Synergistic Effects of N Fertilization and Irrigation on Soil Bacterial Community in Super Rice Paddies
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
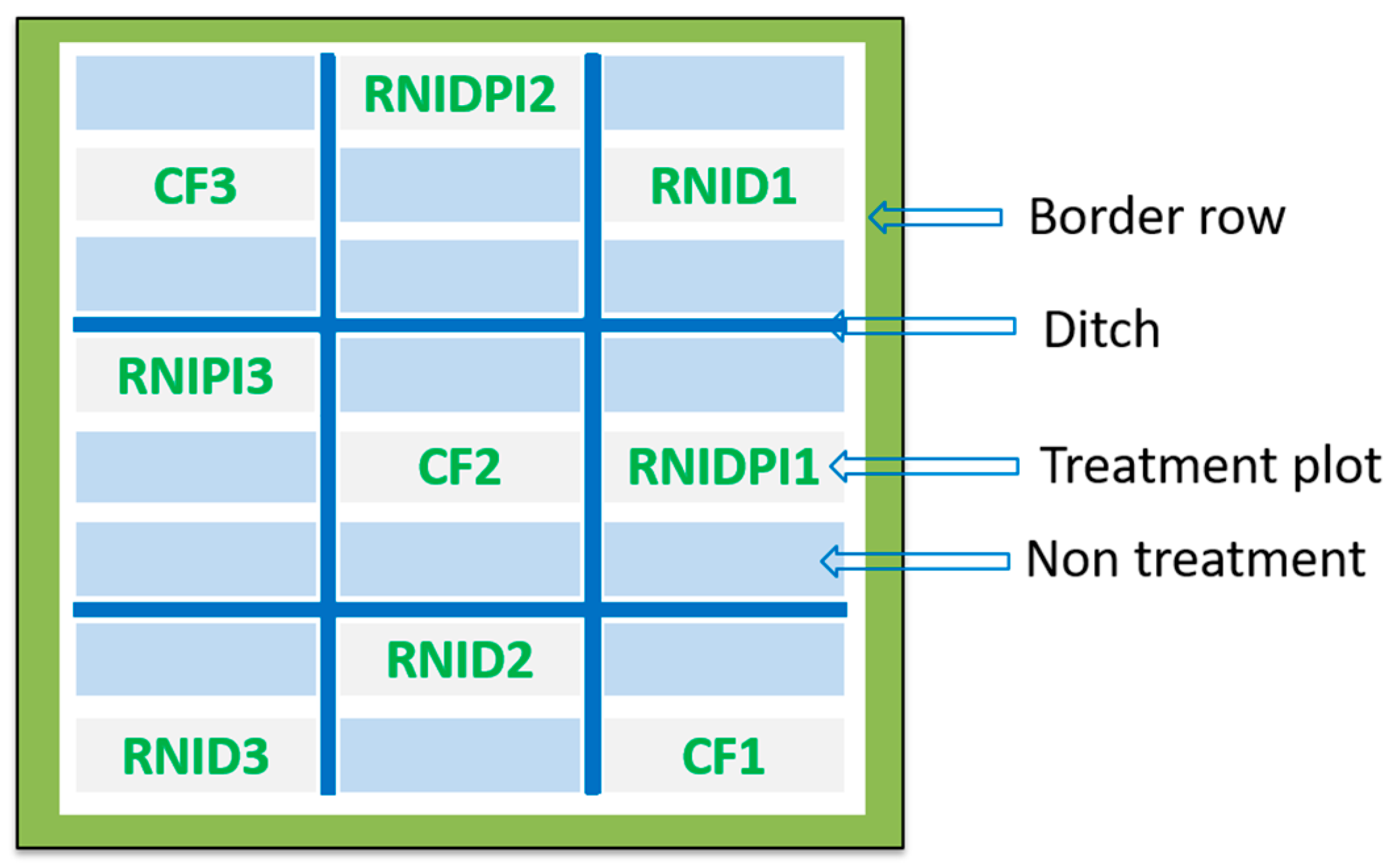
2.1. Study Site and Experimental Setup
2.2. Determination of Soil Properties
2.3. Rice Yield Component Determination
2.4. Bacterial Community Analyses
Data Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Soil Fertility Parameters and Rice Grain Yield
3.2. Distributions and Diversities of Soil Bacterial Taxa in Different Treatments
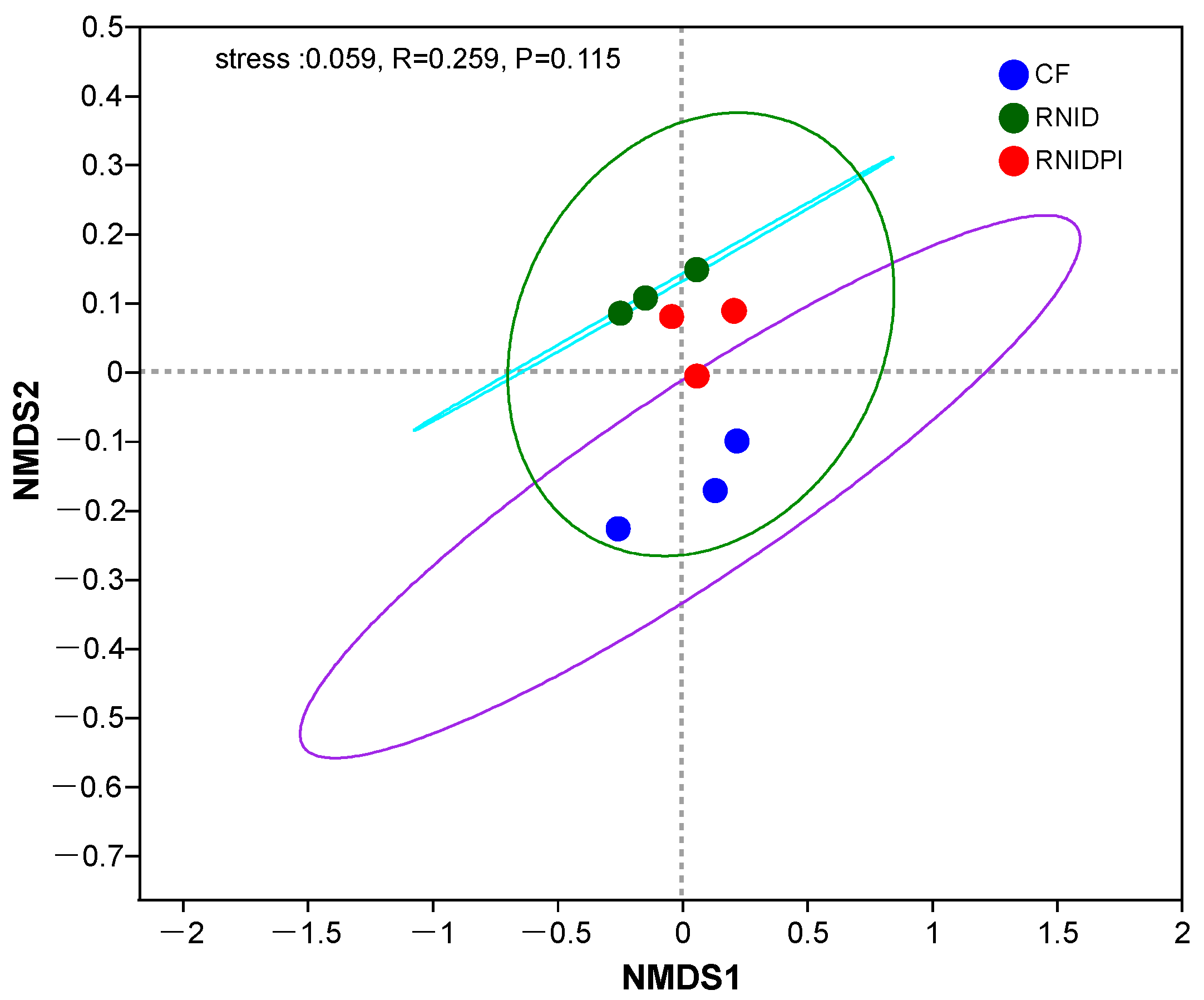
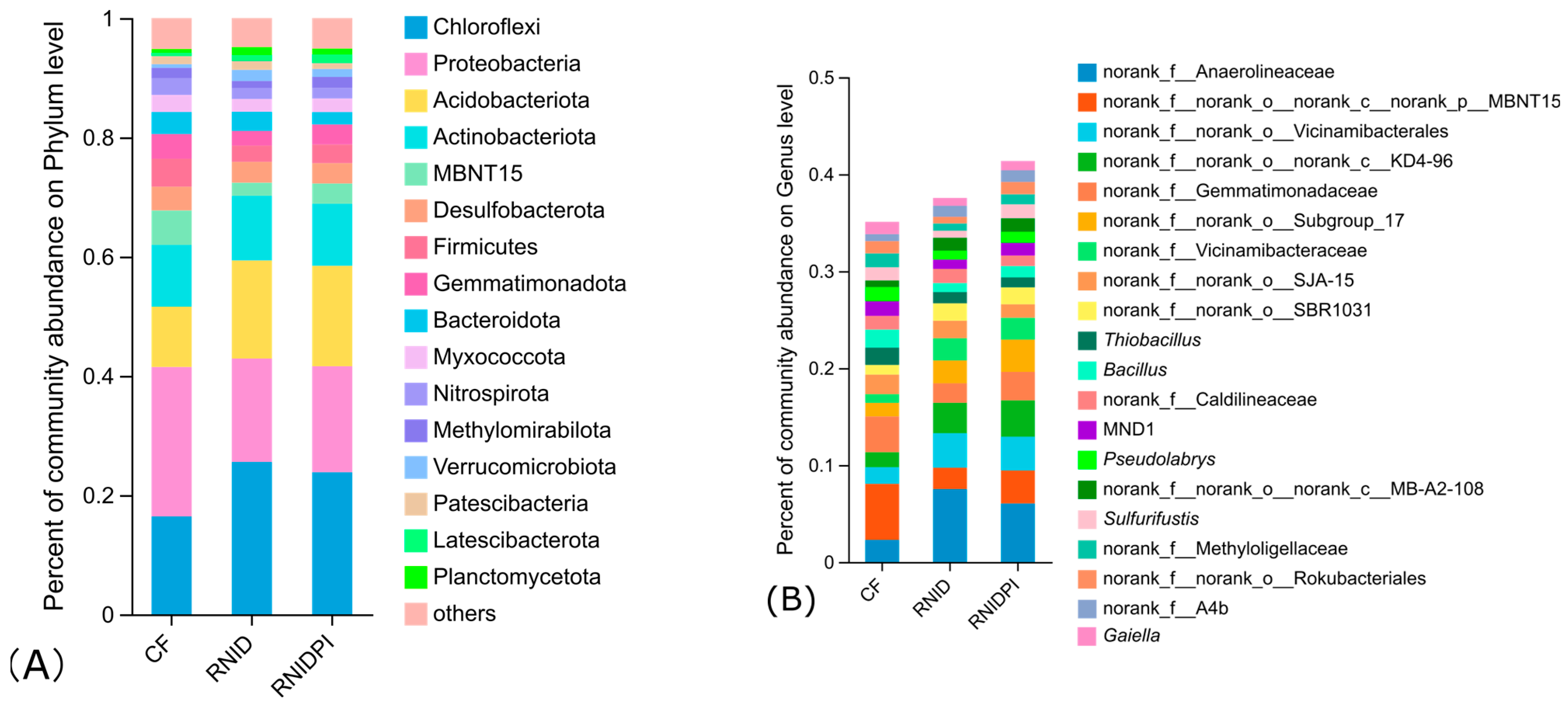
3.3. The Bacterial Community Composition in Different Treatments
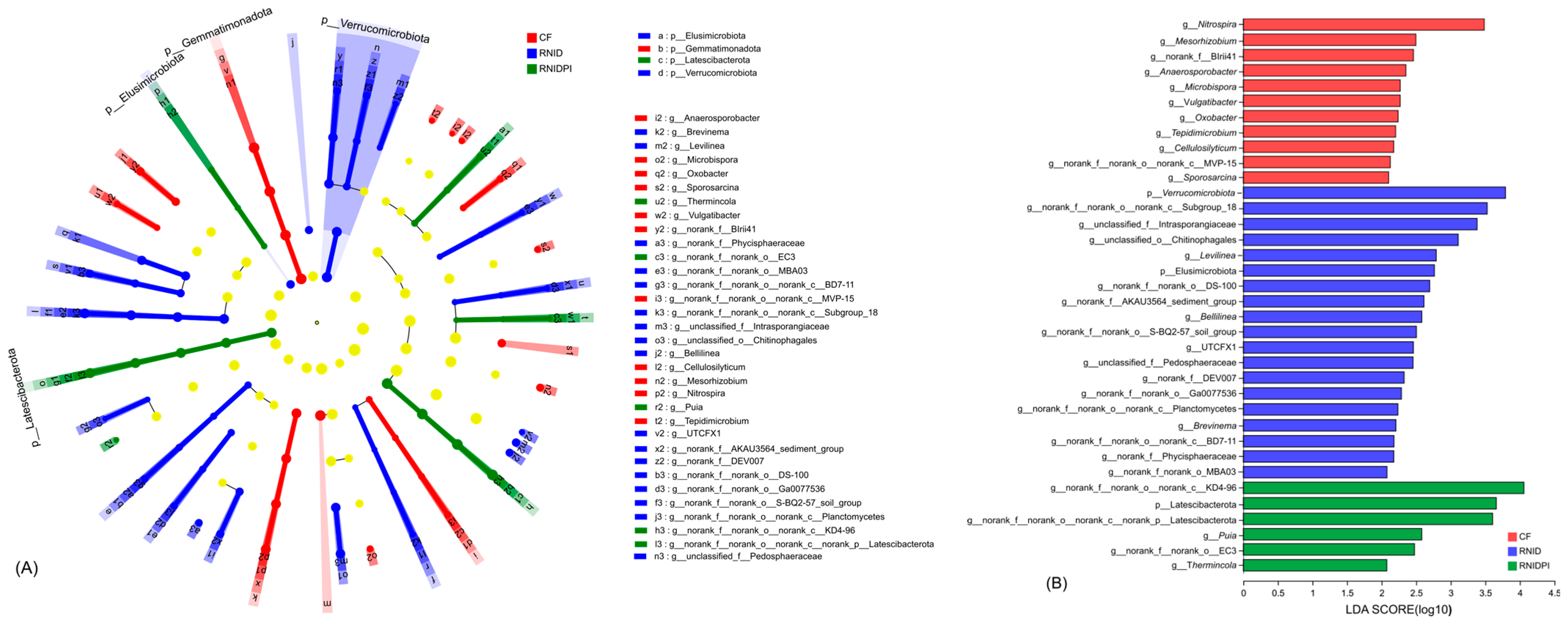
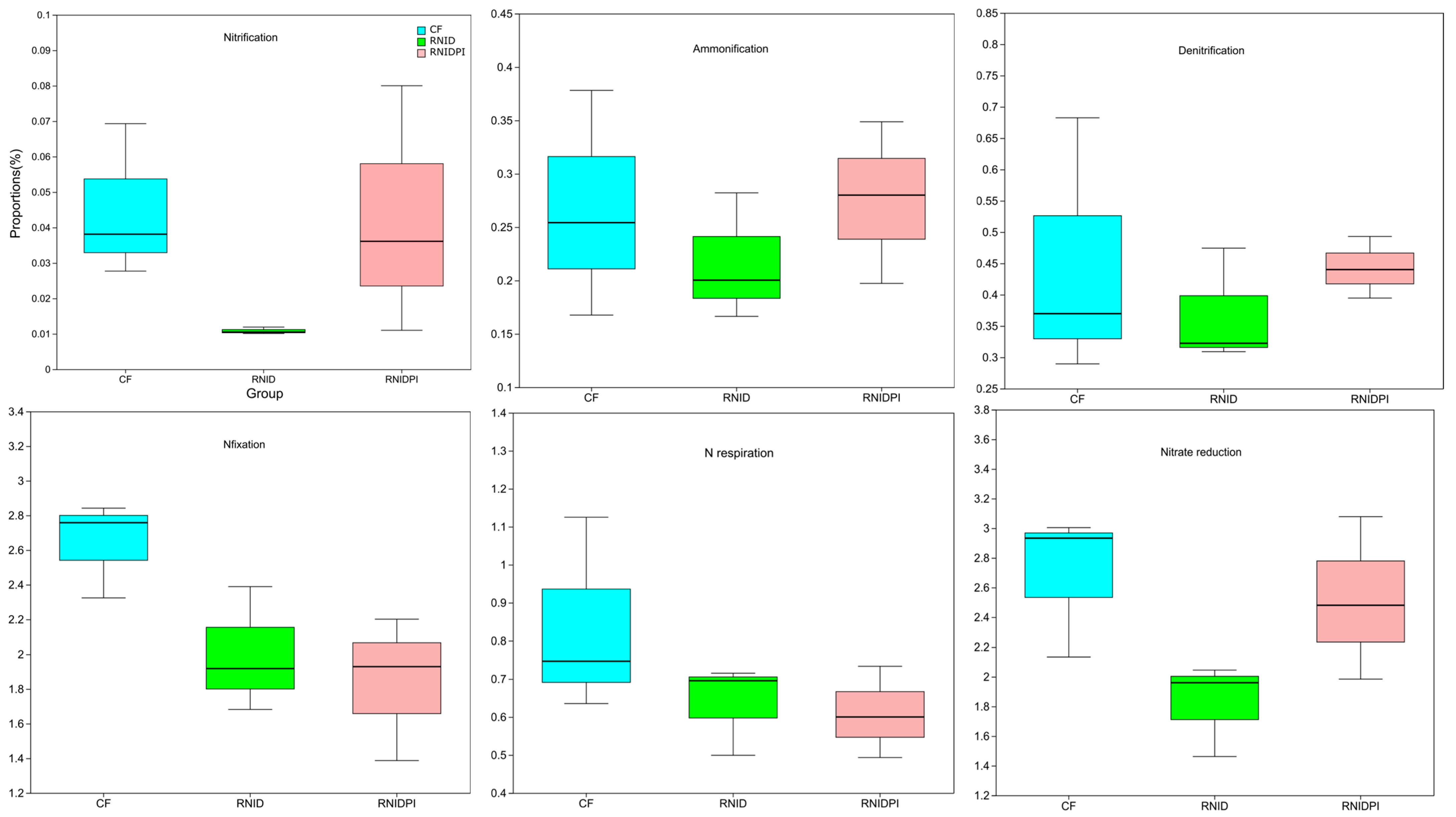
3.4. Functional Characteristics of Soil Bacteria
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- China Rice Research Institute; National Rice Industry Technology Research and Development Center. China Rice Industry Data Analysis Report of 2022; China Agricultural Science and Technology Press: Beijing, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, M.; Tang, Q.; Ao, H.; Zou, Y. Yield potential and stability in super hybrid rice and its production strategies. J. Integr. Agric. 2017, 16, 1009–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; He, A.; Ye, C.; Liu, S.; Lu, J.; Gao, M.; Fan, Y.; Lu, B.; Tian, X.; Zhang, Y. Root morphological traits and spatial distribution under different nitrogen treatments and their relationship with grain yield in super hybrid rice. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, Z.; Huang, J.; Zhu, L.; Cao, X.; Zhu, C.; Zhong, C.; Jin, Q.; Zhang, J. Effects of N application strategies on N leaching loss in paddy soil and N use characteristics in different super hybrid rice cultivars. Paddy Water Environ. 2019, 18, 27–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Hou, D.; Peng, X.; Ma, B.; Shao, S.; Jing, W.; Gu, J.; Liu, L.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Y.; et al. Optimizing integrative cultivation management improves grain quality while increasing yield and nitrogen use efficiency in rice. J. Integr. Agric. 2019, 18, 2716–2731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Peng, S. Yield potential and nitrogen use efficiency of China’s super rice. J. Integr. Agric. 2017, 16, 1000–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, K.; Delgado-Baquerizo, M.; Guo, X.; Wang, D.; Zhu, Y.; Chu, H. Biodiversity of key-stone phylotypes determines crop production in a 4-decade fertilization experiment. ISME J. 2020, 15, 550–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Ju, X.; Powlson, D.; Oenema, O.; Smith, P. Nitrogen surplus benchmarks for controlling N pollution in the main crop-ping systems of China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 6678–6687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, H.; Zhu, X.; Huang, S.; Linquist, B.; Kuzyakov, Y.; Wassmann, R.; Minamikawa, K.; Martinez-Eixarch, M.; Yan, X.; Zhou, F.; et al. Greenhouse gas emissions and mitigation in rice agriculture. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2023, 4, 716–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Liu, X.; Hua, Z.; Xue, H.; Mei, S.; Wang, P. Comparison of nitrogen loss weight in ammonia volatilization, runoff, and leaching between common and slow-release fertilizer in paddy field. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2021, 232, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zhang, G.; Wang, D.; Liu, Q. Abiotic and biotic effects of long-term straw retention on reactive nitrogen runoff losses in a rice–wheat cropping system in the Yangtze Delta region. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2021, 305, 107162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, H.; Jiang, Z.; Wang, W.; Xu, R.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Li, A.; Liang, Y.; Ou, S.; et al. Genomic basis of geographical adaptation to soil nitrogen in rice. Nature 2021, 590, 600–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, H.; Hu, T.; Mahmoud, A.; Li, J.; Zhu, R.; Jiao, X.; Jing, P. A quantitative review of the effects of biochar application on rice yield and nitrogen use efficiency in paddy fields: A meta-analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 830, 154792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuypers, M.M.M.; Marchant, H.K.; Kartal, B. The microbial nitrogen-cycling network. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2018, 16, 263–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yildiz, E.; Yaman, M.; Ercisli, S.; Sumbul, A.; Sonmez, O.; Gunes, A.; Bozhuyuk, M.R.; Kviklys, D. Effects of rhizobacteria application on leaf and fruit nutrient content of different apple scion–rootstock combinations. Horticulturae 2022, 8, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Liu, Q.; Li, Z.; Cheng, W.; Sun, J.; Guo, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhou, J.; Meng, D.; Li, H.; et al. Environmental factors shaping the diversity of bacterial communities that promote rice production. BMC Microbiol. 2018, 18, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islam, T.; Hoque, M.N.; Gupta, D.R.; Mahmud, N.U.; Sakif, T.I.; Sharpe, A.G. Improvement of growth, yield and associated bacteriome of rice by the application of probiotic Paraburkholderia and Delftia. Front Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1212505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, Y.; Gu, C.; Xiao, X.; Gao, Y.; Zhao, Y. Microbial inoculations promoted the rice plant growth by regulating the root-zone bacterial community composition and potential function. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2023. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, W.; Beebout, S.S.; Zhang, H.; Liu, L.; Yang, J.; Zhang, J. Grain yield, water and nitrogen use efficiencies of rice as influenced by irrigation regimes and their interaction with nitrogen rates. Field Crops Res. 2016, 193, 54–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.; Hu, J.; Xia, Q.; Zhang, S.; Li, X.; Pan, X.; Zhao, R.; Wang, R.; Yan, W.; Shangguan, Z.; et al. Soil microbial mechanisms promoting ultrahigh rice yield. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2020, 143, 107741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pittol, M.; Durso, L.; Valiati, V.H.; Fiuza, F.M. Agronomic and environmental aspects of diazotrophic bacteria in rice fields. Ann. Microbiol. 2016, 66, 511–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Z.; Su, W.; Chen, H.; Barberán, A.; Zhao, H.; Yu, M.; Yu, L.; Brookes, P.C.; Schadt, C.W.; Chang, S. Long-term nitrogen fertilization decreases bacterial diversity and favors the growth of Actinobacteria and Proteobacteria in agro-ecosystems across the globe. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2018, 24, 3452–3461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooq, M.S.; Wang, X.; Uzair, M.; Fatima, H.; Fiaz, S.; Maqbool, Z.; Rehman, O.U.; Yousuf, M.; Khan, M.R. Recent trends in nitrogen cycle and eco-efficient nitrogen management strategies in aerobic rice system. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 960641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daniel, G.; Kate, M.S. Long-term effects of mineral fertilizers on soil microorganisms—A review. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2014, 75, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, S.M.; Gaihre, Y.K.; Islam, M.R.; Akter, M.; Al Mahmud, A.; Singh, U.; Sander, B.O. Effects of water management on greenhouse gas emissions from farmers’ rice fields in Bangladesh. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 734, 139382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, X.; Wu, L.; Lu, R.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, J.; Jin, Q. Irrigation and fertilization management to optimize rice yield, water productivity and nitrogen recovery efficiency. IRRI Sci. 2021, 39, 235–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Chen, M.; Li, X.; Dai, Q.; Xu, K.; Guo, B.; Hu, Y.; Wang, W.; Huo, Z. Effects of soil types and irrigation modes on rice root morphophysiological traits and grain quality. Agronomy 2021, 11, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Li, Z.; Letuma, P.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, W.; Chen, H.; Lin, W. A positive response of rice rhizosphere to alternate moderate wetting and drying irrigation at grain filling stage. Agric. Water Manag. 