Nematodes Associated with Terrestrial Slugs in Mid-Atlantic (Delaware, USA) Soybean
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
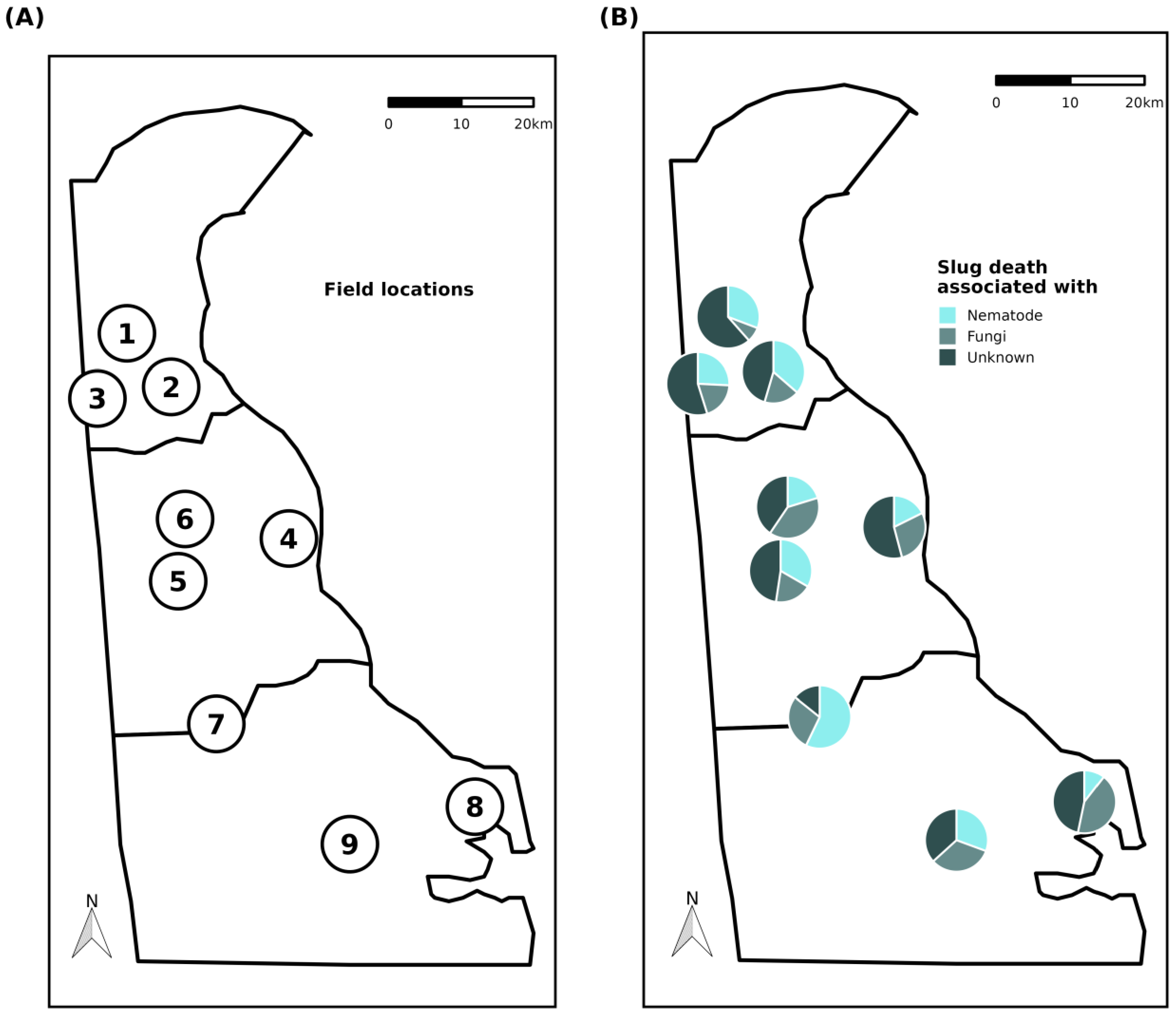
2.1. Field Location
2.2. Slug Sampling
2.3. Ground Cover
2.4. Soil Type
2.5. Slug Parasitic Nematodes
2.6. Molecular Identification of Slug Parasitic Nematodes
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
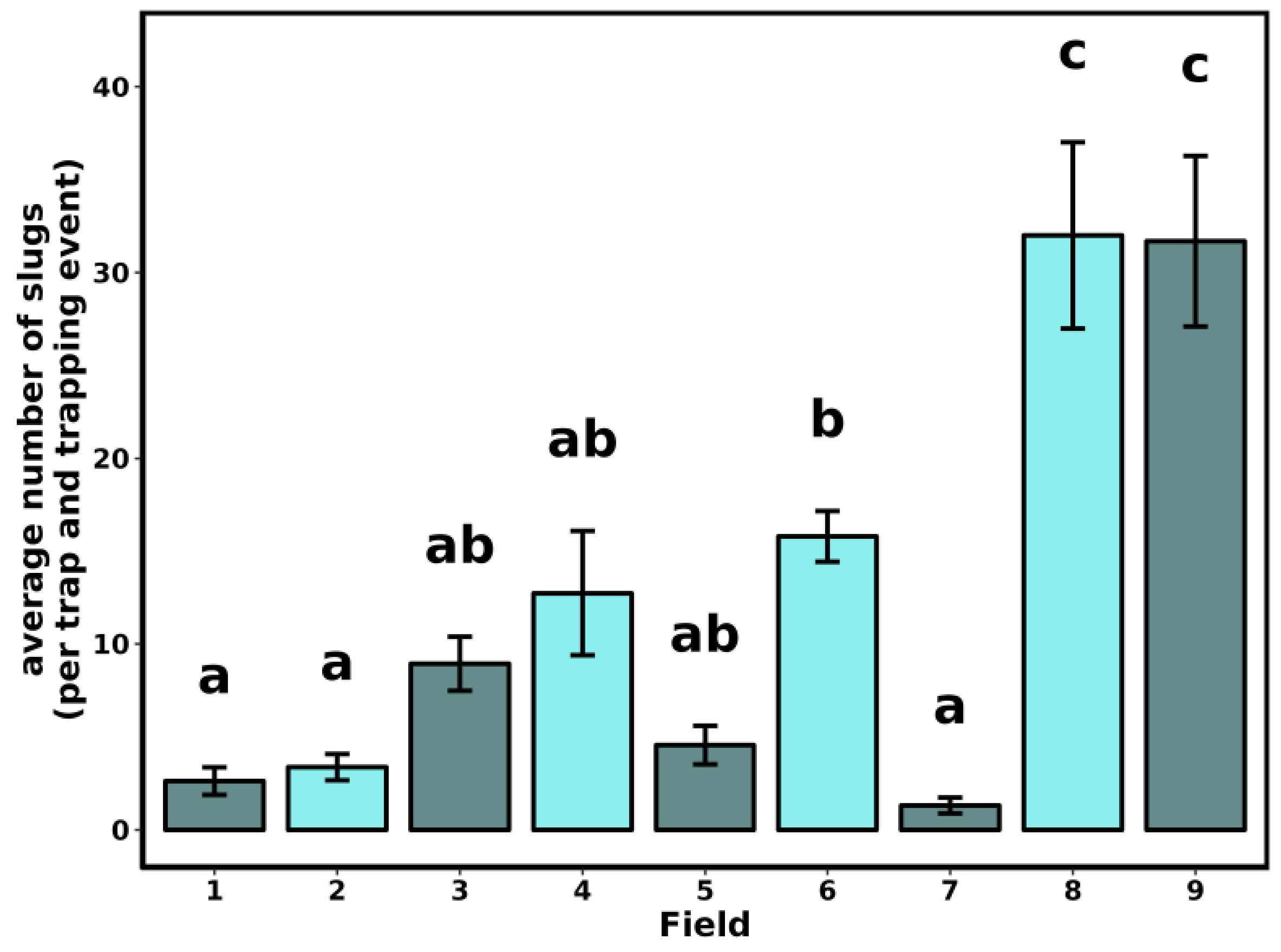
3.1. Slug Sampling
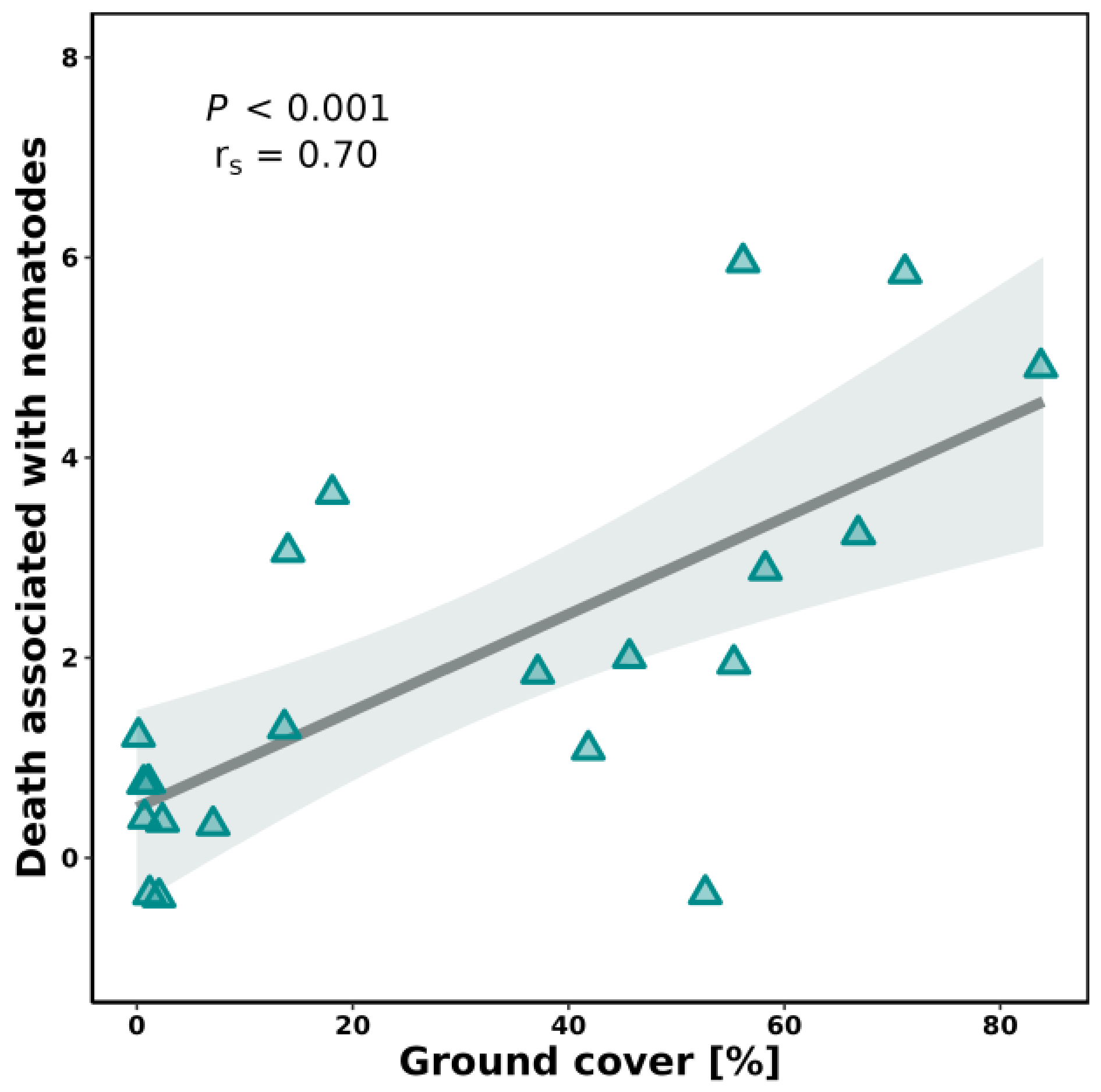
3.2. Ground Cover
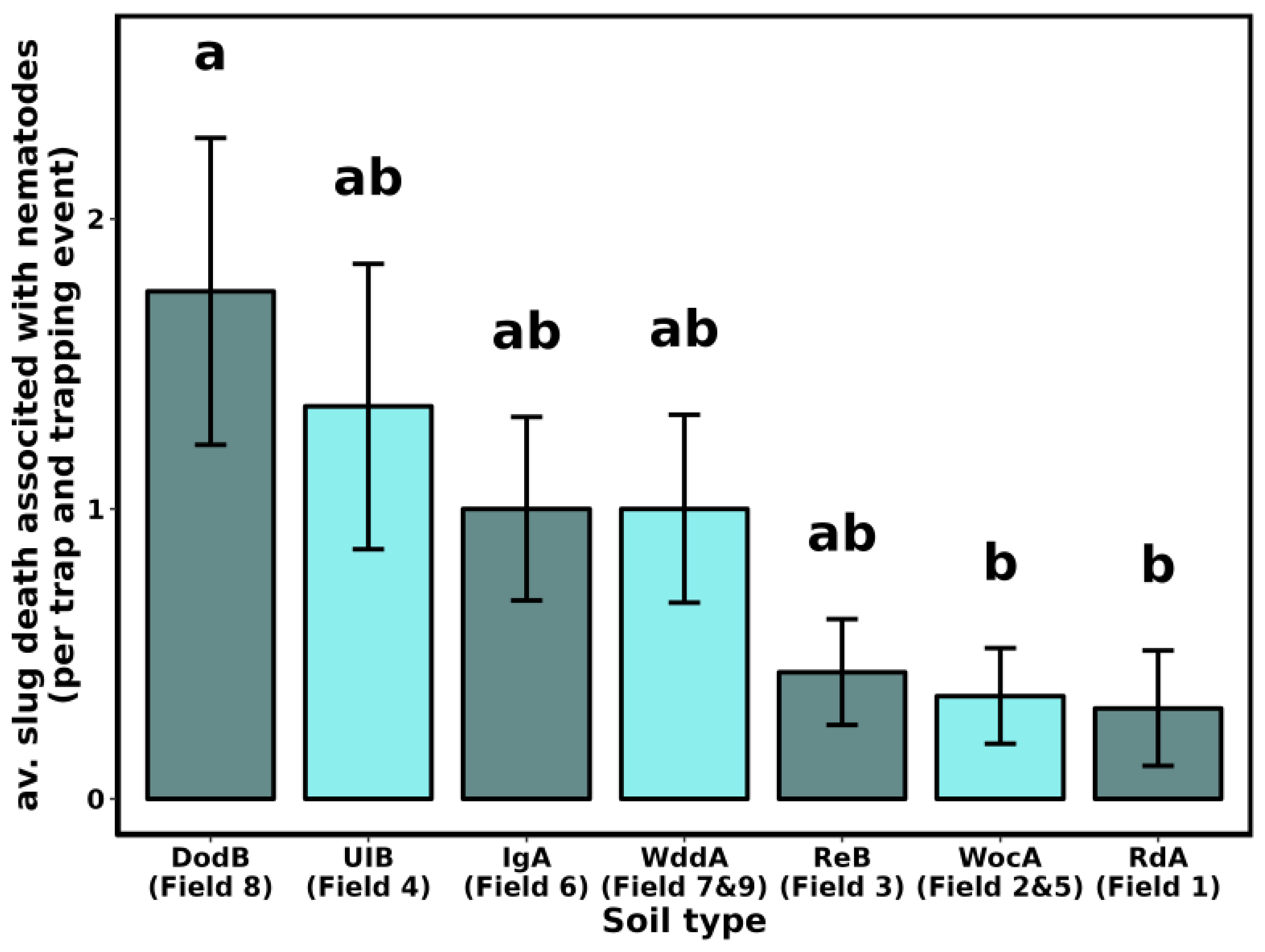
3.3. Slug Parasitic Nematodes
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Douglas, M.R.; Tooker, J.F. Slug (Mollusca: Agriolimacidae, Arionidae) Ecology and Management in No-Till Field Crops, With an Emphasis on the mid-Atlantic Region. J. Integr. Pest Manag. 2012, 3, C1–C9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Gall, M.; Tooker, J.F. Developing ecologically based pest management programs for terrestrial molluscs in field and forage crops. J. Pest Sci. 2017, 90, 825–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tulli, M.C.; Carmona, D.M.; López, A.N.; Manetti, P.L.; Vincini, A.M.; Cendoya, G. Predation on the slug Deroceras reticulatum (Pulmonata: Stylommatophora) by Scarites anthracinus (Coleoptera: Carabidae). Ecol. Austral 2009, 19, 55–61. [Google Scholar]
- Rees, M.; Brown, V.K. Interactions between Invertebrate Herbivores and Plant Competition. J. Ecol. 1992, 80, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beeby, A.; Richmond, L. Differential growth rates and calcium-allocation strategies in the garden snail Cantareus aspersus. J. Molluscan Stud. 2007, 73, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busscher, W. Soil Tillage in Agroecosystems. Vadose Zone J. 2005, 4, 442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kay, P.; Grayson, R.; Mciwem, P.K. Using water industry data to assess the metaldehyde pollution problem. Water Environ. J. 2013, 28, 410–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodler, L.K. Metaldehyde toxicosis. Vererinary Med. 2003, 98, 213–215. [Google Scholar]
