Yield, Nutritional Composition, and In Vitro Ruminal Digestibility of Conventional and Brown Midrib (BMR) Corn for Silage as Affected by Planting Population and Harvest Maturity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Sites and Climate Data
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Harvesting and Ensiling
2.4. Forage Processing and Analyses
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Weather Conditions
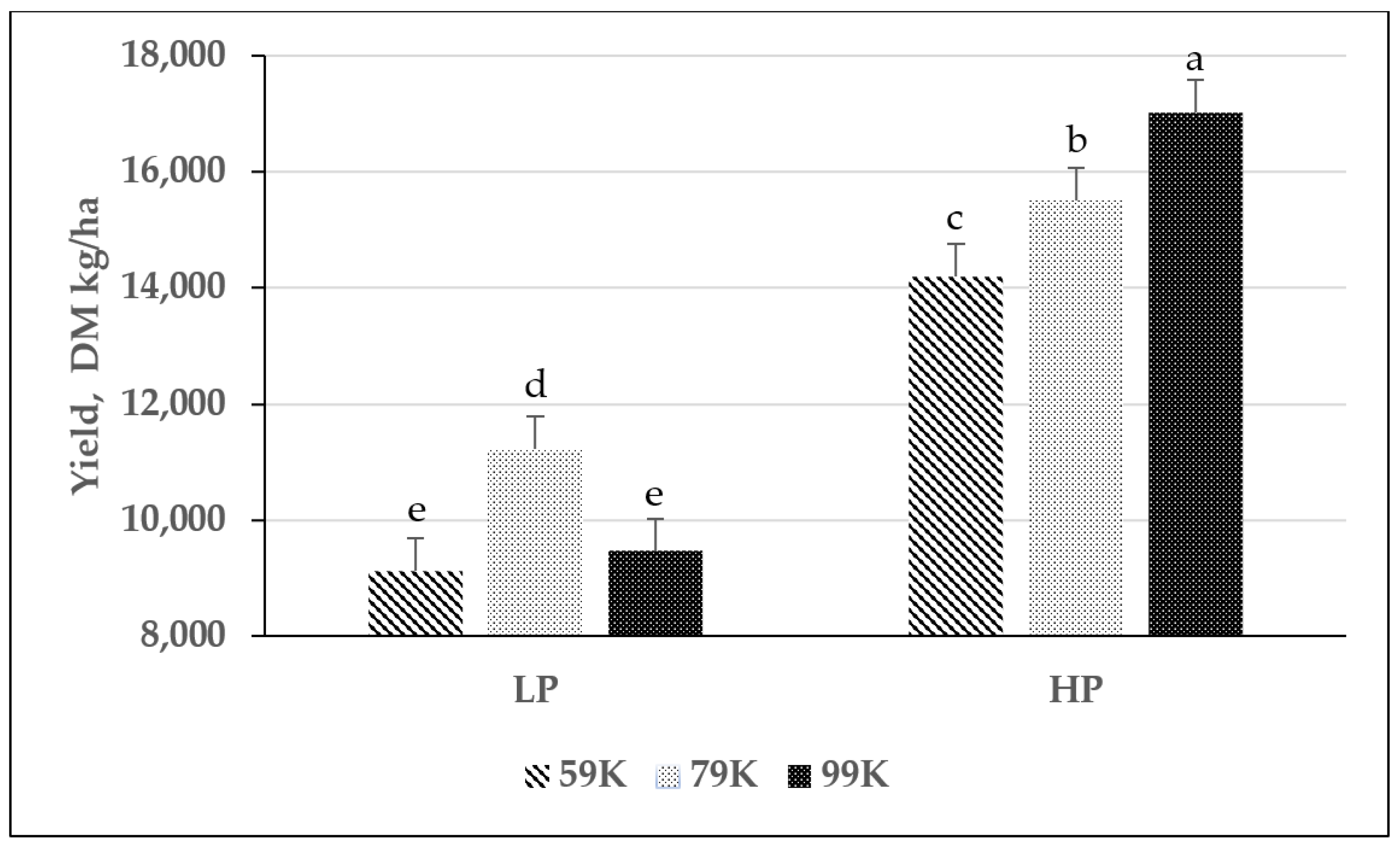
3.2. Forage Yield of Corn Silage
3.3. Chemical Composition of Corn Silage
3.4. In-Vitro Digestibility of Corn Silage
4. Discussion
4.1. Forage Yield of Corn Silage
4.2. Chemical Composition of Corn Silage
4.3. In-Vitro Digestibility of Corn Silage
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Oba, M.; Allen, M. Effects of Brown Midrib 3 mutation in corn silage on productivity of dairy cows fed two concentrations of dietary neutral detergent fiber: 1. Feeding behavior and nutrient utilization. J. Dairy Sci. 2000, 83, 1333–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwab, E.C.; Shaver, R.D.; Shinners, K.J.; Lauer, J.G.; Coors, J.G. Processing and chop length effects in brown-midrib corn silage on intake, digestion, and milk production by dairy cows. J. Dairy Sci. 2002, 85, 613–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kung, L., Jr.; Moulder, B.M.; Mulrooney, C.M.; Teller, R.S.; Schmidt, R.J. The effect of silage cutting height on the nutritive value of a normal corn silage hybrid compared with brown midrib corn silage fed to lactating cows. J. Dairy Sci. 2008, 91, 1451–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bal, M.A.; Coors, J.G.; Shaver, R.D. Impact of the maturity of corn for use as silage in the diets of dairy cows on intake, digestion, and milk production. J. Dairy Sci. 1997, 80, 2497–2503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cusicanqui, J.A.; Lauer, J.G. Plant density and hybrid influence on corn forage yield and quality. Agron. J. 1999, 91, 911–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, G.; Alfonso, M.; Depino, S.; Alessandri, E. Effect of planting density on nutritional quality of green-chopped corn for silage. J. Dairy Sci. 2014, 97, 5918–5921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, K.; Liu, B.; Liu, P.; Wang, Z. The optimal plant density of maize for dairy cow forage production. Agron. J. 2020, 112, 1849–1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, G.; Teets, C.L. Effect of planting density on yield, nutritional quality, and ruminal in vitro digestibility of corn for silage grown under on-farm conditions. Prof. Anim. Sci. 2017, 33, 420–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, G.; Teets, C.L.; Huffard, J.B.; Aguerre, M.J. Effects of planting population, genotype, and nitrogen fertilization on dry matter yield, nutrient composition, in vitro ruminal neutral detergent fiber disappearance, and nitrogen and phosphorus removal of corn for silage. Anim. Feed. Sci. Technol. 