The Effect of Faecal Sludge Biochar on the Growth and Yield of Tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) Cultivar Micro-Tom
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Biochar
2.2. Soil
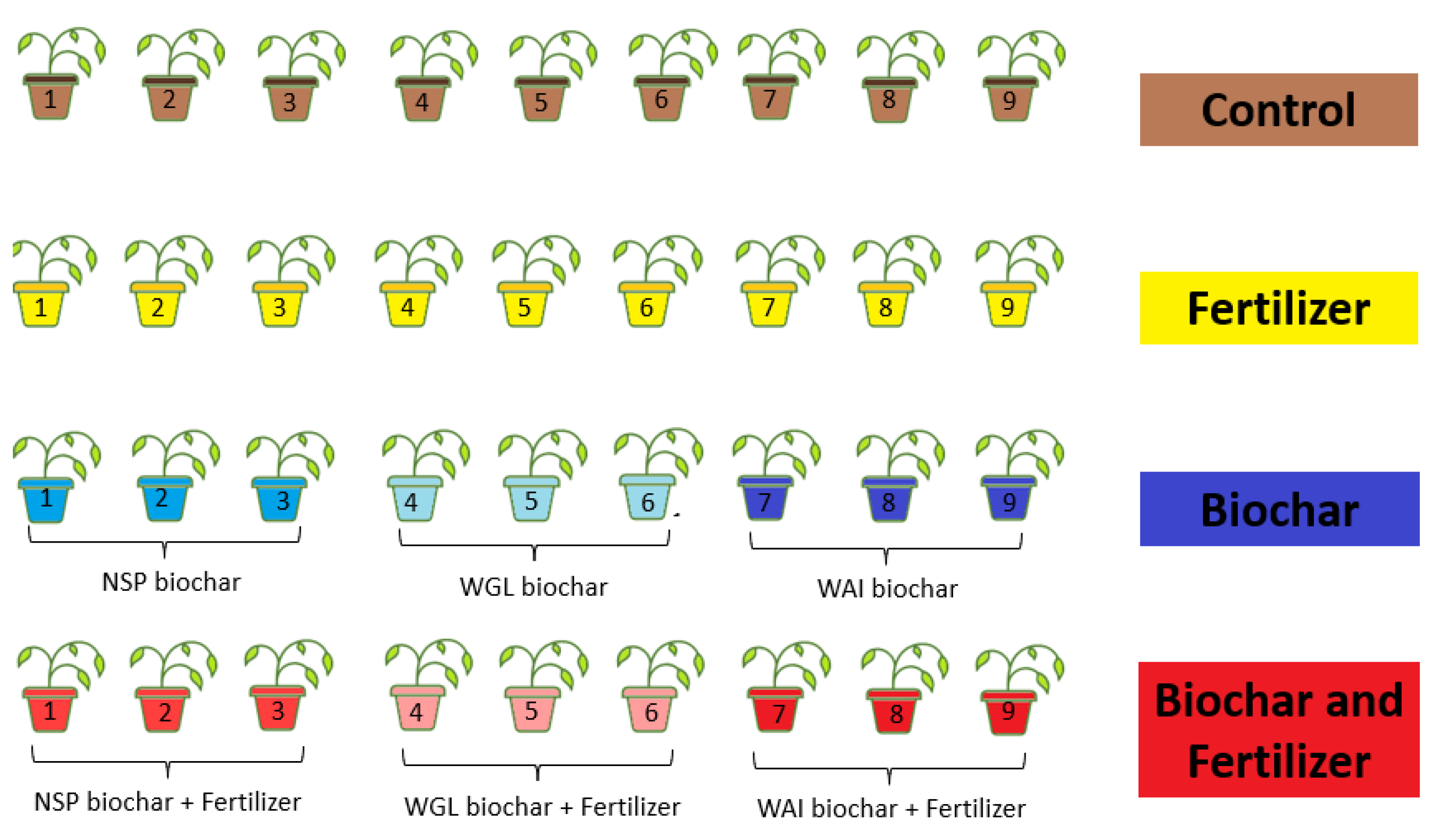
2.3. Plant Growth Experiment
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Plant Growth Responses
3.1.1. Plant height and leaf length
3.1.2. Above and Below Ground Biomass
3.2. Fruit Production
3.3. Soil Properties
4. Discussion
4.1. Implications for Plant growth and Crop Yield
4.2. Implications for Soil Properties
4.3. Implications for Food Security
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WHO; UNICEF. Progress on Household Drinking Water, Sanitation and Hygiene 2000–2017: Special Focus on Inequalities; United Nations Children’s Fund (UNICEF); World Health Organization: New York, NY, USA, 2019.
