Abstract
Homestead aquaponic production has been proposed as a reasonable alternative for obtaining food within the framework of the circular economy. However, little is known about the ability of homestead aquaponics to contribute to a healthy diet and the savings it represents on the cost of such diets for inhabitants of economically depressed communities. In the present work, based on a case study, the nutritional contribution of vegetables and fish produced in one year has been calculated, with the goal of determining the contribution of aquaponics to the healthy diet of an adult during this study period. The amount of external food products that should be purchased, the nutritional contribution of the complete diet (comparing it with that of a Mediterranean diet), and its cost have also been determined. The results show that achieving a balanced diet in macronutrients, minerals and essential nutrients with aquaponics is feasible, with a real cost of about 3.07 euros per person per day, amounting to a mean savings of 22% compared to the market price of food. The percentage of nutrient contribution of aquaponic foods exceeds in most cases 20%, being especially high for protein, dietary fiber, some minerals such as potassium, and vitamins.
1. Introduction
Unequal food production and distribution reflects complex factors related to political will, resource scarcity, land affordability, energy costs, fertilizer, and transportation infrastructure [1]. Consequently, there is a need to change the economic model of infinite growth into sustainable development, that starts with innovative, agroecological farming systems that balance human needs while maintaining the capacity of the biosphere to provide the necessary goods and services [2]. Food production through aquaponics meets these sustainability requirements since it integrates hydroponic plant production with aquaculture, where fish waste is microbially converted into hydroponic nutrients that are absorbed by the plants [3]. Aquaponics aligns with the principles of creating an ecosystem-based approach to farming as it has a great potential to produce local food for subsistence [4] while minimizing inputs and contaminant effluents [5]. This farming system is perfectly adjusted within the circular economy framework and has been classified as one of the ten technologies that could have a relevant impact on society, yet has not been fully considered [6].
One advantage of aquaponic food production is the small footprint required to produce a significant amount of food, reducing transportation costs and providing healthy food inside city centers or food deserts. Locally produced aquaponic food includes all three dimensions of sustainability: (1) creating local economic value, (2) reducing the environmental effects of food transport (carbon footprint reduction), and (3) improving personal well-being by providing healthier, more nutritious, fresher, and better-tasting food [7]. In this sense, aquaponic food production farming systems have the potential to both support environmental sustainability and nourish human health, as well as the challenge of providing healthy diets to an ever-growing human population [8].
Food security is reached “when all people, at all times, have physical and economical access to sufficient, safe, nutritious food that meets their dietary needs and food preferences for an active and healthy life” [9]. A combination of food products that only meets energetic needs could be enough for short-term survival, but not for long-term health or well-being, as reported in the background paper for the State of Food Security and Nutrition in the World 2020 [10]. In this report, three increasing levels of diet quality were defined as a stairway of affordability from subsistence to health: (a) energy sufficient diets to meet the needs for short-term subsistence, (b) nutrient adequate diets to meet required levels of all essential nutrients and (c) healthy diets including foods from varied groups, culturally acceptable and with a minimum standard for palatability.
However, healthy diets are always more expensive than diets aimed at satisfying only caloric needs, as has already been pointed out in previous studies, and may be less palatable than diets based on empty calories with high sugar and fat content [10,11]. If we also consider that, according to Engel’s law [12], the increase in food prices has a disproportionate effect on households with less income, where the percentage of income allocated to the purchase of food increases significantly, the conclusion is that the differences between the diets consumed by the social classes with high and low income are accentuated [11].
As previously stated, a nutritious and varied diet is essential to maintain good health. Diets based on animal-sourced foods are rich in certain nutrients, e.g., vitamins A and B12, iron, and zinc, are therefore of high importance for vulnerable populations [13]. The same applies to fresh vegetables, which are rich in vitamins and minerals with direct benefits for eradicating extreme poverty and hunger, reducing child mortality, and improving maternal health [14]. In this context, aquaponic homestead production can be an important form of social protection, as fish protein, vegetables and fruits are recognized as the core components of a healthy diet. These core components also tend to account for a large component of the diet cost [11]. Backyard subsistence farming can contribute to household autonomy and potentially lower diet costs when offset by family labor [15]. Nevertheless, in the scientific literature it is not possible to find information on the nutritional contribution of this type of production system to achieve a healthy diet, nor the balance of food items, such as staple crops subsistence farmers should purchase from external sources. Having these data is essential to assess the real cost that a healthy diet would have for the users of these homestead production systems.
