Abstract
The input of exogenous organic matter could affect the transformation of soil carbon (C) and nitrogen (N), and their C- and N-priming effects (CPE and NPE) play a key role in the balance of soil C and N. However, little is known about how the interaction effect between straw and straw biochar regulates CPE and NPE. Therefore, we conducted a 90-day incubation experiment, which included five treatments: no straw and straw biochar (CK), 1.5% straw (S), 0.53% straw biochar (B), 1.5% straw + 0.53% straw biochar (SB), and 1.5% straw + 1.06% straw biochar (SB1). Our findings revealed that cumulative soil CO2 emissions were increased by 95.52–216.53% through the short-term input of exogenous organic matter input; however, this trend gradually weakened with decreasing dissolved organic C (DOC) content. The cumulative NPE generated by the addition of exogenous organic matter was much smaller than the cumulative CPE. Under the B and S treatments, the cumulative CPE and NPE were negative throughout the entire incubation period. The SB treatment remarkably boosted the microbial biomass nitrogen (MBN) content; however, the SB1 treatment was more effective in inhibiting soil C and N mineralization processes than SB treatment. Moreover, the cumulative CPE and NPE were mainly regulated by N. We conclude that the combination of straw and straw biochar preferentially stimulated soil C mineralization, but that this effect decreased with time, which may be due to the consumption of labile DOC caused by the initial positive CPE, while soil N mineralization had a lag effect.
1. Introduction
As the largest traditional agricultural country in the world, China produces over 1 billion tons of straw annually [], most of which is not effectively utilized, resulting in various environmental problems and social impacts. On 8 March 2021, the National Development and Reform Commission reported the “Guiding Opinions on the Comprehensive Utilization of Bulk Solid Waste during the 14th Five Year Plan”, proposing to “vigorously promote the comprehensive utilization of straw and promote the improvement of quality and efficiency in the straw comprehensive utilization industry” []. Crop straw is a renewable biomass resource that plays an important role in perfecting circumstantial levels and boosting the synthetic green route to economic and social advancement by improving the integrated application efficiency of straw resources. Returning straw to the field is beneficial for the resource utilization of crop waste, improving soil structure, and increasing soil organic carbon (SOC) content [,,]. Crop straw is rich in nutrients such as C, N, phosphorus, and potassium. Therefore, returning straw to the field is of great significance in sustainable agriculture.
Most researchers carbonized straw into biochar and added it to soil to improve the soil, achieving significant results [,,]. Crop straw is the most discarded biomass and is also a commonly used raw material for producing biochar. The application of straw biochar has a higher potential for SOC sequestration than straw returned to the field, and the long-term returning of straw to the field is beneficial for soil nitrogen utilization efficiency []. Hu et al. (2021) have shown that, compared to returning straw to the field, the application of straw biochar obviously improved the SOC, total N, microbial biomass carbon (MBC), and MBN in the soil surface, while both straw and straw biochar reduced the leaching of nitrate N []. In addition, Zhang et al. (2020) conducted a 6-year study on rice-wheat rotation and found that the application of biochar increased the biomass of crop roots, straw, and grains by 3–19%, 10–19%, and 10–16%, respectively, relative to the application of N fertilizer alone []. This increased the N and phosphorus utilization efficiency of grains by 20–53% and 38–230%, respectively, and increased the SOC, total N (TN), and phosphorus contents. In particular, the application of biochar has great potential in SOC sequestration and emission reductions. Biochar could effectively reduce the rate of soil CO2 emissions. Wang et al. (2020) showed that, compared to the control, crop biochar decreased total soil CO2 emissions by 33.41%, and the total CO2 emissions of wheat straw biochar treatment were 90.25% lower than those of wheat straw treatment []. Zhang et al. (2017) indicated that the application of straw remarkably boosted the SOC storage ratio and CO2 emissions but had no noticeable impact on soil N2O and CH4 emissions []. However, straw biochar amendments sensibly reduced N2O emissions and notably increased SOC sequestration butdid not affect soil CO2 emissions. In summary, straw biochar can improve soil productivity while reducing greenhouse gas intensity in wheat and corn planting systems. Of course, some studies may also draw the opposite conclusion, that the application of biochar does not reduce greenhouse gas emissions, for example, in rice fields that have been submerged for a long time []. Therefore, C and N cycling not only affect crop growth, but are also closely related to some environmental issues, such as soil degradation, nutrient leaching, and greenhouse gas emissions []. In addition, the availability of C and N is considered the main factor limiting plant or crop growth, and the application of an exogenous organic substrate could affect the effectiveness of the soil’s own C and N [,]. Therefore, it is necessary to understand the impact of the addition of external organic matter on the transformation of soil C and N, especially the mineralization of C and N.
Returning straw to the field is worth advocating for in the current context of C neutrality. The input of straw can provide a portion of nutrients (such as C, N, phosphorus, and potassium), but the crop straw’ ability to provide these is limited. The content of available C and N in soil is mainly controlled by the balance of the mineralization fixation process, and the mineralization process of SOC and N is mainly mediated by soil enzyme activities and the microbial community []. Although straw input only occupies a tiny portion of SOC and total N, it is important in the mineralization of exogenous C and N and the transformation of organic substances. The research has shown that adding biomass organic matter with a high C/N rate produces a negative PE, while low-biomass organic materials have the opposite effect [,]. Organic materials can affect the conversion process of soil C and N. Currently, most research has focused on the PE of different organic materials on soil C and N []. However, there are few reports on the PE of crop stover on soil C and N excitation. Therefore, it is necessary to explore the impact of crop straw input on the dynamic mineralization of soil C and N, and the relationship between soil C and N mineralization and various influencing factors.