- Bailey, S. Molluscicidal baits for control of terrestrial gastropods. In Molluscs as Crop Pests; Barker, G.M., Ed.; CABI Publishing: Wallingford, UK, 2002; pp. 33–54. [Google Scholar]
- Langan, A.M.; Taylor, A.; Wheater, C.P. Effects of metaldehyde and methiocarb on feeding preferences and survival of a slug predator (Pterostichus melanarius (F.): Carabidae, Pterostichini). J. Appl. Èntomol. 2004, 128, 51–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dean, S. Tillage Practices with Updated Alfalfa Seedings and Final Acreages; USDA-NASS: Washington, DC, USA, 2014; p. 2. [Google Scholar]
- Lövei, G.L.; Sunderland, K.D. Ecology and Behavior of Ground Beetles (Coleoptera: Carabidae). Annu. Rev. Èntomol. 1996, 41, 231–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, M.; Rae, R. Phasmarhabditis hermaphrodita as a control agent for slugs. In Nematode Pathogenesis of Insects and Other Pests; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 509–521. [Google Scholar]
- Mc Donnell, R.; De Ley, T.I.; Paine, T.D. Susceptibility of neonate Lissachatina fulica (Achatinidae: Mollusca) to a US strain of the nematode Phasmarhabditis hermaphrodita (Rhabditidae: Nematoda). Biocontrol Sci. Technol. 2018, 28, 1091–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grewal, P.; Grewal, S.; Taylor, R.; Hammond, R. Application of Molluscicidal Nematodes to Slug Shelters: A Novel Approach to Economic Biological Control of Slugs. Biol. Control 2001, 22, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaworska, M. Laboratory Infection of Slugs (Gastropoda: Pulmonata) with Entomopathogenic Nematodes (Rhabditida: Nematoda). J. Invertebr. Pathol. 1993, 61, 223–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rae, R.G.; Tourna, M.; Wilson, M.J. The slug parasitic nematode Phasmarhabditis hermaphrodita associates with complex and variable bacterial assemblages that do not affect its virulence. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2010, 104, 222–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, J.; Ivanova, E.; Sirgel, W.; Malan, A.; Wilson, M. Diversity and distribution of nematodes associated with terrestrial slugs in the Western Cape Province of South Africa. J. Helminthol. 2011, 86, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schley, D.; Bees, M.A. The role of time delays in a non-autonomous host–parasitoid model of slug biocontrol with nematodes. Ecol. Model. 2006, 193, 543–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wynne, R.; Morris, A.; Rae, R. Behavioural avoidance by slugs and snails of the parasitic nematode Phasmarhabditis hermaphrodita. Biocontrol Sci. Technol. 2016, 26, 1129–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puža, V.; Mráček, Z.; Nermut, J. Novelties in Pest Control by Entomopathogenic and Mollusc-Parasitic Nematodes. Intech. Open 2016, 71–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koppenhöfer, A.M.; Shapiro-Ilan, D.I.; Hiltpold, I. Entomopathogenic Nematodes in Sustainable Food Production. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2020, 4, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speiser, B.; Zaller, J.; Neudecker, A. Size-specific susceptibility of the pest slugs Deroceras reticulatum and Arion lusitanicus to the nematode biocontrol agent Phasmarhabditis hermaphrodita. Biocontrol 2001, 46, 311–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glen, D.; Wilson, M.; Brain, P.; Stroud, G. Feeding Activity and Survival of Slugs, Deroceras reticulatum, Exposed to the Rhabditid Nematode, Phasmarhabditis hermaphrodita: A Model of Dose Response. Biol. Control 2000, 17, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, M.J.; Glen, D.M.; George, S.K. The rhabditid nematode Phasmarhabditis hermaphrodita as a potential biological control agent for slugs. Biocontrol Sci. Technol. 