- UNICEF; WHO. Progress on Drinking Water, Sanitation and Hygiene-Joint Monitoring Programme 2017 Update and SDG Baselines; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017; Volume 66. [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, J.; Joseph, S. Biochar for Environmental Management: Science, Technology and Implementation, 2nd ed.; Routledge: Milton Park Abingdon, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- European Biochar Certificate (EBC). Guidelines for a Sustainable Production of Biochar. Eur. Biochar Found. 2016, 1–22, Version 6.2E of 4th February 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Zhou, D.; Zhu, L. Transitional adsorption and partition of nonpolar and polar aromatic contaminants by biochars of pine needles with different pyrolytic temperatures. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 5137–5143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomczyk, A.; Sokołowska, Z.; Boguta, P. Biochar physicochemical properties: Pyrolysis temperature and feedstock kind effects. Rev. Environ. Sci. Bio/Technol. 2020, 19, 191–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, K.; Quicker, P. Properties of biochar. Fuel 2018, 217, 240–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrafioti, E.; Bouras, G.; Kalderis, D.; Diamadopoulos, E. Biochar production by sewage sludge pyrolysis. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2013, 101, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhang, H.; Huang, H.; Xiao, R.; Li, R.; Zhang, Z. Influence of temperature and residence time on characteristics of biochars derived from agricultural residues: A comprehensive evaluation. Process. Saf. Environ. Prot. 2020, 139, 218–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glaser, B.; Haumaier, L.; Guggenberger, G.; Zech, W. The ‘Terra Preta’ phenomenon: A model for sustainable agriculture in the humid tropics. Sci. Nat. 2001, 88, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaskin, J.W.; Speir, A.; Morris, L.M.; Ogden, L.; Harris, K.; Lee, D.; Das, K.C. Potential for Pyrolysis Char To Affect Soil Moisture and Nutrient Status of a Loamy sand Soil; Georgia Institute of Technology: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Novak, J.M.; Busscher, W.J.; Laird, D.L.; Ahmedna, M.; Watts, D.W.; Niandou, M.A.S. Impact of Biochar Amendment on Fertility of a Southeastern Coastal Plain Soil. Soil Sci. 2009, 174, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glaser, B.; Lehmann, J.; Zech, W. Ameliorating physical and chemical properties of highly weathered soils in the tropics with charcoal—A review. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2002, 35, 219–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, J.; Rillig, M.C.; Thies, J.; Masiello, C.A.; Hockaday, W.C.; Crowley, D. Biochar effects on soil biota—A review. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2011, 43, 1812–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Windeatt, J.H.; Ross, A.B.; Williams, P.T.; Forster, P.M.; Nahil, M.A.; Singh, S. Characteristics of biochars from crop residues: Potential for carbon sequestration and soil amendment. J. Environ. Manag. 2014, 146, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Lee, X.-Q.; Wang, B. Characterization of biochars produced from seven biomasses grown in three different climate zones. Chin. J. Geochem. 2015, 34, 592–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekuria, W.; Noble, A. The Role of Biochar in Ameliorating Disturbed Soils and Sequestering Soil Carbon in Tropical Agricultural Production Systems International Water Management Institute (IWMI), 127 Sunil Mawatha, Pelawatte. Appl. Environ. Soil Sci. 2013, 2013, 354965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salinger, M.J.; Sivakumar, M.V.K.; Motha, R. Reducing Vulnerability of Agriculture and Forestry to Climate Variability and Change: Workshop Summary and Recommendations. In Increasing Climate Variability and Change; Salinger, J., Sivakumar, M., Motha, R.P., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gwenzi, W.; Chaukura, N.; Mukome, F.N.; Machado, S.; Nyamasoka, B. Biochar production and applications in sub-Saharan Africa: Opportunities, constraints, risks and uncertainties. J. Environ. Manag. 