Therefore, the goals of the current work were to: (1) evaluate the effect of combining straw and straw biochar on soil C and N mineralization, (2) explore the influencing factors of C and N mineralization, and (3) clarify the effect of different exogenous organic substrates on CPE and NPE.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Soil Sampling, Straw, and Straw Biochar
The soils were obtained from a field that underwent years of continuous tobacco rice rotation. The acquisition location was located in Ningxiang city (28°19 N, 112°29′ E), Hunan Province, with an average annual temperature of 17.6 °C and an average annual precipitation of 1358.3 mm []. After the rice harvest, soil samples (0–20 cm) from five replicates within the emblematic fields formed a sample. Crop residues and crop roots were removed, air-dried naturally, and crushed to 2 mm for later use. The soil is sandy loam classified as Fluvisols according to FAO classification. The properties of SOC, TN, NH4–N, and NO3–N were 20.37 g·kg–1, 1.1 g·kg–1, 1.26 mg·kg–1, and 29.91 mg·kg–1, respectively.
Rice straw (Oryza sativa L.) and tobacco straw (Nicotiana tabacum L.) were also gathered from the same region. The collected straw was washed and air-dried, and then the air-dried rice straw and tobacco straw were cut into 1–2 mm pieces. They were dried at 60 °C for 48 h, crushed through a 1 mm sieve and placed in a self-sealing bag for later use. Biochar was made from tobacco straw in a tube furnace at 500 °C for 2 h. The contents of C and N in rice straw are 60.32% and 2.64% (C/N = 22.85), respectively, while the C and N contents in tobacco straw charcoal are 62.49% and 1.80% (C/N = 34.72), respectively (using an elemental analyzer (Elementar variole Ⅲ, Frankfurt an der Oder, Germany) to determine).
2.2. Incubation Experiment
The incubation experiment was conducted in a laboratory with three factors taken into consideration, including straw addition alone (S), straw biochar addition alone (B), straw and straw biochar addition (SB), and sampling time (ST). The straw management was taken as the main factor. This study set up five treatments: CK, (no straw and straw biochar), S, (1.5% straw, C/N = 22.85), B, (0.53% straw biochar C/N = 34.72), SB (1.5% straw + 0.53% straw biochar, C/N = 25.15), and SB1 (1.5% straw + 1.06% straw biochar, C/N = 26.71). The incubation method was as follows: 200 g of soil was weighted, and deionized water was added to a cultivation bottle to 70% of the field capacity. The samples were incubated for one week at 25 °C to activate soil microbial activity. After preincubation, the straw and straw biochar were mixed evenly with the soil according to the experimental design and then incubated in a 25 °C constant-temperature incubator for 90 days. During the incubation period, the moisture was maintained at 70% of the field capacity using the weighing method. The mineralization of soil C was measured at 2, 5, 9, 13, 17, 25, 44, 57, 72, and 90 days. The mineralization of soil N was measured at 1, 5, 13, 25, 57, 72, and 90 days, and then destructive sampling was performed to determine the soil NH4+–N and NO3––N contents. SOC, DOC, MBC, MBN, and soil enzyme activities (β-glucosidase enzyme, cellulase enzyme, and urease enzyme) determined at 25, 57, and 90 days. The entire experiment consisted of 50 bottles of soil samples, with 10 replicates per treatment, of which 3 were used to track changes in CO2 content, and the remaining 7 were used for destructive sampling each time.
2.3. Sample Analysis
A total of 0.5 mol·L−1 NaOH (20 mL) was used to absorb CO2 released from soil respiration, and the CO2 absorbed by the alkaline solution was titrated with HCl (1 mol·L−1). The SOC was determined using the K2Cr2O7-H2SO4 oxidation method. The chloroform fumigation method was used to measure the soil MBC and MBN, with the SOC of the nonfumigated soil extract being the soil DOC content and the soil MBC and MBN being the difference between fumigated and nonfumigated soil, divided by 0.45 and 0.54, respectively. The samples were extracted with 2 mol·L−1 KCl and centrifuged and filtered before being measured using a flow analyzer to obtain the contents of soil NH4+-–N and NO3−–N. The soil enzymes β-glucosidase, cellulase, and urease were determined by an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) at wavelengths of 540 nm, 630 nm, and 405 nm, respectively.
The soil CO2 emissions are calculated using Formula (1):
where V0 is the bulk of HCl used for bare test titration, mL; V is the bulk of HCl used for each treatment consumption, mL; n is the amount of substance in HCl solution, mol·L−1; 44 is the molar mass of CO2, g·mol−1; and m is the quality of soil samples, g.
CO2 (mg·g−1) = 1/2 (V0 − V) × n × 44/m
The CO2 emissions rate is calculated using Formula (2):
where ΔT is the cultivation time, d.
CO2 (mg·kg−1·d−1) = amount of organic carbon mineralization/ΔT
The cumulative CO2 emissions from soil are the total CO2 emissions from cultivation to the day of measurement. CPE is the difference between the mineralization amount of native SOC after adding exogenous organic matter and the mineralization amount of SOC with the control.
The inorganic N content (mg·kg−1) in soil is the sum of the NH4+-N content and NO3−-N content in the soil. The net N mineralization (mg·kg−1) in soil is the divergence between the soil inorganic N content after incubation and the soil inorganic N content before incubation. NPE is the distinction in net N mineralization between soil and control soil after the addition of exogenous organic matter.
