Abstract
Sulfur (S) is an essential nutrient for plant growth, influencing not only crop yields but also the composition and function of soil microbial communities. However, the differential effects of S fertilization on abundant and rare taxa in agricultural soils remain poorly understood. This study investigates the impact of different S fertilizer types on maize yield and the structure and stability of soil microbial communities, with a particular focus on abundant and rare taxa. S fertilization led to significant increases maize yield on two typical soils (black soil and sandy soil) (5.3–24.3%) and altered soil properties, including reducing pH (0.04–0.20) and increasing the available sulfur (AS) content (3.8–8.0 mg kg−1), with ammonium sulfate having a more pronounced effect than elemental sulfur. Microbial analysis revealed distinct impacts on the diversity and community structure of both abundant and rare taxa. Elemental sulfur reduced the alpha diversity of abundant taxa more than ammonium sulfate, while NMDS indicated significant shifts in community structures, particularly among abundant taxa. Network analysis showed that S fertilization decreased the complexity of microbial interactions among rare taxa, with ammonium sulfate leading to simpler networks and elemental sulfur resulting in higher modularity. SEM highlighted that the diversity of rare taxa played a crucial role in influencing maize yield, alongside direct effects from soil properties such as AS and SAR (aryl sulfatase). Functional predictions demonstrated that amino acid metabolism and xenobiotic biodegradation and metabolism pathways were enriched in rare taxa, suggesting significant implications for soil health and crop productivity. This study provides new insights into the roles of abundant and rare bacterial taxa under S fertilization, emphasizing their importance in optimizing fertilization strategies for enhanced crop yield in specific soil types.
1. Introduction
S is the fourth most prevalent essential macronutrient required by all living organisms [1]. The reduction in S inputs from industrially produced atmospheric acidic deposition, along with fertilizers and pesticides containing lower S content, has resulted in widespread S deficiency in plants [2,3], This deficiency is now recognized as a significant yield-limiting factor [4,5]. In maize, simultaneous deficiency of S nutrients has been shown to negatively affect yield [6]. The application of sulfur-containing fertilizers in agricultural ecosystems enhances soil properties, reduces pH, and increases the availability of nutrients to plants [7,8]. Therefore, it is crucial to develop effective strategies to increase the S content in crops to mitigate the adverse effects of S deficiency on both plants and humans [1]. Consequently, there is a growing global demand for sulfur-containing fertilizers.
In agricultural production, ammonium sulfate and elemental sulfur are commonly used sources of S fertilizers. They enhance soil nutrient conditions and promote crop growth and yield by supplying the S essential for plant development. Ammonium sulfate is a fast-acting nitrogen and S fertilizer, containing approximately 21% nitrogen and 24% S. Ammonium sulfate dissolves easily in water and can rapidly supply crops with nitrogen and S after application, supporting protein synthesis and plant photosynthesis [9,10]. Elemental sulfur is a slow-release S fertilizer that is primarily converted into plant-absorbable sulfate ions (SO42−) through microbial oxidation. The oxidation process of elemental sulfur is relatively slow, making it suitable for sulfur-deficient soils that need long-term improvement. The application of S promotes microbial activity [11]. Ammonium sulfate and elemental sulfur are widely used in agriculture. By adjusting the application method and rate of S application, the crop growth environment can be optimized, S utilization efficiency enhanced, and sustainable agricultural development promoted.
The application of S fertilizers in agricultural production not only supplies essential sulfur to crops but also may impact the physicochemical properties of the soil through various pathways, consequently affecting the composition and function of the rhizosphere microbial community. The transformation of S fertilizers (e.g., ammonium sulfate and elemental sulfur) in the soil reduces soil pH. Such changes in pH can influence the composition of the rhizosphere microbial community, potentially causing the abundance of certain bacterial groups to increase or decrease [12]. The application of S fertilizers not only directly increases the S content in the soil but may also modify the soil’s nutrient structure through interactions with other nutrient elements. The nitrogen and S from ammonium sulfate aid in promoting microbial growth, but excessive nitrogen might intensify microbial competition, disrupting the balance of the microbial community. S fertilizers directly affect microbial metabolic activity by increasing the available sulfur content in the soil [13]. Consequently, sufficient sulfur supply can stimulate the growth of specific sulfur-oxidizing bacteria and other sulfur-dependent microbes, thereby altering the structure of the soil microbial community [14].
