The Controlling Factors of Soil Selenium Content in a Selenium-Deficient Area in Southwest China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
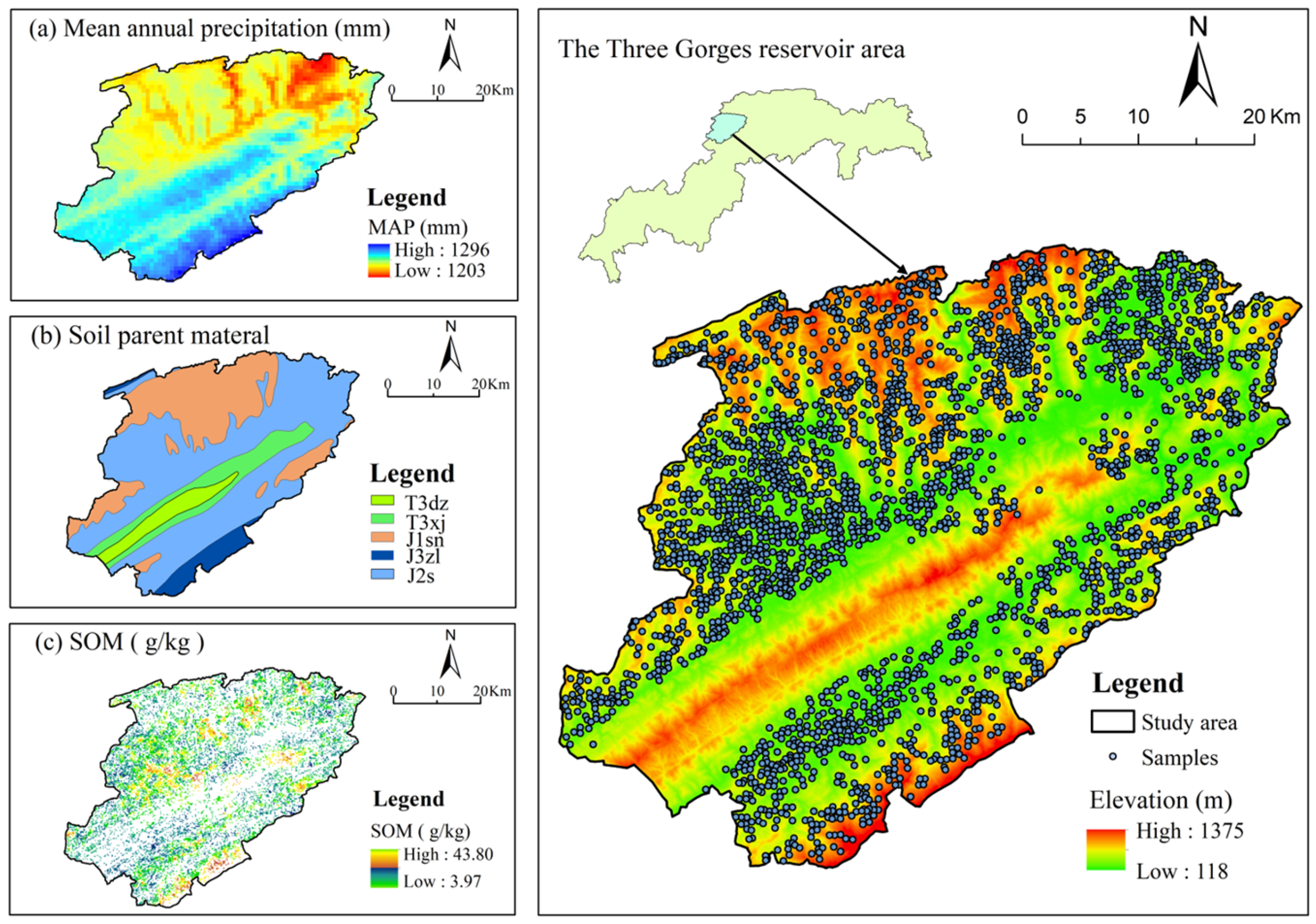
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sample Collection and Processing
2.3. Data Acquisition
2.3.1. Descriptive Statistics
2.3.2. Spatial Autocorrelation Analysis
2.3.3. Complex Network Theory
2.3.4. Random Forest
2.3.5. Shapley Additive Explanations
3. Results
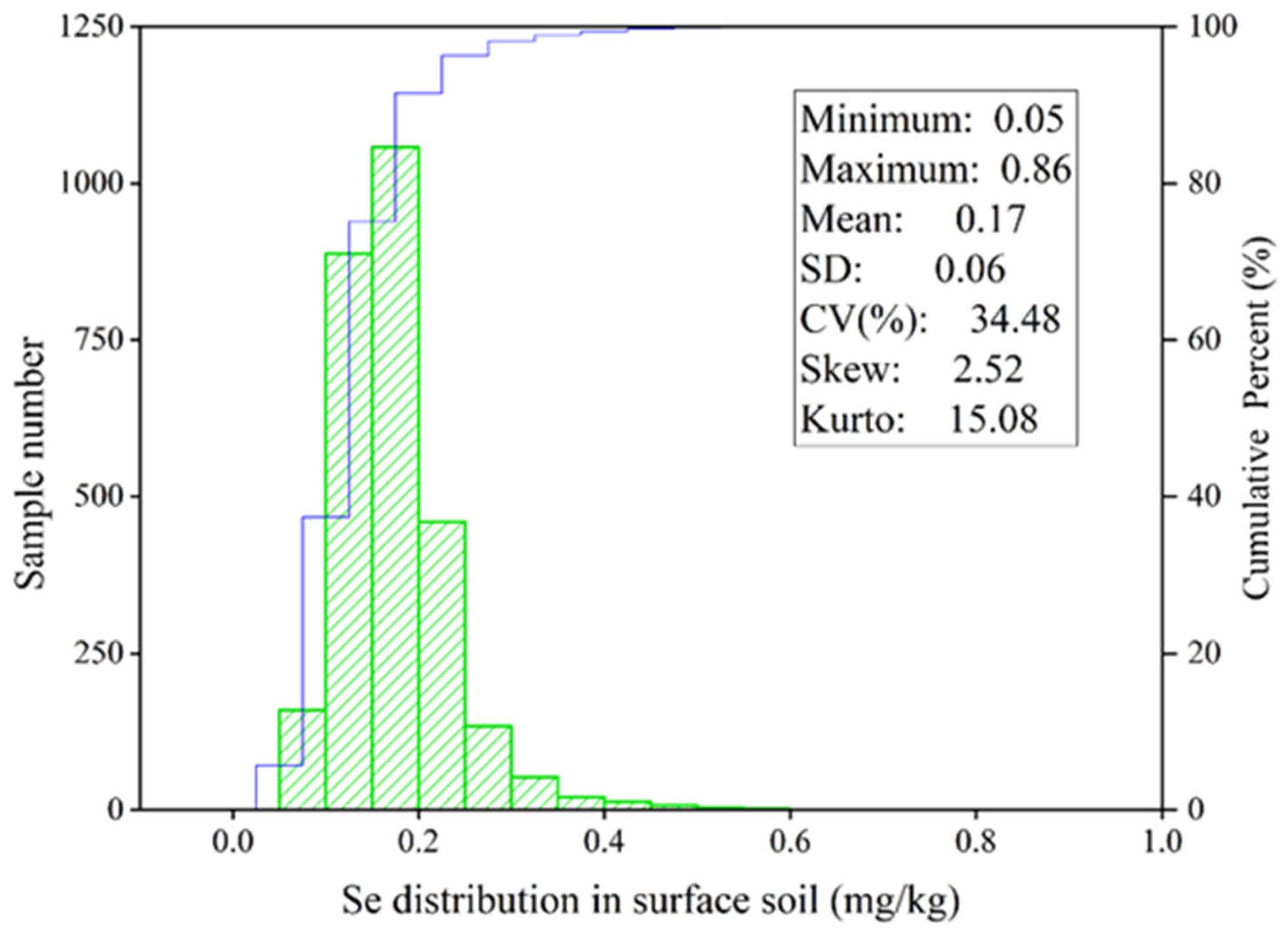
3.1. Data Analysis of Se and Environmental Factors
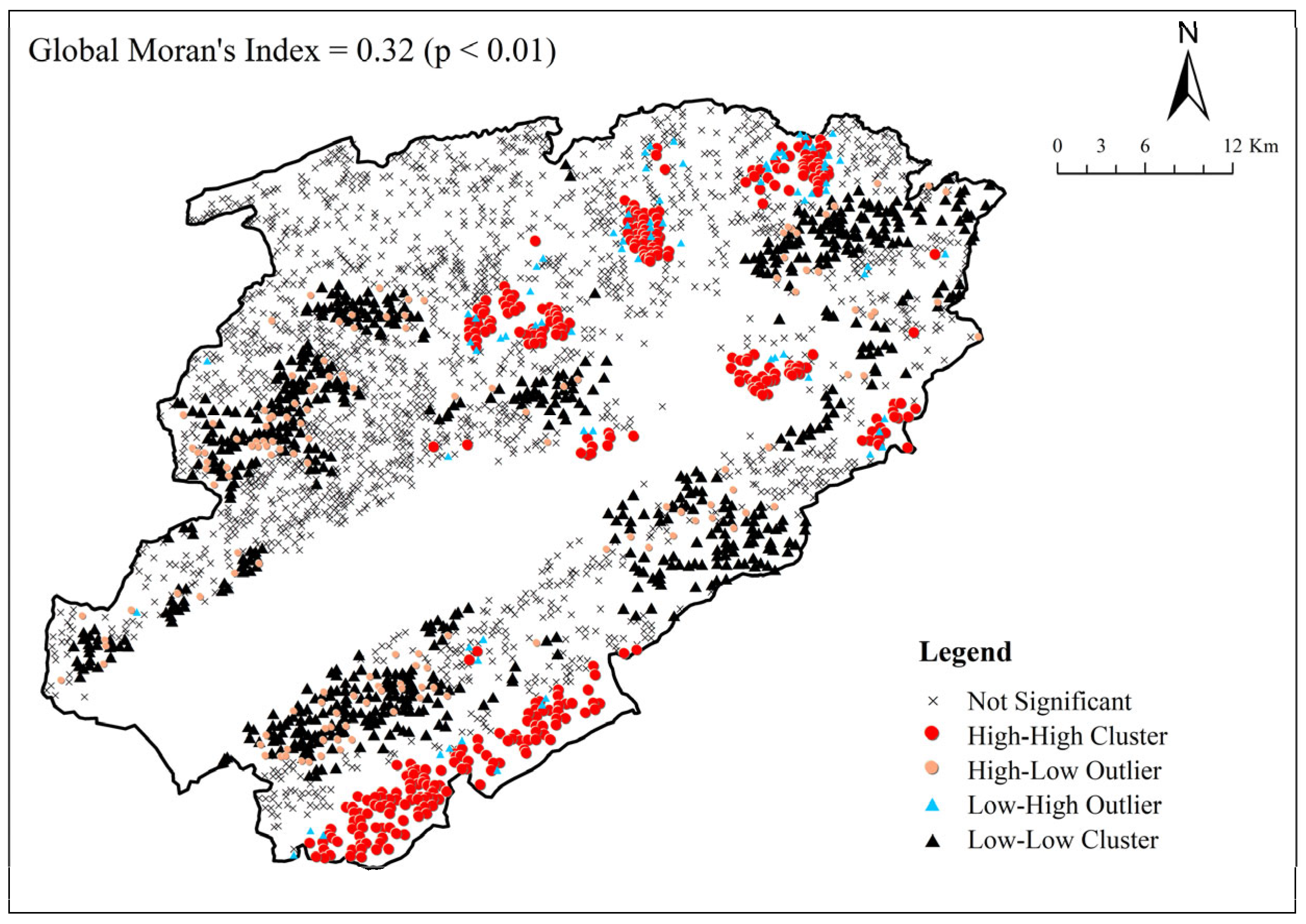
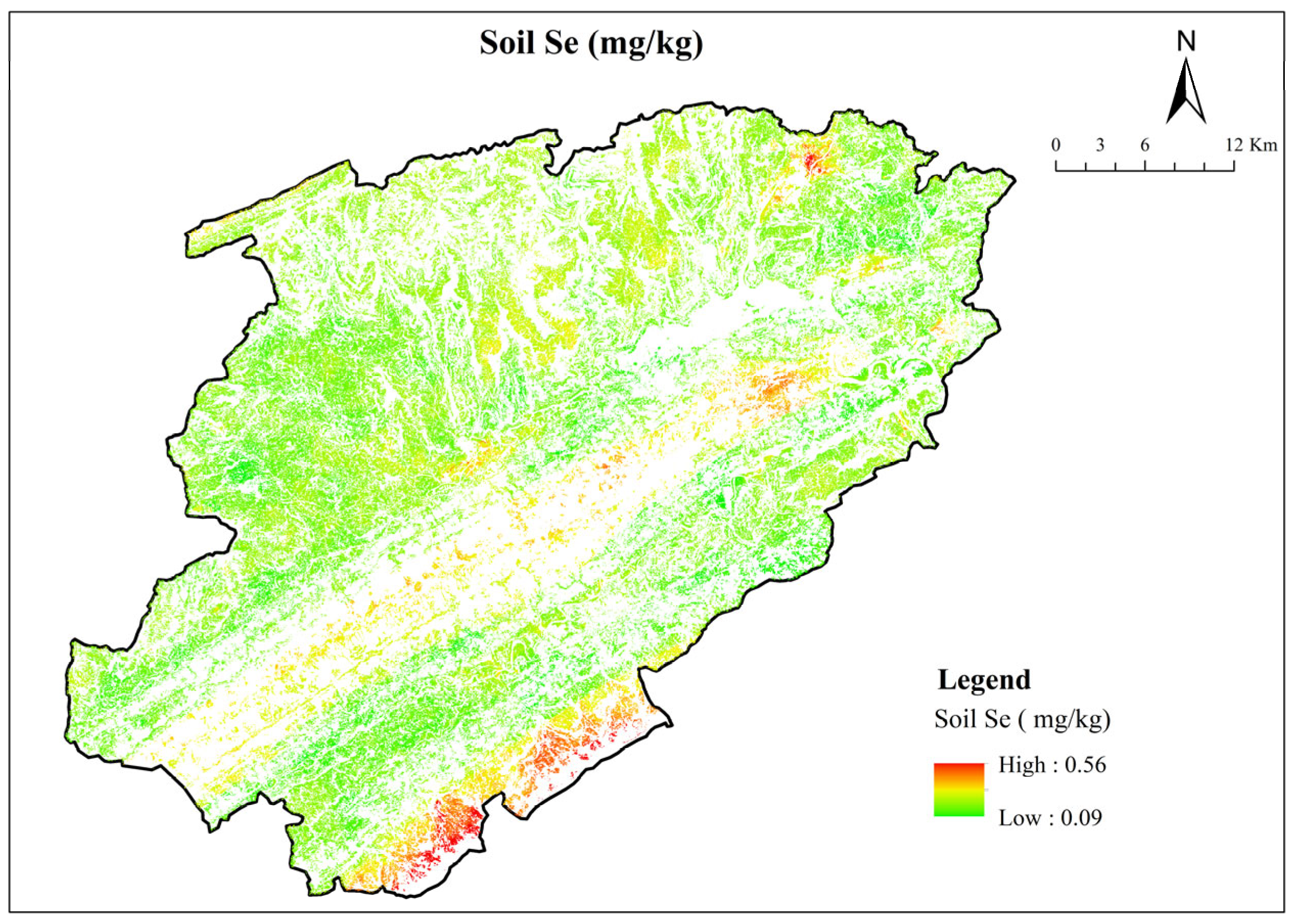
3.2. Spatial Distribution Characteristics of Soil Se
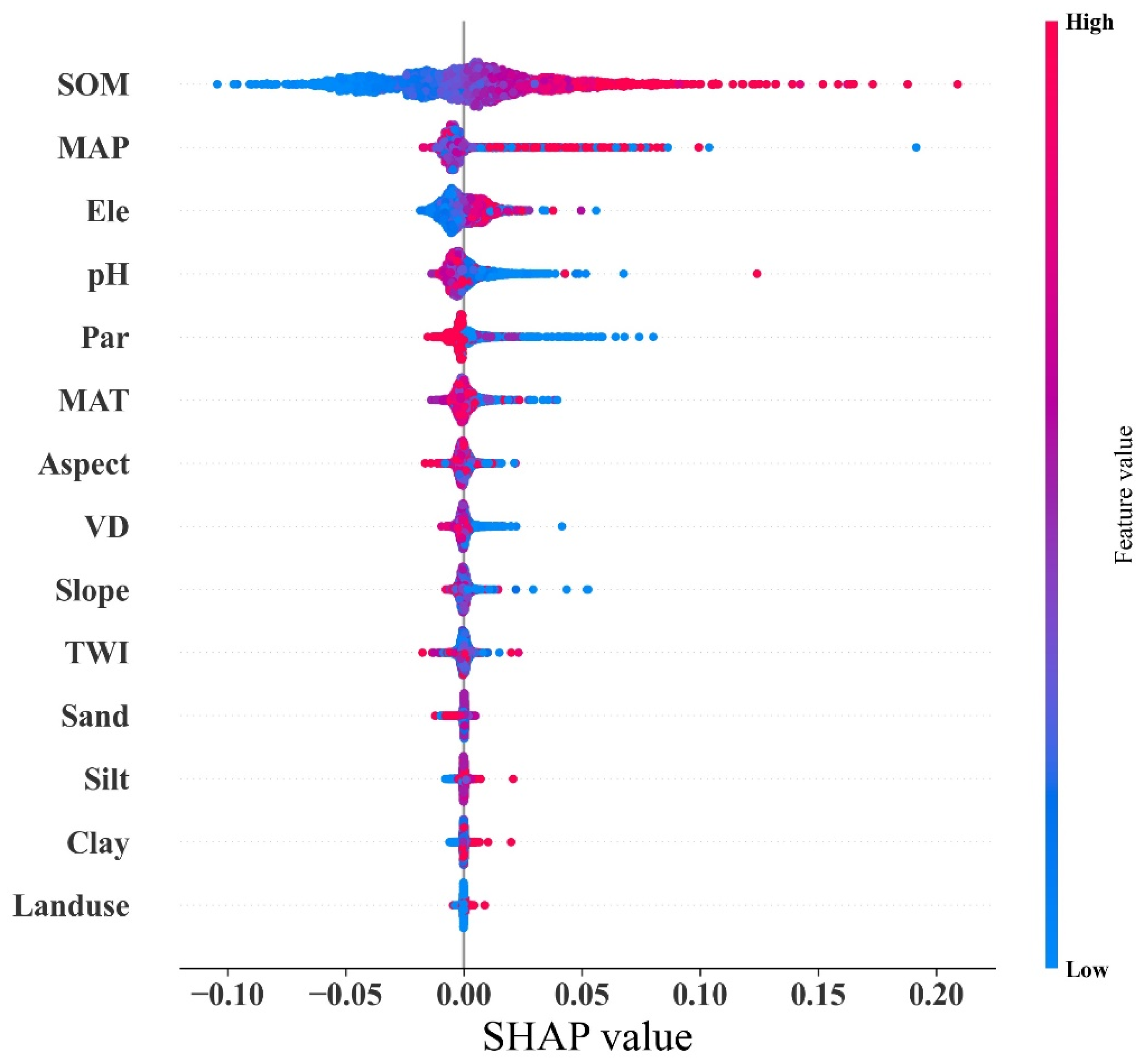
3.3. Control Factors for Soil Se Content
4. Discussion
4.1. Se Content in Surface Soil
4.2. Spatial Distribution Characteristics of Soil Se
4.3. Driving Factors of Se Content
4.3.1. Effect of SOM on Soil Se Content
4.3.2. Effect of MAP on Se Content
4.3.3. Land Use with Little Influence on Soil Se
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dinh, Q.T.; Cui, Z.; Huang, J.; Tran, T.A.T.; Wang, D.; Yang, W. Selenium Distribution in the Chinese Environment and Its Relationship with Human Health: A Review. Environ. Int. 2018, 112, 294–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roman, M.; Jitaru, P.; Barbante, C. Selenium Biochemistry and Its Role for Human Health. Metallomics 2014, 6, 25–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kieliszek, M.; Błazejak, S. Current Knowledge on the Importance of Selenium in Food for Living Organisms: A Review. Molecules 2016, 21, 609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hawkes, W.C.; Turek, P.J. Effects of Dietary Selenium on Sperm Motility in Healthy Men. J. Androl. 2001, 22, 764–772. [Google Scholar]
- Selinus, O.; Alloway, B.; Centeno, J.A.; Finkelman, R.B.; Fuge, R. Essentials of Medical Geology: Revised Edition; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; ISBN 9789400743755. [Google Scholar]
- Bajaj, M.; Eiche, E.; Neumann, T.; Winter, J.; Gallert, C. Hazardous Concentrations of Selenium in Soil and Groundwater in North-West India. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 189, 640–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartikainen, H. Biogeochemistry of Selenium and Its Impact on Food Chain Quality and Human Health. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2005, 18, 309–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, V.K.; McDonald, T.J.; Sohn, M.; Anquandah, G.A.K.; Pettine, M.; Zboril, R. Biogeochemistry of Selenium. A Review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2015, 13, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haug, A.; Graham, R.D.; Christophersen, O.A.; Lyons, G.H. How to Use the World’s Scarce Selenium Resources Efficiently to Increase the Selenium Concentration in Food. Microb. Ecol. Health Dis. 2007, 19, 209–228. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, J.; Yang, J.; Wu, H.; Gao, J.; Tang, S.; Ma, S. Spatial Distribution and Environmental Impact Factors of Soil Selenium in Hainan Island, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 811, 151329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Yang, B.; Xu, K.; Zheng, D.; Tian, J. Distribution of Se in the Rocks, Soil, Water and Crops in Enshi County, China. Appl. Geochem. 2020, 122, 104707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, J.; Gao, J.; Fu, Y.; Tang, S.; Cai, Y.; Yang, J.; Wu, H.; Ma, S. Vertical Distribution and Major Influencing Factors of Soil Selenium in Tropical Climate: A Case Study of Chengmai County, Hainan Island. Chemosphere 2023, 312, 137207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, W.; Cicchella, D.; Liu, T.; Yang, S.; Zhou, Y.; Hu, B. Origin, Distribution and Enrichment of Selenium in Oasis Farmland of Aksu, Xinjiang, China. J. Geochem. Explor. 2021, 223, 106723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, T.; Cui, G.; Su, X.; He, J.; Tong, S.; Liu, Y. The Origin of Soil Selenium in a Typical Agricultural Area in Hamatong River Basin, Sanjiang Plain, China. Catena 2020, 185, 104355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nascimento, C.W.A.D.; Bruno Viera da Silva, F.; de Brito Fabricio Neta, A.; Miranda Biondi, C.; Aparecida da Silva Lins, S.; Bezerra de Almeida Júnior, A.; Preston, W. Geopedology-Climate Interactions Govern the Spatial Distribution of Selenium in Soils: A Case Study in Northeastern Brazil. Geoderma 2021, 399, 115119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blazina, T.; Sun, Y.; Voegelin, A.; Lenz, M.; Berg, M.; Winkel, L.H.E. Terrestrial Selenium Distribution in China Is Potentially Linked to Monsoonal Climate. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, G.X.; Meharg, A.A.; Li, G.; Chen, Z.; Yang, L.; Chen, S.C.; Zhu, Y.G. Distribution of Soil Selenium in China Is Potentially Controlled by Deposition and Volatilization? Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 20953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Y.; He, J.; Niu, X.; Song, T.; Fu, L.; Liu, K.; Bi, E. Selenium Distribution in Cultivated Argosols and Gleyosols of Dry and Paddy Lands: A Case Study in Sanjiang Plain, Northeast China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 836, 155528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Gao, Y. Biogeochemical Cycling of Selenium in Chinese Environments. Appl. Geochem. 2001, 16, 1345–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Tian, X.; Liu, R.; Liu, S.; Zuza, A.V. Key Driving Factors of Selenium-Enriched Soil in the Low-Se Geological Belt: A Case Study in Red Beds of Sichuan Basin, China. Catena 2021, 196, 104926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laik, R.; Kumara, B.H.; Pramanick, B.; Singh, S.K.; Nidhi; Alhomrani, M.; Gaber, A.; Hossain, A. Labile Soil Organic Matter Pools Are Influenced by 45 Years of Applied Farmyard Manure and Mineral Nitrogen in the Wheat—Pearl Millet Cropping System in the Subtropical Condition. Agronomy 2021, 11, 2190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, H.; Wang, L.; Liao, X.; Wang, J.; Kong, C. Effects of Topography and Soil Properties on Soil Selenium Distribution and Bioavailability (Phosphate Extraction): A Case Study in Yongjia County, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 633, 240–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, H.B.; Zhu, J.M.; Su, H. Selenium Fractions in Organic Matter from Se-Rich Soils and Weathered Stone Coal in Selenosis Areas of China. Chemosphere 2012, 86, 626–633. [Google Scholar]
- Supriatin, S.; Weng, L.; Comans, R.N.J. Selenium Speciation and Extractability in Dutch Agricultural Soils. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 532, 368–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Liang, D.; Peng, Q.; Cui, Z.; Huang, J.; Lin, Z. Interaction between Selenium and Soil Organic Matter and Its Impact on Soil Selenium Bioavailability: A Review. Geoderma 2017, 295, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolu, J.; Thiry, Y.; Bueno, M.; Jolivet, C.; Potin-Gautier, M.; Le Hécho, I. Distribution and Speciation of Ambient Selenium in Contrasted Soils, from Mineral to Organic Rich. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 479–480, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, K.; Tang, J.; Chen, H.; Li, D.; Liu, Y. Impact of Land Use/Land Cover Change on the Topsoil Selenium Concentration and Its Potential Bioavailability in a Karst Area of Southwest China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 708, 135201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, J.; Huang, K.; Liu, Y.; Yang, C.; Wang, Z. Global Reconstruction of Complex Network Topology via Structured Compressive Sensing. IEEE Syst. J. 2021, 15, 1959–1969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Xu, E.; Zhang, H. Complex Network and Redundancy Analysis of Spatial-Temporal Dynamic Changes and Driving Forces behind Changes in Oases within the Tarim Basin in Northwestern China. Catena 2021, 201, 105216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Hao, H.; Zhang, Z.; Mao, X.; Xu, J.; Lv, Y.; Chen, W.; Ge, D. A Field Study to Estimate Heavy Metal Concentrations in a Soil-Rice System: Application of Graph Neural Networks. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 832, 155099. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, L.; Wang, L.; Liang, T.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Xiao, J.; Dong, L.; Zhang, H. Geostatistical Analyses and Co-Occurrence Correlations of Heavy Metals Distribution with Various Types of Land Use within a Watershed in Eastern QingHai-Tibet Plateau, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 653, 849–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, J.; Li, B. Determining the Influence Factors of Soil Organic Carbon Stock in Opencast Coal-Mine Dumps Based on Complex Network Theory. Catena 2019, 173, 433–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.; Shang, J.; Zhu, Q.; Ling, C.; Xie, W.; Qiang, B. RFRSF: Employee Turnover Prediction Based on Random Forests and Survival Analysis. In Proceedings of the 21st International Conference on Web Information Systems Engineering—WISE 2020, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 20–24 October 2020, Part II; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 503–515. [Google Scholar]
