How Much Phosphorus Uptake Is Required for Achieving Maximum Maize Grain Yield? Part 1: Luxury Consumption and Implications for Yield
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
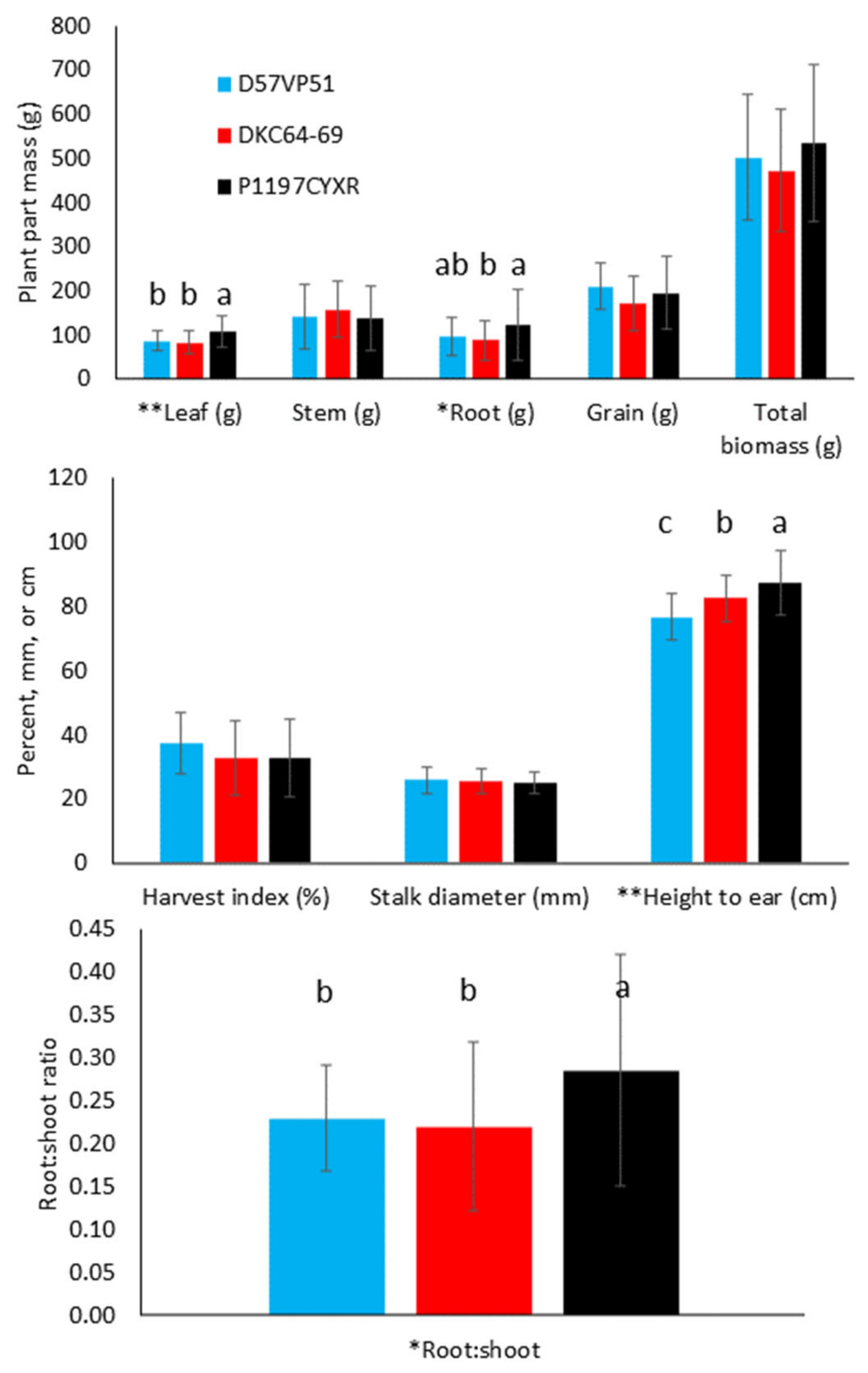
3.1. Effect of Hybrid
3.2. Impact of Phosphorus Treatment
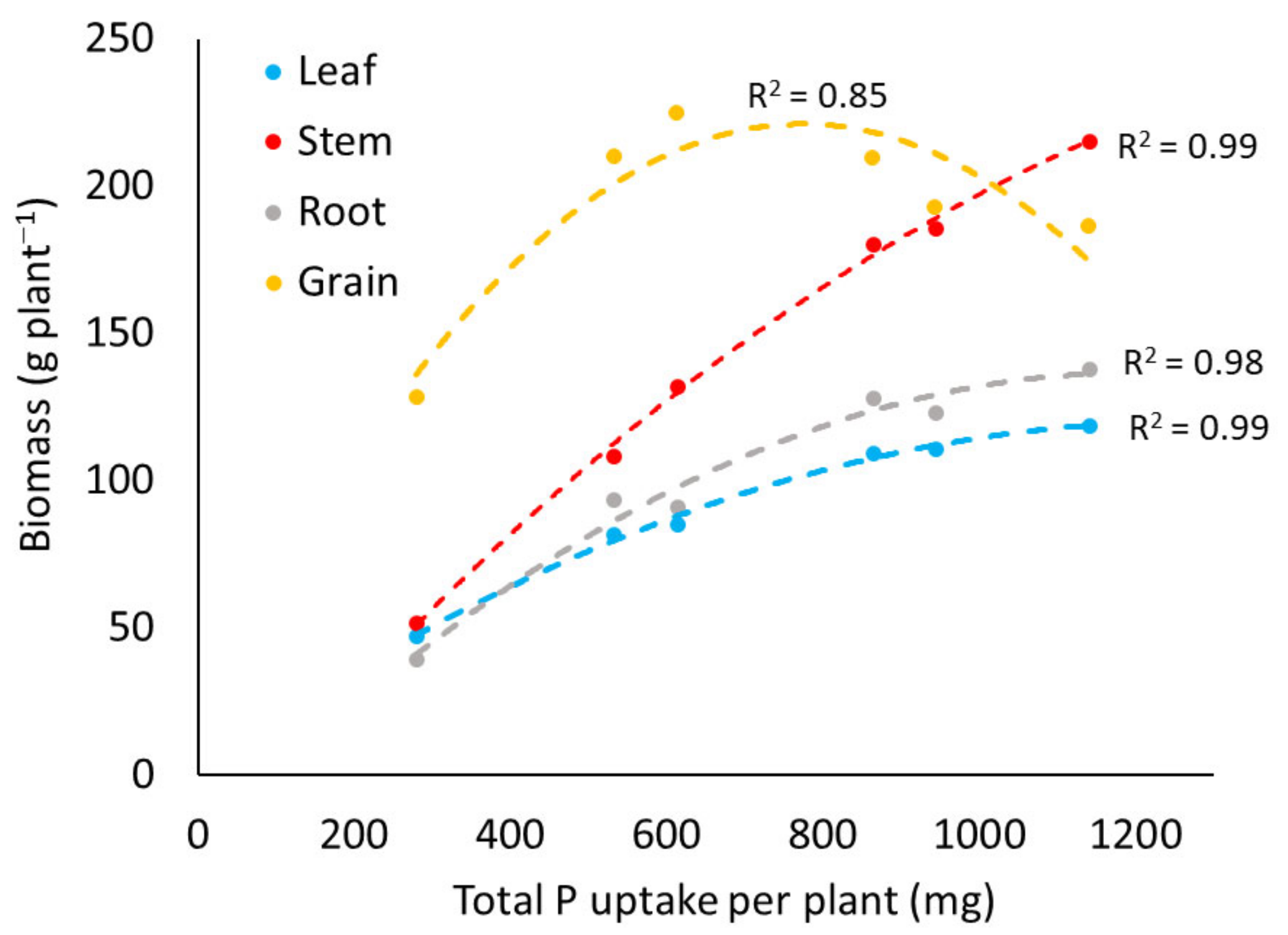
3.2.1. Biomass Production
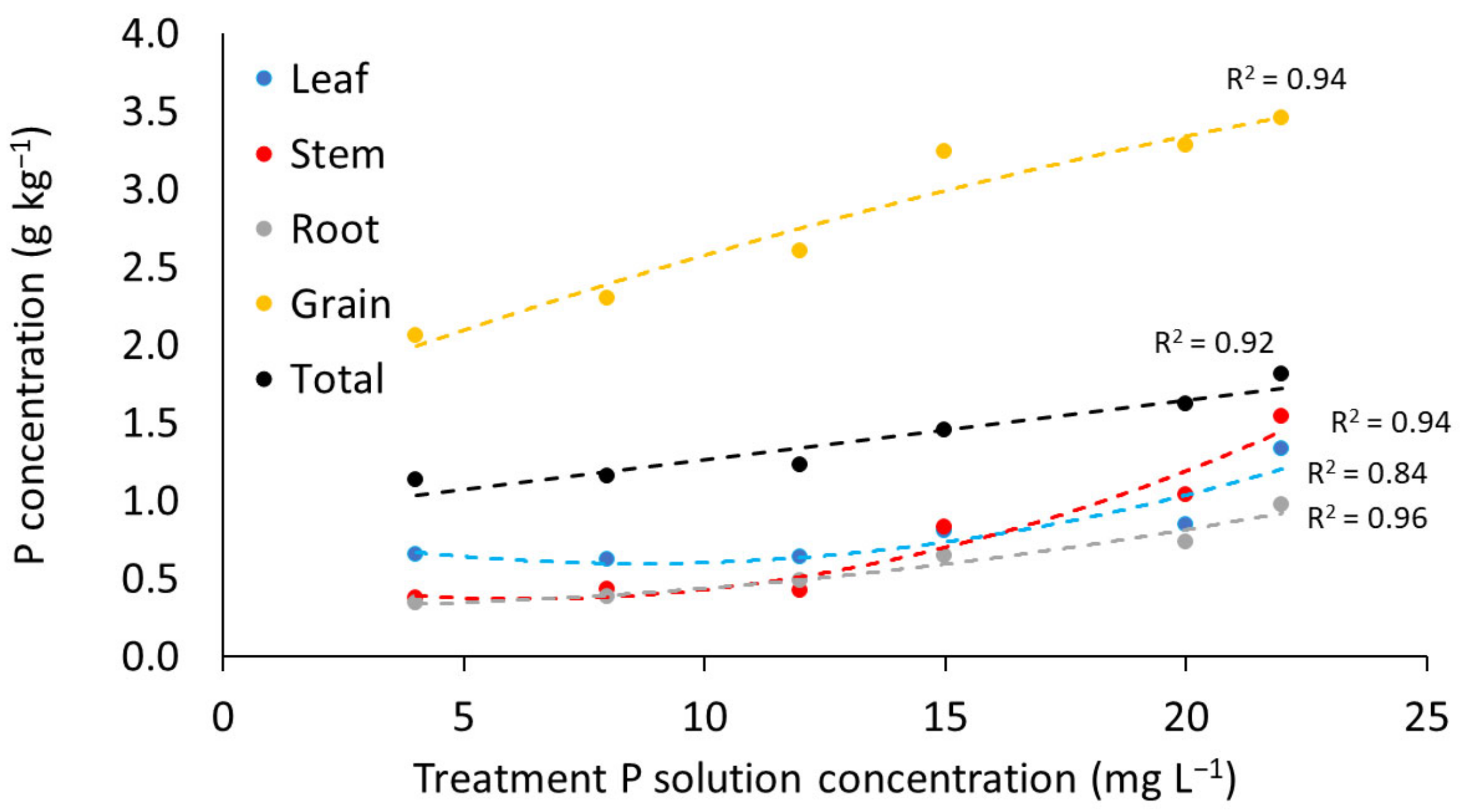
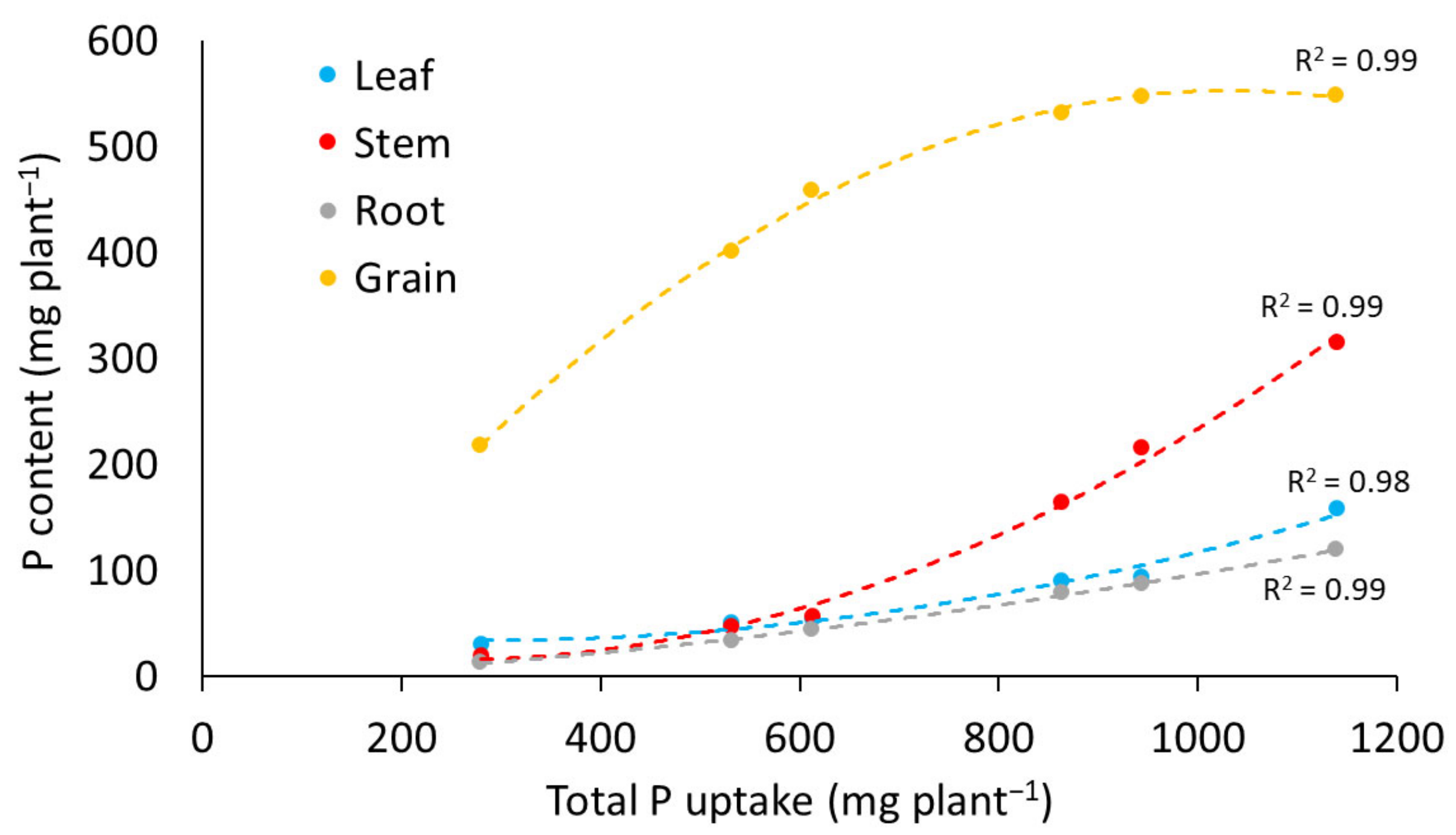
3.2.2. Phosphorus Content
3.2.3. Breakpoint Analysis of Phosphorus Uptake and Yield
4. Implications and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kamprath, E.J. The role of soil chemistry in the diagnosis of nutrient disorders in tropical situations. In The Mineral Nutrition of Legumes in Tropical and Subtropical Soils, Proceedings of the Workshop Held at CSIRO Cunningham Laboratory, Brisbane, QLD, Australia, 16–21 January 1978; under the auspices of the US/Australia Co-operative Science Program; CSIRO: Victoria, Australia, 1978; pp. 313–327. [Google Scholar]
- Wendt, R.C.; Corey, R.B. Available P determination by equilibration with dilute SrCl2. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 1981, 12, 557–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, F.R.; Lins, I.D.G. A phosphorus soil test interpretation for corn grown on acid soils varying in crystalline clay content. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 1984, 15, 1481–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, F.R. Current phosphorus availability indices: Characteristics and shortcomings. Soil Test. Prospect. Improv. Nutr. Recomm. 1994, 40, 101–113. [Google Scholar]