2020, 268, 114615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Der Bedrosian, M.C.; Nestor, K.E., Jr.; Kung, L., Jr. The effects of hybrid, maturity, and length of storage on the composition and nutritive value of corn silage. J. Dairy Sci. 2012, 95, 5115–5126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AOAC International. Official Methods of Analysis, 18th ed.; AOAC International: Rockville, MD, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- AOAC International. Official Methods of Analysis, 17th ed.; AOAC International: Rockville, MD, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Van Soest, J.P.; Robertson, J.B.; Lewis, B.A. Methods for dietary fiber, neutral detergent fiber, and non-starch polysaccharides in relation to animal nutrition. J. Dairy Sci. 1991, 74, 3583–3597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, M.B. Determination of Starch, Including Maltooligosaccharides, in Animal Feeds: Comparison of Methods and a Method Recommended for AOAC Collaborative Study. J. AOAC Int. 2009, 92, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, G.; Mertens, D.R. Chemical and physical characteristics of corn silages and their effects on in vitro disappearance. J. Dairy Sci. 2005, 88, 4414–4425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalo, R.; Rattalino Edreira, J.I.; Archontoulis, S.V.; Yang, H.S.; Grassini, P. Do shallow water tables contribute to high and stable maize yields in the US Corn Belt? Glob. Food Secur. 2018, 18, 27–34. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, M.; Feng, Y.; Shi, Y.; Shen, H.; Huifeng, H.; Luo, Y.; Longchao, X.; Kan, J.; Xing, A.; Wang, S.; et al. Yield and quality properties of silage maize and their influencing factors in China. Sci. China Life Sci. 2022, 65, 1655–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, J.E.; Geadelmann, J.L.; Marten, G.C. Effect of the Brown Midrib-Allele on maize silage quality and yield. Crop Sci. 1983, 23, 493–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, W.J.; Cherney, D.J.R. Influence of Brown Midrib, leafy, and transgenic hybrids on corn forage production. Agron. J. 2001, 93, 790–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salaman, H.S.A. Yield and nutritive value of maize (Zea mays L.) forage as affected by plant density, sowing date and age at harvest. Ital. J. Agron. 2019, 14, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tine, M.A.; Mcleod, K.R.; Erdman, R.A.; Baldwin, R.L. Effects of brown midrib corn silage on the energy balance of dairy cattle. J. Dairy Sci. 2001, 84, 885–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coons, E.M.; Fredin, S.M.; Cotanch, K.W.; Dann, H.M.; Ballard, C.S.; Brouillette, J.P.; Grant, R.J. Influence of a novel bm3 corn silage hybrid with floury kernel genetics on lactational performance and feed efficiency of Holstein cows. J. Dairy Sci. 2019, 102, 9814–9826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holt, M.S.; Eun, J.