Deficiencies of Secondary Nutrients in Crop Plants—A Real Challenge to Improve Nitrogen Management
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Uptake and Accumulation of Calcium and Magnesium by Crop Plants
- (1)
- The low content of available nutrients in the soil rooting zone. This is typical for sandy soils and in regions of the world with high precipitation [40];
- (2)
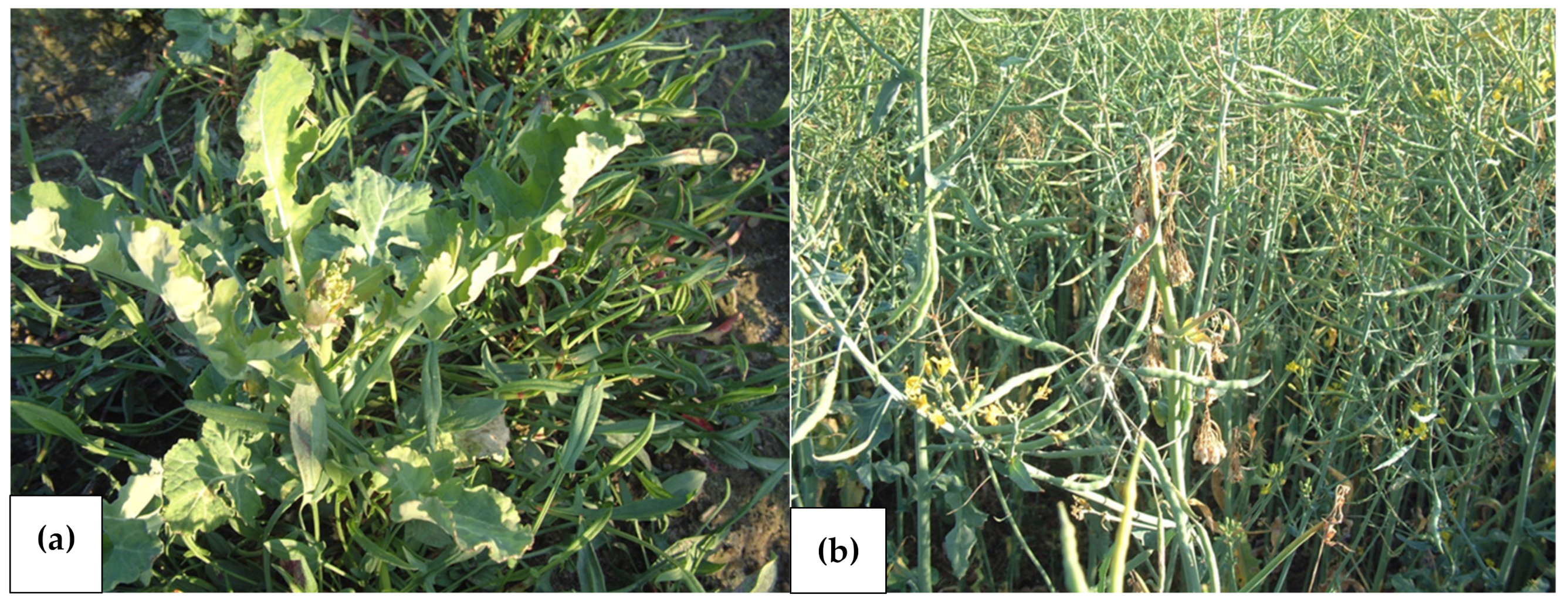
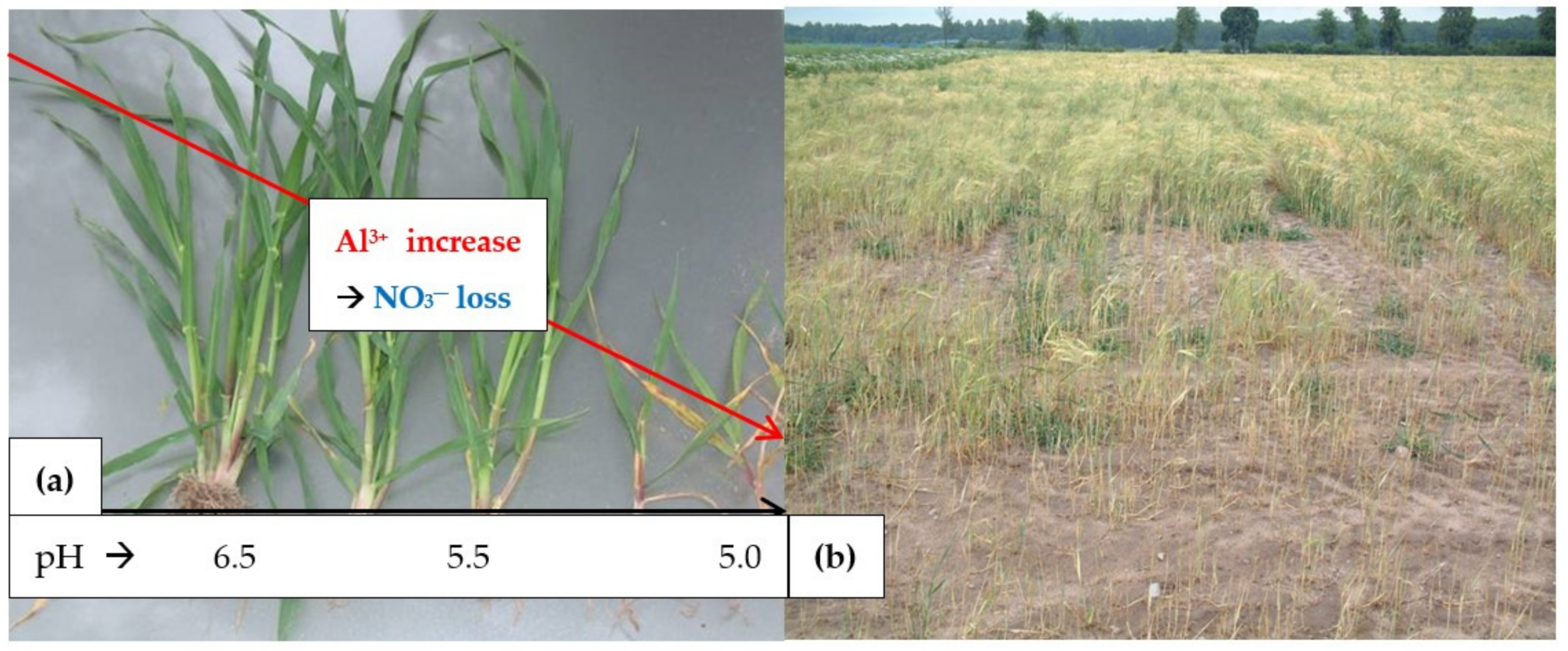
- Soil acidity and the excessive content of Al3+, which is a strong Ca2+ antagonist [41];
- (3)
- (4)
- Excessive fertilization with nitrogen fertilizers containing ammonium (N–NH4). Ammonium exerts a strong negative effect on the uptake of both nutrients from the soil solution [11];
- (5)
- Weather conditions, such as drought leading to a shortage of water in the soil.
3. Physiological Basis for Use of Calcium and Magnesium in Crop Production
3.1. Calcium
- (1)
- Conditions for nutrient uptake, both by stimulating the growth of the primary root (seminal roots) and initiating the lateral roots;
- (2)
- Signaling the disorder in plant growth by increasing its content in the plant indicative parts;
- (3)
- The relationship between the supply of N and other nutrients, being decisive for their uptake and utilization by the plant;
- (4)
- Plant health, as a result of both a balanced nutritional status and indirect reduction of pathogen pressure;
- (5)
- Intensification of N2 fixation as a result of greater root nodulation of legumes in soil rich in available Ca;
- (6)
- The quality of the products of grown crops—this applies mainly to the market quality of fruits, leafy vegetables, and potato tubers.
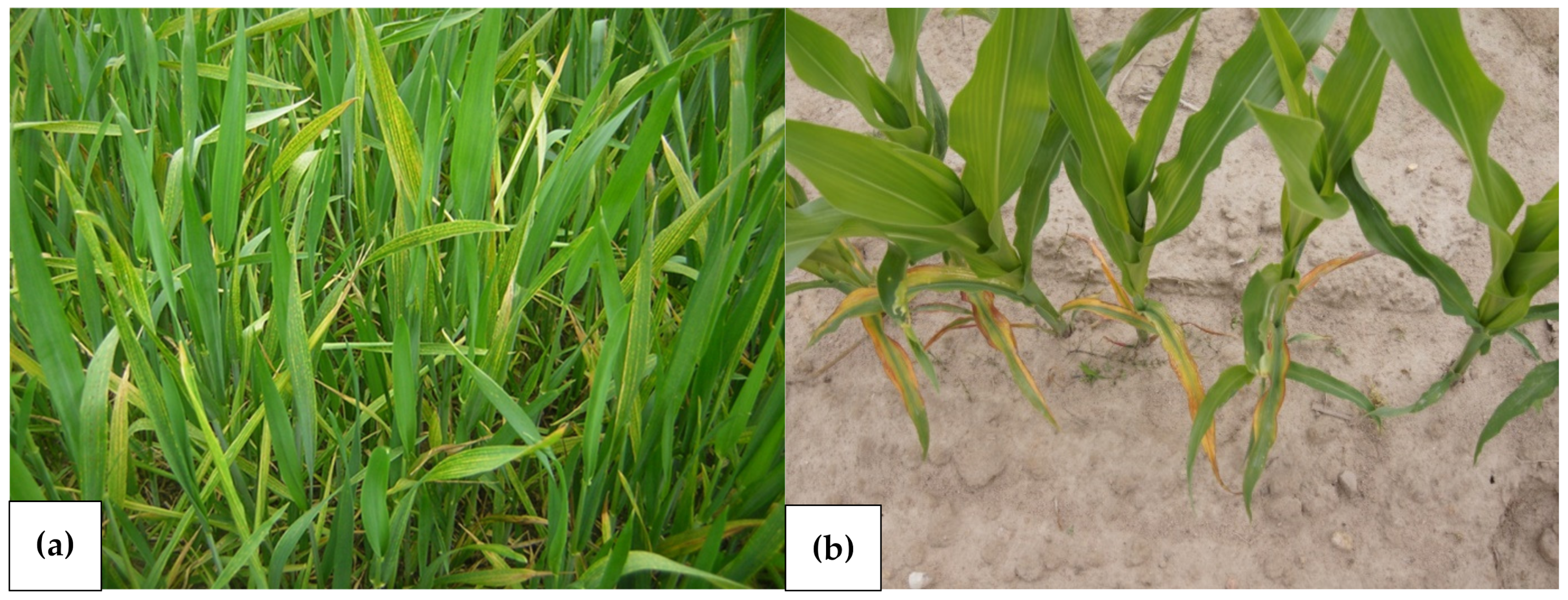
3.2. Magnesium
- (1)
- Optimal weather conditions → leaves > grain > stem > cob-covering leaves > cob core;
- (2)
- Water shortage → leaves > cob core = stem = grain > cob-covering leaves.
3.2.1. Early Adaptation
3.2.2. Advanced Adaptation
3.2.3. Critical Adaptation
3.2.4. Growth Rate Degradation
4. Roles of Sulfur in Plant Crop Nutritional Homeostasis
4.1. Sulfur Uptake and Assimilation
- (1)
- What is the source of S (or, where does the plant get the required amount of S from)?