2015, 150, 250–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nyamapfene, K.W. The Soils of Zimbabwe; Nehanda Publishers: Harare, Zimbabwe, 1991; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- World Bank. Ending Poverty and Hunger by 2030 an Agenda for the Global Food System, 2nd ed.; World Bank Group: Washington, DC, USA, 2015; pp. 3–6. [Google Scholar]
- Ricker-Gilbert, J. Inorganic Fertiliser Use among Smallholder Farmers in Sub-Saharan Africa: Implications for Input Subsidy Policies; The Role of Smallholder Farms in Food and Nutrition Security; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2020; pp. 81–98. [Google Scholar]
- Sheahan, M.; Barrett, C.B. Ten striking facts about agricultural input use in Sub-Saharan Africa. Food Policy 2016, 67, 12–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, L.; Camps-Arbestain, M.; Shen, Q.; Lehmann, J.; Singh, B.; Sabir, M. Biochar effects on crop yields with and without fertilizer: A meta-analysis of field studies using separate controls. Soil Use Manag. 2019, 36, 2–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacCarthy, D.S.; Darko, E.; Nartey, E.K.; Adiku, S.G.K.; Tettey, A. Integrating Biochar and Inorganic Fertilizer Improves Productivity and Profitability of Irrigated Rice in Ghana, West Africa. Agronomy 2020, 10, 904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Uexküll, H.R.; Mutert, E. Global extent, development and economic impact of acid soils. In Plant–Soil Interactions at Low pH: Principles and Management; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1995; pp. 5–19. [Google Scholar]
- FAO. Climate Change, Water and Food Security Technical Background Document From the Expert Consultation Held on Security; FAO: Quebec City, QC, Canada, 2008; Volume 18. [Google Scholar]
- WWAP. The United Nations World Water Development Report 2018: Nature-Based Solutions for Water; 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Novak, J.M.; Busscher, W.J.; Watts, D.W.; Amonette, J.E.; Ippolito, J.A.; Lima, I.M.; Gaskin, J.; Das, K.C.; Steiner, C.; Ahmedna, M.; et al. Biochars Impact on Soil-Moisture Storage in an Ultisol and Two Aridisols. Soil Sci. 2012, 177, 310–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herath, H.; Camps-Arbestain, M.; Hedley, M. Effect of biochar on soil physical properties in two contrasting soils: An Alfisol and an Andisol. Geoderma 2013, 209–210, 188–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco-Canqui, H. Biochar and Soil Physical Properties. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2017, 81, 687–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omondi, M.O.; Xia, X.; Nahayo, A.; Liu, X.; Korai, P.K.; Pan, G. Quantification of biochar effects on soil hydrological properties using meta-analysis of literature data. Geoderma 2016, 274, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uzoma, K.C.; Inoue, M.; Andry, H.; Fujimaki, H.; Zahoor, A.; Nishihara, E. Effect of cow manure biochar on maize productivity under sandy soil condition. Soil Use Manag. 2011, 27, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulcahy, D.N.; Mulcahy, D.L.; Dietz, D. Biochar soil amendment increases tomato seedling resistance to drought in sandy soils. J. Arid. Environ. 