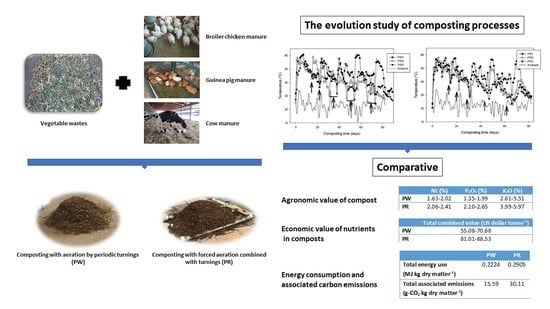
Agronomic, Economic and Environmental Comparative of Different Aeration Systems for On-Farm Composting
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Procedure for the Composting Process
2.2. Economic Value of the Final Composts
2.3. Environmental Assessment of the Composting Process
2.4. Analytical and Statistical Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Effect of the Aeration System on the Thermal Profile of the Piles
3.2. Effect of the Aeration System on the Evolution of the Principal Physicochemical and Biological Parameters of the Piles during Composting
3.3. Agronomic and Economic Value of the Final Composts
3.4. Energy Consumption and Its Associated Carbon Emissions According to the Aeration System Used
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- FAOSTAT. Available online: http://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#data (accessed on 9 January 2023).
- Banco Central del Ecuador. Información Estadística Mensual No. 2050-Diciembre. 2022. Available online: https://contenido.bce.fin.ec/home1/estadisticas/bolmensual/IEMensual.jsp (accessed on 9 January 2023).
- The World Bank. World Development Indicators. Available online: https://databank.worldbank.org/source/world-development-indicators (accessed on 9 January 2023).
- Gavilanes-Terán, I.; Jara-Samaniego, J.; Idrovo-Novillo, J.; Bustamante, M.A.; Moral, R.; Paredes, C. Windrow composting as horticultural waste management strategy—A case study in Ecuador. Waste Manag. 2016, 48, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romero, C.M.; Li, C.L.; Owens, J.; Ribeiro, G.O.; Mcallister, T.A.; Okine, E.; Hao, X.Y. Nutrient cycling and greenhouse gas emissions from soil amended with biochar-manure mixtures. Pedosphere 2021, 31, 289–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghirardini, A.; Grillini, V.; Verlicchi, P. A review of the occurrence of selected micropollutants and microorganisms in different raw and treated manure-Environmental risk due to antibiotics after application to soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 707, 136118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhongqi, H.; Pagliari, P.; Waldrip, H.M. Applied and Environmental Chemistry of Animal Manure: A Review. Pedosphere 2016, 26, 779–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, K.; Schneider, K.; McConkey, B. Components of phosphorus loss from agricultural landscapes, and how to incorporate them into risk assessment tools. Front. Earth Sci. 2018, 6, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- FAO Regional Office for Latin America and the Caribbean. Available online: http://www.fao.org/americas/noticias/ver/en/c/452128/ (accessed on 3 August 2022).
- De Corato, U. Agricultural waste recycling in horticultural intensive farming systems by on-farm composting and compost-based tea application improves soil quality and plant health: A review under the perspective of a circular economy. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 738, 139840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pergola, M.; Persiani, A.; Palese, A.M.; Di Meo, V.; Pastore, V.; D’Adamo, C.; Celano, G. Composting: The way for a sustainable agriculture. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2018, 123, 744–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pergola, M.; Piccolo, A.; Palese, A.M.; Ingrao, C.; Di Meo, V.; Celano, G. A combined assessment of the energy, economic and environmental issues associated with on farm manure composting processes: Two case studies in South of Italy. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 172, 3969–3981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pergola, M.; Persiani, A.; Pastore, V.; Palese, A.M.; D’Adamo, C.; De Falco, E.; Celano, G. Sustainability assessment of the green compost production chain from agricultural waste: A case study in southern Italy. Agronomy 2020, 10, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gabhane, J.; William, S.P.; Bidyadhar, R.; Bhilawe, P.; Anand, D.; Vaidya, A.N.; Wate, S.R. Additives aided composting of green waste: Effects on organic matter degradation compost maturity and quality of the finished compost. