Identification of the bZIP Gene Family and Investigation of Their Response to Drought Stress in Dendrobium catenatum
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Identification of the bZIP Family Members of D. catenatum
2.2. Phylogenetic Analysis of bZIP Proteins
2.3. Analysis of Gene Structure, Conserved Motifs, and Promoter Cis-Regulatory Elements
2.4. Spatial Expression Profile Analysis Using RNA-Seq Data
2.5. Stress Treatments
2.6. Gene Expression Analysis under Drought Treatment
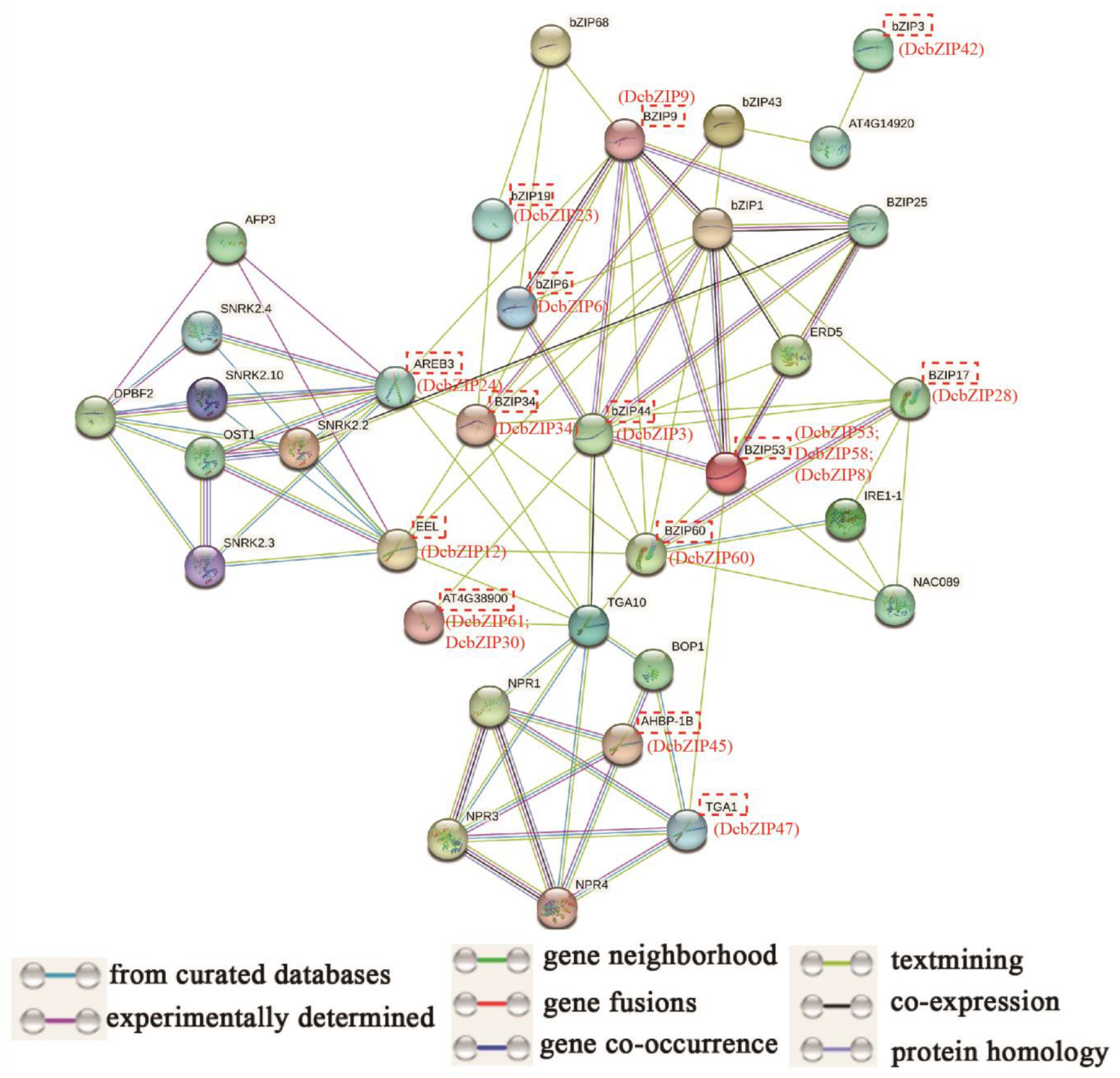
2.7. Analysis of Co-Expression and Protein–Protein Interaction Networks of DcbZIP Proteins
3. Results
3.1. Identification and Physicochemical Properties of bZIP Family in D. catenatum
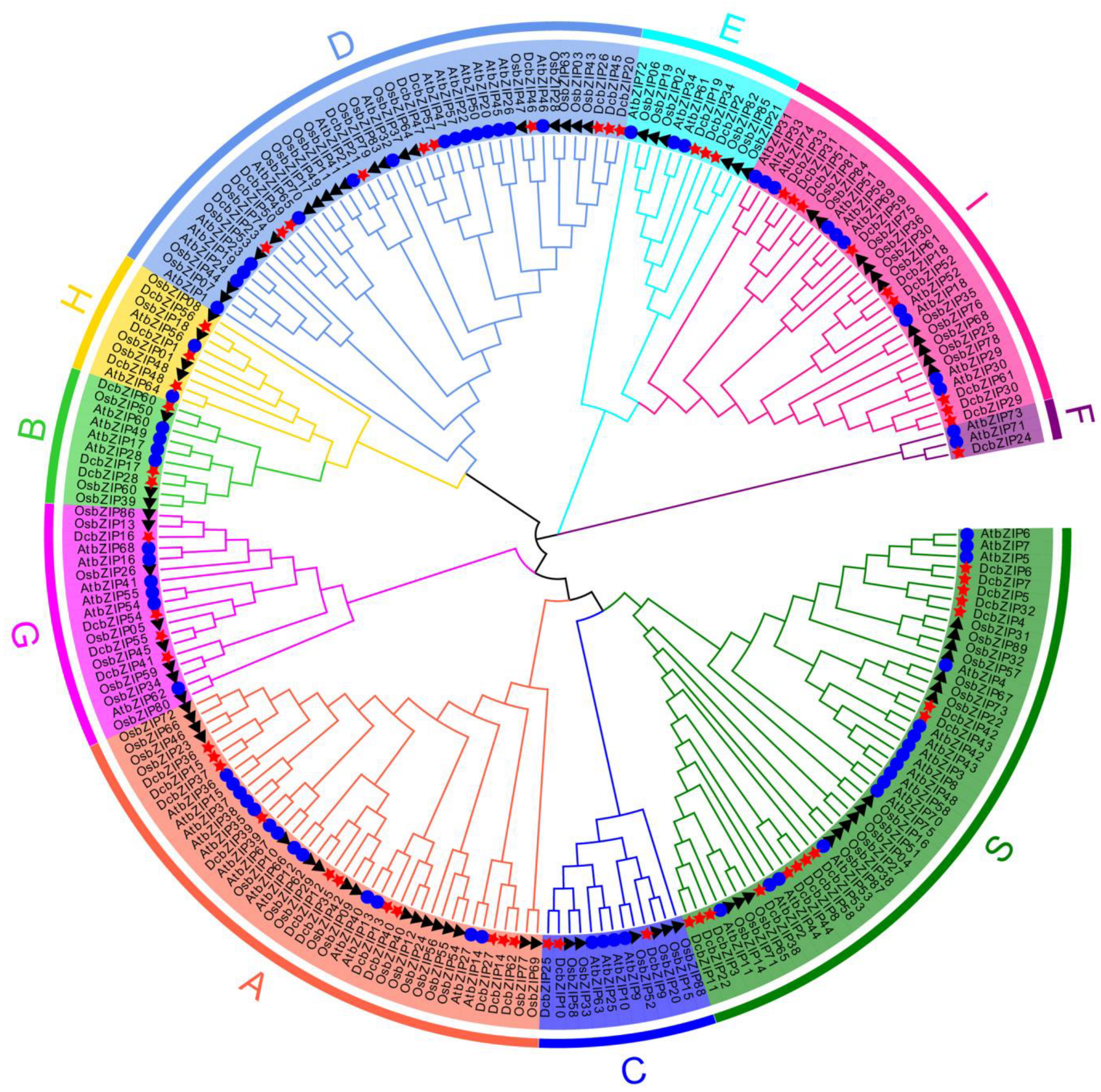
3.2. Phylogenetic Analysis of bZIP Proteins
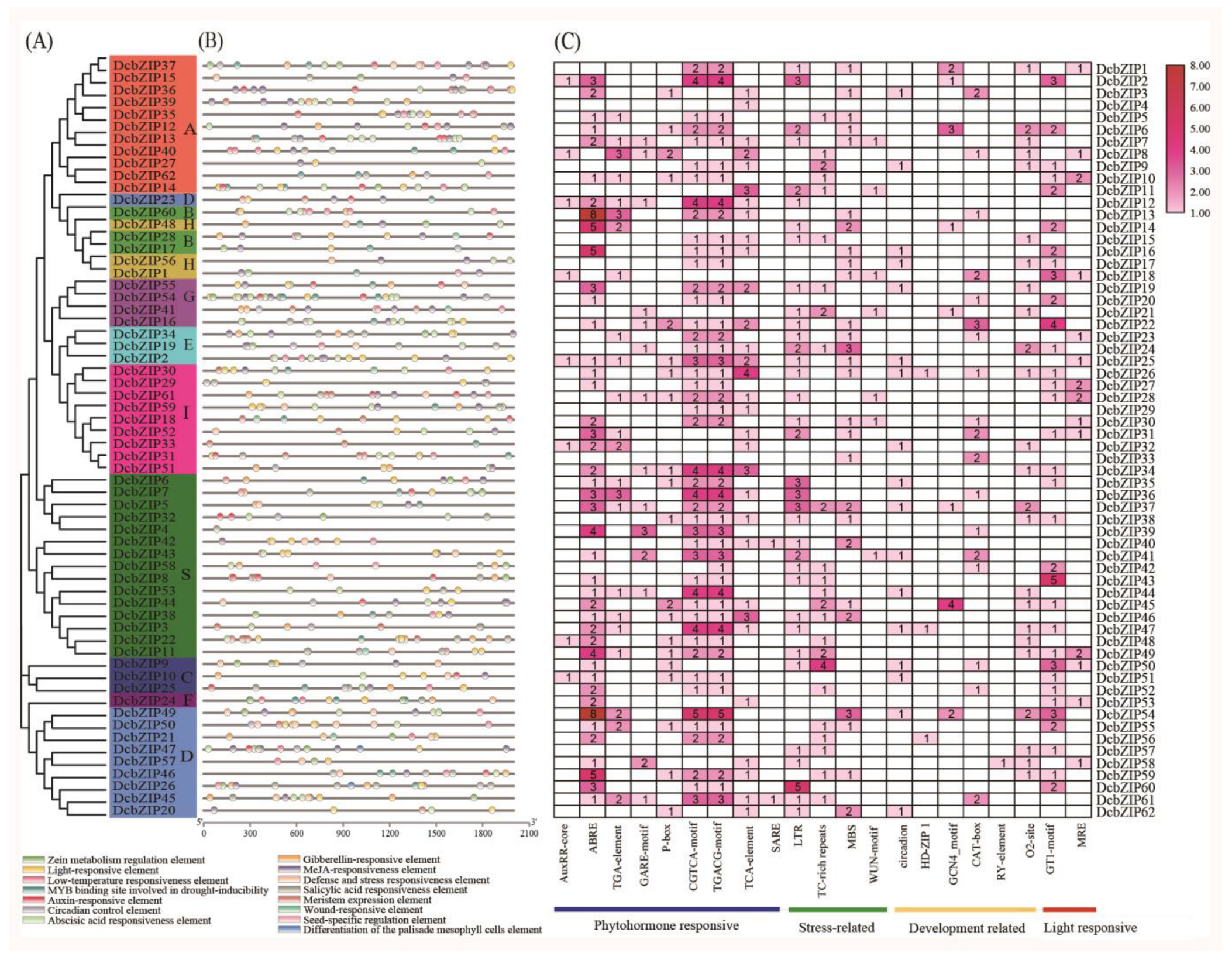
3.3. Conserved Motif and Gene Structure of bZIP Family Genes
3.4. Cis-Element Analysis of bZIP Gene Promoters in D. catenatum
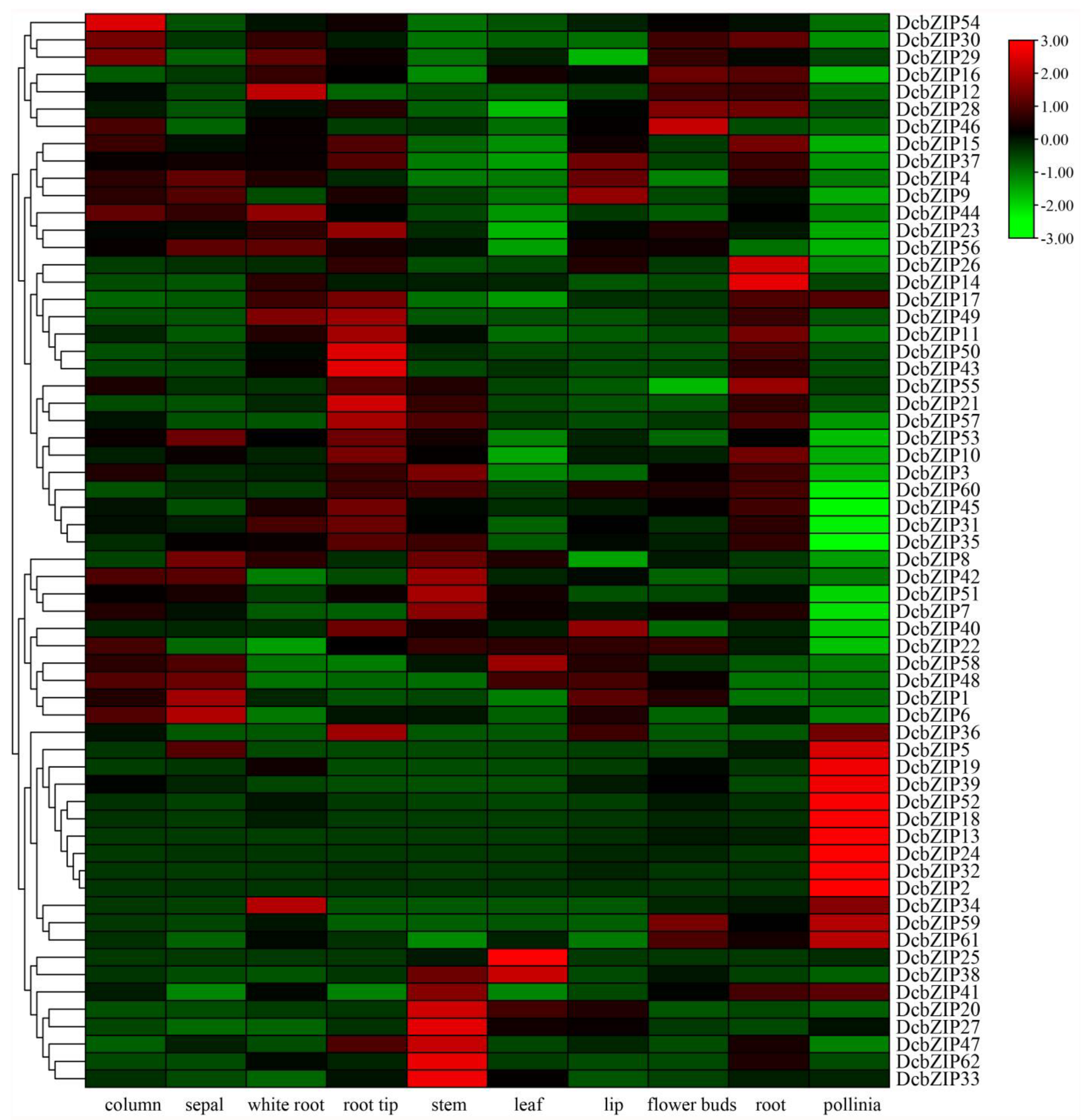
3.5. Tissue-Specific Expression Profile of DcbZIP Gene Based on RNA-Seq
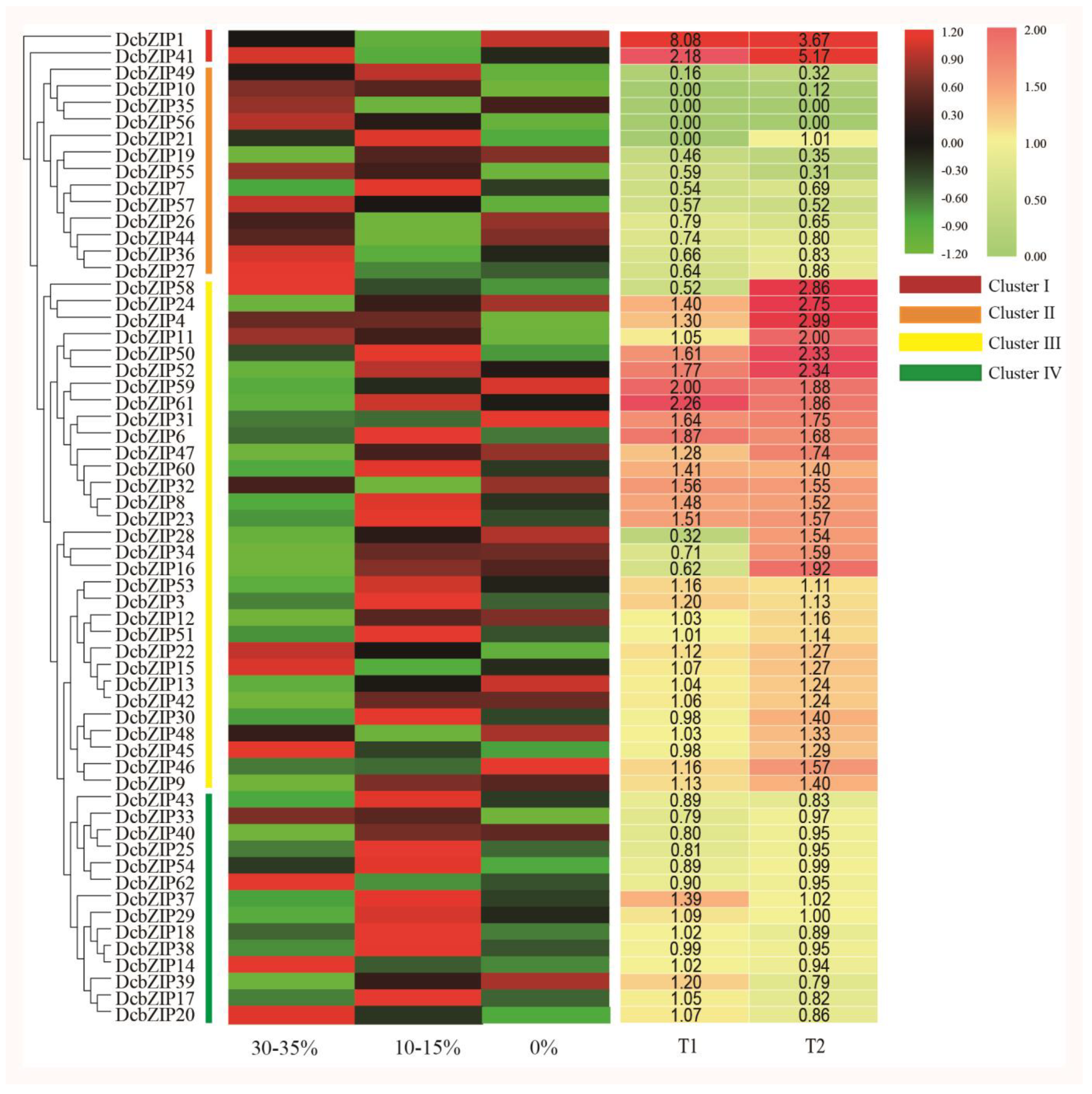
3.6. DcbZIP Gene Expression under Drought Stress Based on RNA-Seq
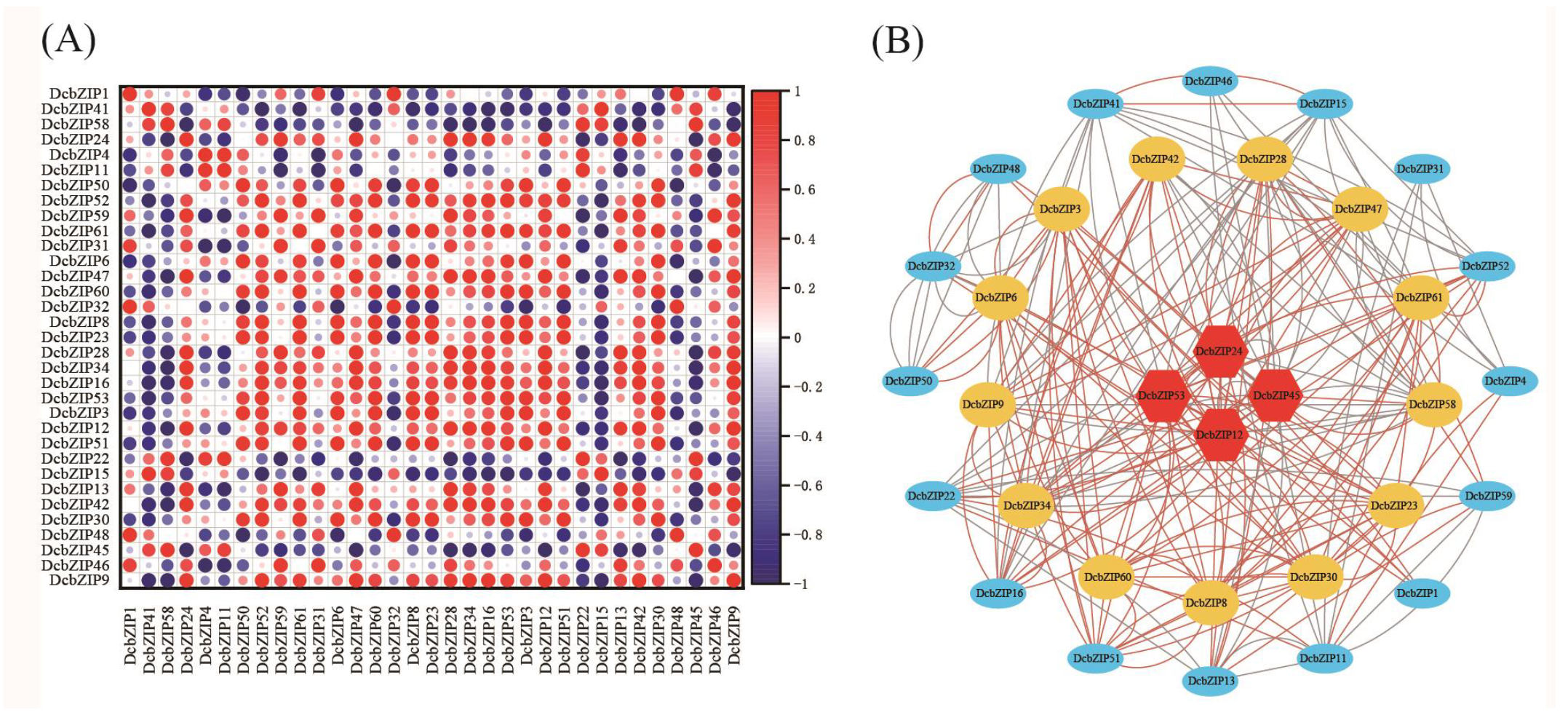
3.7. Analysis of Drought-Related DcbZIP Genes
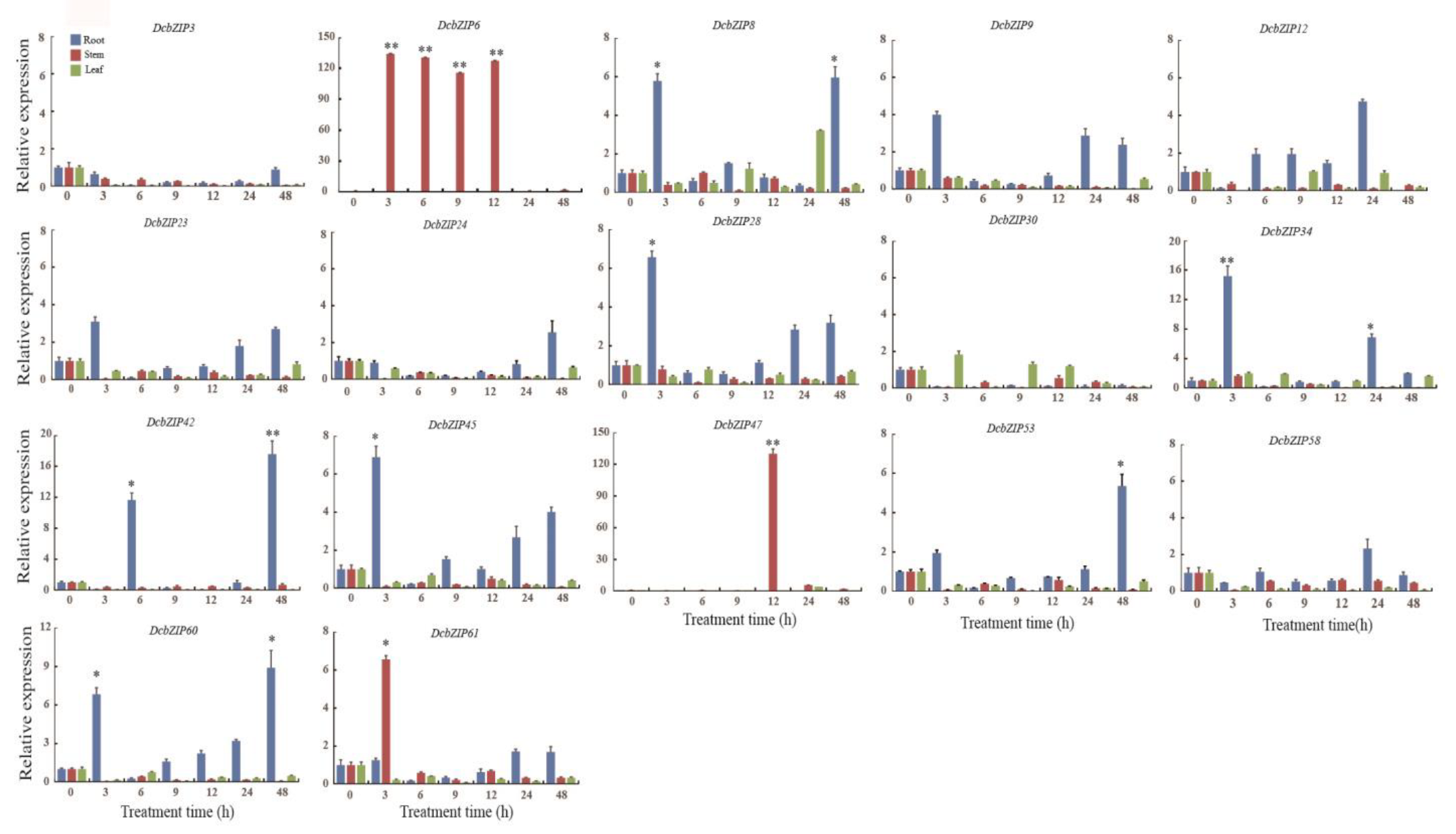
3.8. Expression Profile Analysis of 17 Core DcbZIP Genes under Drought Stress Using RT-qPCR
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Izawa, T.; Foster, R.; Chua, N.H. Plant bZIP protein DNA binding specificity. J. Mol. Biol. 1993, 230, 1131–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasuga, M.; Liu, Q.; Miura, S.; Yamaguchi-Shinozaki, K.; Shinozaki, K. Improving plant drought, salt, and freezing tolerance by gene transfer of a single stress-inducible transcription factor. Nat. Biotechnol. 1999, 17, 287–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Rodríguez, P.; Riaño-Pachón, D.M.; Corrêa, L.G.; Rensing, S.A.; Kersten, B.; Mueller-Roeber, B. PlnTFDB: Updated content and new features of the plant transcription factor database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, D822–D827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Riechmann, J.L.; Heard, J.; Martin, G.; Reuber, L.; Jiang, C.; Keddie, J.; Adam, L.; Pineda, O.; Ratcliffe, O.J.; Samaha, R.R.; et al. Arabidopsis transcription factors: Genome-wide comparative analysis among eukaryotes. Science 2000, 290, 2105–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jakoby, M.; Weisshaar, B.; Dröge-Laser, W.; Vicente-Carbajosa, J.; Tiedemann, J.; Kroj, T.; Parcy, F. bZIP transcription factors in Arabidopsis. Trends Plant Sci. 2002, 7, 106–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsieh, W.P.; Hsieh, H.L.; Wu, S.H. Arabidopsis bZIP16 transcription factor integrates light and hormone signaling pathways to regulate early seedling development. Plant Cell 2012, 24, 3997–4011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yoshida, T.; Fujita, Y.; Sayama, H.; Kidokoro, S.; Maruyama, K.; Mizoi, J.; Shinozaki, K.; Yamaguchi-Shinozaki, K. AREB1, AREB2, and ABF3 are master transcription factors that cooperatively regulate ABRE-dependent ABA signaling involved in drought stress tolerance and require ABA for full activation. Plant J. 2010, 61, 672–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, F.; Maeta, E.; Terashima, A.; Takumi, S. Positive role of a wheat HvABI5 ortholog in abiotic stress response of seedlings. Physiol. Plant 2008, 134, 74–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, S.C.; Choi, H.W.; Hwang, I.S.; Choi, D.S.; Hwang, B.K. Functional