Effects of a Mixture of Brevibacillus brevis with Other Bacillus sp. Strains against Gray Mold and on Enzyme Activities of Grape
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Microbial Strains and Cultural Conditions
2.2. Compatibility between Bacterial Isolates
2.3. Inhibitory Activities of Different Microbial Combinations
2.4. Sensitivity of Mixed Microbial Combination to Different Conditions
2.5. Spectrum of Inhibitory Activity of Mixed Microbial Combination In Vitro
2.6. Effect of Mixed Microbial Combination on Decay of Grape Fruits and Leaves In Vivo
2.7. Effects of Mixed Microbial Combination on Defense Enzymes
2.8. Data Analysis
3. Results
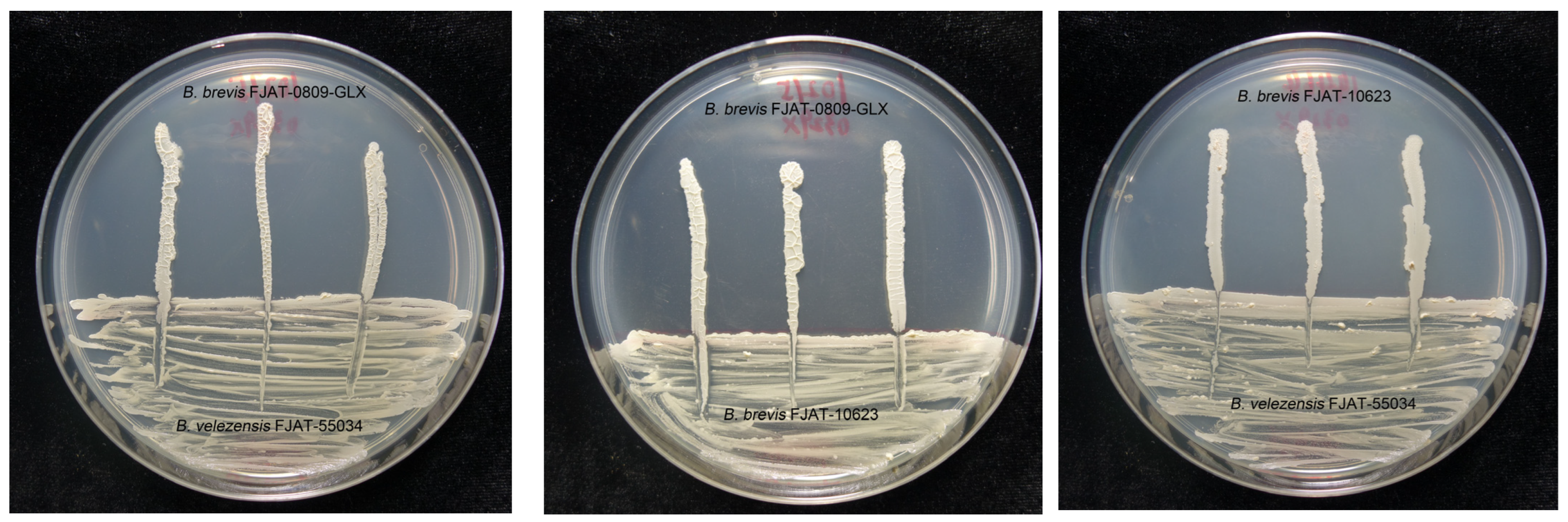
3.1. In Vitro Compatibility between Bacterial Isolates
3.2. Inhibitory Activities of Different Microbial Combinations
3.3. Sensitivity of Mixed Microbial Combination to Different Conditions
3.4. Antifungal Activity of Mixed Microbial Combination In Vitro
3.5. Effect of Mixed Microbial Combination on Decay of Grape Fruits and Leaves In Vivo
3.6. PPO and CAT Activities of Grape Fruits Treated with Mixed Microbial Combination
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Solairaj, D.; Legrand, N.N.G.; Yang, Q.Y.; Zhang, H.Y. Isolation of pathogenic fungi causing postharvest decay in table grapes and in vivo biocontrol activity of selected yeasts against them. Physiol. Molecul. Plant Pathol. 2020, 110, 101478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renzo, F.; Lucia, L.; Gianfranco, R. Analyses of sylem vessel size on grapevine cultivars and relationship with incidence of esca disease a threat to grape quality. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 1177. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, W.T.; Huang, K.L.; Guo, F.; Qu, W.; Yang, J.J.; Liang, Z.H.; Luo, Y.B. Postharvest grapefruit seed extract and chitosan treatments of table grapes to control Botrytis cinerea. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2007, 46, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evelyn, S.M.; Jocelyn, B.E.; Miguel, L.; Juan, R.; Iván, B.; Reinaldo, C.V.; Rubén, P. Effect of cuticular waxes compounds from table grapes on growth, germination and gene expression in Botrytis cinerea. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 32, 74. [Google Scholar]
- Marsico, A.D.; Velenosi, M.; Perniola, R.; Bergamini, C.; Sinonin, S.; David, V.V.; Maggiolini, F.A.M.; Hervè, A.; Cardone, M.F.; Ventura, M. Native vineyard non-saccharomyces yeasts used for biological control of Botrytis cinerea in stored table grape. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junior, O.J.C.; Youssef, K.; Koyama, R.; Ahmed, S.; Dominguez, A.R.; Mühlbeier, D.T.; Roberto, S.R. Control of gray mold on clamshell-packaged ‘benitaka’ table grapes using sulphur dioxide pads and perforated liners. Pathogens 2019, 8, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karabulut, O.A.; Gabler, F.M.; Mansour, M.; Smilanick, J.L. Postharvest ethanol and hot water treatments of table grapes to control gray mold. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2004, 34, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caterina, R.; Rita, M.D.M.A.; Crescenza, D.; Stefania, P.; Giulio, F.; Michele, D.C.; Donato, P.; Patrizia, N.; Francesco, F. Use of biocontrol agents and botanicals in integrated management of Botrytis cinerea in table grape vineyards. Pest Manag. Sci. 2018, 74, 715–725. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.Y.; Godana, E.A.; Sui, Y.; Yang, Q.Y.; Zhang, X.Y.; Zhao, L.N. Biological control as an alternative to synthetic fungicides for the management of grey and blue mould diseases of table grapes: A review. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2020, 46, 450–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latorre, B.A.; Spadaro, I.; Rioja, M.E. Occurrence of resistant strains of Botrytis cinerea to anilinopyrimidine fungicides in table grapes in Chile. Crop Protect. 