- Hengl, T.; Heuvelink, G.B.M.; Kempen, B.; Leenaars, J.G.B.; Walsh, M.G.; Shepherd, K.D.; Sila, A.; MacMillan, R.A.; De Jesus, J.M.; Tamene, L.; et al. Mapping Soil Properties of Africa at 250 m Resolution: Random Forests Significantly Improve Current Predictions. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0125814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, X.; Yu, K.; Deng, Y.; Liu, J.; Lai, Z. Spatial Variability of Soil Organic Carbon and Total Nitrogen in the Hilly Red Soil Region of Southern China. J. For. Res. 2020, 31, 2385–2394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeraatpisheh, M.; Ayoubi, S.; Jafari, A.; Tajik, S.; Finke, P. Digital Mapping of Soil Properties Using Multiple Machine Learning in a Semi-Arid Region, Central Iran. Geoderma 2019, 338, 445–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, D.; Su, B.; Shao, S.; Yang, J.; Fan, M.; Wu, J.; Gao, C. Distribution and Determinants of Organic Carbon and Available Nutrients in Tropical Paddy Soils Revealed by High–Resolution Sampling. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2021, 320, 107580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundberg, S.M.; Lee, S.I. A Unified Approach to Interpreting Model Predictions. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2017, 30, 4766–4775. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Wu, W.; Liu, H. Exploring the Influencing Factors in Identifying Soil Texture Classes Using Multitemporal Landsat-8 and Sentinel-2 Data. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Huang, K.; Zhang, K.; Weng, Q.; Zhang, H.; Wang, F. Predicting Heavy Metal Adsorption on Soil with Machine Learning and Mapping Global Distribution of Soil Adsorption Capacities. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 14316–14328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.; Zhu, W.; Wang, W.; Li, R.; Hou, S.; Wang, D.; Yang, L. Selenium in Soil and Endemic Diseases in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2002, 284, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faithfull, N.T. Methods in Agricultural Chemical Analysis: A Practical Handbook; CABI: Wallingford, UK, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Nelson, D.W.A.; Sommers, L. Total Carbon, Organic Carbon, and Organic Matter. In Methods of Soil Analysis: Part 2 Chemical and Microbiological Properties; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1983; Volume 9, pp. 539–579. [Google Scholar]
