Effects of Bio-Organic Fertilizer on Soil Infiltration, Water Distribution, and Leaching Loss under Muddy Water Irrigation Conditions
Abstract
1. Introduction
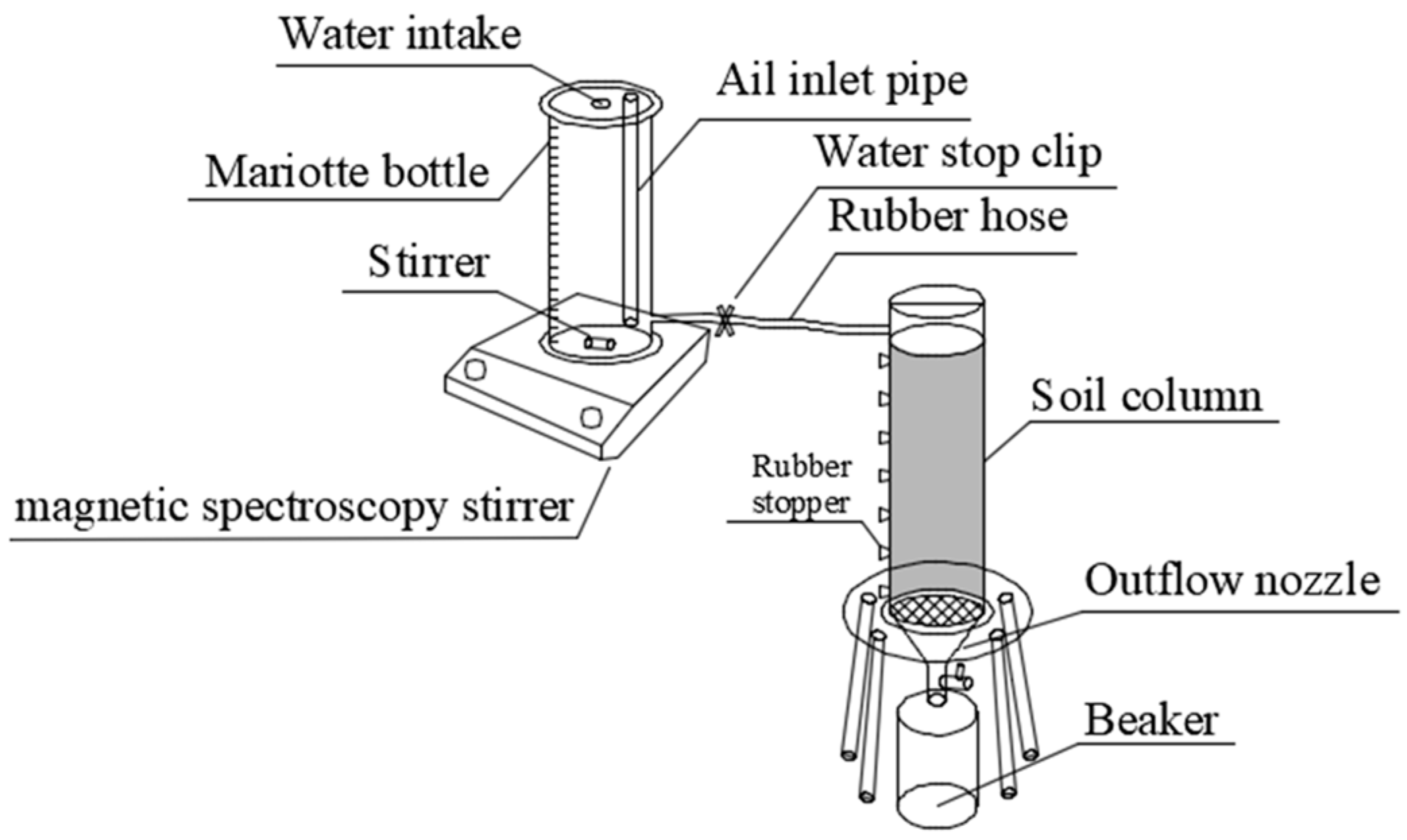
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Material Preparation
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Measurements and Calculations
