Identification, Characterization, and Growth-Promoting Effects of Bacterial Endophytes Isolated from Okra (Abelmoschus esculentus L.)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection and Isolation of Endophytic Bacteria
2.2. Identification of Endophytic Bacteria
2.3. Characterization of Endophytic Bacteria
2.4. Effect of Inoculation on Plant Growth Promotion
2.5. Colonization of Endophytes in Okra Plant
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Isolation and Identification of Endophytic Bacteria
3.2. Selection and Characterization of Isolated Endophytic Bacteria
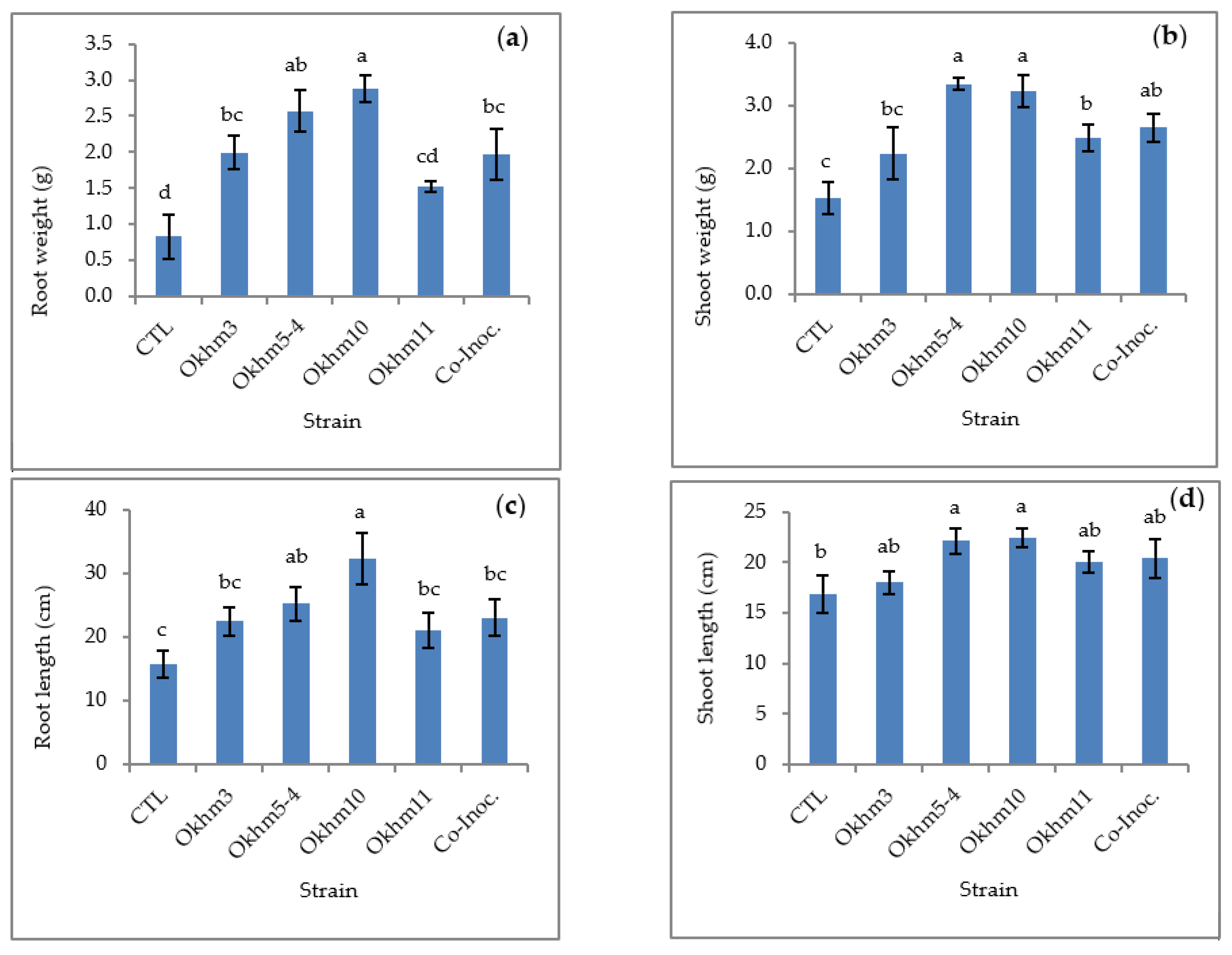
3.3. Effect of Plant Growth Promotion of Isolated Strains in Okra Plant
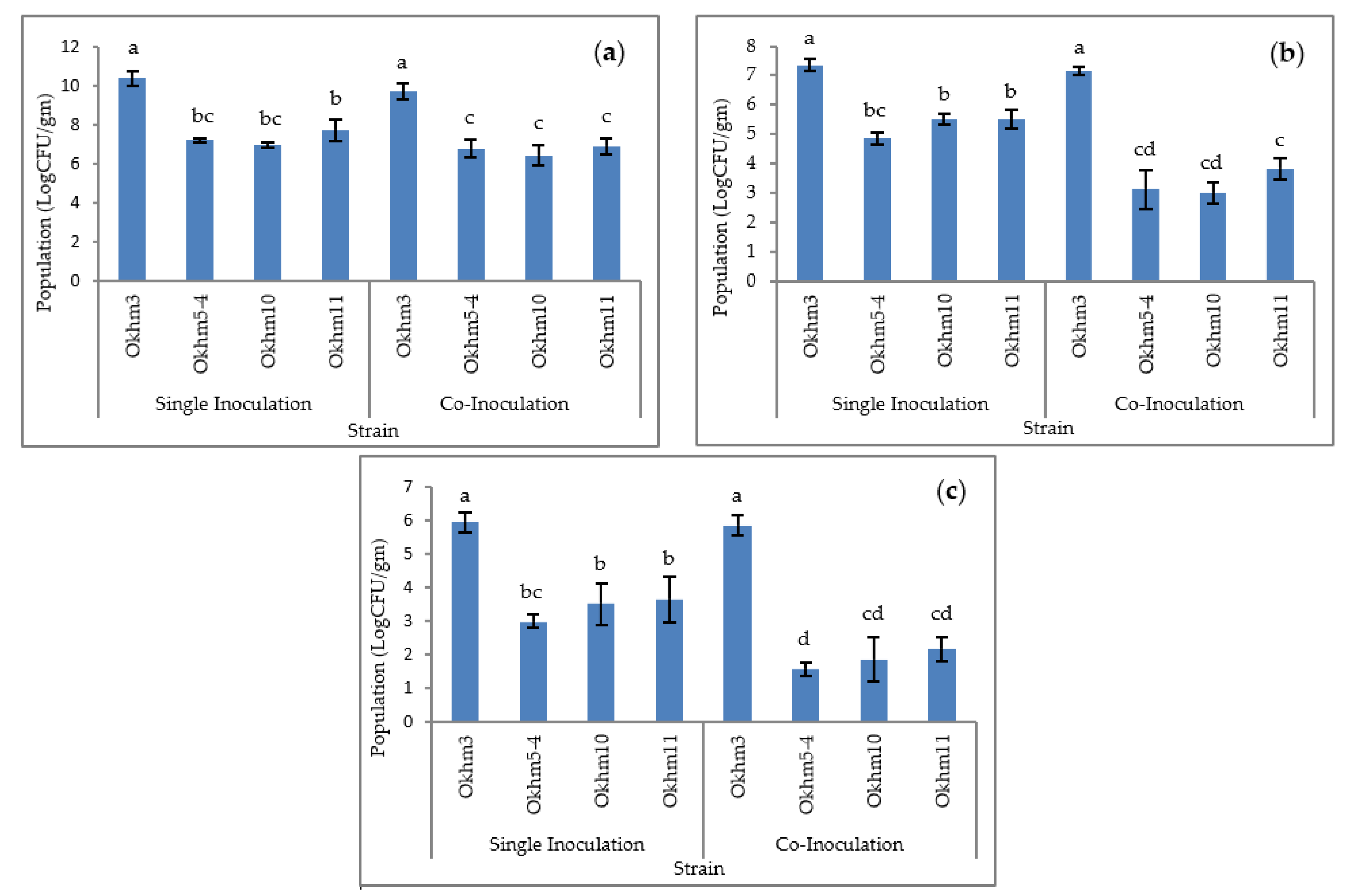
3.4. Effect of Colonization of Isolated Strains in Okra Plant
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tilman, D.; Balzer, C.; Hill, J.; Befort, B.L. Global food demand and the sustainable intensification of agriculture. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 20260–20264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitchell, C.; Hunter, R.G.; Smith, M.E.; Schipanski, L.W.; Atwood, D.A.M. Agriculture in 2050: Recalibrating targets for sustainable intensification. BioScience 2017, 67, 386–391. [Google Scholar]
- Adesemoye, A.O.; Torbert, H.A.; Kloepper, J.W. Plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria allow reduced application rates of chemical fertilizers. Microb. Ecol. 2009, 58, 921–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, W.; Lin, M.; Zhou, H.; Wu, H.; Li, Z.; Lin, W. The effects of chemical and organic fertilizer usage on rhizosphere soil in tea orchards. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0217018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, L.F.O.; Hower, J.C.; Izquierdo, M.; Querol, X. Complex nanominerals and ultrafine particles assemblages in phosphogypsum of the fertilizer industry and implications on human exposure. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 5117–5122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atılgan, A.; Coşkan, A.; Saltuk, B.; Erkan, V.M. Antalya yöresindeki seralarda kimyasal ve organik gübre kullanım düzeyleri ve olası çevre etkileri. Ekoloji 2007, 15, 37–47. [Google Scholar]
- Ashrafuzzaman, M.; Hossen, F.A.; Ismail, M.R.; Hoque, M.A.; Islam, M.Z.; Shahidullah, S.M.; Meon, S. Efficiency of plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR) for the enhancement of rice growth. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2009, 8, 1247–1252. [Google Scholar]
- Kaymak, H.C. Potential of PGPR in agricultural innovations. In Plant Growth and Health Promoting Bacteria; Maheshwari, D., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; Volume 18, pp. 45–79. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, S.; Reddy, C.; Phogat, M.; Korav, S. Role of bio-fertilizers towards sustainable agricultural development: A review. J. Pharm. Phytochem. 2018, 7, 1915–1921. [Google Scholar]
