Named Entity Recognition of Chinese Crop Diseases and Pests Based on RoBERTa-wwm with Adversarial Training
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Introduction to Data Set
2.1.1. Data Sources
2.1.2. Data Annotation
2.2. Proposed Approach
2.2.1. RoBERTa-wwm Model
2.2.2. Adversarial Training
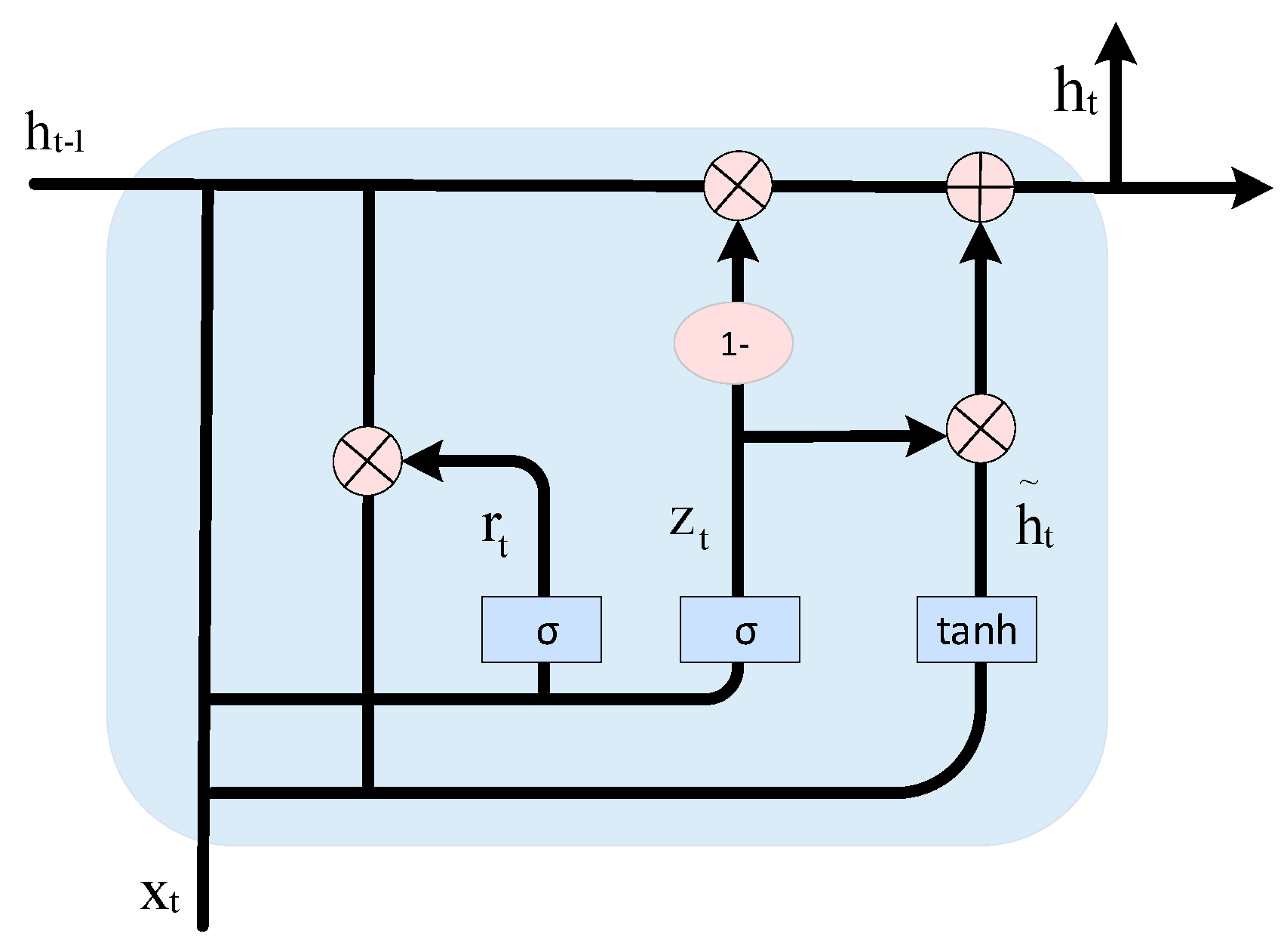
2.2.3. BiGRU Model
2.2.4. Full Connection Layer
2.2.5. Conditional Random Fields Model
3. Results
3.1. Experimental Parameter Setup
3.2. Experimental Results
3.2.1. Comparative Model Results
- 1.