In Seville, Spain, the “Polígono Sur” community with a population of around 50,000 people is recognized as one of the most marginalized and poorest neighborhoods in the country. Residents from this community have the lowest life expectancy rates compared to the rest of Seville due to high rates of unemployment and school absenteeism [16]. As a consequence of low family income and high food prices, fresh produce and protein-rich animal sourced foods such as fresh fish is limited. In recent years, technology transfer projects on subsistence aquaponics farming have been developed and extended to the community by the Aquaponic Research Group of the Higher Technical School of Agricultural Engineering (ETSIA) of the University of Seville, installing a small-scale prototype in a high school in Polígono Sur to study food production [17] and economic profitability [15] of these backyard systems to contribute fresh fish and produce in the community.
The hypothesis proposed by this study is that, based on the production data available from the above-mentioned research, it is possible to assess its contribution to a healthy diet and plan the external foods that would be necessary to buy, achieving a final price lower than that of a diet based on 100% purchased food.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Location and Description of the Aquaponic System
The research was carried out at the Secondary School “Joaquín Romero Murube”, located in the Polígono Sur neighborhood (Seville, Spain).
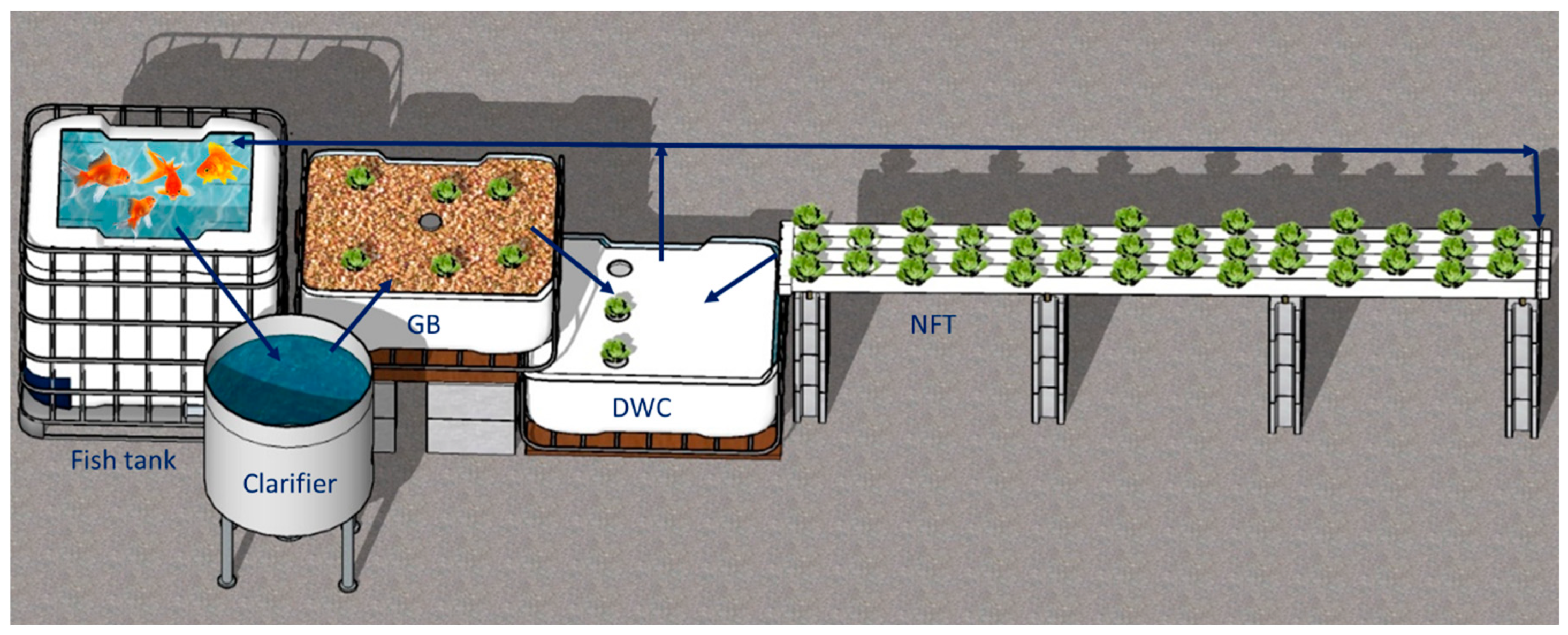
A microscale aquaponic systems (MAS) was fabricated following the recommended designs by FAO [4] and was maintained in a 45 m2 polyethylene greenhouse. The MAS (Figure 1) consisted of a fish production tank made from an IBC (intermediate bulk container) (1.0 m × 1.2 m × 1.0 m) with 0.95 m3 of water, a 0.45 m3 cylindrical-conical shape clarifier, and three different hydroponic subsystems: (1) Nutrient Film Technique (NFT): consisting in five 5 m length and 0.11 m diameter PVC pipes, each with 12 holes (0.05 m diameter), (2) a 0.4 m deep media growing bed (GB): built from an IBC cut in half with 0.4 m3 of pre-washed expanded clay, and (3) a 0.40 m deep water culture (DWC) tank containing 0.54 m3 of water and covered with an extruded polystyrene foam sheet with 3 holes (0.05 m diameter) to support plant growth. The DWC tank also served as sump tank for the entire system. From the sump, 80% of the return water is recirculated to the fish tank by a submersible SunSun JTP (4800 Lh−1 and 32 w) pump. The remaining 20% of the return water was recirculated to the NFT hydroponic sub-system. The total plant culture area was 4.56 m2. The total recirculating water volume of the single loop aquaponic system was 1.8 m3.