- (2)
- Does the farmer have the operational measures to correct the nutritional status of S before the critical stages of yield formation?
- (3)
- To what extent does S deficiency:
- disturb the N economy of the plant?
- limit the formation of yield components and, ultimately, yield?
- (1)
- The low content of available S:
- sandy soil;
- low content of organic matter, as the key S source in arable soils.
- (2)
- The limited access of roots to the soil available S pool, due to the reduced depth of the plant rooting zone:
- toxicity of Al3+;
- low content and supply of mineral nitrogen;
- soil compaction;
- excess water content.
- (3)
- Agronomic:
- lack or insufficient dose of S fertilizers;
- too-high frequency of S-sensitive plants in the crop rotation;
- too-high biomass of harvest residues poor in S, resulting in immobilization of S-SO4.
4.2. Sulfur Functions in Crop Plants
- (1)
- The Fe–S clusters, impacting the management of C and N:
- chlorophyll synthesis, photosynthesis;
- nitrogenase (N2 reduction);
- nitrate reductase (NO2− → NH3);
- sulfite reductase (SO32− → SH−)l
- synthesis of storage proteins, sulfur amino-acids (cysteine, cysteine, methionine), and components limiting the nutritional quality of harvested products.
- (2)
- Synthesis of S metabolites:
- cysteine, as a precursor of methionine, coenzyme A, glutathione (GSH), biotin, glucosinolates;
- derivatives of methionine, such as lignins, flavonoids, and ethylene.
- (3)
- Crop yield and quality of main product (seeds, grain, tubers, roots, fruits):
- increased yield of crops;
- increased harvest index of seed crops;
- enhanced content of gluten in wheat grain, leading to higher bread-making quality;
- increased synthesis of organo-sulfurous compounds (a classical example is allicin);
- biofortification of edible plant parts with essential micronutrients.
- (1)
- Mineral S compounds, such as hydrogen sulfide; elemental sulfur, sulfur dioxide, CS2, H2S, K2S, thiosulfates;
- (2)
- Phenols and polyphenols;
- (3)
- Lignins, as organic building materials of cell walls, providing a biophysical barrier in leaves and other plant-covering tissues against pathogens and insects;
- (4)
- Plant-specific S defense compounds, such as glutathione, glucosinolates, phytoalexins, S-rich proteins;
- (5)
- Plant hormones, such as ethylene and jasmonic acid.
5. Secondary Nutrients and Nitrogen Fertilizer Productivity
5.1. Amelioration of Factors Limiting Nitrogen Uptake Use Efficiency
- Calcium carbonate hydrolysis:
- Neutralization of toxic aluminum:
5.2. Amelioration of Factors Limiting Nitrogen Utilization Use Efficiency
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
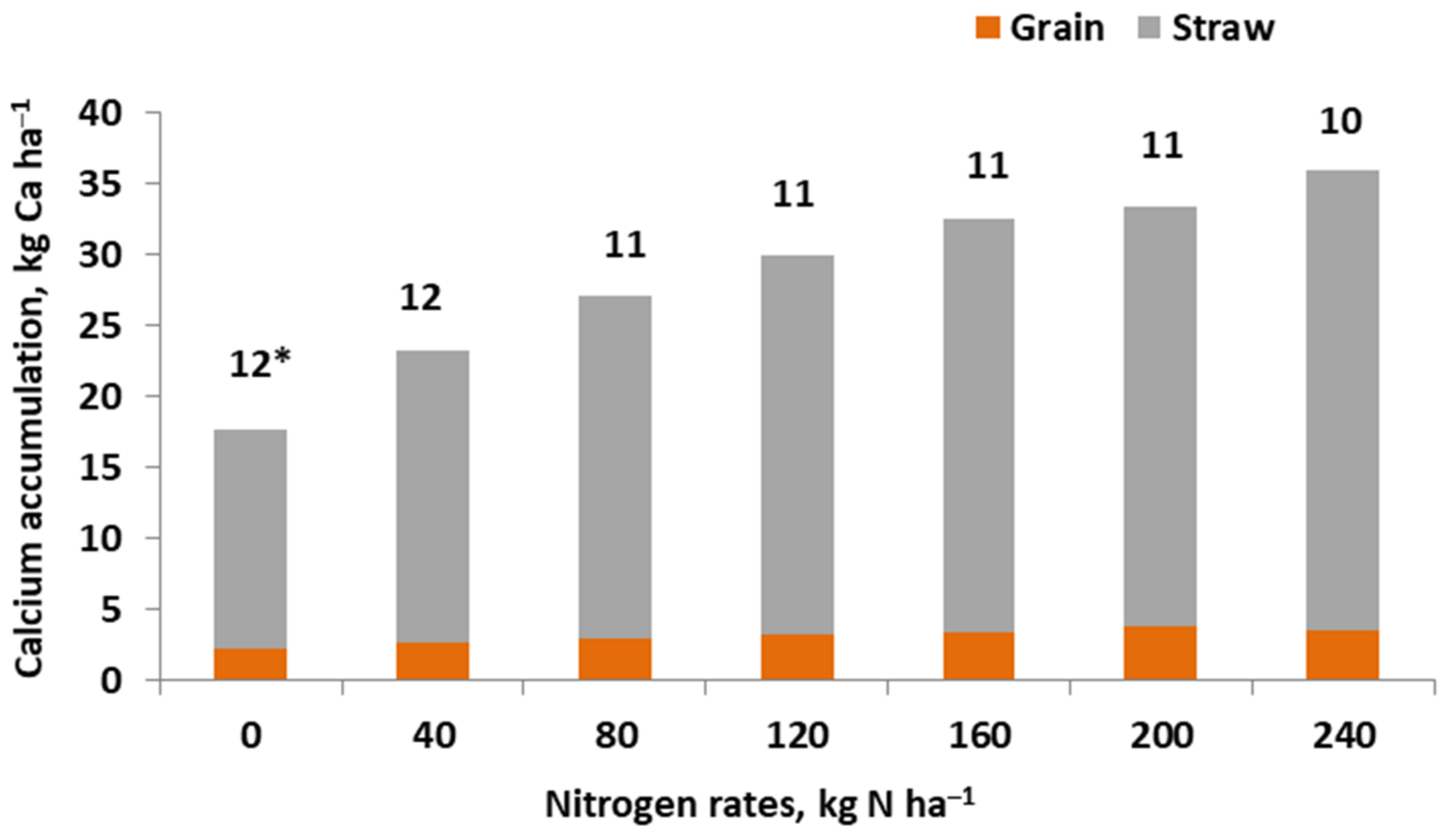
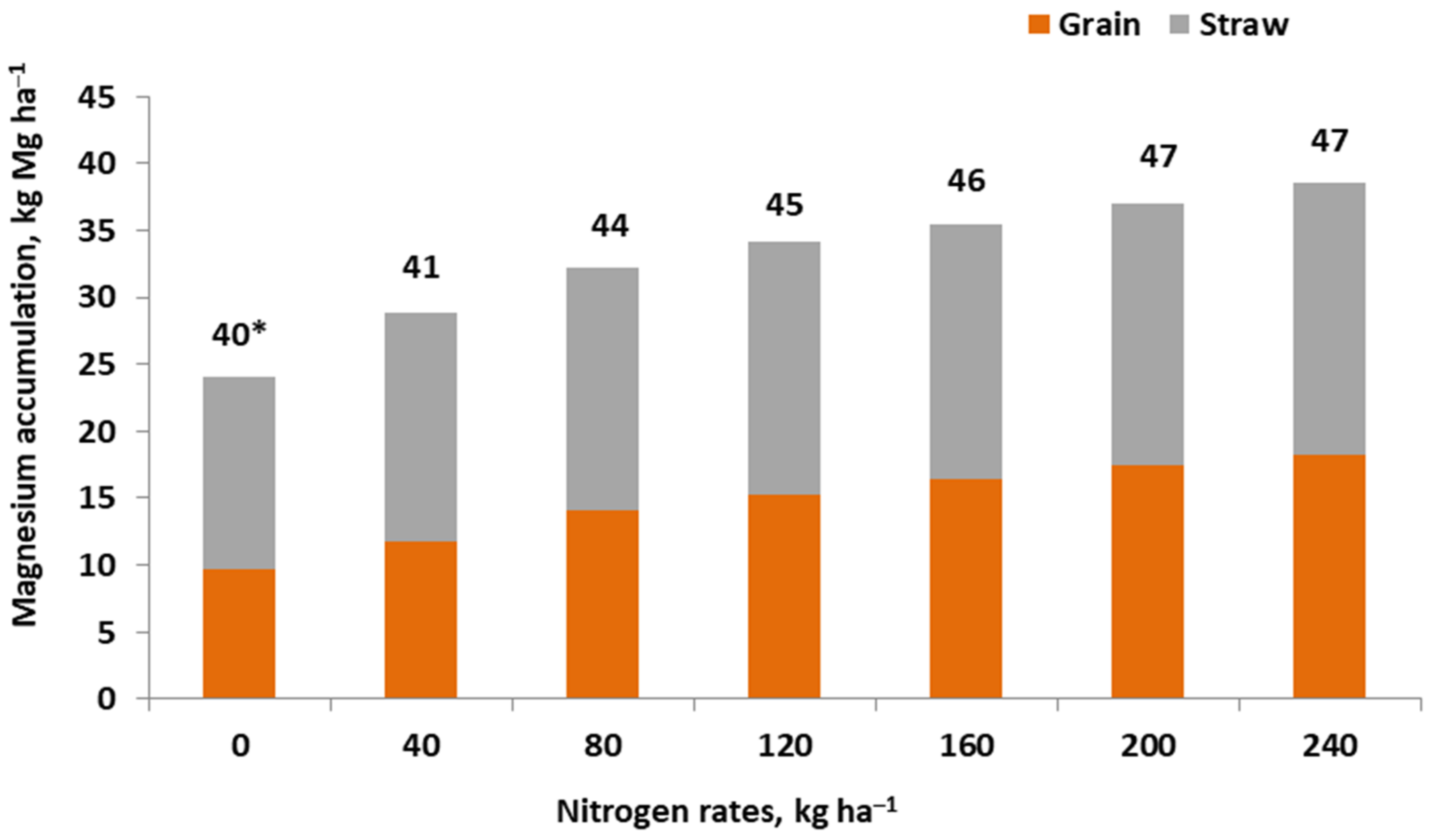
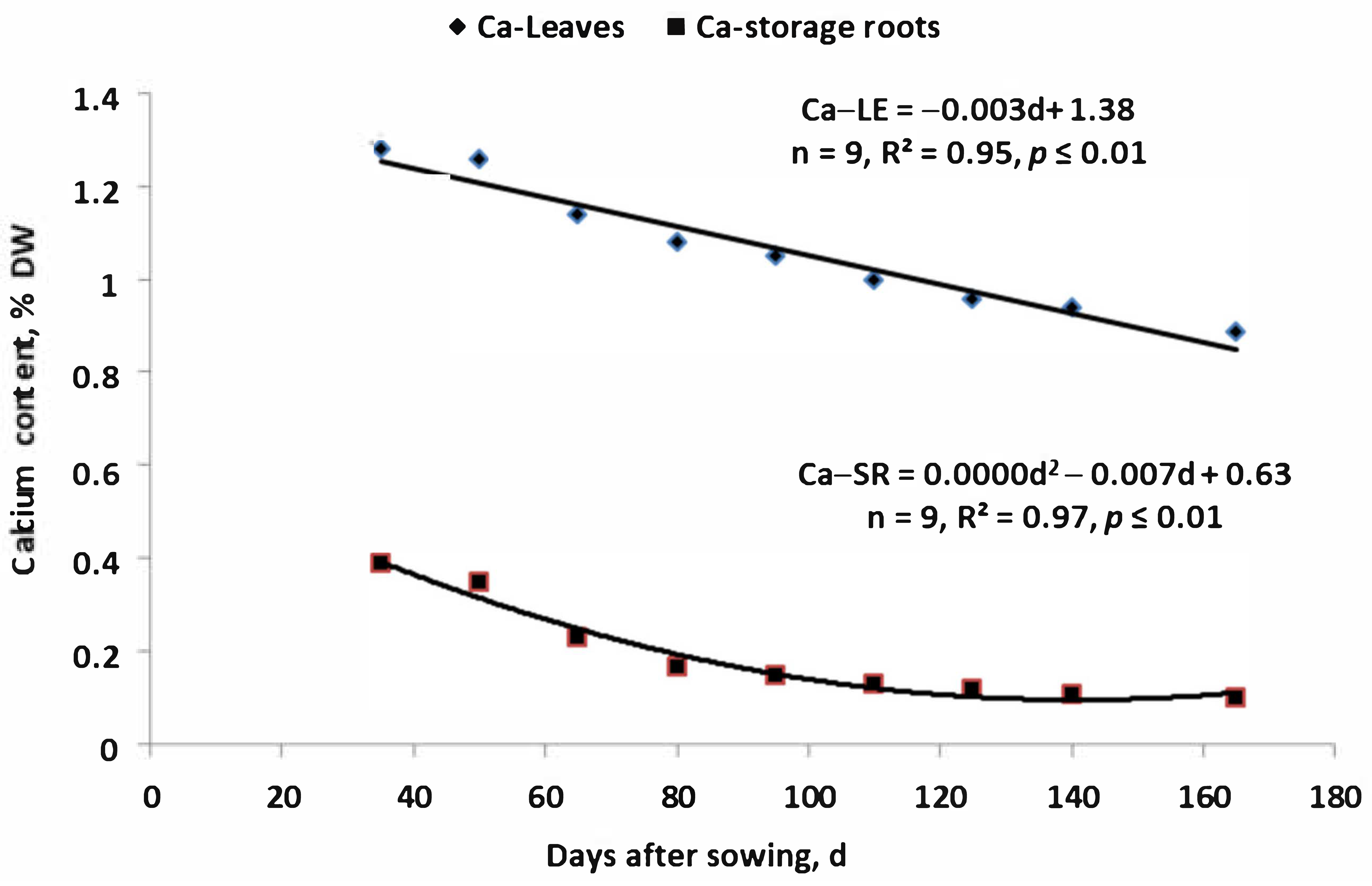
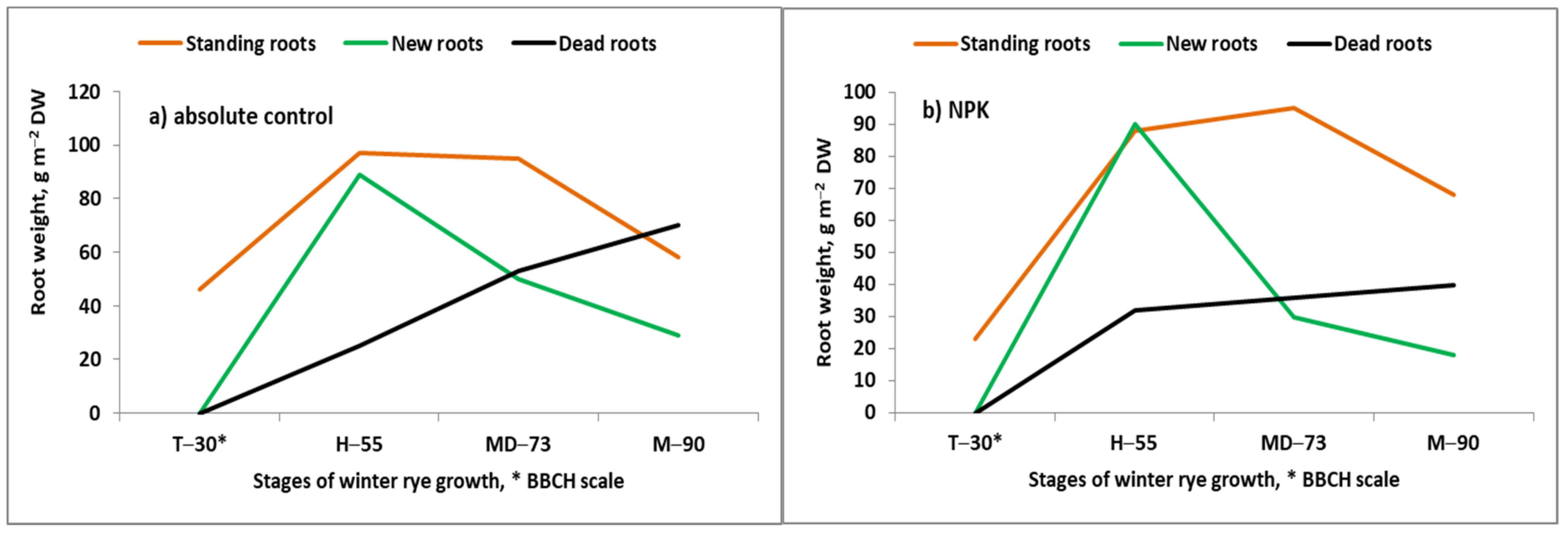
References
- Ray, D.K.; Mueller, N.D.; West, P.C.; Foley, J.A. Yield trends are insufficient to double global crop production by 2050. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e66428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conijn, J.G.; Bindraban, P.S.; Schröder, J.J.; Jongschaap, R.E.E. Can our global food system meet food demand within planetary boundries? Agric. Ecosys. Environ. 2018, 251, 244–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houlton, B.Z.; Almaraz, M.; Aneja, V.; Austin, V.T.; Bai, E.; Cassman, K.G.; Compton, J.E.; Davidson, E.A.; Erisman, J.W.; Galloway, J.N.; et al. A world co-benefits: Solving the global nitrogen challenge. Earth’s Future 2019, 7, 865–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Röös, E.; Bajželj, B.; Smith, P.; Patel, M.; Little, D.; Garnett, T. Greedy or needy? Land use and climate impacts of food in 2050 under different livestock futures. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2017, 47, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cirera, X.; Masset, E. Income distribution trends and future food demand. