Abstract
Salinity is a prominent environmental stressor that significantly impacts plant growth and development. Here, we conducted research on the physiological and transcriptomic mechanism of a wild cucumber, Cucumis hystrix Chakr, under NaCl stress. Physiological data showed that contents of malondialdehyde, peroxide (H2O2), proline, soluble sugar, and activities of antioxidant enzymes of superoxide dismutase, peroxidase, ascorbate peroxidase, and glutathione reductase in wild cucumber plants were increased significantly after NaCl treatment. Transcriptomic analysis revealed that 3509 transcripts were differentially expressed in leaves and 5516 transcripts in roots after NaCl treatment. Numerous genes were related to the signal transduction, transcription factor, ion transport, osmotic metabolism, and reactive oxygen species scavenging. Moreover, the thioredoxin H type gene of Cucumis hystrix Chakr (ChTrxh) was isolated and characterized. Our study demonstrated that the transgenic tobacco plants overexpressing ChTrxh exhibited enhanced tolerance to NaCl stress compared to wild-type plants. These findings contribute valuable insights into the functional characteristics of important genes in wild cucumber under NaCl stress.
1. Introduction
Salinity stress is a worldwide concern that severely affects the growth, development, and yield of crops. The area of soil salinization is gradually increasing due to environmental factors and human-induced soil degradation. This stress leads to osmotic stress and ion toxicity, resulting in the excessive accumulation of ions within plants. Consequently, the primary effects of salinity stress often lead to secondary stresses, such as oxidative damage [1]. Plants employ various biochemical and molecular mechanisms to deal with salt stress [2].
The responses of plants to salt stress have been extensively investigated, particularly with regard to transcriptomic analysis in various plants species. Many stress-responsive genes have been identified by RNA sequencing (RNA-seq) technology under salt stress [3,4,5,6]. Some wild species of plants, having high levels of salt tolerance, are important resources for investigating the adaptive mechanisms that form the basis of salt tolerance. RNA-Seq analysis was employed to investigate the transcriptome of wild barley (H. spontaneum) [7], wild cotton (Gossypium klotzschianum) [8], wild rice [9], and wild recretohalophyte Reaumuria trigyna [10] under salt stress. These plants offer the potential to provide new insights into stress-tolerant mechanisms and theoretical guidance for the cultivation of resilient agronomic crops.
Cucumis hystrix Chakr. (HH, 2n = 24) serves as the wild counterpart to cultivated cucumber [11]. Previous research highlighted the presence of several potentially advantageous disease-resistant and abiotic stress-tolerant traits in Cucumis hystrix Chakr., which could be utilized for enhancing cucumber (C. sativus L., CC, 2n = 14) traits [12]. Additionally, new resistance against downy mildew has also been discovered in the wild species, C. hystrix Chakr [13]. Nonetheless, the response of wild cucumber to salt stress remains uninvestigated.
Therefore, this study aimed to investigate the physiological and transcriptomic responses of wild cucumber under NaCl stress. The research will contribute new insights into the salt tolerance mechanisms exhibited by wild cucumber and will serve as valuable research for identifying novel salt resistance genes to enhance the salt tolerance of various crops.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials and Salt Treatment
The seeds of C. hystrix were collected in PuEr, Yunnan province, China (Figure S1). The seeds were surface-sterilized, washed with sterile water, and germinated in a dark incubator at 28 °C on moisture filter paper. After germination, the seeds were transferred to vermiculite pots for 15 days. Subsequently, plantlets of uniform size were transplanted into plastic containers filled with a nutrient solution, following our previously established hydroponic growth protocol [14]. Experiments were conducted with two treatment groups: the control group (CK), receiving 0 mM NaCl treatment), and the NaCl treatment group, receiving 100 mM NaCl treatment for a duration for 24 h. Each treatment was replicated three times using individual samples.
2.2. Malondialdehyde, Peroxide Contents, Antioxidant Enzyme Activities Analysis
The malondialdehyde (MDA) contents measurement was carried out with the thiobarbituric acid reaction method [15]. Peroxide (H2O2) contents were measured according to a previous method [16].
Superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity was assessed by measuring the inhibition of photochemical reduction of nitroblue tetrazolium (NBT) spectrophotometrically at 560 nm [15]. One unit (U) of SOD activity is defined as the enzyme amount needed to inhibit 50% of NBT reduction under the given experimental conditions. Peroxidase (POD) activities were assessed by monitoring the increase in absorbance at 470 nm, resulting from the oxidation of guaiacol by H2O2 [17]. Ascorbate peroxidase (APX) activities were assessed by Cakmak and Marschner [17]. Glutathione reductase (GR) activities were assessed by analyzing the NADPH oxidation rate [18].
2.3. Proline and Soluble Sugar Contents Analysis
The free proline and soluble sugar contents in the leaves and roots of wild cucumber were analyzed following the methods described by Bates (1973) [19] and Yemm (1954) [20], respectively.
2.4. Library Construction and Sequencings
When leaves and roots of the control and NaCl-treated wild cucumber were collected, a total of 12 samples were sent to the Gene Denovo Biotechnology Co., Ltd., located in Guangzhou, China, for RNA extraction services. Subsequently, library construction and RNA sequencing were performed using an Illumina HiSeqTM 2000 Sequence system (San Diego, CA, USA).
2.5. De Novo Transcriptome Assembly and Functional Annotation
The raw sequence data underwent filtering to eliminate the adaptor sequence as well as low-quality reads. This resulted in the acquisition of clean reads, which were used for subsequent analyses due to their high quality. The clean reads were de novo assembled using the “Trinity” program. Gene expression levels were determined using the fragments per kilobase of transcript per million mapped reads (FPKM) method. To provide gene functional descriptions, all assembled transcripts were compared with the NCBI non-redundant (nr) protein database, Gene Ontology terms (GO), and the Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG), using the BLASTX algorithm with an E value threshold of 10−5. In our study, we assessed differentially expressed genes (DEGs) by implementing a default screening condition of a false discovery rate (FDR) <0.05 and an absolute fold change ≥2. Subsequently, the DEGs underwent enrichment analysis of GO functions and KEGG pathways. The creation of heatmaps was performed in R using the pheatmap package (R3.6.2 version).
2.6. Total RNA Extraction and qRT-PCR Validation
The total RNA was extracted using an EastepTM Universal RNA Extraction Kit (Promega, Shanghai, China). Gene-specific primers were designed based on the unique sequences of the reference using Primer Premier 5.0. The actin gene was selected as the internal control (Table S1). The qRT-PCR assays were carried out using an SYBR Premix Ex Taq (Takara, Dalian, China) and an iCycler iQ real-time PCR detection system (BIORAD), following the instructions provided by the manufacturers. Three biological replicates were performed, and the relative expression levels were calculated using the 2−ΔΔCT method.
2.7. The Isolation of ChTrxh and Its Overexpression Transgenic Tobacco Plants Characterization
The complete coding sequence of ChTrxh was identified in Unigene0040254 and amplified using PCR. To construct the overexpression vector, the full-length ChTrxh sequence was amplified with the gene-specific primers, ChTrxh-F (5′- CTGTTGATACATATGATGGCAGAAATGGGGAAAG-3′), and ChTrxh-R (5′- ATCATCGATGAATTCATAGGCTTGAATGTTTGG-3′) utilizing a Pfu DNA polymerase (Vazyme, Nanjing, China). The resulting PCR fragment was then ligated into the binary plant vector pRI101 using a ClonExpress II one-step cloning kit (Vazyme, Nanjing, China). The binary plasmid was subsequently transferred into Agrobacterium LBA4404 (Agrobacterium tumefaciens). Tobacco seedlings (Nicotiana tabacum cv. NC89) were cultivated on a sterile MS medium and were utilized for leaf-disc transformation. Transgenic tobacco plants were obtained using the leaf plate method [21]. To confirm the presence of the transgene, genomic PCR and Western blot analysis were performed. The T2-generation transgenic plants were selected for subsequent stress treatment.
2.8. Western Blot Analysis
Western blot was performed following the protocol described by Bai et al. (2023) [22]. Proteins derived from both wild-type (WT) and transgenic plants were separated on a 12% (v/w) SDS-polyacrylamide gel. Subsequently, the proteins were transferred onto a polyvinylidene difluoride (PVDF) membrane and incubated with a mouse polyclonal anti-GFP antibody from Beyotime (Nanjing, China). To detect the presence of the target protein, a goat peroxidase-conjugated anti-mouse antibody at a dilution of 1:4000 from Sigma was used. The visual representation of the detected proteins was achieved through chemiluminescence using an ECL system from Bio-Rad (Hercules, CA, USA).
2.9. Analysis of Transgenic Plants under Salt Stress
Seeds were germinated on petri dishes containing Murashige and Skoog (MS) medium with either 0 mM or 100 mM NaCl. The daily germination rate was documented. The phenotype of the seedlings was subsequently photographed after an 11-day period.
2.10. Statistical Analysis
The experiments were conducted with a minimum of three repetitions, each consisting of three or more biological replicates. The data were subjected to a one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) or a t-test. Error bars were included on the graphs, where different letters denoted significant differences (p < 0.05).