2.4. Evaluation Models and Indicators
2.5. Data Statistics and Analysis
3. Results
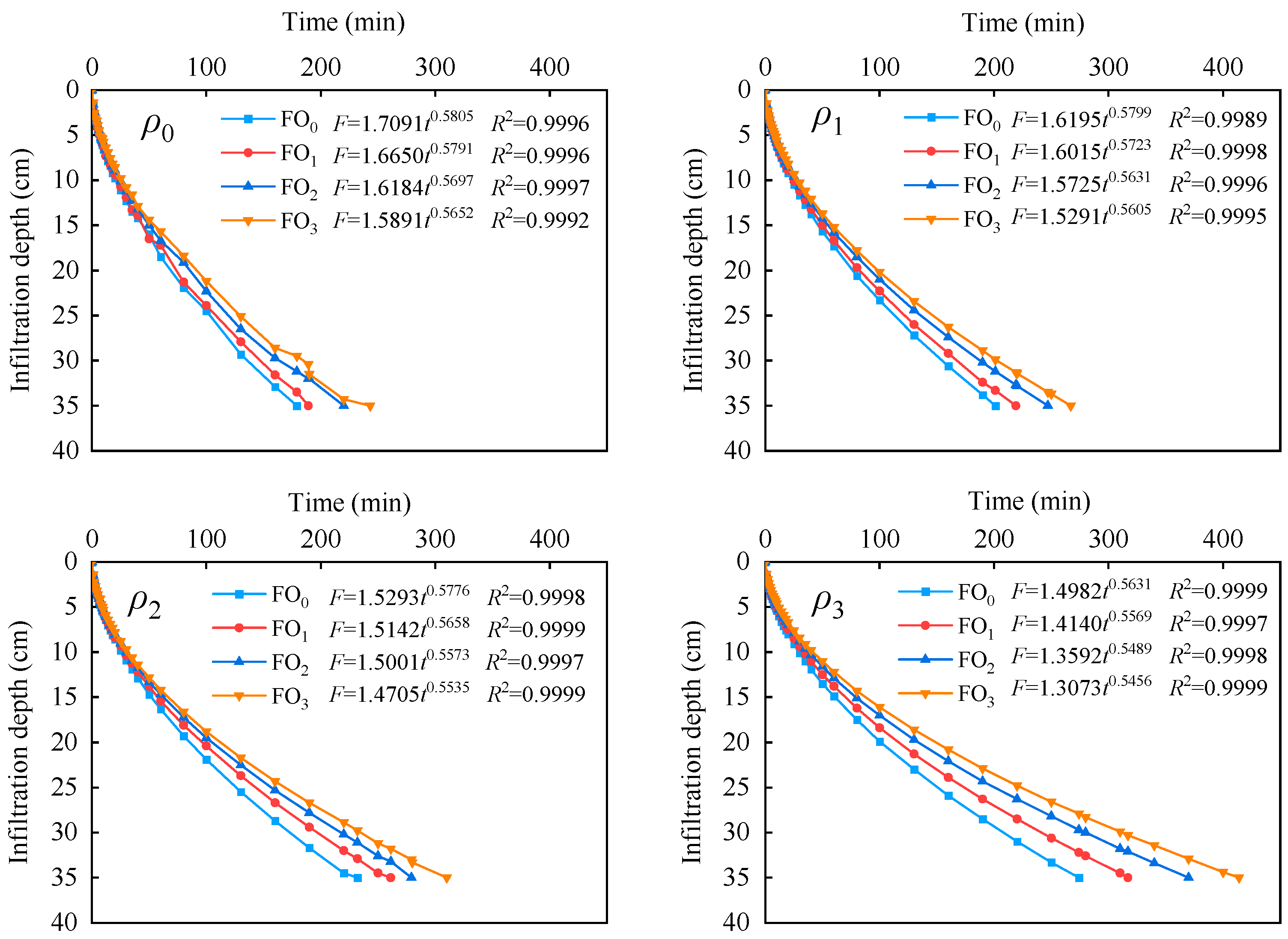
3.1. Wetting Front
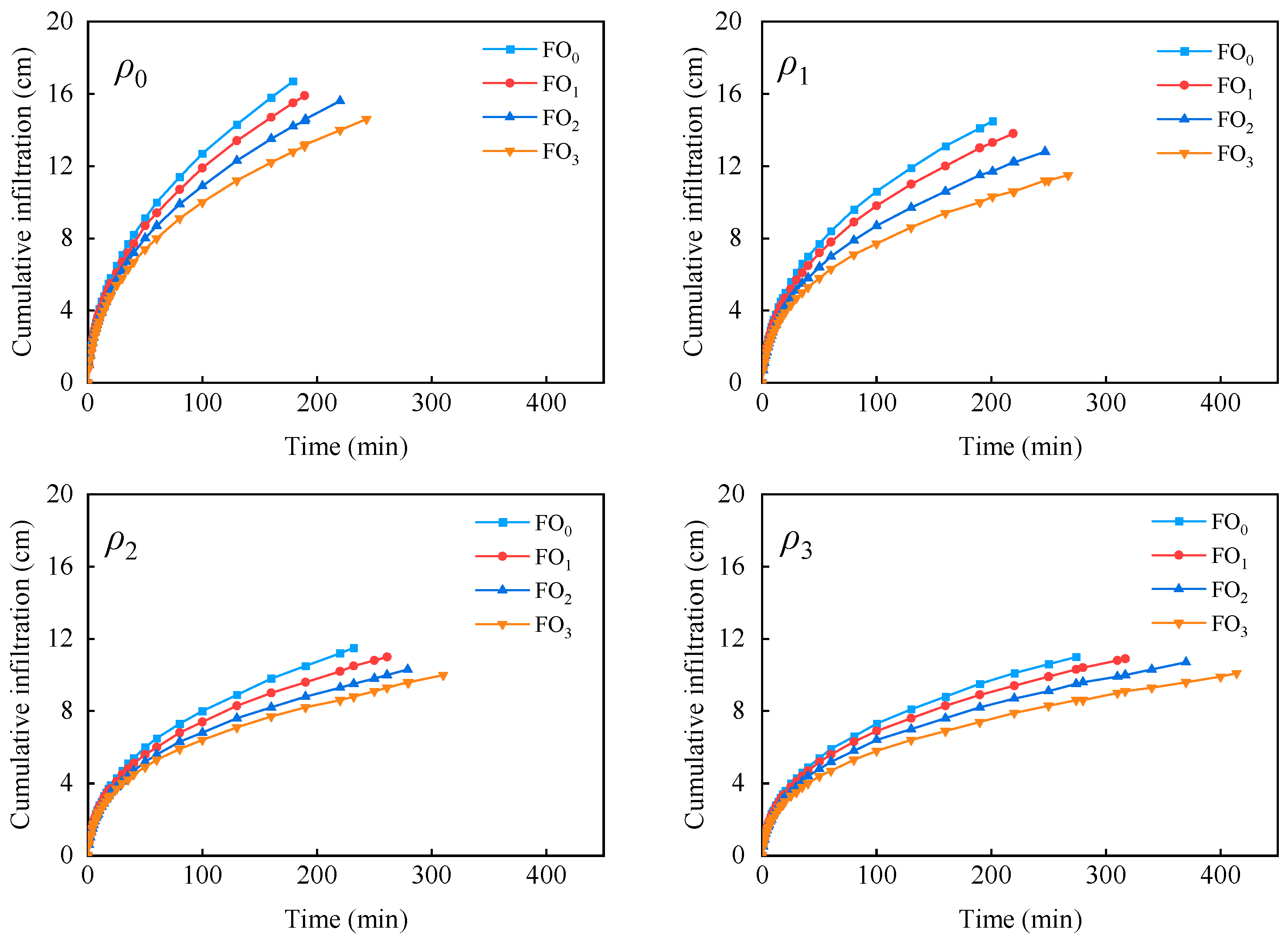
3.2. Cumulative Infiltration
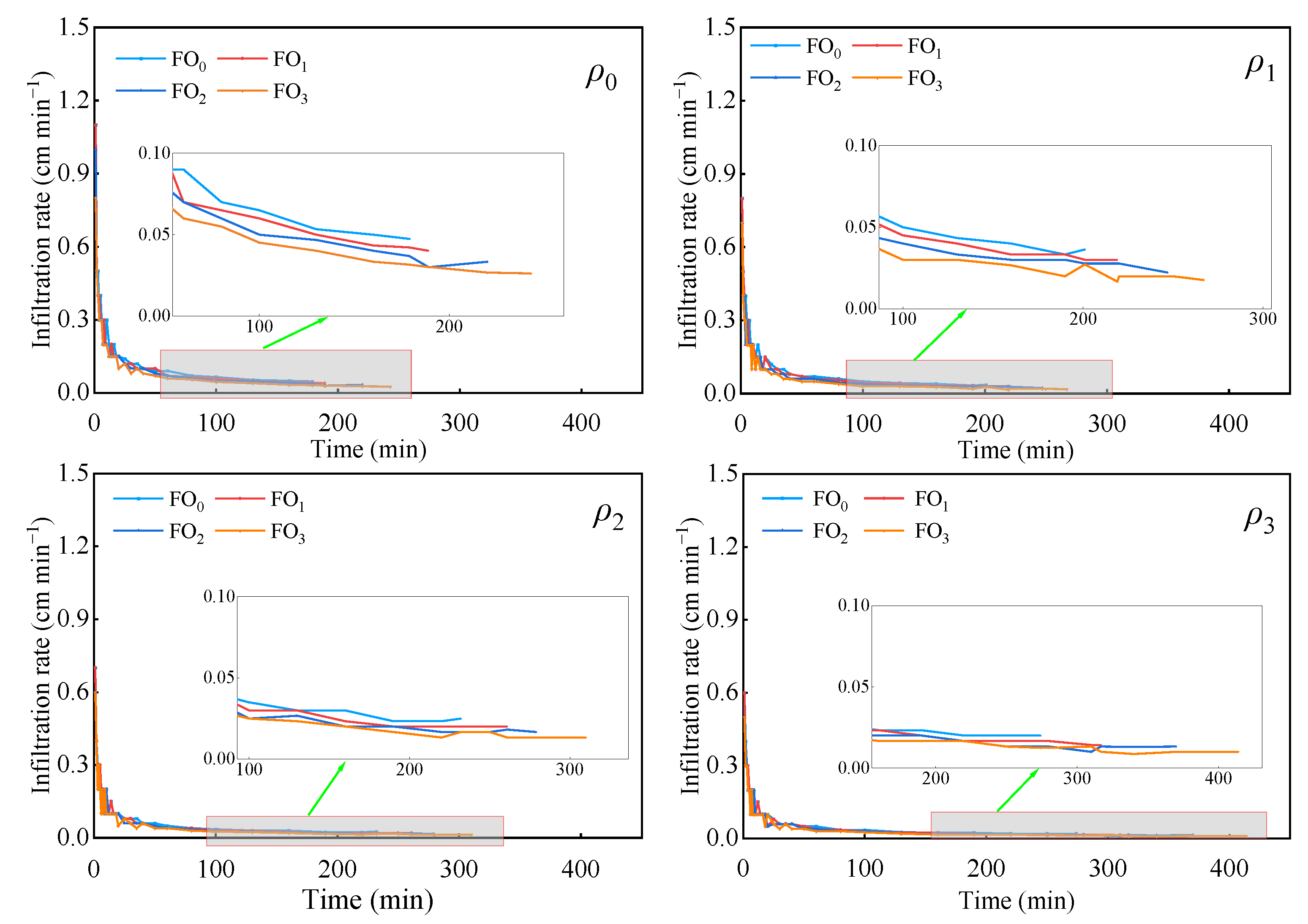
3.3. Infiltration Rate and Parameters