roles of the pepper pathogen-induced bZIP transcription factor, CAbZIP1, in enhanced resistance to pathogen infection and environmental stresses. Planta 2006, 224, 1209–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leite, J.P.; Barbosa, E.G.; Marin, S.R.; Marinho, J.P.; Carvalho, J.F.; Pagliarini, R.F.; Cruz, A.S.; Oliveira, M.C.; Farias, J.R.; Neumaier, N.; et al. Overexpression of the activated form of the AtAREB1 gene (AtAREB1ΔQT) improves soybean responses to water deficit. Genet. Mol. Res. 2014, 13, 6272–6286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landschulz, W.H.; Johnson, P.F.; McKnight, S.L. The leucine zipper: A hypothetical structure common to a new class of DNA binding proteins. Science 1988, 240, 1759–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ellenberger, T.E.; Brandl, C.J.; Struhl, K.; Harrison, S.C. The GCN4 basic region leucine zipper binds DNA as a dimer of uninterrupted alpha helices: Crystal structure of the protein-DNA complex. Cell 1992, 71, 1223–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corrêa, L.G.; Riaño-Pachón, D.M.; Schrago, C.G.; dos Santos, R.V.; Mueller-Roeber, B.; Vincentz, M. The role of bZIP transcription factors in green plant evolution: Adaptive features emerging from four founder genes. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e2944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Chen, N.; Chen, F.; Cai, B.; Santo, S.D.; Tornielli, G.B.; Pezzotti, M.; Cheng, Z.M. Genome-wide analysis and expression profile of the bZIP transcription factor gene family in grapevine (Vitis vinifera). BMC Genom. 2014, 13, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baloglu, M.C.; Eldem, V.; Hajyzadeh, M.; Unver, T. Genome-wide analysis of the bZIP transcription factors in cucumber. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e96014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, M.; Liu, Y.; Shi, H.; Guo, M.; Chai, M.; He, Q.; Yan, M.; Cao, D.; Zhao, L.; Cai, H.; et al. Evolutionary and expression analyses of soybean basic Leucine zipper transcription factor family. BMC Genom. 2018, 19, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, Z.; Sun, J.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, P.; Zhang, L.; Wu, S.; Ma, D.; Cao, Q.; Li, Z.; Xu, T. Genome-wide identification, structural and gene expression analysis of the bZIP transcription factor family in sweet potato wild relative Ipomoea trifida. BMC Genet. 2019, 20, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, L.; Yarra, R. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of bZIP transcription factors in oil palm (Elaeis guineensis Jacq.) under abiotic stress. Protoplasma 2022, 259, 469–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Zhang, Y.X.; Wang, Q.; Tao, X.Y.; Fang, J.; Zheng, W.J.; Zhu, L.W.; Jia, B.; Heng, W.; Li, S.W. Identification of bZIP transcription factors and their responses to brown spot in pear. Genet. Mol. Biol. 2022, 45, e20210175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Yu, H.; Cao, P.B.; Fawal, N.; Mathé, C.; Azar, S.; Cassan-Wang, H.; Myburg, A.A.; Grima-Pettenati, J.; Marque, C.; et al. Explosive tandem and segmental duplications of multigenic families in Eucalyptus grandis. Genome Biol. Evol. 2015, 7, 1068–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, W.; Tang, N.; Yang, J.; Peng, L.; Ma, S.; Xu, Y.; Li, G.; Xiong, L. Feedback regulation of ABA signaling and biosynthesis by a bZIP transcription factor targets drought-resistance-related genes. Plant Physiol. 