2013, 88, 222–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gold, M.; Cunningham, M.; Bleuler, M.; Arnheiter, R.; Schönborn, A.; Niwagaba, C.; Strande, L. Operating parameters for three resource recovery options from slow-pyrolysis of faecal sludge. J. Water, Sanit. Hyg. Dev. 2018, 8, 707–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woldetsadik, D.; Drechsel, P.; Marschner, B.; Itanna, F.; Gebrekidan, H. Effect of biochar derived from faecal matter on yield and nutrient content of lettuce (Lactuca sativa) in two contrasting soils. Environ. Syst. Res. 2017, 6, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Ni, J.; Wang, X.; Zhou, X. Recovery of Ammonium in Urine by Biochar Derived from Faecal Sludge and its Application as Soil Conditioner. Waste Biomass-Valorization 2017, 9, 1619–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andriessen, N.; Ward, B.J.; Strande, L. To char or not to char? Review of technologies to produce solid fuels for resource recovery from faecal sludge. J. Water Sanit. Hyg. Dev. 2019, 9, 210–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarenga, P.; Mourinha, C.; Farto, M.; Palma, P.; Sengo, J.; Morais, M.-C.; Cunha-Queda, C. Ecotoxicological assessment of the potential impact on soil porewater, surface and groundwater from the use of organic wastes as soil amendments. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2016, 126, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barani, V.; Hegarty-Craver, M.; Rosario, P.; Madhavan, P.; Perumal, P.; Sasidaran, S.; Basil, M.; Raj, A.; Berg, A.B.; Stowell, A.; et al. Characterization of fecal sludge as biomass feedstock in the southern Indian state of Tamil Nadu. Gates Open Res. 2018, 2, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krueger, B.C.; Fowler, G.D.; Templeton, M.R.; Moya, B. Resource recovery and biochar characteristics from full-scale faecal sludge treatment and co-treatment with agricultural waste. Water Res. 2019, 169, 115253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niwagaba, C.B.; Mbéguéré, M.; Strande, L. Faecal sludge quantification, characterisation and treatment objectives. In Faecal Sludge Management: Systems Approach for Implementation and Operation; Strande, L., Ronteltap, M., Eds.; IWA Publishing: London, UK, 2014; pp. 19–44. [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham, M.; Gold, M.; Strande, L. Literature Review: Slow Pyrolysis of Faecal Sludge. 2016, p. 85. Available online: https://www.dora.lib4ri.ch/eawag/islandora/object/eawag%3A14834/datastream/PDF/view (accessed on 9 October 2021).
- Sainju, U.M.; Dris, R.; Singh, B. Mineral nutrition of tomato. Food Agric. Environ. 2003, 1, 176–184. [Google Scholar]
- Gil, R.; Bojacá, C.R.; Schrevens, E. Understanding the heterogeneity of smallholder production systems in the Andean tropics—The case of Colombian tomato growers. NJAS Wagening. J. Life Sci. 2019, 88, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mango, N.; Mapemba, L.; Tchale, H.; Makate, C.; Dunjana, N.; Lundy, M. Comparative analysis of tomato value chain competitiveness in selected areas of Malawi and Mozambique. Cogent Econ. Finance 2015, 3, 1088429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Njenga, P.; Willilo, S.; Hine, J. First Mile Transport Challenges for Smallholder Tomato Farmers along Ihimbo-Itimbo Road, Kilolo District Tanzania Final Report Safe and sustainable transport for rural communities. Int. Forum Rural Transp. Dev. 2015, 35. Available online: https://assets.publishing.service.gov.uk/media/57a0899ae5274a31e000018a/61280-Njenga-Willilo-Hine-IFRTD-2015-FirstMileTransportTomatoesTanzania-Final-AFCAP-Tan2015c-v160114.pdf (accessed on 11 November 2022).
- Meissner, R.; Jacobson, Y.; Melamed, S.; Levyatuv, S.; Shalev, G.; Ashri, A.; Elkind, Y.; Levy, A. A new model system for tomato genetics. Plant J. 1997, 12, 1465–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, M.L.; Carvalho, R.F.; Benedito, V.A.; Peres, L.E.P. Small and remarkable. Plant Signal. Behav. 2010, 5, 267–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholas, H.L.; Mabbett, I.; Apsey, H.; Robertson, I. Physico-chemical properties of waste derived biochar from community scale faecal sludge treatment plants. Gates Open Res. 2022, 6, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenth, R.; Singmann, H.; Love, J.; Buerkner, P.; Herve, M. emmeans: Estimated marginal means, aka least-squares mean. R Package Version 1(7): 3. 2022. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/emmeans/index.html (accessed on 30 June 2022).