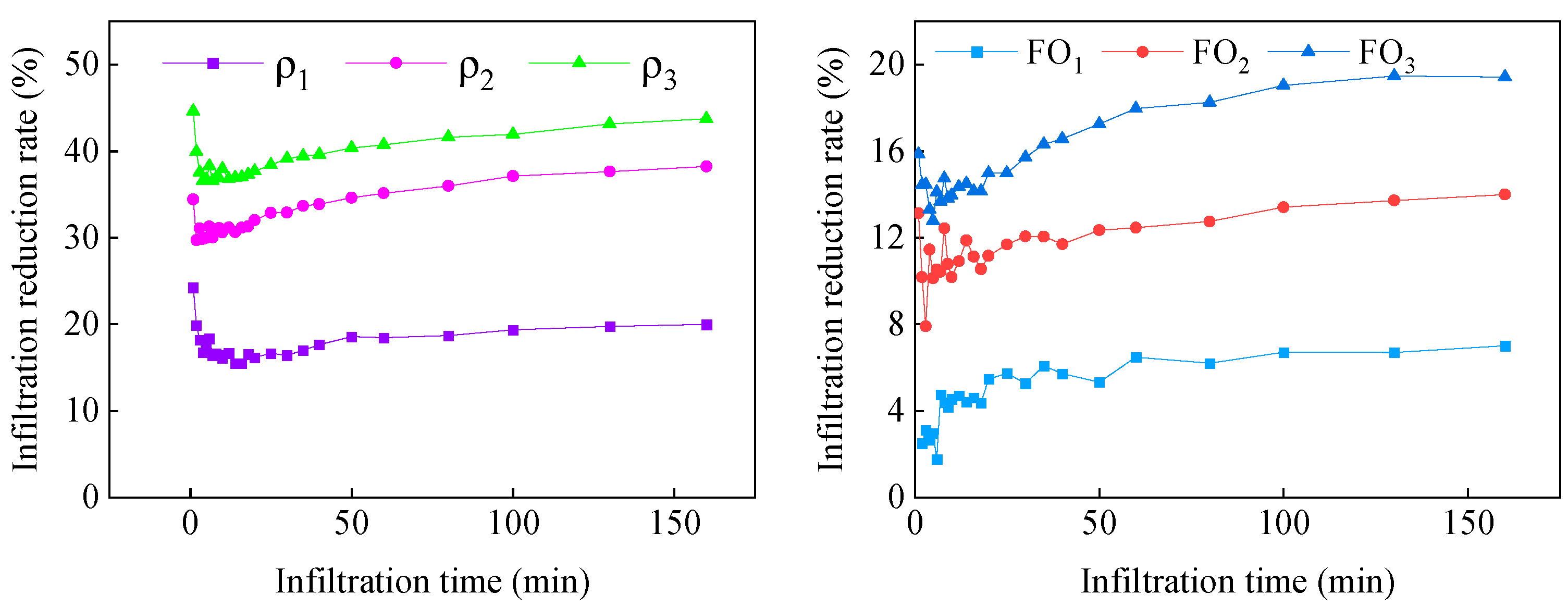
3.4. Infiltration Reduction Rate
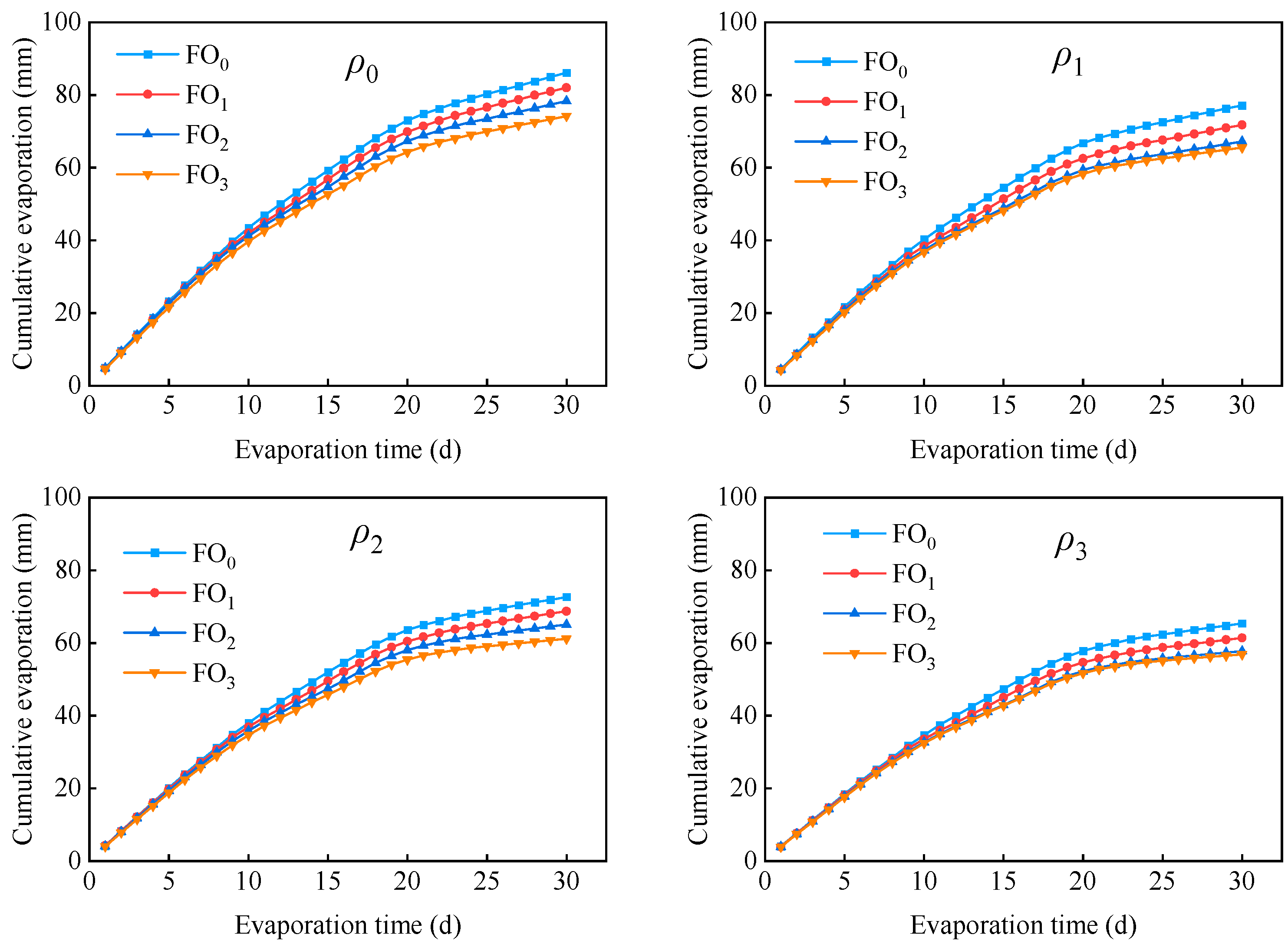
3.5. Soil Water Evaporation
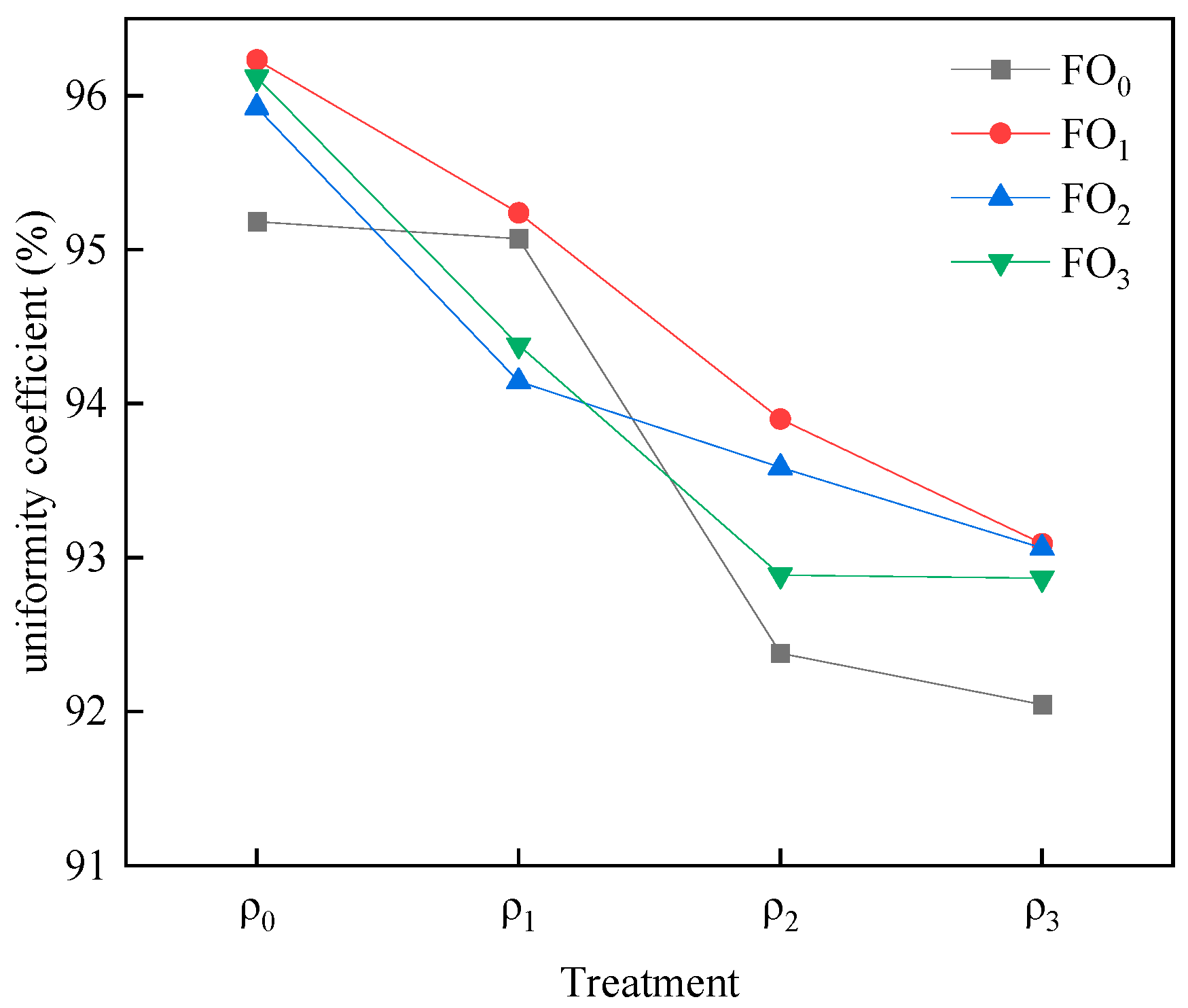
3.6. Soil Moisture Content
3.7. Leaching Characteristic
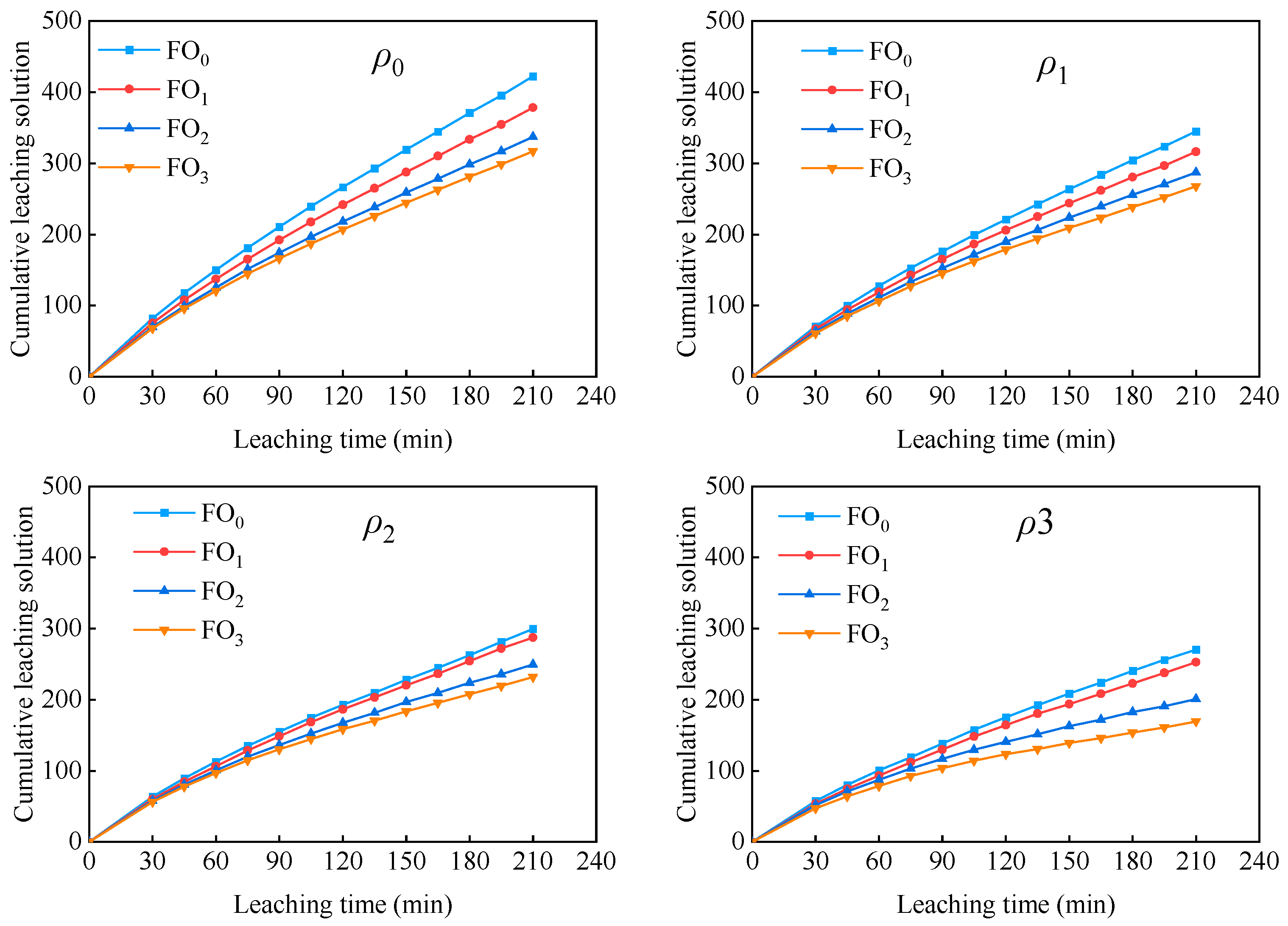
3.7.1. Leaching Solution Volume
3.7.2. pH Value, Conductivity, and TDS
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- Muddy water irrigation and bio-organic fertilizer exerted substantial influence on water infiltration. The cumulative infiltration amount, infiltration rate, and cumulative evaporation amount declined as the muddy water sediment concentration and bio-organic fertilizer increased. Of the three infiltration models (Kostiakov model, Philip model, and Horton model), the Kostiakov infiltration model was appropriate for fitting soil water infiltration under muddy water sediment concentration and bio-organic fertilizer conditions.
