Adsorption of Pb2+ and Cd2+ in Agricultural Water by Potassium Permanganate and Nitric Acid-Modified Coconut Shell Biochar
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Test Materials
2.2. Characterization of Biochar
2.3. Adsorption Experiment
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Determination of Optimal MHBC Conditions
3.2. Characterization
2R-COOH + M2+ → (R-COOH) 2M + 2H2+
3.3. Optimization of MHBC Dose
3.4. Adsorption Kinetics
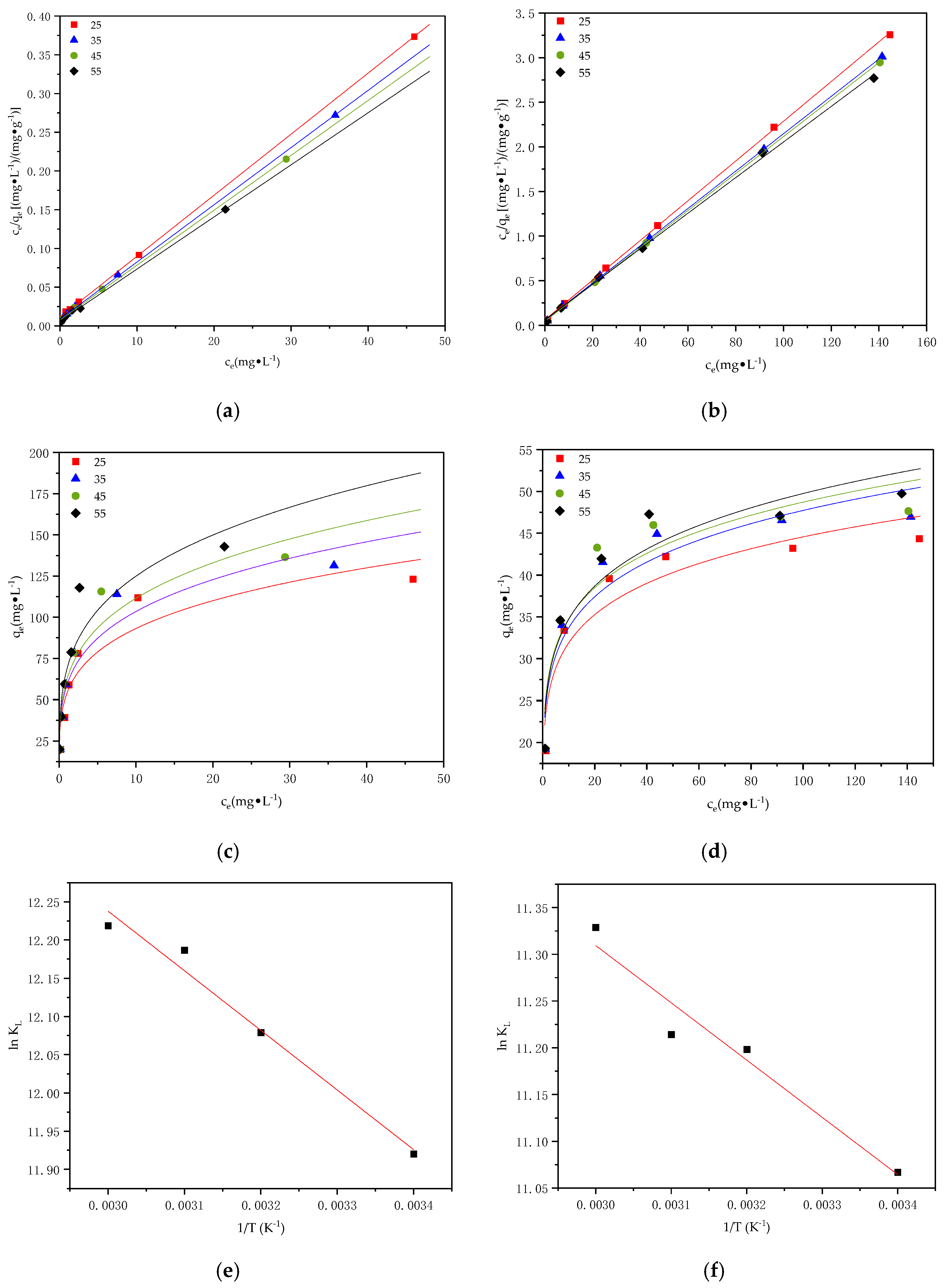
3.5. Adsorption Thermodynamics
3.6. pH
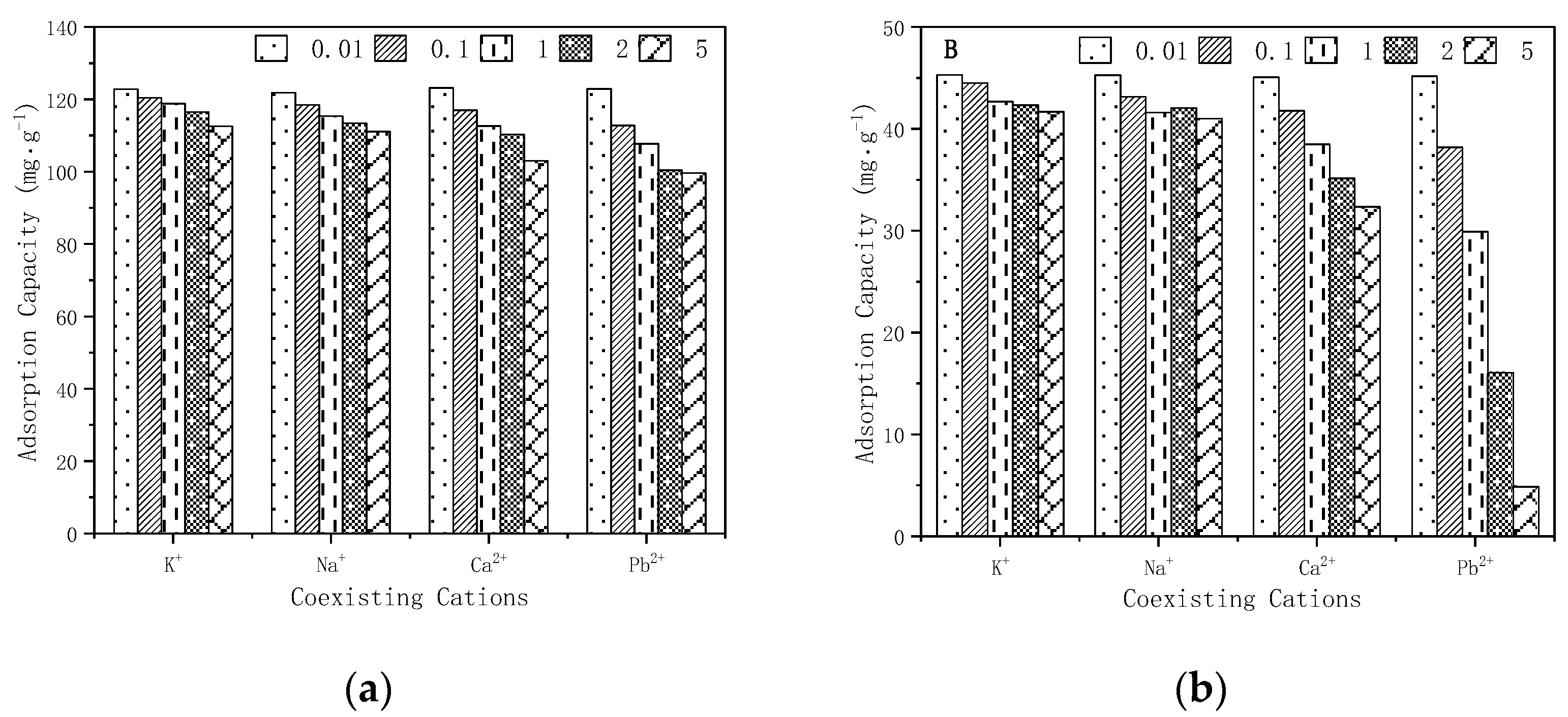
3.7. Coexisting Ion
3.8. Reuse
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Briffa, J.; Sinagra, E.; Blundell, R. Heavy metal pollution in the environment and their toxicological effects on humans. Heliyon 2020, 6, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, T.Y.; Xue, D.W.; Zhao, L.M.; Zhang, X.Y. Concentration of heavy metals in vegetables and potential health risk assessment in China. Environ. Geochem. Health 2018, 40, 313–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.K.; Mao, X.Y.; Hamoud, Y.A.; Zhu, N.Y.; Shao, X.H.; Wang, Q.L.; Shaghaleh, H. Nitrogen Removal for Low Concentration Ammonium Wastewater by Adsorption, Shortcut Simultaneous Nitrification and Denitrification Process in MBBR. Water 2023, 15, 1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.K.; Zhu, N.Y.; Shaghaleh, H.; Mao, X.Y.; Shao, X.H.; Wang, Q.L.; Hamoud, Y.A. The Effect of Functional Ceramsite in a Moving Bed Biofilm Reactor and Its Ammonium Nitrogen Adsorption Mechanism. Water 2023, 15, 1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.Y.; Ma, Z.W.; van der Kuijp, T.J.; Yuan, Z.W.; Huang, L. A review of soil heavy metal pollution from mines in China: Pollution and health risk assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 468, 843–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burakov, A.E.; Galunin, E.V.; Burakova, I.V.; Kucherova, A.E.; Agarwal, S.; Tkachev, A.G.; Gupta, V.K. Adsorption of heavy metals on conventional and nanostructured materials for wastewater treatment purposes: A review. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 148, 702–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harvey, P.J.; Handley, H.K.; Taylor, M.P. Identification of the sources of metal (lead) contamination in drinking waters in north-eastern Tasmania using lead isotopic compositions. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 12276–12288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Wang, J.; Wu, D.; Li, X.; Luo, Y.; Han, C.; Ma, W.; He, S. Investigating the Heavy Metal Adsorption of Mesoporous Silica Materials Prepared by Microwave Synthesis. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2017, 12, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mao, X.Y.; Sun, J.J.; Shaghaleh, H.; Jiang, X.S.; Yu, H.Z.; Zhai, S.M.; Hamoud, Y.A. Environmental Assessment of Soils and Crops Based on Heavy Metal Risk Analysis in Southeastern China. Agronomy 2023, 13, 1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopinathan, R.; Bhowal, A.; Garlapati, C. Adsorption Characteristics of Activated Carbon for the Reclamation of Colored Effluents Containing Orange G and New Solid-Liquid Phase Equilibrium Model. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2017, 62, 558–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grotzner, M.; Melchiors, E.; Schroeder, L.H.; dos Santos, A.R.; Moscon, K.G.; de Andrade, M.A.; Martinelli, S.H.S.; Xavier, C.R. Pulp and Paper Mill Effluent Treated by Combining Coagulation-Flocculation-Sedimentation and Fenton Processes. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2018, 229, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaafarzadeh, N.; Baboli, Z.; Noorimotlagh, Z.; Martinez, S.S.; Ahmadi, M.; Alavi, S.; Mirzaee, S.A. Efficient adsorption of bisphenol A from aqueous solutions using low-cost activated carbons produced from natural and synthetic carbonaceous materials. Desalination Water Treat. 2019, 154, 177–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karnib, M.; Kabbani, A.; Holail, H.; Olama, Z. Heavy Metals Removal Using Activated Carbon, Silica and Silica Activated Carbon Composite. Energy Procedia 2014, 50, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fan, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Li, M.; Niu, D.; Sang, W.; Verpoort, F. Investigating the sorption behavior of cadmium from aqueous solution by potassium permanganate-modified biochar: Quantify mechanism and evaluate the modification method. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 8330–8339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dewage, N.B.; Fowler, R.E.; Pittman, C.U.; Mohan, D.; Mlsna, T. Lead (Pb2+) sorptive removal using chitosan-modified biochar: Batch and fixed-bed studies. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 25368–25377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.H.; Liu, W.J.; Jiang, R.F.; Wang, Z.S. Study on the adsorption mechanism of activated carbon removing low concentrations of heavy metals. Desalination Water Treat. 2016, 57, 7812–7822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.T.; Cao, X.; Ouyang, X.; Sohi, S.P.; Chen, J.W. Adsorption kinetics of magnetic biochar derived from peanut hull on removal of Cr (VI) from aqueous solution: Effects of production conditions and particle size. Chemosphere 2016, 145, 336–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomczyk, A.; Sokolowska, Z.; Boguta, P. Biochar physicochemical properties: Pyrolysis temperature and feedstock kind effects. Rev. Environ. Sci. Bio. Technol. 2020, 19, 191–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Doumer, M.E.; Rigol, A.; Vidal, M.; Mangrich, A.S. Removal of Cd, Cu, Pb, and Zn from aqueous solutions by biochars. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 2684–2692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.H.; Ok, Y.S.; Kim, S.H.; Cho, J.S.; Heo, J.S.; Delaune, R.D.; Seo, D.C. Competitive adsorption of heavy metals onto sesame straw biochar in aqueous solutions. Chemosphere 2016, 142, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.Y.; Liu, Y.X.; Lu, H.H.; Yang, R.Q.; Yang, S.M. Competitive adsorption of Pb(II), Cu(II), and Zn(II) ions onto hydroxyapatite-biochar nanocomposite in aqueous solutions. J. Solid State Chem. 2018, 261, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Zong, Y. Pore structure and environmental serves of biochars derived from different feedstocks and pyrolysis conditions. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 30401–30409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalina, M.; Sovova, S.; Svec, J.; Trudicova, M.; Hajzler, J.; Kubikova, L.; Enev, V. The Effect of Pyrolysis Temperature and the Source Biomass on the Properties of Biochar Produced for the Agronomical Applications as the Soil Conditioner. Materials 2022, 15, 8855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.B.; Gao, P.; Chu, G.; Pan, B.; Peng, J.H.; Xing, B.S. Enhanced adsorption of Cu(II) and Cd(II) by phosphoric acid-modified biochars. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 229, 846–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicola, R.; Costisor, O.; Ciopec, M.; Negrea, A.; Lazau, R.; Ianasi, C.; Piciorus, E.M.; Len, A.; Almasy, L.; Szerb, E.I.; et al. Silica-Coated Magnetic Nanocomposites for Pb2+ Removal from Aqueous Solution. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 2726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wongrod, S.; Simon, S.; Guibaud, G.; Lens, P.N.L.; Pechaud, Y.; Huguenot, D.; van Hullebusch, E.D. Lead sorption by biochar produced from digestates: Consequences of chemical modification and washing. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 219, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ianasi, C.; Piciorus, M.; Nicola, R.; Ciopec, M.; Negrea, A.; Niznansky, D.; Len, A.; Almasy, L.; Putz, A.M. Removal of cadmium from aqueous solutions using inorganic porous nanocomposites. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2019, 36, 688–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Yin, M.L.; Tsang, D.C.W.; Yang, S.T.; Liu, J.; Li, X.; Song, G.; Wang, J. Mechanisms of U(VI) removal by biochar derived from Ficus microcarpa aerial root: A comparison between raw and modified biochar. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 697, 134115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salam, M.A.; Owija, N.Y.; Kosa, S. Removal of the toxic cadmium ions from aqueous solutions by zero-valent iron nanoparticles. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 18, 2391–2404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Banna, M.F.; Mosa, A.; Gao, B.; Yin, X.Q.; Wang, H.Y.; Ahmad, Z. Scavenging effect of oxidized biochar against the phytotoxicity of lead ions on hydroponically grown chicory: An anatomical and ultrastructural investigation. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 170, 363–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyuan, Y.A.O.; Zhifeng, D.O.U.; Guangmin, H.; Rencheng, L.I.U. Pyrolysis and pyrolysis kinetics of coconut shell, coconut shell residue and de-ashed coconut shell residue. J. Chem. Ind. Eng. 2007, 58, 1210–1214. [Google Scholar]