3. Results
3.1. Physiological Responses of Wild Cucumber to NaCl Stress
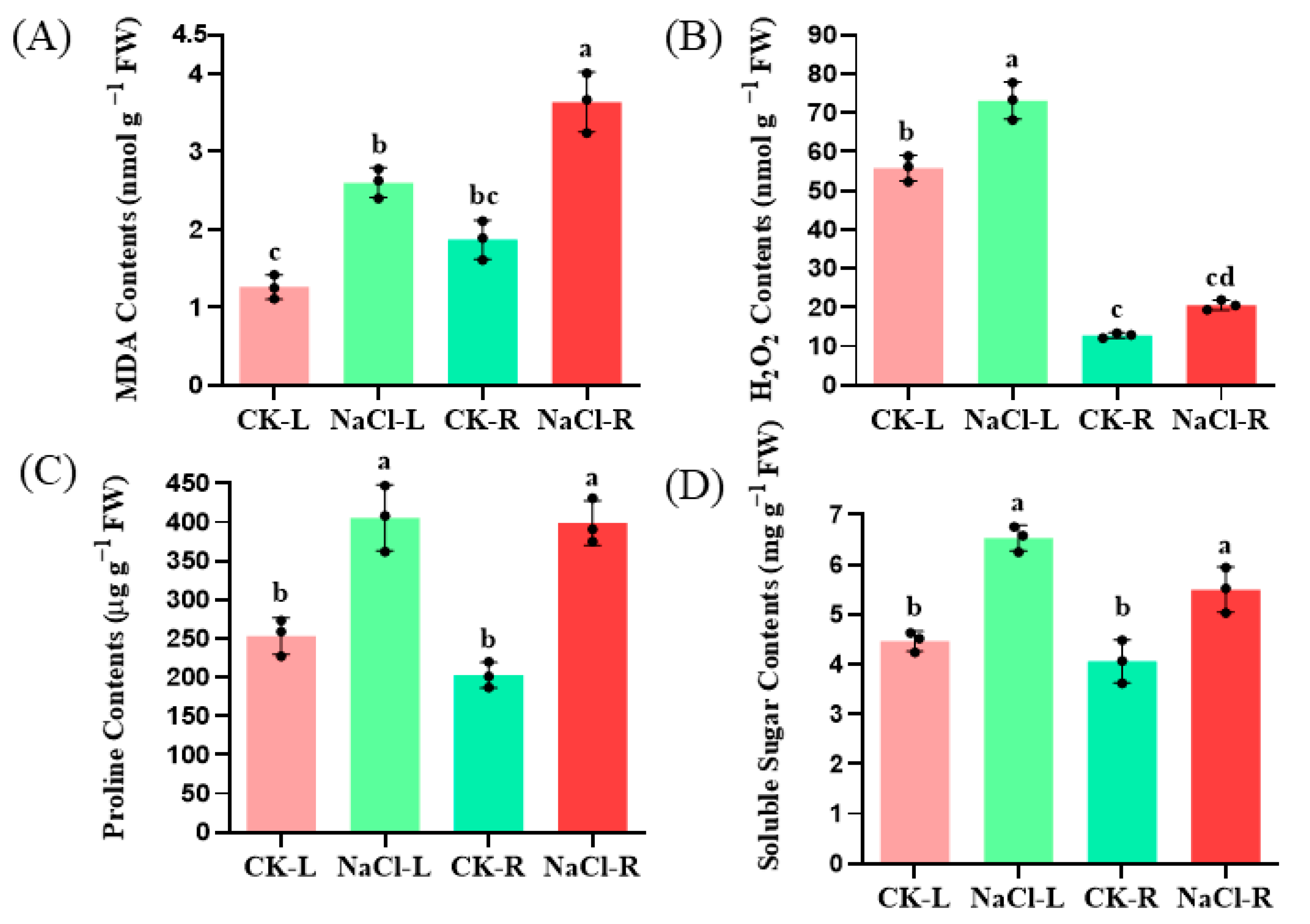
Hydroponically grown wild cucumber seedlings were subjected to 24-h with 100 mM NaCl. The MDA contents increased by 94.44% and 116.67%, respectively, in the root and leaves of the wild cucumber after NaCl treatment (p < 0.05). The H2O2 levels in the root and leaves of the wild cucumber increased by 81.81% and 30.91%, respectively, following treatment with NaCl, with the most significant increase observed in the leaves. Furthermore, the levels of proline and soluble sugar, two well-known osmoprotectants, were analyzed. The proline contents were approximately 2.10-fold levels of the control in the root after NaCl treatment (p < 0.05). The soluble sugar contents increased by 29.51% and 13.00%, respectively, after NaCl treatment in the root and leaves (p < 0.05) (Figure 1).
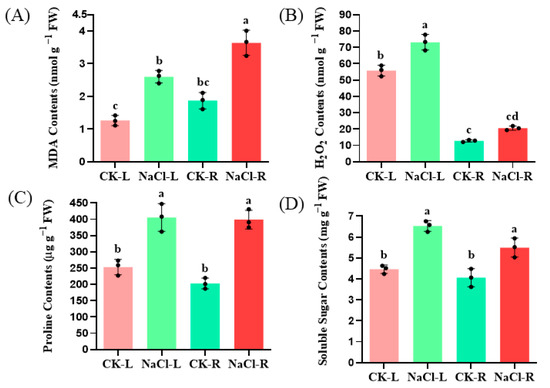
Figure 1.
Effect of NaCl stress on the level of lipid peroxidation (A), H2O2 contents (B), proline (C) and soluble sugar (D) contents in the roots and leaves of wild cucumber. CK means control. The values presented are the means of three replicates ± standard error (SE). Different letters indicate statistical significance at a level of p < 0.05.
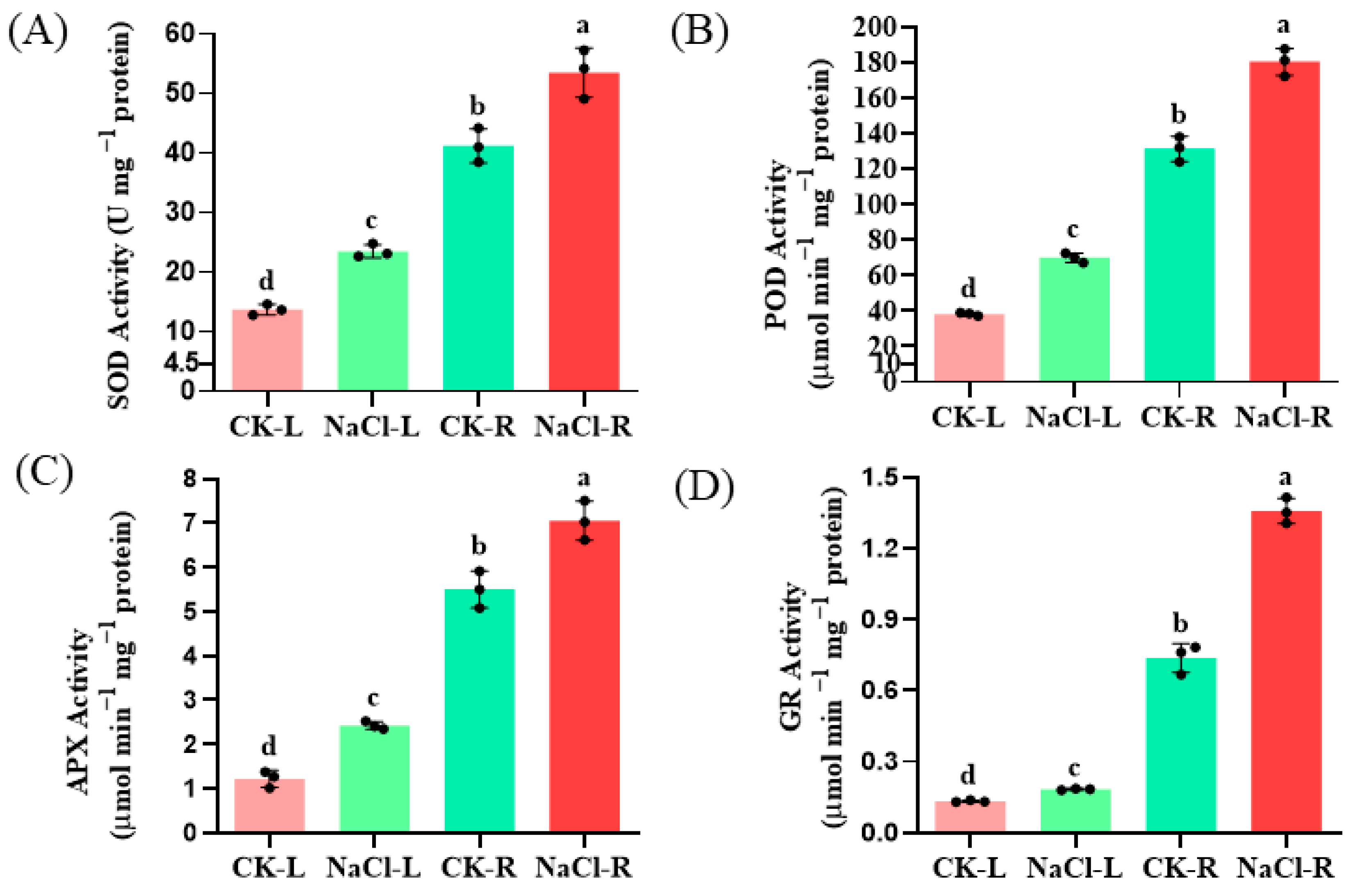
Furthermore, the activities of superoxide dismutase (SOD), peroxidase (POD), ascorbate peroxidase (APX), and glutathione reductase (GR) in the roots increased by 1.31-, 1.38-, 1.26-, and 1.72-fold, respectively, following NaCl treatment (p < 0.05). These findings suggest that these ROS-scavenging enzymes participate in the detoxification of NaCl-induced ROS induced in wild cucumber plants (Figure 2).
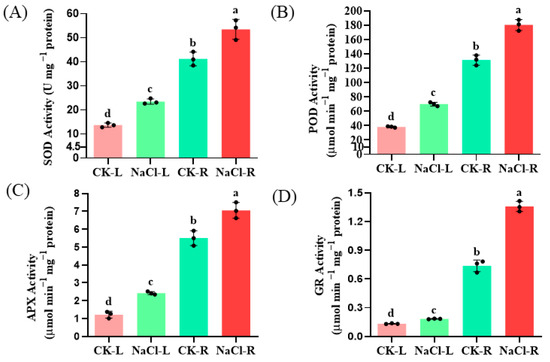
Figure 2.
Effect of NaCl stress on the antioxidant enzyme activities of SOD (A), POD (B), APX (C) and GR (D) in the roots and leaves of wild cucumber. CK means control. The presented values represent the means of three replicates ± standard error (SE), with different letters indicating statistical significance at a level of p < 0.05.