- (2)
- Muddy water irrigation was able to reduce soil moisture content and water uniformity but increased infiltration reduction rate. Moreover, as the bio-organic fertilizer level increased, both the soil moisture content and infiltration reduction rate exhibited an upward trajectory.
- (3)
- The cumulative volume and pH value of the leaching solution exhibited a decline as the muddy water sediment concentration and bio-organic fertilizer increased, whereas the conductivity and total dissolved solids (TDS) displayed an increase with increasing muddy water sediment concentration and a decrease with increasing bio-organic fertilizer. In comparison to ρ0, muddy water infiltration manifested a decrease in cumulative leaching solution volume, ranging from 14.85% to 46.55%, accompanied by an increase in conductivity, ranging from 15.56% to 86.83%, and a rise in TDS, ranging from 9.19% to 29.39%. Conversely, in contrast to FO0, the application of bio-organic fertilizer resulted in a reduction in cumulative leaching solution volume by 4.14% to 37.31%, a decline in conductivity by 18.62% to 44.94%, and a decrease in TDS by 9.44% to 25.14%.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cao, J.H.; Chen, P.P.; Gao, X.D.; Zou, Q.F.; Fang, Y.J.; Gu, X.B.; Zhao, X.N.; Li, Y.N. Effects of plastic film residue and emitter flow rate on soil water infiltration and redistribution under different initial moisture content and dry bulk density. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 807, 151381. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Shao, D.G.; Ji, B.; Gu, W.Q.; Yao, M.L. Biochar effects on soil properties, water movement and irrigation water use efficiency of cultivated land in Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 829, 154520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasirian, A.; Maghrebi, M.F.; Mohtashami, A. Numerical and Experimental Assessment of Suspended Material Effects on Water Loss Reduction from Irrigation Channels. IJST-T CIV Eng. 2022, 46, 2483–2493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duo, L.H.; Hu, Z.Q. Soil Quality Change after Reclaiming Subsidence Land with Yellow River Sediments. Sustainability 2018, 10, 4310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.J.; Wang, W.Y.; Shao, M.A.; Wang, Z.R.; Lv, D.Q. Mechanism and Simulating Model for Muddy Water Infiltration. Trans. CSAE 1999, 15, 141–144. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, R.; Fei, L.J.; Chen, L.; Zhong, Y. Effect of sediment concentration on single point source free infiltration characteristics of muddy waterin layered soil with film hole irrigation. J. Soil. Water Conserv. 2020, 34, 43–49, 55. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, Y.; Fei, L.J.; Zhu, S.J.; Kang, S.X.; Liu, L.H.; Hao, K.; Jie, F.L. Infiltration Characteristics of Muddy Water Film-Hole lrrigation and Formation Characteristics of Dense Layers. J. Soil. Water Conserv. 2022, 36, 238–246, 254. [Google Scholar]
- Bristow, K.L.; Simunek, J.; Helalia, S.A.; Siyal, A.A. Numerical simulations of the effects furrow surface conditions and fertilizer locations have on plant nitrogen and water use in furrow irrigated systems. Agr. Water Manag. 2020, 232, 106044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, N.; Jin, L.; Wang, S.Y.; Li, J.W.; Liu, F.H.; Liu, Z.C.; Luo, S.L.; Wu, Y.; Lyu, J.; Yu, J.H. Reduced Chemical Fertilizer Combined with Bio-Organic Fertilizer Affects the Soil Microbial Community and Yield and Quality of Lettuce. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 863325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nest, T.V.; Vandecasteele, B.; Ruysschaert, G.; Cougnon, M.; Merckx, R.; Reheul, D. Effect of organic and mineral fertilizers on soil P and C levels, crop yield and P leaching in a long term trial on a silt loam soil. Agr. Ecosyst. Env. 2014, 197, 309–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.Y.; Xu, W.C.; Sun, Y.M.; Niu, J.Y.; Fang, Z.S. Effects of Different Organic Manures Application on Soil Moisture, Yield and Quality of Oil Flax. J. Soil. Water Conserv. 2014, 28, 307–312. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, H.M.; Li, C.; Xiao, X.P.; Pan, X.C.; Cheng, K.K.; Shi, L.H.; Li, W.Y.; Wen, L.; Wang, K. Effects of long-term fertiliser regime on soil organic carbon and its labile fractions under double cropping rice system of southern China. Acta Agric. Scand. Sect. B—Soil Plant Sci. 2020, 70, 409–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Li, H.Y.; Tan, L.; Li, Q.; Liu, W.; Zhang, C.X.; Gao, Y.; Wei, X.C.; Gong, Q.; Zheng, X.Q. What role does organic fertilizer actually play in the fate of antibiotic resistome and pathogenic bacteria in planting soil. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 317, 115382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Na, W. Relationship between the Flood Cement and Cement Sand in the Yellow River Helong Reach Based on the Typical Sediment Content. J. Irrig. Drain. 2019, 38, 107–110. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.X.; Fu, J.; Wu, M.X.; Gao, X.; Ma, L.M. High-efficiency Sediment Transport Requirements for operation of the Xiaolangdi Reservoir in the Lower Yellow River. Water Supply 2022, 22, 8572–8586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.P.; Zhang, S.Y.; Shi, Z.Y.; Zhou, H.X.; Zheng, H.W.; Hu, J.H.; Mei, J.; Bai, L.; Jia, J.L. Effects of mixed-based biochar on water infiltration and evaporation in aeolian sand soil. J. Arid Land 2022, 14, 374–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diao, S.; Wang, H.Q.; Qiu, C. Differences and discussion on determination methods of soll pH value. Environ. Eng. 2015, 33, 1015–1017. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, S.P.; Ge, M.S.; Zhang, Q.W. Sprinkler irrigation uniformity assessment: Relational analysis of Christiansen uniformity and Distribution uniformity. Irrig. Drain. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, X.G.; Li, Y.B.; Ma, X.Y. Effects on Infiltration and Evaporation When Adding Rapeseed-Oil Residue or Wheat Straw to a Loam Soil. Water 2017, 9, 700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Q.; Zhang, H.P.; Shen, Y.F.; Li, S.Q. Effects of biochar on water infiltration, evaporation and nitrate leaching in semi-arid loess area. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2015, 31, 128–134. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.; Wu, F.P.; Wang, H.; Ouyang, Z. Influence of biochar on biogas infiltration and infiltration reduction effect of clayey and sandy red soil. J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2023, 42, 578–588. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.H.; Wang, Q.J.; Shan, Y.Y.; Guo, Y.; Mu, W.Y.; Wei, K.; Sun, Y. Effect of Sodium Carboxymethyl Cellulose on Water and Salt Transport Characteristics of Saline-Alkali Soil in Xinjiang, China. Polymers 2022, 14, 2884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Javadi, A.; Mostafazadeh-Fard Shayannejad, M.; Mosaddeghi, M.R.; Ebrahimian, H. Soil physical and chemical properties and drain water quality as affected by irrigation and leaching managements. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2019, 65, 321–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos Santos, W.M.; Gonzaga, M.I.S.; da Silv, A.J.; de Almeida, A.Q. Improved water and ions dynamics in a clayey soil amended with different types of agro-industrial waste biochar. Soil. Till Res. 2022, 223, 105482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.H.; Fei, J.; Chen, L.; Hao, K. Effects of sediment concentration of muddy water on water and nitrogen transport characteristics under film hole irrigation with fertilizer infiltration. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2020, 36, 120–129. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.H.; Fei, L.J.; Chen, L.; Hao, K.; Zhang, Q.J. Effects of initial soil moisture content on soil water and nitrogen transport under muddy water film hole infiltration. Int. J. Agr. Biol. Eng. 2021, 14, 182–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.N.; Zhao, Z.L.; Li, J.; Wang, H.M.; Guo, G.M.; Wu, W.B. Effects of muddy water irrigation with different sediment particle sizes and sediment concentrations on soil microbial communities in the Yellow River Basin of China. Agr. Water Manag. 2022, 270, 107750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.B.; Li, E.C.; Zhao, Y.; Liang, Q.H. Effect of water-sediment regulation and its impact on coastline and suspended sediment concentration in Yellow River Estuary. Water Sci. Eng. 2018, 10, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.; Fei, L.J.; Zhu, S.J.; He, J.; Kang, S.X. Effect of sediment concentration of muddy water on one-dimensional vertical infiltration characteristics and dense layer formation characteristics. Soil 2022, 54, 602–609. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, W.; Sun, X.H.; Ma, J.J.; Guo, X.H.; Zheng, L.J. Evaporation and Soil Surface Resistance of the Water Storage Pit Irrigation Trees in the Loess Plateau. Water 2019, 11, 648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Y.Z.; Li, Y.; Luo, X.Q.; Liu, Y.; Yue, X.J.; Yao, B.; Xue, J.M.; Zhang, L.Y.; Fan, J.; Xu, X.Y.; et al. Manure properties, soil conditions and managerial factors regulate greenhouse vegetable yield with organic fertilizer application across China. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 1009631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, L.; Jin, N.; Wang, S.Y.; Li, J.W.; Meng, X.; Xie, Y.D.; Wu, Y.; Luo, S.L.; Lyu, J.; Yu, J.H. Changes in the Microbial Structure of the Root Soil and the Yield of Chinese Baby Cabbage by Chemical Fertilizer Reduction with Bio-Organic Fertilizer Application. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e01215-22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brar, B.S.; Singh, J.; Singh, G.; Kaur, G. Effects of Long Term Application of Inorganic and Organic Fertilizers on Soil Organic Carbon and Physical Properties in Maize-Wheat Rotation. Agronomy 2015, 5, 220–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.T.; Zhang, H.Y.; Liu, Q.J.; Zong, H.; Yu, X.X. Effect of long-term application of manure and nitrogen fertilizer on infiltration for a wheat-maize rotation system. Land Degrad. Dev. 2018, 29, 3250–3261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.P.; Shao, M.G.; Wang, J.; Li, T.C. Effects of Earthworm Cast Application on Water Evaporation and Storage in Loess Soil Column Experiments. Sustainability 2020, 12, 3112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.Y.; Mu, X.M.; Wang, S.Y.; Gu, C.J.; Tan, X.J. Study on the Effects of Different Vegetation Restoration on Soil lnfiltration and Suitable Models in the Loess Hilly Region. J. Soil. Water Conserv. 2023, 37, 67–75. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, X.L.; Zhang, Z.B.; Cui, J.J.; Liu, Z.J.; Chen, Z.J.; Zhou, J.B. Strategies to mitigate nitrate leaching in vegetable production in China: A meta-analysis. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 18382–18391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dal Molin, S.J.; Ernani, P.R.; Soldatelli, P.; Cassol, P.C. Leaching and Recovering of Nitrogen Following N Fertilizers Application to the Soil in a Laboratory Study. Commun. Soil Sci. Plan. 2018, 49, 1099–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodur, S.; Shrestha, U.B.; Maraseni, T.N.; Deo, R.C. Environmental and economic impacts and trade-offs from simultaneous management of soil constraints, nitrogen and water. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 222, 960–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, R.R.; Fei, L.J.; Kang, S.X. Numerical Study on the Characteristics of Mult-point Interference lnfiltration Wetted Body in Muddy Water Film Hole lrrigation. J. Soil. Water Conserv. 2022, 36, 190–195. [Google Scholar]
