Straw Inputs Improve Soil Hydrophobicity and Enhance Organic Carbon Mineralization
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Site
2.2. Corn Straw
2.3. Experimental Design
2.4. Sample Collection
2.5. Physical and Chemical Analysis
2.5.1. SWR Determination
2.5.2. Soil Aggregates
2.5.3. CO2-C Emission
2.6. Analytical Methods
3. Results
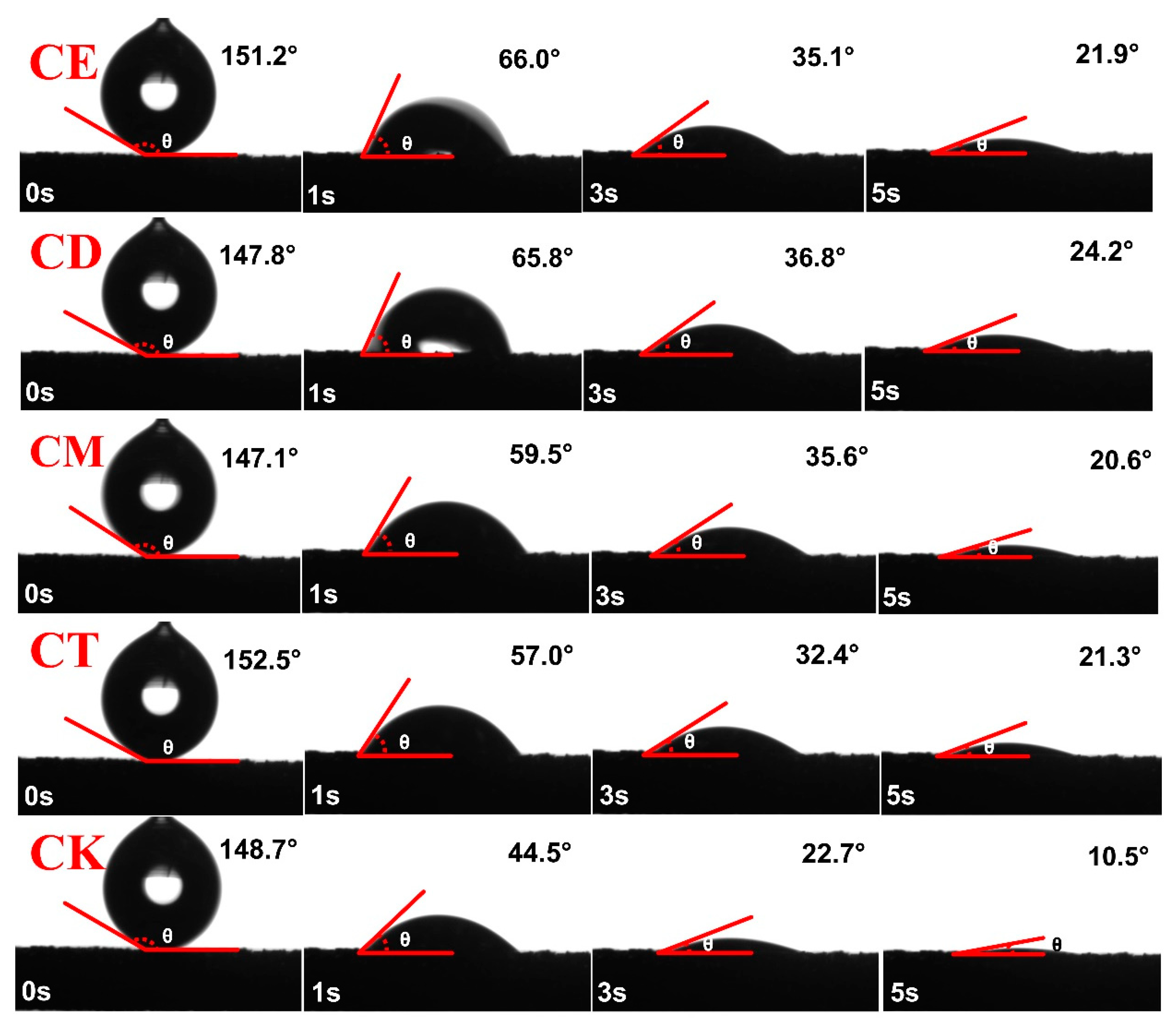
3.1. SWR
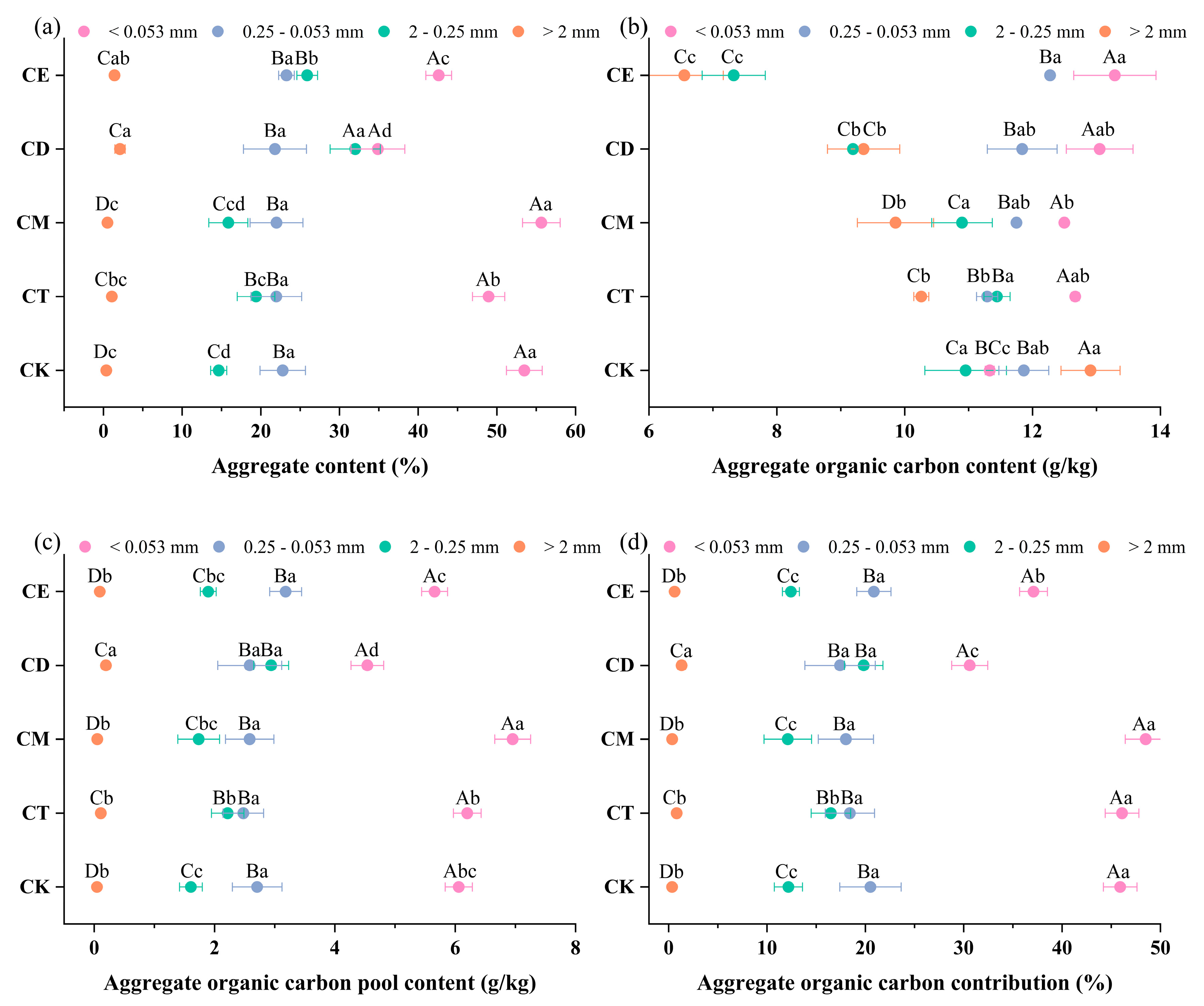
3.2. Soil Aggregates
3.3. CO2-C Emission Characteristics
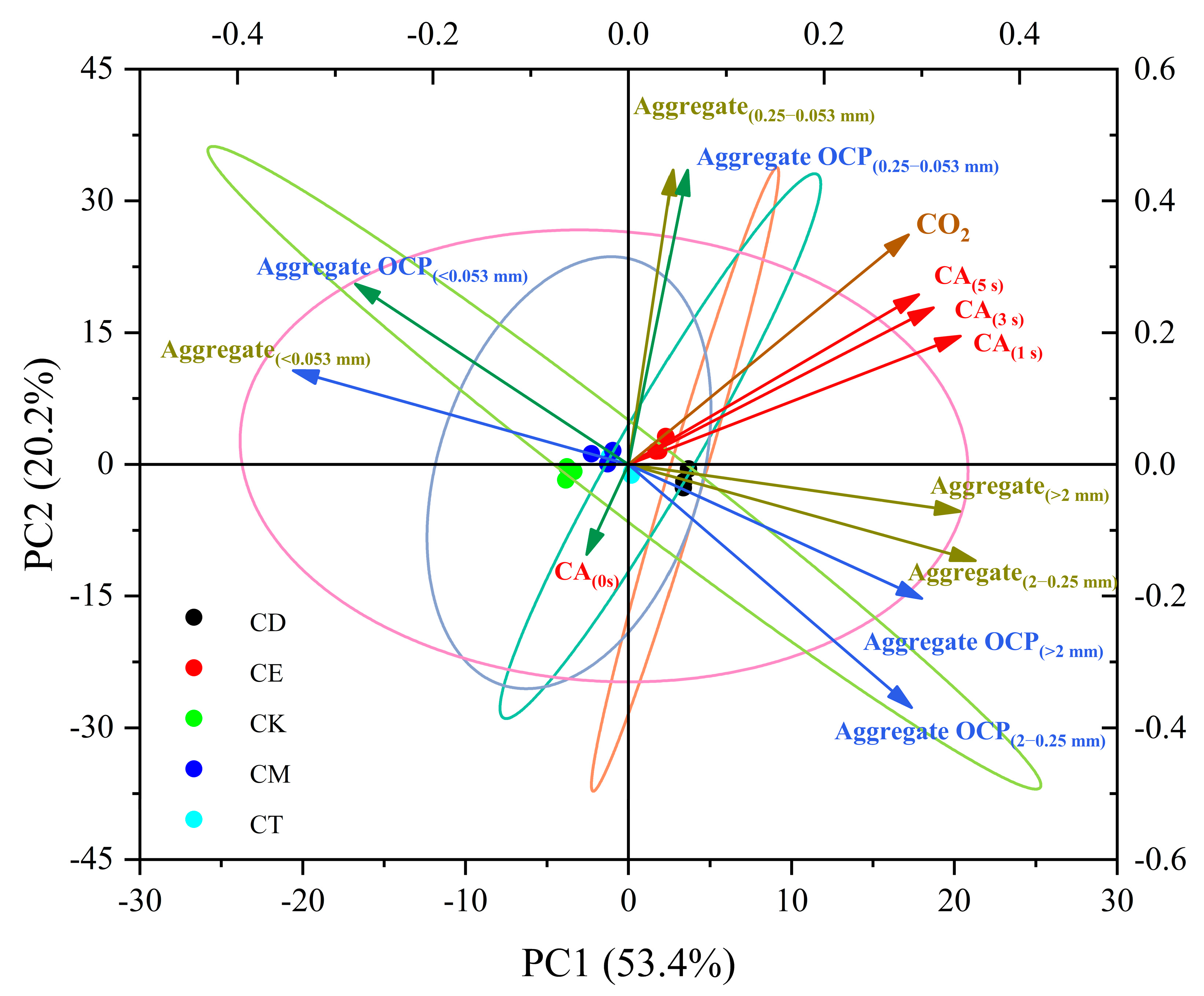
3.4. Relationship Analysis of SWR, Soil Aggregates, and CO2-C Emission under Different Straw Addition Methods
4. Discussion
4.1. Different Straw Addition Methods Affect SWR
4.2. Enhancement of SWR Improves Aggregate Stability
4.3. Different Straw-Return Methods Change the SWR and Thus Affect CO2 Emission
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, H.; Dai, M.; Dai, S.; Dong, X. Current Status and Environment Impact of Direct Straw Return in China’s Cropland—A Review. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 159, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Lai, D.Y.F.; Wang, C.; Pan, T.; Zeng, C. Effects of Rice Straw Incorporation on Active Soil Organic Carbon Pools in a Subtropical Paddy Field. Soil Tillage Res. 2015, 152, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guenet, B.; Neill, C.; Bardoux, G.; Abbadie, L. Is There a Linear Relationship between Priming Effect Intensity and the Amount of Organic Matter Input? Appl. Soil Ecol. 2010, 46, 436–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, D.; Li, X.; Gregorich, E.; McLaughlin, N.; Zhang, X.; Chen, X.; Zhang, S.; et al. Effect of Long-Term Tillage and Cropping System on Portion of Fungal and Bacterial Necromass Carbon in Soil Organic Carbon. Soil Tillage Res. 2022, 218, 105307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyamadzawo, G.; Nyamangara, J.; Nyamugafata, P.; Muzulu, A. Soil Microbial Biomass and Mineralization of Aggregate Protected Carbon in Fallow-Maize Systems under Conventional and No-Tillage in Central Zimbabwe. Soil Tillage Res. 2009, 102, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goebel, M.-O.; Bachmann, J.; Woche, S.K.; Fischer, W.R. Soil Wettability, Aggregate Stability, and the Decomposition of Soil Organic Matter. Geoderma 2005, 128, 80–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devine, S.; Markewitz, D.; Hendrix, P.; Coleman, D. Soil Aggregates and Associated Organic Matter under Conventional Tillage, No-Tillage, and Forest Succession after Three Decades. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e84988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raiesi, F. Carbon and N Mineralization as Affected by Soil Cultivation and Crop Residue in a Calcareous Wetland Ecosystem in Central Iran. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2006, 112, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Six, J.; Elliott, E.T.; Paustian, K. Soil Macroaggregate Turnover and Microaggregate Formation: A Mechanism for C Sequestration under No-Tillage Agriculture. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2000, 32, 2099–2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whalen, J.K.; Bottomley, P.J.; Myrold, D.D. Carbon and Nitrogen Mineralization from Light- and Heavy-Fraction Additions to Soil. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2000, 32, 1345–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuentes, M.; Hidalgo, C.; Etchevers, J.; De León, F.; Guerrero, A.; Dendooven, L.; Verhulst, N.; Govaerts, B. Conservation Agriculture, Increased Organic Carbon in the Top-Soil Macro-Aggregates and Reduced Soil CO2 Emissions. Plant Soil 2012, 355, 183–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotrufo, M.F.; Soong, J.L.; Horton, A.J.; Campbell, E.E.; Haddix, M.L.; Wall, D.H.; Parton, W.J. Formation of Soil Organic Matter via Biochemical and Physical Pathways of Litter Mass Loss. Nat. Geosci. 