2018, 207, 26–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.Y.; Huang, X.; Tan, W.; Xu, J.; Li, Y. High manure load reduces bacterial diversity and network complexity in a paddy soil under crop rotations. Soil Ecol. Lett. 2020, 2, 104–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Zhu, C.; Zhong, C.; Hussain, S.; Zhu, L.; Wu, L.; Jin, Q. Mixed-nitrogen nutrition-mediated enhancement of drought tolerance of rice seedlings associated with photosynthesis, hormone balance and carbohydrate partitioning. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2018, 84, 451–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Zhang, J.; Yu, Y.; Ma, Q.; Kong, Y.; Pan, W.; Wu, L.; Jin, Q. Alternate wetting–drying enhances soil nitrogen availability by altering organic nitrogen partitioning in rice-microbe system. Geoderma 2022, 424, 115993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Wu, C.; Wei, X.; Liu, Y.; Chen, X.; Qin, H.; Wu, J.; Su, Y.; Ge, T.; Hu, Y. Characterization of nirS- and nirK-containing communities and potential denitrification activity in paddy soil from eastern China. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2021, 319, 107561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, K.; Zhong, X.; Huang, N.; Lampayan, R.M.; Liu, Y.; Pan, J.; Peng, B.; Hu, X.; Fu, Y. Nitrogen losses and greenhouse gas emissions under different N and water management in a subtropical double-season rice cropping system. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 609, 46–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, D.; Dai, X.; Xie, Y.; He, M. Alternate furrow irrigation improves grain yield and nitrogen use efficiency in winter wheat. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 244, 106606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Jing, W.; Zhao, B.; Wang, W.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Gu, J.; Liu, L.; Wang, Z.; Yang, J. Alternative fertilizer and irrigation practices improve rice yield and resource use efficiency by regulating source-sink relationships. Field Crops Res. 2021, 265, 108124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.C.; Zhou, Q.; Zhang, J.H. Moderate wetting and drying increases rice yield and reduces water use, grain arsenic level, and methane emission. Crop J. 2017, 5, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Xie, H.; Wang, G.; Yuan, L.; Qian, X.; Wang, W.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, H.; Liu, L.; et al. Reducing environmental risk by improving crop management practices at high crop yield levels. Field Crops Res. 2021, 265, 108123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, M.; Zhou, S.; Zhou, Y.; Jia, Z.; Guo, T.; Wang, J. Cadmium pollution of soil-rice ecosystems in rice cultivation dominated regions in China: A review. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 280, 116965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, S. Soil Agro-Chemistrical Analysis, 3rd ed.; Agriculture Press China: Beijing, China, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida, S. Physiological aspects of grain yield. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. 1972, 23, 437–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faith, D.P.; Minchin, P.R.; Belbin, L. Compsitional dissimilarity as a robust measure of ecological distance. Vegetatio 1987, 69, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, Y.; Evans, S.E.; Friesen, M.L.; Tiemann, L.K. Effect of nitrogen fertilization on the abundance of nitrogen cycling genes in agricultural soils: A meta-analysis of field studies. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2018, 127, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, A.F.D.B.; Almeida, R.E.M.D.; Bruno, C.L.; Trivelin, P.C.; Linquist, B.; Favarin, J.L. Aerobic rice system improves water productivity, nitrogen recovery and crop performance in Brazilian weathered lowland soil. Field Crops Res. 2018, 218, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Chen, Y.; Li, T.; Yu, F.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, K.; Zhang, H.; Gu, J.; Yang, J.; Liu, L. Alternate wetting and moderate soil drying irrigation counteracts the negative effects of lower nitrogen levels on rice yield. Plant Soil. 2022, 481, 367–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, L.; Lam, S.K.; Chen, D.; Wang, J.; Tang, Q.; Yan, X. Can knowledge-based N management produce more staple grain with lower greenhouse gas emission and reactive nitrogen pollution? A meta-analysis. Glob. Change Biol. 2017, 23, 1917–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, H.; Yang, S.; Jiang, Z.; Xu, Y.; Jiao, X. Effect of irrigation and fertilizer management on rice yield and nitrogen loss: A meta-analysis. Plants 2022, 11, 1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Lan, Z.; Hu, S.; Bai, Y. Effects of nitrogen enrichment on belowground communities in grassland: Relative role of soil nitrogen availability vs. soil acidification. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2015, 89, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gou, X.; Ni, H.; Sadowsky, M.J.; Chang, X.; Liu, W.; Wei, X. Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi alleviate erosion-induced soil nutrient losses in experimental agro-ecosystems. Catena 2022, 220, 106687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Fan, S.; Sun, H.; Chen, C.; Wang, A.; Jiang, L.; Ma, D. Rhizosphere-associated microbiomes of rice (Oryza sativa L.) under the effect of increased nitrogen fertilization. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 730506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.; Yang, J.; Liu, C.; Gu, B.; Han, M.; Li, J.; Li, N.; Liu, N.; An, N.; Dai, J. Effects of long-term biochar and biochar-based fertilizer application on brown earth soil bacterial communities. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2020, 309, 107285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Baca, C.P.; Rivers, A.R.; Maul, J.E.; Kim, W.; Poudel, R.; McClung, A.M.; Roberts, D.P.; Reddy, V.R.; Barnaby, J.Y. Rice plant–soil microbiome interactions driven by root and shoot biomass. Diversity 2021, 13, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Guan, D.; Zhou, B.; Zhao, B.; Ma, M.; Qin, J.; Jiang, X.; Chen, S.; Cao, F.; Shen, D. Influence of 34-years of fertilization on bacterial communities in an intensively cultivated black soil in northeast China. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2015, 90, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boubekri, K.; Soumare, A.; Mardad, I.; Lyamlouli, K.; Ouhdouch, Y.; Hafidi, M.; Kouisni, L. Multifunctional role of Actinobacteria in agricultural production sustainability: A review. Microbiol. Res. 2022, 261, 127059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, H.; Xiao, X.; Li, C.; Shi, L.; Cheng, K.; Wen, L.; Li, W.; Wang, K. Influences of different manure N input on soil ammonia-oxidizing archaea and bacterial activity and community structure in a double-cropping rice field. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2020, 130, 937–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Luo, Y.; Tao, Q.; White, P.J.; Sun, G.; Li, M.; Luo, J.; He, Y.; Li, B.; Li, Q. The exacerbation of soil acidification correlates with structural and functional succession of the soil microbiome upon agricultural intensification. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 828, 154524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Luo, X.; Chen, Y.; Ye, X.; Wang, H.; Cao, Z.; Ran, W.; Cui, Z. Succession of composition and function of soil bacterial communities during key rice growth stages. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Wan, W.; Lin, H.; Pan, X.; Lin, L.; Yang, Y. Nitrogen rather than phosphorus driving the biogeographic patterns of abundant bacterial taxa in a eutrophic plateau lake. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 806, 150947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno, J.L.; Bastida, F.; Ondoño, S.; García, C.; Manuela, A.A.; Francisco, R.L. Agro-forestry management of Paulownia plantations and their impact on soil biological quality: The effects of fertilization and irrigation treatments. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2017, 117, 46–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.F.; Ma, C.L.; Li, F.S. Microbial community structure and function in paddy soil as affected by water-saving irrigation mode. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2022, 113, 103450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, W.; Liao, Q.; Fu, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, W. Effects of micro-nano bubble aerated irrigation and levels of nitrogen fertilizer on nitrogen accumulation and metabolism in super rice. Irrig. Drain. 2022, 64, 297–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Chen, L.; Chen, S.; Chu, G.; Wang, D.; Zhang, X. Rhizosphere aeration improves nitrogen transformation in soil, and nitrogen absorption and accumulation in rice plants. Rice Sci. 2020, 27, 162–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bose, H.; Sahu, R.P.; Sar, P. Impact of arsenic on microbial community structure and their metabolic potential from rice soils of West Bengal, India. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 841, 156486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauber, C.L.; Strickland, M.S.; Bradford, M.A.; Fierer, N. The influence of soil properties on the structure of bacterial and fungal communities across land-use types. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2008, 40, 2407–2415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.; Yan, W.; Canisares, L.P.; Wang, S.; Brodie, E.L. Alterations in soil pH emerge as a key driver of the impact of global change on soil microbial nitrogen cycling: Evidence from a global meta-analysis. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2023, 32, 145–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marschner, P. Processes in submerged soils-linking redox potential, soil organic matter turn over and plants to nutrient cycling. Plant Soil 2021, 464, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Tian, D.; Wang, B.; Wang, J.; Wang, S.; Chen, H.Y.H.; Xu, X.; Wang, C.; He, N.; Niu, S. Microbes drive global soil nitrogen mineralization and availability. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2019, 25, 1078–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


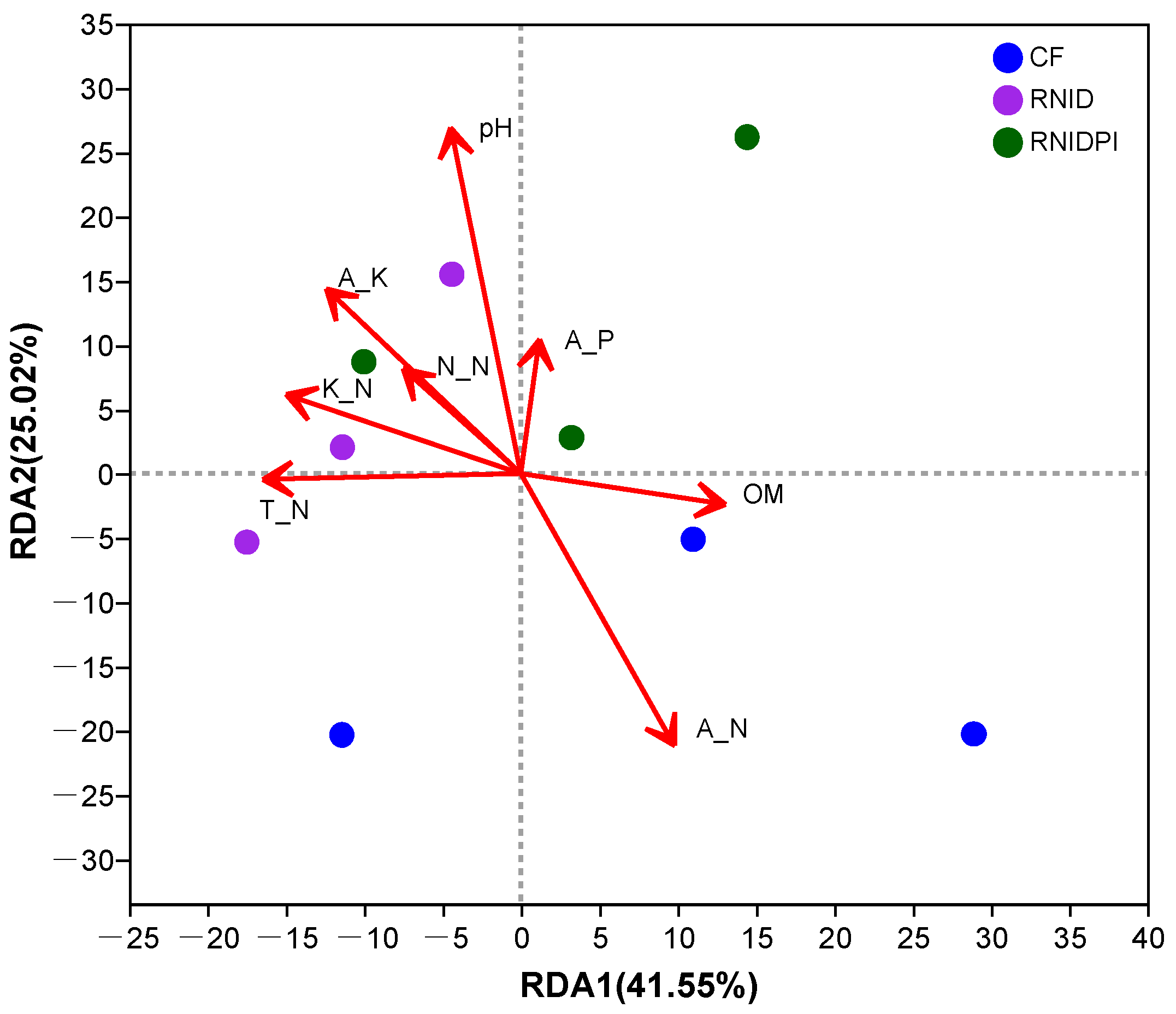
| Treatments | pH | OM (g kg−1) | T_N (g kg−1) | A_P (mg kg−1) | A_K (mg kg−1) | K_N (mg kg−1) | A_N (mg kg−1) | N_N (mg kg−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CF | 6.78 ± 0.11 b | 19.45 ± 1.34 b | 0.92 ± 0.04 b | 47.7 ± 6.96 b | 102.6 ± 3.95 bc | 68.86 ± 7.2 b | 6.96 ± 1.06 b | 2.06 ± 0.1 b |
| RNID | 6.95 ± 0.09 a | 18.26 ± 1.96 b | 0.92 ± 0.04 b | 50.6 ± 6.58 b | 126.3 ± 3.95 a | 68.86 ± 7.1 b | 4.77 ± 0.61 c | 2.06 ± 0.1 b |
| RNIDPI | 7.02 ± 0.05 a | 19.55 ± 0.97 b | 0.92 ± 0.03 b | 58.2 ± 7.44 b | 115.712 ± 12.7 ab | 78.21 ± 3.06 a | 4.93 ± 0.25 c | 2.74 ± 0.52 a |
| Treatments | Spikelets (m−2) | Grains per Spikelet | 1000 Grain Weight (g) | Yield (t ha−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CF | 259.2 ± 1.2 c | 172.68 ± 4.2 b | 26.13 ± 0.12 b | 10.02 ± 0.15 b |
| RNID | 283.9 ± 3.3 b | 178.33 ± 5.66 b | 26.18 ± 0.3 b | 10.16 ± 0.31 b |
| RNIDPI | 292.9 ± 1.2 a | 182.25 ± 2.87 a | 26.72 ± 0.09 a | 11.44 ± 0.39 a |