- Nosratabad, A.R.F.; Etesami, H.; Shariati, S. Integrated use of organic fertilizer and bacterial inoculant improves phosphorus use efficiency in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) fertilized with triple superphosphate. Rhizosphere 2017, 3, 109–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawwam, G.E.; Elbeltagy, A.; Emara, H.M.; Abbas, I.H.; Hassan, M.M. Beneficial effect of plant growth promoting bacteria isolated from the roots of potato plant. Annal. Agric. Sci. 2013, 58, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ALKahtani, M.D.F.; Attia, K.A.; Hafez, Y.M.; Khan, N.; Eid, A.M.; Ali, M.A.M.; Abdelaal, K.A.A. Chlorophyll fluorescence parameters and antioxidant defense system can display salt tolerance of salt acclimated sweet pepper plants treated with chitosan and plant growth promoting rhizobacteria. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ALKahtani, M.D.F.; Fouda, A.; Attia, K.A.; Al-Otaibi, F.; Eid, A.M.; Ewais, E.E.-D.; Hijri, M.; St-Arnaud, M.; Hassan, S.E.-D.; Khan, N.; et al. Isolation and characterization of plant growth promoting endophytic bacteria from desert plants and their application as bioinoculants for sustainable agriculture. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitter, E.K.; Tosi, M.; Obregón, D.; Dunfield, K.E.; Germida, J.J. Rethinking crop nutrition in times of modern microbiology: Innovative Biofertilizer Technologies. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2021, 5, 606815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadeem, S.M.; Ahmad, M.; Zahir, Z.A.; Javaid, A.; Ashraf, M. The role of mycorrhizae and plant growth promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR) in improving crop productivity under stressful environments. Biotechnol. Adv. 2014, 32, 429–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glick, B.R. The enhancement of plant growth by free living bacteria. Can. J. Microbiol. 1995, 41, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Maurya, B.R.; Raghuwanshi, R. Isolation and characterization of PGPR and their effect on growth, yield and nutrient content in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2014, 3, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cakmakci, R.; Dönmez, F.; Aydın, A.; Şahin, F. Growth promotion of plants by plant growth- promoting rhizobacteria under greenhouse and two different field soil conditions. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2006, 38, 1482–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelaal, K.; AlKahtani, M.; Attia, K.; Hafez, Y.; Király, L.; Künstler, A. The role of plant growth-promoting bacteria in alleviating the adverse effects of drought on plants. Biology 2021, 10, 520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ALKahtani, M.; Hafez, Y.; Attia, K.; Al-Ateeq, T.; Ali, M.A.M.; Hasanuzzaman, M.; Abdelaal, K. Bacillus thuringiensis and silicon modulate antioxidant metabolism and improve the physiological traits to confer salt tolerance in lettuce. Plants 2021, 10, 1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babalola, O.O.; Sanni, A.I.; Odhiambo, G.D.; Torto, B. Plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria do not pose any deleterious effect on cowpea and detectable amounts of ethylene are produced. World J. Microbiol. Biotech. 