2015, 8, 776–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comino, F.; Aranda, V.; Domínguez-Vidal, A.; Ayora-Cañada, M.J. Thermal Destruction of Organic Waste Hydrophobicity for Agricultural Soils Application. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 202, 94–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Blas, E.; Rodríguez-Alleres, M.; Almendros, G. Speciation of Lipid and Humic Fractions in Soils under Pine and Eucalyptus Forest in Northwest Spain and Its Effect on Water Repellency. Geoderma 2010, 155, 242–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaumann, G.E.; Braun, B.; Kirchner, D.; Rotard, W.; Szewzyk, U.; Grohmann, E. Influence of Biofilms on the Water Repellency of Urban Soil Samples. Hydrol. Process. 2007, 21, 2276–2284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aranda, V.; Calero, J.; Plaza, I.; Ontiveros-Ortega, A. Long-Term Effects of Olive Mill Pomace Co-Compost on Wettability and Soil Quality in Olive Groves. Geoderma 2016, 267, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mataix-Solera, J.; Cerdà, A.; Arcenegui, V.; Jordán, A.; Zavala, L.M. Fire Effects on Soil Aggregation: A Review. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2011, 109, 44–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco-Canqui, H.; Lal, R. Extent of Soil Water Repellency under Long-Term No-till Soils. Geoderma 2009, 149, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wu, Q.J.; Wu, L.; Ritsema, C.J.; Dekker, L.W.; Feyen, J. Effects of Soil Water Repellency on Infiltration Rate and Flow Instability. J. Hydrol. 2000, 231–232, 265–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piccolo, A.; Mbagwu, J.S.C. Role of Hydrophobic Components of Soil Organic Matter in Soil Aggregate Stability. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1999, 63, 1801–1810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czachor, H.; Doerr, S.H.; Lichner, L. Water Retention of Repellent and Subcritical Repellent Soils: New Insights from Model and Experimental Investigations. J. Hydrol. 2010, 380, 104–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Jonge, L.W.; Moldrup, P.; Jacobsen, O.H. Soil-Water Content Dependency of Water Repellency in Soils. Soil Sci. 2007, 172, 577–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawamoto, K.; Moldrup, P.; Komatsu, T.; de Jonge, L.W.; Oda, M. Water Repellency of Aggregate Size Fractions of a Volcanic Ash Soil. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2007, 71, 1658–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lützow, M.v.; Kögel-Knabner, I.; Ekschmitt, K.; Matzner, E.; Guggenberger, G.; Marschner, B.; Flessa, H. Stabilization of Organic Matter in Temperate Soils: Mechanisms and Their Relevance under Different Soil Conditions—A Review: Mechanisms for Organic Matter Stabilization in Soils. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2006, 57, 426–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.; Yang, H.; Huang, C.; Ju, X. Effects of Nitrogen Management and Straw Return on Soil Organic Carbon Sequestration and Aggregate-Associated Carbon: Organic Fertilizer Benefit for SOC Sequestration. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2018, 69, 913–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Qi, J.-Y.; Zhang, X.-Z.; Li, S.-S.; Latif Virk, A.; Zhao, X.; Xiao, X.