3.2. RNA-Seq and De Novo Assembly
To investigate the underlying molecular mechanisms of salt response in the wild cucumber, RNA-Seq analysis was conducted on leaf and root samples from both NaCl-treated and control seedlings. Each condition was represented by three biological replicates, resulting in a total of 12 libraries for analysis. The sequencing process generated an average of 20.00–33.95 million reads per sample. A high-quality dataset was obtained, with over 95% of the reads having Phred-like quality scores at the Q20, ensuring accurate sequencing results. Following the removal of adaptors, reads with unknown nucleotides, and low-quality reads, a set of 19.99–33.35 million clean reads with a GC content ranging from 44.4 to 46.27% were obtained (Table S2).
Using the Trinity assembling program, a de novo assembly was performed, resulting in 49,005 unigenes. The N50 value, which represents the length at which 50% of the total assembly is contained in contigs of that length or longer, was found to be 1896 bp. In total, the assembled bases amounted to 54,803,657 bp. The length distribution of the unigenes varied, with the maximum length being 24,241 bp and the minimum length being 201 bp. On average, the length of the unigenes was 1118 bp. The most frequent length range for the unigenes was between 100 and 299 bp, accounting for 19.80% of the total unigenes. The length distribution of the unigenes and the distribution of unique-mapped reads of the assembled unigenes are presented in Figure S2. The RNA-seq sequence data have been deposited in the NCBI. The Biosample accessions for the data range from SAMN117789 to SAMN1177800.
3.3. Unigene Function Annotation
The unigenes were annotated using a Blastx program, with an E-value threshold of 10−5, against protein databases in the following priority order: Nr, Swiss-Prot, KEGG and KOG. Out of the 49,005 unigenes, a total of 32,141 (65.59%) were successfully annotated using the Nr database. Similarly, 24,323 (49.63%) unigenes were annotated using the Swiss-Prot database. The KEGG database annotated 13,912 (28.39%) unigenes, while the KOG database annotated 19,995 (40.80%) unigenes (Figure S3A).
In the analysis, it was found that 43.21% of the sequences were successfully mapped to known genes in the Nr database for plants, indicating that a significant proportion of the unigenes had a match with existing genes. Additionally, around 17.11% of the unigenes displayed a similarity of over 80% with previously deposited sequences (Figure S3B). Further investigation revealed that approximately 72.86% of the annotated unigenes could be identified to species from the top six hits: Cucumis sativus (50.13%), Cucumis melo (15.01%), Theobroma cacao (3.14%), Medicago truncatula (2.35%), Brassica napus (2.21%), Gossypium arboretum (1.21%) (Figure S3C).
The functional categories of the 49,005 unigenes were analyzed and categorized into 44 Gene Ontology (GO) terms. In the three main categories, the assignment to the “metabolic processes” (10,103), accounted for the majority, followed by “cellular processes” (9088), and “single organisms” (7006). Within the cellular components category, the majority of the unigenes were classified into three highly represented GO terms: “cell part” (7271), “cell” (7273) and “organelle” (5339). For the molecular functions category, the two largest proportions of genes were found in the “binding” (9144) and “catalytic activity” (8654) categories. Together, these two categories accounted for 84.72% of the total molecular functions identified in the dataset (Figure S4).
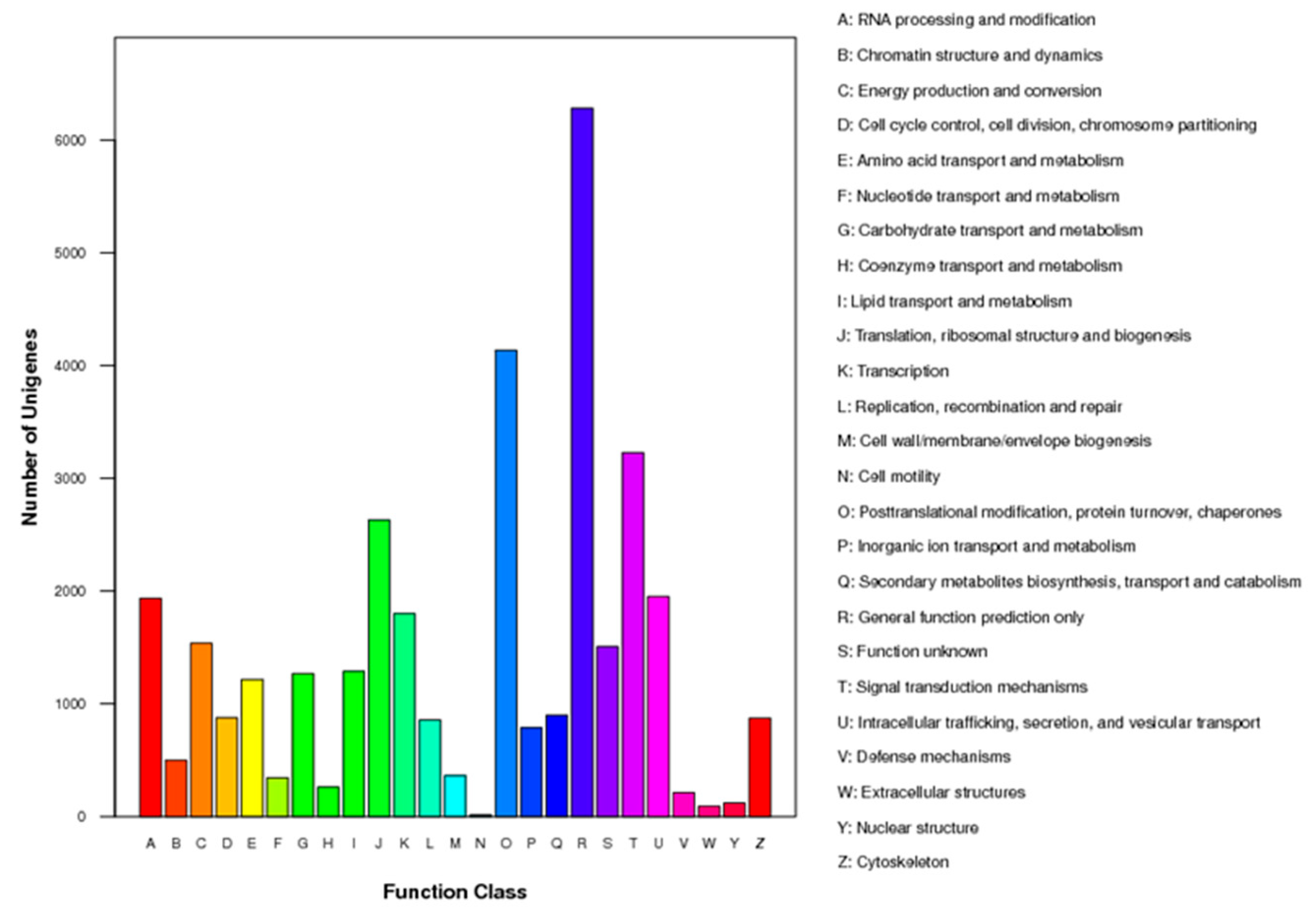
Out of the 34,987 unigenes analyzed, they were assigned to KOG functional classification and divided into 25 specific categories based on sequence homology (Figure 3). The most common category was “general functional prediction only”, with 6282 unigenes falling into this category. Following that, the categories of “posttranslational modification, protein turnover, chaperones” and “signal transduction mechanisms” were well represented with 4137 and 3227 unigenes, respectively.
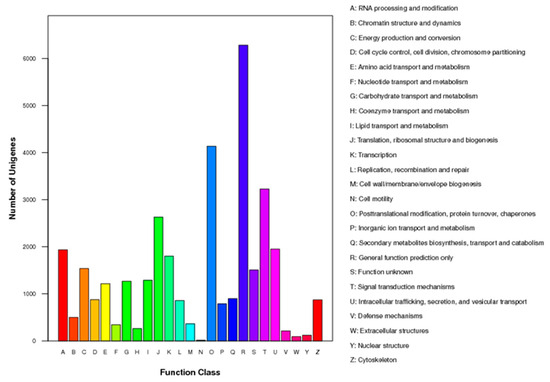
Figure 3.
Histogram presentation of KOG classification. The y-axis indicates the number of unigenes in each specific functional category.
3.4. Analysis and Functional Classifications of DEGs in Leaves and Roots of Wild Cucumber
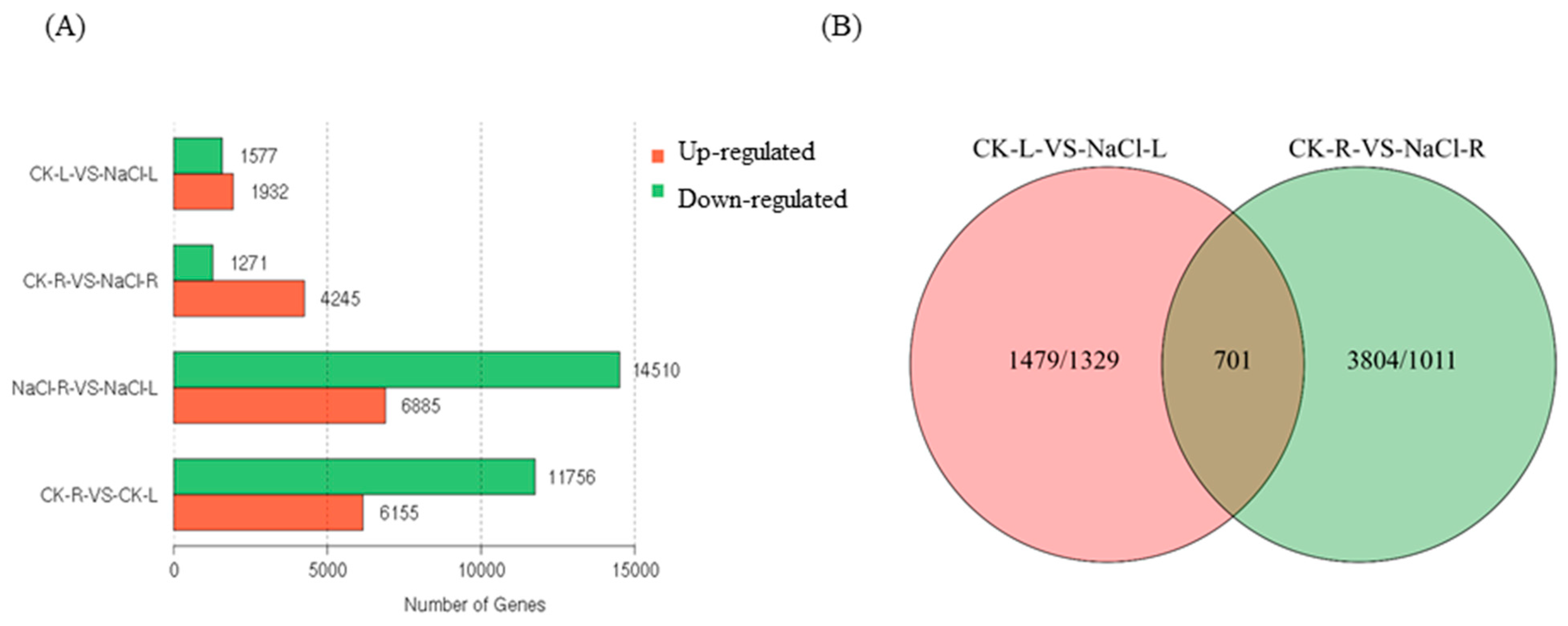
To determine the genes that exhibited differential expression under NaCl-induced stress in wild cucumber, we conducted a comparative analysis of the DEG profiles to assess the variations in gene expression. The comparison between CK-L and NaCl-L revealed a significant up-regulation of 1932 genes and a down-regulation of 1577 genes. Similarly, the comparison between CK-R and NaCl-R showed an up-regulation of 4245 genes and a down-regulation of 1271 genes (Figure 4A).