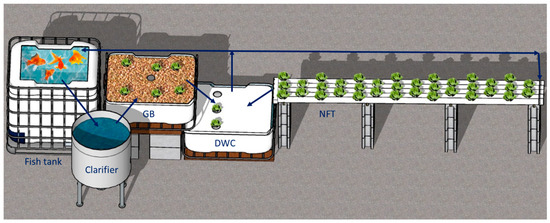
Figure 1.
Schematic of the MAS with the three hydroponic sub-systems: Grow Bed (GB), Deep Water Culture (DWC) and Nutrient Film Technique (NFT). Blue arrows indicate water flow.
This system was maintained over a full year from 24 April 2018 to 24 April 2019. Management and maintenance were carried out by research team as a family would; selecting and introducing plant species according to the season, and harvesting plants and fish at the most suitable point for consumption (maturity stage for vegetables and desired weight for fish). The water was heated by means of a self-constructed thermo-solar panel which powered a water heater when water temperatures fell below 20 °C.
2.2. Plants and Fish Production
Twenty-two species of vegetables were cultivated in the MAS for one-year period, with a crop rotation and polyculture between fruits, vegetables and herbs and fish, with the objective of providing a family with a diversity of products to achieve a nutritionally healthy diet.
Red hybrid tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus × Oreochromis mossambicus) fingerlings were initially acquired from the ‘Aula del Mar’ hatchery (Malaga, Spain). When the fish mean weigh reached 15 g, the tilapias were transferred to the Joaquín Romero Murube secondary school. Once there, 110 fingerlings were introduced in the MAS (total biomass: 1615 g). Fish were fed four times a day with Skretting TI-3 tilapia compound feed (32.6% of protein and 6% of fat). The fish feed rate was between 1 and 4% of total fish weight and was adjusted to accommodate fish growth. The maximum fish density reached was 20 kg m−3 as fish were harvested in a staggered manner. Throughout the year, a total of 33.5 kg of tilapia and 177.7 kg of different plant species and cultivars (tomato, watermelon, eggplant, cucumber, pepper, basil, onion, stevia, pumpkin, melon, chard, broccoli, cauliflower, cabbage, strawberry, potato and lettuce) were produced [17].
2.3. Calculation of Food Groups and Nutritional Contribution of Aquaponic Production
The main groups and subgroups of foods required for a healthy Mediterranean diet were identified using the classification proposed by the United States Departments of Agriculture (USDA) and of Health and Human Services (HHS) [18]. It should be noted that foods produced in aquaponic systems (fish, vegetables, fruits, herbs, etc.) are highly perishable and contribute to the total cost of a healthy diet (63% of the total cost). The remainder of the food groups, except dairy and meat, correspond to non-perishable foods (cereal grains and their derivatives, legume grains, fats and oils, etc.), which are easily found in the market and at affordable prices. The recommended daily amounts of the different food groups that are part of a healthy, 2000 calories per person per day Mediterranean diet according to USDA and HHS [18], are displayed in Table 1.

Table 1.
Healthy Mediterranean diet with recommended daily amounts (cup equivalents or grams) from food groups, subgroups and components [18].
Each vegetable produced by the MAS was assigned to the corresponding food group, including the fish, to determine estimated nutritional deficiencies in the different food groups. Using these data, a list of food items to purchase were provided to complement the nutritional requirements not satisfied with aquaponics production. To do this, the foods most consumed by Spaniards during the trial period (2018–2019) [19] were added to each of the defined categories until the estimated average caloric intake of 2000 kcal per person was reached.
Since there is no evidence that the nutritional composition of foods, fish [20] and vegetables [21] produced in aquaponic systems, differ from those produced in conventional systems, the nutritional contributions of all the ingredients of the diet were estimated for the total energy, protein, carbohydrates, fiber, minerals and vitamins provided by the MAS. For these calculations, the USDA “FoodData Central” database [22] tables on nutritional value of foods were used.