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 114, 382–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.Y.; Zheng, X.Q.; Cao, H.Y.; Tan, L.; Yang, B.; Cheng, W.M.; Xu, Y. Reduction of antibiotic resistance genes under different conditions during composting process of aerobic combined with anaerobic. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 325, 124710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, G.; Kong, X.; Kang, J.; Su, N.; Fei, J.; Luo, G. Fungal community succession contributes to product maturity during the co-composting of chicken manure and crop residues. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 328, 124845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Xu, Z.; Jiang, T.; Huda, N.; Li, G.; Luo, W. Gaseous emission and maturity in composting of livestock manure and tobacco wastes: Effects of aeration intensities and mitigation by physiochemical additives. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2020, 19, 100899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.; Kazmi, A.A.; Ahmed, N. Study on effects of temperature, moisture and pH in degradation and degradation kinetics of aldrin, endosulfan, lindane pesticides during full-scale continuous rotary drum composting. Chemosphere 2014, 102, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idrovo-Novillo, J.; Gavilanes-Terán, I.; Bustamante, M.A.; Paredes, C. Composting as a method to recycle renewable plant resources back to the ornamental plant industry: Agronomic and economic assessment of composts. Process Saf. Environ. Protect. 2018, 116, 388–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afonso, S.; Arrobas, M.; Pereira, E.L.; Rodrigues, M.A. Recycling nutrient-rich hop leaves by composting with wheat straw and farmyard manure in suitable mixtures. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 284, 112105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, L.Y.; Bong, C.P.C.; Lee, C.T.; Klemeš, J.J.; Sarmidi, M.R.; Lim, J.S. Review on the current composting practices and the potential of improvement using two-stage composting. Chem. Eng. Trans. 2017, 61, 1051–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palaniveloo, K.; Amran, M.A.; Norhashim, N.A.; Mohamad-Fauzi, N.; Peng-Hui, F.; Hui-Wen, L.; Kai-Lin, Y.; Jiale, L.; Chian-Yee, M.G.; Jing-Yi, L.; et al. Food waste composting and microbial community structure profiling. Processes 2020, 8, 723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Bai, Z.; Yao, Y.; Gao, B.; Chadwick, D.; Chen, Q.; Hu, C.; Ma, L. Composting with negative pressure aeration for the mitigation of ammonia emissions and global warming potential. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 195, 448–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stegenta-Dąbrowska, S.; Randerson, P.F.; Białowiec, A. Aerobic biostabilization of the organic fraction of municipal solid waste-monitoring hot and cold spots in the reactor as a novel tool for process optimization. Materials 2022, 15, 3300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasapoor, M.; Adl, M.; Pourazizi, B. Comparative evaluation of aeration methods for municipal solid waste composting from the perspective of resource management: A practical case study in Tehran, Iran. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 184, 528–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- US Composting Council. Field Guide to Compost Use. 2001. Available online: http://www.mncompostingcouncil.org/uploads/1/5/6/0/15602762/fgcu.pdf (accessed on 30 July 2022).
- Ministerio de Agricultura y Ganadería. Sistema de Información Pública Agropecuaria. 2021. Available online: http://sipa.agricultura.gob.ec/ (accessed on 9 January 2023).
- IPCC. Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change Guidelines for National Greenhouse Gas Inventories. 2006. Available online: https://www.ipcc-nggip.iges.or.jp/public/2006gl/index.html (accessed on 30 July 2022).