- Effectiveness of the embedding method:
- 2.
- Effectiveness of the downstream model:
3.2.2. Results for RGC-ADV Model
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Athanassiou, C.G.; Phillips, T.W.; Wakil, W. Biology and Control of the Khapra Beetle, Trogoderma granarium, a Major Quarantine Threat to Global Food Security. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2019, 64, 131–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.S. Construction and Application of Knowledge Map of Crop Diseases and Pests Based on ALBERT. Master’s Thesis, Anhui Agricultural University, Hefei, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Fountas, S.; Espejo-Garcia, B.; Kasimati, A.; Mylonas, N.; Darra, N. The Future of Digital Agriculture: Technologies and Opportunities. IT Prof. 2020, 22, 24–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Luo, R.; Cai, Z.P. Overview of Chinese Named Entity Recognition. Comput. Sci. Explor. 2022, 16, 296–304. [Google Scholar]
- Drury, B.; Roche, M. A survey of the applications of text mining for agriculture. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2019, 163, 104864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grishman, R.; Sundheim, B. Message Understanding Conference—6: A Brief History. In Proceedings of the 16th International Conference on Computational Linguistics, Copenhagen, Denmark, 5-9 August 1996; pp. 466–471. [Google Scholar]
- Sung, M.; Jeong, M.; Choi, Y.; Choi, Y.; Kim, D.; Lee, J.; Kang, J. BERN2: An advanced neural biomedical named entity recognition and normalization tool. Bioinformatics 2022, 38, 4837–4839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.C.; Chou, P.Y.; Lucky, F.; Wu, S. Detection of environmental pollution events contained in online news text based on joint theme features. J. Geoinf. Sci. 2019, 21, 1510–1517. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Z.C.; Chou, P.Y.; Wang, H.B.; Wu, S. Typhoon event information extraction method combining event and context features. J. Surv. Mapp. Sci. Technol. 2019, 36, 209–214. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Q.R.; Zhu, P.; Luo, Y.F.; Dong, Q.W. Research progress of Chinese named entity recognition in financial field. J. East China Norm. Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2021, 5, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.Y.; Wang, F. Research on agricultural named entity recognition based on conditional random field. J. Hebei Agric. Univ. 2014, 37, 132–135. [Google Scholar]
- Kanwal, S.; Malik, K.; Shahzad, K.; Aslam, F. Urdu Named Entity Recognition: Corpus Generation and Deep Learning Applications. ACM Trans. Asian Low-Resour. Lang. Inf. Process. 2019, 19, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lawrence, R.; Biinghwang, J. An introduction to hidden Markov models. IEEE ASSP Mag. 1986, 3, 4–16. [Google Scholar]
- Mccallum, A.; Freitag, D.; Pereira, F. Maximum Entropy Markov Models for Information Extraction and Segmentation. ICML 2000, 17, 591–598. [Google Scholar]
- Lafferty, J.; Mccallum, A.; Pereira, F.C.N. Conditional Random Fields: Probabilistic Models for Segmenting and Labeling Sequence Data. Proc. ICML 2001, 2001, 282–289. [Google Scholar]
- Malarkodi, C.; Lex, E.; Devi, S. Named Entity Recognition for the Agricultural Domain. Res. Comput. Sci. 2016, 117, 121–132. [Google Scholar]
- Georgescu, T. Natural Language Processing Model for Automatic Analysis of Cybersecurity-Related Documents. Symmetry 2020, 12, 354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lecun, Y.; Bengio, Y.; Hinton, G. Deep learning. Nature 2015, 521, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haykin, S. Neural Networks: A Comprehensive Foundation; Prentice Hall PTR: USA, 1998; Available online: https://dl.acm.org/doi/abs/10.5555/521706 (accessed on 13 March 2022.).