-S.; Thacker, C.R.; Young, A.J.; Dai, X.; Nestor, K.E., Jr. Effects of feeding brown midrib corn silage with a high dietary concentration of alfalfa hay on lactational performance of Holstein dairy cows for the first 180 days of lactation. J. Dairy Sci. 2013, 96, 515–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferraretto, L.F.; Fonseca, A.C.; Sniffen, C.J.; Formigoni, A.; Shaver, R.D. Effect of corn silage hybrids differing in starch and neutral detergent fiber digestibility on lactation performance and total-tract nutrient digestibility by dairy cows. J. Dairy Sci. 2015, 98, 395–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, G.; Galyon, H.; Silva-Reis, A.I.; Pereyra, A.A.; Richardson, E.S.; Teets, C.L.; Blevins, P.; Cockrum, R.R.; Aguerre, M.J. Ruminal fiber degradation kinetics within and among summer annual grasses as affected by the brown midrib mutation. Animals 2022, 12, 2536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oba, M.; Allen, M.S. Effects of brown midrib 3 mutation in corn silage on dry matter intake and productivity of high yielding dairy cows. J. Dairy Sci. 1999, 82, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bal, M.A.; Shaver, R.D.; Shinners, K.J.; Coors, J.G.; Lauer, J.G.; Straub, R.J.; Koegel, R.G. Stage of maturity, processing, and hybrid effects on ruminal in situ disappearance of whole-plant corn silage. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2000, 86, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| ss | April | May | June | July | August | September |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Precipitation, mm | ||||||
| LP | 179 | 281 | 51 | 91 | 158 | -- |
| HP | 183 | 195 | 78 | 53 | 134 | 124 |
| 30-year mean | 101 | 99 | 103 | 108 | 119 | 100 |
| Temperature, °C | ||||||
| LP | 14.3 | 17.9 | 23.5 | 26.6 | 25.7 | -- |
| HP | 15.6 | 18.8 | 24.3 | 27.6 | 26.2 | 22.1 |
| 30-year mean | 15.6 | 20.0 | 24.2 | 26.2 | 25.6 | 22.4 |
| Cumulative GDD, °C 1 | ||||||
| LP early | 456 | 1173 | 2024 | 2160 | -- | |
| LP late | 456 | 1173 | 2024 | 2692 | -- | |
| HP early | -- | 541 | 1421 | 2275 | 2391 | |
| HP late | -- | 541 | 1421 | 2275 | 2811 |
| Yield, kg DM/ha | DM, % | pH | |
|---|---|---|---|
| FIELD | |||
| LP | 9938 b | 32.7 | 3.67 b |
| HP | 15,580 a | 33.2 | 3.74 a |
| SEM | 320 | 0.30 | 0.02 |
| POPULATION | |||
| 59K | 11,664 b | 33.3 | 3.71 |
| 79K | 13,365 a | 32.8 | 3.70 |
| 99K | 13,248 a | 32.7 | 3.70 |
| SEM | 393 | 0.36 | 0.02 |
| HYBRID | |||
| Conv1 | 13,239 | 32.1 b | 3.70 |
| Conv2 | 12,437 | 35.0 a | 3.70 |
| BMR1 | 12,556 | 32.1 b | 3.71 |
| BMR2 | 12,749 | 32.6 b | 3.71 |
| SEM | 330 | 0.34 | 0.02 |
| MATURITY | |||
| Early | 11,885 b | 27.0 b | 3.68 b |
| Late | 13,633 a | 38.9 a | 3.73 a |
| SEM | 255 | 0.26 | 0.02 |
| Interactions, p-values | |||
| Field × Population | 0.04 | 0.26 | 0.60 |
| Field × Hybrid | 0.11 | 0.10 | 0.47 |
| Field × Maturity | 0.13 | <0.01 | <0.01 |
| Population × Hybrid | 0.43 | 0.59 | 0.64 |
| Population × Maturity | 0.38 | 0.52 | 0.15 |
| Hybrid × Maturity | 0.16 | 0.12 | 0.31 |
| Item | Ash | CP | aNDFom | ADL | ADL %aNDFom | Starch |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FIELD | ||||||
| LP | 4.48 b | 10.0 a | 46.8 a | 3.05 b | 6.56 b | 21.2 b |
| HP | 4.77 a | 9.1 b | 42.8 b | 3.55 a | 8.31 a | 28.0 a |
| SEM | 0.05 | 0.10 | 0.36 | 0.22 | 0.53 | 0.34 |
| POPULATION | ||||||
| 59K | 4.65 | 9.7 a | 44.1 b | 3.09 | 7.05 | 24.7 a,b |
| 79K | 4.71 | 9.8 a | 45.8 a | 3.46 | 7.63 | 23.5 c |
| 99K | 4.51 | 9.1 b | 44.4 b | 3.35 | 7.63 | 25.6 a |
| SEM | 0.06 | 0.12 | 0.41 | 0.19 | 0.44 | 0.42 |
| HYBRID | ||||||
| Conv1 | 4.65 b,c | 9.5 | 45.4 a | 3.83 a | 8.44 a | 25.0 b,c |