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2010, 365, 2821–2834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mapes, B.R.; Prager, S.D.; Bene, C.; Gonzalez, C.E. Healthy and sustainable diets from today to 2050–the role of international trade. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0264729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taiz, L. Agriculture, plant physiology, and human population growth: Past, present, and future. Theor. Exp. Plant Physiol. 2013, 25, 167–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omara, P.; Aula, L.; Oyebiyi, F.; Raun, W.R. World cereal nitrogen use efficiency trends: Review and current knowledge. Agrosys. Geosci. Environ. 2019, 2, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anas, M.; Liao, F.; Verma, K.K.; Sarwar, M.A.; Mahmood, A.; Chen, Z.-L.; Li, Q.; Zeng, X.-P.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y.-R. Fate of nitrogen in agriculture and environment: Agronomic, eco-physiological and molecular approaches to improve nitrogen use efficiency. Biol. Res. 2020, 53, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moll, R.H.; Kamprath, E.J.; Jackson, W.A. Analysis and interpretation of factors which contribute to efficiency of nitrogen utilization. Agron. J. 1982, 74, 562–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marschner, H. Mineral Nutrition of Higher Plants, 2nd ed.; Elsevier Ltd., Academic Press: London, UK, 1995; 899p. [Google Scholar]
- Grzebisz, W.; Diatta, J.; Barłóg, P.; Biber, M.; Potarzycki, J.; Łukowiak, R.; Przygocka-Cyna, K.; Szczepaniak, W. Soil fertility clock–crop rotation as a paradigm in nitrogen fertilizer productivity control. Plants 2022, 11, 2841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weih, M.; Hamner, K.; Pourazari, F. Analyzing plant nutrient uptake and utilization efficiencies: Comparison between crops and approaches. Plant Soil 2018, 430, 7–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, N. Role of Plant Nutrients in Plant Growth and Physiology. In Plant Nutrients and Abiotic Stress Tolerance; Hasanuzzaman, M., Fujita, M., Oku, H., Nahar, K., Hawrylak-Nowak, B., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2018; pp. 51–93. [Google Scholar]
- Lynch, J.P.; Wojciechowski, T. Opportunities and challenges in the subsoil: Pathways to deeper rooted crops. J. Exp. Bot. 2015, 66, 2199–2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kell, D.B. Breeding crop plants with deep roots: Their role in sustainable carbon, nutrient and water sequestration. Ann. Bot. 2011, 108, 407–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, J.L. Steep, cheap and deep: An ideotype to optimize water and N acquisition by maize root systems. Ann. Bot. 2013, 112, 347–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, W.M.; Roberts, T.L. Food security and the role of fertilizer in supporting it. Procedia Engine 2012, 46, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahabka, J.E.; van Es, H.M.; McClenahan, E.J.; Cox, W.J. Spatial analysis of maize response to nitrogen fertilizer in Central New York. Precision Agric. 2004, 5, 463–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, L.K.; Bali, S.K. A review of methods to improve nitrogen use efficiency in agriculture. Sustainability 2018, 10, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, L.; Wang, S.; Ye, W. Establishment and application of critical nitrogen dilution curves for rice based on leaf dry matter. Agronomy 2020, 10, 367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. Impact of the Ukraine-Russia Conflict on Global Food Security and Related Matters under the Mandate of the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nation (FAO). CL 170/6. May 2022. Available online: https://www.fao.org/3/nj164en/nj164en.pdf (accessed on 20 August 2022).
- Strubenhoff, H. The War in Ukraine Triggered a Global Food Shortage. 2022. Available online: www.brookings.edu/blog/future-development/2022/06/14/the-war-in-ukraine-triggered-a-global-food-shortage/ (accessed on 20 August 2022).