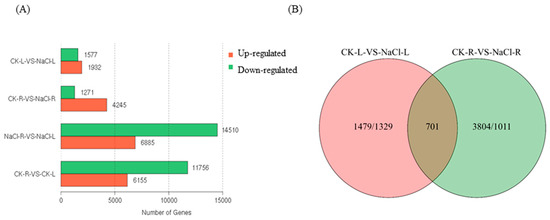
Figure 4.
The analysis of DEGs in the leaves and roots of wild cucumber under NaCl stress. (A) The number of DEGs in each comparison, with up-regulated genes indicated in red and down-regulated genes in green. (B) Venn diagrams illustrate the distribution of DEGs among the comparisons of CK-L vs. NaCl-L and CK-R vs. NaCl-R.
The distribution of DEGs among the comparisons of CK-L vs. NaCl-L and CK-R vs. NaCl-R is illustrated in Figure 4B using a Venn diagram. Remarkably, there were 701 DEGs that exhibited similar expression patterns in both CK-L vs. NaCl-L and CK-R vs. NaCl-R.
The significant changes in DEGs in leaves and roots of the CK vs. the NaCl treatment were analyzed for GO classification and enrichment. Within the up- and down-regulated unigenes of CK-R vs. NaCl-R and CK-L vs. NaCl-L, the most prominent genes in the biological process category of GO annotation, were related to the “metabolic process”, “cellular process” and “single-organism process”. In the cellular component category, the major genes were associated with the “cell”, “cell part” and “organelle”. Regarding the molecular function category, the dominant genes exhibited “catalytic activity”, “binding”, and “structural molecule activity” or “nucleic acid transcription factor activity” (the up-regulated genes in CK-L vs. NaCl-L) (Figure S5).
Pathway enrichment analysis was conducted to identify the metabolic pathways and signal transduction pathways that showed significant enrichment in DEGs. In CK-R vs. NaCl-R, a total of 1526 genes were assigned a KEGG ID and categorized into 122 pathways (Table S3). Similarly, in CK-L vs. NaCl-L, 646 genes were assigned a KEGG ID and categorized into 112 pathways (Table S4). Subsequently, pathways with Q values indicating significant enrichment among the DEGs were selected after multiple testing corrections. The 20-pathway enrichment is shown in Figure S6. In CK-L vs. NaCl-L, the top five pathways are “ribosome”, “plant hormone signal transduction”, “phenylpropanoid biosysnthesis”, “starch and sucrose metabolism”, and “plant-pathogen metabolism”. In CK-R vs. NaCl-R, the top five pathways are “ribosome”, “protein processing in endoplasmic reticulum”, “endocytosis”, “oxidative phosphorylation”, and “phagosome”.
3.5. Identification of Salt Responsive Genes Expressed during the Salt Stress Treatment
3.5.1. DEGs Encoding Signaling Transduction Proteins
In the leaves, DEGs encoding signaling-related genes were identified, including six calmodulin or calmodulin-like proteins, two calcium-dependent protein kinase, two CBL-interacting serine/threonine-protein kinases, and six mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase. In the roots, eight calmodulin or calmodulin-like proteins, one calcium-dependent protein kinase, five DEGs of mitogen-activated protein kinase, one mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase, and four mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase were found, and all these DEGs were up-regulated. Additionally, four calcineurin genes were found and up-regulated in the root, while they were not found in the leaves (Table S5, Figure 5A).
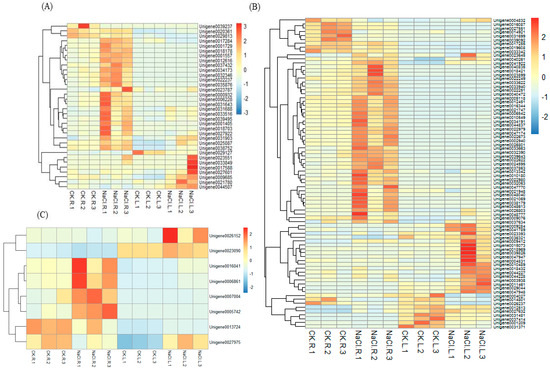
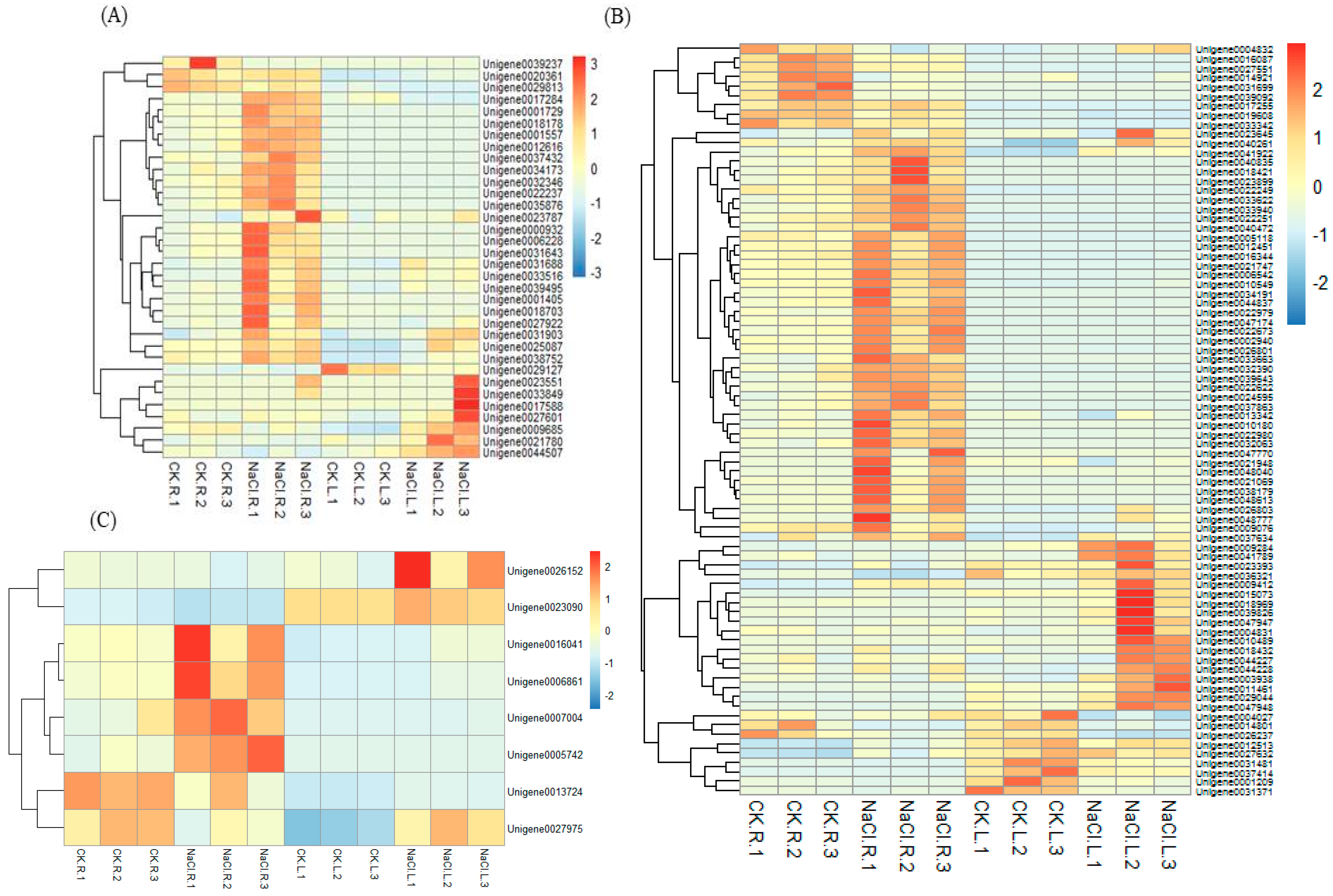
Figure 5.
Heatmap analysis of the expression levels of signal transduction DEGs (A), ROS scavenging DEGs (B) and osmotic stress-related DEGs (C).
3.5.2. DEGs Encoding Transcription Factors
In leaves, we identified 159 DEGs encoding a transcription factor; among them, 45 were down-regulated and 114 were up-regulated. The predominantly expressed transcription factors were the ethylene-responsive transcription factor (ERF) (39), the basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH) (18), MYB (16), WRKY(23), the heat stress transcription factor (10), and GATA (4) families. In roots, we identified 138 DEGs encoding a transcription factor; among these, 55 were down-regulated and 83 were up-regulated. The transcription factors predominantly expressed in response to salt stress include members of the ERF (40), bHLH (11), MYB (13), WRKY (18), heat stress transcription factor (7), and GATA (6, all down-regulated) families. This suggests their significant role in response to salt stress (Table S5).