To define the daily nutritional requirements of an adult, the average value for men and women aged 31 to 50 years was calculated [18]. Those requirements were compared with the nutritional contribution of aquaponic products, computing the percentage of contribution associated to the MAS, and the total contribution to the final diet (aquaponics produces and purchased food).
For the determination of the total cost of the diet, costs of purchased foods were estimated using retail market prices in Spain in 2019 [19] and, for aquaponics produced foods, the market prices were attributed utilizing data in a previous study [15]. The sum of both costs was considered the market price of the healthy diet for the studied systems. The real cost of the aquaponic diet was determined using only running costs, ignoring the cost attributable to family labor. This exception is justifiable due to the high rate of unemployment in the neighborhood under study. The difference between the market price of aquaponic products and the running costs associated with their production is considered the financial savings achieved with these systems, and it is calculated as a percentage of the total market price of the diet.
3. Results
3.1. Plant and Fish Production
The total weight of horticultural production, number of plants and fruits, average production per plant and average weight of fruits or leaves in the different hydroponic subsystems were recorded. The fish production was also monitored and growth indicators calculated.
Total annual production per plant production area in MAS was 38.96 kg m−2, while the total tilapia production was 33.5 kg. An in-depth description of the total productions of the 22 plant species and cultivars and fish throughout the year of study can be found in Suárez-Cáceres et al. [17], and is summarized in Table 2.

Table 2.
Composition of 2000 kcal diet including aquaponics food production from MAS and purchased food products compared with daily recommendation (cup equivalents or grams) for one adult.
3.2. Contribution of Aquaponic Production to a Healthy Diet
Table 2 shows the total production of MAS, along with the amount of purchased food products necessary to achieve a 2000 kcal diet that complies with the daily recommendations of cup equivalents or grams for an adult. Production in MAS only accounted for highly perishable products such as fresh fish and vegetables. Long-life foods such as dried cereals or derived products (flour, pasta, bread, rice, etc.), dried legume grains, and oils nor food from land animals such as dairy, meat or eggs (foods necessary for a healthy diet) should be purchased separately by the family.
The MAS produced a surplus of dark leafy green vegetables, with respect to the amount recommended for a balanced Mediterranean diet (3.52 cups excess), due to their high production of lettuces. There was also a surplus in the food category Other Vegetables (0.68 cups) which was associated to cucumber, pepper, eggplant and zucchini productivity.
Although initially it might be thought that aquaponic systems would provide adequate amounts of all fresh vegetables, excesses in some categories were detected, such as those mentioned above, there were deficits in others such as red and orange, starchy vegetables and fruits. Therefore, purchased foods (potatoes, red pepper, and pumpkin) were included for these latter food categories.
In aquaponic systems, plants capable of extracting large amounts of nitrogen from fish effluents are usually grown, so it is not common to plant legumes. For this reason, all foods in the category Beans, Peas, and Lentils were purchased (15.1 kg). Other non-perishable products were purchased, such as grains (60 kg), sugar (2.2 kg) and oils (32.88 kg) and included in the item of Energy Foods. Even though sugar is not an advisable element in a healthy Mediterranean diet, its use is common in Spanish diets. Sugar recommendations are limited to a maximum of 12% of the total energy in the diet. In our case, the amounts corresponding for Sugar Calories were below 1.5% of total energy of the diet.
In relation to protein foods, a significant fraction corresponded to the contribution of fish from the aquaponic system. Increased fish productivity contributed to an excess of protein in the diet (31.78 g per person and day more), though not reaching the recommended values for the protein food categories dairy, meat, poultry and eggs and nuts, seeds, and soy products.
Once the foods provided by the MAS and those purchased to complete the energy needs calculated for adults between 31 and 50 years of age were identified, the contribution of macronutrients, minerals and vitamins of these foods was determined using the USDA “FoodData Central” database [22]. The results for calculated diets are shown in Table 3.

Table 3.
Daily nutritional contributions of MAS (total and percentage of the final value provided by diet), purchased food and final diet in relation to daily nutritional goals.
Regarding the contribution of macronutrients in the diet, energy content provided by the MAS was low, accounting for just 8.92% of final diet. To achieve an adequate energy content, purchased food played an important role by contributing the majority of non-perishable energetic products (grains, dry legumes, nuts and seed, oil and sugar). However, increasing energy contents with purchased food derived to an increment in protein, exceeding daily recommendations, as it was stated above.
Contributions of aquaponic products to total contents in carbohydrates and fiber were around 7.5 and 20%, respectively. Carbohydrates in the calculated diet provided about 52% of total energy, a value within the established acceptable distribution range of 45–65%. The dietary fiber content was also adequate, with values greater than the required 28 g.