2.4. Statistical Analysis
Microsoft Excel 2017 was used to organize the data, and SPSS 21.0 was used for analysis of variance and multiple comparisons (Tukey test, p ≤ 0.05). Multivariate analysis of variance was exploited to explore the effects of straw, straw biochar, sampling time (25 days, 57 days, and 90 days), and their interactions with soil C mineralization, N mineralization, cumulative CPE and NPE, as well as with soil properties such as TOC, DOC, MBC, MBN, and enzyme activities. The software Origin 2021 was used for mapping and conducting univariate regression methods to explore the direct relationship between cumulative CPE and NPE and soil properties, and a correlation coefficient (R2) was selected to evaluate goodness of fit. The relative effects of soil properties on CPE and NPE were quantitatively visualized by performing Aggregation Boosted Tree Analysis (ABT) in Python. Path analysis was constructed using the plspm package in R and was used to discuss the major influences of soil parameters on the cumulative CPE and NPE. We counted the standardized total influences (direct plus indirect effects from the path analysis) of different indices on the cumulative CPE and NPE.
3. Results
3.1. Mineralization of Soil Organic C
The CO2 emissions rate and cumulative CO2 emissions were influenced by straw, straw biochar, sampling time, and their interactions (Figure 1a–f and Table 1). Throughout the 90-day cultivation period, the soil CO2 emissions rate under different treatments showed a trend of initially sharply increasing, gradually decreasing, and finally stabilizing (Figure 1a), and showed a clear phased pattern. The soil’s cumulative CO2 emissions under different treatments increased with increasing incubation time, and the cumulative CO2 emissions under straw, straw biochar, and their combination treatments were significantly larger than those under CK (Figure 1b). Compared to CK, exogenous organic matter significantly increased the cumulative CO2 emissions by 95.52–216.53% within 0–25 days. Likewise, the cumulative CO2 emissions at the early stage (0–25 days) of the incubation period were relatively high, while in the middle stage (25–57 days) and later stage (57–90 days), they were relatively low (Figure 1c).

Figure 1.
Soil organic C mineralization (a–c) and cumulative CPE (d–f) in soil. Values are means ± standard errors. Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different treatments in the same period. Different uppercase letters indicate significant differences among different incubation periods; p < 0.05. CK, (no straw and straw biochar), S, (1.5% straw), B, (0.53% straw biochar), SB (1.5% straw + 0.53% straw biochar), and SB1 (1.5% straw + 1.06% straw biochar).

Table 1.
Multivariate ANOVA for the effects of straw (S), straw biochar (B), and sampling time (ST) on soil C and N mineralization, soil properties, and soil enzyme activities.
The magnitude of the CPE and cumulative CPE varied with straw, straw biochar, sampling time, and their interactions (Figure 1d–f and Table 1). The variation patterns of the CPE and soil CO2 emissions rate were similar, and the CPE first increased, then decreased and gradually stabilized under the different treatments (Figure 1d). With increasing time, the cumulative CPE under treatment B gradually decreased, and this trend gradually decreased compared to CK after 25 days (Figure 1c). The cumulative CPE gradually increased and gradually stabilized with the prolongation of cultivation time in the SB and SB1 treatments (Figure 1e). The cumulative CPE within 0–25 days was significantly higher than that between 25–57 days and 57–90 days (Figure 1f). During the entire incubation period, the addition of straw biochar induced a negative CPE, while the SB and SB1 amendments induced a positive CPE (Figure 1f), indicating that the individual application of straw biochar significantly inhibited the mineralization of local organic C.
3.2. Mineralization of Soil N
Except for no significant differences in soil NH4+–N content caused by straw biochar, the interaction between sampling time and straw and straw biochar,, straw, biochar, sampling time and their interactions had a noticeable impact on soil NH4+–N, NO3−–N, and net N mineralization (Table 1). The changes in soil NH4+–N, NO3−–N, and net N mineralization, along with the incubation time, are shown in Figure 2a–c. Under each treatment, the soil NH4+-N content substantially increased before 13 days (Figure 2a), but significantly decreased and remained stable after 13 days of incubation. The soil NH4+–N content of each treatment was larger than that of CK and showed an increasing trend after 72 days (except for the CK treatment). In contrast, soil NO3−–N showed the opposite trend. The soil NO3−–N content was relatively high in CK, and the content of NO3−–N increased with time in treatments B and SB, while that in SB1 decreased after the 57th day, and that in the S treatment gradually stabilized after the 5th day (Figure 2b). The net N mineralization rate of the CK and B treatments reached its peak on the 25th day and continued to decrease thereafter (Figure 2c). During the entire cultivation period, the S treatment showed a negative net N mineralization value and maintained this balance on the 5th day; the SB and SB1 treatments consistently maintained relatively high soil net N mineralization levels (Figure 2c).


Figure 2.
Soil NH4+–N content (a), NO3−–N content (b), net N mineralization rate (c), NPE (d), and cumulative NPE (e,f). Values are means ± standard errors. Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different treatments in the same period. Different uppercase letters indicate significant differences among different incubation periods; p < 0.05. CK, (no straw and straw biochar), S, (1.5% straw), B, (0.53% straw biochar), SB (1.5% straw + 0.53% straw biochar), and SB1 (1.5% straw + 1.06% straw biochar).