3.5.3. DGEs Encoding Transporters
Additionally, 50 DEGs in leaves were predicted to encode diverse transporters, such as the ABC transporter (8), auxin transporter or auxin transporter-like protein (3), amino acid transporter (5), vacuolar type H+-ATPase (3), metal transporter (3, all up-regulated), polyol transporter (4), phosphate transporter (4), choline transporter-like protein (1), potassium transporter (1, up-regulated), etc. In roots, 102 DEGs encoding transporters were identified, such as the ABC transporter (24), amino acid transporter (10), choline transporter or choline-like transporter (4), the potassium transporter (2, down-regulated), vacuolar type H+-ATPase (15, all up-regulated), H+-PPase family transporter (7, all up-regulated), sodium transporter HKT1 (1, down-regulated), zinc transporter (4), phosphate transporter (5), sugar transporter (4), polyol transporter (5), etc. (Table S5).
3.5.4. DEGs Encoding ROS Scavenging Enzymes
A total of 41 and 59 DEGs were identified as putative enzyme-coding genes involved in the ROS scavenging system in the leaves and root of wild cucumber under salt stress, respectively. These DEGs were further categorized into glutathione S-transferase (GST) family proteins (12), superoxide dismutase (SOD, 2), peroxidase (POD, 15), glutaredoxin (7), thioredoxin superfamily protein isoform and thioredoxin-like protein (4), and 1-Cys peroxiredoxin (1) in leaves. In the root, they were categorized into GST family proteins (25), SOD (3, up-regulated), POD (23), glutathione peroxidase (4, up-regulated), L-ascorbate peroxidase (1, up-regulated), glutathione reductase (1, up-regulated), and glutaredoxin (2, up-regulated) (Table S5, Figure 5B).
3.5.5. DEGs Encoding Osmotic Substances
In the present study, one unigene encoding pyrroline-5-carboxylate reductase was found up-regulated in the root. Three genes encoding trehalose-phosphate phosphatase were found up-regulated in the leaves after NaCl treatment. Three genes encoding alpha, alpha-trehalose-phosphate synthase were found up-regulated only in the root (Table S5, Figure 5C).
3.6. Verification of the Expression Level of Some Transcripts Using qRT-PCR
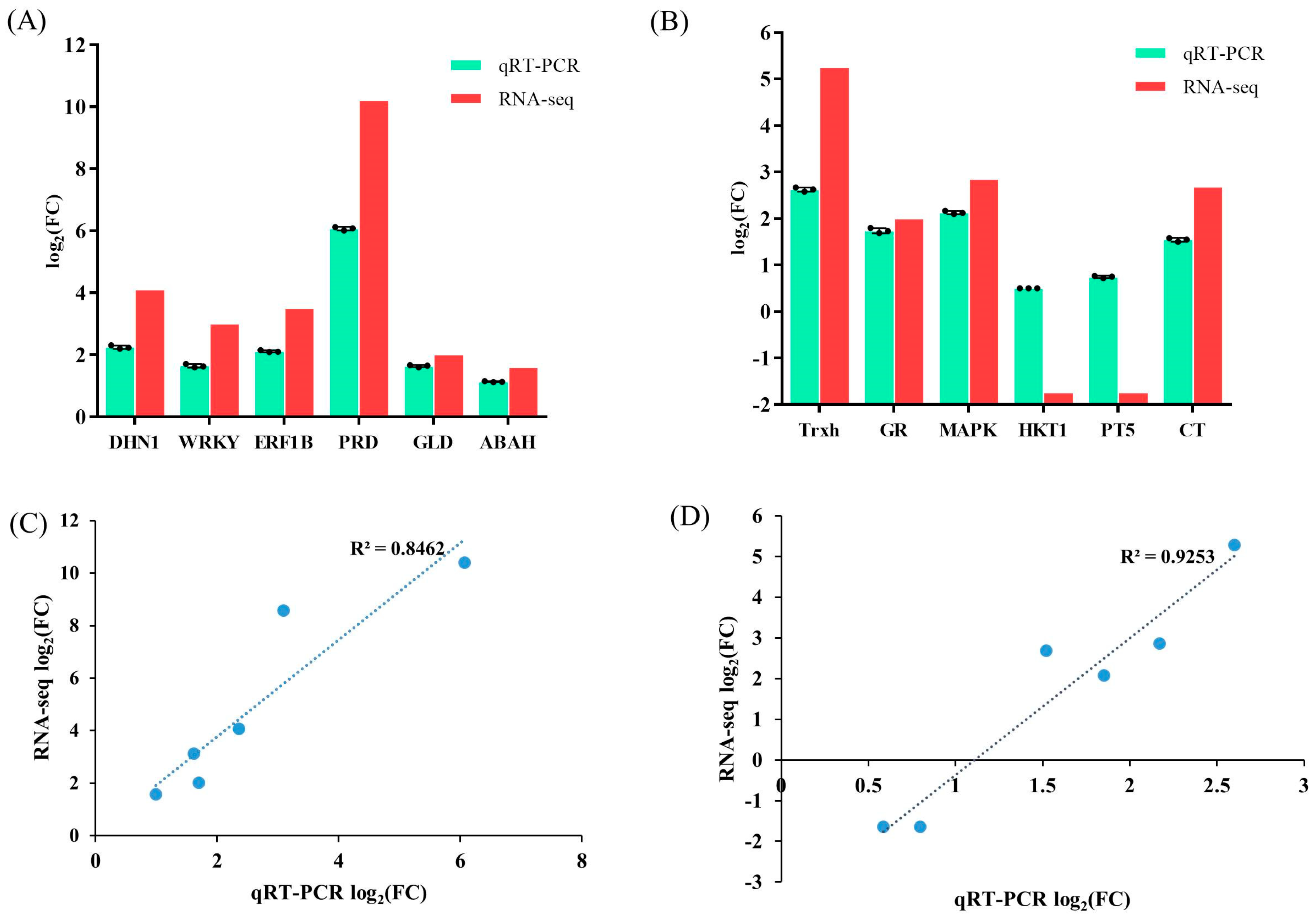
To validate the gene expression levels obtained from RNA-seq, 12 DEGs with distinct expression patterns were randomly selected for qRT-PCR analysis. The findings demonstrate that although there were variations in the fold-change values between the qRT-PCR and RNA-seq, the expression patterns of the unigenes were consistent with the RNA-Seq data. The correlation coefficients between qPCR- and FPKM-derived expressions in the leaves and roots of the wild cucumber were 0.8462 and 0.9253, respectively. Collectively, these results demonstrate the high reliability of the RNA-seq data (Figure 6).
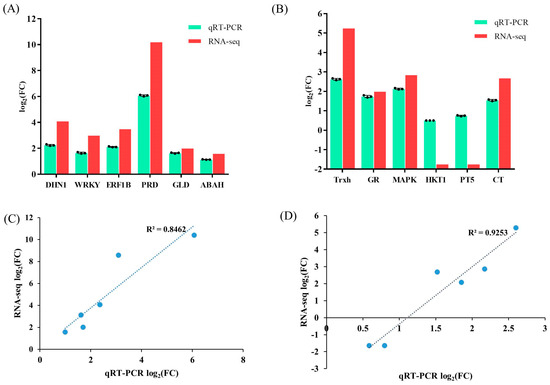
Figure 6.
The differential gene expression values of selected genes obtained through total RNA sequencing (RNA-seq) and qPCR in leaves (A) and roots (B) of wild cucumber. Additionally, the correlations between the RNA-Seq and qRT-PCR of selected DEGs were analyzed in leaves (C) and roots (D) of wild cucumber. R2 was the Pearson correlation coefficient. The bars plot represents the mean log2 fold change ± SE with three replicates (n = 3).
3.7. The Characterization and Functional Analysis of Overexpressed ChTrxh Transgenic Tobacco under NaCl Stress
According to the sequence of Unigene0040254, the ORF of ChTrxh was isolated. The ORF amplified from Cucumis hystrix was 348 bp and the sequence is shown in Figure S7. Trxs play important roles in defending against oxidative stress [23]. To further investigate the function of ChTrxh under salt stress, 10 transgenic tobacco lines overexpressing ChTrxh were obtained through kanamycin screening. The genomic PCR analysis confirmed the presence of the target band in the expected size, which was absent in WT (Figure S8A). Additionally, the Western blot results demonstrated a significant increase in ChTrxh protein expression in OE1, OE2, and OE3 transgenic plants compared to the WT (Figure S8B). The findings collectively indicate the successful overexpression of ChTrxh in tobacco.