As for lipid contributions, total lipids and saturated fatty acids (SFA) were found adequate with ≤35% of total energy provided by lipids, and ≤10% of energy provided by SFA. However, linoleic and linolenic acid contents resulted lower than those required (14.5 and 1.35 g, respectively). Despite the reduced relevance of the lipid contribution of aquaponic products to the final diet (around 3%), a low influence on SFA and monounsaturated fatty acids (MUFA) was observed in the final lipid profile (around 3.7 and 1.3, respectively), while the contribution to polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA) was much higher (around 6.9%), especially for linolenic acid (around 20%).
Mineral contribution of diets was found adequate for all considered elements, except for calcium, zinc, and sodium. However, these nutrients are not limiting, as deficits for calcium and zinc are not important and sodium is low cost, and commonly utilized in salts in Mediterranean cuisine. The percentage of minerals provided by the aquaponic products was close to or above 20% of the total minerals found in the diet, except for the deficiencies in calcium and zinc minerals for which values close to 13% were reached.
Deficits have only been found for three essential nutrients (vitamins E and D and choline), for which aquaponic products provided between 24 and 38% of the total diet. For vitamin K, on the other hand, there was a significant excess, contributed by the high production of lettuce in these systems. Approximately 91% of the total vitamin K in the diets came from aquaponic (dark green vegetables production). For the rest of nutrients in this category, adequate nutrition was achieved with a high contribution provided from aquaponics products (15.5–49%). Vitamin A was one of the most prominent among the vitamins provided by aquaponic systems, due to its high content in many of the red, orange and yellow fruits and vegetables produced.
3.3. Final Price of a Mediterranean Healthy Diet Complemented with MAS Food
To estimate the savings that can be achieved through household aquaponic food production from the total costs of a healthy Mediterranean diet, the equivalent market value (including production costs) was determined for the aquaponic products in a previous study [15]. The market prices of purchased food were calculated using the average price of food published by the Ministry of Agriculture, Fisheries and Food of Spain in the year in which the study was conducted [19]. Table 4 shows the results of the economic balance of the results of incorporating food from aquaponic systems to formulate a healthy diet. The market price of a healthy diet fell from 3.95 to 3.07 euros. This price reduction represents savings of 22.25% between years 2018 and 2019.

Table 4.
Economic balance of the formulation of healthy Mediterranean diets using aquaponic food production.
4. Discussion
The supplementation of aquaponic products with purchased foods commonly consumed by Spaniards during this study period was relatively simple. However, differences were observed between the quantities of some foods assigned to follow the guidelines of a healthy Mediterranean diet and those consumed on average by Spaniards in 2019. By comparison, the annual per capita consumption in 2019 in Spain was 10 kg of fresh fish and 57 kg of fresh vegetables [19], while in our study fish and vegetables produced per family member were 16.8 and 88.9 kg, respectively. It can be stated that Spaniards consumed less fish than recommended by the USDA and HHS [18], probably in response to the increase in the price of fish [23].
Some foods like dark leafy greens would satisfy the requirements, even providing an excess for them, which also occurred with the “Other Vegetables” group. Conversely, for red and orange, starchy vegetables and for legumes (beans, peas, lentils) the quantities produced by the aquaponics system were insufficient, so it was necessary to purchase food from all those categories. In order to maximize production in the aquaponic system, the importance of crop planning and rotation each month, taking into account the seasonality of the vegetables and fish growth, is necessary to meet the nutritional needs of the family. From a practical point of view, it would be preferable to reduce the number of “dark green” (mainly lettuce) and “other vegetables” produced and dedicate the space to the production of “red and orange” vegetables and “fruits” and purchase dried legumes as they are inexpensive, readily available and are easy to preserve.
Due to the characteristics of aquaponics production systems, it was also necessary to consider the purchase of other food groups such as grains, dairy products, meat, poultry and eggs, nuts, seeds and oil. However, the production of fish made it possible to satisfy these additional nutritional needs and perhaps obtain a surplus that could be sold or exchanged for other deficit foods.
It is important to highlight that an important fraction of the food produced from the MAS corresponded to fresh products of high nutritional quality (nutrient-dense foods), which are often expensive and difficult to acquire for the inhabitants of disadvantaged communities. On the contrary, most of the foods purchased are usually easily available in the markets, and can have unbalanced nutritional values due to their high energy contents (grains, oils, sugar, etc.).