In natural ecosystems, the distribution of species within microbial communities is typically unbalanced, with a few species being abundant and the majority being rare [15,16]. Abundant and rare bacterial taxa play different roles in ecosystem function [17]. Abundant taxa are often associated with primary ecosystem functions, while rare taxa may play crucial roles in responding to environmental changes and maintaining ecological diversity [18,19]. Thus, differentiating between them helps to achieve a more comprehensive understanding of microbial community dynamics and their responses to environmental changes. Primary ecosystem processes are generally dominated by these abundant taxa [15]. However, recent research has increasingly underscored the significance of rare taxa [20]. For instance, rare bacterial species have been shown to play crucial roles in sulfate reduction [21] and phenanthrene degradation [22], as well as mediating ecosystem stability and function [23,24]. Notably, no study has yet examined the effects of S application on both abundant and rare bacteria.
While previous studies have investigated the role of S, there is a gap in systematic research regarding the specific effects of different S fertilizer types on microbial communities (particularly rare and abundant taxa) under diverse soil conditions and how these impacts are translated into crop yield. In order to comprehensively understand the impact of different S sources on the rare and abundant bacterial communities in soil, and to investigate the influence of soil physical and chemical properties as well as microbial properties on maize yield, we collected soil samples from two typical soils (black and sandy soil) in northeastern China. The aim is to comprehensively evaluate the effects of different S sources on the diversity and community structure of rare and abundant bacteria in soil. Additionally, we explore the coupled effects of soil properties and microbial information on the regulation of crop yield (SEM).
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Field Sites and Sample Collection
In 2017, field experiments were conducted on two typical soil types from maize-growing regions in Northeast China, black soil (43°20′ N, 124°00′ E) and sandy soil (43°21′ N, 124°05′ E). According to the WRB classification, black soil and sandy soil are classified as Chernozems and Arenosols, respectively. Throughout the experiment, the average temperature was 6.3 °C, with total rainfall reaching 576.8 mm. The annual average sunshine duration was 2644 h, and during the crop growth period (May to October), there were 1435 sunshine hours. The accumulated annual temperature above 0 °C was 3255 °C, and above 10 °C was 3032 °C, with an approximately 156-day frost-free period. The fundamental characteristics of the soil were as follows. The black soil possesses a clay content of 43.1%, a silt content of 24.0%, and a sand content of 33.5%. Its pH (measured at a soil to water ratio of 2.5:1) was 6.63, with an organic matter (OM) of 23.2 g·kg−1. Additionally, it contains available nitrogen (AN), phosphorus (AP), potassium (AK), and AS at concentrations of 106.6, 38.4, 191.3, and 13.2 mg·kg−1 respectively. Conversely, the sandy has a clay content of 11.4%, a silt content of 9.1%, and a sand content of 74.2%. Its pH (at a soil to water ratio of 2.5:1) was 5.77, with an OM of 16.2 g·kg−1. The AN, AP, AK, and AS in the loess were 61.7, 25.0, 160.9, and 11.3 mg·kg−1, respectively.
The experiment included three treatments: S0 (0 kg S ha−1), S90 (90 kg S ha−1, ammonium sulphate), and s90 (90 kg S ha−1, elemental sulfur). Each treatment had three replicates, and all plots were arranged using a randomized block design, with a plot size of 60 square meters. In addition to the S treatments, nitrogen fertilizer (N) at 210 kg ha−1, phosphorus fertilizer (P2O5) at 90 kg ha−1, and potassium fertilizer (K2O) at 90 kg ha−1 were applied. All fertilizers were applied in a single dose as basal fertilizer (band application). The tested maize variety was Liangyu 99 (Guoshenyu 2012008). Maize was planted at a density of 65,000 plants per hectare. Additional agricultural activities were conducted each year as required, with weed control and pest management following the traditional practices of local farmers.
