Variations in Soil Organic Carbon Fractions and Microbial Community in Rice Fields under an Integrated Cropping System
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experiment Design
2.2. Soil Collection and Analysis
2.3. Microbial Community Composition
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Soil Nutrients
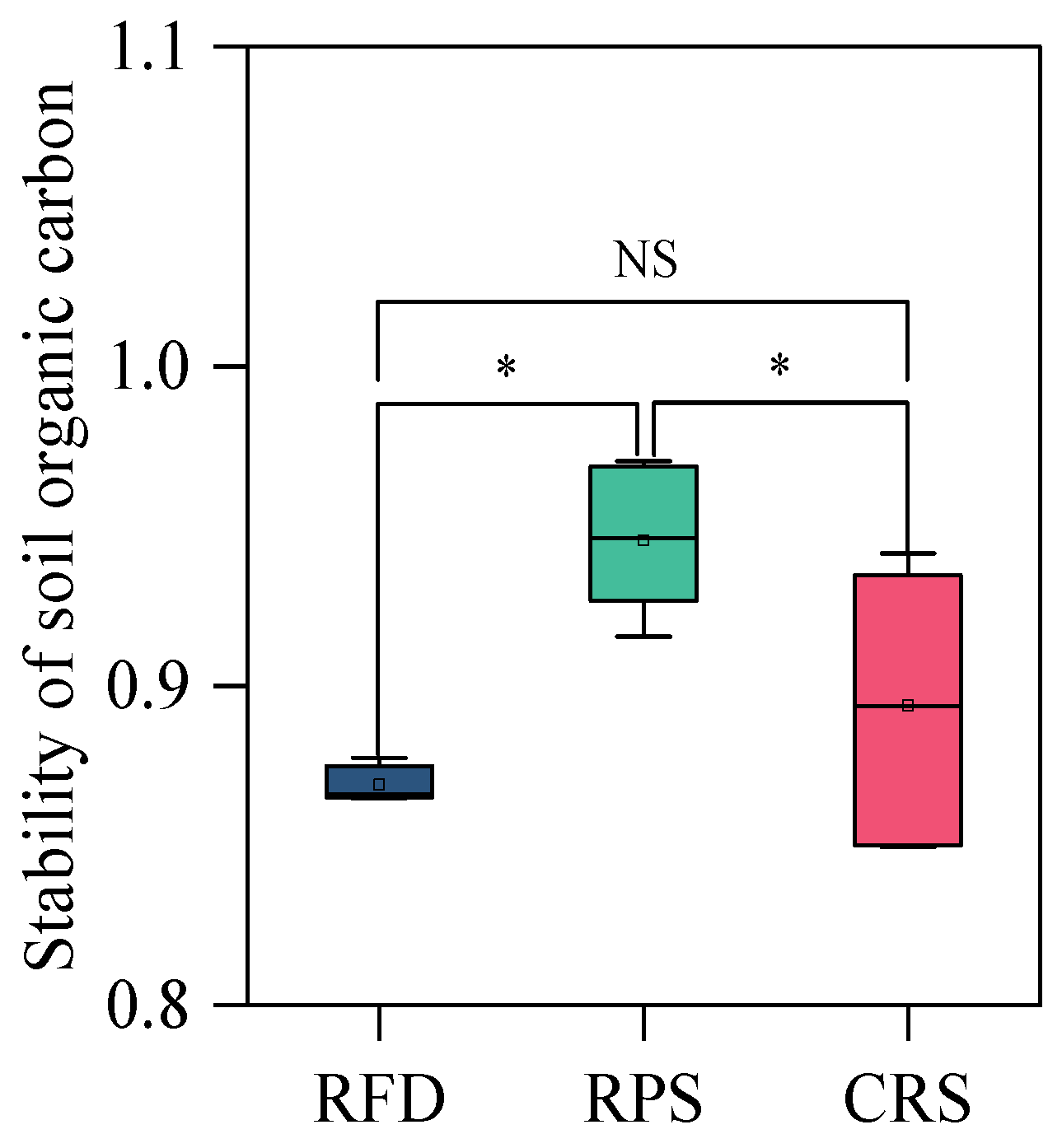
3.2. Soil Organic Carbon Fractions
3.3. Soil C-Hydrolyzing Enzyme Activity
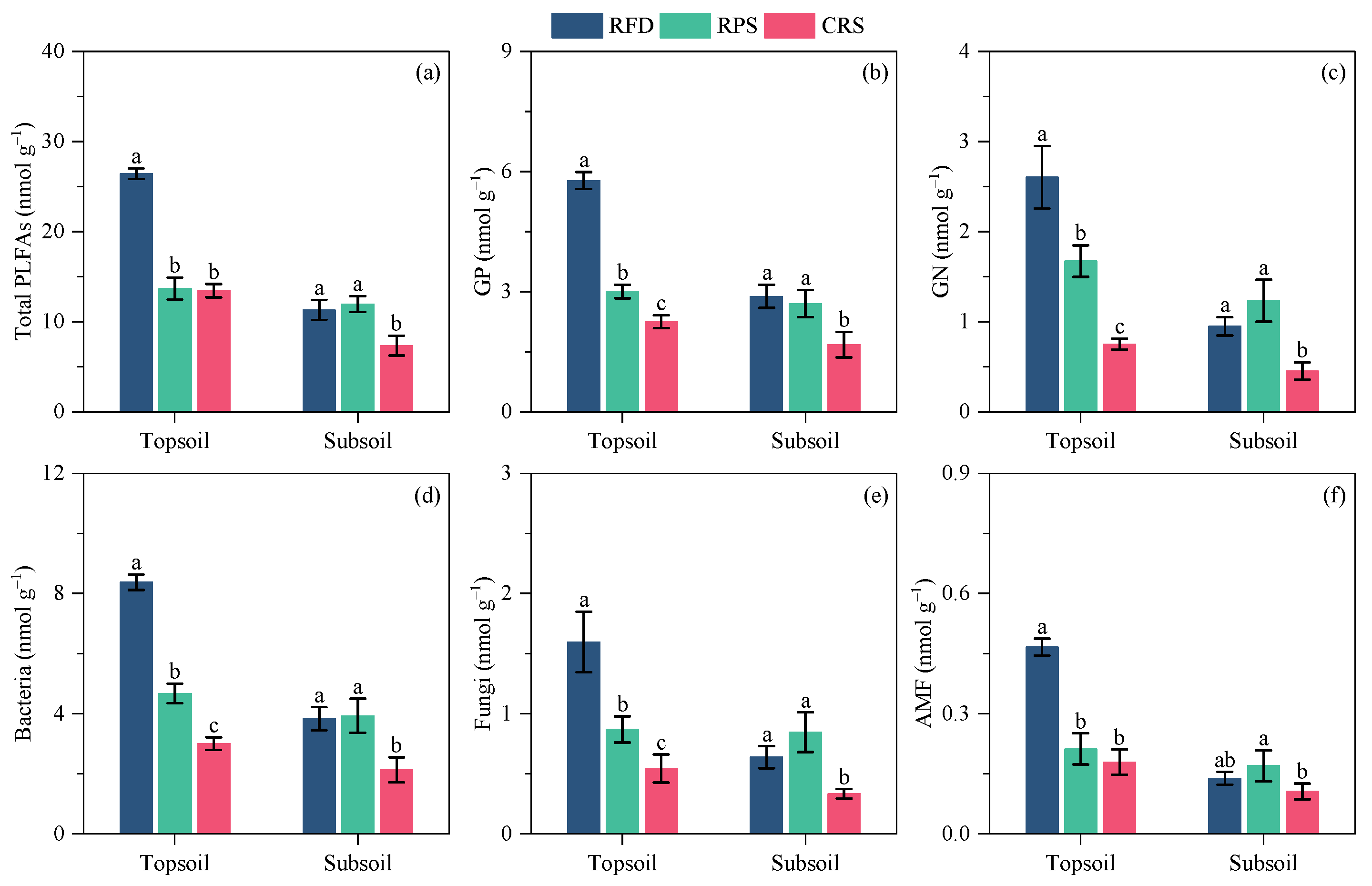
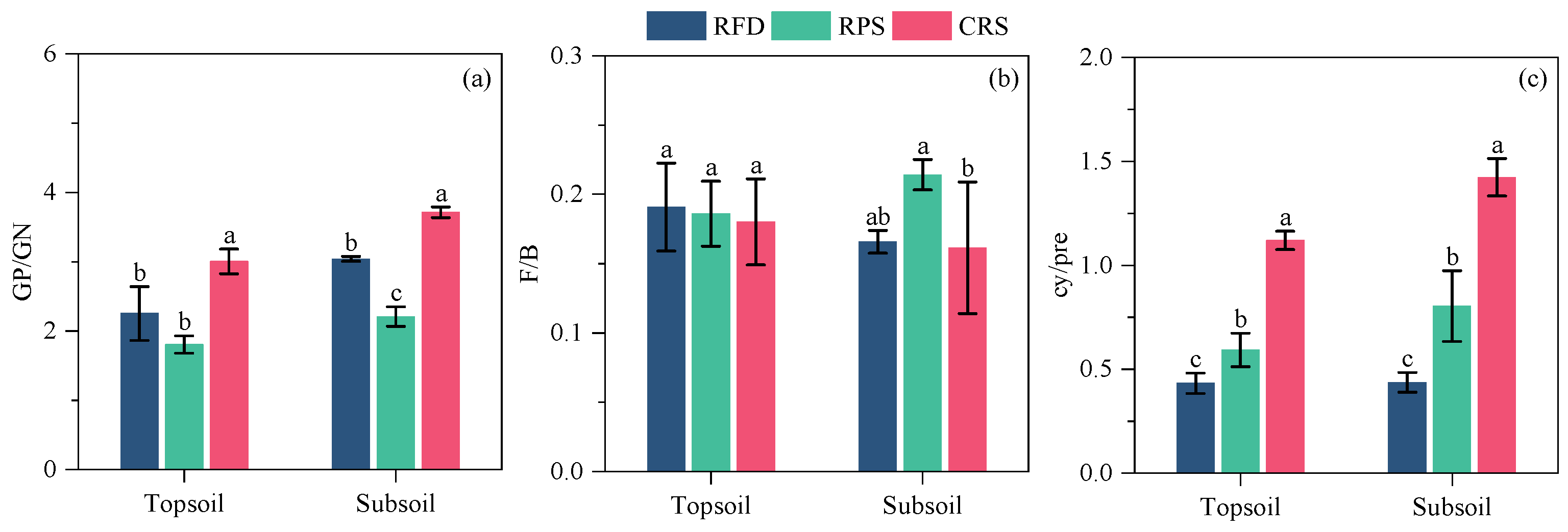
3.4. Soil Microbial Community Characteristics
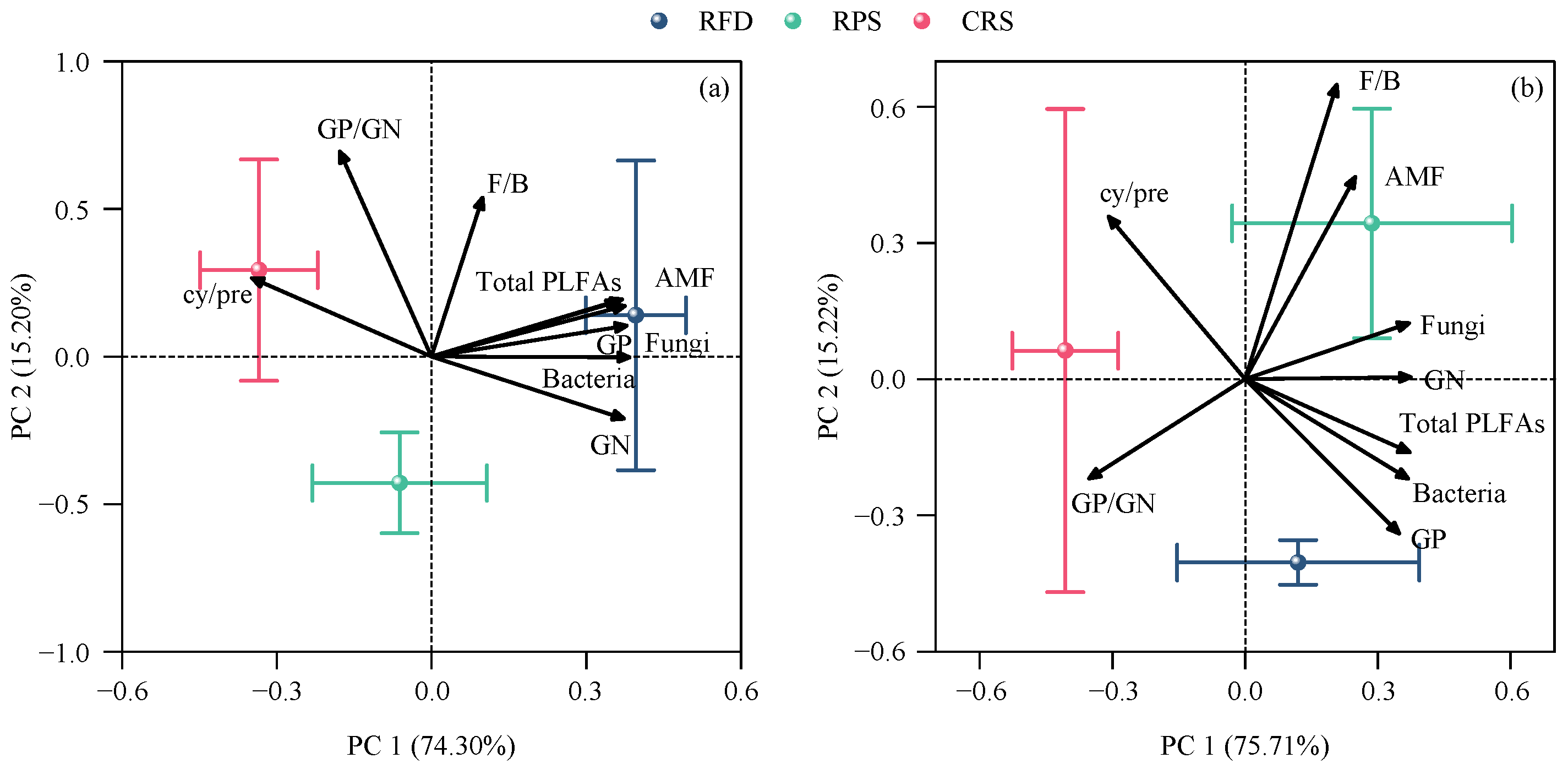
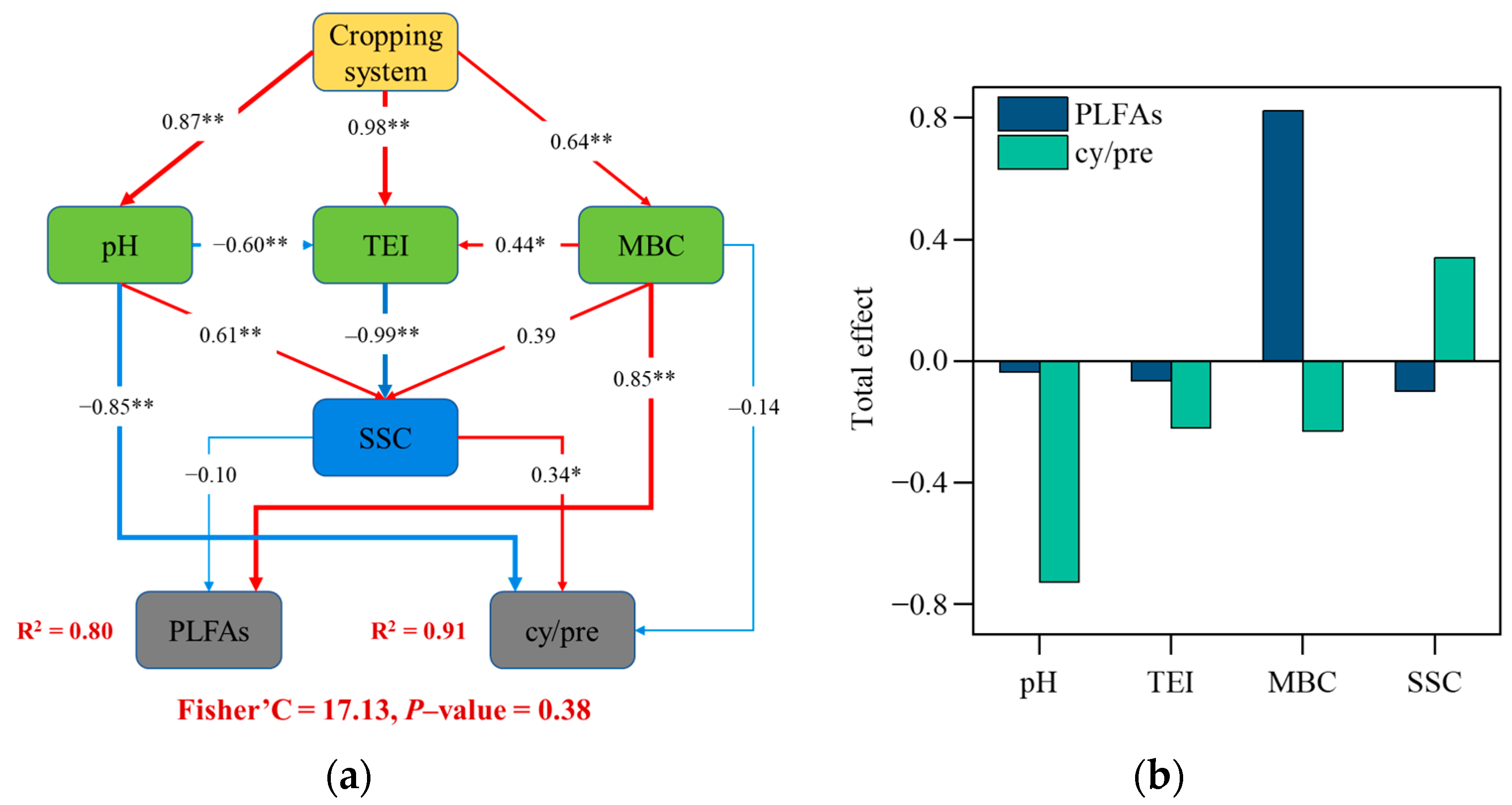
3.5. Relationship between Soil Microbial Community and Soil Variables
4. Discussion
4.1. Response of Soil Organic Carbon Fractions to Cropping Systems
4.2. Response of Soil Microbial Community Characteristics to Cropping Systems
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xie, K.Z.; Xu, P.Z.; Yang, S.H.; Lu, Y.S.; Jiang, R.P.; Gu, W.J.; Li, W.Y.; Sun, L.L. Effects of supplementary composts on microbial communities and rice productivity in cold water paddy fields. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 25, 569–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matin, N.H.; Jalali, M. The effect of waterlogging on electrochemical properties and soluble nutrients in paddy soils. Paddy Water Environ. 2017, 15, 443–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.L.; Wang, W.; Tian, W.W.; Xie, K.J. Waterlogging accelerates the loss of soil organic carbon from abandoned paddy fields in the hilly terrain in subtropical China. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 14549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, F.L.; Wu, Y.W.; Cui, S.L.; Wang, X.L.; Wei, G.; Liu, Q.L.; Lan, T.Q.; Liu, F.; Zhao, B.; Feng, D.J.; et al. Effect of chemical fertilizer application on maize production in China over the past 15 Years: A meta-analysis. Agronomy 2022, 12, 3005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macedo, I.; Terra, J.A.; Siri-Prieto, G.; Velazco, J.I.; Carrasco-Letelier, L. Rice-pasture agroe-cosystem intensification affects energy use efficiency. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 278, 123771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cogle, A.L.; Rao, K.P.C.; Yule, D.F.; Smith, G.D.; George, P.J.; Srinivasan, S.T.; Jangawad, L. Soil management for Alfisols in the semiarid tropics: Erosion, enrichment ratios and run-off. Soil Use Manag. 