- Barber, S.A. Soil Nutrient Bioavailability: A Mechanistic Approach; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1995; ISBN 0471587478. [Google Scholar]
- Baligar, V.C.; Barber, S.A. Genotypic Differences of Corn for Ion Uptake 1. Agron. J. 1979, 71, 870–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, J.P.; Brown, K.M. Root Strategies for Phosphorus acquisition. In TheEcophysiology of Plant-Phosphorus Interactions; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; pp. 83–116. [Google Scholar]
- Wiethorn, M.; Penn, C.; Camberato, J. A research method for semi-automated large-scale cultivation of maize to full maturity in an artificial environment. Agronomy 2021, 11, 1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlen, D.L.; Flannery, R.L.; Sadler, E.J. Aerial accumulation and partitioning of nutrients by corn. Agron. J. 1988, 80, 232–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruns, H.A.; Ebelhar, M.W. Nutrient uptake of maize affected by nitrogen and potassium fertility in a humid subtropical environment. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2006, 37, 275–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setiyono, T.D.; Walters, D.T.; Cassman, K.G.; Witt, C.; Dobermann, A. Estimating maize nutrient uptake requirements. F. Crop. Res. 2010, 118, 158–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, P.; Gustafson, D.; Wicks III, Z. Study on nitrogen concentration of corn hybrids. Am. J. Agric. Biol. Sci. 2011, 6, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Djaman, K.; Irmak, S.; Martin, D.L.; Ferguson, R.B.; Bernards, M.L. Plant nutrient uptake and soil nutrient dynamics under full and limited irrigation and rainfed maize production. Agron. J. 2013, 105, 527–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciampitti, I.A.; Vyn, T.J. Nutrient sufficiency concepts for modern corn hybrids: Impacts of management practices and yield levels. Crop Manag. 2014, 13, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woli, K.P.; Sawyer, J.E.; Boyer, M.J.; Abendroth, L.J.; Elmore, R.W. Corn era hybrid macronutrient and dry matter accumulation in plant components. Agron. J. 2018, 110, 1648–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bartholomew, R.P.; Janssen, G. Luxury consumption of potassium by plants and its significance. J. Am. Soc. Agron. 1929, 21, 751–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, J.T.; Orchard, E.R.; Sumner, M.E. Leaf Composition and Yield Response of Corn in Relation to Quantity-Intensity Parameters for Potassium. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1970, 34, 94–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binford, G.D.; Blackmer, A.M.; El-Hout, N.M. Tissue test for excess nitrogen during corn production. Agron. J. 1990, 82, 124–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penn, C.J.; Camberato, J.J.; Wiethorn, M.W. How Much Phosphorus Uptake is Required for Achieving Maximum Maize Grain Yield? Part 2: Impact of phosphorus uptake on grain quality and partitioning of nutrients. Agronomy, 2023; accepted. [Google Scholar]
- Takkar, P.N.; Mann, M.S.; Bansal, R.L.; Randhawa, N.S.; Singh, H. Yield and Uptake Response of Corn to Zinc, as Influenced by Phosphorus Fertilization. Agron. J. 1976, 68, 942–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barry, D.A.J.; Miller, M.H. Phosphorus nutritional requirement of maize seedlings for maximum yield. Agron. J. 1989, 81, 95–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, J.; Dhaliwal, S.S.; Mavi, M.S. Zinc fractions and nutrition of maize (Zea mays L.) as affected by Olsen-P levels in soil. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2021, 120, 257–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Chen, X.-X.; Liu, Y.-M.; Liu, D.-Y.; Chen, X.-P.; Zou, C.-Q. Zinc uptake by roots and accumulation in maize plants as affected by phosphorus application and arbuscular mycorrhizal colonization. Plant Soil 2017, 413, 59–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heckman, J.R.; Sims, J.T.; Beegle, D.B.; Coale, F.J.; Herbert, S.J.; Bruulsema, T.W.; Bamka, W.J. Nutrient removal by corn grain harvest. Agron. J. 2003, 95, 587–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Phosphorus Treatment (mg L−1) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4 | 8 | 12 | 15 | 20 | 22 | ||||||||
