Grazing Regulates Changes in Soil Microbial Communities in Plant-Soil Systems
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Site and Sampling
2.2. Determination of the Physical and Chemical Properties of the Soil
2.3. DNA Collection and High-Throughput Sequencing
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Soil Factors and Vegetation Traits under Different Grazing Intensities
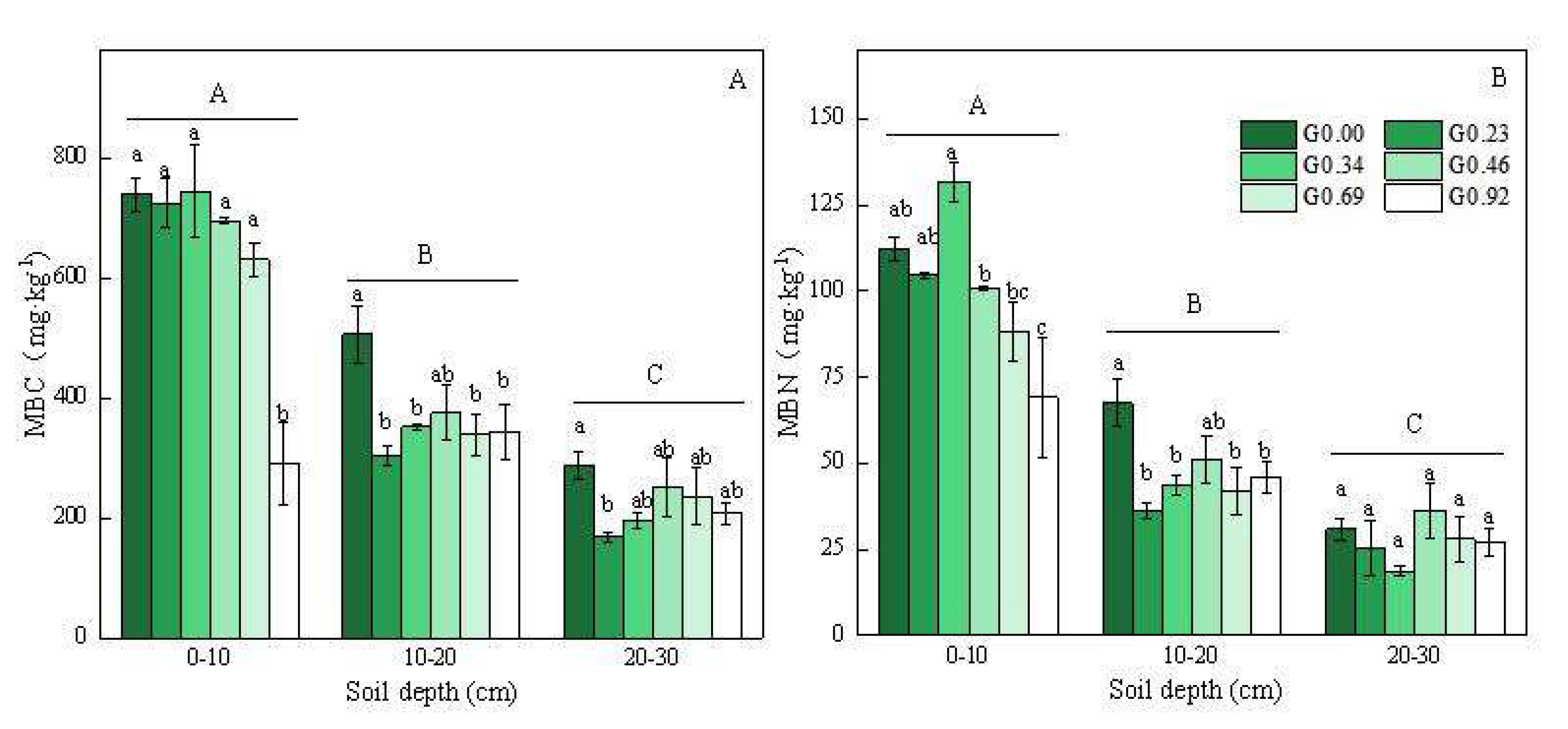
3.2. Changes in the Soil Microbial Biomass Carbon and Nitrogen under Different Grazing Intensities
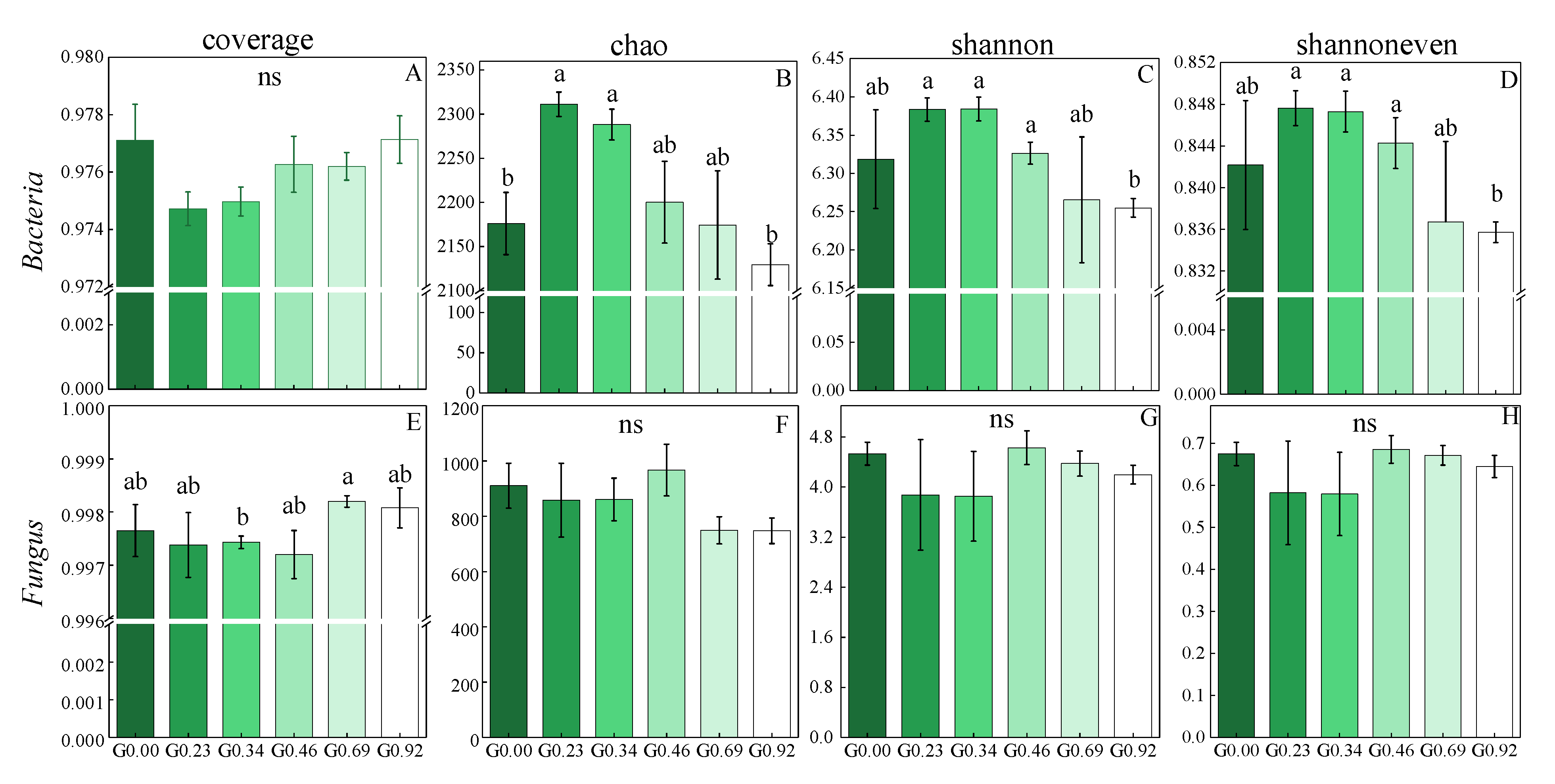
3.3. Changes in Soil Microbial Diversity in Response to Different Grazing Intensities
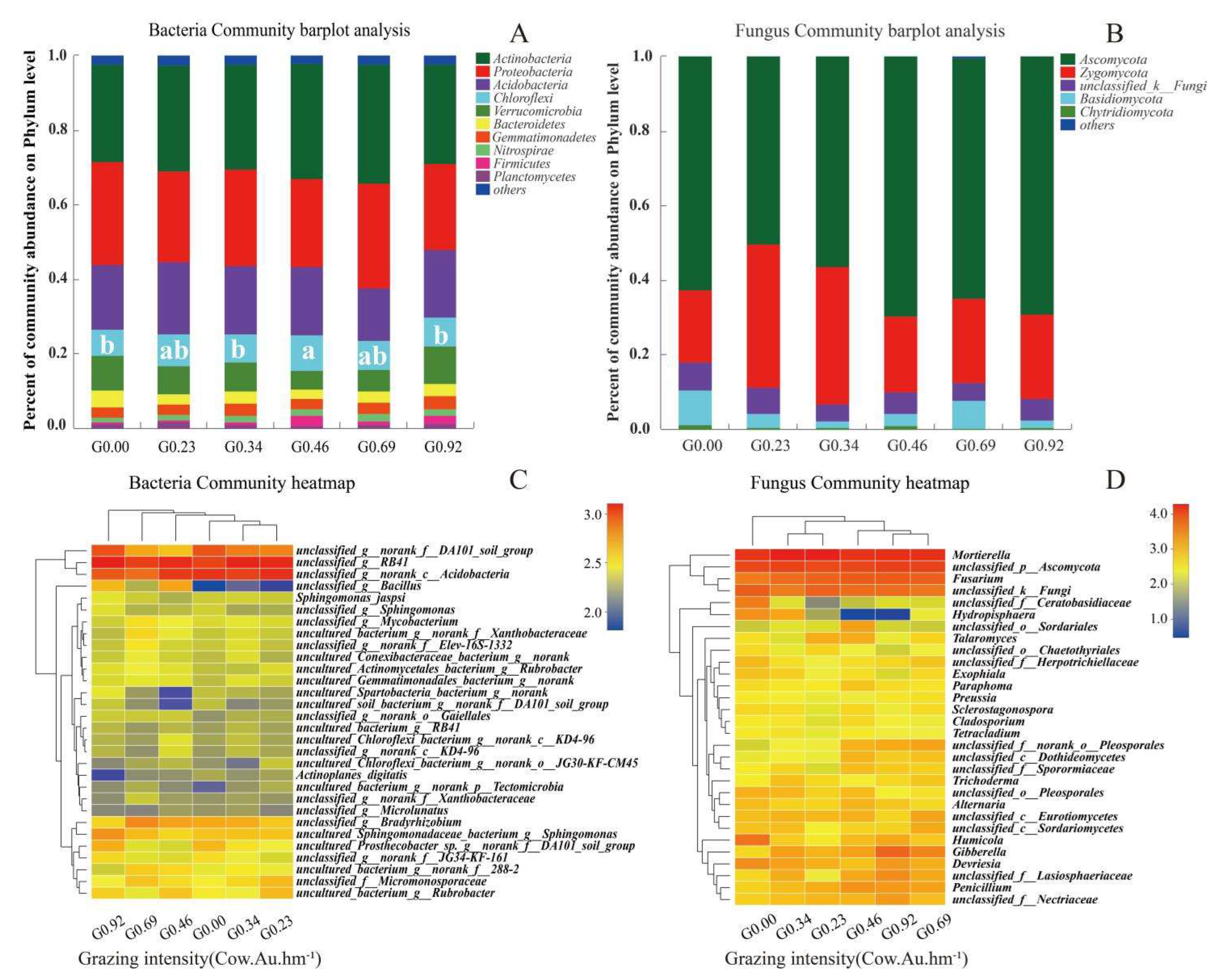
3.4. The Relative Abundance of Dominant Microbial Taxa under Different Grazing Intensities
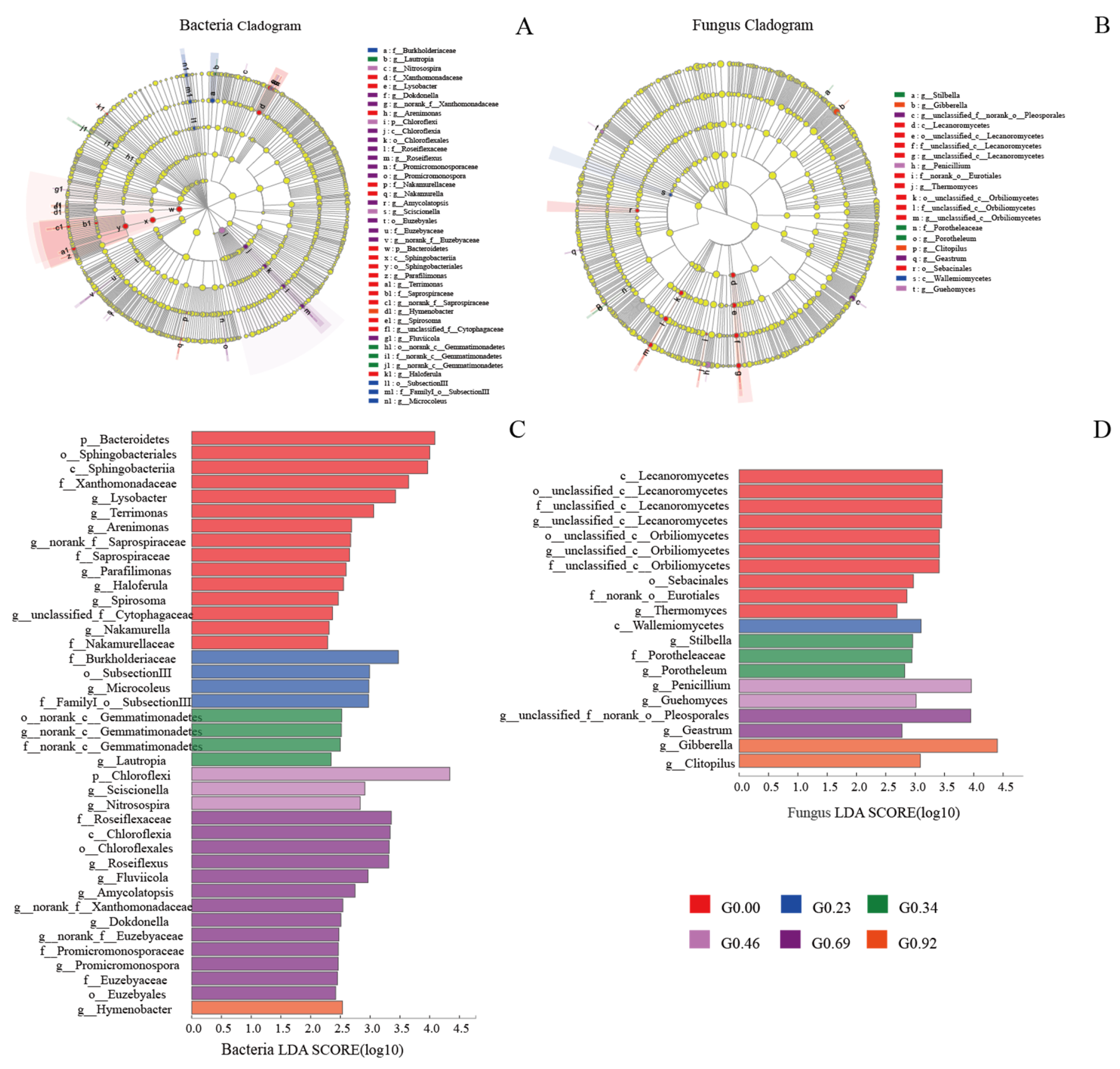
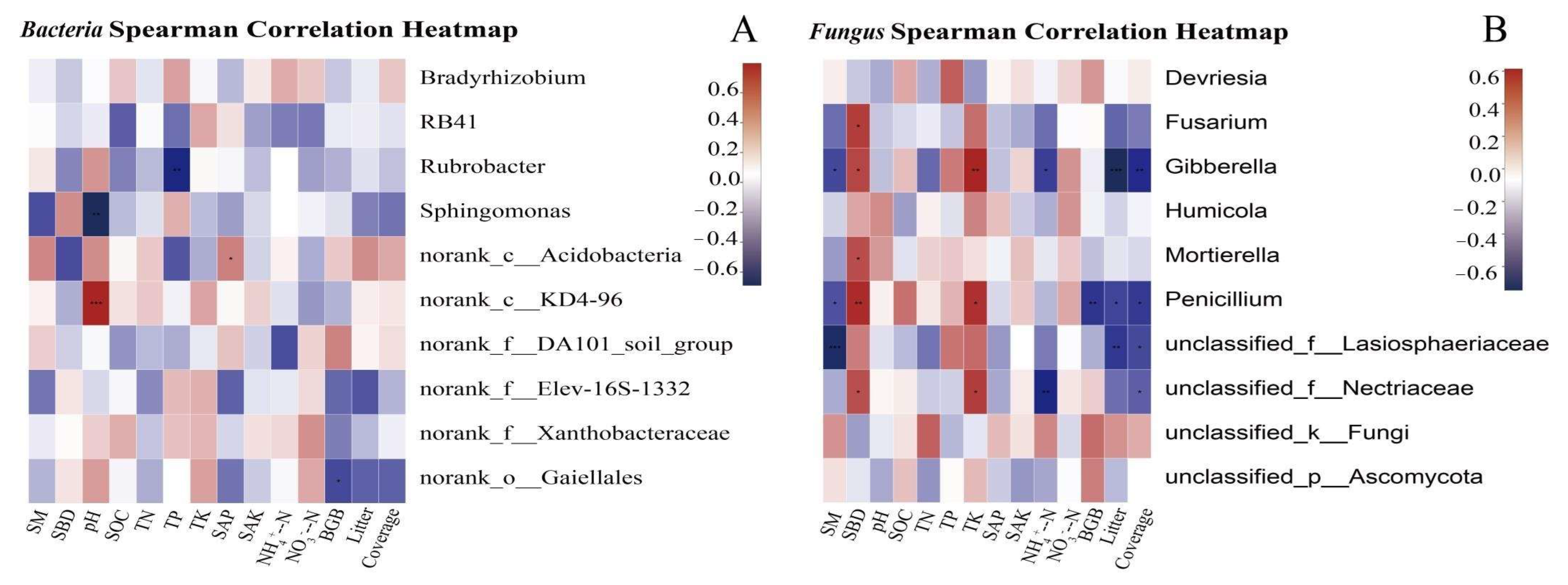
3.5. Microbial Taxa with Statistically Significant Differences
3.6. Relationship between the Microbial Community Structure and Environmental Characteristics
3.6.1. Correlation between Plant and Soil Properties and the Relative Abundance of the Microbial Community
3.6.2. Major Environmental Factors Driving the Overall Changes in the Microbial Community Composition
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SM | soil moisture |
| SBD | soil bulk density |
| SOC | soil organic carbon |
| TN | total nitrogen |
| TP | total phosphorus |
| TK | total potassium |
| SAP | soil available phosphorus |
| SAK | soil available potassium |
| NH4+-N | soil ammonium nitrogen |
| NO3−-N | soil nitrate nitrogen |
| BGB | belowground biomass |
References
- Yang, Y.; Wu, L.; Lin, Q. Responses of the functional structure of soil microbial community to livestock grazing in the Tibetan alpine grassland. Glob. Change Biol. 2013, 19, 637–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, M.N.; Winding, A. Microorganisms as Indicators of Soil Health; Technical Report No. 388; National Environmental Research Institute: Roskilde, Danmark, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Lecain, D.R.; Morgan, J.A.; Schuman, G.E.; Reeder, J.D.; Hart, R.H. Carbon exchange and species composition of grazed pastures and exclosures in the shortgrass steppe of colorado. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2002, 93, 421–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branson, F.A.; Miller, R.F. Effects of increased precipitation and grazing management on northeastern montana rangelands. J. Range Manag. 1981, 34, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, H.Y.; Cao, G.M.; Li, G.R.; Zhou, J.J.; Jiao, W.Y.; Li, J.P.; Zhan, P. Effect of grazing disturbance on plant community of alpine meadow dominated by Potentilla froticosa shrub on Qilian Mountain. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2009, 18, 235–241. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, R.R.; Xin, X.P.; Yan, Y.C. Impacts of Differing Grazing Rates on Canopy Structure and Species Composition in Hulunber Meadow Steppe. Rangel. Ecol. Manag. 2015, 68, 54–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Chen, X.; Hou, F.; Wu, Y.; Cheng, Y. Bacterial and fungal community structures in loess plateau grasslands with different grazing intensities. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 606. [Google Scholar]
- Na, X.F.; Zheng, G.Q.; Peng, L. Changes of microbial diversity in the rhizosphere of Lycium barbarum l. from Ningxia. Chin. J. Soil Sci. 2016, 53, 241–252. [Google Scholar]
- Ford, H.; Rousk, J.; Garbutt, A.; Jones, L.; Jones, D.L. Grazing effects on microbial community composition, growth and nutrient cycling in salt marsh and sand dune grasslands. Biol. Fert. Soils. 2013, 49, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, S.; Zheng, H.; Lin, Q.; Li, G.; Xi, Z.; Zhao, X. Effects of livestock grazing intensity on soil biota in a semiarid steppe of inner mongolia. Plant Soil 2011, 340, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, G.L.; Chen, G.; Ning, F. Dynamic changes of soil microbial and enzyme activities in typical grassland during restoration and succession. Grassl. J. 2012, 20, 292–297. [Google Scholar]