- Levis, J.W.; Barlaz, M.A. Composting Process Model Documentation; North Carolina State University: Raleigh, NC, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Roletto, E.; Barberis, R.; Consiglio, M.; Jodice, R. Chemical parameters for evaluating compost maturity. BioCycle 1985, 26, 46–47. [Google Scholar]
- Paredes, C.; Roig, A.; Bernal, M.P.; Sánchez-Monedero, M.A.; Cegarra, J. Evolution of organic matter and nitrogen during co-composting of olive mill wastewater with solid organic wastes. Biol. Fert. Soils 2000, 32, 222–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haugh, R.T. The Practical Handbook of Compost Engineering, 1st ed.; Taylor and Francis Inc.: London, UK, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Azim, K.; Soudi, B.; Boukhari, S.; Perissol, C.; Roussos, S.; Thami Alami, I. Composting parameters and compost quality: A literature review. Org. Agr. 2018, 8, 141–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EPA. United States Environment Protection Agency. Environmental Regulations and Technology Control of Pathogens and Vector Attraction in Sewage Sludge; EPA625-/R-92/-103; EPA: Cincinnati, OH, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Bernal, M.P.; Sommer, S.G.; Chadwick, D.; Qing, C.; Guoxue, L.; Michel, F.C., Jr. Current approaches and future trends in compost quality criteria for agronomic, environmental, and human health benefits. Adv. Agron. 2017, 144, 143–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onwosi, C.O.; Igbokwe, V.C.; Odimba, J.N.; Eke, I.E.; Nwankwoala, M.; Iroh, I.N.; Ezeogu, L.I. Composting technology in waste stabilization: On the methods, challenges and future prospects. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 190, 140–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Wang, Z.; Awasthi, M.K.; Jiang, Y.; Li, R.; Ren, X.; Zhao, J.; Shen, F.; Wang, M.; Zhang, Z. Evaluation of medical stone amendment for the reduction of nitrogen loss and bioavailability of heavy metals during pig manure composting. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 220, 297–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.H.; Li, G.; Jiang, Z.W.; Li, M.Q.; Ma, C.F.; Li, X.T.; Li, Q.L. Investigating the variation of dissolved organic matters and the evolution of autotrophic microbial community in composting with organic and inorganic carbon sources. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 304, 123013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabir, F.; Tow, W.W.; Hamauzu, Y.; Katayama, S.; Tanaka, S.; Nakamura, S. Antioxidant and cytoprotective activities of extracts prepared from fruit and vegetable wastes and by-products. Food Chem. 2015, 167, 358–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouhia, Y.; Lyamlouli, K.; El Fels, L.; Youssef, Z.; Ouhdouch, Y.; Hafdi, M. Effect of microbial inoculation on lipid and phenols removal during the co-composting of olive mill solid sludge with green waste in bioreactor. Waste Biomass Valoriz. 2021, 12, 1417–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Meng, Q.; Zhu, Q.; Niu, Q.; Yan, H.; Li, K.; Li, G.; Li, X.; Liu, H.; Liu, Y.; et al. Efficient decomposition of lignocellulose and improved composting performances driven by thermally activated persulfate based on metagenomics analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 794, 148530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zucconi, F.; Pera, A.; Forte, M.; de Bertoldi, M. Evaluating toxicity of immature compost. BioCycle 1981, 22, 54–57. [Google Scholar]