- Gai, X.P.; Liu, H.B.; Zhai, L.M.; Wang, H.Y. Effects of Corn-Stalk Biochar on Inorganic Nitrogen Leaching from Soil. J. Agro-Env. Sci. 2015, 34, 310–318. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Miao, H.T.; Chang, X.F.; Wu, G.L. Higher species diversity improves soil water infiltration capacity by increasing soil organic matter content in semiarid grasslands. Land Degrad. Dev. 2019, 30, 1599–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Treatments | Kostiakov | Philip | Horton | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Muddy Water Sediment Concentration | Bio-Organic Fertilizer | K | α | R2 | RMSE | S | R2 | RMSE | g | R2 | RMSE |
| ρ0 | FO1 | 0.836 | 0.564 | 0.935 | 0.063 | 0.836 | 0.891 | 0.071 | 0.236 | 0.818 | 0.092 |
| FO2 | 0.808 | 0.577 | 0.943 | 0.062 | 0.804 | 0.885 | 0.072 | 0.250 | 0.836 | 0.086 | |
| FO3 | 0.782 | 0.595 | 0.964 | 0.046 | 0.743 | 0.903 | 0.060 | 0.241 | 0.854 | 0.073 | |
| FO4 | 0.775 | 0.617 | 0.992 | 0.016 | 0.679 | 0.955 | 0.035 | 0.186 | 0.899 | 0.053 | |
| ρ1 | FO1 | 0.760 | 0.589 | 0.978 | 0.026 | 0.699 | 0.951 | 0.038 | 0.180 | 0.892 | 0.056 |
| FO2 | 0.732 | 0.605 | 0.981 | 0.026 | 0.665 | 0.938 | 0.041 | 0.197 | 0.877 | 0.058 | |
| FO3 | 0.665 | 0.611 | 0.965 | 0.029 | 0.591 | 0.934 | 0.038 | 0.185 | 0.866 | 0.053 | |
| FO4 | 0.638 | 0.637 | 0.978 | 0.025 | 0.559 | 0.924 | 0.039 | 0.203 | 0.881 | 0.049 | |
| ρ2 | FO1 | 0.611 | 0.610 | 0.973 | 0.028 | 0.562 | 0.922 | 0.040 | 0.206 | 0.871 | 0.051 |
| FO2 | 0.587 | 0.633 | 0.972 | 0.039 | 0.543 | 0.886 | 0.048 | 0.215 | 0.857 | 0.054 | |
| FO3 | 0.573 | 0.643 | 0.972 | 0.024 | 0.499 | 0.922 | 0.036 | 0.191 | 0.885 | 0.043 | |
| FO4 | 0.523 | 0.636 | 0.942 | 0.037 | 0.481 | 0.883 | 0.043 | 0.202 | 0.863 | 0.046 | |
| ρ3 | FO1 | 0.576 | 0.626 | 0.978 | 0.020 | 0.507 | 0.935 | 0.033 | 0.188 | 0.885 | 0.043 |
| FO2 | 0.548 | 0.633 | 0.955 | 0.030 | 0.485 | 0.909 | 0.037 | 0.195 | 0.873 | 0.044 | |
| FO3 | 0.520 | 0.637 | 0.950 | 0.029 | 0.454 | 0.916 | 0.033 | 0.164 | 0.894 | 0.037 | |
| FO4 | 0.481 | 0.642 | 0.963 | 0.024 | 0.421 | 0.920 | 0.029 | 0.182 | 0.897 | 0.024 | |
| Treatments | Black | Rose | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Muddy Water Sediment Concentration | Bio-Organic Fertilizer | F | B | RMSE | R2 | C | D | RMSE | R2 |
| ρ0 | FO1 | 19.85 | −18.81 | 2.0257 | 0.993 | 8.84 | 1.46 | 3.5172 | 0.980 |
| FO2 | 18.82 | −17.21 | 1.9238 | 0.993 | 8.83 | 1.32 | 3.3568 | 0.979 | |
| FO3 | 17.81 | −15.25 | 1.8608 | 0.993 | 9.12 | 1.14 | 3.2234 | 0.979 | |
| FO4 | 16.91 | −14.16 | 1.9459 | 0.991 | 8.97 | 1.03 | 3.2460 | 0.976 | |
| ρ1 | FO1 | 17.76 | −15.82 | 2.0813 | 0.991 | 8.76 | 1.17 | 3.4488 | 0.976 |
| FO2 | 16.40 | −13.71 | 2.0313 | 0.990 | 8.76 | 0.98 | 3.2769 | 0.974 | |
| FO3 | 15.17 | −11.41 | 2.0311 | 0.989 | 9.05 | 0.76 | 3.1218 | 0.973 | |
| FO4 | 14.89 | −11.16 | 2.1434 | 0.987 | 8.97 | 0.73 | 3.2034 | 0.970 | |
| ρ2 | FO1 | 16.92 | −15.30 | 2.2182 | 0.989 | 8.25 | 1.13 | 3.5015 | 0.973 |
| FO2 | 15.85 | −13.45 | 2.0758 | 0.989 | 8.35 | 0.96 | 3.2655 | 0.973 | |
| FO3 | 14.98 | −12.05 | 2.1390 | 0.987 | 8.43 | 0.83 | 3.2291 | 0.970 | |
| FO4 | 14.07 | −10.56 | 2.2990 | 0.983 | 8.54 | 0.68 | 3.2653 | 0.966 | |
| ρ3 | FO1 | 15.24 | −13.38 | 2.1572 | 0.987 | 7.75 | 0.96 | 3.2804 | 0.970 |
| FO2 | 14.15 | −11.49 | 2.0451 | 0.987 | 7.87 | 0.79 | 3.0669 | 0.970 | |
| FO3 | 13.26 | −9.94 | 2.0985 | 0.984 | 8.02 | 0.64 | 3.0057 | 0.967 | |
| FO4 | 13.08 | −9.66 | 2.1728 | 0.982 | 8.05 | 0.61 | 3.0496 | 0.965 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Peng, Y.; Fei, L.; Jie, F.; Hao, K.; Liu, L.; Shen, F.; Fan, Q. Effects of Bio-Organic Fertilizer on Soil Infiltration, Water Distribution, and Leaching Loss under Muddy Water Irrigation Conditions. Agronomy 2023, 13, 2014. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13082014
Peng Y, Fei L, Jie F, Hao K, Liu L, Shen F, Fan Q. Effects of Bio-Organic Fertilizer on Soil Infiltration, Water Distribution, and Leaching Loss under Muddy Water Irrigation Conditions. Agronomy. 2023; 13(8):2014. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13082014
Chicago/Turabian StylePeng, Youliang, Liangjun Fei, Feilong Jie, Kun Hao, Lihua Liu, Fangyuan Shen, and Qianwen Fan. 2023. "Effects of Bio-Organic Fertilizer on Soil Infiltration, Water Distribution, and Leaching Loss under Muddy Water Irrigation Conditions" Agronomy 13, no. 8: 2014. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13082014
APA StylePeng, Y., Fei, L., Jie, F., Hao, K., Liu, L., Shen, F., & Fan, Q. (2023). Effects of Bio-Organic Fertilizer on Soil Infiltration, Water Distribution, and Leaching Loss under Muddy Water Irrigation Conditions. Agronomy, 13(8), 2014. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13082014