Straw, straw biochar, sampling time, and their interactions had an emphatic impact on the cumulative NPE (Table 1). Except for treatment B, the addition of exogenous organic matter caused a precipitous decrease in NPE before 25 days and then piecemeal improvement. Compared with other treatments, the NPE was the lowest before the 72nd day under the S treatment (Figure 2d). The cumulative NPE gradually decreased with increasing incubation time, while the SB and SB1 treatments gradually increased after the 57th day (Figure 2e). Except for the SB1 treatment and cumulative NPE in the SB treatment within 57–90 days, the other treatments resulted in negative cumulative NPE during the experiment (Figure 2f).
3.3. Dynamic Changes in Soil SOC, DOC, MBC, and MBN
The addition of exogenous organic matter improved the SOC, MBC, and MBN contents throughout the entire incubation cycle (Figure 3a,c,d) but decreased the content of DOC in soils with the extension of incubation time (Figure 3b). It was also found that sampling time had a very significant influence on DOC content after conducting multiple-factor analysis of variance (Table 1).

Figure 3.
SOC (a), DOC (b), MBC (c), and MBN (d) contents in soils after 25, 57, and 90 days of incubation. Values are means ± standard errors. Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different treatments in the same period. Different uppercase letters indicate significant differences among different incubation periods; p < 0.05. SOC, soil organic carbon; DOC, dissolved organic carbon; MBC, microbial biomass carbon; MBN, microbial biomass nitrogen. CK, (no straw and straw biochar), S, (1.5% straw), B, (0.53% straw biochar), SB (1.5% straw + 0.53% straw biochar), and SB1 (1.5% straw + 1.06% straw biochar).
The SOC content was influenced by straw, straw biochar, sampling time, and the interaction of straw biochar with sampling time (Table 1). The SB1 treatment maintained a relatively high SOC content within 90 days, while the SOC content decreased with time under the S and SB treatments. The SOC content did not seem to show significant changes throughout the entire culture period under the B treatment (Figure 3a), indicating that biochar has a C fixation effect. Except for the interaction between straw biochar and sampling time, other factors were important influencing dominants on DOC (Table 1). The soil DOC content showed a gradually decreasing trend over time under different treatments (Figure 3b), indicating that organic matter mineralization occurred during the incubation process. The DOC content under the B and SB1 treatments was higher than that under the S and SB treatments during the same period, explaining how biochar could prevent the loss of internal DOC content.
The application of straw and straw biochar had a dominant impact on the soil MBC content (Table 1). Regardless of the period, the MBC content in the soil under the SB1 treatment was the highest, followed by that under the S treatment, and there was no significant change in the soil MBC content under each treatment during the 90-day incubation period (Figure 3c). The straw, straw biochar, sampling time, and the interaction between straw and straw biochar resulted in significant differences in soil MBN (Table 1). Compared with CK, the input of exogenous organic matter remarkably boosted the MBN content in the soil. The soil MBN content under the SB and SB1 treatments was higher than that of the other treatments, and the MBN content in each treatment showed a decreasing trend over time (Figure 3d).
3.4. Activities of Extracellular Enzymes in Soil
Soil β-glucosidase and soil cellulase enzyme activities were remarkably influenced by biomass tapes, sampling time, and their interrelationships, and the enzyme activity of urease was impacted by straw biochar, sampling time, the combined effect of straw and biochar, and the interaction between straw biochar and sampling time (Table 1). There was no measurable difference in β-glucosidase enzyme activity among the three stages (Figure 4a; p > 0.05), and the input of exogenous organic matter obviously increased soil cellulase and urease activities at 57 and 90 days (Figure 4b,c). Compared to the control treatment, the enzyme activities of β-glucosidase and cellulase were increased by 38.60–89.90% and 12.70–28.00%, 54.91–119.73% and 11.46–44.03%, and 48.97–117.06% and 3.18–43.05% in the S, SB, and SB1 treatments, respectively, at the three incubation periods (Figure 4a,b). Higher β-glucosidase enzyme and cellulase enzyme activities were observed in the SB treatment during the total incubation period (Figure 4a,b). However, treatment B reduced soil β-glucosidase enzyme activity and cellulase activity during the total treatment period (except for cellulase activity in the middle stage of incubation; Figure 4a,b).

Figure 4.
Soil β-glucosidase (a), cellulase (b), and urease (c) enzyme activities after 25, 57, and 90 days of incubation in soils. Values are means ± standard errors. Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different treatments in the same period. Different uppercase letters indicate significant differences among different incubation periods; p < 0.05. CK, (no straw and straw biochar), S, (1.5% straw), B, (0.53% straw biochar), SB (1.5% straw + 0.53% straw biochar), and SB1 (1.5% straw + 1.06% straw biochar).