- Wakelin, S.A.; Gregg, A.L.; Simpson, R.J.; Li, G.D.; Riley, I.T.; Mckay, A.C. Pasture management clearly affects soil microbial community structure and Ncycling bacteria. Pedobiologia 2009, 52, 237–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Wang, J.; Hao, Y.; Wang, Y. Intermediate grazing intensities by sheep increase soil bacterial diversities in an Inner Mongolian steppe. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2010, 46, 817–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.W.; Gan, J.G.; Han, Z.W. Carbon and Nitrogen content of microbial biomass in artificial grassland under different grazing intensities. Acta Grassl. Sin. 2003, 11, 343–345. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, C.Y.; Shao, J.F.; Jiang, D.M.; Cui, Z.B. Effects of Fence Enclosure on Soil Nutrients and Biological Activities in Highly Degraded Grasslands. J. Northeast. Univ. (Nat. Sci.) 2011, 32, 427–430. [Google Scholar]
- Gou, Y.N.; Nan, Z.B. Effects of grazing on soil microorganisms in grassland. Acta. Ecol. Sin. 2015, 24, 194–205. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.F.; Shen, J.P.; Zhang, C.J. Changes of soil ammonia oxidation and denitrifying microorganisms under different grazing intensities. Acta. Ecol. Sinica. 2018, 38, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Xun, W.; Yan, R.; Ren, Y.; Jin, D.; Xiong, W.; Zhang, G. Grazing-induced microbiome alterations drive soil organic carbon turnover and productivity in meadow steppe. Microbiome 2018, 6, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.F.; Peng, J.J.; Yuan, S. Influence of ecological restoration on vegetation and soil microbiological properties in Alpine-cold semi-humid desertified land. Ecol. Eng. 2016, 94, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Dong, S.; Gao, Q. Soil bacterial and fungal diversity differently correlated with soil biochemistry in alpine grassland ecosystems in response to environmental changes. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 43077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Niu, H.; Wang, Y.; Cui, X.; Li, Y.; Yu, Z. Response of soil bacterial communities to moisture and grazing in the Tibetan alpine steppes on a small spatial scale. Geomicrobiol. J. 2019, 36, 559–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regan, K.M.; Nunan, N.; Boeddinghaus, R.S.; Baumgartner, V.; Marhan, S. Seasonal controls on grassland microbial biogeography: Are they governed by plants, abiotic properties or both. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2014, 71, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.H.; Mcsorley, R.; Bohlen, P.; Gathumbi, S.M. Cattle grazing increases microbial biomass and alters soil nematode communities in subtropical pastures. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2006, 38, 1956–1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhao, J.; Xin, X.P.; Wang, M.; Pan, F.J.; Yan, R.R.; Li, L.H. Effects of stocking rate on interannual ecosystem biomass and soil nitrogen processes in a meadow steppe of northeast China. Plant Soil 2022, 473, 9–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vance, E.D.; Brookes, P.C.; Jenkinson, D.S. An extraction method for measuring soil microbial biomass C. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1987, 19, 703–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huws, S.A.; Edwards, J.E.; Kim, E.J.; Scollan, N.D. Specificity and sensitivity of eubacterial primers utilized for molecular profiling of bacteria within complex microbial ecosystems. J. Microbiol Meth. 2007, 70, 565–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rousk, J.; Baath, E.; Brookes, P.C. Soil bacteria and fungal communities across a pH gradient in an arable soil. ISME J. 2010, 4, 1340–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, C.E. A mathematical theory of communication. Bell Syst. Tech. J. 1948, 27, 379–423, 623–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segata, N.; Izard, J.; Waldron, L. Metagenomic biomarker discovery and explanation. Genome Biol. 2011, 12, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Jia, L.X.; Qiao, J.R.; Li, M.R.; Zhang, F.; Chen, D.L. Effects of heavy grazing on soil nutrient and microbial diversity in desert steppe. Chin. J. Grassl. 2019, 41, 72–79. [Google Scholar]
- Lienhard, P.; Tivet, F.; Chabanne, A. No-till and cover crops shift soil microbial abundance and diversity in Laos tropical grassland. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2013, 33, 375–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruess, R.W.; Mc Naughton, S.J. Grazing and the dynamics of nutrient and energy regulated microbial processes in the Serengeti grasslands. Oikos 1987, 49, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jangid, K.; Williams, M.A.; Franzluebbers, A.J.; Sanderlin, J.S.; Reeves, J.H.; Jenkins, M.B.; Endale, D.M.; Coleman, D.C.; Whitman, W.B. Relative impacts of land-use, management intensity and fertilization upon soil microbial community structure in agricultural systems. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2008, 40, 2843–2853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Death, R.G.; Barquín, J. Geographic location alters the diversity-disturbance response. Freshw Sci. 2012, 31, 636–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.H.; Chen, J.Q.; Han, X.G.; Zhang, W.H.; Shao, C.L. Grassland Ecosystems of China; Springer: Singapore, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Bardgett, R.D.; Wardle, D.A.; Yeates, G.W. Linking above-ground and belo-wground interactions: How plant responses to foliar herbivory influence soil organisms. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1998, 30, 1867–1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Wu, J.; Ma, M.; Nielsen, U.N.; Wang, J.; Du, G. Nematode communities response to long-term grazing disturbance on Tibetan plateau. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2015, 69, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Nielsen, U.N.; Yang, X.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, X.; Du, G.; Li, G.; Chen, S.; Xiao, S. Grazing induces direct and indirect shrub effects on soil nematode communities. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2018, 121, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randy, O.C.; Contreras-Cornejo, H.A.; Lourdes, M.R.; José, L.B. The role of microbial signals in plant growth and development. Plant Signal. Behav. 2009, 4, 701–712. [Google Scholar]
- Chapin, F.S., III; Matson, P.A.; Vitousek, P. Principles of Terrestrial Ecosystem Ecology, 2nd ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, X.; Wang, Y.; Niu, H.; Wu, J.; Wang, S.; Schnug, E.; Rogasik, J.; Fleckenstein, J.; Tang, Y.H. Effect of long-term grazing on soil organic carbon content in semiarid steppes in inner mongolia. Ecol. Res. 2005, 20, 519–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, N.P.; Yu, Q.; Wu, L.; Wang, Y.; Han, X.G. Carbon and nitrogen store and storage potential as affected by land-use in a Leymus chinensis grassland of northern China. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2008, 40, 2952–2959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardgett, R.D. The Biology of Soil, a Community and Ecosystem Approach; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.L.; Hao, X.Y.; Zhao, M.L.; Han, G.D.; Willms, W.D. Influence of historic sheep grazing on vegetation and soil properties of a desert steppe in Inner Mongolia. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2008, 128, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.P.; Li, Y.Q.; Zhao, X.Y.; Luo, Y.Q.; Shang, W. Light fraction and total organic carbon and nitrogen stores in desertified sandy grassland soil as affected by grazing and livestock exclusion. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2010, 24, 182–186. [Google Scholar]
- Björsne, A.K.; Rütting, T.; Ambus, P. Combined climate factors alleviate changes in gross soil nitrogen dynamics in heathlands. Biogeochemistry 2014, 120, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, S.Q.; Zhang, J.B.; Cai, Z.C. Effects of soil moisture on gross N transformations and N2O emission in acid subtropical forest soils. Biol. Fert. Soils 2014, 50, 1099–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.Z.; Shen, Z.X.; Fu, G. A meta-analysis of the effects of experimental warming on soil carbon and nitrogen dynamics on the Tibetan Plateau. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2015, 87, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, T.B.; Zeng, S.M.; Qin, H.L.; Zhou, K.X.; Yang, H.; Lan, F.N.; Huang, F.; Cao, J.H.; Müller, C. Low nitrate retention capacity in calcareous soil under woodland in the karst region of southwestern China. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2016, 97, 99–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellano, H.A.; Chart’eris, A.F.; Müller, C.; Jansen-Willems, A.; González-López, J.; Bedmar, E.J.; Carrillo, P.; Cárdenas, L.M. Occurrence and 15N-quantification of simultaneous nitrification and denitrification in N-fertilised soils incubated under oxygen-limiting conditions. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2020, 143, 107757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafftte, A.; Florio, A.; Andrianarisoa, K.S.; Chatelliers, C.C.D.; Schloter, H.B.; Ndaw, S.M.; Periot, C.; Schloter, M.; Zeller, B.; Poly, F.; et al. Biological inhibition of soil nitrification by forest tree species affects Nitrobacter populations. Environ. Microbiol. 2020, 22, 1141–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bengtsson, G.; Bengtson, P.; Mnsson, K.F. Gross nitrogen mineralization-, immobilization, and nitrification rates as a function of soil C/N ratio and microbial activity. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2003, 35, 143–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, A.K.M.A.; Raison, R.J.; Khanna, P.K. Effect of fertilize application and fire regime on soil mineralization in an Australia subalpine eucalypt forest. Biol. Fert. Soils 1995, 19, 246–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yergeau, E.; Kowalchuk, G.A. Responses of Antarctic soil microbial communities and associated functions to temperature and freeze-thaw cycle frequency. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 10, 2223–2235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
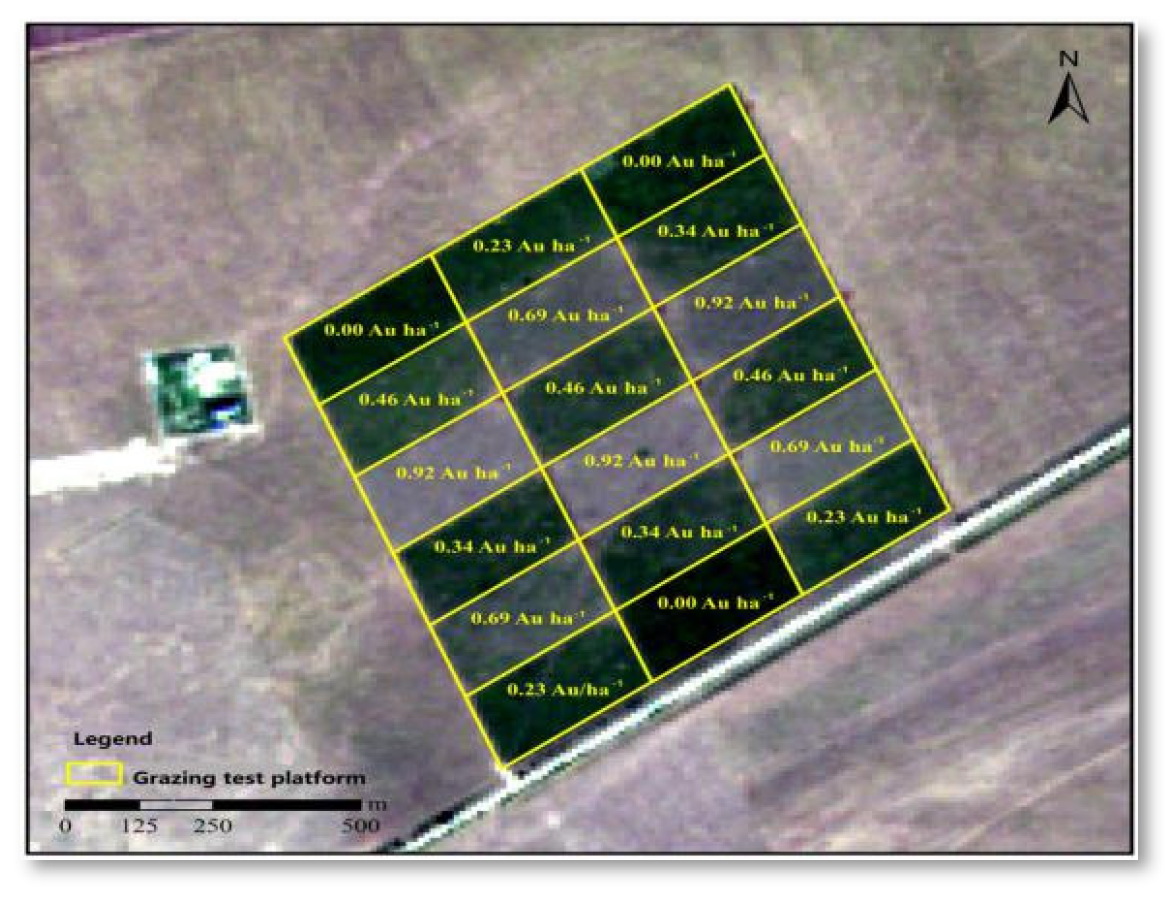


| Soil Properties | Vegetation Characteristics | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Factors | SM (%) | SBD (g/cm3) | pH | SOC (g/kg) | TN (g/kg) | TP (g/kg) | TK (g/kg) | AP (mg/kg) | AK (mg/kg) | NH4+-N (mg/kg) | NO3−-N(mg/kg) | BGB (g/m2) | Litter (g/m2) | Coverage (%) |
| G0.00 | 20.81 ± 1.00 a | 0.96 ± 0.02 a | 6.94 ± 0.45 a | 39.23 ± 0.07 a | 3.37 ± 0.11 ab | 0.43 ± 0.03 a | 15.85 ± 0.45 b | 3.73 ± 0.17 a | 309.80 ± 77.40 a | 5.72 ± 0.95 a | 20.09 ± 3.21 b | 1,162.38 ± 145.85 a | 206.28 ± 27.41 a | 84.65 ± 0.63 a |
| G0.23 | 20.34 ± 0.57 ab | 0.99 ± 0.03 a | 6.59 ± 0.16 a | 41.26 ± 1.14 a | 3.39 ± 0.08 ab | 0.38 ± 0.01 a | 17.28 ± 0.44 ab | 3.80 ± 0.17 a | 314.44 ± 12.46 a | 5.38 ± 0.66 a | 16.08 ± 1.20 b | 972.48 ± 69.38 ab | 135.48 ± 15.77 b | 80.25 ± 1.16 ab |
| G0.34 | 19.53 ± 0.65 ab | 1.01 ± 0.01 a | 6.59 ± 0.12 a | 42.72 ± 2.52 a | 3.34 ± 0.09 ab | 0.44 ± 0.00 a | 17.62 ± 0.28 a | 3.74 ± 0.55 a | 279.32 ± 35.12 a | 6.22 ± 1.17 a | 18.91 ± 2.28 b | 1,011.36 ± 112.08 ab | 105.36 ± 31.84 b | 80.12 ± 1.80 ab |