- Novak, J.M.; Lima, I.; Xing, B.; Gaskin, J.W.; Steiner, C.; Das, K.C.; Ahmedna, M.; Rehrah, D.; Watts, D.W.; Busscher, W.J.; et al. Characterization of designer biochar produced at different temperatures and their effects on a loamy sand. Ann. Environ. Sci. 2009, 3, 195–206. [Google Scholar]
- Akhtar, S.S.; Li, G.; Andersen, M.N.; Liu, F. Biochar enhances yield and quality of tomato under reduced irrigation. Agric. Water Manag. 2014, 138, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tartaglia, M.; Arena, S.; Scaloni, A.; Marra, M.; Rocco, M. Biochar Administration to San Marzano Tomato Plants Cultivated Under Low-Input Farming Increases Growth, Fruit Yield, and Affects Gene Expression. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaccari, F.; Maienza, A.; Miglietta, F.; Baronti, S.; Di Lonardo, S.; Giagnoni, L.; Lagomarsino, A.; Pozzi, A.; Pusceddu, E.; Ranieri, R.; et al. Biochar stimulates plant growth but not fruit yield of processing tomato in a fertile soil. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2015, 207, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.K.; Strezov, V.; Nelson, P. Comparative Assessment of the Effect of Wastewater Sludge Biochar on Growth, Yield and Metal Bioaccumulation of Cherry Tomato. Pedosphere 2015, 25, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velli, P.; Manolikaki, I.; Diamadopoulos, E. Effect of biochar produced from sewage sludge on tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) growth, soil chemical properties and heavy metal concentrations. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 297, 113325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polzella, A.; De Zio, E.; Arena, S.; Scippa, G.S.; Scaloni, A.; Montagnoli, A.; Chiatante, D.; Trupiano, D. Toward an understanding of mechanisms regulating plant response to biochar application. Plant Biosyst. Int. J. Deal. All Asp. Plant Biol. 2018, 153, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndoung, O.C.N.; de Figueiredo, C.C.; Ramos, M.L.G. A scoping review on biochar-based fertilizers: Enrichment techniques and agro-environmental application. Heliyon 2021, 7, e08473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razzaghi, F.; Obour, P.B.; Arthur, E. Does biochar improve soil water retention? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Geoderma 2019, 361, 114055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revell, K.T.; Maguire, R.O.; Agblevor, F.A. Influence of Poultry Litter Biochar on Soil Properties and Plant Growth. Soil Sci. 2012, 177, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeffery, S.; Verheijen, F.G.A.; van der Velde, M.; Bastos, A.C. A quantitative review of the effects of biochar application to soils on crop productivity using meta-analysis. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2011, 144, 175–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nigussie, A.; Kissi, E.; Misganaw, M.; Ambaw, G. Effect of Biochar Application on Soil Properties and Nutrient Uptake of Lettuces (Lactuca sativa) Grown in Chromium Polluted Soils. Environ. Sci. 2012, 12, 369376. [Google Scholar]
- Atkinson, C.J.; Fitzgerald, J.D.; Hipps, N.A. Potential mechanisms for achieving agricultural benefits from biochar application to temperate soils: A review. Plant Soil 2010, 337, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chintala, R.; Mollinedo, J.; Schumacher, T.E.; Malo, D.D.; Julson, J.L. Effect of biochar on chemical properties of acidic soil. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2013, 60, 393–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.-H.; Xu, R.-K.; Qian, W.; Wang, R.-H. Comparison of the ameliorating effects on an acidic ultisol between four crop straws and their biochars. J. Soils Sediments 2011, 11, 741–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tag, A.T.; Duman, G.; Ucar, S.; Yanik, J. Effects of feedstock type and pyrolysis temperature on potential applications of biochar. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2016, 120, 200–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, J.; Joseph, S. Biochar for Environmental Management: Science, Technology and Implementation; Routledge: Milton Park Abingdon, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Song, W.; Guo, M. Quality variations of poultry litter biochar generated at different pyrolysis temperatures. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2012, 94, 138–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Wei, L.L.; Sun, J.N.; Shao, H.B.; Chang, S.X. What is more important for enhancing nutrient bioavailability with biochar application into a sandy soil: Direct or indirect mechanism? Ecol. Eng. 2013, 52, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Z.; Zhang, X.; Tang, C.; Muhammad, N.; Wu, J.; Brookes, P.C.; Xu, J. Potential role of biochars in decreasing soil acidification—A critical review. Sci. Total. Environ. 