2016, 171, 2810–2825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, C.; Mao, B.; Ou, S.; Wang, W.; Liu, L.; Wu, Y.; Chu, C.; Wang, X. OsbZIP71, a bZIP transcription factor, confers salinity and drought tolerance in rice. Plant Mol. Biol. 2014, 84, 19–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Schlappi, M.R.; Mao, B.; Wang, W.; Wang, A.; Chu, C.C. The bZIP73 transcription factor controls rice cold tolerance at the reproductive stage. Plant Biotech. J. 2019, 17, 1834–1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, Y.; Yu, T.F.; Ma, J.; Chen, J.; Zhou, Y.B.; Chen, M.; Ma, Y.Z.; Wei, W.L.; Xu, Z.S. The soybean bZIP transcription factor gene GmbZIP2 confers drought and salt resistances in transgenic plants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, M.; Liu, Y.; Cai, H.; Guo, M.; Chai, M.; She, Z.; Ye, L.; Cheng, Y.; Wang, B.; Qin, Y. The bZIP transcription factor GmbZIP15 negatively regulates salt- and drought-stress responses in soybean. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.Y.; Meng, D.; Li, M.J.; Cheng, L.I. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of the bZIP gene family in apple (Malus domestica). Tree Genet. Genomes 2016, 12, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhu, J.; Li, X.; Wang, S.; Wu, J. Salt and drought stress and ABA responses related to bZIP genes from V. radiata and V. angularis. Gene 2018, 651, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, X.; Chen, J.; Zhang, J.; Liao, Y.; Dai, L.; Wang, B.; Liu, L.; Peng, D. Transcriptome profiling and identification of transcription factors in ramie (Boehmeria nivea L. Gaud) in response to PEG treatment, using illumina paired-end sequencing technology. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 3493–3511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zotz, G.; Winkler, U. Aerial roots of epiphytic orchids: The velamen radicum and its role in water and nutrient uptake. Oecologia 2013, 171, 733–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, L.H.; Wan, X.; Deng, H.; Zheng, B.Q.; Li, B.J.; Wang, Y. Data descriptor: RNA-seq transcriptomic profiling of crassulacean acid metabolism pathway in Dendrobium catenatum. Sci. Data 2018, 5, 180252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A. Effects of bionic cultivation modes on yield and quality of Dendrobium officinale. J. Anhui Sci. Technol. Univ. 2022, 36, 44–48. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.T.; Cui, Z.; Li, Y.X.; Kang, Y.Q.; Song, X.Q.; Wang, J.; Zhou, Y. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of MYB transcription factor superfamily in Dendrobium catenatum. Front. Genet. 2021, 26, 714696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.T.; Xu, Y.; Ding, Y.D.; Yu, W.G.; Wang, J.; Lai, H.G.; Zhou, Y. Identification and expression analysis of WRKY gene family in response to abiotic stress in Dendrobium catenatum. Front. Genet. 2022, 3, 800019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.X.; Zhang, T.T.; Xing, W.T.; Wang, J.; Yu, W.G.; Zhou, Y. Comprehensive genomic characterization of the NAC transcription factors and their response to drought stress in Dendrobium catenatum. Agronomy 2022, 12, 2753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.Q.; Xu, Q.; Bian, C.; Tsai, W.C.; Yeh, C.M.; Liu, K.W.; Yoshida, K.; Zhang, L.S.; Chang, S.B.; Chen, F.; et al. The Dendrobium catenatum Lindl. genome sequence provides insights into polysaccharide synthase, floral development and adaptive evolution. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 19029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salih, H.; Gong, W.; He, S.; Sun, G.; Sun, J.; Du, X. Genome-wide characterization and expression analysis of MYB transcription factors in Gossypium hirsutum. BMC Genet. 2016, 17, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Chai, M.; Zhang, M.; He, Q.; Su, Z.; Priyadarshani, S.V.G.N.; Liu, L.; Dong, G.; Qin, Y. Genome-wide analysis, characterization, and expression profile of the basic leucine zipper transcription factor family in pineapple. Int. J. Genom. 2020, 2020, 3165958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Thomas, H.R.; Frank, M.H.; He, Y.; Xia, R. TBtools: An integrative toolkit developed for interactive analyses of big biological data. Mol. Plant 2020, 13, 1194–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bray, N.L.; Pimentel, H.; Melsted, P.; Pachter, L. Near-optimal probabilistic RNA-seq quantification. Nat. Biotechnol. 2016, 34, 525–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, X.; Zou, L.H.; Zheng, B.Q.; Tian, Y.Q.; Wang, Y. Transcriptomic profiling for prolonged drought in Dendrobium catenatum. Sci. Data 2018, 5, 180233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, P.; Markiel, A.; Ozier, O.; Baliga, N.S.; Wang, J.T.; Ramage, D.; Amin, N.; Schwikowski, B.; Ideker, T. Cytoscape: A software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks. Genome Res. 2003, 13, 2498–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seifert, E. OriginPro 9.1: Scientific data analysis and graphing software-software review. J. Chem. Inf. Model 2014, 54, 1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szklarczyk, D.; Gable, A.L.; Lyon, D.; Junge, A.; Wyder, S.; Huerta-Cepas, J.; Simonovic, M.; Doncheva, N.T.; Morris, J.H.; Bork, P.; et al. STRING v11: Protein-protein association networks with increased coverage, supporting functional discovery in genome-wide experimental datasets. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D607–D613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nijhawan, A.; Jain, M.; Tyagi, A.K.; Khurana, J.P. Genomic survey and gene expression analysis of the basic leucine zipper transcription factor family in rice. Plant Physiol. 2008, 146, 333–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Malik, W.A.; Afzal, M.; Chen, X.; Cui, R.; Lu, X.; Wang, S.; Wang, J.; Mahmood, I.; Ye, W. Systematic analysis and comparison of ABC proteins superfamily confer structural, functional and evolutionary insights into four cotton species. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2021, 177, 114433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, C.F.; Running, M.P.; Williams, R.W.; Meyerowitz, E.M. The PERIANTHIA gene encodes a bZIP protein involved in the determination of floral organ number in Arabidopsis thaliana. Genes Dev. 1999, 13, 334–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hörberg, J.; Reymer, A. Specifically bound BZIP transcription factors modulate DNA supercoiling transitions. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 18795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Ye, M.; Wang, R.; Wang, D.; Chen, Q. Systematic identification and functional analysis of potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) bZIP transcription factors and overexpression of potato bZIP transcription factor StbZIP-65 enhances salt tolerance. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 15, 155–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, B.; Vanitha, J.; Ramachandran, S.; Jiang, S.Y. Genome-wide expansion and expression divergence of the basic leucine zipper transcription factors in higher plants with an emphasis on sorghum. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2011, 53, 212–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourabed, E.; Golmohamadi, F.G.; Monfared, P.S.; Razavi, S.M.; Shobbar, Z.S. Basic leucine zipper family in barley: Genome-wide characterization of members and expression analysis. Mol. Biotechnol. 2015, 57, 12–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, K.; Chen, J.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Chen, S.; Lin, Y.; Pan, S.; Zhong, X.; Xie, D. Genome-wide analysis of bZIP-encoding genes in maize. DNA Res. 2012, 19, 463–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, Y.; Xu, D.; Jia, L.; Huang, X.; Ma, G.; Wang, S.; Zhu, M.; Zhang, A.; Guan, M.; Lu, K.; et al. Genome-wide identification and structural analysis of bZIP transcription factor genes in Brassica napus. Genes 2017, 8, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, M.; Wang, Z.; Ren, W.; Yan, S.; Xing, N.; Zhang, Z.; Li, H.; Ma, W. Identification of the bZIP gene family and regulation of metabolites under salt stress in Isatis indigotica. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 1011616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manzoor, M.A.; Manzoor, M.M.; Li, G.; Abdullah, M.; Han, W.; Wenlong, H.; Shakoor, A.; Riaz, M.W.; Rehman, S.; Cai, Y. Genome-wide identification and characterization of bZIP transcription factors and their expression profile under abiotic stresses in Chinese pear (Pyrus bretschneideri). BMC Plant Biol. 2021, 21, 413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Li, J.; Li, H.; Yang, Y.; Guang, Y.; Zhou, Y. The bZIP gene family in watermelon: Genome-wide identification and expression analysis under cold stress and root-knot nematode infection. PeerJ 2019, 7, e7878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, W.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Xie, K.; Zhang, C.; Xi, Y.; Sun, F. Genome-wide analysis of the abiotic stress-related bZIP family in switchgrass. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2020, 47, 4439–4454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Ye, S.; Du, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Du, J.; Zhang, Q. Identification and expression analysis of bZIP members under abiotic stress in mung bean (Vigna radiata). Life 2022, 12, 938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.; Hong, J.; Ha, J.; Kang, J.; Kim, S.Y. ABFs, a family of ABA-responsive element binding factors. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 1723–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Finkelstein, R.R.; Lynch, T.J. The Arabidopsis abscisic acid response gene ABI5 encodes a basic leucine zipper transcription factor. Plant Cell 2000, 12, 599–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lopez-Molina, L.; Mongrand, S.; Chua, N.H. A postgermination developmental arrest checkpoint is mediated by abscisic acid and requires the ABI5 transcription factor in Arabidopsis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 4782–4787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wellmer, F.; Schäfer, E.; Harter, K. The DNA binding properties of the parsley bZIP transcription factor CPRF4a are regulated by light. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 6274–6279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chattopadhyay, S.; Ang, L.H.; Puente, P.; Deng, X.W.; Wei, N. Arabidopsis bZIP protein HY5 directly interacts with light-responsive promoters in mediating light control of gene expression. Plant Cell 1998, 10, 673–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Gao, W.; Li, H.; Wang, Y.; Li, D.; Xue, C.; Liu, Z.; Liu, M.; Zhao, J. Genome-wide analysis of the bZIP gene family in Chinese jujube (Ziziphus jujuba Mill.). BMC Genom. 2020, 21, 483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Zeng, L.; Chen, R.; Wang, Y.; Song, J. Genome-wide identification and characterization of stress-associated protein (SAP) gene family encoding A20/AN1 zinc-finger proteins in Medicago truncatula. Arch. Biol. Sci. 2018, 70, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Wang, L.; Tie, W.; Yan, Y.; Ding, Z.; Liu, J.; Li, M.; Peng, M.; Xu, B.; Jin, Z. Genome-wide analyses of the bZIP family reveal their involvement in the development, ripening and abiotic stress response in banana. Sci. Rep. 2016, 22, 30203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jin, Z.; Xu, W.; Liu, A. Genomic surveys and expression analysis of bZIP gene family in castor bean (Ricinus communis L.). Planta 2014, 239, 299–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sornaraj, P.; Luang, S.; Lopato, S.; Hrmova, M. Basic leucine zipper (bZIP) transcription factors involved in abiotic stresses: A molecular model of a wheat bZIP factor and implications of its structure in function. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2016, 1860, 46–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujita, Y.; Yoshida, T.; Yamaguchi-Shinozaki, K. Pivotal role of the AREB/ABF-SnRK2 pathway in ABRE-mediated transcription in response to osmotic stress in plants. Physiol. Plant 2013, 147, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.X.; Srivastava, R.; Che, P.; Howell, S.H. Salt stress responses in Arabidopsis utilize a signal transduction pathway related to endoplasmic reticulum stress signaling. Plant J. 2007, 51, 897–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Z.; Chen, X.; Guan, X.; Liu, Y.; Chen, H.; Wang, T.; Mouekouba, L.D.; Li, J.; Wang, A. A genome-wide survey of homeodomain-leucine zipper genes and analysis of cold-responsive HD-Zip I members’ expression in tomato. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2014, 78, 1337–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, M.M.; Bhaskara, G.B.; Wen, T.N.; Lin, W.D.; Nguyen, T.T.; Chong, G.L.; Verslues, P.E. Phosphoproteomics of Arabidopsis highly ABA-induced 1 identifies AT-Hook-Like10 phosphorylation required for stress growth regulation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 2354–2363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Danquah, A.; de Zelicourt, A.; Colcombet, J.; Hirt, H. The role of ABA and MAPK signaling pathways in plant abiotic stress responses. Biotechnol. Adv. 2014, 32, 40–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.Y.; Zhang, C.B.; Zhu, Q.W.; Guo, F.; Chai, R.; Wang, M.X.; Deng, X.Y.; Dong, T.T.; Meng, X.Q.; Zhu, M.K. Genome-and transcriptome-wide systematic characterization of bZIP transcription factor family identifies promising members involved in abiotic stress response in sweetpotato. Sci. Hortic. 2022, 303, 111185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Li, Y.; Cai, H.; Bai, X.; Ji, W.; Ding, X.; Zhu, Y. The Arabidopsis AtbZIP1 transcription factor is a positive regulator of plant tolerance to salt, osmotic and drought stresses. J. Plant. Res. 2012, 125, 429–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Gene Name | Gene ID | Locus | Length | MW(kDa) | pI | Subcellular Localization | Group |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DcbZIP1 | LOC110102063 | NW_021318745.1:471271…486572 | 153 | 16.97 | 9.98 | nuclear | H |