3.5. The Relationship between the Mineralization Rate of Soil Organic C and N and Various Influencing Factors
The relative influence of the soil properties on the cumulative CPE and cumulative NPE over the entire period was estimated by the ABT models (Figure 5a). The main influencing factors of cumulative CPE and cumulative NPE are different. Urease activity and MBN were the main influencing factors determining the cumulative CPE during the entire stage (accounting for over 20% of the variation). In addition, the content of SOC was also an important influencing factor on cumulative CPE (p < 0.05). The content of NO3−–N and the activity of cellulase, and β-glucosidase enzymes played prominent roles in regulating the cumulative NPE, which revealed 20.5%, 19.9, and 17.7% of the changes, respectively. In addition, the MBN (accounting for 13.5% of the alteration) and DOC (12.8%) contents were the principal factors affecting the cumulative NPE. Pearson correlation analysis was conducted to elucidate various responses of cumulative CPE and cumulative NPE to soil characteristics (Table 2). The results showed that MBN and SOC had a positive impact on the cumulative CPE (p < 0.01 and p < 0.05), while urease activity had a negative impact (p < 0.01). NO3−–N, MBN, β-glucosidase activity, and cellulase activity promoted cumulative NPE, while DOC had a negative effect. We also found a linear negative correlation between cumulative CPE and urease activity and a linear positive correlation with MBN content (Figure 5b,c); NO3−–N, cellulase, and β-glucosidase activity were all linearly positively correlated with cumulative NPE (Figure 5d–f).

Figure 5.
Relative influence of soil properties on the cumulative CPE and NPE during the entire incubation period, as estimated by the ABT models (a). Relationships between cumulative CPE and urease activity (b) and MBN (c). Relationships between cumulative NPE and NO3−-N(d), cellulase activity (e), and β-glucosidase activity (f).

Table 2.
Pearson correlations between cumulative CPE and cumulative NPE and soil properties.
Figure 6 shows the relationship between cumulative CPE, cumulative NPE and major factors, determined by path analysis. SOC had a significant impact on cumulative CPE by affecting MBC content (Figure 6a), while SOC also indirectly affected urease activity and NH4+–N by affecting DOC content, and thus had a strong impact on cumulative CPE. The regulation of MBN content by cellulase activity and NO3−–N content had a noticeable impact on the cumulative CPE, and urease activity also directly affected the cumulative CPE. Overall, the soil MBN and urease activity exhibited a strong relationship with cumulative CPE. The content of NO3−–N had an emphatic impact on cumulative NPE by indirectly affecting MBN and directly affecting cumulative NPE. The activities of soil cellulase and glucosidase had a particularly worthwhile influence on the cumulative NPE, and the activity of β-glucosidase also had a noticeable negative effect on the cumulative NPE by affecting the DOC content in addition to its direct regulatory effect. In summary, NO3−–N, cellulase activity, and β-glucosidase activity were the primary influencing factors for the cumulative NPE (Figure 6b).
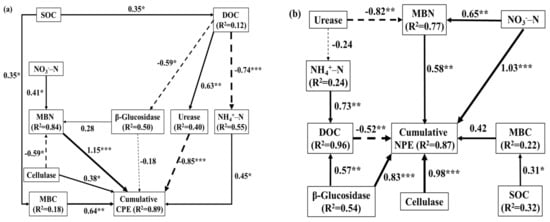
Figure 6.
Path analysis diagram of direct and indirect effects of soil properties on the cumulative CPE (a) and cumulative NPE (b) during the entire incubation period. The width of the arrows indicates the strength of the standardized path coefficient. The solid lines indicate positive path coefficients, dashed lines indicate negative path coefficients, and R2 values represent the proportion of the variance explained for each endogenous variable. The asterisks indicate the significance level: * p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01; *** p < 0.001.
4. Discussion
4.1. Effects of Exogenous Organic Matter Input on Soil C
The application of fertilizers, organic fertilizers, and straw residues in agricultural management could all affect soil C mineralization. However, there is still controversy over whether straw, straw biochar, and their combined addition are beneficial for the decomposition of SOC and C mineralization. In this study, the CO2 emission rates of all treatments showed a sharp increase followed by a slow decrease, and the results of most studies were similar to our results [,]. Biochar contains a certain amount of carbonate, which is quickly converted into CO2 when it enters the soil. This also explains why the CO2 emissions generated by biochar amendment were higher than those of amended straw on the first day, as shown in Figure 1a. After this, the CO2 emissions of treatment B rapidly decreased throughout the entire incubation period and were lower than those of treatment S, while the DOC content under treatment B was significantly higher than that of treatment S (Figure 3b), indicating that biochar has potential for C fixation, and porous biochar could adsorb DOC to avoid microbial degradation []. In addition, the mixed application of straw and straw biochar (SB and SB1) resulted in significantly higher cumulative CO2 emissions throughout the entire incubation period compared to the other treatments (Figure 1b). This may be because straw and straw biochar contain more unstable C components (volatile matter, DOC, etc.) that were more prone to mineralization []. This also explained why the DOC content under the SB and SB1 treatments in Figure 3b was significantly lower than that under the S and B treatments. In addition, compared with CK, we also discovered that exogenous organic matter markedly improved the mineralization of soil C within 0–25 days but was remarkably reduced within 25–57 days (Figure 1c). Moreover, after the end of incubation, the cumulative CO2 emissions of treatment B were lower than those of the treatment CK, indicating that the addition of biochar reduced the mineralization of native SOC.