| Parameter | Units | Mean | Std | Mean | Std | Mean | Std | Mean | Std | Mean | Std | Mean | Std |
| Leaf biomass ** | g plant−1 | 47 | 10.0 | 82 | 10.9 | 85 | 8.1 | 109 | 23.3 | 111 | 23.1 | 119 | 24.5 |
| Stem biomass ** | g plant−1 | 52 | 15.7 | 109 | 30.4 | 132 | 40.0 | 181 | 43.5 | 186 | 59.6 | 216 | 52.2 |
| Root biomass ** | g plant−1 | 40 | 22.0 | 94 | 53.5 | 91 | 30.2 | 128 | 42.6 | 123 | 45.0 | 138 | 88.5 |
| Grain yield ** | g plant−1 | 128 | 22.2 | 210 | 34.3 | 225 | 31.6 | 210 | 95.6 | 193 | 83.3 | 187 | 67.7 |
| Total biomass ** | g plant−1 | 248 | 43.1 | 462 | 67.0 | 499 | 61.3 | 595 | 67.6 | 583 | 95.3 | 630 | 153.5 |
| Stalk diameter ** | mm | 18.4 | 1.87 | 26.1 | 2.87 | 26.4 | 1.91 | 27.2 | 0.76 | 27.2 | 2.09 | 27.5 | 1.36 |
| Height to ear ** | cm | 76.2 | 8.85 | 80.7 | 8.33 | 81.3 | 5.15 | 81.9 | 10.03 | 84.8 | 9.33 | 87.8 | 7.68 |
| Description | Model | P-Uptake Breakpoint | Corresponding Biomass Breakpoint | p-Value | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (mg plant−1) | (g plant−1 or Relative Value) | ||||
| Grain yield averaged across hybrid | Linear-plateau | 519 | 205 | 0.05 | 0.84 |
| Linear-linear | 584 | 227 | 0.01 | 0.99 | |
| Relative grain yield | Linear-plateau | 518 | 0.85 | <0.01 | 0.60 |
