E.; Talebi, R.; Kanouni, H. Foliar application of Fe, Zn and NPK nano-fertilizers on seed yield and morphological traits in chickpea under rainfed condition. J. Res. Ecol. 2016, 4, 221–228. [Google Scholar]
- Mahil, E.I.T.; Kumar, B.A. Foliar application of nanofertilizers in agricultural crops–A review. J. Farm. Sci. 2019, 32, 239–249. [Google Scholar]
- Rossi, L.; Fedenia, L.N.; Sharifan, H.; Ma, X.; Lombardini, L. Effects of foliar application of zinc sulfate and zinc nanoparticles in coffee (Coffea arabica L.) plants. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 135, 160–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Variable | Value |
|---|---|
| Density (kg m−3) | 105 |
| Interpretive levels (m2 g−1) | 40 |
| Purity (%) | 99.8 |
| Diameter (nm) | 6 |
| Particle shape | Spherical |
| Color | Yellowish white |
| Variable | Value |
|---|---|
| Nitrogen (%) | 6 |
| Phosphorus (ppm) | 10.4 |
| Potassium (ppm) | 250 |
| Organic carbon (%) | 0.6 |
| Zn (mg/kg) | 0.19 |
| Fe (mg/kg) | 4.12 |
| Sand (%) | 39 |
| Silt (%) | 35 |
| Clay (%) | 26 |
| Lime T.N.V. | 13 |
| Saturation % (SP) | 43 |
| Electrical conductivity (dSm−1) | 1.1 |
| pH | 7.8 |
| Texture | Loamy clay |
| Depth (cm) | 0–30 |
| Month | Mean Temperature (°C) | Total Rainfall (mm) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2020 | 2021 | 2020 | 2021 | |
| April | 12.6 | 12.4 | 21.8 | 9.6 |
| May | 17.3 | 17.0 | 50.4 | 42.2 |
| June | 21.8 | 22.8 | 2.2 | 3.1 |
| July | 24.9 | 25.9 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| August | 25.0 | 23.9 | 0.3 | 10.0 |
| September | 20.1 | 20.1 | 3.2 | 2.4 |
| Average | 20.3 | 20.4 | 13.0 | 11.2 |
| Source of Variance | BY | CP | SC | SY | 1000 SW |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Replication | 4809.0 ns | 0.12 ns | 0.16 ns | 190.3 ns | 53.0 ** |
| ZnO application | 57,159.8 ** | 1.1 ** | 0.65 ** | 3190.9 ** | 50.2 ns |
| Error | 3559.7 | 0.1 | 0.058 | 65.3 | 51.2 |
| CV (%) | 8.8 | 9.7 | 8.2 | 65.3 | 13.19 |
| ZnO Rate (g L−1) | BY | CP | SC | SY |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 6583 c | 30.81 c | 27.30 c | 1974 d |
| 4 | 6721 b | 34.00 b | 28.89 b | 2007 c |
| 6 | 6806 a | 35.33 a | 30.37 a | 2030 ab |
| 8 | 6827 a | 35.47 a | 31.51 a | 2038 ab |
| 10 | 6833 a | 35.61 a | 32.33 a | 2042 a |
| 12 | 6823 b | 32.23 b | 28.48 b | 2027 b |
| 14 | 6813 b | 32.01 b | 28.39 b | 2024 b |
| Source of Variance | BY | CP | SC | SY | 1000 SW | PH | SD | BP | HI | OY | OC | WUE (SY) | WUE (BY) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R | 2189 ns | 2.0 ns | 1.1 ns | 325.4 ns | 0.1 ns | 7.9 ns | 0.8 ns | 0.1 ns | 0.1 ns | 186.7 ns | 0.22 ns | 0.02 ns | 0.00002 ns |
| I | 3,986,641 ** | 158.6 ** | 429.5 ** | 3088 ** | 56.6 ** | 3798.5 ** | 20.6 ** | 13.4 ** | 7.7 ** | 98,064.7 ** | 47.7 ** | 0.12 ** | 1.16 ** |
| Z | 143,066 ** | 21.0 ** | 17.0 ** | 23,521 ** | 3.8 ns | 133.4 ** | 0.9 ** | 1.1 ** | 0.33 ** | 12,930.8 ** | 10.6 ** | 0.001 ** | 0.009 ** |
| I × Z | 3233 ** | 0.21 ns | 0.1 ns | 650.8 ** | 0.8 ** | 0.18 ns | 0.005 ns | 0.01 ns | 0.32 ** | 166.8 ** | 0.144 ns | 0.0035 ** | 0.0005 ** |
| Error | 760.58 | 0.561 | 0.569 | 141.6 | 0.024 | 4.2 | 0.6 | 0.023 | 0.02 | 35.2 | 0.18 | 0.009 | 0.003 |
| CV (%) | 9.3 | 3.3 | 2.9 | 6.2 | 8.4 | 5.9 | 3.3 | 6.6 | 6.4 | 9.2 | 5.21 | 1.61 | 1.37 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ghiyasi, M.; Rezaee Danesh, Y.; Amirnia, R.; Najafi, S.; Mulet, J.M.; Porcel, R. Foliar Applications of ZnO and Its Nanoparticles Increase Safflower (Carthamus tinctorius L.) Growth and Yield under Water Stress. Agronomy 2023, 13, 192. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13010192
Ghiyasi M, Rezaee Danesh Y, Amirnia R, Najafi S, Mulet JM, Porcel R. Foliar Applications of ZnO and Its Nanoparticles Increase Safflower (Carthamus tinctorius L.) Growth and Yield under Water Stress. Agronomy. 2023; 13(1):192. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13010192
Chicago/Turabian StyleGhiyasi, Mahdi, Younes Rezaee Danesh, Reza Amirnia, Solmaz Najafi, José M. Mulet, and Rosa Porcel. 2023. "Foliar Applications of ZnO and Its Nanoparticles Increase Safflower (Carthamus tinctorius L.) Growth and Yield under Water Stress" Agronomy 13, no. 1: 192. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13010192
APA StyleGhiyasi, M., Rezaee Danesh, Y., Amirnia, R., Najafi, S., Mulet, J. M., & Porcel, R. (2023). Foliar Applications of ZnO and Its Nanoparticles Increase Safflower (Carthamus tinctorius L.) Growth and Yield under Water Stress. Agronomy, 13(1), 192. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13010192