Soil samples were collected in September 2019, with sampling tools sterilized in advance by autoclave steam. Rhizosphere soil samples were obtained using the shaking root method. Five random sampling points were selected within each plot, and the rhizosphere soil samples from these five points were combined uniformly to represent one plot treatment. The soil samples were placed in polyethylene zip-lock bags and transported to the laboratory in an icebox. A total of 18 composite rhizosphere soil samples were obtained from the experimental area. Upon arrival at the laboratory, visible plant and animal residues, as well as stones, were promptly removed. The samples were then passed through a 2 mm sterile mesh sieve and mixed uniformly. The soil samples were divided into two portions, with one portion used for microbial extraction and the other for testing soil physicochemical properties. All soil samples were promptly transported back to the laboratory and preserved at −80 °C, with DNA extraction and sequencing performed within a month to reduce any potential effects on microbial communities. The remaining soil samples were stored at 4 °C for the measurement of soil properties.
2.2. Soil Properties and Maize Yield Determination
Maize yields were measured at the harvesting stage, and the number of plants, ears, and total fresh weight of maize ears within the yield area (18 m2) were recorded [25]. The yields were adjusted to 14% moisture content for standardization [25].
Soil pH was determined using a pH meter at a soil: water ratio of 1:2.5. The soil organic matter (OM) was analyzed by the potassium dichromate volumetric. The AS content was extracted using KH2PO4 and quantified using an Inductive Coupled Plasma Emission Spectrometer (SHIMADZU, ICPS-7500, Japan).
SAR activity was assessed by its catalysis of the conversion of potassium p-nitrobenzenesulfate to p-nitrophenol, which was subsequently measured using a spectrophotometer (You Ke, 721, Shang hai, China).
2.3. Illumina MiSeq High-Throughput Sequencing and Data Analysis
Soil DNA was extracted using the Fast DNA SPIN extraction Kits (MP Biomedicals, Santa Ana, CA, USA), following the manufacturer’s instructions, with a negative control included. The V3–V4 region of the 16S rRNA genes were amplified using the primer 338F (5′-ACTCCTACGGGAGGCAGCA-3′) and the reverse primer 806R (5′-GGACTACHVGGGTWTCTAAT-3′). For multiplex sequencing, unique 7-bp barcodes specific to each sample were added to the primers. The PCR mixture included 5 μL of Q5 reaction buffer (5×), 5 μL of Q5 High-Fidelity GC buffer (5×), 0.25 μL of Q5 High-Fidelity DNA Polymerase (5 U/μL), 2 μL of dNTPs (2.5 mM), 1 μL of each primer (Forward and Reverse, 10 μM), 2 μL of DNA template, and 8.75 μL of ddH2O. The thermal cycling conditions began with an initial denaturation at 98 °C for 2 min, followed by 25 cycles of denaturation at 98 °C for 15 s, annealing at 55 °C for 30 s, and extension at 72 °C for 30 s, ending with a final extension at 72 °C for 5 min. PCR amplicons were purified with Agencourt AMPure Beads (Beckman Coulter, Indianapolis, IN, USA) andquantified using the PicoGreen dsDNA Assay Kit (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA). After quantification, the amplicons were pooled in equal amounts, and paired-end 2 × 300 bp sequencing was carried out using the Illumina MiSeq platform with MiSeq Reagent Kit v3 at Shanghai Personal Biotechnology Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China).
Additionally, low-quality sequences were filtered according to established criteria [26,27]. OTUs representing less than 0.001% of total sequences across all samples were discarded. To minimize differences in sequencing depth across samples, an averaged, rounded rarefied OTU table was generated by averaging 100 evenly resampled OTU subsets at 90% of the minimum sequencing depth for subsequent analysis.