- Plant Health Association California. Western Fertilizer Handbook, 10th ed.; Waveland Press, Inc.: Long Grove, IL, USA, 2022; 371p. [Google Scholar]
- Reid, R.; Hayes, J. Mechanisms and control of nutrient uptake by plants. Inter. Rev. Cytol. 2003, 229, 73–114. [Google Scholar]
- Clarkson, D.T. Nutrient interception and transport by root system. In Physiological Processes Limiting Plant Productivity; Johnson, C.B., Ed.; Butterworths: London, UK, 2013; pp. 307–330. [Google Scholar]
- Quintana, J.M.; Harrisosn, H.C.; Nienhuis, J.; Palta, J.P.; Kmiecik, K. Differences in pod calcium concentration in eight snap bean and dry bean cultivars. HortScience 1999, 34, 932–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
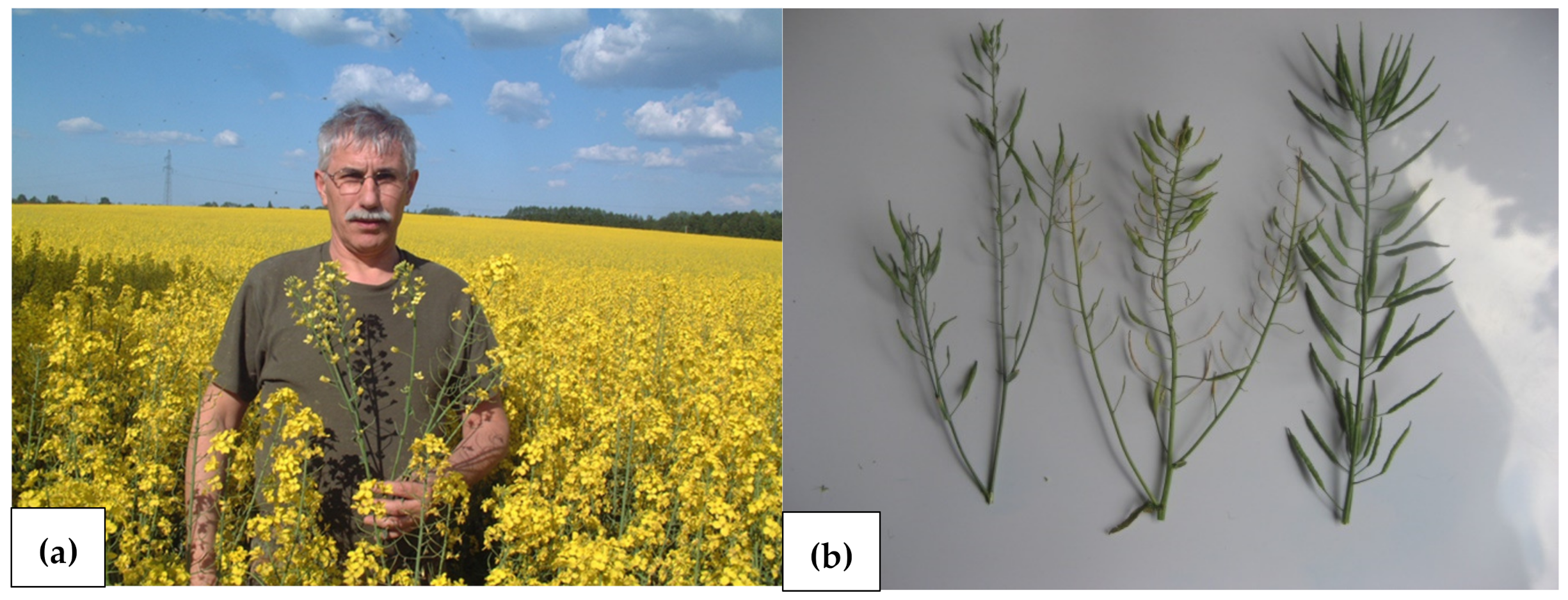
- Zhao, F.J.; Evans, E.J.; Bilsborrow, P.E.; Syers, J.K. Sulphur uptake and redistribution in double and single low varieties of oilseed rape (Brassica napus L.). Plant Soil 1993, 150, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grzebisz, W.; Łukowiak, R. Nitrogen gap amelioration is a core for sustainable intensification of agriculture—A concept. Agronomy 2021, 11, 419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Q.; Yue, S.; Chen, X.; Cui, Z.; Ye, Y.; Ma, W.; Tong, Y.; Zhang, F. Understanding dry matter and nitrogen accumulation with time-course for high-yielding wheat production in China. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e68783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Noordwijk, M.; Cadisch, G. Access and excess problems in soil nutrition. Plant Soil 2002, 247, 25–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blecharczyk, A. The reaction of winter rye and spring barley to the plant crop rotation system and fertilization in a long-term experiment. Rocz. Akad. Rol. Pozn. 2002, 236, 128, (In Polish with English summary). [Google Scholar]
- Grzebisz, W. Effect of soil fertility on roots dynamics of winter rye during the growing season. In Root Ecology and its Practical Application; Kutschera., L., Hubl, E., Lichtenegger, E., Person, H., Sobotik, M., Eds.; University of Natural Resources and Life Sciences: Wien, Austria, 1992; pp. 385–388. [Google Scholar]
- Meier, U. BBCH Monograph. In Growth Stages of Mono- and Dicotyledonous Plants, 2nd ed.; Federal Biological Research Center for Agriculture and Forestry: Berlin, Germany, 2001; Available online: http://www.jki.bund.de/fileadmin/dam_uploads/_veroeff/bbch/BBCH-Skala_Englisch.pdf (accessed on 14 November 2021).
- Nowicki, B. The Impact of Micronutrient Supplementary Foliar Feeding of Winter Wheat and Fungicide Protection on the Nitrogen Balance of Plants in Critical Stages of Crop Formation; Manuscript (in Polish). Library of the Poznan University of Life Sciences: Poznan, Poland, 2020; 254p. [Google Scholar]
- Szczepaniak, W.; Grzebisz, W.; Potarzycki, J.; Łukowiak, R.; Przygocka-Cyna, K. The magnesium and calcium mineral status of maize at physiological maturity as a tool for an evaluation of yield forming conditions. J. Elem. 2015, 21, 881–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stepaniuk, M.; Głowacka, A. Yield of winter oilseed rape (Brassica napus L. var. napus) in a short−term monoculture and the macronutrient accumulation in relation to the dose and method of sulfur application. Agronomy 2021, 12, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, A.; Mueller, R.T. Calcium uptake and distribution in plants. J. Plant Nutr. 1980, 2, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De, M.; Moore, A.D.; Mikkelsen, R.L. In-season accumulation and partitioning of macronutrients and micronutrients in irrigated sugar beet production. J. Sugar Beet Res. 2019, 56, 54–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brady, N.C.; Weil, R.R. The Nature and Properties of Soils, 15th ed.; Pearson Education: Boston, MA, USA, 2017; 1071p. [Google Scholar]
- Barłóg, P.; Grzebisz, W.; Łukowiak, R. Fertilizers and fertilization strategies mitigating soil factors constraining efficiency of nitrogen in plant production. Plants 2022, 11, 1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grzebisz, W.; Barłog, P.; Kryszak, J.; Łukowiak, R. Pre-anthesis nutritional status of spelt wheat as a toll for predicting the attainable grain yield. Agronomy 2019, 9, 558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grzebisz, W.; Frąckowiak, K.; Potarzycki, J.; Diatta, J.; Szczepaniak, W. The unexploited potential of nutrient analysis at the onset of tuberization for tuber yield production. Agronomy 2020, 10, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potarzycki, J.; Grzebisz, W. The in-season variability in the calcium concentration in potato organs and its relationships with the tuber yield. J. Elem. 2020, 25, 107–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, K.; Cakmak, I.; Wang, I.; Zhang, F.; Guo, S. Synergistic and antagonistic interactions between potassium and magnesium in higher plants. Crop J. 2021, 9, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grzebisz, W. Crop response to magnesium fertilization as affected by nitrogen supply. Plant Soil 2013, 368, 23–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potarzycki, J.; Grzebisz, W.; Szczepaniak, W. Magnesium fertilization increases nitrogen use efficiency in winter wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Plants 2022, 11, 2600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grzebisz, W.; Szczepaniak, W.; Łaczny, S.; Łański, M.; Zawieja, A. Indices of total and unit nutrient uptake by high yielding winter oilseed rape under conditions of intensive magnesium fertilization. Fragm. Agron. 2018, 35, 23–36. [Google Scholar]
- Heckman, J.R.; Sims, J.T.; Beegle, D.B.; Coale, F.J.; Herbert, S.J.; Bruulsema, T.W.; Bamka, W.J. Nutrient removal by corn grain harvest. Agron. J. 2003, 95, 587–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grzebisz, W. Technology of Crop Plants Fertilization–Yield Physiology. Part II. Cereals and Maize; PWRiL: Poznań, Poland, 2012; 279p. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Costa Crusciol, C.A.; Fernandes, A.M.; de Almeida Carmeis Filho, A.C.; de Cassia Felix Alvarez, R. Macronutrient uptake and removal by upland rice cultivars with different plant architecture. Rev. Bras. Cienc. Solo 2016, 40, e0150115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bender, R.R.; Haegele, J.W.; Ruffo, M.L.; Below, F.E. Nutrient uptake, partitioning, and remobilization in modern transgenic insect-protected maize hybrids. Agron J. 2013, 105, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirzel, J.; Undurraga, P. Nutritional Management of cereals cropped under irrigation conditions. In Crop Production; Goyal, A., Asil, M., Eds.; InTech: London, UK, 2013; pp. 99–130. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, J.B., Jr. Agronomic Handbook; CRC Press LLC: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2003; 450p. [Google Scholar]