- Jenny, H. Factors of Soil Formation: A System of Quantitative Pedology; Courier Corporation: North Chelmsford, MA, USA, 1994; ISBN 0486681289. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.C.; Wan, H.S.; Zhou, M.H.; Wu, W.; Liu, H. bin Soil Total and Organic Carbon Mapping and Uncertainty Analysis Using Machine Learning Techniques. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 143, 109420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, G.W.; Dai, Y.; Liu, B.; Ye, A.; Yuan, H. A Soil Particle-Size Distribution Dataset for Regional Land and Climate Modelling in China. Geoderma 2012, 171–172, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiefelsdog, M. The Saddlepoint Approximation of Moran’s I and Local Moran’s Ii’s Reference Distribution and Their Numerical Evaluation. Geogr. Anal. 2002, 34, 187–206. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, W.; Zhao, K.; Zhang, C.; Wu, J.; Tunney, H. Outlier Identification of Soil Phosphorus and Its Implication for Spatial Structure Modeling. Precis. Agric. 2016, 17, 121–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Tang, Y.; Luo, L.; Xu, W. Outlier Identification and Visualization for Pb Concentrations in Urban Soils and Its Implications for Identification of Potential Contaminated Land. Environ. Pollut. 2009, 157, 3083–3090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anselin, L. Local Indicators of Spatial Association—LISA. Geogr. Anal. 1995, 27, 93–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, W.C.; Wu, W.; Liu, H. Bin Horizontal and Vertical Variation of Soil Clay Content and Its Controlling Factors in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 864, 161141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, L.I.-K. A Concordance Correlation Coefficient to Evaluate Reproducibility. Biometrics 1989, 45, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, K.; Hu, M.; Weng, Q.; Zhang, H. Spatial Heterogeneity Modeling of Water Quality Based on Random Forest Regression and Model Interpretation. Environ. Res. 2021, 202, 111660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, L.; Dai, Q.; Song, C.; Liu, B.; Guo, F.; Dai, T. Revealing Drivers of Haze Pollution by Explainable Machine Learning. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2022, 9, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shand, C.A.; Eriksson, J.; Dahlin, A.S.; Lumsdon, D.G. Selenium Concentrations in National Inventory Soils from Scotland and Sweden and Their Relationship with Geochemical Factors. J. Geochem. Explor. 