| Conv2 | 4.15 d | 9.4 | 43.0 b | 3.50 a,b | 8.25 a | 27.0 a |
| BMR1 | 4.95 a | 9.7 | 45.9 a | 2.65 c | 5.83 c | 22.3 d |
| BMR2 | 4.75 b,c | 9.6 | 44.8 a | 3.21 b | 7.24 b | 24.1 b,c |
| SEM | 0.07 | 0.14 | 0.47 | 0.21 | 0.48 | 0.46 |
| MATURITY | ||||||
| Early | 4.79 a | 9.9 a | 45.8 a | 2.94 b | 6.47 b | 22.5 b |
| Late | 4.46 b | 9.1 b | 43.7 b | 3.66 a | 8.41 a | 26.7 a |
| SEM | 0.05 | 0.10 | 0.34 | 0.17 | 0.41 | 0.33 |
| Interactions, p-values | ||||||
| Field × Population | 0.44 | 0.32 | 0.60 | 0.49 | 0.58 | 0.27 |
| Field × Hybrid | <0.01 | 0.02 | 0.23 | 0.59 | 0.70 | 0.01 |
| Field × Maturity | 0.22 | 0.26 | <0.01 | <0.01 | 0.02 | <0.01 |
| Population × Hybrid | 0.74 | 0.37 | 0.68 | 0.05 | 0.03 | 0.09 |
| Population × Maturity | 0.95 | 0.24 | 0.17 | 0.26 | 0.20 | 0.01 |
| Hybrid × Maturity | 0.35 | 0.54 | 0.42 | 0.41 | 0.40 | 0.11 |
| Item | IVDMD 1 | IVTDMD 2 | IVNDFD 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| FIELD | |||
| LP | 67.3 | 74.0 | 45.4 A |
| HP | 65.3 | 74.5 | 39.5 B |
| SEM | 0.92 | 0.85 | 2.07 |
| POPULATION | |||
| 60K | 66.5 | 74.3 | 42.6 |
| 75K | 65.5 | 74.0 | 42.3 |
| 90K | 66.9 | 74.9 | 42.5 |
| SEM | 0.75 | 1.05 | 1.64 |
| HYBRID | |||
| Conv1 | 63.8 c | 70.9 c | 38.6 c |
| Conv2 | 65.1 b,c | 74.6 b | 37.5 c |
| BMR1 | 70.5 a | 78.3 a | 51.8 a |
| BMR2 | 65.6 b | 73.5 b,c | 41.8 b |
| SEM | 0.80 | 1.10 | 1.63 |
| MATURITY | |||
| Early | 66.7 | 74.8 | 43.4 a |
| Late | 65.9 | 74.0 | 41.5 b |
| SEM | 0.69 | 0.80 | 1.52 |
| Interactions, p-values | |||
| Field × Population | 0.44 | 0.40 | 0.15 |
| Field × Hybrid | 0.45 | 0.24 | 0.75 |
| Field × Maturity | <0.01 | 0.07 | <0.01 |
| Population × Hybrid | 0.99 | 0.22 | 0.78 |
| Population × Maturity | 0.35 | 0.43 | 0.51 |
| Hybrid × Maturity | 0.11 | 0.33 | 0.78 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Peña, O.M.; Velasquez, C.; Ferreira, G.; Aguerre, M.J. Yield, Nutritional Composition, and In Vitro Ruminal Digestibility of Conventional and Brown Midrib (BMR) Corn for Silage as Affected by Planting Population and Harvest Maturity. Agronomy 2023, 13, 1414. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13051414
Peña OM, Velasquez C, Ferreira G, Aguerre MJ. Yield, Nutritional Composition, and In Vitro Ruminal Digestibility of Conventional and Brown Midrib (BMR) Corn for Silage as Affected by Planting Population and Harvest Maturity. Agronomy. 2023; 13(5):1414. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13051414
Chicago/Turabian StylePeña, Omar Manuel, Cesar Velasquez, Gonzalo Ferreira, and Matias Jose Aguerre. 2023. "Yield, Nutritional Composition, and In Vitro Ruminal Digestibility of Conventional and Brown Midrib (BMR) Corn for Silage as Affected by Planting Population and Harvest Maturity" Agronomy 13, no. 5: 1414. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13051414
APA StylePeña, O. M., Velasquez, C., Ferreira, G., & Aguerre, M. J. (2023). Yield, Nutritional Composition, and In Vitro Ruminal Digestibility of Conventional and Brown Midrib (BMR) Corn for Silage as Affected by Planting Population and Harvest Maturity. Agronomy, 13(5), 1414. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13051414