2006, 23, 747–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadegari, M.; Rahmani, H.A.; Noormohammadi, G.; Ayneband, A. Evaluation of bean (Phaseolus vulgaris) seeds inoculation with Rhizobium phaseoli and plant growth promoting rhizobacteria on yield and yield components. Pak. J. Biol. Sci. 2008, 15, 1935–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallmann, J.; Quadt-Hallmann, A.; Mahaffee, W.F.; Kloepper, J.W. Bacterial endophytes in agricultural crops. Can. J. Microbiol. 1997, 43, 895–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenblueth, M.; Martínez-Romero, E. Bacterial endophytes and their interactions with hosts. Am. Phytopathol. Soc. 2006, 19, 827–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryan, R.P.; Germaine, K.; Franks, A.; Ryan, D.J.; Dowling, D.N. Bacterial endophytes: Recent developments and applications. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2008, 278, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhungana, S.A.; Itoh, K. Effects of co-inoculation of indole-3-acetic acid-producing and -degrading bacterial endophytes on plant growth. Horticulturae 2019, 5, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehin, A.; Puri, R.R.; Hafiz, M.H.R.; Itoh, K. Effect of co-inoculation of bacillus sp. strain with bacterial endophytes on plant growth and colonization in tomato plant (Solanum lycopersicum). Microbiol. Res. 2021, 12, 480–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Sullivan, D.J.; O’Gara, F. Traits of fluorescent Pseudomonas spp. involved in suppression of plant root pathogens. Microbiol. Rev. 1992, 56, 662–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.S.; Gao, J.; Chen, X.; Zhang, M.; Yang, F.; Du, Y.; Moe, T.S.; Munir, I.; Xue, J.; Zhang, X. Isolation and characterization of plant growth-promoting endophytic bacteria Paenibacillus polymyxa SK1 from Lilium lancifolium. BioMed Res. Int. 2020, 2020, 8650957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobson, C.B.; Pasternak, J.J.; Glick, B.R. Partial purification and characterization of 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate deaminase from the plant growth promoting rhizobacterium Pseudomonas putida GR 12–2. Can. J. Microbiol. 1994, 40, 1019–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamalero, E.; Glick, B.R. Plant ethylene modulation by beneficial bacteria. Plant Physiol. 2015, 169, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terakado-Tonooka, J.; Fujihara, S.; Ohwaki, Y. Possible contribution of Bradyrhizobium on nitrogen fixation in sweet potatoes. Plant Soil. 2013, 367, 639–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.A.; Hafiz, M.H.R.; Salehin, A.; Hayashi, S.; Itoh, K. NifH gene analysis of endophytic bacteria of sweet potato under various climatic locations. Res. J. Biotech. 2022, 17, 90–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bangera, M.G.; Thomashow, L.S. Characterization of a genomic locus required for synthesis of the antibiotic 2, 4-diacetylphloroglucinol by the biological control agent Pseudomonas fluorescens Q2–87. Mol. Plant Microbe. Interact. 1996, 9, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Liu, Z. A review of plant antipathogenic constituents: Source, activity and mechanism. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2022, 188, 105225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benhamou, N.; Kloepper, J.W.; Quadt-Hallman, A.; Tuzun, S. Induction of defence related ultrastructural modifications in pea root tissues inoculated with endophytic bacteria. Plant Physiol. 