| DcbZIP2 | LOC110094784 | NW_021319121.1:1711930…1713378 | 254 | 28.36 | 6.6 | nuclear | E |
| DcbZIP3 | LOC110115573 | NW_021320155.1:215…1462 | 155 | 17.66 | 9.03 | nuclear | S |
| DcbZIP4 | LOC110112903 | NW_021359921.1: 258…816 | 138 | 15.59 | 11.53 | nuclear | S |
| DcbZIP5 | LOC110095238 | NW_021319911.1:476590…477012 | 140 | 15.67 | 11.58 | nuclear | S |
| DcbZIP6 | LOC110113945 | NW_021318751.1:434550…435351 | 146 | 16.76 | 10.47 | nuclear | S |
| DcbZIP7 | LOC110114248 | NW_021318952.1:1141827…1142966 | 149 | 17.16 | 11.09 | nuclear | S |
| DcbZIP8 | LOC110109372 | NW_021318890.1:45595…46690 | 130 | 15.24 | 8.49 | nuclear | S |
| DcbZIP9 | LOC110095100 | NW_021319641.1:962641…966712 | 356 | 38.76 | 5.18 | nuclear | C |
| DcbZIP10 | LOC110099409 | NW_021319484.1:1588342…1604864 | 311 | 34.37 | 5.57 | nuclear | C |
| DcbZIP11 | LOC110116565 | NW_021394673.1:450792…454576 | 317 | 35.95 | 6.49 | mitochondrial | S |
| DcbZIP12 | LOC110098756 | NW_021319202.1:1038678…1046470 | 338 | 38.28 | 9.30 | nuclear | A |
| DcbZIP13 | LOC110100055 | NW_021319455.1:997836…1000675 | 222 | 24.82 | 5.91 | nuclear | A |
| DcbZIP14 | LOC110112185 | NW_021318640.1:185732…187053 | 265 | 28.71 | 9.30 | mitochondrial | A |
| DcbZIP15 | LOC110115326 | NW_021319048.1:847890…872251 | 406 | 42.69 | 9.13 | cytoplasmic | A |
| DcbZIP16 | LOC110096541 | NW_021319431.1:31825…50187 | 409 | 43.33 | 6.33 | nuclear | G |
| DcbZIP17 | LOC110099255 | NW_021319682.1:13603178…13607863 | 683 | 74.16 | 6.38 | nuclear | B |
| DcbZIP18 | LOC110104466 | NW_021319842.1:67813…111270 | 398 | 43.50 | 6.16 | nuclear | I |
| DcbZIP19 | LOC110116528 | NW_021319455.1:2008465…2012390 | 259 | 28.90 | 6.41 | nuclear | E |
| DcbZIP20 | LOC110113515 | NW_021320183.1:270501…301718 | 466 | 51.39 | 6.36 | nuclear | D |
| DcbZIP21 | LOC110096667 | NW_021319983.1:403141…412564 | 489 | 54.63 | 5.71 | nuclear | D |
| DcbZIP22 | LOC110113543 | NW_021320019.1:9020891…9022087 | 167 | 18.71 | 8.66 | nuclear | S |
| DcbZIP23 | LOC110102116 | NW_021318705.1:1911115…1924234 | 273 | 29.49 | 5.94 | nuclear | D |
| DcbZIP24 | LOC110110500 | NW_021319360.1:1021557…1023609 | 321 | 36.95 | 5.29 | nuclear | F |
| DcbZIP25 | LOC110109220 | NW_021319982.1:676693…690196 | 362 | 39.53 | 5.89 | nuclear | C |
| DcbZIP26 | LOC110091873 | NW_021319588.1:431917…450124 | 427 | 47.22 | 6.82 | nuclear | D |
| DcbZIP27 | LOC110102106 | NW_021318705.1:1988364…1989735 | 162 | 18.00 | 9.76 | nuclear | A |
| DcbZIP28 | LOC110096161 | NW_021318623.1:23442…27784 | 692 | 74.94 | 6.08 | nuclear | B |
| DcbZIP29 | LOC110116680 | NW_021319255.1:1051643…1056686 | 542 | 59.41 | 6.21 | nuclear | I |
| DcbZIP30 | LOC110099156 | NW_021318726.1:1712729…1719118 | 522 | 56.71 | 6.21 | nuclear | I |
| DcbZIP31 | LOC110102661 | NW_021319579.1:559884…583214 | 350 | 38.19 | 6.88 | nuclear | I |
| DcbZIP32 | LOC110106152 | NW_021318595.1:5943723…5946939 | 226 | 25.65 | 11.36 | nuclear | S |
| DcbZIP33 | LOC110096611 | NW_021319126.1:383344…398145 | 339 | 37.15 | 6.13 | nuclear | I |
| DcbZIP34 | LOC110103109 | NW_021320146.1:675175…678827 | 319 | 34.65 | 5.90 | nuclear | E |
| DcbZIP35 | LOC110098225 | NW_021318839.1:350918…367871 | 311 | 34.83 | 9.50 | nuclear | A |
| DcbZIP36 | LOC110092531 | NW_021318711.1:1796647…1806328 | 396 | 42.68 | 9.19 | nuclear | A |
| DcbZIP37 | LOC110109339 | NW_021318998.1:251776…260296 | 407 | 43.50 | 7.70 | nuclear | A |