- Neto, M.E.; Moreira Lara, L.; de Oliveira, S.M.; dos Santos, R.F.; Braccini, A.L.; Inou, T.T.; Batista, M.A. Nutrient removal by grain in modern soybean varieties. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 615019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canadian Fertilizer Institute. Nutrient Uptake and Removal by Field Crops Western Canada; Canadian Fertilizer Institute: Ottawa, Canada, 2001; 10p. [Google Scholar]
- Aulakh, M.S. Content and uptake of nutrients by pulses and oilseed crops. Ind. J. Ecol. 1985, 12, 238–242. [Google Scholar]
- Grzebisz, W. Technology of Crop Plants Fertilization–Yield Physiology. Part II. Oil, Roots, Legumes; PWRiL: Poznań, Poland, 2011; 414p. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Westermann, D.T. Nutritional requirements of potatoes. Am. J. Potato Res. 2005, 82, 301–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Fertilizer Industry Association. World Fertilizer Use Manual; IFA: Paris, France, 1992; 632p. [Google Scholar]
- Knez, M.; Stangoulis, C.R. Calcium bio-fortification of crops-challenges and projected benefits. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 669053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barłóg, P.; Grzebisz, W.; Diatta, J.B. Effect of timing and nitrogen fertilizers on nutrients content and uptake by winter oilseed rape. Part II. Dynamics of nutrient uptake. Chem. Agric. 2005, 6, 113–123. [Google Scholar]
- White, P.J. Calacium. In Handbook of Plant Nutrition, 2nd ed.; Barker, A.V., Pilbeam, D.J., Eds.; CRC Press, Taylor and Francis Group: Bocan Raton, FL, USA, 2015; pp. 165–198. [Google Scholar]
- Thor, K. Calcium–Nutrient and messenger. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, P.J. Calcium in plants. Ann. Bot. 2003, 92, 487–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, S.; Uozumu, N. Calcium-regulated phosphorylation systems controlling uptake and balance of plant nutrients. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Waadt, R.; Nuhkat, M.; Kollist, H.; Hedrich, R.; Roelfsema, M.R. Calcium signals in guard cells enhance the efficiency by abscisic acid triggers stomatal closure. New Phytol. 2019, 224, 177–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somssich, I.; Hahlbrock, K. 1998. Pathogen defense in plants—a paradigm of biological complexity. Trends Plant Sci. 1998, 3, 86–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lecourieux, D.; Ranyeva, R.; Pugin, A. Calcium in plant defense-signalling pathways. New. Phytol. 2006, 171, 249–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granqvist, E.; Sun, J.; Op den camp, R.; Pujic, P.; Hill, L.; Normand, P.; Morris, R.J.; Downie, J.A.; Geurts, R.; Oldroyd, G.E.D. Bacterial-induced calcium oscillations are common to nitrogen-fixing associations of noduling legumes and non-legumes. New Phytol. 2015, 207, 551–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, G.; Swart, S.; Lugtenberg, B.J.J.; Kijne, J.W. Molecular mechanisms of attachment of Rhizobium bacteria to plant roots. Mol. Microbiol. 1992, 6, 2897–2903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Freitas, S.T.; Talamani Do Amarante, C.V.; Mitcham, E.J. Calcium disorders in plants. In Postharvest Ripening Physiology of Crops; Pareek, S., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2016; pp. 477–512. [Google Scholar]
- White, P. The pathways of calcium movement to the xylem. J. Exp. Bot. 2001, 52, 891–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marschner, H. 1991. Mechanism of adaptation of plants to acid soils. Plant Soil 1991, 134, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerendás, J.; Führs, H. The significance of magnesium for crop quality. Plant Soil 2013, 368, 101–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, M.-S.; Zhao, F.-J.; Fairweather-tait, S.; Poulton, P.; Dunham, S.; McGrath, S. Evidence of decreasing mineral density in wheat grain over the last 160 years. J. Trace Elements Med. Biol. 2008, 22, 315–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, D. Declining fruit and vegetable nutrient composition: What is the evidence? HortSci. 2009, 44, 15–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grzebisz, W. Magnesium. In Handbook od Plant Nutrition, 2nd ed.; Barker, A.V., Pilbeam, D.J., Eds.; CRC Press, Taylor and Francis Group: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2015; pp. 199–260. [Google Scholar]
- Shaul, O. Magnesium transport and function in plants: The tip of the iceberg. Biometals 2002, 15, 309–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weih, M.; Liu, H.; Colombi, T.; Keller, T.; Jäck, O.; Vallenback, P.; Westerbergh, A. Evidence for magnesium–phosphorus synergism and co-limitation of grain yield in wheat agriculture. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 9012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaudhry, A.H.; Nayab, S.; Hussainn, S.B.; Ali, M.; Pan, Z. Current understanding on magnesium deficiency and future outlooks for sustainable agriculture. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Hassan, M.U.; Nadeem, F.; Wu, L.; Zhang, F.; Li, X. Magnesium fertilization improves crop yield in most production systems: A meta–analysis. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 10, 1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potarzycki, J. Effect of magnesium or zinc supplementation at the background of nitrogen rate on nitrogen management by maize canopy cultivated in monoculture. Plant Soil Environ. 2011, 57, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szczepaniak, W.; Barłóg, P.; Łukowiak, R.; Przygocka-Cyna, K. Effect of balanced nitrogen fertilization in four-year rotation on plant productivity. J. Central Europ. Agric. 2013, 14, 64–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grzebisz, W.; Potarzycki, J. Effect of magnesium fertilization systems on grain yield formation by winter wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) during the grain filling period. Agronomy 2022, 12, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pogłodziński, R.; Barłóg, P.; Grzebisz, W. Effect of nitrogen and magnesium sulfate application on sugar beet yield and quality. Plant Soil Environ. 2021, 67, 507–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grzebisz, W.; Przygocka-Cyna, K.; Szczepaniak, W.; Diatta, J.; Potarzycki, J. Magnesium as a nutritional tool of nitrogen efficient management—Pant production and environment. J. Elem. 2010, 15, 771–788. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, W.; Nazim, H.; Liang, Z.; Yang, D. Magnesium deficiency in plants: An urgent problem. Crop J. 2016, 4, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szczepaniak, W.; Grzebisz, W.; Potarzycki, J.; Łukowiak, R.; Przygocka-Cyna, K. Nutritional status of winter oilseed rape in cardinal stages of growth as yield indicator. Plant Soil Environ. 2015, 61, 291–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnug, E.; Haneklaus, S. Sulfur deficiency in Brassica. Lanbauforschung Völkenrode 1994, 144, 31. [Google Scholar]