1996, 112, 919–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grichko, V.; Glick, B. Amelioration of flooding stress by ACC deaminase-containing plant growth-promoting bacteria. Plant Physiol. Biotechnol. 2001, 39, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, P.; Sutar, S.; Malik, S.K.; John, J.; Yadav, S.; Bhat, K.V. Numerical taxonomy of Abelmoschus Medik. (Malvaceae) in India. Bangladesh J. Plant Taxon. 2015, 22, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kochhar, S.L. Okra (Lady’s finger). In Tropical Crops, a Textbook of Economic Botany; Kochhar, S.L., Ed.; Macmillan Publishers: London, UK, 1986; pp. 263–264. [Google Scholar]
- Benchasri, S. Okra (Abelmoschus esculentus (L.) Moench) as a valuable vegetable of the world. Ratar. Povrt. 2012, 49, 105–112. [Google Scholar]
- Mkhabela, S.S.; Shimelis, H.; Gerrano, A.S.; Mashilo, J. Phenotypic and genotypic divergence in Okra (Abelmoschus esculentus (L.) Moench) and implications for drought tolerance breeding: A review. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2022, 145, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bawa, S.H.; Badrie, N. Nutrient profile, bioactive components, and functional properties of okra (Abelmoschus esculentus (L.) Moench). In Fruit, Vegetables, and Herbs: Bioactive Foods in Health Promotion; Watson, R.R., Preedy, V.R., Eds.; Academic Press: London, UK, 2016; pp. 365–409. [Google Scholar]
- Onakpa, M. Ethnomedicinal, phytochemical and pharmacological profile of genus Abelmoschus. Phytopharmacology 2013, 4, 648–669. [Google Scholar]
- Premalatha, R.; Vijayaraghavan, R. Isolation and characterization of plant growth promoting bacterial endophytes and their effect on okra (Abelmoschus esculentus L.) seedling growth. Bull. Env. Pharmacol. Life Sci. 2020, 9, 60–64. [Google Scholar]
- Vimal, S.R.; Singh, A.K.; Singh, J.S. Influence of Pseudomonas spp. on okra (Abelomuscus esculantaus L.) growth parameters and antioxidant activities under soil salinity. Microbiol. Res. 2020, 11, 8443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakria, M.; Udonishi, K.; Ogawa, T.; Yamamoto, A.; Saeki, Y.; Akao, S. Influence of inoculation technique on the endophytic colonization of rice by Pantoea sp. isolated from sweet potato and by Enterobacter sp. isolated from sugarcane. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2008, 54, 224–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina-Romero, D.; Baez, A.; Quintero-Hernández, V.; Castañeda-Lucio, M.; Fuentes-Ramírez, L.E.; del Rocio Bustillos-Cristales, M.; Rodríguez-Andrade, O.; Morales-García, Y.E.; Munive, A.; Muñoz-Rojas, J. Compatible bacterial mixture, tolerant to desiccation, improves maize plant growth. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0187913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marimuthu, S.; Subbian, P.; Ramamoorthy, V.; Samiyappan, R. Synergistic effect of combined application of Azospirillum and Pseudomonas fluorescens with inorganic fertilizers on root rot incidence and yield of cotton. J. Plant Dis. Prot. 2002, 109, 569–577. [Google Scholar]