1993, 3, 503–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, L.; Grewal, P.S. Infection Behavior of the Rhabditid Nematode Phasmarhabditis hermaphrodita to the Grey Garden Slug Deroceras reticulatum. J. Parasitol. 2001, 87, 1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, M.; Glen, D.; Pearce, J.; Rodgers, P. Monoxenic culture of the slug parasite Phasmarhabditis hermaphrodita (Nematoda: Rhabditidae) with different bacteria in liquid and solid phase. Fundam. Appl. Nematol. 1995, 18, 159–166. [Google Scholar]
- MacMillan, K.; Haukeland, S.; Rae, R.; Young, I.; Crawford, J.; Hapca, S.; Wilson, M. Dispersal patterns and behaviour of the nematode Phasmarhabditis hermaphrodita in mineral soils and organic media. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2009, 41, 1483–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, A. Ueber eine Nematodenlarve und gewisse Verschiedenheiten in den Geschlechtsorganen der Nematoden. Z. Fur Wiss. Zool. 1859, 10, 176–178. [Google Scholar]
- Mengert, H. Nematoden und schnecken. Z. Für Morphol. Und Okol. Der Tiere 1953, 41, 311–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, A. Monographie Der Nematoden; Reimer, G., Ed.; Walter De Gruyter Incorporated: Berlin, Germany, 1866. [Google Scholar]
- Nermuť, J.; Půža, V.; Mekete, T.; Mráček, Z. Phasmarhabditis bonaquaense n. sp. (Nematoda: Rhabditidae), a new slug-parasitic nematode from the Czech Republic. Zootaxa 2016, 4179, 530–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nermuť, J.; Půža, V.; Mráček, Z. Phasmarhabditis apuliae n. sp. (Nematoda: Rhabditidae), a new rhabditid nematode from milacid slugs. Nematology 2016, 18, 1095–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nermuť, J.; Půža, V.; Mekete, T.; Mráček, Z. Phasmarhabditis bohemica n. sp. (Nematoda: Rhabditidae), a slug-parasitic nematode from the Czech Republic. Nematology 2017, 19, 93–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azzam, K.M. Description of the nematode Phasmarhabditis tawfiki n. sp. isolated from Egyptian terrestrial snails and slugs. J. Egypt. Ger. Soc. Zool. 2003, 42, 79–88. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, R.-E.; Ye, W.; Ren, X.; Zhao, Z. Morphological and Molecular Characterization of Phasmarhabditis huizhouensis sp. nov. (Nematoda: Rhabditidae), a New Rhabditid Nematode from South China. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0144386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Ley, I.T.; Holovachov, O.; Mc Donnell, R.J.; Bert, W.; Paine, T.D.; De Ley, P. Description of Phasmarhabditis californica n. sp. and first report of P. papillosa (Nematoda: Rhabditidae) from invasive slugs in the USA. Nematology 2016, 18, 175–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanova, E.S.; Spiridonov, S.E. Phasmarhabditis meridionalis sp. n.(Nematoda: Rhabditidae) from a land snail Quantula striata (Gastropoda: Dyakiidae) from southern Vietnam. Russ. J. Nematol. 2017, 25, 129–140. [Google Scholar]
- Ross, J.L.; Pieterse, A.; Malan, A.P.; Ivanova, E. Phasmarhabditis safricana n. sp. (Nematoda: Rhabditidae), a parasite of the slug Deroceras reticulatum from South Africa. Zootaxa 2018, 4420, 391–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorgadze, O.; Troccoli, A.; Fanelli, E.; Tarasco, E.; De Luca, F. Phasmarhabditis thesamica n. sp. (Nematoda: Rhabditidae), a new slug nematode from southern slope of Caucasus, Georgia. Nematology 2022, 24, 617–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chichester, L.F.; Getz, L.L. The terrestrial slugs of northeastern North America. Sterkiana 1973, 51, 11–42. [Google Scholar]
- Patrignani, A.; Ochsner, T.E. Canopeo: A Powerful New Tool for Measuring Fractional Green Canopy Cover. Agron. J. 2015, 107, 2312–2320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USDA NRCS. Web Soil Survey. Available online: https://websoilsurvey.sc.egov.usda.gov/App/HomePage.htm (accessed on 12 March 2022).