-P.; Zhang, H.-L. Effects of Tillage and Residue Management on Soil Aggregates and Associated Carbon Storage in a Double Paddy Cropping System. Soil Tillage Res. 2019, 194, 104339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messiga, A.J.; Ziadi, N.; Angers, D.A.; Morel, C.; Parent, L.-E. Tillage Practices of a Clay Loam Soil Affect Soil Aggregation and Associated C and P Concentrations. Geoderma 2011, 164, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerschlauer, F.; Dannenmann, M.; Kühnel, A.; Meier, R.; Kolar, A.; Butterbach-Bahl, K.; Kiese, R. Gross Nitrogen Turnover of Natural and Managed Tropical Ecosystems at Mt. Kilimanjaro, Tanzania. Ecosystems 2016, 19, 1271–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leelamanie, D.A.L.; Karube, J.; Yoshida, A. Characterizing Water Repellency Indices: Contact Angle and Water Drop Penetration Time of Hydrophobized Sand. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2008, 54, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bünemann, E.K.; Bongiorno, G.; Bai, Z.; Creamer, R.E.; De Deyn, G.; de Goede, R.; Fleskens, L.; Geissen, V.; Kuyper, T.W.; Mäder, P.; et al. Soil Quality—A Critical Review. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2018, 120, 105–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cervera-Mata, A.; Aranda, V.; Ontiveros-Ortega, A.; Comino, F.; Martín-García, J.M.; Vela-Cano, M.; Delgado, G. Hydrophobicity and Surface Free Energy to Assess Spent Coffee Grounds as Soil Amendment. Relationships with soil quality. CATENA 2021, 196, 104826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, E.T. Aggregate Structure and Carbon, Nitrogen, and Phosphorus in Native and Cultivated Soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1986, 50, 627–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, D.W.; Sommers, L.E. Total Carbon, Organic Carbon, and Organic Matter. In Methods of Soil Analysis; Agronomy Monographs; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1983; pp. 539–579. ISBN 978-0-89118-977-0. [Google Scholar]
- Doerr, S.H.; Shakesby, R.A.; Walsh, R.P.D. Soil Water Repellency: Its Causes, Characteristics and Hydro-Geomorphological Significance. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2000, 51, 33–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mainwaring, K.; Hallin, I.L.; Douglas, P.; Doerr, S.H.; Morley, C.P. The Role of Naturally Occurring Organic Compounds in Causing Soil Water Repellency: Soil Water Repellency from Organic Compounds. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2013, 64, 667–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maryganova, V.; Szajdak, L.W.; Tychinskaya, L. Hydrophobic and Hydrophilic Properties of Humic Acids from Soils under Shelterbelts of Different Ages. Chem. Ecol. 2010, 26, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olk, D.C.; Bloom, P.R.; De Nobili, M.; Chen, Y.; McKnight, D.M.; Wells, M.J.M.; Weber, J. Using Humic Fractions to Understand Natural Organic Matter Processes in Soil and Water: Selected Studies and Applications. J. Environ. Qual. 2019, 48, 1633–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, J.; Chen, Y.; Jamroz, E.; Miano, T. Preface: Humic Substances in the Environment. J. Soils Sediments 2018, 18, 2665–2667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogelmann, E.S.; Reichert, J.M.; Prevedello, J.; Consensa, C.O.B.; Oliveira, A.É.; Awe, G.O.; Mataix-Solera, J. Threshold Water Content beyond Which Hydrophobic Soils Become Hydrophilic: The Role of Soil Texture and Organic Matter Content. Geoderma 2013, 209–210, 177–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matějková, Š.; Šimon, T. Application of FTIR Spectroscopy for Evaluation of Hydrophobic/Hydrophilic Organic Components in Arable Soil. Plant Soil Environ. 