2002, 21, 957–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvo, H.; Marco, P.; Blanco, D.; Oria, R.; Venturini, M.E. Potential of a new strain of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens BUZ-14 as a biocontrol agent of postharvest fruit diseases. Food Microbiol. 2017, 63, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, X.; Zheng, Z.; Li, X.P.; Wei, J.; Wu, B. Effect of nitrous oxide against Botrytis cinerea and phenylpropanoid pathway metabolism in table grapes. Sci. Horticult. 2019, 254, 99–105. [Google Scholar]
- Wafaa, M.H. Isolation of bioactive antibiotic peptides from Bacillus brevis and Bacillus polymyxa against Botrytis grey mould in strawberry. Arch. Phytopathol. Plant Protect. 2008, 41, 477–491. [Google Scholar]
- Kasfi, K.; Taheri, P.; Jafarpour, B.; Saeed, T. Identification of epiphytic yeasts and bacteria with potential for biocontrol of grey mold disease on table grapes caused by Botrytis cinerea. Span. J. Agric. Res. 2018, 16, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.L.; Shan, W.H.; Hu, H.Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, Q.; Wang, K.; Bian, F.G. Control effect of mixed inoculation of different biocontrol strains on Botrytis cinerea. Chin. J. Biol. Control 2020, 36, 265–271. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, L.; Zhou, L.X.; Liu, Y. Preliminary probe on antagonistic mechanisms of the Pichia pastoris G5 against Botrytis cinerea. Biotech. Bullet. 2017, 33, 210–215. [Google Scholar]
- Garrido, C.C.; Usall, J.; Torres, R.; Teixidό, N. Effective control of Botrytis bunch rot in commercial vineyards by large-scale application of Candida sake CPA-1. BioControl 2017, 62, 161–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santiago, R.; Huiliñir, C.; Cottet, L.; Castillo, A. Microbiological characterization for a new wild strain of Paenibacillus polymyxa with antifungal activity against Botrytis cinerea. BioControl 2016, 103, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, T.; Zhang, P.A.; Zhang, K.K.; Jiu, S.T.; Zhu, X.D.; Song, C.N.; Jia, H.F.; Fang, J.G. Isolation and identification of endophytes from grape bleeding sap and their disease resistance function analysis. Acta Hortic. Sin. 2018, 45, 2106–2120. [Google Scholar]
- Boubakri, H.; Hadj-Brahim, A.; Schmitt, C.; Soustre-Gacougnolle, I.; Mliki, A. Biocontrol potential of chenodeoxycholic acid (CDCA) and endophytic Bacillus subtilis strains against the most destructive grapevine pathogens. N. Z. J. Crop Hort. 2015, 43, 261–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinke, K.; Mohite, O.S.; Weber, T.; Kovács, Á.T. Phylogenetic distribution of secondary metabolites in the Bacillus subtilis species complex. mSystems 2021, 6, e00057-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, C.A. Biological control of postharvest diseases of fruit. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2012, 133, 181–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Xie, J.; Zhou, Y.H.; Deng, L.L.; Yao, S.X.; Zeng, K.F. Inhibitory effect of Pichia membranaefaciens and Kloeckera apiculata against Monilinia fructicola and their biocontrol ability of brown rot in postharvest plum. Biol. Control 2017, 114, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, L.O.; Lima, J.S.; Magalhães, V.C.; Gava, C.A.T.; Soares, A.C.F.; Marbach, P.A.S.; Souza, J.T.D. Compatibility and combination of selected bacterial antagonists in the biocontrol of sisal bole rot disease. BioControl 2018, 63, 595–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nada, O.; Vallance, J.; Gerbore, J.; Yacoub, A.; Rey, P. Combining potential oomycete and bacterial biocontrol agents as a tool to fight tomato rhizoctonia root rot. BioControl 2021, 155, 104521–104532. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, R.R.; Singh, D.; Singh, R. Biological control of postharvest diseases of fruits and vegetables by microbial antagonistis: A review. BioControl 2009, 50, 205–221. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Y.H.; Zheng, Z.H.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, Y.G.; Wang, X.F. Mechanism of rhizosphere micro-ecology in controlling soil-borne fungal diseases: A review. J. China Agric. Univ. 2021, 26, 100–113. [Google Scholar]