- Amara, M.A.T.; Dahdoh, M.S.A. Effect of inoculation with plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR) on yield and uptake of nutrients by wheat grown on sandy soil. Egypt. J. Soil Sci. 1997, 37, 467–484. [Google Scholar]
- Puri, R.R.; Dangi, S.; Dhungana, S.A.; Itoh, K. Diversity and plant growth promoting ability of culturable endophytic bacteria in Nepalese sweet potato. Ad. Microbiol. 2018, 8, 734–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehin, A.; Hafiz, M.H.R.; Hayashi, S.; Adachi, F.; Itoh, K. Effects of the biofertilizer OYK (Bacillus sp.) inoculation on endophytic microbial community in sweet potato. Horticulturae 2020, 6, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, J.C.; Ladha, J.K.; Dazzo, F.B. Rhizobia inoculation improves nutrient uptake and growth of lowland rice. Soil Sci. Soc. 2000, 64, 1644–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asghar, H.N.; Zahir, Z.A.; Arshad, M.; Khaliq, A. Relationship between production of auxins by rhizobacteria and their growth promoting activities in Brassica juncea. L. Bio. Fertil. Soil. 2002, 35, 231–237. [Google Scholar]
- Vestberg, M.; Kukkonen, S.; Saari, K.; Prikka, P.; Huttunen, J.; Tainio, L.; Devos, N.; Weekers, F.; Kevers, C.; Thonart, P.; et al. Microbial inoculation for improving the growth and health of micropropagated strawberry. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2004, 27, 243–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, A.L.M.; Stoffels, M.; Schmid, M.; Reis, V.M.; Baldani, J.I.; Hartmann, A. Colonization of sugarcane plantlets by mixed inoculations with diazotrophic bacteria. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2008, 45, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felici, C.; Vettori, L.; Giraldi, E.; Forino, L.M.C.; Toffanin, A.; Tagliasacchi, A.M.; Nuti, M. Single and co-inoculation of Bacillus subtilis and Azospirillum brasilense on Lycopersicon esculentum: Effects on plant growth and rhizosphere microbial community. Appl. Soil. Ecol. 2008, 40, 260–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincent, J.M. A manual for practical study of root nodule bacteria. In IBP Handbook No. 15; Blackwell Scientific Publishers: Oxford, UK, 1970; p. 164. [Google Scholar]
- Minamisawa, K.; Isawa, T.; Nakatsuka, Y.; Ichikawa, N. New Bradyrhizobium japonicum strains that possess high copy numbers of the repeated sequence RS alpha. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1998, 64, 1845–1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weisburg, W.G.; Barns, S.M.; Pelletier, D.A.; Lane, D.J. 16S ribosomal DNA amplification for phylogenetic study. J. Bacteriol. 1991, 173, 697–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altschul, S.F.; Madden, T.L.; Schäffer, A.A.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Miller, W.; Lipman, D.J. Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: A new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997, 25, 3389–3402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larkin, M.A.; Blackshields, G.; Brown, N.P.; Chenna, R.; McGettigan, P.A.; McWilliam, H.; Valentin, F.; Wallace, I.M.; Wilm, A.; Lopez, R.; et al. Clustal W and Clustal X version 2. Bioinformatics 2007, 23, 2947–2948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Tamura, K. MEGA7: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, S.A.; Weber, R.A. Colorimetric estimation of indoleacetic acid. Plant Physiol. 1951, 26, 192–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pikovskaya, R. Mobilization of phosphorus in soil in connection with vital activity of some microbial species. Mikrobiologiya 1948, 17, 362–370. [Google Scholar]