- Samsudin, M.H.; Hassan, M.A.; Idris, J.; Ramli, N.; Mohd Yusoff, M.Z.; Ibrahim, I.; Othman, M.R.; Mohd Ali, A.A.; Shirai, Y. A one-step self-sustained low temperature carbonization of coconut shell biomass produced a high specific surface area biochar-derived nano-adsorbent. Waste Manag. Res. 2019, 37, 551–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamran, U.; Park, S.J. MnO2-decorated biochar composites of coconut shell and rice husk: An efficient lithium ions adsorption-desorption performance in aqueous media. Chemosphere 2020, 260, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.K.; Xu, F.; Xie, Y.L.; Wang, C.; Zhang, A.K.; Li, L.L.; Xu, H. Effect of modified coconut shell biochar on availability of heavy metals and biochemical characteristics of soil in multiple heavy metals contaminated soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 645, 702–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, W.D.; Li, J.H.; Lan, T.; Muller, K.; Niazi, N.K.; Chen, X.; Xu, S.; Zheng, L.R.; Chu, Y.C.; Li, J.W.; et al. Unraveling sorption of lead in aqueous solutions by chemically modified biochar derived from coconut fiber: A microscopic and spectroscopic investigation. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 576, 766–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.R.; Zhang, Z.M.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Y.; Hu, S.; Xiang, J.; Hu, X. Steam reforming of acetic acid over Ni/biochar catalyst treated with HNO3: Impacts of the treatment on surface properties and catalytic behaviors. Fuel 2020, 278, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Zhang, C.; Liu, B.; Liu, G.; Xing, B. A New Paradigm for Environmental Chemistry and Toxicology; Jiang, G.B., Ed.; Springer: Singapore, 2019; pp. 153–196. [Google Scholar]
- Ajeng, A.A.; Abdullah, R.; Ling, T.C.; Ismail, S.; Lau, B.F.; Ong, H.C.; Chew, K.W.; Show, P.L.; Chang, J.S. Bioformulation of biochar as a potential inoculant carrier for sustainable agriculture. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2020, 20, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanhaei, B.; Ayati, A.; Lahtinen, M.; Sillanpaa, M. Preparation and characterization of a novel chitosan/Al2O3/magnetite nanoparticles composite adsorbent for kinetic, thermodynamic and isotherm studies of Methyl Orange adsorption. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 259, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.J.; Li, X.D.; Xu, S.X.; Zhao, X.Y.; Ni, M.J.; Cen, K.F. Comparison of adsorption behavior of PCDD/Fs on carbon nanotubes and activated carbons in a bench-scale dioxin generating system. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 10463–10470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.Q.; Li, K.X.; Sun, G.H.; Wang, J.L. Synthesis and characterization of activated carbon with a high mesoporosity. New Carbon Mater. 2011, 26, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.L.; Zhou, D.D.; Zhu, L.Z. Transitional adsorption and partition of nonpolar and polar aromatic contaminants by biochars of pine needles with different pyrolytic temperatures. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 5137–5143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantrell, K.B.; Hunt, P.G.; Uchimiya, M.; Novak, J.M.; Ro, K.S. Impact of pyrolysis temperature and manure source on physicochemical characteristics of biochar. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 107, 419–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keiluweit, M.; Nico, P.S.; Johnson, M.G.; Kleber, M. Dynamic Molecular Structure of Plant Biomass-Derived Black Carbon (Biochar). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 1247–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, B.L.; Johnson, E.J.; Chefetz, B.; Zhu, L.Z.; Xing, B.S. Sorption of polar and nonpolar aromatic organic contaminants by plant cuticular materials: Role of polarity and accessibility. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 6138–6146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.L.; Pan, B.C.; Li, H.Y.; Zhang, W.M.; Lv, L.; Wu, J. Selective Removal of Cu(II) Ions by Using Cation-exchange Resin-Supported Polyethyleneimine (PEI) Nanoclusters. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 3508–3513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, I.A.; Jafarzadeh, M.; Sipaut, C.S. Synthesis of organo-functionalized nanosilica via a co-condensation modification using gamma-aminopropyltriethoxysilane (APTES). Ceram. Int. 2009, 35, 1883–1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Yang, L.; Wang, C.Q.; Zhang, Q.P.; Liu, Q.C.; Li, Y.D.; Xiao, R. Adsorption of Cd(II) from aqueous solutions by rape straw biochar derived from different modification processes. Chemosphere 2017, 175, 332–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohan, D.; Pittman, C.U.; Bricka, M.; Smith, F.; Yancey, B.; Mohammad, J.; Steele, P.H.; Alexandre-Franco, M.F.; Gomez-Serrano, V.; Gong, H. Sorption of arsenic, cadmium, and lead by chars produced from fast pyrolysis of wood and bark during bio-oil production. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2007, 310, 57–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, T.Y.; Jiang, J.; Xu, R.K.; Li, Z. Adsorption of Pb(II) on variable charge soils amended with rice-straw derived biochar. Chemosphere 2012, 89, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trakal, L.; Veselska, V.; Safarik, I.; Vitkova, M.; Cihalova, S.; Komarek, M. Lead and cadmium sorption mechanisms on magnetically modified biochars. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 203, 318–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, H.H.; Tang, J.C.; Huang, Y.; Gai, L.S.; Zeng, E.Y.; Liber, K.; Gong, Y.Y. Removal of hexavalent chromium from aqueous solutions by a novel biochar supported nanoscale iron sulfide composite. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 322, 516–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, Y.S.; McKay, G. Pseudo-second order model for sorption processes. Process Biochem. 1999, 34, 451–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, Y.S.; McKay, G. Kinetic models for the sorption of dye from aqueous solution by wood. Process Saf. Environ. Protect. 1998, 76, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cui, X.Q.; Fang, S.Y.; Yao, Y.Q.; Li, T.Q.; Ni, Q.J.; Yang, X.E.; He, Z.L. Potential mechanisms of cadmium removal from aqueous solution by Canna indica derived biochar. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 562, 517–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapica, J.; Pelech, R.; Przepiorski, J.; Morawski, A.W. Kinetics of the adsorption of copper and lead ions from aqueous solution on to WD-ekstra activated carbon. Adsorpt. Sci. Technol. 2002, 20, 441–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masoumi, A.; Ghaemy, M.; Bakht, A.N. Removal of Metal Ions from Water Using Poly(MMA-co-MA)/Modified-Fe3O4 Magnetic Nanocomposite: Isotherm and Kinetic Study. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2014, 53, 8188–8197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loganathan, P.; Shim, W.G.; Sounthararajah, D.P.; Kalaruban, M.; Nur, T.; Vigneswaran, S. Modelling equilibrium adsorption of single, binary, and ternary combinations of Cu, Pb, and Zn onto granular activated carbon. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 16664–16675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jia, Y.; Zhang, Y.S.; Fu, J.G.; Yuan, L.X.; Li, Z.; Liu, C.; Zhao, D.; Wang, X.B. A novel magnetic biochar/MgFe-layered double hydroxides composite removing Pb2+ from aqueous solution: Isotherms, kinetics and thermodynamics. Colloid Surf. A-Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2019, 567, 278–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faust, M.; Seipenbusch, M. Highly controlled structuring of Pt nanoparticles on TiO2 and on ZrO2 by a modified MOCVD process. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2014, 259, 577–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arthy, M.; Saravanakumar, M.P. Isotherm modeling, kinetic study and optimization of batch parameters for effective removal of Acid Blue 45 using tannery waste. J. Mol. Liq. 2013, 187, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zama, E.F.; Zhu, Y.G.; Reid, B.J.; Sun, G.X. The role of biochar properties in influencing the sorption and desorption of Pb(II), Cd(II) and As(III) in aqueous solution. J. Clean Prod. 2017, 148, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cantu, Y.; Remes, A.; Reyna, A.; Martinez, D.; Villarreal, J.; Ramos, H.; Trevino, S.; Tamez, C.; Martinez, A.; Eubanks, T.; et al. Thermodynamics, kinetics, and activation energy studies of the sorption of chromium(III) and chromium(VI) to a Mn3O4 nanomaterial. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 254, 374–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, H.Y.; Gao, B.; Wang, S.S.; Fang, J.; Xue, Y.W.; Yang, K. Removal of Pb(II), Cu(II), and Cd(II) from aqueous solutions by biochar derived from KMnO4 treated hickory wood. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 197, 356–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lin, L.N.; Qiu, W.W.; Wang, D.; Huang, Q.; Song, Z.G.; Chau, H.W. Arsenic removal in aqueous solution by a novel Fe-Mn modified biochar composite: Characterization and mechanism. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2017, 144, 514–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Argun, M.E.; Dursun, S.; Ozdemir, C.; Karatas, M. Heavy metal adsorption by modified oak sawdust: Thermodynamics and kinetics. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 141, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benzaoui, T.; Selatnia, A.; Djabali, D. Adsorption of copper (II) ions from aqueous solution using bottom ash of expired drugs incineration. Adsorpt. Sci. Technol. 2018, 36, 114–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mall, I.D.; Srivastava, V.C.; Agarwal, N.K. Removal of Orange-G and Methyl Violet dyes by adsorption onto bagasse fly ash—Kinetic study and equilibrium isotherm analyses. Dyes. Pigment. 