| Linear-linear | 583 | 0.95 | <0.01 | 0.67 | |
| Total biomass averaged across hybrid | Linear-plateau | 731 | 603 | 0.01 | 0.98 |
| Linear-linear | 673 | 558 | 0.01 | 0.99 | |
| Relative total biomass | Linear-plateau | 798 | 0.95 | <0.01 | 0.93 |
| Linear-linear | 736 | 0.88 | <0.01 | 0.94 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Penn, C.J.; Camberato, J.J.; Wiethorn, M.A. How Much Phosphorus Uptake Is Required for Achieving Maximum Maize Grain Yield? Part 1: Luxury Consumption and Implications for Yield. Agronomy 2023, 13, 95. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13010095
Penn CJ, Camberato JJ, Wiethorn MA. How Much Phosphorus Uptake Is Required for Achieving Maximum Maize Grain Yield? Part 1: Luxury Consumption and Implications for Yield. Agronomy. 2023; 13(1):95. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13010095
Chicago/Turabian StylePenn, Chad J., James J. Camberato, and Matthew A. Wiethorn. 2023. "How Much Phosphorus Uptake Is Required for Achieving Maximum Maize Grain Yield? Part 1: Luxury Consumption and Implications for Yield" Agronomy 13, no. 1: 95. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13010095
APA StylePenn, C. J., Camberato, J. J., & Wiethorn, M. A. (2023). How Much Phosphorus Uptake Is Required for Achieving Maximum Maize Grain Yield? Part 1: Luxury Consumption and Implications for Yield. Agronomy, 13(1), 95. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13010095