- Zhao, R.X.; Yang, C.X.; Zheng, J.H.; Li, J.; Wang, J. Agricultural Intelligent Knowledge Service: Overview and Future Perspectives. Smart Agric. (Chin. Engl.) 2022, 4, 105–125. [Google Scholar]
- Hochreiter, S.; Schmidhuber, J. Long Short-Term Memory. Neural Comput. 1997, 9, 1735–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elman, J.L. Finding Structure in Time. Cogn. Sci. 1990, 14, 179–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lecun, Y.; Boser, B.; Denker, J.S.; Henderson, D.; Howard, R.E.; Hubbard, W.; Jackel, L.D. Backpropagation Applied to Handwritten Zip Code Recognition. Neural Computation. 1989, 1, 541–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuster, M.; Paliwal, K.K. Bidirectional recurrent neural networks. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 1997, 45, 2673–2681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Graves, A.; Mohamed, A.R.; Hinton, G. Speech recognition with deep recurrent neural networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 26–31 May 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, K.; Van Merrienboer, B.; Gulcehre, C.; Bahdanau, D.; Bougares, F.; Schwemk, H.; Bengio, Y. Learning Phrase Representations Using RNN Encoder-Decoder for Statistical Machine Translation; Association for Computational Linguistics (ACL): Doha, Qatar, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.F.; Ding, J.; Hu, F.K.; Wang, X. Survey on large scale enterprise-level knowledge graph practices. Comput. Eng. 2020, 46, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.L.; Tang, L.Y.; Hu, Y.; Jiang, F.; Peng, L.; Feng, X.C. The extraction method of knowledge entities and relationships of landscape plants based on ALBERT model. J. Glob. Inf. Sci. 2021, 23, 1208–1220. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Ott, M.; Goyal, N.; Du, J.; Joshi, M.; Chen, D.; Levy, O.; Lewis, M.; Zettlemoyer, L.; Stoyanov, V. RoBERTa: A robustly optimized BERT pretraining approach. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1907.11692. [Google Scholar]
- Miyato, T.; Dai, A.M.; Goodfellow, I. Adversarial Training Methods for Semi-Supervised Text Classification. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations, Toulon, France, 24–26 April 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Szegedy, C.; Zaremba, W.; Sutskever, I.; Bruna, J.; Erhan, D.; Goodfellow, I.; Fergus, R. Intriguing properties of neural networks. arXiv 2013, arXiv:1312.6199. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, S.; KAREN. A statistical interpretation of term specificity and its application in retrieval. J. Doc. 1972, 28, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Li, C.Z.; Du, H.C. Named Entity Recognition for Terahertz Domain Knowledge Graph based on Albert-BiLSTM-CRF. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 4th Information Technology, Networking, Electronic and Automation Control Conference (ITNEC), Chongqing, China, 12–14 June 2020; pp. 2602–2606. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H. Statistical Learning Methods 2nd Edition; Tsinghua University Press: Beijing China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Y.Y. Institute of Plant Protection, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, China’s Crop Diseases and Insect Pests; China Agricultural Publishing House: BeiJing, China, 2015; p. 1746. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, S.S.; Lu, P.L.; Zhang, H.F.; Ge, C.B.; Chen, S.L. Characteristic analysis of crop planting area and yield change in Fujian Province. China Seed Ind. 2022, 8, 73–79. [Google Scholar]
- Statistical Yearbook of Fujian Province. Available online: https://tjj.fujian.gov.cn/xxgk/ndsj/ (accessed on 10 March 2022.).
- China Crop Germplasm Information Network—Crop Disease and Pest Knowledge Website. Available online: https://www.cgris.net/disease/default.html (accessed on 13 March 2022).