2012, 121, 4–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, H.; Kamada, A.; Usuki, M.; Yanai, J. Total Selenium Content of Agricultural Soils in Japan. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2009, 55, 616–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Soil Survey Office. Soil Species of China; China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 1998; pp. 318–336. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, G.D.; Droz, B.; Greve, P.; Gottschalk, P.; Poffet, D. Selenium Deficiency Risk Predicted to Increase under Future Climate Change. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 2848–2853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roulier, M.; Bueno, M.; Coppin, F.; Nicolas, M.; Thiry, Y.; Rigal, F.; Le Hécho, I.; Pannier, F. Atmospheric Iodine, Selenium and Caesium Depositions in France: I. Spatial and Seasonal Variations. Chemosphere 2021, 273, 128971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, H.; Carignan, J. Ocean to Continent Transfer of Atmospheric Se as Revealed by Epiphytic Lichens. Environ. Pollut. 2009, 157, 2790–2797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, S.; Xia, Y.; Hu, Y.; Chen, X.; Rui, Y. Stoichiometry of Carbon, Nitrogen, and Phosphorus in Soil: Effects of Agricultural Land Use and Climate at a Continental Scale. Soil Tillage Res. 2021, 209, 104903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Environmental Factors | Type a | Resolution (m) or Scale | Source | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Topography | Elevation | NF | 30 | DEM e (https://www.usgs.gov/, accessed on 17 May 2022) |
| Valley depth (VD) | NF | 30 | DEM | |
| Aspect | NF | 30 | DEM | |
| Slope | NF | 30 | DEM | |
| Topographic wetness index (TWI) | NF | 30 | DEM | |
| Climate | Mean annual precipitation (MAP) | NF | 1000 | WorldClim dataset (https://www.worldclim.org/, accessed on 8 May 2022) |
| Mean annual temperature (MAT) | NF | 1000 | WorldClim database | |
| Soil properties | Soil pH (pH) | NF | - | Laboratory analysis |
| Soil organic matter (SOM) | NF | - | Laboratory analysis | |
| Soil texture b | NF | 1000 | The “soil particle size distribution in China” dataset | |
| Others | Land use c | CF | 1:10,000 | Land use map |
| Parent material d | CF | 1:250,000 | Geological map | |
| Environmental Factors | Minimum | Maximum | Mean | CV(%) | Skew | Kurtosis | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Topography | Elevation (m) | 154 | 1278 | 470 | 50.59 | 0.59 | −0.71 |