- Janisiewicz, W.J.; Korsten, L. Biological control of postharvest diseases of fruit. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2002, 40, 411–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomas, R.G.; Bernardo, M.A.; Alejandra, N.G.; Gabriel, R.E.; Roberto, G.C.C.; Luis, G. Hernandez-Montiel. Enhanced biocontrol of fruit rot on muskmelon by combination treatment with marine Debaryomyces hansenii and Stenotrophomonas rhizophila and their potential modes of action. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2019, 151, 61–67. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, T.T.; Tao, G.; Zhao, X.L.; Wang, Q.; Li, S.D. Biological control of four kinds of microbial preparations against main diseases of pepper. Chin. J. Biol. Control 2020, 36, 258–264. [Google Scholar]
- Bouqellah, N.; Naureen, Z.; Woodwards, S. Multitrophic interactions between Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. lycopersici and Brevibacillus brevis and their role in induction of defense enzymes in tomato plants. Curr. Opin. Biotech. 2011, 22, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, S.G.; Seddon, B. Mode of antagonism of Brevibacillus brevis against Botrytis cinerea in vitro. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2001, 91, 652–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, J.M.; Liu, B.; Chen, Z.; Shi, H.; Liu, G.H.; Ge, C.B. Identification of ethylparaben as the antimicrobial substance produced by Brevibacillus brevis FJAT-0809-GLX. Microbiol. Res. 2015, 172, 48–56. [Google Scholar]
- Che, J.M.; Liu, B.; Liu, G.H.; Chen, Q.Q.; Huang, D.D. Induced mutation breeding of Brevibacillus brevis FJAT-0809-GLX for improving ethylparaben production and its application in the biocontrol of Lasiodiplodia theobromae. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2018, 146, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, J.M.; Liu, B.; Lin, Y.Z.; Tang, W.Q.; Tang, J.Y. Draft genome sequence of biocontrol bacterium Brevibacillus brevis strain FJAT-0809-GLX. Genome Announc. 2013, 1, e00160-13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, J.M.; Liu, B.; Ruan, C.Q.; Tang, J.Y.; Huang, D.D. Biocontrol of Lasiodiplodia theobromae, which causes black spot disease of harvested wax apple fruit, using a strain of Brevibacillus brevis FJAT-0809-GLX. Crop Prot. 2015, 67, 178–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, J.M.; Liu, G.H.; Liu, B.; Chen, Q.Q.; Chen, M.C. Control of banana postharvest antracnose by Brevibacillu sp. strains. Microbiol. China 2020, 47, 1753–1762. [Google Scholar]
- Du, G.F.; Li, X.L.; Qi, Z.Q.; Shen, L.B.; Han, X.; Qin, Y.L.; Cao, Z.M.; Yang, Y. Inhibitory mechanism of ferrous sulfate combined with Bacillus subtilis on Phytophthora capsici. Plant Protect. 2020, 46, 142–149. [Google Scholar]
- AboElyousr, K.A.M.; Ibrahim, O.H.M.; AlQurashi, A.D.; Mousa, M.A.A.; Saad, M.M. Biocontrol potential of endophytic fungi for the eco-friendly management of root rot of Cuminum cyminum caused by Fusarium solani. Agronomy 2022, 12, 2612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, W.; Lumsden, R.D.; Lewis, J.A.; Hebbar, P.K. Seed treatment using pre-infiltration and biocontrol agents to reduce damping-off of corn caused by species of Pythium and Fusarium. Plant Dis. 1998, 3, 294–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhimo, V.Y.; Biasi, A.; Kumar, A.; Feygenberg, O.; Salim, S.; Vero, S.; Wisniewski, M.; Droby, S. Yeasts and bacterial consortia from kefir grains are effective biocontrol agents of postharvest diseases of fruits. Microorgainisms 2020, 8, 428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiva, Y.; Ramesh, G.C.; Binayak, R.P. Evaluation of Trichoderma spp., Pseudomonas fluorescence and Bacillus subtilis for biological control of Ralstonia wilt of tomato. F1000Research 2017, 6, 2028. [Google Scholar]