- Grant, C.; Hawkesford, M.J. Sulfur. In Handbook od Plant Nutrition, 2nd ed.; Barker, A.V., Pilbeam, D.J., Eds.; CRC Press, Taylor and Francis Group: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2015; pp. 261–304. [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi, H. Sulfate transport systems in plant: Functional diversity and molecular mechanisms underlying regulatory coordination. J. Exp. Bot. 2019, 70, 4075–4087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruyama-Nakashita, A.; Nakamura, Y.; Yamaya, T.; Takahashi, H. Regulation of high-affinity sulphate transporters in plants: Towards systematic analysis of Sulphur signaling and regulation. J. Exp. Bot. 2004, 55, 1843–1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sondergaard, T.E.; Schulz, A.; Palmgren, M.G. Energization of transport processes in plants. Roles of the plasma membrane H+-ATPase. Plant Physiol. 2004, 136, 2475–2482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchner, P.; Takahashi, H.; Hawkesford, M.J. Plant sulphate transporters; co-ordination of uptake, intracellular and long-distance transport. J. Exp. Bot. 2004, 55, 1765–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Kok, L.J.; Castro, A.; Durenkamp, M.; Koralewska, A.; Posthumus, F.S.; Stuiver, C.E.E.; Ynag, L.; Stulen, I. Pathways of plant sulfur uptake and metabolism—An overview. Landbauforsch. Volkenrode 2005, 282, 5–13. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Y. Assembly and transfer of iron-sulfur clusters in the plastid. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, K. Sulfur assimilatory metabolism. The long and smelling road. Plant Physiol. 2004, 136, 2443–2450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkesford, M.J. Plant responses to Sulphur deficiency and the genetic manipulation of sulphate transporters to improve S-Utilization efficiency. J. Exp. Bot. 2000, 51, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidian, J.C.; Kopriva, S. Regulation of sulfate uptake and assimilation—the same or not the same. Plant 2010, 392, 314–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blake-Kalff, M.M.A.; Harrison, K.R.; Hawkesford, M.J.; Zhao, F.J.; McGrath, S.P. Distribution of sulfur within oilseed rape leaves in response to sulfur deficiency during vegetative growth. Plant Physiol. 1998, 118, 1337–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haneklaus, S.; Brauer, A.; Bloem, E.; Schnug, E. Relationship between sulfur deficiency in oilseed rape (Brassica napus L.) and its attractiveness for honeybees. Landbauforschung Völkenrode Sonderheft 2004, 283, 24–37. [Google Scholar]
- Scherer, H.W. Sulphur in crop production—invited paper. Europ. J. Agron. 2001, 14, 81–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giehl, R.F.H.; von Wirén, N. Root nutrient foraging. Plant Physiol. 2014, 166, 509–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahzad, Z.; Amtmann, A. Food for thought: How nutrients regulate root system architecture. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2017, 39, 8087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klikocka, H.; Marks, M. Sulphur and nitrogen fertilization as a potential means of agronomic biofortification to improve the content and uptake of microelements in spring wheat grain DM. J. Chem. 2018, 2018, 9326820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulczycki, G. The effect of elemental sulfur fertilization on plant yields and soil properties. Adv. Agron. 2021, 167, 105–182. [Google Scholar]
- Zenda, T.; Liu, S.; Dong, A.; Duan, H. Revising Sulphur–the once neglected nutrient: It’s role in plant growth, metabolism, stress tolerance and crop production. Agriculture 2021, 11, 626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayan, O.M.; Kumar, P.; Yadav, B.; Dua, M.; Johri, A.K. Sulfur nutrition and its role in plant growth and development. Plant Signal. Behav. 2022, e2030082-3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanzotti, V. The analysis of onion and garlic. J. Chromatogr. 2006, 1112, 3–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filipek-Mazur, B.; Tabak, M.; Gorczyca, O.; Lisowska, A. Effect of sulfur-containing fertilizers on the qunattity and quality of spring oilseed rape and winter wheat yield. J. Elem. 2019, 24, 1383–1394. [Google Scholar]
- Chorianopoulou, S.N.; Bouranis, D.L. The role of sulfur in agronomic biofortification with essesntial micronutrients. Plants 2022, 11, 1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burkitbayev, M.; Bachilova, N.; Kurmanbayeva, M.; Tolnova, K.; Yerezhepova, N.; Zhumagul, M.; Mamurova, A.; Turysbek, B.; Demeu, G. Effect of sulfur-containing agrochemicals on growth, yield, and protein content of soybeans (Glycine max (L.) Merr). Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 28, 891–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamal, A.; Moon, Y.-S.; Abdin, M.Z. Sulphur—a general overview and interaction with nitrogen. Aust. J. Crop Sci. 2010, 4, 523–529. [Google Scholar]
- Datnoff, L.E.; Wade, H.E.; Huber, D.M. Mineral Nutrition and Plant Disease; Amer Phytopathological Society: Saint Paul, MN, USA, 2007; 278p. [Google Scholar]
- Tweedy, B.G. Inorganic sulfur as a fungicide. Residue Rev. 1981, 78, 43–68. [Google Scholar]
- Cooper, R.M.; Williams, J.S. Elemental sulfur as an induced antifungal substance in plant defense. J. Exp. Bot. 2004, 55, 1947–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nwachukwu, I.D.; Slusarenko, A.J.; Gruhlke, M.C.H. Sulfur and sulfur compounds in plant defense. Nat. Prod. Comm. 2012, 7, 395–400. [Google Scholar]