- White, G.F.; Rose, M.C.; Styr, B.; Báez-Mendoza, R.; Mastrobattista, E.P.; Ni, J.; Huang, C. A Method for Obtaining Infective Nematode Larvae from Cultures. Science 1927, 66, 302–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, B.D.; Schrank, B.; Huynh, C.; Shownkeen, R.; Waterston, R.H. A genetic mapping system in Caenorhabditis elegans based on polymorphic sequence-tagged sites. Genetics 1992, 131, 609–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaxter, M.L.; De Ley, P.; Garey, J.R.; Liu, L.X.; Scheldeman, P.; Vierstraete, A.; Vanfleteren, J.R.; Mackey, L.Y.; Dorris, M.; Frisse, L.M.; et al. A molecular evolutionary framework for the phylum Nematoda. Nature 1998, 392, 71–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denver, D.R.; Morris, K.; Thomas, W.K. Phylogenetics in Caenorhabditis elegans: An Analysis of Divergence and Outcrossing. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2003, 20, 393–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elkin, C.J.; Richardson, P.M.; Fourcade, H.M.; Hammon, N.M.; Pollard, M.J.; Predki, P.F.; Glavina, T.; Hawkins, T.L. High-Throughput Plasmid Purification for Capillary Sequencing. Genome Res. 2001, 11, 1269–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- NCBI Resource Coordinators. Database resources of the National Center for Biotechnology Information. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, D8–D13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria; Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 24 October 2022).
- Ogren, R.E. A Contribution to the Life Cycle of Cosmocercoides in Snails (Nematoda: Cosmocercidae). Trans. Am. Microsc. Soc. 1953, 72, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogren, R.E. The nematode Cosmocercoides dukae as a parasite of the slug. In Proceedings of the Pennsylvania Academy of Science 26 March 1959, State College, PA, USA; Volume 33, pp. 236–241.