- Someya, T. Counting methods of aerobic cellulose decomposers in paddy soils. Rep. Inst. Agric. Res. Tohoku Univ. 1980, 31, 43–58. [Google Scholar]
- Suyama, K.; Yamamoto, H.; Naganawa, T.; Iwata, T.; Komada, H. A plate count method for aerobic cellulose decomposers in soil by congo red staining. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 1993, 39, 361–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Rajkumar, M.; Luo, Y.M.; Freitas, H. Inoculation of endophytic bacteria on host and non-host plants-effects on plant growth and Ni uptake. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 195, 230–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poly, F.; Monrozier, L.J.; Bally, R. Improvement in the RFLP procedure for studying the diversity of nifH genes in communities of nitrogen fixers in soil. Res. Microbiol. 2001, 152, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dworkin, M.; Foster, J. Experiments with some microorganisms which utilize ethane and hydrogen. J. Bacteriol. 1958, 75, 592–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonard, L.T. A simple assembly for use in the testing of cultures of rhizobia. J. Bacteriol. 1943, 45, 523–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoagland, D.R.; Arnon, D.I. The water-culture method for growing plants without soil. Calif. Agric. Exp. Stn. Circ. 1950, 347, 1–32. [Google Scholar]
- Kalavati, P.; Sharma, M.C.; Modi, H.A. Growth promoting effect of potassium solubilizing microorganisms on okra (Abelmoscus Esculantus). Inter. J. Agric. Sci. Res. 2013, 3, 181–188. [Google Scholar]
- Gaiero, J.R.; McCall, C.A.; Thompson, K.A.; Day, N.J.; Best, A.S.; Dunfield, K.E. Inside the root microbiome: Bacterial root endophytes and plant growth promotion. Am. J. Bot. 2013, 100, 1738–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlAli, H.A.; Khalifa, A.; Almalki, M. Plant growth-promoting bacterium from non-agricultural soil improves okra plant growth. Agriculture 2022, 12, 873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anwar, H.; Wang, X.; Hussain, A.; Rafay, M.; Ahmad, M.; Latif, M.; Jamshaid, M.U.; Khalid, I.; Dar, A.; Mustafa, A. Comparative effects of bio-wastes in combination with plant growth-promoting bacteria on growth and productivity of okra. Agronomy 2021, 11, 2065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, S.H.; Gururani, M.A.; Chun, S.C. Isolation and characterization of plant growth promoting endophytic diazotrophic bacteria from korean rice cultivars. Microbiol. Res. 2014, 169, 83–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eleiwa, M.E.; Hamed, E.R.; Shehata, H.S. The role of biofertilizers and/or some micronutrients on wheat plant (Triticum aestivum L.) growth in newly reclaimed soil. J. Med. Plants Res. 2012, 6, 3359–3369. [Google Scholar]