The mineralization of native soil C by straw biochar showed a negative CPE on the 5th day of incubation (Figure 1d), and the cumulative CPE under treatment B also decreased with time (Figure 1e), indicating that straw biochar could inhibit the mineralization of soil C and reduce CO2 emissions. At the early stage of incubation, the content of DOC was higher under treatment B (Figure 3b), but its β-glucosidase enzyme activity was lower, indicating that the soil biological activity was also relatively low in the early stage, and easily decomposed DOC could be retained. Although biochar could adsorb DOC and lead to a decrease in DOC content, the easily degradable components in straw could promote microbial growth [], and microorganisms could produce higher levels of MBC by regulating their community structure. This may be the reason why the cumulative CPE was lower in the S treatment than in the SB and SB1 treatments, and the MBC content was lower than that in the SB1 treatment but higher than that in the SB treatment. The MBC content under treated SB1 was prominently larger than that under other treatments throughout the entire incubation period, which could be explained by the special biochar structure, which provided space for microbial development and reproduction []. Furthermore, the addition of straw alone also significantly boosted MBC content, and the combination of straw and straw biochar provided a better habitat for microorganisms [,], resulting in a higher MBC content under the SB1 treatment. In addition, the cumulative CPE under treatment B was lower than that under treatment S, and the cumulative CPE with SB1 treatment was also lower than that with SB treatment, especially at the early and middle stages of incubation. This indicated that the presence of straw biochar in the soils had a certain inhibitory influence on soil C mineralization, and the straw biochar amendment substantially promoted the SOC content (Figure 3a). This result illustrated that, even in the presence of straw, the stability and C fixation effect of straw biochar were obvious. In addition, under the treatment with straw addition (S, SB, and SB1), the β-glucosidase enzyme activity and cellulase activity were relatively high, and this trend became more pronounced with the extension of cultivation time. The input of straw could provide a C source for microorganisms and stimulate their growth, resulting in an increase in the production of extracellular enzymes, thereby promoting the mineralization of soil C []. However, under the treatment adding biochar alone, soil urease activity was higher, and the increase in urease activity significantly inhibited CO2 emissions, resulting in a negative cumulative CPE (Figure 1). Table 2 and Figure 5b also show a remarkable negative connection between soil urease activity and cumulative CPE. This viewpoint is demonstrated in Figure 6a, which illustrates that urease activity has a negative impact on cumulative CPE.
4.2. Effects of Exogenous Organic Matter Input on Soil N
The mineralization of soil N was also impacted through the input of exogenous organic matter [,]. In this work, with increasing time, NH4+–N showed a decreasing and stabilizing trend, while NO3−–N increased and gradually stabilized (except for the S treatment), resulting in a trend of first increasing and then decreasing net N mineralization. The variation pattern of soil net N mineralization and NO3−–N was similar, indicating a close correlation between net N mineralization and NO3−–N content. The accumulation of NH4+–N in soil could trigger nitrification, while the accumulation of NO3−–N leads to denitrification [,]. Additionally, the soil NO3−–N was significantly larger than that of NH4+–N, indicating that the preferential decomposition of DOC consumed a large amount of O2 throughout the entire cultivation process, resulting in a local anaerobic environment and denitrification reaction, and soil N was immobilized []. This phenomenon was confirmed by Figure 2f, where the cumulative NPE was negative during both the early and middle stages of cultivation, mainly influenced by DOC content (accounting for 12.8% of the change is shown in Figure 5a). In addition, we found that the cumulative CPE was basically positive from 0–25 days to 25–57 days of incubation, while the cumulative NPE was negative. The cumulative CPE and cumulative NPE were exactly the opposite, indicating that C mineralization was more severe than N mineralization after external organic matter input, leading to a decrease in microbial activity due to the low C availability [], thereby inhibiting N mineralization. The positive cumulative NPE in the later stage of the SB and SB1 treatments may be regulated by more factors. Similarly, a recent study has shown that factors such as soil MBN, DOC, TOC, and soil texture have a stronger impact on NPE [].
In addition, the addition of exogenous organic matter increased MBN. It is worth noting that, compared to adding straw or biochar alone, the addition of straw and biochar together obviously increased the MBN content, leading to an increase in cumulative NPE in the later stage. In addition, the urease activity related to the N cycle seems to not be affected by the combination of straw and straw biochar, but rather by the amount of straw biochar (Figure 4c). The C/N ratio following the addition of an exogenous organic substrate was believed to affect soil N mineralization or fixation []. Some scholars believe that a high C/N ratio promotes microbial growth in the short-term, resulting in C mineralization, while N produced due to N content limitations is rapidly immobilized []. In this study, the effect was more pronounced after adding straw biochar, especially in the first 5 days of cultivation. Furthermore, the C/N ratio of straw was 22.85, and the C/N ratio of straw biochar was 34.72. This further proves that the S treatment could inhibit N mineralization and boost N fixation, while the B treatment could inhibit the production of C mineralization and facilitate C fixation. After straw was converted into straw biochar, due to its aromatic ring structure, which is not easily decomposed, and high C/N ratio [,], both of their combinations could achieve a better effect, increasing and fixing C.
The addition of exogenous organic matter could cause the mineralization of soil C and N, leading to positive or negative priming effects, while soil C and N mineralization were influenced by different soil properties. In this work, urease activity, MBN, and TOC were the main influencing factors on cumulative CPE, while NO3−–N, cellulase activity, β-glucosidase enzyme activity, and MBN were important influencing factors on cumulative NPE. In summary, the three soil enzyme activities and MBN content have a greater impact on the cumulative CPE and NPE (Figure 5 and Figure 6), and the regulation of soil N is more important than that of soil C. Therefore, the CPE and NPE in soil are mainly driven by N constraints rather than C constraints.