- Gavilanes-Terán, I.; Paredes, C.; Pérez-Espinoza, A.; Bustamante, M.A.; Gálvez-Sola, L.; Jara-Samaniego, J. Opportunities and challenges of organic waste management from the agroindustrial sector in South America: Chimborazo province case study. Commun. Soil Sci. Plan. 2015, 46, 137–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernal, M.P.; Alburquerque, J.A.; Moral, R. Composting of animal manures and chemical criteria for compost maturity assessment: A review. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 5444–5453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iglesias Jiménez, E.; Pérez García, V. Determination of maturity indexes for city refuse composts. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 1992, 38, 331–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| VW | BCM | GPM | CM | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Corg (%) | 36.0 | 28.4 | 48.8 | 35.6 |
| Nt (%) | 0.53 | 2.44 | 2.62 | 2.60 |
| Corg/Nt | 67.9 | 11.6 | 18.6 | 13.7 |
| P (g kg−1) | 3.72 | 8.36 | 5.80 | 9.26 |
| K (g kg−1) | 29.6 | 12.2 | 34.2 | 10.1 |
| Ca (g kg−1) | 13.0 | 7.6 | 10.0 | 18.8 |
| Mg (g kg−1) | 6.44 | 7.10 | 3.52 | 9.26 |
| Na (g kg−1) | 0.87 | 4.45 | 2.06 | 1.02 |
| Fe (mg kg−1) | 1130 | 3002 | 560 | 2387 |
| Mn (mg kg−1) | 67 | 167 | 40 | 151 |
| Cu (mg kg−1) | 10 | 39 | 9 | 24 |
| Zn (mg kg−1) | 49 | 126 | 83 | 51 |
| Composting Phase | pH | EC (dS m−1) | OM (%) | Corg/Nt | Nt (%) | Cw (%) | Polyphenols (mg kg−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PW1: vegetable wastes + broiler chicken manure | |||||||
| I | 7.0 | 3.52 | 69.9 | 23.6 | 1.70 | 7.07 | 11,003 |
| TP | 6.6 | 3.38 | 62.3 | 18.3 | 2.02 | 5.31 | 10,869 |
| EBP | 8.4 | 3.43 | 47.4 | 12.5 | 2.11 | 1.34 | 6564 |
| M | 8.6 | 3.30 | 41.7 | 12.4 | 2.02 | 1.36 | 5894 |
| LSD | 0.4 | 0.46 | 7.4 | 0.5 | 0.09 | 1.13 | 1219 |
| PW2: vegetable wastes + guinea pig manure | |||||||
| I | 8.0 | 5.86 | 80.1 | 23.8 | 1.99 | 4.70 | 9745 |
| TP | 8.5 | 5.53 | 71.7 | 21.4 | 1.99 | 4.66 | 9470 |
| EBP | 9.7 | 5.38 | 53.5 | 14.6 | 2.00 | 1.09 | 7385 |
| M | 9.8 | 5.38 | 53.3 | 15.1 | 1.73 | 1.40 | 6581 |
| LSD | 0.5 | 0.20 | 11.5 | 0.4 | 0.09 | 0.91 | 1436 |
| PW3: vegetable wastes + cow manure | |||||||
| I | 7.2 | 4.06 | 78.4 | 24.5 | 1.87 | 5.91 | 7622 |
| TP | 7.7 | 3.83 | 73.6 | 23.0 | 1.81 | 5.29 | 5716 |
| EBP | 9.2 | 3.07 | 44.4 | 13.4 | 1.88 | 1.37 | 2757 |
| M | 9.4 | 3.12 | 40.9 | 15.0 | 1.63 | 1.03 | 2116 |
| LSD | 0.3 | 0.31 | 9.5 | 0.6 | 0.08 | 0.96 | 700 |
| PR1: vegetable wastes + broiler chicken manure | |||||||
| I | 6.8 | 3.90 | 73.2 | 23.2 | 1.77 | 6.83 | 10,257 |
| TP | 7.1 | 4.25 | 67.5 | 18.6 | 2.12 | 4.97 | 9028 |
| EBP | 8.9 | 4.41 | 53.5 | 13.1 | 2.35 | 2.22 | 7722 |
| M | 9.1 | 5.10 | 49.1 | 12.6 | 2.41 | 1.61 | 5946 |
| LSD | 0.4 | 0.37 | 11.9 | 0.5 | 0.10 | 1.33 | 2005 |
| PR2: vegetable wastes + guinea pig manure | |||||||
| I | 7.9 | 5.24 | 79.5 | 24.6 | 1.91 | 4.53 | 8399 |
| TP | 8.5 | 4.58 | 72.1 | 21.9 | 1.97 | 4.33 | 7131 |
| EBP | 9.7 | 5.09 | 60.3 | 15.4 | 2.26 | 1.97 | 6430 |
| M | 9.8 | 5.83 | 59.4 | 14.5 | 2.39 | 1.61 | 6203 |