2006, 18, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.X.; Lu, X.N.; Zhang, J.E.; Wei, H.; Li, M.J.; Lan, N.; Luo, H. Intercropping perennial aquatic plants with rice improved paddy field soil microbial biomass, biomass carbon and biomass nitrogen to facilitate soil sustainability. Soil Tillage Res. 2021, 208, 104908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, N.F.; Li, S.X.; Li, T.; Cavalieri, A.; Weiner, J.; Zheng, X.Q.; Ji, X.Y.; Zhang, J.Q.; Zhang, H.L.; Zhang, H.; et al. Ecological intensification of rice production through rice-fish co-culture. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 234, 1002–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambus, J.V.; Awe, G.O.; Carvalho, P.C.D.F.; Reichert, J.M. Integrated crop-livestock systems in lowlands with rice cultivation improve root environment and maintain soil structure and functioning. Soil Tillage Res. 2023, 227, 105592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinojosa, M.B.; García-Ruíz, R.; Egla, B.V.; Carreira, J.A. Microbiological rates and enzyme activities as indicators of functionality in soils affected by the Aznalcóllar toxic spill. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2004, 36, 1637–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore-Kucera, J.; Dick, R.P. PLFA profiling of microbial community structure and seasonal shifts in soils of a douglas−fir chronosequence. Microb. Ecol. 2008, 55, 500–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzoni, S.; Schimel, J.P.; Porporato, A. Responses of soil microbial communities to water stress: Results from a meta-analysis. Ecology 2012, 93, 930–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, K.K.; Chen, H.Y.; Dai, W.; Wang, J.; Cao, L.K.; Sha, Z.M. Microbe-mediated reduction of methane emission in rice-frog crop ecosystem. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2022, 174, 104415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afri, H.; Murwantoko, M.; Indah, I. Dynamic change in bacterial communities in the integrated rice-fish farming system in Sleman, Yogyakarta, Indonesia. Aquac. Res. 2021, 52, 5566–5578. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, S.M.; Lv, W.G.; Zhu, H.T.; Zhang, D.S.; Fu, Z.S.; Zhang, H.L.; Xu, S.X. Effect of nitrogen application rate on soil fungi community structure in a rice-fish mutualistic system. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 16188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.B.; He, Z.F.; Wu, L.P.; Liu, S.J.; Luo, L.C.; Ye, X.X.; Gao, H.J.; Ma, C. Impacts of co-culture of rice and aquatic animals on rice yield and quality: A meta-analysis of field trials. Field Crops Res. 2022, 280, 108468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, Q.; Hu, X.F.; Cheng, C.; Luo, Z.Q.; Luo, F.; Xue, Y.; Jiang, Y.J.; Mu, Z.; Liu, L.M.; Yang, M.Y. Ecological effects of rice-duck integrated farming on soil fertility and weed and pest control. J. Soils Sediments 2016, 16, 2395–2407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashir, M.A.; Wang, H.Y.; Pan, J.T.; Khoshnevisan, B.; Sun, W.T.; Zhai, L.M.; Zhang, X.S.; Wang, N.; Rehim, A.; Liu, H.B. Variations in soil nutrient dynamics and their composition in rice under integrated rice-crab co-culture system. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 281, 125222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, L.; Sun, Y.; Wang, L.Y.; Guo, G.Q.; Song, L.L.; Wang, C.; Wu, G.G.; Zang, X.Y.; Cai, X.M.; Li, S.X.; et al. Ecosystem sustainability of rice and aquatic animal co-culture systems and a synthesis of its underlying mechanisms. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 880, 163314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, G.; Sun, M.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Z.C.; Zhang, G.B.; Nie, S.A.; Xu, H.Q.; Wang, H. Ecological rice-cropping systems mitigate global warming—A meta-analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 789, 147900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Yang, Q.N.; Zhang, C.; Li, X.D.; Chen, J.; Zhang, X.L.; Chen, J.J.; Liu, K.X. Rice-fish-duck system regulation of soil phosphorus fraction conversion and availability through organic carbon and phosphatase activity. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 979234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.L.; Li, D.C. Field Guidelines for Describing and Sampling Soils; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, R.K. Methods for Soil Agrochemical Analysis; China Agricultural Science and Technology Press: Beijing, China, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Saiya-Cork, K.R.; Sinsabaugh, R.L.; Zak, D.R. The effects of long term nitrogen deposition on extracellular enzyme activity in an Acer saccharum forest soil. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2002, 34, 1309–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bossio, D.A.; Scow, K.M. Impacts of carbon and flooding on soil microbial communities: Phospholipid fatty acid profiles and substrate utilization patterns. Microb. Ecol. 1998, 35, 265–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frostegard, A.; Baath, E. The use of phospholipid fatty acid analysis to estimate bacterial and fungal biomass in soil. Biol. Fertil. Soils 1996, 22, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kourtev, P.S.; Ehrenfeld, J.G.; Haggblom, M. Exotic plant species alter the microbial community structure and function in the soil. Ecology 2002, 83, 3152–3166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Peng, C.; Zhang, W.J.; Li, S.Y.; An, T.T.; Xu, Y.D.; Ge, Z.; Xie, N.H.; Wang, J.K. Subsoiling tillage with straw incorporation improves soil microbial community characteristics in the whole cultivated layers: A one-year study. Soil Till. Res. 2022, 215, 105188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blair, G.J.; Lefroy, R.D.; Lisle, L. Soil carbon fractions based on their degree of oxidation, and the development of a carbon management index for agricultural systems. Aust. J. Agric. Res. 1995, 46, 1459–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, P.J.; Li, Y.X.; Liu, S.W.; Liu, J.L.; Ding, Z.; Ma, M.G.; Tang, X.G. Afforestation influences soil organic carbon and its fractions associated with aggregates in a karst region of Southwest China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 814, 152710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wu, C.F.; Deng, S.P.; Zhang, J.L.; Hou, J.Y.; Wang, C.; Fu, Z.C. Effect of different washing solutions on soil enzyme activity and microbial community in agricultural soil severely contaminated with cadmium. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 54641–54651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esmaeilzadeh-Salestani, K.; Bahram, M.; Seraj, R.G.M.; Gohar, D.; Tohidfar, M.; Eremeev, V.; Talgre, L.; Khaleghdoust, B.; Mirmajlessi, S.M.; Luik, A.; et al. Cropping systems with higher organic carbon promote soil microbial diversity. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2021, 319, 107521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, G.H.; Peng, C.L.; Yuan, J.F.; Xu, X.Y.; Zhao, S.J.; Xu, D.B.; Wu, J.S. Changes in soil microbial community composition and organic carbon fractions in an integrated rice–crayfish farming system in subtropical China. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 2856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowles, T.M.; Acosta-Martinez, V.; Calderon, F.; Jackson, L.E. Soil enzyme activities, microbial communities, and carbon and nitrogen availability in organic agroecosystems across an intensively-managed agricultural landscape. Soil. Biol. Biochem. 