2012, 58, 192–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommer, R.; Ryan, J.; Masri, S.; Singh, M.; Diekmann, J. Effect of Shallow Tillage, Moldboard Plowing, Straw Management and Compost Addition on Soil Organic Matter and Nitrogen in a Dryland Barley/Wheat-Vetch Rotation. Soil Tillage Res. 2011, 115–116, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, H.; Zhang, Q.; Shao, H.; Gao, C.; Zhang, X. Effects of Fertilization and Straw Return Methods on the Soil Carbon Pool and CO2 Emission in a Reclaimed Mine Spoil in Shanxi Province, China. Soil Tillage Res. 2019, 195, 104361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stemmer, M.; Von Lützow, M.; Kandeler, E.; Pichlmayer, F.; Gerzabek, M.H. The Effect of Maize Straw Placement on Mineralization of C and N in Soil Particle Size Fractions. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 1999, 50, 73–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wingeyer, A.B.; Walters, D.T.; Drijber, R.A.; Olk, D.C.; Arkebauer, T.J.; Verma, S.B.; Wedin, D.A.; Francis, C.A. Fall Conservation Deep Tillage Stabilizes Maize Residues into Soil Organic Matter. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2012, 76, 2154–2163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.M.; He, L.; Zhang, Z.D.; Wang, H.B.; Zhao, L.P. Simulation of Accumulation and Mineralization (CO2 Release) of Organic Carbon in Chernozem under Different Straw Return Ways after Corn Harvesting. Soil Tillage Res. 2016, 156, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.; Yang, N.; Lu, C.; Qin, X.; Siddique, K.H.M. Soil Organic Carbon, Total Nitrogen, Available Nutrients, and Yield under Different Straw Returning Methods. Soil Tillage Res. 2021, 214, 105171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haynes, R. Labile Organic Matter as an Indicator of Organic Matter Quality in Arable and Pastoral Soils in New Zealand. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2000, 32, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallett, P.D.; Baumgartl, T.; Young, I.M. Subcritical Water Repellency of Aggregates from a Range of Soil Management Practices. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2001, 65, 184–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liyanage, T.D.P.; Leelamanie, D.A.L. Influence of Organic Manure Amendments on Water Repellency, Water Entry Value, and Water Retention of Soil Samples from a Tropical Ultisol. J. Hydrol. Hydromech. 2016, 64, 160–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKissock, I.; Gilkes, R.J.; Walker, E.L. The Reduction of Water Repellency by Added Clay Is Influenced by Clay and Soil Properties. Appl. Clay Sci. 2002, 20, 225–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, W.J.; Sanderman, J.; Melillo, J.M. Decreased Soil Organic Matter in a Long-Term Soil Warming Experiment Lowers Soil Water Holding Capacity and Affects Soil Thermal and Hydrological Buffering. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2020, 125, e2019JG005158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zavala, L.M.; González, F.A.; Jordán, A. Intensity and Persistence of Water Repellency in Relation to Vegetation Types and Soil Parameters in Mediterranean SW Spain. Geoderma 2009, 152, 361–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosentino, D.; Hallett, P.D.; Michel, J.C.; Chenu, C. Do Different Methods for Measuring the Hydrophobicity of Soil Aggregates Give the Same Trends in Soil Amended with Residue? Geoderma 2010, 159, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogelmann, E.S.; Reichert, J.M.; Reinert, D.J.; Mentges, M.I.; Vieira, D.A.; De Barros, C.A.P.; Fasinmirin, J.T. Water Repellency in Soils of Humid Subtropical Climate of Rio Grande Do Sul, Brazil. Soil Tillage Res. 2010, 110, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behrends Kraemer, F.; Hallett, P.D.; Morrás, H.; Garibaldi, L.; Cosentino, D.; Duval, M.; Galantini, J. Soil Stabilisation by Water Repellency under No-till Management for Soils with Contrasting Mineralogy and Carbon Quality. Geoderma 2019, 355, 113902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, C.M.M.; Michelsen, P.P.; Oades, J.M. Amelioration of Water Repellency: Application of Slow-Release Fertilisers to Stimulate Microbial Breakdown of Waxes. J. Hydrol. 2000, 231–232, 342–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olorunfemi, I.E.; Fasinmirin, J.T. Land Use Management Effects on Soil Hydrophobicity and Hydraulic Properties in Ekiti State, Forest Vegetative Zone of Nigeria. CATENA 2017, 155, 170–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma’Shum, M.; Tate, M.E.; Jones, G.P.; Oades, J.M. Extraction and Characterization of Water-Repellent Materials from Australian Soils. J. Soil Sci. 1988, 39, 99–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horne, D.J.; McIntosh, J.C. Hydrophobic Compounds in Sands in New Zealand—Extraction, Characterisation and Proposed Mechanisms for Repellency Expression. J. Hydrol. 2000, 231–232, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graber, E.R.; Tagger, S.; Wallach, R. Role of Divalent Fatty Acid Salts in Soil Water Repellency. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2009, 73, 541–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morley, C.P.; Mainwaring, K.A.; Doerr, S.H.; Douglas, P.; Llewellyn, C.T.; Dekker, L.W. Organic Compounds at Different Depths in a Sandy Soil and Their Role in Water Repellency. Soil Res. 2005, 43, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhillon, G.S.; Gillespie, A.; Peak, D.; Van Rees, K.C.J. Spectroscopic Investigation of Soil Organic Matter Composition for Shelterbelt Agroforestry Systems. Geoderma 2017, 298, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atanassova, I.; Doerr, S. Organic Compounds of Different Extractability in Total Solvent Extracts from Soils of Contrasting Water Repellency. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2010, 61, 298–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doerr, S.H.; Llewellyn, C.T.; Douglas, P.; Morley, C.P.; Mainwaring, K.A.; Haskins, C.; Johnsey, L.; Ritsema, C.J.; Stagnitti, F.; Allinson, G.; et al. Extraction of Compounds Associated with Water Repellency in Sandy Soils of Different Origin. Soil Res. 2005, 43, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capriel, P.; Beck, T.; Borchert, H.; Gronholz, J.; Zachmann, G. Hydrophobicity of the Organic Matter in Arable Soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1995, 27, 1453–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKissock, I.; Gilkes, R.J.; van Bronswijk, W. The Relationship of Soil Water Repellency to Aliphatic C and Kaolin Measured Using DRIFT. Soil Res. 2003, 41, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Peñaloza, F.A.; Cerdà, A.; Zavala, L.M.; Jordán, A.; Giménez-Morera, A.; Arcenegui, V. Do Conservative Agriculture Practices Increase Soil Water Repellency? A Case Study in Citrus-Cropped Soils. Soil Tillage Res. 2012, 124, 233–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Schaeffer, S.; Sun, Z.; Zhang, J.; An, T.; Wang, J. Carbon Stabilization in Aggregate Fractions Responds to Straw