- Künstler, A.; Gullner, G.; Ádám, A.L.; Nagy, J.K.; Király, L. The versatile roles of sulfur-containing biomolecules in plant defense-A road to disease resistance. Plants 2020, 9, 1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloem, E.; Haneklaus, S.; Schnug, E. Milestones in plant sulfur research on sulfur-resistance (SIR) in Europe. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 5, 779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Han, X.; Feng, D.; Yuan, D.; Huang, L.-J. Signalling crosstalk between silicic acid and ethylene/jasmonate in plant defense: Do we understand what they are whispering? Inter. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vojtovic, D.; Luhova, L.; Petrivalsky, M. Something smells bad to plant pathogens: Production of hydrogen sulfide and its role in plant defense responses. J. Adv. Res. 2020, 27, 199–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haneklaus, S.; Bloem, E.; Schnug, E. Effect of foliar-applied elemental sulfur on Fusarium infection in barley. Landbauforsch. Völkenrode 2007, 57, 213–217. [Google Scholar]
- Klikocka, H.; Haneklaus, S.; Bloem, E.; Schnug, E. Influence of sulfur fertilization on infection of potato tubers with Rhizotania silani and Streptomyces scabies. J. Plant Nutr. 2005, 28, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luce, M.S.; Whalen, J.K.; Ziadi, N.; Zebarth, B.J. Nitrogen dynamics and indices to predict soil nitrogen supply in humid temperate soils. Adv. Agron. 2011, 112, 55–102. [Google Scholar]
- Grzebisz, W.; Niewiadomska, A.; Przygocka-Cyna, K. Nitrogen hotspots on the farm—A practice-oriented approach. Agronomy 2022, 12, 1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rich, S.M.; Watt, M. Soil conditions and cereal root system architecture: Review and considerations for linking Darvin and Weaver. J. Exp. Bot. 2013, 64, 193208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jobbággy, E.G.; Jackson, R.B. The distribution of soil nutrients with depth: Global patterns and the imprint of plants. Biogeochemistry 2001, 53, 51–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raynaud, X.; Leadley, P. Soil characteristics play a key role in modeling nutrient competition in plant communities. Ecology 2004, 85, 2200–2214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermans, C.; Hammond, J.P.; White, P.J.; Verbruggen, N. How do plants respond to nutrient shortage by biomass allocation. Trends Plant Sci. 2006, 11, 610–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nibou, C.; Gibbs, D.J.; Coates, J.C. Branching out in new directions: The control of root architecture by lateral root formation. New Phytol. 2008, 179, 595–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rout, G.R.; Samantaray, S.; Das, P. Aluminum toxicity in plants: A review. Agronomie 2001, 21, 3–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meriño-Gergichevich, C.; Alberdi, M.; Ivanov, A.G.; Reyes-Diaz, R. Al3+—Ca2+ interaction in plants growing in acid soils: Al-phytotoxicity response to calcareous amendments. J. Soil Sci. Plant Butr. 2010, 10, 217–243. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, C.; Weligama, C.; Sale, P. Subsurface soil acidification in farming systems: Its possible causes and management options. Mol. Environ. Soil Sci. Prog. Soil Sci. 2013, 13, 20. [Google Scholar]
- Rahman, N.A.; Lee, S.-H.; Chung, H.; Kabir, A.H.; Jones, C.S.; Lee, K.-W. Importance of mineral nutrition for mitigating aluminum toxicity in plants on acid soils: Current status and opportunities. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmeis Filho, A.C.A.; Crusciol, C.A.C.; Guimaraes, T.N.; Calonego, J.C.; Mooney, S.C. Impact of amendments on the physical properties of soil under tropical long-term no till conditions. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0167564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watts, D.B.; Dikc, W.A. Sustainable use of FGD gypsum in agricultural systems: Introduction. J. Environ. Qual. 2014, 42, 246–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebedev, A.L. Kinetics of gypsum dissolution in water. Geochemistry Inter. 2015, 53, 811–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Dick, W.A. Gypsum as an agricultural amendment: General use guidelines. Bull. Ohio State Univ. 2011, 945, 36. [Google Scholar]
- Zielewicz, W.; Swędrzyńska, D.; Swędrzyński, A.; Grzebisz, W.; Goliński, P. The influence of calcium sulfate and different doses of potassium on the soil enzyme activity and the yield of the sward with a misture of alfalfa and grasses. Agriculture 2022, 12, 485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shainberg, I.; Summer, M.E.; Miller, W.P.; Farina, M.P.; Pavan, M.A.; Fey, M.V. Use of gypsum on soils: A review. Adv. Soil Sci. 1989, 9, 111. [Google Scholar]
- Summer, M. Gypsum improves subsoil roots growth. In Proceedings of the International Symposium “Root Research and Applications” RootRAP, Vienna, Austria, 2–4 September 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Cuervo-Alzate, J.E.; Osorio, N.W. Gypsum incubation tests to evaluate its potential to effects on acidic soils of Colombia. Rev. Fac. Nac. Agron. Medellin 2020, 73, 9349–9359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, W.L.; Kidwell, K.K.; McCracken, V.A.; Bolton, R.P.; Allen, M. Economically optimal wheat yield, protein and nitrogen use component responses to varying N supply and genotype. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wooding, A.R.; Kavale, S.; MacRitchie, F.; Stoddard, F.L.; Wallace, A. Effects of nitrogen and sulfur fertilizer on protein composition, mixing requirements, and dough strength of four wheat cultivars. Cereal Che. 2000, 77, 798–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stępniewska, S. Milling value of grain of selected cultivars from crop years 2012–2014. Acta Agrophysica 2016, 23, 105–117. [Google Scholar]
- Hlisnikovský, L.; Čermák, P.; Kunzová, E.; Barłog, P. The effect of application of potassium, magnesium, and Sulphur on wheat and barley grain yield and protein content. Agron. Res. 2019, 17, 1905–1917. [Google Scholar]
- Potarzycki, J.; Przygocka-Cyna, K.; Wendel, J.; Biniek, Ł.; Ridiger, B. The impact of Sulphur fertilization on yield of winter wheat. Fragm. Agron. 2015, 32, 63–72. [Google Scholar]