- Egamberdieva, D. Indole-acetic acid production by root associated bacteria and its role in plant growth and development. In Auxins: Structure, Biosynthesis and Functions; Keller, A.H., Fallon, M.D., Eds.; Nova Science Publishers Inc.: Hauppauge, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 103–122. [Google Scholar]
- Dias, A.C.F.; Costa, F.E.C.; Andreote, F.D.; Lacava, P.T.; Teixeira, M.A.; Assumpcao, L.C.; Araujo, W.L.; Azevedo, J.L.; Melo, I.S. Isolation of Micropropagated strawberry endophytic bacteria and assessment of their potential for plant growth promotion. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2009, 25, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patten, C.L.; Glick, B.R. Role of Pseudomonas putida indoleacetic in development of the host plant root system. Appl. Environ. Microbial. 2002, 68, 3795–3801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, M.; Sheng, J.; Chen, L.; Men, Y.; Gan, L.; Guo, S.; Shen, L. Bacterial community compositions of tomato (Lycopersicum esculentum Mill.) seeds and plant growth promoting activity of ACC deaminase producing Bacillus subtilis (HYT-12-1) on tomato seedlings. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 30, 835–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahadir, P.S.; Liaqat, F.; Eltem, R. Plant growth promoting properties of phosphate solubilizing Bacillus species isolated from the Aegean Region of Turkey. Turk. J. Bot. 2018, 42, 183–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plazinski, J.; Rolfe, B.G. Analysis of the pectolytic activity of Rhizobium and Azospirillum strains isolated Trifoliumrepens. J. Plant Physiol. 1985, 120, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbamondi, G.R.; Tommonaro, G.; Weyens, N.; Thijs, S.; Sillen, W.; Gkorezis, P.; Iodice, C.; de Melo Rangel, W.; Nicolaus, B.; Vangronsveld, J. Plant growth-promoting effects of rhizospheric and endophytic bacteria associated with different tomato cultivars and new tomato hybrids. Chem. Biol. Technol. Agric. 2016, 3, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, M.E.; Burlingham, S.K. Production of plant growth substances by Azotobacter chroococcum. J. Gen. Microbiol. 1968, 53, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akiyoshi, D.E.; Refier, D.A.; Gordon, M.P. Cytokinin production by Agrobacterium and Pseudomonas spp. J. Bacteriol. 1987, 169, 4242–4248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, C.S.; Agostini, F.; Simon, A.M.; Whyte, J.; Townend, J.; Lifert, C.; Killham, K.; Mullins, C. Influence of soil type and pH on the colonization of sugar beet seedlings by antagonistic Pseudomonas and Bacillus strains, and on their control of Pythium damping-off. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2004, 110, 1025–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dandurand, L.; Knudsen, G. Influence of Pseudomonas fluorescens on hyphal growth and biocontrol activity of Trichoderma harzianum in the spermosphere and rhizosphere of pea. Phytopathology 1993, 83, 265–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, L.J.A.; Probanza, A.; Ramos, B.; Barriuso, J.; Gutierrez Mañero, F.J. Effects of inoculation with plant growth promoting rhizobacteria (PGPRs) and Sinorhizobium fredii on biological nitrogen fixation, nodulation and growth of Glycine max