| G0.46 | 18.47 ± 0.90 bc | 1.02 ± 0.04 a | 6.89 ± 0.10 a | 44.07 ± 3.15 a | 3.41 ± 0.03 a | 0.41 ± 0.04 a | 18.84 ± 0.59 a | 3.70 ± 0.73 a | 354.71 ± 73.45 a | 5.85 ± 1.48 a | 17.94 ± 2.39 b | 605.31 ± 59.90 c | 67.02 ± 27.94 bc | 78.01 ± 1.34 b |
| G0.69 | 18.01 ± 0.19 c | 1.03 ± 0.01 a | 6.47 ± 0.09 a | 43.78 ± 4.63 a | 3.18 ± 0.04 ab | 0.48 ± 0.05 a | 18.93 ± 0.89 a | 3.46 ± 0.28 a | 307.49 ± 56.78 a | 4.66 ± 1.08 a | 34.97 ± 8.63 a | 790.75 ± 70.41 bc | 0.00 ± 0.00 c | 78.23 ± 10.49 b |
| G0.92 | 17.94 ± 0.59 c | 1.05 ± 0.04 a | 6.59 ± 0.05 a | 38.32 ± 1.80 a | 3.13 ± 0.09 b | 0.46 ± 0.08 a | 18.69 ± 0.42 a | 3.24 ± 0.12 a | 330.37 ± 25.75 a | 3.22 ± 0.00 a | 21.31 ± 1.47 b | 849.41 ± 96.75 abc | 0.00 ± 0.00 c | 68.84 ± 2.87 c |
| TN (g/kg) | SAN (mg/kg) | NH4+-N (mg/kg) | NO3−-N (mg/kg) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MBC (mg/kg) | 0.78 ** | −0.06 | 0.53 * | −0.12 | |
| MBN (mg/kg) | 0.71 ** | −0.02 | 0.55 * | −0.11 | |
| Bacteria | Shannon | 0.07 | −0.02 | 0.40 | −0.32 |
| Shannon evenness | −0.02 | −0.08 | 0.40 | −0.33 | |
| Fungus | Shannon | −0.36 | −0.15 | 0.01 | 0.15 |
| Shannon evenness | −0.40 | −0.16 | −0.05 | 0.19 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; Wang, M.; Wang, X.; Li, R.; Zhang, R.; Xun, W.; Li, H.; Xin, X.; Yan, R. Grazing Regulates Changes in Soil Microbial Communities in Plant-Soil Systems. Agronomy 2023, 13, 708. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13030708
Zhang Y, Wang M, Wang X, Li R, Zhang R, Xun W, Li H, Xin X, Yan R. Grazing Regulates Changes in Soil Microbial Communities in Plant-Soil Systems. Agronomy. 2023; 13(3):708. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13030708
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Yu, Miao Wang, Xu Wang, Ruiqiang Li, Ruifu Zhang, Weibing Xun, Hui Li, Xiaoping Xin, and Ruirui Yan. 2023. "Grazing Regulates Changes in Soil Microbial Communities in Plant-Soil Systems" Agronomy 13, no. 3: 708. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13030708
APA StyleZhang, Y., Wang, M., Wang, X., Li, R., Zhang, R., Xun, W., Li, H., Xin, X., & Yan, R. (2023). Grazing Regulates Changes in Soil Microbial Communities in Plant-Soil Systems. Agronomy, 13(3), 708. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13030708