2017, 581–582, 601–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kätterer, T.; Roobroeck, D.; Andrén, O.; Kimutai, G.; Karltun, E.; Kirchmann, H.; Nyberg, G.; Vanlauwe, B.; de Nowina, K.R. Biochar addition persistently increased soil fertility and yields in maize-soybean rotations over 10 years in sub-humid regions of Kenya. Field Crop. Res. 2019, 235, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woolf, D.; Lehmann, J.; Cowie, A.; Cayuela, M.L.; Whitman, T.; Sohi, S. 8 Biochar for Climate Change Mitigation: Navigating from Science to Evidence-Based Policy. Soil Clim. 2018, 219–248. Available online: https://rdg.ent.sirsidynix.net.uk/client/en_GB/library/search/detailnonmodal/ent:$002f$002fSD_ILS$002f0$002fSD_ILS:1879511/ada?qu=soil+and+climate&lm=EXCL_LR2 (accessed on 21 April 2022).
- Lehmann, J.; Silva, J.P., Jr.; Steiner, C.; Nehls, T.; Zech, W.; Glaser, B. Nutrient availability and leaching an an archaeological Anthrosol and a Ferralsol. Plant Soil 2003, 249, 343–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, B.; Lehmann, J.; Solomon, D.; Kinyangi, J.; Grossman, J.; O’Neill, B.; Skjemstad, J.O.; Thies, J.; Luizão, F.J.; Petersen, J.; et al. Black Carbon Increases Cation Exchange Capacity in Soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2006, 70, 1719–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, D.A.; Johnson, G.R.; Spolek, G.A. Amending greenroof soil with biochar to affect runoff water quantity and quality. Environ. Pollut. 2011, 159, 2111–2118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadeghi, S.H.; Hazbavi, Z.; Harchegani, M.K. Controllability of runoff and soil lossfrom small plots treated by vinasse-produced biochar. Sci Total Environ. 2016, 541, 483–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Field, C.B.; Barros, V.; Stocker, T.F.; Dahe, Q. Managing the Risks of Extreme Events and Disasters to Advance Climate Change Adaptation: Special Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Mansoor, S.; Kour, N.; Manhas, S.; Zahid, S.; Wani, O.A.; Sharma, V.; Wijaya, L.; Alyemeni, M.N.; Alsahli, A.A.; El-Serehy, H.A.; et al. Biochar as a tool for effective management of drought and heavy metal toxicity. Chemosphere 2020, 271, 129458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zech, W.; Haumaier, L.; Hempfling, R.; MacCarthy, P.; Clapp, C.E.; Malcolm, R.L.; Bloom, P.R. Ecological Aspects of Soil Organic Matter in Tropical Land Use. Humic Subst. Soil Crop Sci. Sel. Read. 2015, 187–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, P.A.; Denning, G.L.; Nziguheba, G. The African Green Revolution moves forward. Food Secur. 2009, 1, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawson, C.; Hilton, J. Fertiliser availability in a resource-limited world: Production and recycling of nitrogen and phosphorus. Food Policy 2011, 36, S14–S22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordell, D.; Rosemarin, A.; Schröder, J.; Smit, A. Towards global phosphorus security: A systems framework for phosphorus recovery and reuse options. Chemosphere 2011, 84, 747–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steen, I. Phosphorus availability in the 21st century: Management of a non-renewable resource. Phosphorus Potassium 1998, 217, 25–31. [Google Scholar]
- Cordell, D.; Drangert, J.-O.; White, S. The story of phosphorus: Global food security and food for thought. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2009, 19, 292–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cisse, L.; Mrabet, T.; Abdelkader, R.; Mazini, A. World Phosphate Production: Overview and Prospects. Phosphorus Res. Bull. 2004, 15, 21–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Günther, F. Hampered effluent accumulation process: Phosphorus management and societal structure. Ecol. Econ. 1997, 21, 159–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Vuuren, D.; Bouwman, A.; Beusen, A. Phosphorus demand for the 1970–2100 period: A scenario analysis of resource depletion. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2010, 20, 428–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonsson, H.; Stintzing, A.R.; Vinneras, B.; Salomon, E. EcoSanRes Publications Series-Guidelines on the use of urine and faeces in Crop Production. J. Indian Water Work. Assoc. 2004, 37, 293–295. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Feng, R.; Mahmood, I.B. Characterization of human manure-derived biochar and energy-balance analysis of slow pyrolysis process. Waste Manag. 2014, 34, 1619–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- FAO; IFAD; UNICEF; WFP; WHO. The State of Food Security and Nutrition in the World 2021; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2021.