| Treatments | Sobs | Shannon | ACE | Coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CF | 4267.7 ± 243.9 b | 7.17 ± 0.15 b | 7965.9 ± 741.2 a | 0.93 |
| RNID | 4853 ± 51.9 a | 7.40 ± 0.1 a | 8865.3 ± 333.1 a | 0.93 |
| RINDPI | 4493.0 ± 124.1 ab | 7.23 ± 0.12 ab | 8198.5 ± 372.5 a | 0.94 |
| Phylum | pH | OM | T-N | A-P | AK | K-N | A_N | N_N | Yield |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chloroflexi | 0.63 | 0.03 | 0.11 | 0.40 | 0.43 | 0.17 | −0.88 ** | −0.08 | 0.20 |
| Proteobacteria | −0.68 * | 0.12 | −0.26 | −0.38 | −0.66 | −0.35 | 0.62 | −0.21 | −0.28 |
| Acidobacteriota | 0.53 | −0.15 | −0.11 | 0.20 | 0.56 | 0.19 | −0.82 ** | 0.10 | 0.43 |
| Actinobacteriota | 0.30 | 0.20 | −0.26 | 0.53 | 0.27 | 0.16 | −0.75 * | −0.06 | −0.03 |
| MBNT15 | −0.25 | 0.53 | −0.47 | −0.02 | −0.13 | −0.25 | 0.17 | −0.42 | −0.13 |
| Desulfobacterota | 0.07 | −0.57 | 0.26 | −0.17 | −0.01 | 0.35 | 0.03 | 0.62 | 0.43 |
| Firmicutes | −0.53 | 0.70 * | −0.21 | 0.02 | −0.41 | 0.02 | 0.62 | −0.25 | −0.20 |
| Gemmatimonadota | −0.08 | 0.60 | −0.26 | 0.10 | −0.40 | 0.03 | 0.35 | −0.19 | 0.15 |
| Bacteroidota | −0.25 | −0.75 * | 0.21 | −0.42 | 0.14 | −0.22 | −0.05 | 0.17 | −0.23 |
| Myxococcota | 0.00 | 0.43 | 0.40 | 0.24 | −0.63 | 0.52 | 0.34 | 0.27 | 0.22 |
| Nitrospirota | −0.27 | 0.12 | 0.37 | −0.17 | −0.62 | 0.11 | 0.88 ** | 0.16 | −0.03 |
| Methylomirabilota | 0.05 | 0.47 | −0.42 | 0.13 | 0.07 | 0.01 | 0.03 | −0.16 | 0.18 |
| Verrucomicrobiota | 0.38 | −0.30 | −0.11 | 0.08 | 0.71 * | −0.14 | −0.82 ** | −0.18 | 0.05 |
| Patescibacteria | 0.02 | −0.57 | 0.47 | −0.20 | 0.24 | 0.13 | −0.22 | 0.26 | 0.03 |
| Latescibacterota | 0.55 | 0.15 | −0.26 | 0.43 | 0.55 | 0.46 | −0.67 * | 0.31 | 0.57 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qian, X.; Huang, J.; Xie, R.; Di, L.; Wang, J.; Wang, G. Synergistic Effects of N Fertilization and Irrigation on Soil Bacterial Community in Super Rice Paddies. Agronomy 2023, 13, 2856. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13122856
Qian X, Huang J, Xie R, Di L, Wang J, Wang G. Synergistic Effects of N Fertilization and Irrigation on Soil Bacterial Community in Super Rice Paddies. Agronomy. 2023; 13(12):2856. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13122856
Chicago/Turabian StyleQian, Xiaoqing, Jianing Huang, Ruqing Xie, Li Di, Juanjuan Wang, and Guiliang Wang. 2023. "Synergistic Effects of N Fertilization and Irrigation on Soil Bacterial Community in Super Rice Paddies" Agronomy 13, no. 12: 2856. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13122856
APA StyleQian, X., Huang, J., Xie, R., Di, L., Wang, J., & Wang, G. (2023). Synergistic Effects of N Fertilization and Irrigation on Soil Bacterial Community in Super Rice Paddies. Agronomy, 13(12), 2856. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13122856