| DcbZIP38 | LOC110097322 | NW_021319772.1:217773…219884 | 141 | 15.69 | 7.65 | nuclear | S |
| DcbZIP39 | LOC110114883 | NW_021318595.1:12862132…12864684 | 357 | 38.96 | 7.60 | nuclear | A |
| DcbZIP40 | LOC110107968 | NW_021319536.1:408463…445084 | 277 | 30.19 | 5.19 | nuclear | A |
| DcbZIP41 | LOC110095320 | NW_021318963.1:1120306…1130172 | 359 | 38.07 | 7.11 | nuclear | G |
| DcbZIP42 | LOC110094070 | NW_021318618.1:1794449…1795054 | 159 | 18.31 | 7.07 | nuclear | S |
| DcbZIP43 | LOC110109278 | NW_021416702.1:86653…87395 | 183 | 21.41 | 6.72 | nuclear | S |
| DcbZIP44 | LOC110099470 | NW_021318619.1:750999…751924 | 132 | 15.65 | 10.09 | nuclear | S |
| DcbZIP45 | LOC110110747 | NW_021318796.1:2352740…2370581 | 427 | 47.26 | 8.46 | nuclear | D |
| DcbZIP46 | LOC110094737 | NW_021319121.1:686641…695563 | 365 | 40.63 | 7.06 | nuclear | D |
| DcbZIP47 | LOC110110388 | NW_021319315.1:2104944…2125602 | 381 | 42.91 | 7.68 | nuclear | D |
| DcbZIP48 | LOC110094083 | NW_021318700.1:245031…246643 | 146 | 16.34 | 8.71 | nuclear | H |
| DcbZIP49 | LOC110091793 | NW_021318565.1:363970…370844 | 447 | 50.01 | 7.32 | nuclear | D |
| DcbZIP50 | LOC110112805 | NW_021318937.1:66248…73259 | 433 | 48.47 | 7.75 | nuclear | D |
| DcbZIP51 | LOC110105751 | NW_021318677.1:122368…135356 | 341 | 37.24 | 6.22 | nuclear | I |
| DcbZIP52 | LOC110114853 | NW_021319083.1:8027963…8050443 | 394 | 42.69 | 5.44 | nuclear | I |
| DcbZIP53 | LOC110099371 | NW_021319442.1:514414…515591 | 143 | 16.69 | 8.85 | nuclear | S |
| DcbZIP54 | LOC110109693 | NW_021378092.1:460796…469115 | 386 | 41.58 | 5.14 | nuclear | G |
| DcbZIP55 | LOC110094315 | NW_021319161.1:846164…858315 | 269 | 30.97 | 8.75 | nuclear | G |
| DcbZIP56 | LOC110101858 | NW_021319436.1:2509122…2519085 | 161 | 18.07 | 9.44 | nuclear | H |
| DcbZIP57 | LOC110111774 | NW_021318920.1:351221…358735 | 369 | 41.59 | 5.68 | nuclear | D |
| DcbZIP58 | LOC110100891 | NW_021318787.1:716526…717410 | 130 | 15.24 | 8.49 | nuclear | S |
| DcbZIP59 | LOC110095296 | NW_021319910.1:646885…655651 | 401 | 44.12 | 5.79 | nuclear | I |
| DcbZIP60 | LOC110113665 | NW_021324968.1:31584…34398 | 335 | 37.95 | 5.13 | nuclear | B |
| DcbZIP61 | LOC110101931 | NW_021319436.1:1660963…1677531 | 361 | 39.45 | 8.47 | nuclear | I |
| DcbZIP62 | LOC110106828 | NW_021319013.1:318529…320289 | 273 | 29.15 | 9.73 | nuclear | A |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, P.; Li, Y.; Zhang, T.; Kang, Y.; Li, W.; Wang, J.; Yu, W.; Zhou, Y. Identification of the bZIP Gene Family and Investigation of Their Response to Drought Stress in Dendrobium catenatum. Agronomy 2023, 13, 236. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13010236
Wang P, Li Y, Zhang T, Kang Y, Li W, Wang J, Yu W, Zhou Y. Identification of the bZIP Gene Family and Investigation of Their Response to Drought Stress in Dendrobium catenatum. Agronomy. 2023; 13(1):236. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13010236
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Peng, Yuxin Li, Tingting Zhang, Yuqian Kang, Wei Li, Jian Wang, Wengang Yu, and Yang Zhou. 2023. "Identification of the bZIP Gene Family and Investigation of Their Response to Drought Stress in Dendrobium catenatum" Agronomy 13, no. 1: 236. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13010236
APA StyleWang, P., Li, Y., Zhang, T., Kang, Y., Li, W., Wang, J., Yu, W., & Zhou, Y. (2023). Identification of the bZIP Gene Family and Investigation of Their Response to Drought Stress in Dendrobium catenatum. Agronomy, 13(1), 236. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13010236