- National Agricultural Extension Service Center. Application Manual of Technical Specifications for Major Crop Diseases and Pests Prediction; China Agricultural Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, W.Q. Atlas of Excellent Crop Germplasm Resources in Fujian Province; China Agricultural Publishing House: BeiJing, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, P.; Dong, W.Y. Chinese Named Entity Recognition Method Based on BERT Embedding. Comput. Eng. 2020, 46, 40–45. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.Q.; Wang, Y.; Li, B.C. Chinese electronic medical record named entity recognition based on RoBERta-wwm dynamic fusion model. IEEE 2022, 6, 242–250. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, Y.M.; Che, W.X.; Liu, T.; Qin, B.; Yang, Z.; Wang, S.; Hu, G. Pre-Training With Whole Word Masking for Chinese BERT. IEEE-ACM Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2021, 29, 3504–3514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madry, A.; Makelov, A.; Schmidt, L.; Tsipras, D.; Vladu, A. Towards Deep Learning Models Resistant to Adversarial Attacks. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 30 April–3 May 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.; Min, C.H.; Yang, Y.L.; Shen, C.; Fang, L.M. Deep learning model against attack and defense in full cloud edge scenario. Comput. Res. Dev. 2022, 59, 2109–2129. [Google Scholar]
- Chung, J.; Gulcehre, C.; Cho, K.H.; Bengio, Y. Empirical Evaluation of Gated Recurrent Neural Networks on Sequence Modeling. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1412.3555. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, S.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhou, B.; Cheng, C. A recurrent neural network approach for remaining useful life prediction utilizing a novel trend features construction method. Meas. J. Int. Meas. Confed. 2019, 146, 279–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; You, S.; Zeng, C.; Yin, H.; Liu, Y. Data source authentication of synchrophasor measurement devices based on 1D-CNN and GRU. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2021, 196, 107207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wu, Y.; Yue, Y. Pest identification via deep residual learning in complex background. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2017, 141, 351–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.J.; Zhang, Q.Q.; Zhang, P.Y.; Yan, Y.H.; Bai, L. Deep neural network speech endpoint detection based on Viterbi algorithm. J. Chongqing Univ. Posts Telecommun. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2018, 30, 210–215. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Y.B.; Li, Y.F.; Chen, Q.L.; Fang, C.; Hu, Y.Y. Network threat intelligence entity extraction integrated with Focal Loss. J. Commun. 2022, 43, 85–92. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, T.Y.; Goyal, P.; Girshick, R.; He, K.; Dolliar, P. Focal Loss for Dense Object Detection. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2020, 42, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiao, Z.; Sun, S.; Ke, S. Chinese Lexical Analysis with Deep Bi-GRU-CRF Network. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1807.01882. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, Q.; Zhao, S.; Liu, C. A BERT-BiGRU-CRF Model for Entity Recognition of Chinese Electronic Medical Records. Complexity 2021, 2021, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.L.; Deng, Q.K. Chinese Position Segmentation Based on ALBERT- BiGRU-CRF Model. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Symposium on Computer Technology and Information Science (ISCTIS), Guilin, China, 4–6 June 2021; pp. 116–120. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Cheng, N.; Song, W. Research on Chinese Event Extraction Method Based on RoBERTa-WWM-CRF. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE 12th International Conference on Software Engineering and Service Science (ICSESS), Beijing, China, 20–22 August 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Nismi Mol, E.A.; Santosh Kumar, M.B. Review on knowledge extraction from text and scope in agriculture domain. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2022, 1–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikolov, T.; Chen, K.; Corrado, G.; Jeffrey, D. Efficient Estimation of Word Representations in Vector Space. arXiv 2013, arXiv:1301.3781. [Google Scholar]