Input Levels under Varied Soil Fertility Levels. Soil Tillage Res. 2020, 199, 104593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Lu, M.; Cui, J.; Li, B.; Fang, C. Effects of Straw Carbon Input on Carbon Dynamics in Agricultural Soils: A Meta-Analysis. Glob. Change Biol. 2014, 20, 1366–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Jia, Z.; Liang, L.; Yang, B.; Ding, R.; Nie, J.; Wang, J. Maize Straw Effects on Soil Aggregation and Other Properties in Arid Land. Soil Tillage Res. 2015, 153, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, T.S.; Bhagat, R.M. Impact of Rice Straw Management Practices on Yield, Nitrogen Uptake and Soil Properties in a Wheat-Rice Rotation in Northern India. Fertil. Res. 1992, 33, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benbi, D.K.; Senapati, N. Soil Aggregation and Carbon and Nitrogen Stabilization in Relation to Residue and Manure Application in Rice–Wheat Systems in Northwest India. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2010, 87, 233–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monreal, C.M.; Schnitzer, M.; Schulten, H.-R.; Campbell, C.A.; Anderson, D.W. Soil Organic Structures in Macro and Microaggregates of a Cultivated Brown Chernozem. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1995, 27, 845–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chenu, C.; Le Bissonnais, Y.; Arrouays, D. Organic Matter Influence on Clay Wettability and Soil Aggregate Stability. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2000, 64, 1479–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leelamanie, D.A.L.; Karube, J. Water Stable Aggregates of Japanese Andisol as Affected by Hydrophobicity and Drying Temperature. J. Hydrol. Hydromech. 2014, 62, 97–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goebel, M.-O.; Bachmann, J.; Reichstein, M.; Janssens, I.A.; Guggenberger, G. Soil Water Repellency and Its Implications for Organic Matter Decomposition—Is There a Link to Extreme Climatic Events? Glob. Change Biol. 2011, 17, 2640–2656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eynard, A.; Schumacher, T.E.; Lindstrom, M.J.; Malo, D.D.; Kohl, R.A. Effects of Aggregate Structure and Organic C on Wettability of Ustolls. Soil Tillage Res. 2006, 88, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kořenková, L.; Matúš, P. Role of Water Repellency in Aggregate Stability of Cultivated Soils under Simulated Raindrop Impact. Eurasian Soil Sci. 2015, 48, 754–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piyaruwan, H.I.G.S.; Leelamanie, D.A.L. Existence of Water Repellency and Its Relation to Structural Stability of Soils in a Tropical Eucalyptus Plantation Forest. Geoderma 2020, 380, 114679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogelmann, E.S.; Reichert, J.M.; Prevedello, J.; Awe, G.O.; Mataix-Solera, J. Can occurrence of soil hydrophobicity promote the increase of aggregates stability? CATENA 2013, 110, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Gong, M.; Zhang, P.; Li, L.; Li, W.; Lee, R. Silver-Embedded Zeolite Crystals as Substrates for Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering. J. Mater. Sci. 2011, 46, 3162–3168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodowski, S.; John, B.; Flessa, H.; Amelung, W. Aggregate-Occluded Black Carbon in Soil: Occluded Black Carbon in Soil. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2006, 57, 539–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Wang, W.; Shen, S. Response of Soil Aggregate Stability and Distribution of Organic Carbon to Alpine Grassland Degradation in Northwest Sichuan. Geoderma Reg. 2020, 22, e00309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonetti, G.; Francioso, O.; Nardi, S.; Berti, A.; Brugnoli, E.; Francesco Morari, E.L. Characterization of Humic Carbon in Soil Aggregates in a Long-Term Experiment with Manure and Mineral Fertilization. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2012, 76, 880–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarthy, J.F.; Ilavsky, J.; Jastrow, J.D.; Mayer, L.M.; Perfect, E.; Zhuang, J. Protection of Organic Carbon in Soil Microaggregates via Restructuring of Aggregate Porosity and Filling of Pores with Accumulating Organic Matter. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2008, 72, 4725–4744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, T.; Schaeffer, S.; Zhuang, J.; Radosevich, M.; Li, S.; Li, H.; Pei, J.; Wang, J. Dynamics and Distribution of 13C-Labeled Straw Carbon by Microorganisms as Affected by Soil Fertility Levels in the Black Soil Region of Northeast China. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2015, 51, 605–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, S.; Dou, S.; Chen, G.; Wang, G.; Zhuang, J. Isotopic Characterization of Sequestration and Transformation of Plant Residue Carbon in Relation to Soil Aggregation Dynamics. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2015, 96, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, D.; He, N.; Zhang, J. Dynamics of Soil Organic Carbon and Aggregate Stability with Grazing Exclusion in the Inner Mongolian Grasslands. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0146757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, J.M.; Bragg, E. Microorganisms and Soil Aggregate Stability. In Soil Restoration; Lal, R., Stewart, B.A., Eds.; Advances in Soil Science; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1985; Volume 17, pp. 133–171. ISBN 978-1-4612-7684-5. [Google Scholar]
- Piccolo, A.; Mbagwu, J.S.C. Effects of Different Organic Waste Amendments on Soil Microaggregates Stability and Molecular Sizes of Humic Substances. Plant Soil 1990, 123, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; Wang, L.; Hou, Y.; Wang, H.; Tsang, Y.F.; Wu, J. Responses of Soil Microbial Community Structure and Activity to Incorporation of Straws and Straw Biochars and Their Effects on Soil Respiration and Soil Organic Carbon Turnover. Pedosphere 2019, 29, 492–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duong, T.T.T.; Baumann, K.; Marschner, P. Frequent Addition of Wheat Straw Residues to Soil Enhances Carbon Mineralization Rate. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2009, 41, 1475–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Sun, B.; Mao, J.; Sui, Y.; Cao, X. Structural Convergence of Maize and Wheat Straw during Two-Year Decomposition under Different Climate Conditions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 7159–7165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Fan, J.; Ding, W.; Bol, R.; Chen, Z.; Luo, J.; Bolan, N. Stage-Specific Response of Litter Decomposition to N and S Amendments in a Subtropical Forest Soil. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2016, 52, 711–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Six, J.; Conant, R.T.; Paul, E.A.; Paustian, K. Stabilization Mechanisms of Soil Organic Matter: Implications for C-Saturation of Soils. Plant Soil 2002, 241, 155–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bimüller, C.; Kreyling, O.; Kölbl, A.; Von Lützow, M.; Kögel-Knabner, I. Carbon and Nitrogen Mineralization in Hierarchically Structured Aggregates of Different Size. Soil Tillage Res. 2016, 160, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.; Pausch, J.; Yu, G.; Blagodatskaya, E.; Gao, Y.; Kuzyakov, Y. Aggregate Size and Their Disruption Affect 14C-Labeled Glucose Mineralization and Priming Effect. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2015, 90, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puget, P.; Chenu, C.; Balesdent, J. Total and Young Organic Matter Distributions in Aggregates of Silty Cultivated Soils. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 1995, 46, 449–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Wright, A.L.; Wang, J.; Li, Z. Long-Term Tillage Effects on the Distribution Patterns of Microbial Biomass and Activities within Soil Aggregates. CATENA 2011, 87, 276–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zuo, Q.; Du, B.; Chen, W.; Wei, D.; Huang, Q. Contrasting Responses of Bacterial and Fungal Communities to Aggregate-Size Fractions and Long-Term Fertilizations in Soils of Northeastern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 635, 784–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franzluebbers, A.J.; Arshad, M.A. Water-Stable Aggregation and Organic Matter in Four Soils under Conventional and Zero Tillage. Can. J. Soil Sci. 1996, 76, 387–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangalassery, S.; Sjögersten, S.; Sparkes, D.L.; Sturrock, C.J.; Mooney, S.J. The Effect of Soil Aggregate Size on Pore Structure and Its Consequence on Emission of Greenhouse Gases. Soil Tillage Res. 2013, 132, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.; Gutknecht, J.L.M.; Herman, D.J.; Keck, D.C.; Firestone, M.K.; Cheng, W. Rhizosphere Priming Effects on Soil Carbon and Nitrogen Mineralization. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2014, 76, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.; Yang, N.; Zhao, J.; Shaaban, M.; Hu, R. Crop Straw Incorporation Mediates the Impacts of Soil Aggregate Size on Greenhouse Gas Emissions. Geoderma 2021, 401, 115342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

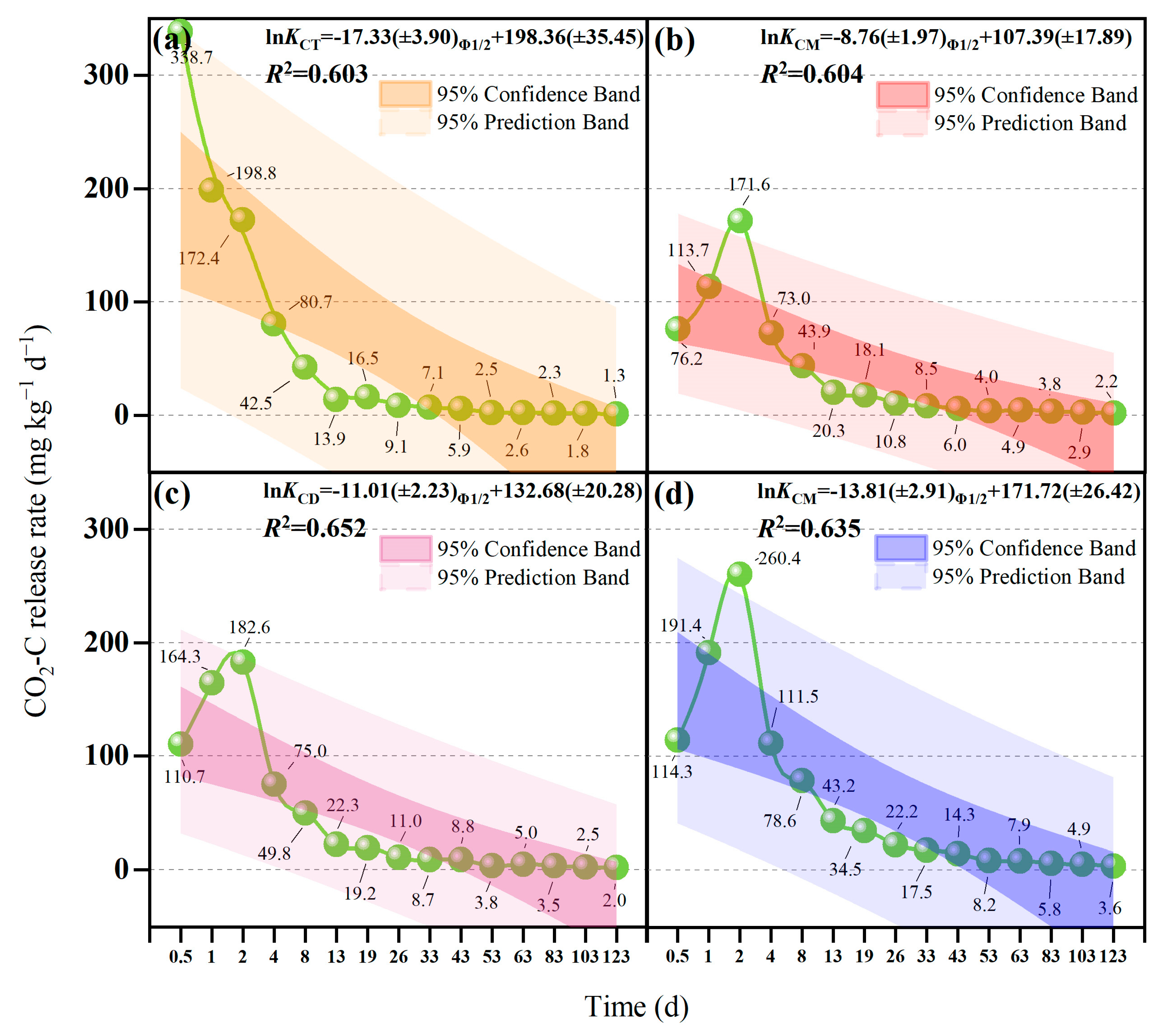


| Treatment | CO2 Emission Peak | First Slow-Emission Platform | Second Slow-Emission Platform | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Peak | Emission Rate | Process | Average Emission Rate | Process | Average Emission Rate | |
| (Days) | (mg kg−1 d−1) | (Days) | (mg kg−1 d−1) | (Days) | (mg kg−1 d−1) | |
| CT | Th 0.5 | 338.7 | Th 0.5–19 | 99.42 ± 6.19b | Th 19–123 | 17.19 ± 1.45c |
| CM | Th 2 | 171.6 | Th 2–26 | 69.44 ± 2.49c | Th 26–123 | 19.09 ± 1.06bc |
| CD | Th 2 | 182.6 | Th 2–26 | 73.59 ± 7.53c | Th 26–123 | 19.42 ± 0.84b |
| CE | Th 2 | 260.4 | Th 2–33 | 115.76 ± 3.96a | Th 33–123 | 26.81 ± 2.60a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, B.-Y.; Dou, S.; Guo, D.; Guan, S. Straw Inputs Improve Soil Hydrophobicity and Enhance Organic Carbon Mineralization. Agronomy 2023, 13, 2618. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13102618
Zhang B-Y, Dou S, Guo D, Guan S. Straw Inputs Improve Soil Hydrophobicity and Enhance Organic Carbon Mineralization. Agronomy. 2023; 13(10):2618. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13102618
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Bo-Yan, Sen Dou, Dan Guo, and Song Guan. 2023. "Straw Inputs Improve Soil Hydrophobicity and Enhance Organic Carbon Mineralization" Agronomy 13, no. 10: 2618. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13102618
APA StyleZhang, B.-Y., Dou, S., Guo, D., & Guan, S. (2023). Straw Inputs Improve Soil Hydrophobicity and Enhance Organic Carbon Mineralization. Agronomy, 13(10), 2618. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13102618