2014, 68, 252–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanjul, E.; Escapa, M.; Montemayor, D.; Addino, M.; Alvarez, M.F.; Grela, M.A.; Iribarne, O. Effect of crab bioturbation on organic matter processing in South West Atlantic intertidal sediments. J. Sea Res. 2015, 95, 206–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Booth, M.T.; Urbanic, M.; Wang, X.; Beaulieu, J.J. Bioturbation frequency alters methane emissions from reservoir sediments. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 789, 148033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Girkin, N.T.; Turner, B.L.; Ostle, N.; Craigon, J.; Sjogersten, S. Root exudate analogues accelerate CO2 and CH4 production in tropical peat. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2018, 117, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.Y.; Liu, Z.J.; Zhou, J.B.; Xu, X.P.; Zhu, Y.J. Long-term straw mulching with nitrogen fertilization increases nutrient and microbial determinants of soil quality in a maize–wheat rotation on China’s Loess Plateau. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 775, 145930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchi, L.; Walder, F.; Banerjee, S.; Colombi, T.; van der Heijden, M.G.A.; Keller, T.; Charles, R.; Six, J. Pedoclimatic factors and management determine soil organic carbon and aggregation in farmer fields at a regional scale. Geoderma 2022, 409, 115632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalbitz, K.; Solinger, S.; Park, J.H.; Michalzik, B.; Matzner, E. Controls on the dynamics of dissolved organic matter in soils: A review. Soil Sci. 2000, 165, 277–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, C.; Wang, T.; Xu, Y.; Deng, J.; Zhao, F.; Yang, G.; Han, X.; Feng, Y.; Ren, G. Differential soil microbial community responses to the linkage of soil organic carbon fractions with respiration across land-use changes. For. Ecol. Manag. 2018, 409, 170–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zsolnay, A.; Gorlitz, H. Water extractable organic matter in arable soils: Effects of drought and long-term fertilization. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1994, 26, 1257–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marschner, B.; Kalbitz, K. Controls of bioavailability and biodegradability of dissolved organic matter in soils. Geoderma 2003, 113, 211–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunina, A.; Dippold, M.; Glaser, B.; Kuzyakov, Y. Turnover of microbial groups and cell components in soil: 13C analysis of cellular biomarkers. Biogeosciences 2017, 14, 271–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datta, A.; Nayak, D.R.; Sinhababu, D.P.; Adhya, T.K. Methane and nitrous oxide emissions from an integrated rainfed rice–fish farming system of Eastern India. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2009, 129, 228–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, H.; Ge, T.; Liu, J.; Chen, X.; Hu, Y.; Wu, J.; Su, Y.; Kuzyakov, Y. Effects of biotic and abiotic factors on soil organic matter mineralization: Experiments and structural modeling analysis. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2018, 84, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautreau, E.; Volatier, L.; Nogaro, G.; Gouze, E.; Mermillod-Blondin, F. The influence of bioturbation and water column oxygenation on nutrient recycling in reservoir sediments. Hydrobiologia 2020, 847, 1027–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piton, G.; Legay, N.; Arnoldi, C.; Lavorel, S.; Clément, J.C.; Foulquier, A. Using proxies of microbial community weighted means traits to explain the cascading effect of management intensity, soil and plant traits on ecosystem resilience in mountain grasslands. J. Ecol. 2019, 108, 876–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotrufo, M.F.; Soong, J.L.; Horton, A.J.; Campbell, E.E.; Haddix, M.L.; Wall, D.H.; Parton, W.J. Formation of soil organic matter via biochemical and physical pathways of litter mass loss. Nat. Geosci. 2015, 8, 776–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paterson, E.; Sim, A.; Osborne, S.M.; Murray, P. Long-term exclusion of plantinputs to soil reduces the functional capacity of microbial communities to mineralise recalcitrant root-derived carbon sources. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2011, 43, 1873–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Boer, W.; Folman, L.; Summerbell, R.C.; Boddy, L. Living in a fungal world: Impact of fungi on soil bacterial niche development. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2005, 29, 795–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, G.C.; Zhang, X.F.; Xin, X.L.; Yang, W.L.; Zhu, A.N.; Yang, J. Soil organic carbon and nitrogen fractions as affected by straw and nitrogen management on the North China Plain. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2023, 342, 108248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanin, N.; Kardol, P.; Farrell, M.; Nilsson, M.C.; Gundale, M.J.; Wardle, D.A. The ratio of Gram-positive to Gram-negative bacterial PLFA markers as an indicator of carbon availability in organic soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2019, 128, 111–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genre, A.; Lanfranco, L.; Perotto, S.; Bonfante, P. Unique and common traits in mycorrhizal symbioses. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2020, 18, 649–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Feng, J.; Wu, J.; Jia, W.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, D.; Cheng, X. Spatial variation in soil microbial community structure and its relation to plant distribution and local environments following afforestation in central China. Soil Tillage Res. 2019, 193, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bremer, E.; Janzen, H.H.; Johnston, A.M. Sensitivity of total, light fraction and mineralizable organic matter to management practices in a Lethbridge soil. Can. J. Soil Sci. 1994, 74, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Abbreviations | Full Name | Assay Method |
|---|---|---|
| pH | Potentiometer method | |
| TN | Total nitrogen | Semi-micro Kjeldahl method |
| TP | Total phosphorus | HF–HClO4–HNO3 digestion |
| TK | Total potassium | HF–HClO4–HNO3 digestion |
| AN | Available nitrogen | Alkalolysis diffusion method |
| AP | Available phosphorus | NaHCO3 leaching-spectrophotometer (V2200, Sunny Hengping instrument Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China) |
| AK | Available potassium | CH3COONH4 leaching-flamephotometer |
| OC | Soil organic carbon | H2SO4–K2Cr2O7 external heating method |
| DOC | Dissolved organic carbon | Deionization leaching-elemental analyzer (CE–440, DHJ Analysis Co., Ltd., Beijing, China) |
| EOC | Easily oxidized organic carbon | KMnO4 oxidation method |
| MBC | Microbial biomass carbon | Chloroform fumigation-potassium sulphate leaching-elemental analyzer |
| HA | Humic acid | Na4P2O7–NaOH leaching and H2SO4 digestion |
| FA | Fulvic acid | |
| BG | β-1,4-glucosidase | A 96-well fluorometric plate reader method |
| CBH | Cellobiohydrolase | |
| BX | Xylosidase | |
| Total PLFAs | Total phospholipid fatty acids | Bossio and Scow [18] |
| GP | Gram-positive bacteria | |
| GN | Gram-negative bacteria | |
| BAC | Bacteria | |
| FUN | Fungi | |
| AMF | Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi | |
| GP/GN | Ratio of Gram-positive bacteria to Gram-negative bacteria | |
| F/B | Ratio of fungi to bacteria | |