- Anderson, R.C. On the development and transmission of Cosmocercoides dukae of terrestrial molluscs in ontario. Can. J. Zool. 1960, 38, 801–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morand, S. Cycle évolutif de Angiostoma aspersae Morand, 1986 parasite de la cavité palléale de Helix aspersa Müller. Ann. Parasitol. Hum. Comparée 1989, 64, 340–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanderburgh, D.J.; Anderson, R.C. The relationship between nematodes of the genus Cosmocercoides Wilkie, 1930 (Nematoda: Cosmocercoidea) in toads (Bufo americanus) and slugs (Deroceras laeve). Can. J. Zool. 1987, 65, 1650–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dillman, A.R.; Chaston, J.M.; Adams, B.J.; Ciche, T.A.; Goodrich-Blair, H.; Stock, S.P.; Sternberg, P.W. An Entomopathogenic Nematode by Any Other Name. PLoS Pathog. 2012, 8, e1002527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, J.L.; Ivanova, E.S.; Sirgel, W.F.; Malan, A.P.; Wilson, M.J. Diversity and distribution of nematodes associated with terrestrial slugs in the Western Cape Province of South Africa. Journal of Helminthology 2012, 86, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehdizadeh, S.; Shokoohi, E.; Abolafia, J. Morphological and molecular characterisation of Panagrolaimus Fuchs, 1930 (Nematoda, Rhabditida, Panagrolaimidae) species from Iran. Russ. J. Nematol. 2013, 21, 99–115. [Google Scholar]
- Félix, M.-A.; Ailion, M.; Hsu, J.-C.; Richaud, A.; Wang, J. Pristionchus nematodes occur frequently in diverse rotting vegetal substrates and are not exclusively necromenic, while Panagrellus redivivoides is found specifically in rotting fruits. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0200851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brophy, T.; Mc Donnell, R.; Howe, D.; Denver, D.; Ross, J.; Luong, L. Nematodes associated with terrestrial slugs in the Edmonton region of Alberta, Canada. J. Helminthol. 2020, 94, e200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mc Donnell, R.J.; Paine, T.D.; Gormally, M.J. ) Slugs: A Guide to the Invasive and Native Fauna of California. Available online: https://anrcatalog.ucanr.edu/pdf/8336.pdf (accessed on 22 February 2023).
- South, A. Terrestrial Slugs: Biology, Ecology and Control; Chapman and Hall Ltd.: London, UK, 1992; p. 428. [Google Scholar]
- CABI. Invasive Species Compedium. Available online: https://www.cabi.org/isc/datasheet/30825#tohistoryOfIntroductionAndSpread (accessed on 2 September 2022).
- Becker, J.E.; Mirochnitchenko, N.A.; Ingram, H.; Everett, A.; McCluney, K.E. Water-seeking behavior among terrestrial arthropods and mollusks in a cool mesic region: Spatial and temporal patterns. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0260070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoja, S.; Eltayef, K.M.; Baxter, I.; Bull, J.C.; Loveridge, E.J.; Butt, T. Fungal volatile organic compounds show promise as potent molluscicides. Pest Manag. Sci. 2019, 75, 3392–3404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, R.C. Nematode Parasites of Vertebrates: Their Development and Transmission; CABI Publishing: Wallingford, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Grewal, P.; Grewal, S.; Tan, L.; Adams, B. Parasitism of molluscs by nematodes: Types of associations and evolutionary trends. J. Nematol. 2003, 35, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudhaus, W. Dispersion of nematodes (Rhabditida) in the guts of slugs and snails. Soil Org. 2018, 90, 101–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Ley, I.T.; McDonnell, R.D.; Lopez, S.; Paine, T.D.; De Ley, P. Phasmarhabditis hermaphrodita (Nematoda: Rhabditidae), a potential biocontrol agent isolated for the first time from invasive slugs in North America. Nematology 2014, 16, 1129–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donnell, R.M.; Lutz, M.S.; Howe, D.K.; Denver, D.R. First Report of the Gastropod-Killing Nematode, Phasmarhabditis hermaphrodita, in Oregon, U.S.A. J. Nematol. 2018, 50, 77–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donnell, R.M.; Colton, A.J.; Howe, D.K.; Denver, D.R. Lethality of four species of Phasmarhabditis (Nematoda: Rhabditidae) to the invasive slug, Deroceras reticulatum (Gastropoda: Agriolimacidae) in laboratory infectivity trials. Biol. Control 2020, 150, 104349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mc Donnell, R.; Colton, A.; Howe, D.; Denver, D. Susceptibility of Testacella haliotidea (Testacellidae: Mollusca) to a U.S. strain of Phasmarhabditis hermaphrodita (Rhabditidae: Nematoda). Biocontrol Sci. Technol. 