| LSD | 0.2 | 0.32 | 7.5 | 0.6 | 0.13 | 1.41 | 1242 |
| PR3: vegetable wastes + cow manure | |||||||
| I | 7.1 | 3.90 | 78.5 | 24.1 | 1.86 | 6.26 | 8439 |
| TP | 7.7 | 3.83 | 76.1 | 23.0 | 1.91 | 5.57 | 7234 |
| EBP | 9.3 | 3.81 | 48.7 | 15.3 | 2.04 | 2.18 | 3753 |
| M | 9.2 | 4.86 | 48.2 | 13.7 | 2.06 | 1.39 | 2889 |
| LSD | 0.3 | 0.33 | 5.7 | 0.6 | 0.10 | 1.00 | 346 |
| Piles | A (%) | k (Days−1) | R2 Adj | F | SEE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PW1 | 69.9 | 0.0320 | 0.9738 | 223.60 *** | 4.06 |
| PW2 | 72.3 | 0.0462 | 0.9957 | 1393.53 *** | 1.73 |
| PW3 | 85.4 | 0.0287 | 0.9855 | 408.21 *** | 3.73 |
| PR1 | 66.1 | 0.0260 | 0.9901 | 598.88 *** | 2.28 |
| PR2 | 64.2 | 0.0338 | 0.9258 | 75.83 ** | 6.30 |
| PR3 | 80.8 | 0.0291 | 0.9227 | 72.63 ** | 8.71 |
| Composting Phase | HI (%) | HR (%) | Pha | Cha/Cfa | GI (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PW1: vegetable wastes + broiler chicken manure | |||||
| I | 13.7 | 37.4 | 36.8 | 0.58 | 0 |
| TP | 14.7 | 36.3 | 39.9 | 0.67 | 1 |
| EBP | 28.6 | 37.9 | 74.6 | 3.00 | 32 |
| M | 33.5 | 42.4 | 78.6 | 3.67 | 51 |
| LSD | 2.1 | 2.4 | 3.3 | 0.12 | 11 |
| PW2: vegetable wastes + guinea pig manure | |||||
| I | 10.0 | 29.4 | 34.0 | 0.52 | 0 |
| TP | 12.3 | 27.0 | 45.5 | 0.83 | 0 |
| EBP | 28.2 | 36.9 | 76.5 | 3.25 | 16 |
| M | 45.3 | 53.7 | 84.6 | 5.50 | 22 |
| LSD | 1.8 | 3.5 | 4.6 | 0.50 | 8 |
| PW3: vegetable wastes + cow manure | |||||
| I | 10.6 | 31.7 | 33.6 | 0.51 | 0 |
| TP | 15.7 | 32.2 | 48.5 | 0.94 | 0 |
| EBP | 27.0 | 35.0 | 77.1 | 3.40 | 23 |
| M | 27.2 | 34.8 | 77.2 | 3.40 | 38 |
| LSD | 2.7 | 2.2 | 3.7 | 0.23 | 5 |
| PR1: vegetable wastes + broiler chicken manure | |||||
| I | 12.7 | 36.8 | 34.5 | 0.53 | 0 |
| TP | 15.9 | 36.1 | 44.2 | 0.79 | 0 |
| EBP | 28.3 | 37.3 | 76.6 | 3.28 | 14 |
| M | 29.4 | 36.9 | 79.2 | 3.82 | 36 |
| LSD | 4.4 | 2.7 | 3.6 | 0.29 | 3 |
| PR2: vegetable wastes + guinea pig manure | |||||
| I | 10.1 | 27.8 | 35.9 | 0.56 | 0 |
| TP | 18.0 | 33.2 | 54.1 | 1.18 | 0 |
| EBP | 23.5 | 31.1 | 75.3 | 3.09 | 12 |
| M | 25.7 | 32.6 | 78.4 | 3.63 | 9 |
| LSD | 1.5 | 2.6 | 4.4 | 1.20 | 3 |
| PR3: vegetable wastes + cow manure | |||||
| I | 10.1 | 33.6 | 29.9 | 0.43 | 0 |
| TP | 13.3 | 28.6 | 46.5 | 0.88 | 0 |
| EBP | 23.4 | 32.1 | 72.4 | 2.64 | 14 |
| M | 24.0 | 32.0 | 74.2 | 2.88 | 14 |
| LSD | 3.0 | 4.8 | 5.3 | 0.70 | 5 |
| Compost PW1 | Compost PW2 | Compost PW3 | Compost PR1 | Compost PR2 | Compost PR3 | F-ANOVA | US Guidelines a | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 8.6 a | 9.8 c | 9.4 b | 9.1 b | 9.8 c | 9.2 b | 34.8 *** | 6.0–7.5 |
| EC (dS m−1) | 3.30 a | 5.38 c | 3.12 a | 5.10 b | 5.83 d | 4.86 b | 413.8 *** | <5 |
| OM (%) | 41.7 a | 53.3 c | 40.9 a | 49.1 b | 59.3 d | 48.2 b | 465.8 *** | 50–60 |
| Cw (%) | 1.36 ab | 1.40 ab | 1.03 a | 1.61 b | 1.61 b | 1.39 ab | 4.8 * | |
| Corg/Nt | 12.4 a | 15.1 d | 15.0 d | 12.6 a | 14.5 c | 13.7 b | 593.8 *** | |
| HI (%) | 33.5 c | 45.3 d | 27.2 b | 29.4 b | 25.7 a | 24.0 a | 53.8 *** | |
| Nt (%) | 2.02 c | 1.73 b | 1.63 a | 2.41 d | 2.39 d | 2.06 c | 663.2 *** | ≥1.0 |
| P (%) | 0.87 b | 0.66 ab | 0.59 a | 1.15 c | 0.92 bc | 0.95 bc | 11.7 ** | ≥1.0 |
| P2O5 (%) | 1.99 b | 1.52 ab | 1.35 a | 2.65 c | 2.10 bc | 2.19 bc | 11.7 ** | |