| cy/pre | Ratio of cyclopropyl PLFAs to precursors PLFAs |
| Variables | RFD vs. CRS | RFD vs. RPS | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Topsoil | Subsoil | Topsoil | Subsoil | |
| pH | 16.43 ± 1.54 * | 16.94 ± 2.36 * | 2.65 ± 0.36 * | −0.72 ± 1.91 ns |
| TN | 41.69 ± 10.53 * | 41.33 ± 4.98 * | 36.24 ± 2.19 * | 63.11 ± 2.33 * |
| TP | 88.07 ± 2.80 * | 81.91 ± 1.94 * | 69.21 ± 4.48 * | 54.71 ± 2.01 * |
| TK | 5.44 ± 5.74 ns | −7.79 ± 3.47 ns | 104.64 ± 6.19 * | 90.19 ± 9.67 * |
| AN | 76.26 ± 5.34 * | 73.38 ± 2.42 * | 53.93 ± 4.37 * | 76.06 ± 0.45 * |
| AP | 197.46 ± 5.33 * | 187.04 ± 9.87 * | 274.01 ± 9.23 * | 359.31 ± 9.50 * |
| AK | 112.30 ± 7.41 * | 15.42 ± 10.37 ns | 41.83 ± 4.58 * | −24.26 ± 4.84 * |
| Variables | RFD vs. CRS | RFD vs. RPS | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Topsoil | Subsoil | Topsoil | Subsoil | |
| OC | 38.39 ± 3.04 * | 35.55 ± 1.42 * | 21.36 ± 0.35 * | 32.54 ± 3.38 * |
| EOC | 22.31 ± 5.96 * | 178.41 ± 3.89 * | 107.77 ± 14.97 * | 444.35 ± 43.18 * |
| DOC | 33.28 ± 2.45 * | 55.23 ± 2.90 * | 12.25 ± 1.07 * | 6.11 ± 3.36 * |
| MBC | 216.44 ± 15.75 * | 51.87 ± 10.95 * | 58.02 ± 14.18 * | 78.39 ± 6.35 ns |
| HA | 57.15 ± 7.59 * | 84.87 ± 13.21 * | 126.74 ±4.09 * | 113.80 ± 12.46 * |
| FA | 66.82 ± 4.45 * | 55.36 ± 1.73 * | 20.20 ± 5.18 * | 23.21 ± 5.18 * |
| HA/FA | −5.82 ± 3.08 ns | 18.98 ± 8.10 ns | 88.85 ± 8.17 * | 73.44 ± 3.16 * |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, C.; Yang, Q.; Chen, J.; Zhang, C.; Liu, K. Variations in Soil Organic Carbon Fractions and Microbial Community in Rice Fields under an Integrated Cropping System. Agronomy 2024, 14, 81. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14010081
Wang C, Yang Q, Chen J, Zhang C, Liu K. Variations in Soil Organic Carbon Fractions and Microbial Community in Rice Fields under an Integrated Cropping System. Agronomy. 2024; 14(1):81. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14010081
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Chao, Qiannan Yang, Jing Chen, Chi Zhang, and Kexue Liu. 2024. "Variations in Soil Organic Carbon Fractions and Microbial Community in Rice Fields under an Integrated Cropping System" Agronomy 14, no. 1: 81. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14010081
APA StyleWang, C., Yang, Q., Chen, J., Zhang, C., & Liu, K. (2024). Variations in Soil Organic Carbon Fractions and Microbial Community in Rice Fields under an Integrated Cropping System. Agronomy, 14(1), 81. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14010081