- Sadras, V.O.; Slafer, G.A. Environmental modulation of yield components in cereals: Heritability reveal a hierarchy of phenotypic plasticities. Field Crops Res. 2012, 127, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Körner, C. Paradigm shift in plant growth control. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2015, 25, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zörb, C.; Ludewig, U.; Hawkesford, M.J. Perspective on wheat yield and quality with reduced nitrogen supply. Trends Plant Sci. 2018, 23, 1029–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weymann, W.; Bottcher, U.; Sieling, K.; Kage, H. Effects of weather conditions during different growth phases on yield formation of winter oilseed rape. Field Crops Res. 2015, 173, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grzebisz, W.; Szczepaniak, W.; Grześ, S. Sources of nutrients for high-yielding winter oilseed rape (Brassica napus L.) during post-flowering growth. Agronomy 2020, 10, 626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulte auf’m Erley, G.; Behrens, T.; Ulas, A.; Wiesler, F.; Horst, W.J. Agronomic traits contributing to nitrogen efficiency of winter oilseed rape cultivars. Field Crops Res. 2011, 124, 114–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szczepaniak, W.; Grzebisz, W.; Barłóg, P.; Przygocka-Cyna, K. Mineral composition of winter oilseed rape (Brassica napus L.) seeds as a tool for oil seed prognosis. J. Cen. Europ. Agric. 2017, 18, 196–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szulc, P.; Bocianowski, J.; Rybus-Zając, M. The effect of soil supplentation with nitrogen and elemental sulfur on chlorphyll content and grain yield of maize (Zea mays L.). Žemdirbystè=Agriculture 2012, 99, 247–254. [Google Scholar]
- Salviagotti, F.; Castellalrin, J.M.; Miralles, D.J.; Pedrol, H.M. Sulfur fertilization improves nitrogen use efficiency in wheat by increasing nitrogen uptake. Field Crops Res. 2009, 113, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagani, A.; Echeverria, H.E.; Andrade, F.H.; Sainz Rozas, H.R. Effects of nitrogen and sulfur application on grain yield, nutrient accumulation, and harvest indexes in maize. J. Plant Nutr. 2012, 35, 1080–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnug, E.; Haneklus, S. Diagnosis of Sulphur nutrition. In Sulphur in Agroecosystems; Schnug, E., Ed.; Kluwer Academic Publisher: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1998; pp. 1–38. [Google Scholar]
- Haneklaus, S.; Fleckenstaein, J.; Schnug, E. Comaprative studies of plant and soil analysis for the Sulphur status of oilseed rape and winter wheat. Z. Pflanzenernähr. Bodenk. 1995, 158, 109–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inal, A.; Günes, A.; Alpaslan, M.; Adak, M.S.; Taban, S.; Erasian, F. Diagnosis of sulfur deficiency and effects of sulfur on yield and yield components of wheat grown in Central Anatolia, Turkey. J. Plant Nutr. 2003, 26, 1483–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grzebisz, W.; Przygocka-Cyna, K. Spring malt barley response to elemental sulfur—the prognostic value of N and S concentrations in malt barley leaves. Plant Soil Environ. 2007, 53, 388–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.J.; Hawkesford, M.J.; Warrilow, A.G.S.; McGrath, S.P.; Clarkson, D.T. responses of two wheat varieties to Sulphur application and diagnosis of Sulphur deficiency. Plant Soil 1996, 181, 317–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reussi Calvo, N.I.; Echeverria, H.E.; Sainz Rozas, H.R. Usefulness of foliar nitrogen-sulfur ratio in spring red wheat. J. Plant Nutr. 2008, 31, 1612–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedlar, O.; Balik, J.; Kulhanek, M.; Cerny, J.; Suran, P. Sulphur nutrition index in relation to uptake and quality of winter wheat grain. Chilean J. Agric. Res. 2019, 79, 486–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potarzycki, J. Influence of nitrogen and magnesium fertilization at the flag leaf stage of winter wheat development on the yield and grain quality. Fertil. Fertil. 2008, 32, 99–109. [Google Scholar]
- Grzebisz, W.; Szczepaniak, W.; Barłóg, P.; Przygocka-Cyna, K.; Potarzycki, J. Phosphorus sources for winter oilseed rape (Brassica napus L.) during reproductive growth–magnesium sulfate management impact on P use efficiency. Archiv. Agron. Soil Sci. 2018, 64, 1646–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potarzycki, J. Yield forming effect of combined application of magnesium, sulphur and zinc in maize fertilization. Fertilizers Fertilization 2010, 39, 44–59. [Google Scholar]
- Talboys, P.J.; Heppell, J.; Roose, T.; Healey, J.R.; Jones, D.L.; Withers, P.J.A. Struvite: A slow-release fertilizer for sustainable phosphorus management. Plant Soil 2016, 401, 109–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

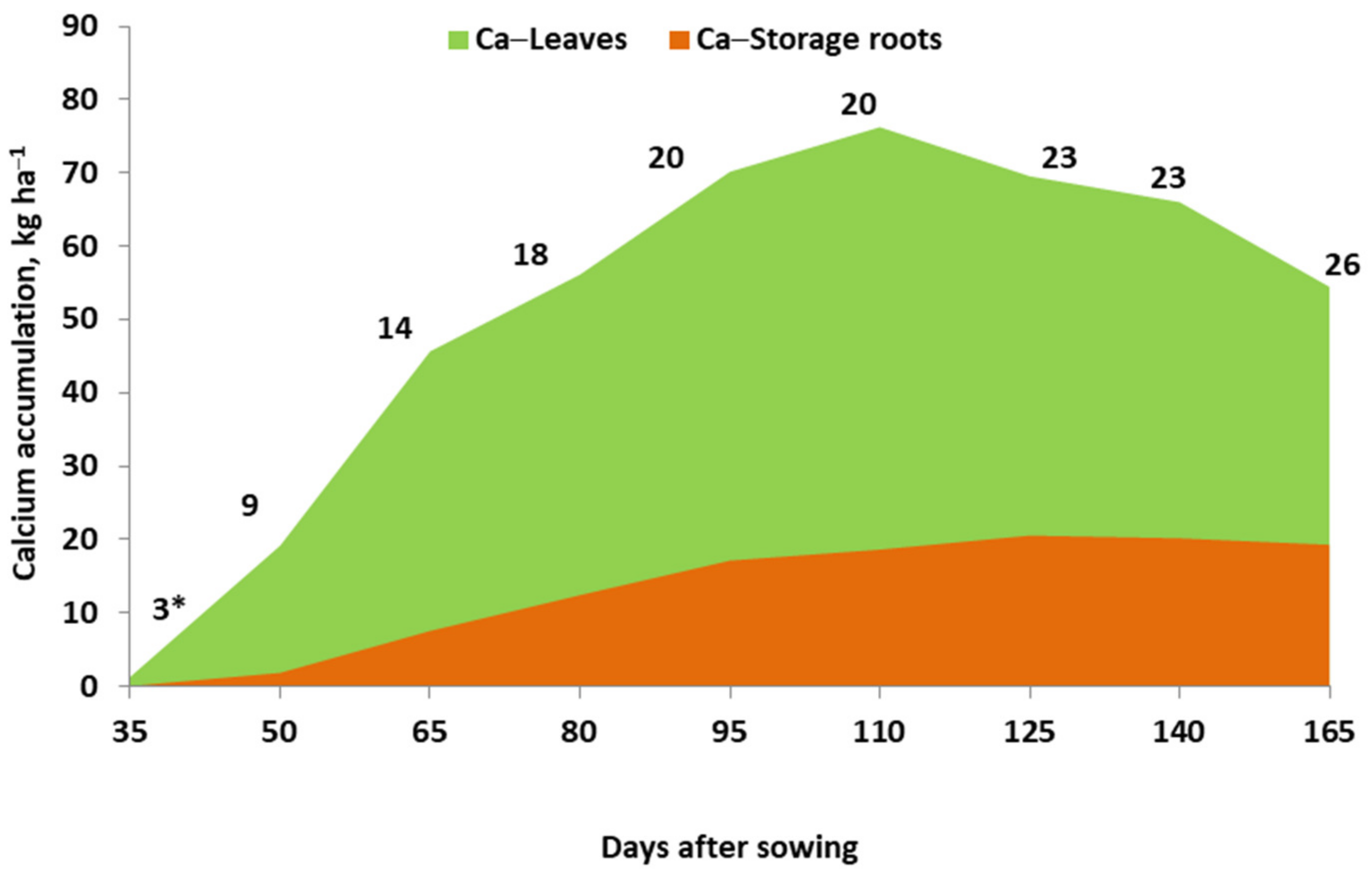


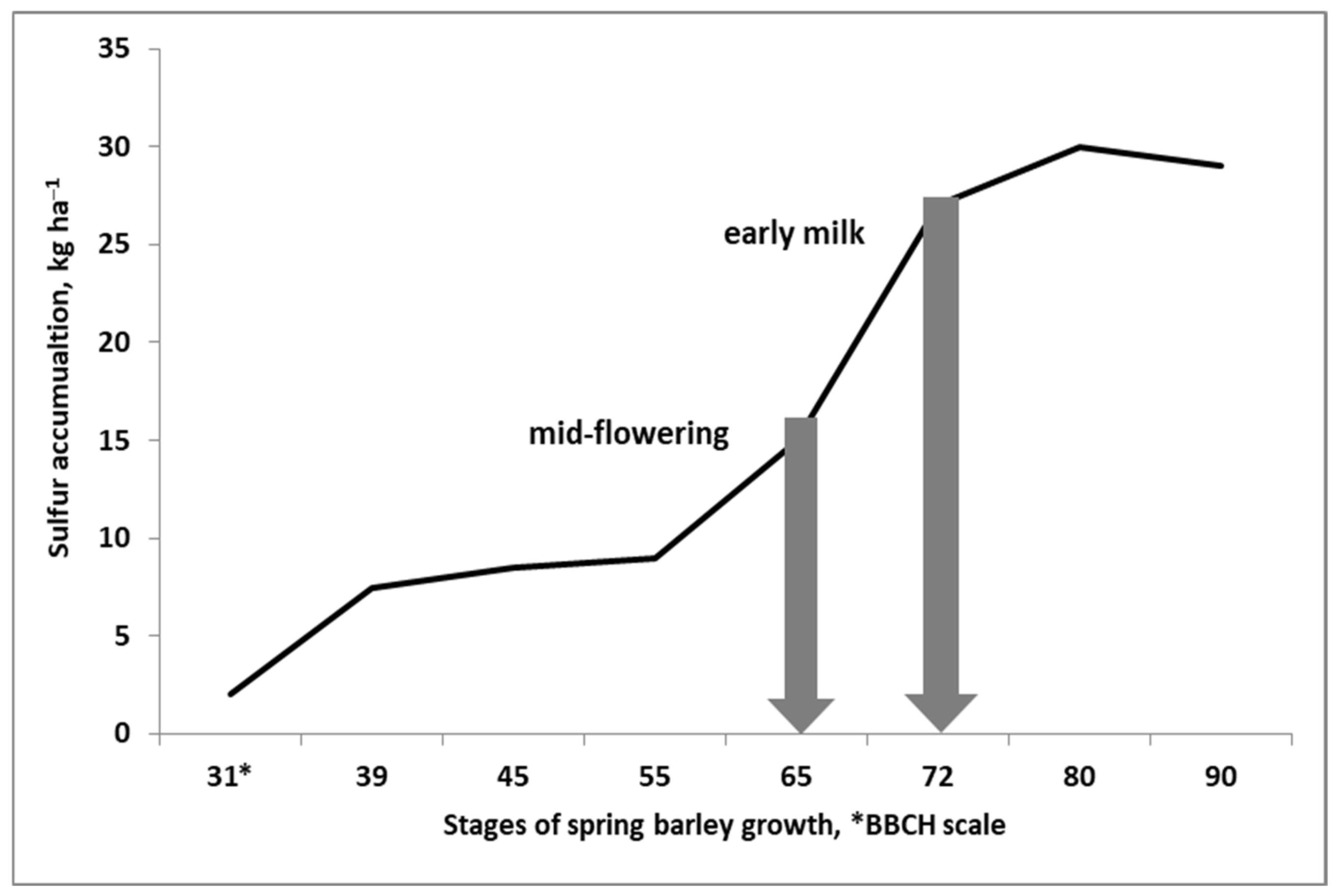



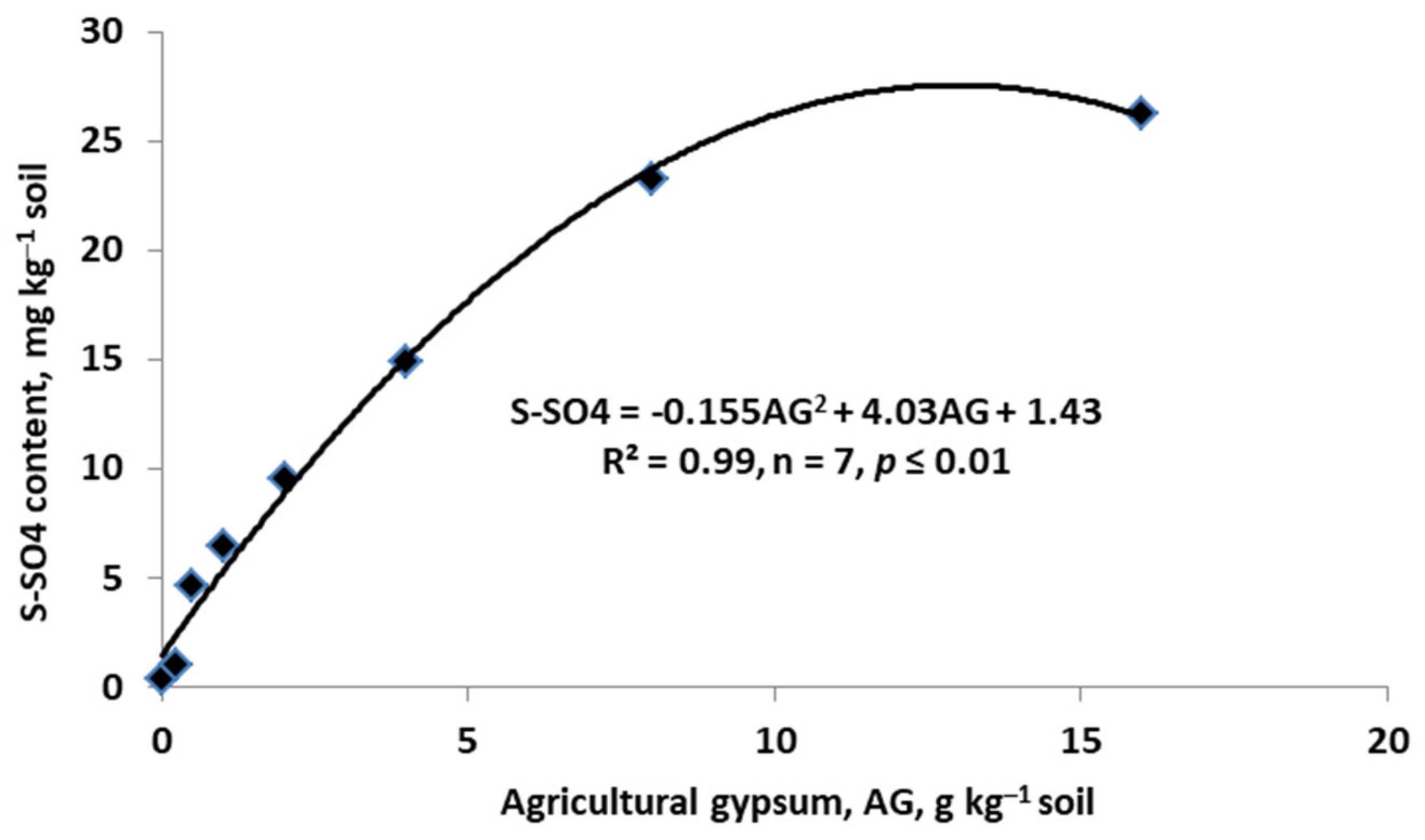
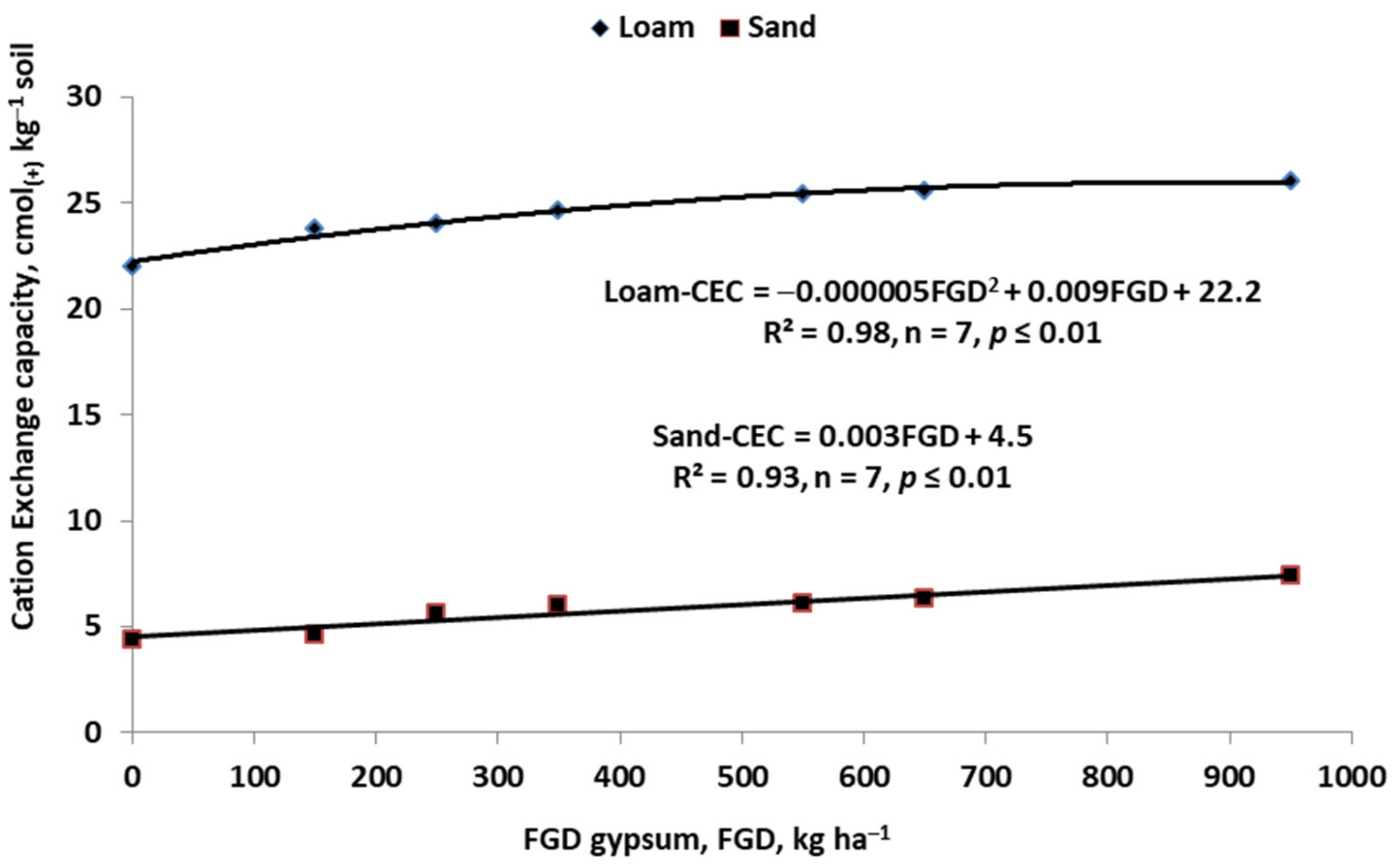
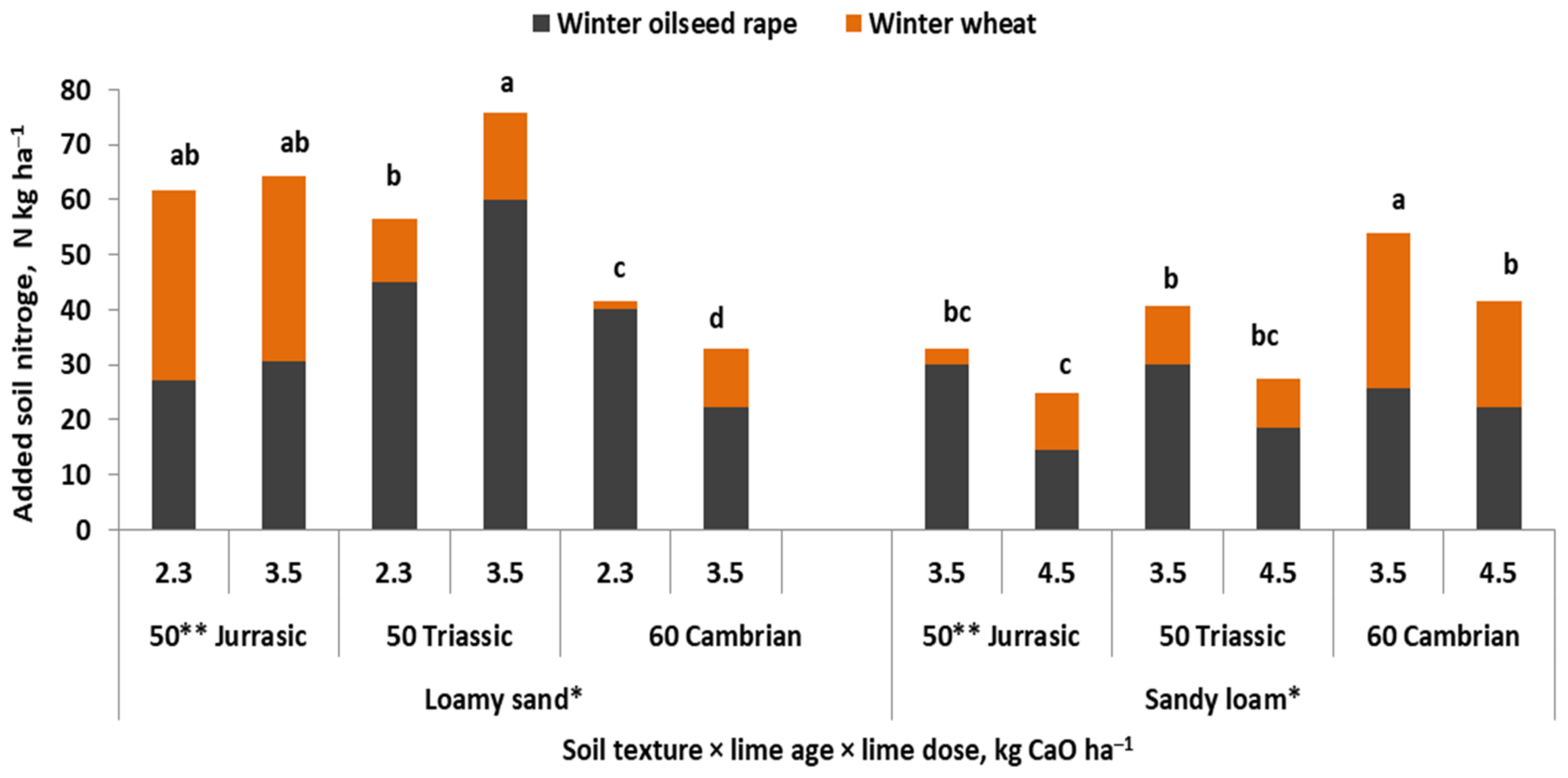
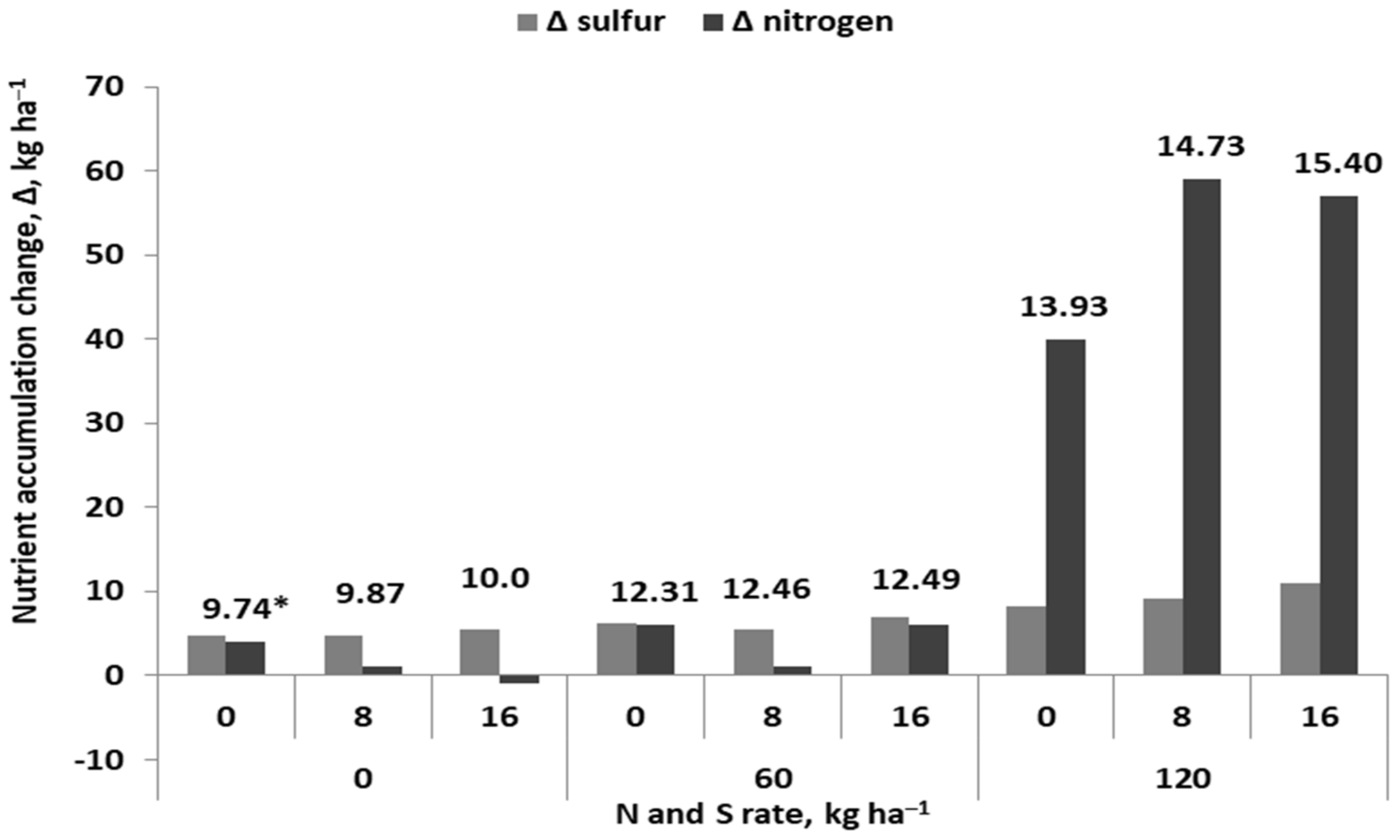

| Crop | N | Ca | Mg | S | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cereals | 2233 | 1.5–4.2 | 0.9–2.1 | 1.5–4 | [50] |
| Paddy rice | 12–17 | 3.9–4.3 | 1.2–1.7 | 1.3–1.7 | [51] |
| Maize | 22–26 14–26 | - 2.1–5.3 | 4.5−5.5 1.9–4.4 | 2.0–2.3 1.4–2.6 | [52] [53] |
| Groundnut | 60 | 4.4 | 5.6 | 4.5 | [54] |
| Soybean | 52.5–61.5 | 1.5–2.5 | 2.3–3.3 | 2.5–3.5 | [55] |
| Oilseed rape 2 | 51–62 | 54–68 | 5.5–6.5 | − | [48] |
| Canola | 57–70 | 24 | 7 | 9.7–11.9 | [56] |
| Mustard | 32.8 | 42 | 8.7 | 17.3 | [57] |
| Potato | 4–5 4.2 | 0.7–0.9 1.6 | 0.4−–0.6 1.1 | 0.2−0.4 0.4 | [58] [59] |
| Sugar cane | 0.8 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.25 | [60] |
| Sugar beet | 4–5 4 | 1.1–2.6 1.8 | 0.6–0.9 1.6 | - 0.4 | [58] [39] |
| Cotton lint Cotton seeds | 117 62.4 | 8.2 67.2 | 13.5 16 | 11.8 - | [54] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Grzebisz, W.; Zielewicz, W.; Przygocka-Cyna, K. Deficiencies of Secondary Nutrients in Crop Plants—A Real Challenge to Improve Nitrogen Management. Agronomy 2023, 13, 66. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13010066
Grzebisz W, Zielewicz W, Przygocka-Cyna K. Deficiencies of Secondary Nutrients in Crop Plants—A Real Challenge to Improve Nitrogen Management. Agronomy. 2023; 13(1):66. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13010066
Chicago/Turabian StyleGrzebisz, Witold, Waldemar Zielewicz, and Katarzyna Przygocka-Cyna. 2023. "Deficiencies of Secondary Nutrients in Crop Plants—A Real Challenge to Improve Nitrogen Management" Agronomy 13, no. 1: 66. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13010066
APA StyleGrzebisz, W., Zielewicz, W., & Przygocka-Cyna, K. (2023). Deficiencies of Secondary Nutrients in Crop Plants—A Real Challenge to Improve Nitrogen Management. Agronomy, 13(1), 66. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13010066