cv. Osumi. Plant Soil. 2004, 267, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietrich, R.; Jessberger, N.; Ehling-Schulz, M.; Märtlbauer, E.; Granum, P.E. The food poisoning toxins of Bacillus cereus. Toxins 2021, 13, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grutsch, A.A.; Nimmer, P.S.; Pittsley, R.H.; Kornilow, K.G.; McKillip, J.L. Molecular pathogenesis of Bacillus spp., with emphasis on the dairy industry. Fine Focus 2018, 4, 203–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
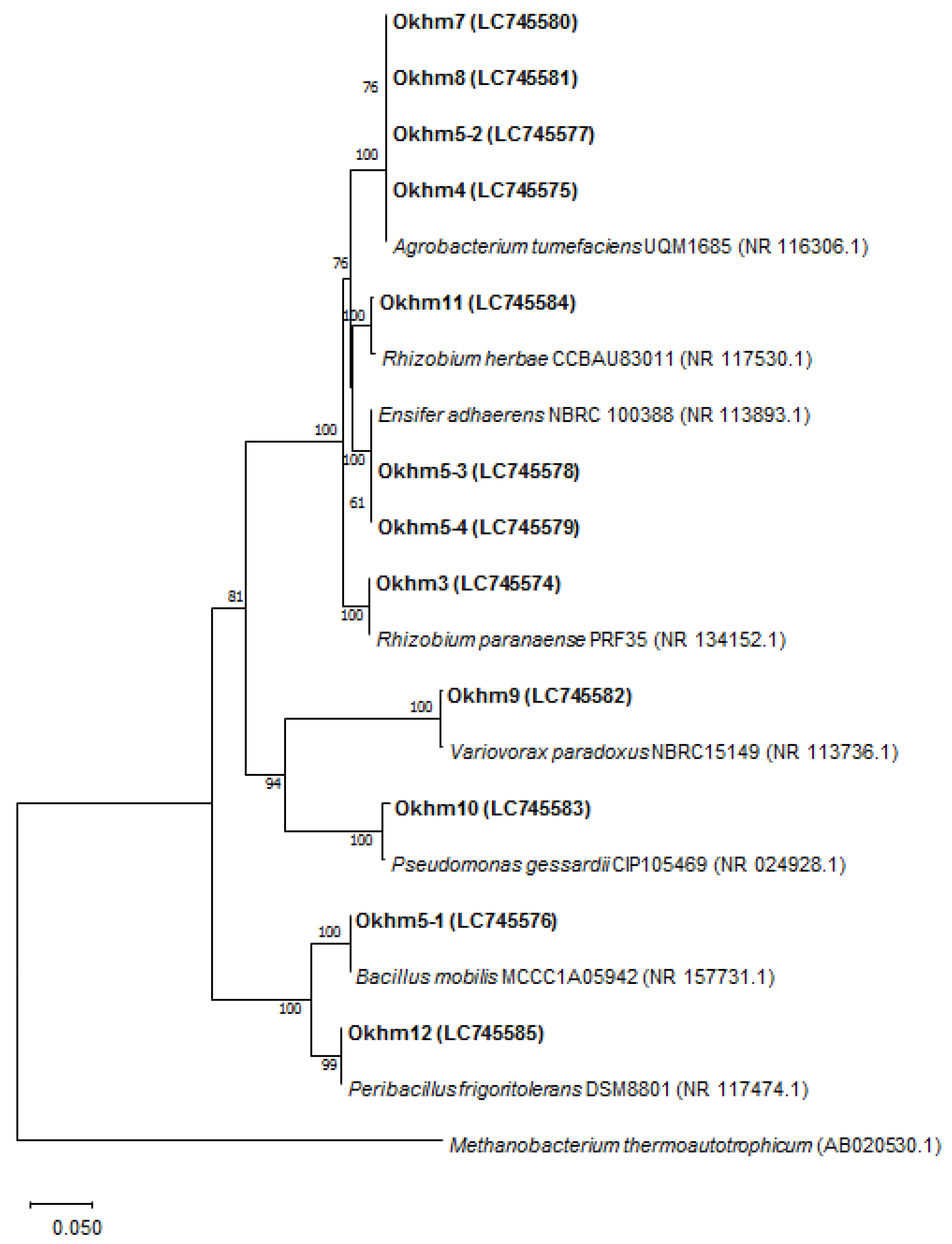
| Strains | Closet Relative a | Acc. No | Id. (%) | Class |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Okhm3 | Rhizobium paranaense PRF 35 | NR_134152.1 | 99 | α-proteobacteria |
| Okhm4 | Agrobacterium tumefaciens UQM 1685 | NR_116306.1 | 99 | α-proteobacteria |
| Okhm5-1 | Bacillus mobilis MCCC 1A05942 | NR_157731.1 | 100 | Bacilli |
| Okhm5-2 | Agrobacterium tumefaciens UQM 1685 | NR_116306.1 | 99 | α-proteobacteria |
| Okhm5-3 | Ensifer adhaerens LMG 20216 | NR_042482.1 | 99 | α-proteobacteria |
| Okhm5-4 | Ensifer adhaerens NBRC 100388 | NR_113893.1 | 99 | α-proteobacteria |
| Okhm7 | Agrobacterium tumefaciens UQM 1685 | NR_116306.1 | 99 | α-proteobacteria |
| Okhm8 | Agrobacterium tumefaciens UQM 1685 | NR_116306.1 | 99 | α-proteobacteria |
| Okhm9 | Variovorax paradoxus NBRC 15149 | NR_113736.1 | 99 | β-proteobacteria |
| OKhm10 | Pseudomonas gessardii CIP 105469 | NR_024928.1 | 99 | γ-proteobacteria |
| Okhm11 | Rhizobium herbae CCBAU 83011 | NR_117530.1 | 99 | α-proteobacteria |
| Okhm12 | Peribacillus frigoritolerans DSM 8801 | NR_117474.1 | 99 | Bacilli |
| Isolates | Closet Relative | Plant Growth-Promoting Properties | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IAA a | Phosphate Solubilization | nifH | Cellulase | Pectinase | ACC Deaminase b | ||
| Okhm3 | Rhizobium paranaense | - | + | - | - | + | + |
| Okhm5-4 | Ensifer adhaerens | - | - | - | - | - | + |
| Okhm10 | Pseudomonas gessardii | + | + | - | - | - | + |
| Okhm11 | Rhizobium herbae | - | + | - | - | - | + |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Salehin, A.; Yamane, S.; Ueno, M.; Hayashi, S. Identification, Characterization, and Growth-Promoting Effects of Bacterial Endophytes Isolated from Okra (Abelmoschus esculentus L.). Agronomy 2023, 13, 1226. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13051226
Salehin A, Yamane S, Ueno M, Hayashi S. Identification, Characterization, and Growth-Promoting Effects of Bacterial Endophytes Isolated from Okra (Abelmoschus esculentus L.). Agronomy. 2023; 13(5):1226. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13051226
Chicago/Turabian StyleSalehin, Ahsanul, Sakiko Yamane, Makoto Ueno, and Shohei Hayashi. 2023. "Identification, Characterization, and Growth-Promoting Effects of Bacterial Endophytes Isolated from Okra (Abelmoschus esculentus L.)" Agronomy 13, no. 5: 1226. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13051226
APA StyleSalehin, A., Yamane, S., Ueno, M., & Hayashi, S. (2023). Identification, Characterization, and Growth-Promoting Effects of Bacterial Endophytes Isolated from Okra (Abelmoschus esculentus L.). Agronomy, 13(5), 1226. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13051226