Sequence data were analyzed using the Quantitative Insights into Microbial Ecology (QIIME2 2019.4) pipeline, following the protocol by Bolyen [28]. Barcode and primer sequences were removed, followed by quality filtering to discard sequences not meeting quality criteria. Chimeric sequences were eliminated using UCHIIME algorithms (QIIME2 (2019.4)), and valid sequences were taxonomically classified. A representative sequence at the ASV level, targeting a 98% identity, was selected. Alpha diversity indices were calculated using QIIME2 (2019.4). The specific sequencing methods were discussed in our previous study [29]
2.4. Statistical Analysis
The sequence data were rarefied to a depth of 40,501 sequences per sample. Operational taxonomic units (OTUs) were referred to as ASVs. We excluded OTUs with fewer than one read to prevent random effects on the identification of rare taxa. We defined bacterial communities with a relative abundance greater than 0.5% as “abundant”, representing 2.5–3.3% of the total OTUs. Bacterial communities with a relative abundance of less than 0.05% were defined as “rare”, comprising 6.8–11.1% of the total OTUs. This classification standard primarily references multiple studies in the field, taking into account both abundance thresholds and the proportion of rare and abundant taxa [30,31,32]. To evaluate the significance of variations in microbial alpha diversity indices, an analysis of variance (ANOVA) with Fisher’s least significant difference (LSD) test (p < 0.05) was conducted.
Non-metric multidimensional scaling (NMDS) is a non-metric multidimensional scaling technique that reduces the dimensionality of the distance matrix between species or samples, enabling their similarities to be visualized in a lower-dimensional space. The NMDS analysis using the Bray–Curtis distance matrix was performed to visualize the differences in rare and abundant microbial community composition among all soil samples using the “vegan” package in R (version 4.2.3). NMDS analysis is considered reliable when the stress value is less than 0.2.
Co-occurrence network analysis was employed to examine the co-occurrence patterns of rhizosphere bacterial communities across different soil types. For each soil type, co-occurrence networks were built based on Spearman’s correlation analysis between ASVs. Only strong (Spearman’s r > 0.6 or r < −0.6) and statistically significant (p < 0.01) correlations were considered for network construction, focusing on ASVs that were likely to interact due to their strong co-occurrence. The primary modules within the networks were visualized using the interactive platform Gephi 0.9.2, and network-level topological characteristics were calculated.
We evaluated the effects of S fertilizer types and soil properties on the abundance and rarity of bacterial communities, using VPA (variance partitioning analysis) in the “vegan” package to identify the driving factors behind these effects.
To investigate the relationship between soil properties, rare and abundant bacterial communities, and maize yield, we used structural SEM implemented through the R package “lavaan” (R version 4.2.3). This method allows us to evaluate the direct and indirect effects of soil properties and bacterial communities on crop yield. Using the ASV table, we selected the first axis of NMDS as the parameter for bacterial community structure. Typically, we use the goodness-of-fit index (GFI) as a comprehensive indicator to evaluate the model’s fit. The best-fit SEM was determined based on the chi-square test (significance level p > 0.05). All analyses were conducted using R (version 4.2.3).
The 16S taxonomic lineage based on Silva database was transformed into the taxonomic lineage of prokaryotes in Kyoto gene and genome encyclopedia database (kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes, KEGG, http://www.genome.jp/kegg/, accessed on 10 August 2024) by PICRUSt2, and the 16S RNA gene sequence was annotated with KEGG function. Linear discriminant analysis (LEfSe, LDA > 2.0) effect size was used to determine the significantly different functions of soil bacterial communities in different S application. Statistical analysis employed R version 4.2.3.
3. Results
3.1. Effects of Different S Types Application on Maize Yield
Compared to the S0 treatment, the application of S significantly increased maize yield in both soils, with increases of 5.3–12.4% in black soil and 18.3–24.3% in sandy soil. Under the same S application rate, maize yield in the S90 treatment was higher than in the s90 treatment by 0.5–0.8 t ha−1, with significant differences observed in black soil (Figure 1).