- Bhattacharyya, R.; Ghosh, B.N.; Mishra, P.K.; Mandal, B.; Rao, C.S.; Sarkar, D.; Das, K.; Anil, K.S.; Lalitha, M.; Hati, K.M.; et al. Soil Degradation in India: Challenges and Potential Solutions. Sustainability 2015, 7, 3528–3570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biederman, L.A.; Harpole, W.S. Biochar and its effects on plant productivity and nutrient cycling: A meta-analysis. GCB Bioenergy 2013, 5, 202–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randolph, P.; Bansode, R.; Hassan, O.; Rehrah, D.; Ravella, R.; Reddy, M.; Watts, D.; Novak, J.; Ahmedna, M. Effect of biochars produced from solid organic municipal waste on soil quality parameters. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 192, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, S.; Qin, D.; Manning, M.; Chen, Z.; Marquis, M.; Averyt, K.B.; Tignor, M.; Miller, H.L. Summary for policymakers. Clim. Chang. 2007, 85, 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Elbeltagy, A.S.; Madkour, M. Impact of climate change on arid lands agriculture. Agric. Food Secur. 2012, 1, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ippolito, J.A.; Novak, J.M.; Busscher, W.J.; Ahmedna, M.; Rehrah, D.; Watts, D.W. Switchgrass Biochar Affects Two Aridisols. J. Environ. Qual. 2012, 41, 1123–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPCC. Global warming of 1.5 °C. An IPCC Special Report on the Impacts of Global Warming of 1.5 °C above Pre-Industrial Levels and Related Global Greenhouse Gas Emission Pathways, in the Context of Strengthening the Global Response to the Threat of Climate Change; World Meteorological Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018.
- Yildirim, E.; Ekinci, M.; Turan, M. Impact of Biochar in Mitigating the Negative Effect of Drought Stress on Cabbage Seedlings. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2021, 21, 2297–2309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Parameter | Unit | WAI BC | NSP BC | WGL BC |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | [] | 11.81 ± 0.01 | 11.82 ± 0.01 | 12.25 ± 0.01 |
| EC | [mScm−1] | 2.70 ± 0.09 | 1.79 ± 0.17 | 9.00 ± 0.02 |
| Moisture | [%] | 3.08 ± 0.01 | 2.15 ± 0.31 | 0.98 ± 0.05 |
| Ash | [%] | 62.3 ± 0.32 | 67.0 ± 2.68 | 88.3 ± 0.21 |
| C | [%] | 21.11 | 23.79 | 8.06 |
| N | [%] | 1.32 | 1.13 | 0.37 |
| H | [%] | 1.55 | 0.73 | 1.15 |
| S | [%] | 0.03 | 0.27 | 0.03 |
| O * | [%] | 13.7 | 7.1 | 2.1 |
| H/C | [] | 0.9 | 0.4 | 1.7 |
| C/N | [] | 18.7 | 24.6 | 25.4 |
| O/C | [] | 0.5 | 0.2 | 0.2 |
| SBET N2 | [m2·g−1] | 3.52 ± 0.78 | 3.69 ± 0.36 | 12.07 ± 4.12 |
| N2 TPV | [cm3·g−1] | 0.011 | 0.011 | 0.019 |
| SBET CO2 | [m2·g−1] | 46.72 ± 7.0 | 74.20 ± 4.0 | 26.11 ± 2.6 |
| CEC | [cmol·kg−1] | 90.0 ± 6.5 | 41.9 ± 2.2 | 129.3 ± 2.3 |
| Treatments | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plant and Soil Parameters | Control | Fertilizer | Biochar | Biochar + Fertilizer |
| Plant height (cm) | 7.3 | 9.3 | 10.5 | 11.5 |
| Tomato number | 1.0 | 1.7 | 5.9 | 13.3 |
| Above ground biomass (g) | 0.6 | 2.4 | 2.7 | 6.0 |
| Below ground biomass (g) | 0.5 | 1.4 | 2.3 | 4.1 |
| Leaf length (cm) | 2.4 | 3.4 | 5.1 | 5.8 |