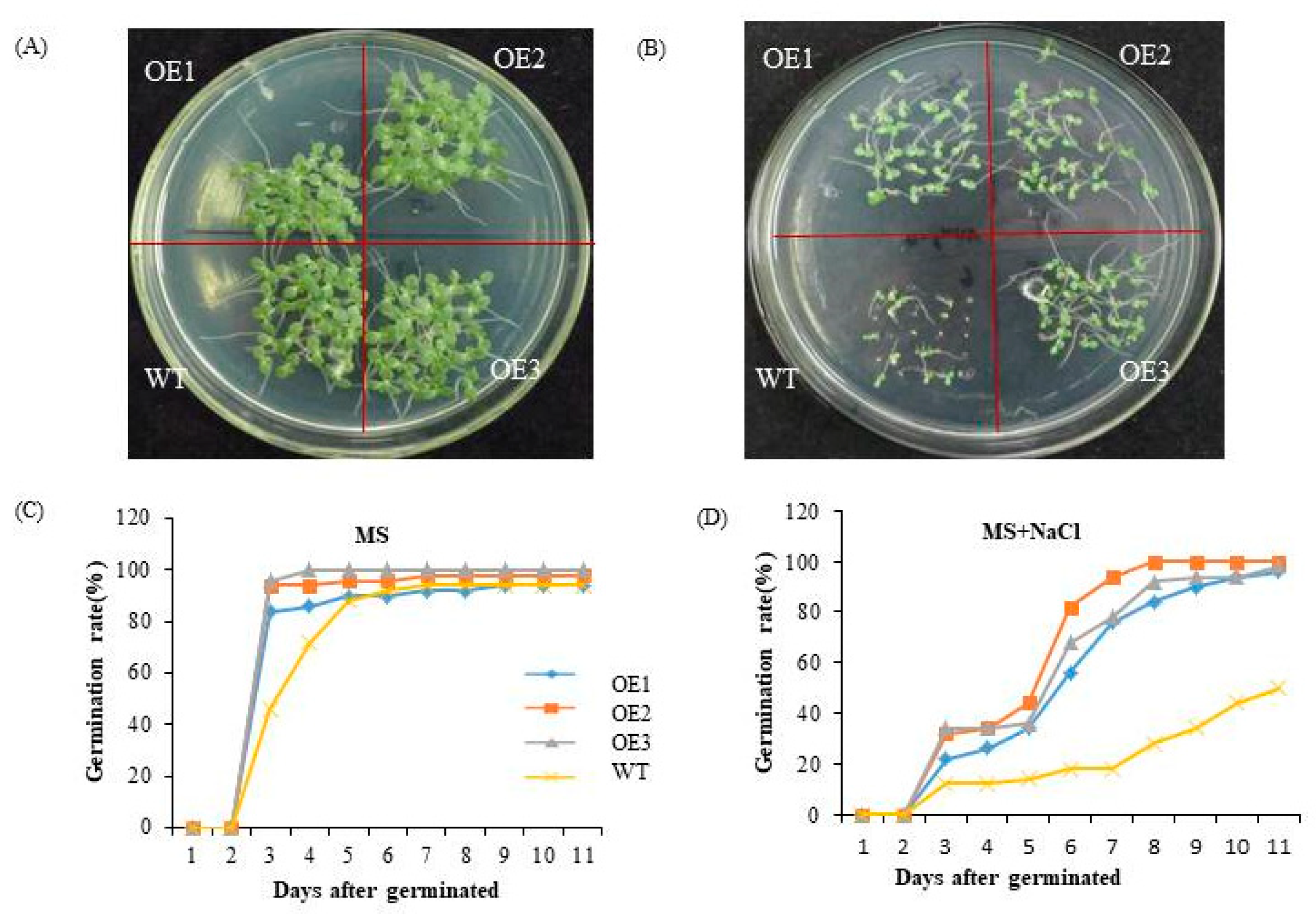
To assess the salt tolerance of ChTrxh overexpressing tobacco plants, the seeds of the transgenic tobacco and WT plants were subjected to MS medium with 0 or 100 mM NaCl for a period of 12 days. As depicted in Figure 7A,C, there was no difference in the seed germination rate between the WT and transgenic tobacco grown on the MS medium. However, under NaCl treatment, the germination rate of ChTrxh transgenic tobacco plants exhibited a significant increase compared to the WT plants. This observation suggested that the overexpression of ChTrxh enhanced the tolerance to NaCl-induced stress (Figure 7B,D).
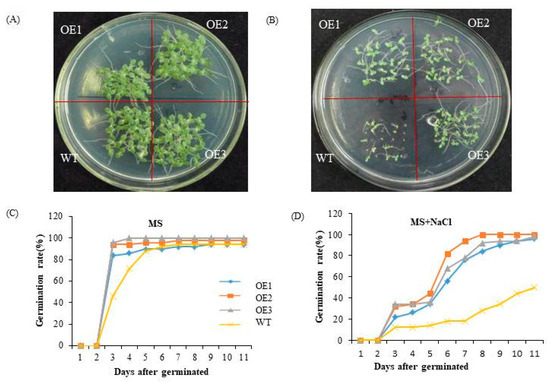
Figure 7.
The functional analysis of ChTrxh overexpression transgenic tobacco seeds under NaCl stress. (A,B) The phenotype of tobacco seeds treated with 0 or 100 mM NaCl on MS medium for 11 days. (C,D) The germination rate of overexpression ChTrxh transgenic tobacco and WT seeds under 0 or 100 mM NaCl stress.
4. Discussion
Wild cucumber holds the potential for plant improvement due to its genes associated with resistance to various pathogens, including powdery mildew, downy mildew, anthracnose, and fusarium wilt [24]. However, the physiological and transcriptome analysis of wild cucumber in response to salt stress is still largely unknown. In this study, we sequenced the transcriptomes of the leaves and roots of wild cucumber under NaCl treatment. A total of 49,005 unigenes were assembled, with 66.7% of them being annotated. Our transcriptome results shed light on the molecular mechanisms underlying the response of wild cucumber to salinity stress.
4.1. Signaling Network of Wild Cucumber in Response to NaCl Stress
The tolerance of plants to NaCl stress is activated through complex signaling pathways that aim to maintain cellular homeostasis. Our data revealed significant differential expression of numerous genes involved in signaling pathways in both the leaves and roots of NaCl-treated wild cucumber plants compared to the control groups.
Calmodulin (CaM), calcineurin B-like proteins (CBLs), calcium-dependent protein kinases (CDPK), and CBL-interacting protein kinases are important components of Ca2+-mediating signaling pathways. The overexpression of GmCaM4 in soybean was found to enhance tolerance to salt stress [25]. Genes of CaM-like (CML) play a significant role in regulating plant growth, development, and responses to salinity and drought stress. In rice, a CML gene, OsDSR-1, improved drought tolerance through scavenging ROS [26]. Calcineurin, a protein phosphatase dependent on both Ca2+- and CaM, is involved in the regulation of Na+, K+ and Ca2+ homeostasis, as well as hormone response in yeast [27]. CDPKs are versatile proteins that possess calcium-binding and signaling capabilities within a single gene product. The involvement of the CDPK gene VaCPK21 from the wild grapevine in response to salt stress was observed [28]. Through overexpression of a CDPK gene, increased tolerance to both salt and drought was achieved in rice [29]. Our study identified several CaM, CBLs, and CDPK genes that showed a significant response to NaCl stress, indicating their crucial roles in salt stress signaling.
Osmotic stress triggers the activation of protein kinases, particularly mitogen-activated kinases (MAPK), which play a crucial role in mediating osmotic homeostasis and/or detoxification responses [30]. MAPKs cascade pathways, consisting of a MAPK kinase kinase (MAPKKK), a MAPK kinase (MAPKK), and a MAPK, have been identified in response to various abiotic stresses, including NaCl stress. Additionally, the isolation of a MAPK gene (CsNMAPK) from cucumber has demonstrated its capability to enhance the tolerance of transgenic tobacco plants in response to both salt and osmotic stress [31]. The overexpression of Medicago MAPKKKK in Arabidopsis was found to enhance salt sensitivity [32]. Our study identified a strong expression of transcripts encoding MAPK, MAPKK, and MAPKKKK, with a particular emphasis on MAPKKKK, indicating the significant involvement of the MAPK cascade t in the salt response of wild cucumber (Table S4).
4.2. Transcription Factors of Wild Cucumber Are Affected by Salt Stress
Several classes of transcription factors were expressed under salt stress in wild cucumber. In our study, the predominantly expressed transcription factors are ERF, bHLH, MYB, and WRKY (Table S4). In G. hirsutum, members of AP2/EREBP, MYB, NAC, and WRKY transcription factor families were identified as highly enriched in the regulation of salt stress responses [33]. Similarly, in the hexaploid hulless oat, the MYB- and MYB-related TF family, bHLH, WRKY, and NAC transcription factor families exhibited expression patterns in response to salinity stress [34].
R2R3-MYB transcription factors in plants play important roles in responding to various abiotic and biotic stresses. For instance, the R2R3-type MYB gene SlMYB102 from the tomato has been found to increase salt tolerance in transgenic tomato [35]. In soybean, the MYB gene GmMYB68 confers salt-alkali resistance [36]. Another example is the wild soybean R2R3-MYB transcription factor GsMYB15, which, when overexpressed, enhances salt stress resistance in transgenic Arabidopsis [37]. Additionally, ethylene response factors, belonging to AP2/ERF superfamily proteins, are part of the largest transcription factors and participate in multiple abiotic stress tolerances, including salt. A transcriptome analysis was conducted to investigate differentially expressed ERF transcription factors in cotton in response to salt stress [38]. Overexpression of the JcERF1, an AP2/ERF-type transcription factor from Jatropha curcas, has been shown to increase salt tolerance in transgenic tobacco [39]. However, potato StERF3 has a negative regulatory effect on salt tolerance in potato [40]. Further investigation is required to understand the function of these transcription factors under salt stress in the next context of our study.
4.3. Transporters Are Affected by Salt Stress in Wild Cucumber
In our study, 152 unigenes encoding transporter proteins were identified including ATPase, ABC transporters, the ion transporter, amino acid transporter, choline transporter, potassium transporter, H+-PPase family transporter, sodium transporter HKT1, zinc transporter, phosphate transporter, sugar transporter, polyol transporter, etc., in wild cucumber roots and leaves (Table S4). Plasma membrane H+-ATPases play a vital role in plant growth and development. The up-regulation of these ATPase genes indicates that wild cucumber possesses a strong ability to maintain an osmotic balance. ATP-binding cassette transporters from extensive gene superfamilies are responsible for the transportation of diverse molecules including heavy metal ions, secondary metabolites, and phytohormones [41]. The overexpression of AtABCG36 in Arabidopsis resulted in enhanced tolerance to salt stress [42].
Ionic stress plays a crucial role in salinity, primarily caused by the excessive accumulation of Na+ in the aboveground portions of plants. Maintaining a balanced Na+/K+ ratio within the cytosolic has emerged as a crucial mechanism for salinity tolerance. To achieve this homeostatic balance, the activity of Na+ and K+ transporters and/or channels is necessary [43]. In our study, we identified three potassium transporters. The results support previous findings that genes involved in ion transport are significantly induced in responses to salinity stress, aiming to maintain or restore cytoplasmic homeostasis [44,45]. Additionally, other transporters, including magnesium transporters, sulfate transporters, and sugar transporters, were up-regulated in salt-stressed wild cucumber. The up-regulation of these genes potentially contributes to the maintenance of homoeostasis in wild cucumber.