| VD (m) | 0 | 520 | 116 | 70.41 | 0.80 | 0.62 | |
| Aspect (°) | 0 | 360 | 190 | 53.71 | −0.08 | −1.12 | |
| Slope (°) | 0 | 54.75 | 11.34 | 60.94 | −0.87 | 0.95 | |
| TWI | 3.49 | 25.23 | 7.67 | 40.82 | 1.95 | 4.56 | |
| Climate | MAP (mm) | 1203 | 1292 | 1244 | 1.25 | 0.30 | 0.19 |
| MAT (°) | 13.25 | 18.17 | 16.85 | 6.12 | −0.83 | −0.30 | |
| Soil properties | Soil pH | 3.98 | 8.55 | 6.05 | 16.90 | 0.56 | −0.63 |
| SOM (g/kg) | 2.59 | 45.74 | 16.44 | 43.03 | 0.78 | 0.41 | |
| Silt (%) | 29.67 | 57.90 | 45.94 | 12.00 | −0.80 | 0.63 | |
| Sand (%) | 16.11 | 50.11 | 32.08 | 27.48 | 0.36 | −0.71 | |
| Clay (%) | 17.00 | 31.40 | 21.98 | 18.90 | 0.68 | −1.02 | |
| T3xj (n = 63) | J1sn (n = 866) | J3zl (n = 131) | J2s (n = 1744) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.23 ± 0.08 b | 0.18 ± 0.05 c | 0.29 ± 0.09 a | 0.16 ± 0.06 c |
| Paddy Field (n = 1810) | Dry Land (n = 994) |
|---|---|
| 0.17 ± 0.06 b | 0.18 ± 0.07 a |
| Item | Factor | Sum of Squares | df | Mean Square | F | Sig |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Se | SOM and Par | 0.90 | 287 | 0.003 | 1.54 | 0.000 ** |
| SOM and pH | 4.9 | 2104 | 0.002 | 0.94 | 0.672 | |
| SOM and Ele | 3.81 | 1758 | 0.002 | 0.77 | 0.919 | |
| MAP and Par | 0.57 | 93 | 0.006 | 2.20 | 0.000 ** | |
| MAP and pH | 6.62 | 2063 | 0.003 | 0.92 | 0.817 | |
| MAP and Ele | 5.26 | 1729 | 0.003 | 1.17 | 0.072 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wan, H.-S.; Zhang, W.-C.; Wu, W.; Liu, H.-B. The Controlling Factors of Soil Selenium Content in a Selenium-Deficient Area in Southwest China. Agronomy 2023, 13, 1031. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13041031
Wan H-S, Zhang W-C, Wu W, Liu H-B. The Controlling Factors of Soil Selenium Content in a Selenium-Deficient Area in Southwest China. Agronomy. 2023; 13(4):1031. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13041031
Chicago/Turabian StyleWan, He-Shuang, Wei-Chun Zhang, Wei Wu, and Hong-Bin Liu. 2023. "The Controlling Factors of Soil Selenium Content in a Selenium-Deficient Area in Southwest China" Agronomy 13, no. 4: 1031. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13041031
APA StyleWan, H.-S., Zhang, W.-C., Wu, W., & Liu, H.-B. (2023). The Controlling Factors of Soil Selenium Content in a Selenium-Deficient Area in Southwest China. Agronomy, 13(4), 1031. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13041031