Once the final diet was calculated by adding the foods purchased to those produced in aquaponics, it was observed that to reach the required energy levels, an excess of protein was obtained. However, this excess of protein is not a cause for concern since humans can safely consume up to 2 g of protein per kg of body weight, tolerating values of 3.5 g per day per kg of body weight in well-adapted subjects [24]. Furthermore, for the rest of the macronutrients (carbohydrates, fiber, lipids and SFA) the nutritional intake of the calculated diet was adequate. Something similar occurred with the mineral content, with a slight deficit in calcium and moderate in sodium that could be easily and cheaply corrected. Only the deficit reported for some essential nutrients such as choline could be of concern, although it could be easily corrected with crop planning that would allow a greater amount of animal sourced food such as chicken eggs to enter the diet without exceeding protein requirements. The excess of vitamin K in the diet was caused by the overproduction of dark green vegetables that are rich in this type of vitamin [25], although it would be resolved with a correct planning of crops, it is not worrying due to the high tolerance in humans, especially to phylloquinone, with values higher than those provided by the calculated diet [26,27].
According to Herforth et al. [10], the daily cost of a healthy diet (USD 3.27–4.57, with a median cost of USD 3.75) can be up to five times more expensive than that of a diet sufficient in energy (USD 0.79), and costlier than that of a diet just adequate in nutrients (USD 2.33). This daily cost is well above the international poverty line of USD 1.90, not to mention the upper limit of the poverty line of USD 1.20 that can realistically be set aside for food [10]. From these data, it can be estimated that about 3 billion people (43.2% of world population) cannot afford the least costly healthy diet, and 1.5 billion people (most of them living in Southern Asia and Sub-Saharan Africa) cannot reach a nutrient adequate diet. This is in contrast to the southern Europe population where only 3.6% of the population cannot afford a healthy diet [10].
The market value of the products consumed in this study with an aquaponics system was 3.95 €, which is within the range previously described for a healthy diet. However, when considering the savings achieved through the self-production of aquaponic food (around 22%), the adjusted daily cost would be reduced to 3.07 €, which is well below the reported range for a healthy diet, yet still above the international poverty line of USD 1.90 [10]. This reduction in the cost of food is even more relevant in the post-pandemic COVID-19 context, as supply chain issues during the pandemic led to an increase in food prices that raised food insecurity to 82% [28].
It is remarkable that the studied MAS can supply a significant component of a healthy diet for an adult, through animal-based food (tilapia) that are rich in vitamins A and B12, iron and zinc [13] and through fresh vegetables, which are rich in different vitamins and minerals [14]. This type of food is essential in resource-poor communities, as seen in sub-Saharan African countries such as Nigeria, where low fish consumption can lead to malnutrition and high rates of stunting among children under 5 years of age [29].
It is even probable that vegetable production in the next seasons would likely have been significantly greater in the current system as the studied MAS was not totally matured. An aquaponic system traditionally requires more than one year to develop a stable and adequate microorganism population in the biofilters.
In view of the present findings, it is important to consider a number of factors for supplying the nutritional needs of a family. The factors include developing scalability within an aquaponic production to identify the optimal size of the systems, the fish and plant species that are easiest to maintain for a family, especially to maintain the diversification of vegetables for self-consumption purposes. Additional studies that evaluate the optimization of production, resources (facilities, species, labor) and the maintenance of this type of production from a technical point of view (water quality, nutrient balance, biosecurity) are needed.
The environmental benefits from this type of urban production must also be mentioned. The reuse of water and effluents from a recirculating aquaculture system in an aquaponic facility contributes towards a greater circular economy framework positively impacting the environment, by converting waste material into a fertilizer input. The repurposing of waste products should be included in the evaluation of greenhouse gases associated, not only with food production in the cities, but also with the transport of food from farms. In this sense, the studies carried out by Lee et al. [30] estimated that in the city of Seoul, CO2 emissions could be reduced by 11.67 million kg per year with urban agriculture productions, which is the equivalent of the amount of CO2 absorbed annually by a 20 km2 pine forest. Furthermore, additional positive contributions of these production systems are notable, such as the improvement of food security and self-sufficiency, which in cities such as Sydney (Australia) could reach 15% of total agricultural production [31].
Policy makers need to make a more focused effort to develop agendas that prioritize the development of urban and peri-urban farms in short- and long-term agriculture planning [29]. The diversification of agricultural products will thus ensure food security, a variety in dietary options, which will make it possible to sustain agro-ecosystem functions and their structures and processes [28]. In this sense, aquaponics is still in a very infantile phase, and there are no mature measures in place to achieve commercial objectives [32]. This makes it significantly more urgent for policy makers and governments to support small-scale and urban farms.