5. Conclusions
Our research showed that the input of exogenous organic matter led to a strong mineralization effect of soil C at the early stage of incubation, while in the later stage, it enhanced the mineralization effect of soil N. The cumulative CPE was opposite to the cumulative NPE, which may be influenced by the content of DOC. The combination of straw and straw biochar preferentially induced soil C mineralization, while the induction of soil N was relatively delayed, which may be regulated by the N of exogenous organic matter. The SB1 treatment could significantly increase the soil TOC and MBC contents, while the soil MBN content was relatively higher under the SB treatment. With increasing incubation time, except for treatment B, the activities of soil β-glucosidase, cellulase, and urease enzymes were obviously increased compared to those of treatment CK. The complexity of the soil led to an increase in factors affecting the cumulative CPE and cumulative NPE. The addition of straw biochar was more conducive to C fixation, while the separate application of straw was beneficial to N fixation. With the combination of straw and straw biochar, SB1 was shown to have a better inhibitory effect on soil C and N mineralization than SB. Therefore, while ensuring the sufficient availability of C sources in straw, future research can consider appropriately increasing the proportion of biochar to achieve better C and N fixation effects.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, C.S. and S.T.; methodology, S.S.; software, S.T. and L.C.; validation, S.T. and Z.Q.; formal analysis, C.S. and L.C.; investigation, S.T. and Z.Q.; resources, P.J.; data curation, C.S. and S.T.; writing—original draft preparation, C.S.; writing—review and editing, C.S., S.T. and S.S.; visualization, L.C.; supervision, Z.Q., S.S. and L.C.; project administration, C.S.; funding acquisition, P.J. and L.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by the Key R&D Projects in Hunan Province (2023NK2010) and the Postgraduate Scientific Research Innovation Project of Hunan Province (QL20220166).
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
Author Zhihua Qiu was employed by the company Truking Technology Limited. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- Li, H.; Dai, M.; Dai, S.; Dong, X. Current status and environment impact of direct straw return in China’s cropland—A review. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Safe 2018, 159, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Zhang, Y.; Luo, E.; Lu, Q. Suggestions for the comprehensive utilization of bulk solid waste in the 14th Five-Year Plan under the background of carbon peaking and carbon neutrality. China Invest. 2021, 22–25. [Google Scholar]
- Qiao, Y.; Miao, S.; Zhong, X.; Zhao, H.; Pan, S. The greatest potential benefit of biochar return on bacterial community structure among three maize-straw products after eight-year field experiment in Mollisols. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2019, 147, 103432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Fan, P.; Li, L.; Tian, H.; Pan, S. Straw Incorporation Coupled with Deep Placement of Nitrogen Fertilizer Improved Grain Yield and Nitrogen Use Efficiency in Direct-Seeded Rice. J. Soil. Sci. Plant Nut. 2020, 20, 2338–2347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.E.A.F. Responses of soil organic carbon and crop yields to 33-year mineral fertilizer and straw additions under different tillage systems. Soil. Till Res. 2021, 209, 104943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.F.; Meng, J.; Wang, Q.X.; Zhang, W.M.; Cheng, X.Y.; Chen, W.F. Effects of straw and biochar addition on soil nitrogen, carbon, and super rice yield in cold waterlogged paddy soils of North China. J. Integr. Agr. 2017, 16, 1064–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabhane, J.W.; Bhange, V.P.; Patil, P.D.; Bankar, S.T.; Kumar, S. Recent trends in biochar production methods and its application as a soil health conditioner: A review. Sn Appl. Sci. 2020, 2, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bousdra, T.; Papadimou, S.G.; Golia, E.E. The Use of biochar in the Remediation of Pb, Cd, and Cu-Contaminated Soils. The Impact of biochar Feedstock and Preparation Conditions on Its Remediation Capacity. Land 2023, 12, 383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Jiang, B.; Shen, J.; Zhu, X.; Yi, W.; Li, Y.; Wu, J. Contrasting effects of straw and straw-derived biochar applications on soil carbon accumulation and nitrogen use efficiency in double-rice cropping systems. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2021, 311, 107286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Sun, B.; Wu, S.; Feng, H.; Gao, M.; Zhang, B.; Liu, Y. After-effects of straw and straw-derived biochar application on crop growth, yield, and soil properties in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) -maize (Zea mays L.) rotations: A four-year field experiment. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 780, 146560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Song, Y.; Wu, Z.; Yan, X.; Gunina, A.; Kuzyakov, Y.; Xiong, Z. Effects of six-year biochar amendment on soil aggregation, crop growth, and nitrogen and phosphorus use efficiencies in a rice-wheat rotation. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 242, 118435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Ren, T.; Yang, H.; Feng, Y.; Feng, H.; Liu, G.; Yin, Q.; Shi, H. Research and Application of Biochar in Soil CO2 Emission, Fertility, and Microorganisms: A Sustainable Solution to Solve China’s Agricultural Straw Burning Problem. Sustainability 2020, 12, 1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.; Cheng, G.; Hussain, Q.; Zhang, M.; Feng, H.; Dyck, M.; Sun, B.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, H.; Chen, J. Contrasting effects of straw and straw–derived biochar application on net global warming potential in the Loess Plateau of China. Field Crop Res. 2017, 205, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, Y.; Gao, J.; Liu, C.; Zhang, W.; Lan, Y.; Li, S.; Meng, J.; Xu, Z.; Tang, L. Interactive effects of straw-derived biochar and N fertilization on soil C storage and rice productivity in rice paddies of Northeast China. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 544, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghorbani, M.; Amirahmadi, E.; Konvalina, P.; Moudrý, J.; Kopecký, M.; Hoang, T.N. Carbon Pool Dynamic and Soil Microbial Respiration Affected by Land Use Alteration: A Case Study in Humid Subtropical Area. Land 2023, 12, 459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lonardo, P.D.; Wal, A.V.D.; Boer, W.D.; Zweers, H. Effect of the amount of organic trigger compounds, nitrogen and soil microbial biomass on the magnitude of priming of soil organic matter. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0216730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lama, S.; Velescu, A.; Leimer, S.; Weigelt, A.; Chen, H.; Eisenhauer, N.; Scheu, S.; Oelmann, Y.; Wilcke, W. Plant diversity influenced gross nitrogen mineralization, microbial ammonium consumption and gross inorganic N immobilization in a grassland experiment. Oecologia 2020, 193, 731–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernard, L.; Basile-Doelsch, I.; Derrien, D.; Fanin, N.; Fontaine, S.; Guenet, B.; Karimi, B.; Marsden, C.; Maron, P.A. Advancing the mechanistic understanding of the priming effect on soil organic matter mineralisation. Funct. Ecol. 2022, 36, 1355–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Dong, L.G.; Fei, S.X.; Yu, X. Responses of Soil Organic Carbon Mineralization and Microbial Communities to Leaf Litter Addition under Different Soil Layers. Forests 2021, 12, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Sun, S.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, B.; Peng, Y.; Zhuo, Y.; Ai, W.; Gao, C.; Wu, B.; Liu, D.; et al. Straw and straw biochar differently affect fractions of soil organic carbon and microorganisms in farmland soil under different water regimes. Environ. Technol. Inno 2023, 32, 103412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Li, S.; Li, K.; Huang, H.; Wan, W.; Huang, Q.; Li, Q.; Li, Y.; Deng, H.; He, T. Effects of Two Types of Straw Biochar on the Mineralization of Soil Organic Carbon in Farmland. Sustainability 2020, 12, 10586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagemann, N.; Joseph, S.; Schmidt, H.P.; Kammann, C.I.; Harter, J.; Borch, T.; Young, R.B.; Varga, K.; Taherymoosavi, S.; Elliott, K.W. Organic coating on biochar explains its nutrient retention and stimulation of soil fertility. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhaoming, C.; Qiang, W.; Huoyan, W.; Li, B.; Jianmin, Z. Crop yields and soil organic carbon fractions as influenced by straw incorporation in a rice–wheat cropping system in southeastern China. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosys 2018, 112, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.Z.; Ren, C.J.; Zhang, L.; Han, X.H.; Wang, J. Changes in soil microbial community are linked to soil carbon fractions after afforestation. Eur. J. Soil. Sci. 2018, 69, 370–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Meng, J.; Han, X.; Lan, Y.; Zhang, W. Past, present, and future of biochar. Biochar 2019, 1, 75–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maguire, V.G.; Bordenave, C.D.; Nieva, A.S.; Llames, M.E.; Ruiz, O.A. Soil bacterial and fungal community structure of a rice monoculture and rice-pasture rotation systems. Appl. Soil. Ecol. 2020, 151, 103535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, D.; He, X.; Wang, G.; Xu, X.; Kuzyakov, Y. Fungi Outcompete Bacteria for Straw and Soil Organic Matter Mineralization. preprint. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, C.S.T.S. Decomposition characteristics of rice straw returned to the soil in northeast China. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosys 2019, 114, 211–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Liang, S.; Dai, Z.; Li, Y.; Xu, J. Plant material and its biochar differ in their effects on nitrogen mineralization and nitrification in a subtropical forest soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 763, 143048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, Q.F.; Chen, Q.H.; Yang, X.R.; Li, H.; Zheng, B.X.; Zhou, W.W.; Liu, X.X.; Dai, P.B.; Li, K.J.; Lin, X.Y. Effects of combined application of nitrogen fertilizer and biochar on the nitrification and ammonia oxidizers in an intensive vegetable soil. Amb. Express 2017, 7, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Qiu, S.; Xu, X.; Ciampitti, I.A.; Zhang, S.; He, P. Change in straw decomposition rate and soil microbial community composition after straw addition in different long-term fertilization soils. Appl. Soil. Ecol. 2019, 138, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Du, Z.; Weng, Z.H.; Sun, K.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Yang, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, Z.; Luo, Y.; et al. Formation of soil organic carbon pool is regulated by the structure of dissolved organic matter and microbial carbon pump efficacy: A decadal study comparing different carbon management strategies. Glob. Change Biol. 2023, 29, 5445–5459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaudel, G.; Poudel, M.; Mosongo, P.S.; Xing, L.; Oljira, A.M.; Zhang, Y.; Bizimana, F.; Liu, B.; Wang, Y.; Dong, W. Meta-analysis of the priming effect on native soil organic carbon in response to glucose amendment across soil depths. Plant Soil. 2022, 479, 107–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Q.; Li, M.; Mgelwa, A.S.; Hu, Y.L. Divergent mineralization of exogenous organic substrates and their priming effects depending on soil types. Biol. Fert. Soils 2023, 59, 87–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Z.; Zou, J.; Zhang, L.; Huang, Q. Morphology, pore size distribution, and nutrient characteristics in biochars under different pyrolysis temperatures and atmospheres. J. Mater. Cycles Waste 2018, 20, 1036–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, Z.H.; Van Zwieten, L.; Singh, B.P.; Tavakkoli, E.; Joseph, S.; Macdonald, L.M.; Rose, T.J.; Rose, M.T.; Kimber, S.W.L.; Morris, S.; et al. Biochar built soil carbon over a decade by stabilizing rhizodeposits. Nat. Clim. Change 2017, 7, 371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).