| Na (%) | 0.45 ab | 0.54 bc | 0.40 a | 0.64 cd | 0.66 d | 0.52 b | 18.9 ** | - |
| K (%) | 2.16 a | 4.57 cd | 2.83 ab | 3.31 bc | 4.96 d | 3.90 bcd | 16.7 ** | - |
| K2O (%) | 2.61 a | 5.51 cd | 3.41 ab | 3.99 bc | 5.97 d | 4.70 bcd | 16.7 ** | - |
| Fe (mg kg−1) | 6362 b | 6040 b | 6641 b | 4005 a | 3358 a | 5616 b | 38.9 *** | - |
| Cu (mg kg−1) | 183 c | 36 a | 49 b | 353 d | 33 a | 34 a | 9407.2 *** | 1500 |
| Mn (mg kg−1) | 328 d | 139 b | 182 c | 583 e | 103 a | 172 bc | 568.4 *** | - |
| Zn (mg kg−1) | 320 c | 183 ab | 240 b | 439 d | 152 a | 139 a | 57.7 *** | 2800 |
| Ni (mg kg−1) | 20 b | 16 b | 9 a | 8 a | 4 a | 3 a | 35.2 *** | 420 |
| Cr (mg kg−1) | 16 b | 10 a | 28 c | 7 a | 6 a | 8 a | 48.5 *** | - |
| Cd (mg kg−1) | 0.92 b | 0.65 ab | 0.53 a | 0.46 a | 0.41 a | 0.30 a | 8.3 * | 39 |
| Pb (mg kg−1) | 30 a | 33 ab | 40 ab | 44 b | 49 b | 48 b | 6.5 * | 300 |
| Nutrient a | Compost PW1 | Compost PW2 | Compost PW3 | Compost PR1 | Compost PR2 | Compost PR3 | F-ANOVA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nt | 25.38 ab | 21.74 a | 20.48 a | 30.28 b | 30.03 b | 25.88 ab | 9.90 ** |
| P2O5 | 60.89 b | 46.36 ab | 41.15 a | 80.93 c | 64.10 bc | 66.70 bc | 11.75 ** |
| K2O | 31.72 a | 66.96 cd | 41.44 ab | 48.43 bc | 72.55 d | 57.18 bcd | 16.81 ** |
| Total combined value | 117.99 | 135.05 | 103.08 | 159.64 | 166.68 | 149.76 |
| Operation | PW | PR |
|---|---|---|
| Energy use in pile conformation (MJ kg dry matter−1) | 0.2177 | 0.2177 |
| Associated emissions (g-CO2 kg dry matter−1) | 15.26 | 15.26 |
| Forced aeration energy use (MJ kg dry matter−1) | 0.0000 | 0.0681 |
| Associated emissions (g-CO2 kg dry matter−1) | 0.00 | 14.52 |
| Pile turning energy use (MJ kg dry matter−1) | 0.0047 | 0.0047 |
| Associated emissions (g-CO2 kg dry matter−1) | 0.33 | 0.33 |
| Total energy use (MJ kg dry matter−1) | 0.2224 | 0.2905 |
| Total associated emissions (g-CO2 kg dry matter−1) | 15.59 | 30.11 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Valverde-Orozco, V.; Gavilanes-Terán, I.; Idrovo-Novillo, J.; Carrera-Beltrán, L.; Basantes-Cascante, C.; Bustamante, M.A.; Paredes, C. Agronomic, Economic and Environmental Comparative of Different Aeration Systems for On-Farm Composting. Agronomy 2023, 13, 929. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13030929
Valverde-Orozco V, Gavilanes-Terán I, Idrovo-Novillo J, Carrera-Beltrán L, Basantes-Cascante C, Bustamante MA, Paredes C. Agronomic, Economic and Environmental Comparative of Different Aeration Systems for On-Farm Composting. Agronomy. 2023; 13(3):929. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13030929
Chicago/Turabian StyleValverde-Orozco, Víctor, Irene Gavilanes-Terán, Julio Idrovo-Novillo, Lourdes Carrera-Beltrán, Cristian Basantes-Cascante, Maria Angeles Bustamante, and Concepción Paredes. 2023. "Agronomic, Economic and Environmental Comparative of Different Aeration Systems for On-Farm Composting" Agronomy 13, no. 3: 929. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13030929
APA StyleValverde-Orozco, V., Gavilanes-Terán, I., Idrovo-Novillo, J., Carrera-Beltrán, L., Basantes-Cascante, C., Bustamante, M. A., & Paredes, C. (2023). Agronomic, Economic and Environmental Comparative of Different Aeration Systems for On-Farm Composting. Agronomy, 13(3), 929. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13030929