5. Conclusions
It was demonstrated that a micro-scale aquaponic system can provide part of a healthy and balanced diet, with enough vegetables and fish for an adult for a whole year. However, there is still a significant lack of studies on the aquaponic production of polycultures (production of different plant species) for self-consumption. It is essential for this type of production to correctly manage the plant species to be cultivated to maximize the supply of essential nutrients and yields, while minimizing the cost of the diet. If planned and executed correctly, a dietary cost savings of 20% can easily be achieved, allowing the most disadvantaged communities to access nutrient-dense foods that they would not otherwise be accessible and affordable. Further work is in progress that integrates new complementary trophic levels and improves the environmental sustainability and profitability of these systems.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, V.M.F.-C. and J.L.-E.; methodology, L.P.-U. and J.A.G.; formal analysis, V.M.F.-C.; investigation, J.L.-E. and G.P.S.-C.; writing—original draft preparation, V.M.F.-C. and G.P.S.-C.; writing—review and editing, V.M.F.-C., L.P.-U., J.A.G., J.L.-E. and G.P.S.-C.; visualization, V.M.F.-C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author, [V.M.F.-C.], upon reasonable request.
Acknowledgments
We are very grateful to the IES Joaquín Romero Murube secondary school for providing the location and for their willingness to help. We thank Manuel Alcón, Alberto Toriz and Alejandro Ponce for their assistance in maintaining aquaponic facilities during the harsh summer in Seville. Our thanks to the partners of the Aquaponics association ‘Plantío Chinampa’, especially to Javier Quevedo and Juan Manuel Selma, for sharing ideas and finding creative solutions. Finally, our gratitude to the Verdes del Sur association, especially Juan Manuel Blanco, and to the more than 200 patrons who made the project “The miracle of the fish” possible.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Joyce, A.; Goddek, S.; Kotzen, B.; Wuertz, S. Aquaponics: Closing the cycle on limited water, land and nutrient resources. In Aquaponics Food Production Systems; Springer International Publishing: New York, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 19–34. [Google Scholar]
- Goddek, S.; Joyce, A.; Kotzen, B.; Dos-Santos, M. Aquaponics and global food challenges. In Aquaponics Food Production Systems: Combined Aquaculture and Hydroponic Production Technologies for the Future; Goddek, S., Joyce, A., Kotzen, B., Burnell, G.M., Eds.; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 3–18. [Google Scholar]
- Short, G.; Yue, C.; Anderson, N.; Russell, C.; Phelps, N. Consumer perceptions of aquaponic systems. Horttechnology 2017, 27, 358–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somerville, C.; Cohen, M.; Pantanella, E.; Stankus, A.; Lovatelli, A. Small-Scale Aquaponic Food Production. Integrated Fish and Plant Farming; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2014; ISBN 9789251085325. [Google Scholar]
- Goddek, S.; Delaide, B.; Mankasingh, U.; Ragnarsdottir, K.V.; Jijakli, H.; Thorarinsdottir, R. Challenges of Sustainable and Commercial Aquaponics. Sustainability 2015, 7, 4199–4224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Woensel, L.; Archer, G. Ten Technologies Which Could Change Our Lives: Potential Impacts and Policy Implications; PE 527.417; 2015. Available online: https://data.europa.eu/doi/10.2861/803452 (accessed on 23 June 2021).
- Gracia, A.; Gómez, M.I. Food Sustainability and Waste Reduction in Spain: Consumer Preferences for Local, Suboptimal, And/Or Unwashed Fresh Food Products. Sustainability 2020, 12, 4148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willett, W.; Rockström, J.; Loken, B.; Springmann, M.; Lang, T.; Vermeulen, S.; Garnett, T.; Tilman, D.; DeClerck, F.; Wood, A.; et al. Food in the Anthropocene: The EAT–Lancet Commission on healthy diets from sustainable food systems. Lancet 2019, 393, 447–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO Rome Declaration on World Food Security and World Food Summit Plan of Action, 13–17 November 1996. p. 43. Available online: https://www.fao.org/3/w3613e/w3613e00.htm (accessed on 23 June 2021).