4.4. ROS Scavenging Substances of Wild Cucumber Play Important Roles in Response to NaCl Stress
Salt stress triggers a rapid elevation in ROS. In this study, the MDA and H2O2 contents increased levels in the roots and leaves, indicating that NaCl stress induced lipid peroxidation and oxidative damage to wild cucumber. Antioxidant enzymes play a crucial role in protecting cells form oxidative damage [46,47]. Following exposure to NaCl stress, the wild cucumber exhibited heightened activities of antioxidant enzymes, including SOD, POD, APX, and GR. This study further identified several DEGs associated with SOD, POD, and APX. These findings strongly suggest that the ROS scavenging system enhances the antioxidative ability of the wild cucumber under NaCl stress.
The ubiquitous and multifunctional conjugating proteins, glutathione transferases (GSTs), have significant importance in stress responses due to their ability to prevent oxidative damage [48]. AtGSTU19 has been identified as a key player in salt stress tolerance in Arabidopsis [49]. In our study, 37 unigenes of GSTs were found in wild cucumber root and leaves, suggesting that GST may play an important role under NaCl stress.
Thioredoxin (Trx) acts as an antioxidant by facilitating redox states changes in target proteins through cysteine thiol-disulfide exchanges, thus modulating ROS scavenging. In Arabidopsis thaliana, Trxs are categorized into six main groups, each of which is distributed across different subcellular compartments such as the chloroplast, mitochondria, and cytosol [50]. The genome of Arabidopisis thaliana contains nine H-type Trx proteins, which are presumed to be located in the cytosol. Trxs play a vital role in response to abiotic stresses. Previous research has shown that an H-Type Trx is involved in tobacco defense responses under oxidative stress [51]. In our study, we observed a significant increase in the expression of thioredoxin H type (Trxh). Transgenic tobacco lines, expressing LmTrxh2 from the halophyte plant Lobularia maritima, exhibited enhanced tolerance to salt stress compared to wild type plants [52]. Trx CDSP32 has been found to mitigate photo-inhibition-induced cadmium in tobacco leaves [53]. The overexpression of ThTrx5, a thioredoxin protein, in Arabidopsis has been shown to enhance salt tolerance. In transgenic ThTrx5 plants, the activities of SOD, POD, and CAT were significantly higher than WT plants under salt stress [54]. To further investigate the role of thioredoxin under NaCl stress, we isolated the full-length sequence of ChTrxh and subsequently overexpressed it in tobacco plants. The germination rate of ChTrxh overexpressed transgenic plants was higher than that of WT, indicating that overexpression of ChTrxh increased NaCl stress tolerance.
4.5. Osmotic Substance Metabolism of Wild Cucumber in Response to NaCl Stress
Organic osmolytes, including proline, soluble sugar, and trehalose, serve as effective osmoprotectants that alleviate osmotic damage induced by salt stress [1]. Physiological measurements demonstrated a significant increase in proline and soluble sugar content in response to salt stress, indicating that wild cucumber possesses a robust capacity for osmotic adjustment.
Pyrroline-5-carboxylate reductase (P5CR) serves as the final enzymatic step in the biosynthesis of proline. One DEG encoding P5CR was identified in the root. On the other hand, pyrroline-5-carboxylate synthase (P5CS) plays a crucial role in proline biosynthesis by facilitating the conversion of glutamate into P5C. In our study, no DEG encoding P5CS in the root and leaves of wild cucumber were found.
Trehalose (Tre) is a growth regulator extensively utilized for enhancing plant stress tolerance. Its synthesis is mediated by the enzymes trehalose phosphate synthase (TPS) and trehalose phosphate phosphatase (TPP) [55]. Here, we observed three TPPs up-regulated in the leaves of wild cucumber and three TPS up-regulated in the roots of wild cucumber after NaCl treatment, suggesting that trehalose accumulation was part of the wild cucumber’s tolerance to NaCl stress.
5. Conclusions
This study aimed to investigate the physiological and molecular responses of wild cucumber to NaCl stress. The results demonstrated that under NaCl stress, there was a significant increase in the levels of MDA, H2O2, proline and soluble sugar. Additionally, the activities of antioxidant enzymes, including SOD, POD, APX, and GR, were found to be elevated. The transcript of differentially expressed genes analyzed by RNA-Seq showed that numerous genes were related to signal transduction, the transcription factor, ion transport, osmotic metabolism, and ROS scavenging in adaptation to salinity stress in wild cucumber. Furthermore, the overexpression of ChTrxh in transgenic tobacco plants resulted in increased NaCl stress tolerance. Some of these novel genes may subsequently be utilized to improve crops in saline soils.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/agronomy13122931/s1, Figure S1: The morphology of the wild cucumber in Puer, Yunnan Province, China; Figure S2 Random distribution of the assembled unigenes and assessment of assembly quality; Figure S3 Characteristics of similarity search of unigenes against Nr databases; Figure S4 Histogram of the gene ontology (GO) classification; Figure S5 Histogram presentation of DEGs’ Gene Ontology classification; Figure S6 Top 20 pathway enrichment of the DEGs in the leaves and roots of wild cucumber; Figure S7 The cDNA sequence of thioredoxin H-type-like of Cucumis hystrix Chakr designated as ChTrxh (Unigene0040254); Figure S8 The characterization of ChTrxh overexpression transgenic tobacco; Table S1: Primer sequences for qRT-PCR analysis; Table S2 Summary of sequences analysis; Table S3 CK-R vs. NaCl-R pathway enrichment; Table S4 CK-L VS. NaCl-L pathway enrichment; Table S5 The main category of up and down regulated DEGs in roots and leaves of wild cucumber.
Author Contributions
H.X. designed and drafted the manuscript; Z.G. and S.Z. performed the experiments and analyzed the data; K.L. helped to analyze the data and revise the paper. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant no. 32260753).
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Zhu, J.K. Plant salt tolerance. Trends Plant Sci. 2001, 6, 66–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parida, A.K.; Das, A.B. Salt tolerance and salinity effects on plants: A review. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2005, 60, 324–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Huang, W.G.; Chen, H.Y.; Wu, G.W.; Yuan, H.M.; Song, X.X.; Kang, Q.H.; Zhao, D.S.; Jiang, W.D.; Liu, Y.; et al. Identification of differentially expressed genes in flax (Linum usitatissimum L.) under saline-alkaline stress by digital gene expression. Gene 2014, 549, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diray-Arce, J.; Clement, M.; Gul, B.; Khan, M.A.; Nielsen, B.L. Transcriptome assembly, profiling and differential gene expression analysis of the halophyte Suaeda fruticosa provides insights into salt tolerance. BMC Genom. 2015, 16, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, X.; Wang, Z.; Song, X.; Xu, J.; Jiang, C.; Zhao, Y.; Ma, C.; Zhang, H. Transcriptomic profiling revealed an important role of cell wall remodeling and ethylene signaling pathway during salt acclimation in Arabidopsis. Plant Mol. Biol. 2014, 86, 303–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villarino, G.H.; Bombarely, A.; Giovannoni, J.J.; Scanlon, M.J.; Mattson, N.S. Transcriptomic Analysis of Petunia hybrida in Response to Salt Stress Using High Throughput RNA Sequencing. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e94651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, A.; Olah, G.; Szczesny, B.; Wood, M.E.; Whiteman, M.; Szabo, C. AP39, A Mitochondrially Targeted Hydrogen Sulfide Donor, Exerts Protective Effects in Renal Epithelial Cells Subjected to Oxidative Stress in Vitro and in Acute Renal Injury in Vivo. Shock 2016, 45, 88–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Xu, Y.; Lu, P.; Wang, X.; Li, Z.; Cai, X.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, Z.; et al. Salt stress responsiveness of a wild cotton species (Gossypium klotzschianum) based on transcriptomic analysis. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0178313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Yang, P.; Cui, F.; Zhang, F.; Luo, X.; Xie, J. Transcriptome Analysis of Salt Stress Responsiveness in the Seedlings of Dongxiang Wild Rice (Oryza rufipogon Griff.). PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0146242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, Z.H.; Zheng, L.L.; Wang, J.; Gao, Z.; Wu, S.B.; Qi, Z.; Wang, Y.C. Transcriptomic profiling of the salt-stress response in the wild recretohalophyte Reaumuria trigyna. BMC Genom. 2013, 14, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sebastian, P.; Schaefer, H.; Telford, I.R.; Renner, S.S. Cucumber (Cucumis sativus) and melon (C. melo) have numerous wild relatives in Asia and Australia, and the sister species of melon is from Australia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 14269–14273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.F.; Luo, X.D.; Qian, C.T.; Jahn, M.M.; Staub, J.E.; Zhuang, F.Y.; Lou, Q.F.; Ren, G. Cucumis monosomic alien addition lines: Morphological, cytological, and genotypic analyses. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2004, 108, 1343–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, H.; Zhao, Z.; Malik, A.A.; Qian, C.; Chen, J. Identification and characterization of potential NBS-encoding resistance genes and induction kinetics of a putative candidate gene associated with downy mildew resistance in Cucumis. BMC Plant Biol. 2010, 10, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.N.; Wang, X.F.; Sun, X.D.; Shi, Q.H.; Yang, F.J.; Du, D.L. Molecular cloning and characterization of a cucumber MAP kinase gene in response to excess NO3− and other abiotic stresses. Sci. Hortic. 2008, 117, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, K.V.M.; Sresty, T.V.S. Antioxidative parameters in the seedlings of pigeonpea (Cajanus cajan (L.) Millspaugh) in response to Zn and Ni stresses. Plant Sci. 2000, 157, 113–128. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, H.N.; Sun, X.D.; Shi, Q.H.; Yang, F.J.; Yang, X.Y.; Wang, X.F. Physiological Responses of Two Cucumber Cultivars to Nitrate Stress. J. Plant Nutr. 2012, 35, 2167–2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cakmak, I.; Marschner, H. Magnesium deficiency and high light intensity enhance activities of superoxide dismutase, ascorbate peroxidase, and glutathione reductase in bean leaves. Plant Physiol. 