2006, 69, 210–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jefferson, W.A.; Hu, C.Z.; Liu, H.J.; Qu, J.H. Reaction of aqueous Cu-Citrate with MnO2 birnessite: Characterization of Mn dissolution, oxidation products and surface interactions. Chemosphere 2015, 119, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.B.; Cao, X.H.; Liang, P.; Liu, Y.H. Adsorption of uranium from aqueous solution using biochar produced by hydrothermal carbonization. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2013, 295, 1201–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.; Li, S.W.; Peng, X.Q.; Liu, W.; Zhang, C.L.; Yang, Y.; Han, L.F.; Du, Z.W.; Sun, K.; Wang, X.K. HNO3 modified biochars for uranium (VI) removal from aqueous solution. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 256, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, D.; Laldanwngliana, C.; Choi, C.H.; Lee, S.M. Manganese-modified natural sand in the remediation of aquatic environment contaminated with heavy metal toxic ions. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 171, 958–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.G.; Zhang, F.S. Removal of lead from water using biochars prepared from hydrothermal liquefaction of biomass. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 167, 933–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukherjee, A.; Zimmerman, A.R.; Harris, W. Surface chemistry variations among a series of laboratory-produced biochars. Geoderma 2011, 163, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.L.; Ma, L.N.Q.; Li, Y.C. Characteristics and mechanisms of hexavalent chromium removal by biochar from sugar beet tailing. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 190, 909–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Q.; Yang, H.; Wang, B.; Xie, J. Effects of coexisting ions on adsorption of Pb~(2+)onto Bentonite/LS-g-AM-co-MAH. Acta Mater. Compos. Sin. 2016, 33, 2181–2186. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, X.D.; Ma, L.N.; Gao, B.; Harris, W. Dairy-Manure Derived Biochar Effectively Sorbs Lead and Atrazine. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 3285–3291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Liu, Y.G.; Liu, S.B.; Li, Z.W.; Tan, X.F.; Huang, X.X.; Zeng, G.M.; Zhou, Y.Y.; Zheng, B.H.; Cai, X.X. Competitive removal of Cd(II) and Pb(II) by biochars produced from water hyacinths: Performance and mechanism. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 5223–5232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Shan, B.Q.; Tang, W.Z.; Zhu, Y.Y. Comparison of cadmium and lead sorption by Phyllostachys pubescens biochar produced under a low-oxygen pyrolysis atmosphere. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 238, 352–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

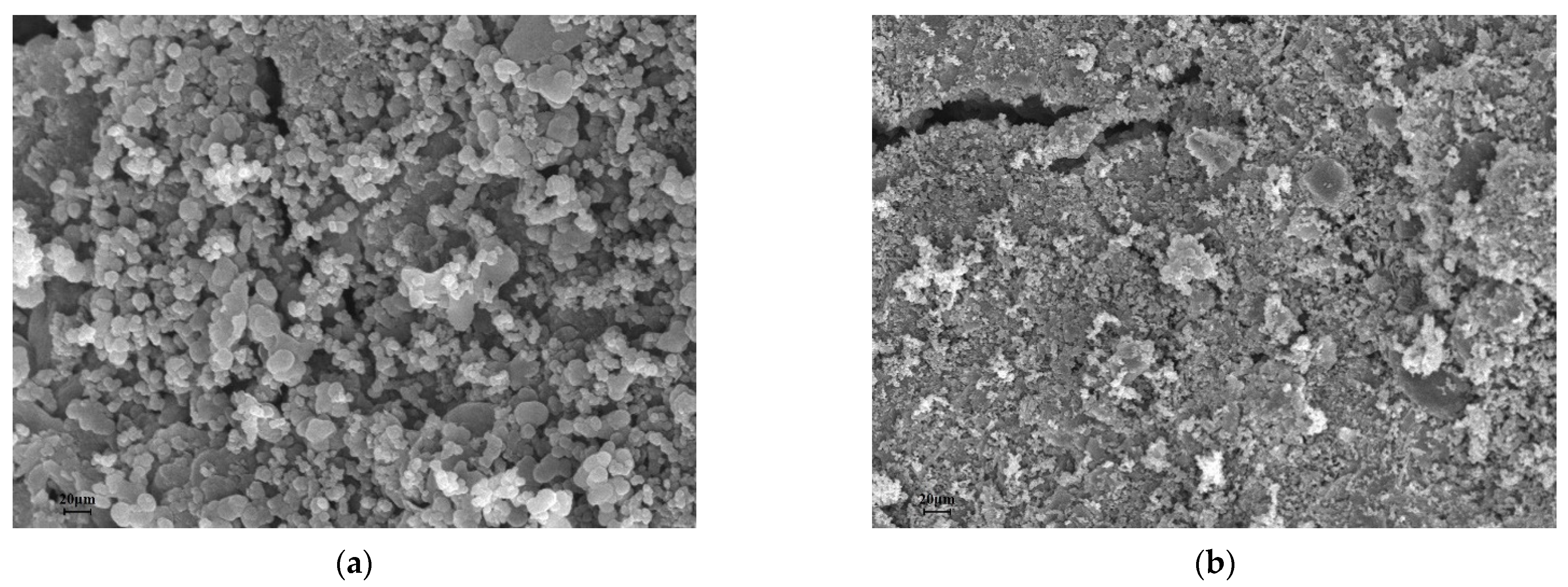
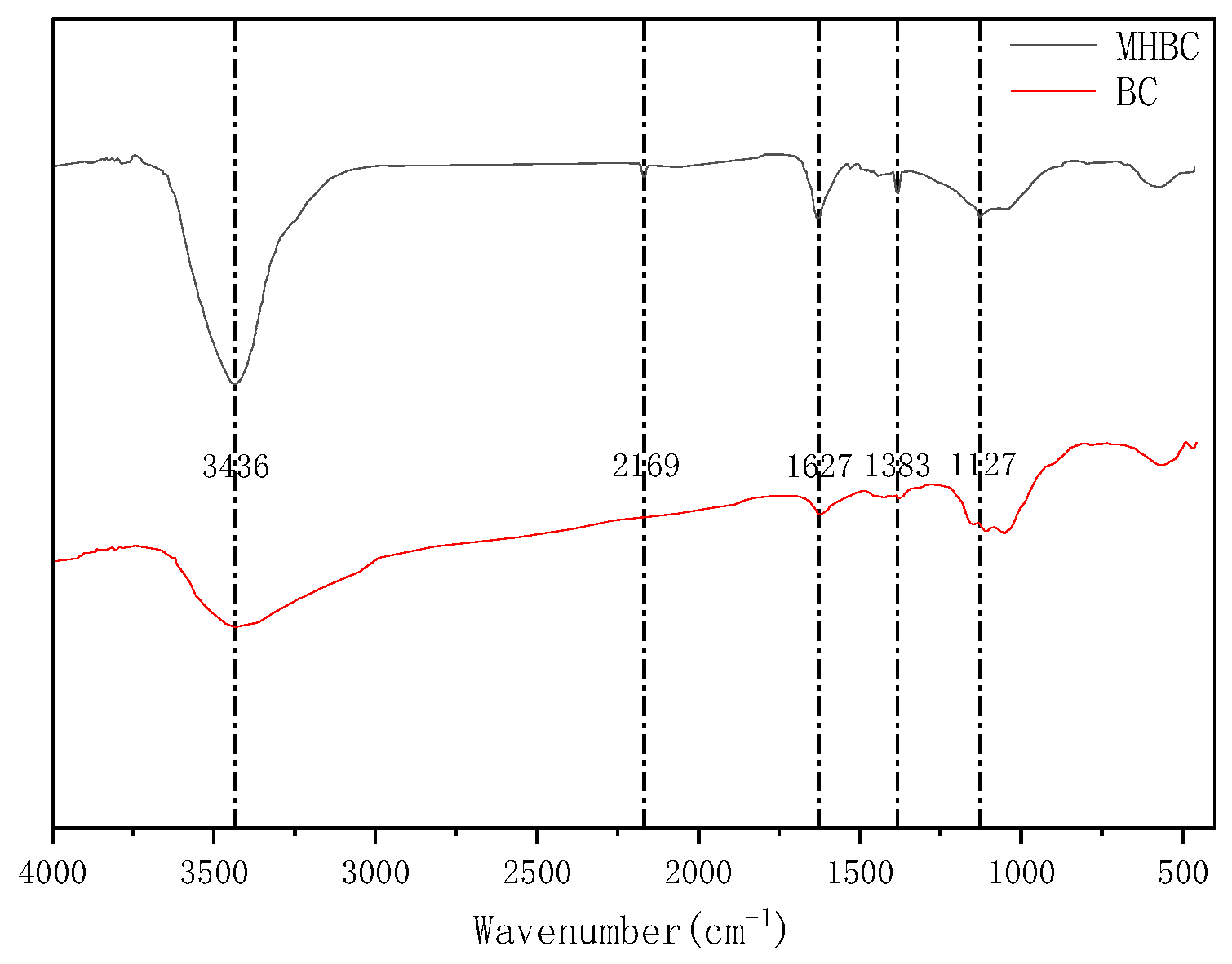
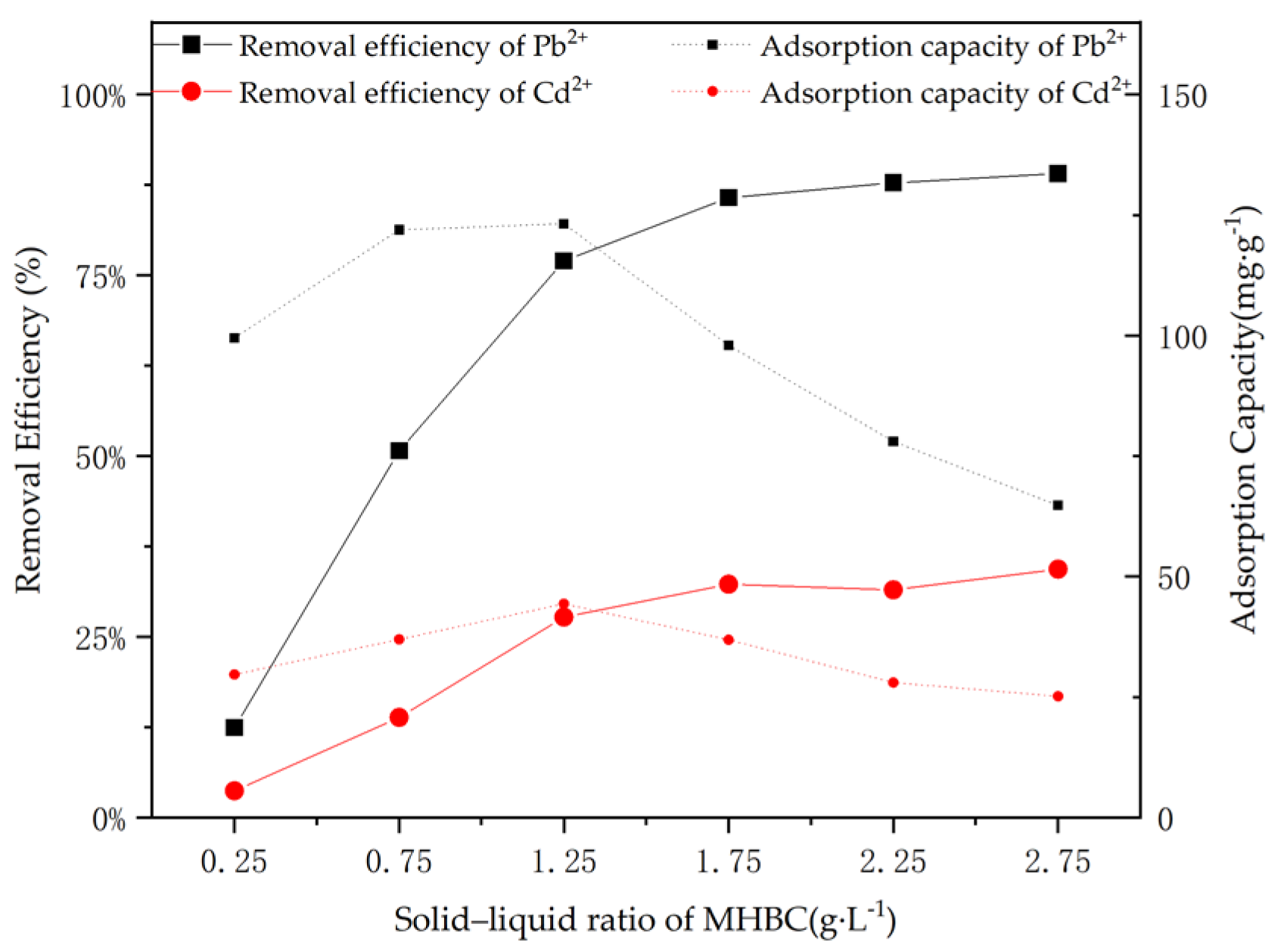
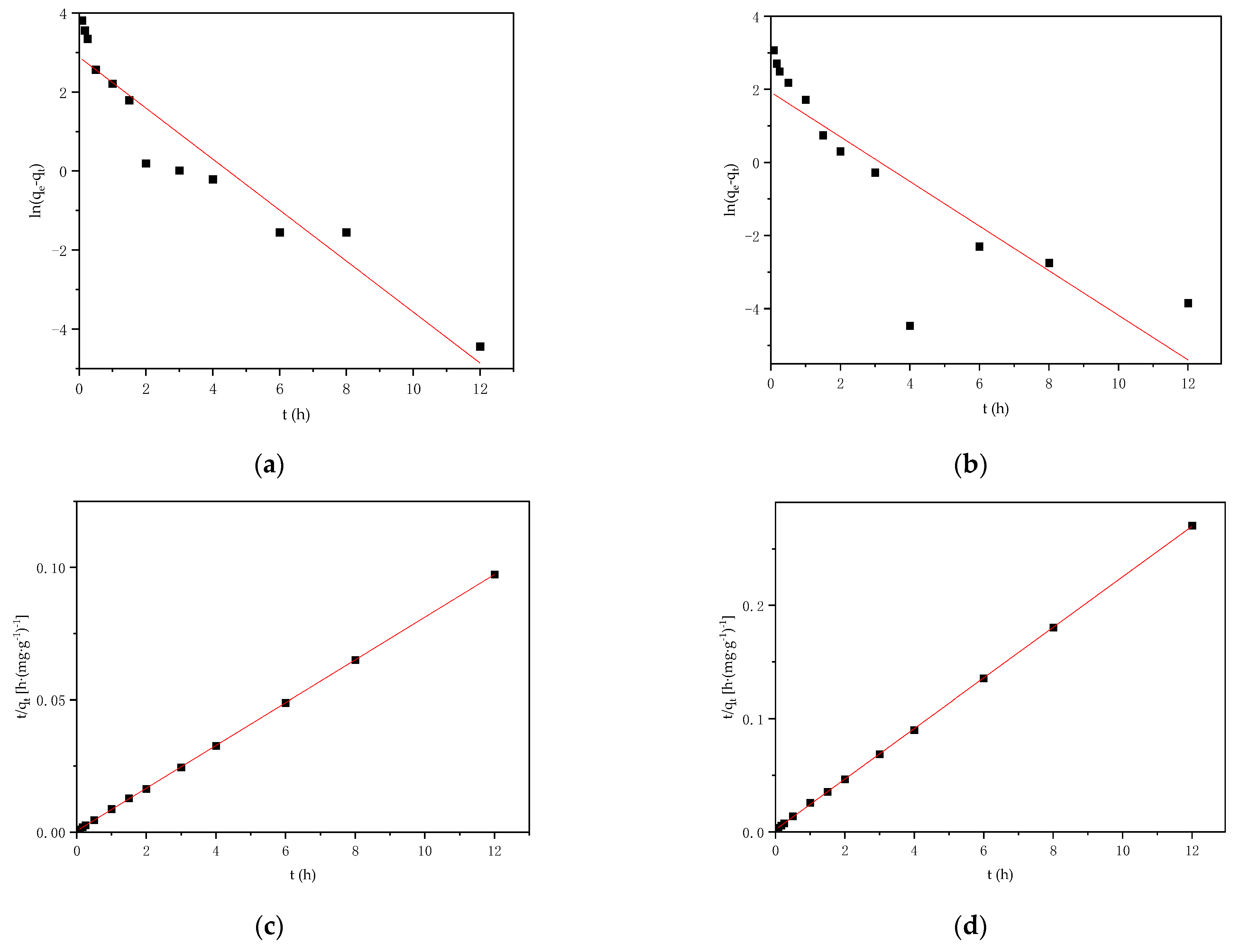



| Sample | Pb | Cd | SBET | Vtot | Pore Width | C | H | O | N |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mg·kg−1 | mg·kg−1 | m2·g−1 | cm3·g−1 | nm | |||||
| BC | 12.37 | 0.19 | 157.46 | 0.21 | 3.80 | 77.62 | 3.91 | 9.15 | 0.33 |