- Li, G.; Zhao, H.; Liu, Y.Y.; Zhang, M.T.; Pang, X.B.; Guo, J.Q.; Li, X.Y.; Zhu, J.B.; Wang, A.Y. Antagonistic effect of the mixed bacteria culture on Verticillium dahlia. Chin. J. Biol. Control 2018, 34, 431–439. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Cai, Y.; Liang, Y.; Ji, P.; Xu, L. Assessment of antifungal activities of a biocontrol bacterium BA17 for managing postharvest gray mold of green bean caused by Botrytis cinerea. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2020, 161, 111086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, X.N.; Han, X.B.; Cao, J.M.; Li, Y.Q.; Yuan, Y.; Gou, J.Y.; Zheng, Y.F.; Meng, C.; Zhang, C.S. Biocontrol potential of Bacillus velezensis EM-1 associated with suppressive rhizosphere soil microbes against tobacco bacterial wilt. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 940156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashyap, A.S.; Manzar, N.; Nebapure, S.M.; Rajawat, M.V.S.; Deo, M.M.; Singh, J.P.; Kesharwani, A.K.; Singh, R.P.; Dubey, S.C.; Singh, D. Unraveling microbial volatile elicitors using a transparent methodology for induction of systemic resistance and regulation of antioxidant genes at expression levels in Chili against bacterial wilt disease. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.W.; Zhao, L.N.; Bai, Y.H.; Lin, R.L.; Legrand, N.N.G.; Dhanasekaran, S.; Li, B.; Gu, X.Y.; Zhang, X.Y.; Zhang, H.Y. The biocontrol efficacy of Sporidiobolus pararoseus Y16 cultured with gamma-aminobutyric acid and its effects on the resistant substances of postharvest grapes. BioControl 2022, 169, 104900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabdwal, B.C.; Sharma, R.; Kumar, A.; Kumar, S.; Singh, K.P.; Srivastava, R.M. Efficacy of different combinations of microbial biocontrol agents against sheath blight of rice caused by Rhizoctonia solani. Egypt. J. Biol. Pest Control 2023, 33, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.Y.; Wang, Y.C.; Ai, D.; Li, Z.R.; Wang, Y.H. Biocontrol yeast T-2 improves the postharvest disease resistance of grape by stimulation of the antioxidant system. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 10, 3219–3229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Che, J.; Lai, C.; Lai, G.; Chen, Q.; Liu, G.; Liu, B. Effects of a Mixture of Brevibacillus brevis with Other Bacillus sp. Strains against Gray Mold and on Enzyme Activities of Grape. Agronomy 2023, 13, 1724. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13071724
Che J, Lai C, Lai G, Chen Q, Liu G, Liu B. Effects of a Mixture of Brevibacillus brevis with Other Bacillus sp. Strains against Gray Mold and on Enzyme Activities of Grape. Agronomy. 2023; 13(7):1724. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13071724
Chicago/Turabian StyleChe, Jianmei, Chengchun Lai, Gongti Lai, Qianqian Chen, Guohong Liu, and Bo Liu. 2023. "Effects of a Mixture of Brevibacillus brevis with Other Bacillus sp. Strains against Gray Mold and on Enzyme Activities of Grape" Agronomy 13, no. 7: 1724. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13071724
APA StyleChe, J., Lai, C., Lai, G., Chen, Q., Liu, G., & Liu, B. (2023). Effects of a Mixture of Brevibacillus brevis with Other Bacillus sp. Strains against Gray Mold and on Enzyme Activities of Grape. Agronomy, 13(7), 1724. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13071724