1992, 98, 1222–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foyer, C.H.; Halliwell, B. The presence of glutathione and glutathione reductase in chloroplasts: A proposed role in ascorbic acid metabolism. Planta 1976, 133, 21–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bates, L.S.; Waldren, R.P.; Teare, I.D. Rapid determination of free proline for water-stress studies. Plant Soil 1973, 39, 205–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yemm, E.W.; Willis, A.J. The estimation of carbohydrates in plant extracts by anthrone. Biochem. J. 1954, 57, 508–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horsch, R.B.; Fry, J.E.; Hoffmann, N.L.; Wallroth, M.; Eichholtz, D.; Rogers, S.G.; Fraley, R.T. A simple and general method for transferring genes into plants. Science 1985, 227, 1229–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, X.G.; Long, J.; He, X.Z.; Yan, J.P.; Chen, X.Q.; Tan, Y.; Li, K.Z.; Chen, L.M.; Xu, H.N. Overexpression of spinach non-symbiotic hemoglobin in Arabidopsis resulted in decreased NO content and lowered nitrate and other abiotic stresses tolerance. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 26400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, X.H.; Wang, Z.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, H.; Yang, M.; Yin, H.; Cui, J.; Chai, H.; Gao, Y.H.; Hu, G.F.; et al. Overexpression of a Thioredoxin-Protein-Encoding Gene, MsTRX, from Medicago sativa Enhances Salt Tolerance to Transgenic Tobacco. Agronomy 2022, 12, 1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Staub, J.; Qian, C.; Jiang, J.; Luo, X.; Zhuang, F. Reproduction and cytogenetic characterization of interspecific hybrids derived from Cucumis hystrix Chakr. × Cucumis sativus L. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2003, 106, 688–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, S.S.; El-Habbak, M.H.; Havens, W.M.; Singh, A.; Zheng, D.M.; Vaughn, L.; Haudenshield, J.S.; Hartman, G.L.; Korban, S.S.; Ghabrial, S.A. Overexpression of GmCaM4 in soybean enhances resistance to pathogens and tolerance to salt stress. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2014, 15, 145–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.M.; Huang, L.F.; Wang, M.L.; Cui, Y.C.; Xia, X.J. OsDSR-1, a calmodulin-like gene, improves drought tolerance through scavenging of reactive oxygen species in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Mol. Breed. 2017, 37, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza, I.; Rubio, F.; Rodriguez-Navarro, A.; Pardo, J.M. The protein phosphatase calcineurin is essential for NaCl tolerance of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 8792–8796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubrovina, A.S.; Kiselev, K.V.; Khristenko, V.S.; Aleynova, O.A. VaCPK21, a calcium-dependent protein kinase gene of wild grapevine Vitis amurensis Rupr., is involved in grape response to salt stress. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 2016, 124, 137–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campo, S.; Baldrich, P.; Messeguer, J.; Lalanne, E.; Coca, M.; San Segundo, B. Overexpression of a Calcium-Dependent Protein Kinase Confers Salt and Drought Tolerance in Rice by Preventing Membrane Lipid Peroxidation. Plant Physiol. 2014, 165, 688–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.K. Regulation of ion homeostasis under salt stress. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2003, 6, 441–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.N.; Li, K.Z.; Yang, F.J.; Shi, Q.H.; Wang, X.F. Overexpression of CsNMAPK in tobacco enhanced seed germination under salt and osmotic stresses. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2010, 37, 3157–3163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ovecka, M.; Takac, T.; Vyplelova, P.; Komis, G.; Bekesova, S.; Luptovciak, I.; Vadovic, P.; Samajova, O.; Hirt, H.; Samaj, J. Overexpression of Medicago mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase SIMKK in Arabidopsis causes salt stress-induced subcellular relocation and enhanced salt sensitivity. New Biotechnol. 2016, 33, S159–S160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Z.; He, S.; Gong, W.; Sun, J.; Pan, Z.; Xu, F.; Lu, Y.; Du, X. Comprehensive analysis of differentially expressed genes and transcriptional regulation induced by salt stress in two contrasting cotton genotypes. BMC Genom. 2014, 15, 760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, B.; Hu, Y.N.; Huo, P.J.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Z.W. Transcriptome analysis of hexaploid hulless oat in response to salinity stress. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0171451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Chen, L.C.; Shi, Q.H.; Ren, Z.H. SIMYB102, an R2R3-type MYB gene, confers salt tolerance in transgenic tomato. Plant Sci 2020, 291, 110356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.X.; Dong, Y.S.; Yang, X.D.; Guo, D.Q.; Qian, X.Y.; Yan, F.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.W.; Wang, Q.Y. Functional activation of a novel R2R3-MYB protein gene, GmMYB68, confers salt-alkali resistance in soybean (Glycine max L.). Genome 2020, 63, 13–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.J.; Wang, Y.Y.; Zhang, Y.X.; Guo, W.; Jiao, Y.Q.; Zhou, X.A. Overexpression of the Wild Soybean R2R3-MYB Transcription Factor GsMYB15 Enhances Resistance to Salt Stress and Helicoverpa armigera in Transgenic Arabidopsis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, L.; Yang, W.W.; Liao, P.; Guo, Y.W.; Kumar, A.; Gao, W. Transcriptome analysis reveals differentially expressed ERF transcription factors associated with salt response in cotton. Plant Sci. 2019, 281, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debbarma, J.; Sarki, Y.N.; Saikia, B.; Boruah, H.P.D.; Singha, D.L.; Chikkaputtaiah, C. Ethylene Response Factor (ERF) Family Proteins in Abiotic Stresses and CRISPR-Cas9 Genome Editing of ERFs for Multiple Abiotic Stress Tolerance in Crop Plants: A Review. Mol. Biotechnol. 2019, 61, 153–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Z.; He, Q.; Wang, H.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Shao, F.; Xie, C. The Potato ERF Transcription Factor StERF3 Negatively Regulates Resistance to Phytophthora infestans and Salt Tolerance in Potato. Plant Cell Physiol. 2015, 56, 992–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, J.; Sengupta, A.; Gupta, K.; Gupta, B. Molecular phylogenetic study and expression analysis of ATP-binding cassette transporter gene family in Oryza sativa in response to salt stress. Comput. Biol. Chem. 2015, 54, 18–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.Y.; Jin, J.Y.; Alejandro, S.; Martinoia, E.; Lee, Y. Overexpression of AtABCG36 improves drought and salt stress resistance in Arabidopsis. Physiol. Plant. 2010, 139, 170–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Assaha, D.V.M.; Ueda, A.; Saneoka, H.; Al-Yahyai, R.; Yaish, M.W. The Role of Na+ and K+ Transporters in Salt Stress Adaptation in Glycophytes. Front. Physiol. 2017, 8, 509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, Q.; Ma, T.; Hu, Q.J.; Liu, B.B.; Wu, Y.X.; Zhou, H.H.; Wang, Q.; Wang, J.; Liu, J.Q. Genome-scale transcriptome analysis of the desert poplar, Populus euphratica. Tree Physiol. 2011, 31, 452–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Jiang, D.C.; Liu, B.B.; Luo, W.C.; Lu, J.; Ma, T.; Wan, D.S. Transcriptome dynamics of a desert poplar (Populus pruinosa) in response to continuous salinity stress. Plant Cell Rep. 2014, 33, 1565–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelhamid, E.; Zoulfa, R.; Nada, N.; Zakia, Z.; Bouchra, B.; Azzouz, K.; Anass, K.; Imad, K.; Mohamed, N. Chaste plant extract is a promising biostimulant for tomato plants’ growth under salt stress. Biomass Convers. Biorefin. 2022, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ennoury, A.; BenMrid, R.; Nhhala, N.; Roussi, Z.; Latique, S.; Zouaoui, Z.; Nhiri, M. River’s Ulva intestinalis L. extract protects common bean plants (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) against salt stress. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2022, 150, 334–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayakumar, H.; Thamilarasan, S.K.; Shanmugam, A.; Natarajan, S.; Jung, H.J.; Park, J.I.; Kim, H.; Chung, M.Y.; Nou, I.S. Glutathione Transferases Superfamily: Cold-Inducible Expression of Distinct GST Genes in Brassica oleracea. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Tian, Y.S.; Xing, X.J.; Peng, R.H.; Zhu, B.; Gao, J.J.; Yao, Q.H. Over-expression of AtGSTU19 provides tolerance to salt, drought and methyl viologen stresses in Arabidopsis. Physiol. Plant. 2016, 156, 164–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calderon, A.; Sanchez-Guerrero, A.; Ortiz-Espin, A.; Martinez-Alcala, I.; Camejo, D.; Jimenez, A.; Sevilla, F. Lack of mitochondrial thioredoxin o1 is compensated by antioxidant components under salinity in Arabidopsis thaliana plants. Physiol. Plant. 2018, 164, 251–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.J.; Ren, H.Y.; Liu, R.X.; Li, B.Y.; Wu, T.Q.; Sun, F.; Liu, H.M.; Wang, X.M.; Dong, H.S. An h-Type Thioredoxin Functions in Tobacco Defense Responses to Two Species of Viruses and an Abiotic Oxidative Stress. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2010, 23, 1470–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, H.; Kaur, H.; Kaur, H.; Srivastava, S. The beneficial roles of trace and ultratrace elements in plants. Plant Growth Regul. 2022, 100, 219–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, F.; Li, Y.H.; Li, F.G.; Wang, Z. Genome-wide characterization and expression analysis of cystathionine beta-synthase genes in plant development and abiotic stresses of cotton (Gossypium spp.). Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 193, 823–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luan, J.; Dong, J.; Song, X.; Jiang, J.; Li, H. Overexpression of Tamarix hispida ThTrx5 Confers Salt Tolerance to Arabidopsis by Activating Stress Response Signals. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iordachescu, M.; Imai, R. Trehalose biosynthesis in response to abiotic stresses. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2008, 50, 1223–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).