| MHBC | 12.38 | 0.18 | 475.36 | 0.38 | 1.65 | 71.58 | 3.22 | 13.37 | 0.52 |
| Sample | Acidic Functional Groups | Carboxyl | Lactone | Phenol |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| mmol·g−1 | mmol·g−1 | mmol·g−1 | mmol·g−1 | |
| BC | 0.43 | 0.11 | 0.13 | 0.17 |
| MHBC | 1.14 | 0.36 | 0.44 | 0.25 |
| Adsorbate | Pseudo-First-Order | Pseudo-Second-Order | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qe,cal (mg·g−1) | k1 (h−1) | R2 | qe,cal (mg·g−1) | k2 (g·mg−1·h−1) | R2 | |
| Pb2+ | 17.90 | 0.65 | 0.904 | 123.92 | 0.13 | 0.999 |
| Cd2+ | 9.13 | 0.59 | 0.906 | 44.80 | 0.24 | 0.999 |
| Adsorbate | Weber–Morris | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| First-Stage | Second-Stage | Third-Stage | |||||||
| C | k | R2 | C | k | R2 | C | k | R2 | |
| Pb2+ | 56.27 | 76.54 | 0.998 | 103.17 | 11.68 | 0.840 | 121.57 | 0.49 | 0.775 |
| Cd2+ | 16.25 | 28.94 | 0.898 | 33.68 | 6.14 | 0.778 | 44.21 | 0.01 | 0.006 |
| T | Langmuir | Freundlich | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qe,cal (mg·g−1) | kL (L·mg−1) | R2 | kF | n | R2 | |
| 25 | 124.31 | 0.73 | 0.993 | 53.63 | 4.17 | 0.855 |
| 35 | 131.54 | 0.85 | 0.990 | 59.06 | 4.49 | 0.833 |
| 45 | 144.29 | 0.95 | 0.976 | 62.06 | 3.93 | 0.896 |
| 55 | 160.41 | 0.98 | 0.958 | 68.25 | 3.81 | 0.848 |
| Table | Langmuir | Freundlich | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qe,cal (mg·g−1) | kL (L·mg−1) | R2 | kF | n | R2 | |
| 25 | 44.37 | 0.57 | 0.968 | 22.82 | 6.88 | 0.872 |
| 35 | 45.82 | 0.65 | 0.956 | 23.69 | 6.88 | 0.883 |
| 45 | 47.16 | 0.66 | 0.953 | 24.20 | 6.79 | 0.886 |
| 55 | 47.46 | 0.78 | 0.941 | 24.39 | 6.54 | 0.876 |
| Temp k | kJ·mol−1 | kJ·mol−1 | kJ·mol−1 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pb2+ | 298 | 150,273.72 | −29.53 | 6.485 | 121.20 |
| 308 | 176,132.16 | −30.93 | |||
| 318 | 196,169.76 | −32.22 | |||
| 328 | 202,551.57 | −33.32 | |||
| Cd2+ | 298 | 64,027.04 | −27.42 | 5.092 | 109.30 |
| 308 | 73,009.44 | −28.68 | |||
| 318 | 74,180.96 | −29.65 | |||
| 328 | 83,195.84 | −30.89 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qin, H.; Shao, X.; Shaghaleh, H.; Gao, W.; Hamoud, Y.A. Adsorption of Pb2+ and Cd2+ in Agricultural Water by Potassium Permanganate and Nitric Acid-Modified Coconut Shell Biochar. Agronomy 2023, 13, 1813. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13071813
Qin H, Shao X, Shaghaleh H, Gao W, Hamoud YA. Adsorption of Pb2+ and Cd2+ in Agricultural Water by Potassium Permanganate and Nitric Acid-Modified Coconut Shell Biochar. Agronomy. 2023; 13(7):1813. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13071813
Chicago/Turabian StyleQin, Hengji, Xiaohou Shao, Hiba Shaghaleh, Wei Gao, and Yousef Alhaj Hamoud. 2023. "Adsorption of Pb2+ and Cd2+ in Agricultural Water by Potassium Permanganate and Nitric Acid-Modified Coconut Shell Biochar" Agronomy 13, no. 7: 1813. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13071813
APA StyleQin, H., Shao, X., Shaghaleh, H., Gao, W., & Hamoud, Y. A. (2023). Adsorption of Pb2+ and Cd2+ in Agricultural Water by Potassium Permanganate and Nitric Acid-Modified Coconut Shell Biochar. Agronomy, 13(7), 1813. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13071813