| Fruit yield (g) | 1.0 | 3.3 | 11.9 | 28.9 |
| pH | 5.5 | 5.3 | 5.8 | 5.5 |
| Water runoff (mL) | 1221 | 1099 | 859 | 470 |
| Electrical conductivity (µScm−1) | 13.8 | 54.4 | 31.6 | 36.0 |
| p Values for Each Parameter Measured | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Treatment Pairwise Comparison | Plant Height | Leaf Length | Above Ground Biomass | Below Ground Biomass | Number of Fruits | Yield | Water Runoff | pH | EC | |
| Biochar | Biochar and fertilizer | 0.626 | 0.787 | 0.002 | 0.629 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.0003 | 0.980 | 0.772 |
| Biochar | Control | 0.0005 | <0.0001 | 0.0001 | 0.0015 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | 0.5195 | 0.0174 |
| Biochar | Fertilizer | 0.3899 | <0.0001 | 0.885 | 0.1957 | <0.0001 | 0.0002 | 0.0026 | 0.0385 | 0.1381 |
| Biochar and fertilizer | Control | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | 0.0006 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | 0.7541 | 0.1035 |
| Biochar and fertilizer | Fertilizer | 0.0394 | <0.0001 | 0.0005 | 0.0272 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | 0.0354 |
| Control | Fertilizer | 0.034 | 0.0001 | 0.0002 | 0.0181 | 0.269 | 0.0056 | 0.3548 | 0.0056 | 0.0006 |
| AIC Model Outputs | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Plant Growth Response | All Treatments | Biochar Presence | Fertilizer Presence |
| Plant height | 136.2828 * | 141.8475 | 154.9203 |
| Leaf length | 74.45228 * | 90.45016 | 130.4761 |
| Above ground biomass | 108.4831 * | 138.5443 | 143.7842 |
| Below ground biomass | 87.85519 * | 96.97702 | 113.2051 |
| Fruit outputs | |||
| Number of fruits | 142.6897 * | 155.8337 | 200.9442 |
| Yield | 191.688 * | 213.0751 | 255.12 |
| Soil properties | |||
| Water runoff | 457.4257 * | 473.0119 | 503.7687 |
| pH | 37.294 | 35.74379 * | 41.23772 |
| EC | 277.1746 * | 303.3129 | 310.2736 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nicholas, H.L.; Devine, A.; Robertson, I.; Mabbett, I. The Effect of Faecal Sludge Biochar on the Growth and Yield of Tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) Cultivar Micro-Tom. Agronomy 2023, 13, 1233. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13051233
Nicholas HL, Devine A, Robertson I, Mabbett I. The Effect of Faecal Sludge Biochar on the Growth and Yield of Tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) Cultivar Micro-Tom. Agronomy. 2023; 13(5):1233. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13051233
Chicago/Turabian StyleNicholas, H. Larissa, Aisling Devine, Iain Robertson, and Ian Mabbett. 2023. "The Effect of Faecal Sludge Biochar on the Growth and Yield of Tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) Cultivar Micro-Tom" Agronomy 13, no. 5: 1233. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13051233
APA StyleNicholas, H. L., Devine, A., Robertson, I., & Mabbett, I. (2023). The Effect of Faecal Sludge Biochar on the Growth and Yield of Tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) Cultivar Micro-Tom. Agronomy, 13(5), 1233. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13051233