- Pennington, J.; Socher, R.; Manning, C. Glove: Global Vectors for Word Representation. In Proceedings of the 2014 conference on empirical methods in natural language processing (EMNLP), Doha, Qatar, 25–29 October 2014; pp. 1532–1543. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.J.; Fan, Y.; Wu, X.J. A Survey of Research son Pretraining Technology for Natural Language Processing. Comput. Sci. 2020, 47, 162–173. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.H.; Wang, C.; Wu, H.; Zhao, C.J.; Teng, G.F.; Huang, S.F.; Liu, Z. Research on the Chinese Named-Entity–Relation-ExtractionMethod for Crop Diseases Based on BERT. Agronomy 2022, 12, 2130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.Q.; Yu, L.; Xia, W.Y.; Feng, Q.; Wu, S.Z.; Chen, Z.P.; Fan, H.W.; Wu, Y. Named Entity Recognition Method in Power Network Dispatching Domain Based on ERNIE-IDCNN-CRF Model. Power Inf. Commun. Technol. 2022, 20, 8. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.B.; Zhang, D.M.; Xiong, S.F.; Ma, X.M.; Xi, L. Named Entity Recognition of Wheat Diseases and Pests fusing ALBERT and Rules. J. Front. Comput. Sci. Technol. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, C.D.; Zeng, C.; Ren, J.W.; Zhang, G. Patent text classification combined with ALBERT and two-way gated circulation unit. Comput. Appl. 2021, 41, 407–412. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.Y.; Yuan, K. Emotional analysis model of college students’ forum based on RoBERTa-WWM. Comput. Eng. 2022, 48, 292–298. [Google Scholar]


| Entity Name | Beginning Part | Inner Part | Other |
|---|---|---|---|
| Diseases and pests | B-DIS | I-DIS | O |
| Other names | B-NAME | I-NAME | O |
| Etiology | B-ETIOLOGY | I-ETIOLOGY | O |
| Damaged part | B-PART | I-PART | O |
| Distribution areas | B-AREA | I-AREA | O |
| Disease date | B-DATE | B-DATE | O |
| Damaged crops | B-CROP | I-CROP | O |
| Prevention and control drug | B-DRUG | I-DRUG | O |
| Illustration | Sample |
|---|---|
| Original text | 稻瘟病的症状 |
| Segmented text | 稻瘟病的症状 |
| BERT’s masking strategy | 稻[MASK]病的[MASK]状 |
| RoBERTa-wwm’s masking strategy | [MASK] [MASK] [MASK]的[MASK] [MASK] |
| Experiment Content | Model | Evaluating Indicator | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Precision (%) | Recall (%) | F1 Score (%) | ||
| Other embedding methods | BiGRU-CRF | 80.08 | 81.14 | 80.56 |
| BERT-BiGRU-CRF | 87.66 | 90.57 | 89.07 | |
| ALBERT-BiGRU-CRF | 85.84 | 85.54 | 85.64 | |
| Our method | RoBERTa-wwm-adv-BiGRU-CRF (RGC-ADV) | 89.23 | 90.90 | 90.04 |
| Other downstream models | RoBERTa-wwm-BiGRU-CRF | 88.56 | 89.66 | 89.09 |
| RoBERTa-wwm-CRF | 85.03 | 86.71 | 85.85 | |
| Entity | Precision (%) | Recall (%) | F1 Score (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Diseases and pests | 95.16 | 92.91 | 94.02 |
| Other names | 91.82 | 90.68 | 91.25 |
| Etiology | 98.51 | 98.85 | 98.68 |
| Damaged part | 76.23 | 80.46 | 78.29 |
| Distribution areas | 93.50 | 97.74 | 95.57 |
| Disease date | 79.76 | 82.72 | 81.21 |
| Damaged crop | 91.10 | 92.80 | 91.94 |
| Prevention and control drug | 87.76 | 91.02 | 89.36 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liang, J.; Li, D.; Lin, Y.; Wu, S.; Huang, Z. Named Entity Recognition of Chinese Crop Diseases and Pests Based on RoBERTa-wwm with Adversarial Training. Agronomy 2023, 13, 941. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13030941
Liang J, Li D, Lin Y, Wu S, Huang Z. Named Entity Recognition of Chinese Crop Diseases and Pests Based on RoBERTa-wwm with Adversarial Training. Agronomy. 2023; 13(3):941. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13030941
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiang, Jianqin, Daichao Li, Yiting Lin, Sheng Wu, and Zongcai Huang. 2023. "Named Entity Recognition of Chinese Crop Diseases and Pests Based on RoBERTa-wwm with Adversarial Training" Agronomy 13, no. 3: 941. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13030941
APA StyleLiang, J., Li, D., Lin, Y., Wu, S., & Huang, Z. (2023). Named Entity Recognition of Chinese Crop Diseases and Pests Based on RoBERTa-wwm with Adversarial Training. Agronomy, 13(3), 941. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13030941