- Herforth, A.; Bai, Y.; Venkat, A.; Mahrt, K.; Ebel, A.; Masters, W.A. Cost and Affordability of Healthy Diets across and within Countries; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2020; ISBN 9789251337257. [Google Scholar]
- Darmon, N.; Drewnowski, A. Contribution of food prices and diet cost to socioeconomic disparities in diet quality and health: A systematic review and analysis. Nutr. Rev. 2015, 73, 643–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engel, E. Die Productions Und Consumtionsverhaltnisse Des Königreichs Sachsen. In Zeitschrift des Statistischen Büreaus des Königlich-Sächsischen Ministeriums des Innerns; von Holtzendorff, F., Brentano, L., Eds.; Dunder and Humblot: Leipzig, Germany, 1857; pp. 8–9. [Google Scholar]
- Ahern, M.B.; Thilsted, S.H.; Kjellevold, M.; Overå, R.; Toppe, J.; Doura, M.; Kalaluka, E.; Wismen, B.; Vargas, M.; Franz, N. Locally-Procured Fish Is Essential in School Feeding Programmes in Sub-Saharan Africa. Foods 2021, 10, 2080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keatinge, J.D.H.; Yang, R.-Y.; Hughes, J.D.; Easdown, W.J.; Holmer, R. The importance of vegetables in ensuring both food and nutritional security in attainment of the Millennium Development Goals. Food Secur. 2011, 3, 491–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobillo-Eguíbar, J.; Fernández-Cabanás, V.M.; Bermejo, L.A.; Pérez-Urrestarazu, L. Economic Sustainability of Small-Scale Aquaponic Systems for Food Self-Production. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, D.E.; Garcia-Ramirez, M.; Balcazar, F.E.; Suarez-Balcazar, Y. A Community-Based Participatory Action Research for Roma Health Justice in a Deprived District in Spain. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 3722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suárez-Cáceres, G.P.; Lobillo-Eguíbar, J.; Fernández-Cabanás, V.M.; Quevedo-Ruiz, F.J.; Pérez-Urrestarazu, L. Polyculture production of vegetables and red hybrid tilapia for self-consumption by means of micro-scale aquaponic systems. Aquac. Eng. 2021, 95, 102181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USDA. HHS Dietary Guidelines for Americans, 9th ed.; 2020–2025; USDA: Washington, DC, USA, 2021; 69, p. 2020.
- MAPA Informe Del Consumo de Alimentación En España. Madrid, Spain. Available online: https://www.mapa.gob.es/en/alimentacion/temas/consumo-tendencias/informe2019_v2_tcm38-540250.pdf (accessed on 23 June 2021).
- Kralik, B.; Weisstein, F.; Meyer, J.; Neves, K.; Anderson, D.; Kershaw, J. From water to table: A multidisciplinary approach comparing fish from aquaponics with traditional production methods. Aquaculture 2022, 552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braglia, R.; Costa, P.; Di Marco, G.; D’Agostino, A.; Redi, E.L.; Scuderi, F.; Gismondi, A.; Canini, A. Phytochemicals and quality level of food plants grown in an aquaponics system. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2021, 102, 844–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USDA FoodData Central. Available online: https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/index.html (accessed on 23 June 2021).
- EUMOFA. European Market Observatory for Fisheries and Aquaculture Products; EUMOFA El Mercado Pesquero de La UE: Luxemburg, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, G. Dietary protein intake and human health. Food Funct. 2016, 7, 1251–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walther, B.; Karl, J.P.; Booth, S.L.; Boyaval, P. Menaquinones, Bacteria, and the Food Supply: The Relevance of Dairy and Fermented Food Products to Vitamin K Requirements. Adv. Nutr. Int. Rev. J. 2013, 4, 463–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holvik, K.; Frøyland, L.; Haugen, M.; Henjum, S.; Løvik, M.; Stea, T.H.; Strand, T.A.; Parr, C.L. Assessment of Dietary Intake of Vitamin K and Maximum Limits for Vitamin K in Food Supplements. Eur. J. Nutr. Food Saf. 2019, 9, 96–98. [Google Scholar]
- Turck, D.; Bresson, J.-L.; Burlingame, B.; Dean, T.; Fairweather-Tait, S.; Heinonen, M.; Hirsch-Ernst, K.I.; Mangelsdorf, I.; McArdle, H.J.; Naska, A.; et al. Dietary reference values for vitamin K. EFSA J. 2017, 15, e04780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijerathna-Yapa, A.; Pathirana, R. Sustainable Agro-Food Systems for Addressing Climate Change and Food Security. Agriculture 2022, 12, 1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjamin, E.O.; Ola, O.; Buchenrieder, G.R. Feasibility Study of a Small-Scale Recirculating Aquaculture System for Sustainable (Peri-)Urban Farming in Sub-Saharan Africa: A Nigerian Perspective. Land 2022, 11, 2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, G.-G.; Lee, H.-W.; Lee, J.-H. Greenhouse gas emission reduction effect in the transportation sector by urban agriculture in Seoul, Korea. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2015, 140, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mcdougall, R.; Rader, R.; Kristiansen, P. Urban agriculture could provide 15% of food supply to Sydney, Australia, under expanded land use scenarios. Land Use Policy 2020, 94, 104554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Memon, A.M.; AlHems, L.M.; Yamaç, S.S.; Barry, M.S.; Alam, A.; AlMuhanna, A. Aquaponics in Saudi Arabia: Initial Steps towards Addressing Food Security in the Arid Region. Agriculture 2022, 12, 2094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).