2022, 32, 262–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rae, R.; Verdun, C.; Grewal, P.S.; Robertson, J.F.; Wilson, M.J. Biological control of terrestrial molluscs using Phasmarhabditis hermaphrodita—Progress and prospects. Pest Manag. Sci. 2007, 63, 1153–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howe, D.K.; Ha, A.D.; Colton, A.; De Ley, I.T.; Rae, R.G.; Ross, J.; Wilson, M.; Nermut, J.; Zhao, Z.; Mc Donnell, R.J.; et al. Phylogenetic evidence for the invasion of a commercialized European Phasmarhabditis hermaphrodita lineage into North America and New Zealand. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0237249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pechova, H.; Foltan, P. The parasitic nematode Phasmarhabditis hermaphrodita defends its slug host from being predated or scavenged by manipulating host spatial behaviour. Behav. Process. 2008, 78, 416–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Field | County | Previous Crop | Soil Type a |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | New Castle | Maize | RdA—Reybold-Queponco complex, fine-loamy, very deep well drained |
| 2 | New Castle | Maize | WocA—Woodbridge loam, Fine-loamy, very deep moderately well drained |
| 3 | New Castle | Maize | ReB—Reybold silt loam, fine-loamy, very deep, well drained |
| 4 | Kent | Maize | UIB—Unicorn loam, coarse-loamy very deep, well drained |
| 5 | Kent | NA | WocA—Woodbridge loam, fine-loamy, very deep moderately well drained |
| 6 | Kent | Maize | IgA—Ingleside sandy loam, coarse-loamy, siliceous, very deep, well drained |
| 7 | Sussex | Maize | WddA—Woodstown sandy loam, fine-loamy, very deep moderately well drained |
| 8 | Sussex | Maize | DodB—Downer sandy loam, coarse-loamy very deep, well drained |
| 9 | Sussex | NA | WddA—Woodstown sandy loam, fine-loamy, very deep moderately well drained |
| Field | Nematode Species | Accession number a | Nematode Order: Family | Association with Slugs | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3, 4, 5, 6 | Cosmocercoides dukae | FJ516753 | Ascaridia: Cosmocercidae | Parasitic, final host | [51,52,53,54,55] |
| 8 | Oscheius sp. 4 | MN082320 | Rhabditida: Rhabditidae | Necromenic, saprophitic | [56] |
| 4 | Panagrolaimus sp. 1 | MN082328 | Rhabditida: Panagrolaimidae | Phoretic, bacterivorous | [57,58] |
| 3, 9 | Panagrolaimus artyukhovskii | MK636578 | Rhabditida: Panagrolaimidae | Phoretic, bacterivorous | [57,58] |
| 5, 8, 9 | Panagrolaimus cf. rigidus | DQ285636 | Rhabditida: Panagrolaimidae | Phoretic, bacterivorous | [57,58] |
| 1, 2, 7, 9 | Panagrolaimus subelongatus | KY119431 | Rhabditida: Panagrolaimidae | Phoretic, bacterivorous | [57,58] |
| 6 | Panagrolaimus trilabiatus | KF011487 | Rhabditida: Panagrolaimidae | Phoretic, bacterivorous | [57,58] |
| 9 | Pristionchus lheritieri | AY284690 | Rhabditida: Diplogastridae | Necromenic, saprophitic | [59] |
| 3, 6, 9 | Rhabditis sp. | MH608279 | Rhabditida: Rhabditidae | Parasitic? | [60] |
| 7, 8 | Rhabditoides inermiformis | AF083017 | Rhabditida: Rhabditidae | Opportunistic | [60] |
| 5, 9 | Unidentified nematode isolate | EU541352 | ?? | ?? | NA |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kunkel, B.; Cissel, W.J.; Tooker, J.F.; Howe, D.K.; Denver, D.R.; Mc Donnell, R.J.; Hiltpold, I. Nematodes Associated with Terrestrial Slugs in Mid-Atlantic (Delaware, USA) Soybean. Agronomy 2023, 13, 645. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13030645
Kunkel B, Cissel WJ, Tooker JF, Howe DK, Denver DR, Mc Donnell RJ, Hiltpold I. Nematodes Associated with Terrestrial Slugs in Mid-Atlantic (Delaware, USA) Soybean. Agronomy. 2023; 13(3):645. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13030645
Chicago/Turabian StyleKunkel, Brian, William J. Cissel, John F. Tooker, Dana K. Howe, Dee R. Denver, Rory J. Mc Donnell, and Ivan Hiltpold. 2023. "Nematodes Associated with Terrestrial Slugs in Mid-Atlantic (Delaware, USA) Soybean" Agronomy 13, no. 3: 645. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13030645
APA StyleKunkel, B., Cissel, W. J., Tooker, J. F., Howe, D. K., Denver, D. R., Mc Donnell, R. J., & Hiltpold, I. (2023). Nematodes Associated with Terrestrial Slugs in Mid-Atlantic (Delaware, USA) Soybean. Agronomy, 13(3), 645. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13030645