Figure 1.
The histogram illustrates the response of maize yield to different S fertilizers (elemental sulfur and ammonium sulfate) in two soil types. Different letters indicate significant differences (p < 0.05) between treatment groups within each soil type. For the analysis of variance results.
3.2. Effects of Different S Types Application on Soil Properties
The effects of different S applications on the properties of two soil types are presented in Table 1. Compared to the S0 treatment, S application significantly reduced soil pH, with the s90 treatment exhibiting the most pronounced effect. In black soil, pH decreased significantly by 0.16–0.20 units after S application, while in sandy soil, pH dropped by 0.04–0.14 units. S application also significantly increased the AS in the soil, with the S90 treatment showing the highest levels in both soils (black soil: 21.3 mg kg−1, sandy soil: 17.5 mg kg−1). In both soils, the increase in AS was greater with the application of ammonium sulfate (5.3–8.0 mg kg−1) compared to elemental sulfur (3.8–5.7 mg kg−1). No significant differences in OM were observed under the application of different S fertilizers. The variation in SAR across treatments followed a pattern consistent with that observed for AS, with the S90 treatment showing the highest value, significantly higher than the S0 and S90 treatments.

Table 1.
Soil characteristics under application of different S applications.
3.3. Effects of Different S Types Application on Bacterial Alpha Diversity and Community Structure
The Shannon index of alpha diversity for both abundant and rare taxa was calculated to examine the differences between elemental sulfur and ammonium sulfate applications (Figure 2). For abundant taxa, significant differences in alpha diversity were observed between the elemental sulfur and ammonium sulfate treatments, with elemental sulfur application showing notably lower values compared to the ammonium sulfate. However, no significant differences in the alpha diversity of rare taxa were detected between the two treatments.
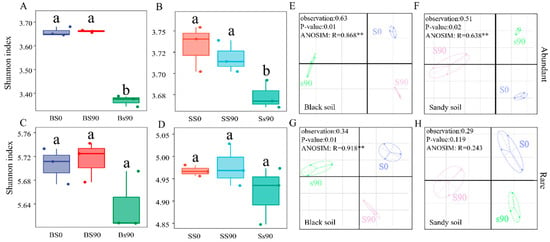
Figure 2.
Alpha diversity of abundant (A,B) and rare taxa (C,D) with different S application in black and sandy soil. Different letters indicate significant differences in treatments within each soil type (p < 0.05). NMDS of abundant (E,F) and rare (G,H) taxa with different S application in black and sandy soil. ANOSIM = analysis of similarities. ANOSIM was used to test the difference in soil bacterial communities between different S application treatments within the same soil type. In the results of the analysis of variance, ** p = 0.01.
To investigate the diversity of species composition within microbial communities under S application across different soil types, we conducted a NMDS analysis. The findings revealed significant differences in the community structures of both abundant and rare taxa in the rhizospheres, with the exception of rare taxa in sandy soil (p = 0.119). The results of the analysis of ANOSIM were consistent with these findings (Figure 2). The NMDS analysis further indicated that the differential S applications accounted for a greater proportion of variance in abundant taxa (51 and 63%) compared to rare taxa (29 and 34%).
3.4. Effects of Different S Types Application on Bacterial Community Stability
To elucidate the alterations in soil microbial communities under various S applications, we constructed microbial networks (Figure 3). Among the abundant taxa, compared to the S0, ammonium sulfate application decreased network density, while elemental sulfur application increased network complexity. In contrast, for the rare taxa, both ammonium sulfate and elemental sulfur treatments resulted in simpler microbial networks, with the elemental sulfur treatment exhibiting a more pronounced effect. The network structure of abundant taxa was more intricate, characterized by a greater number of edges and nodes (Figure 3A–F). However, the rare taxa exhibited a higher modularity index (Table S1), indicating more distinct community modules.
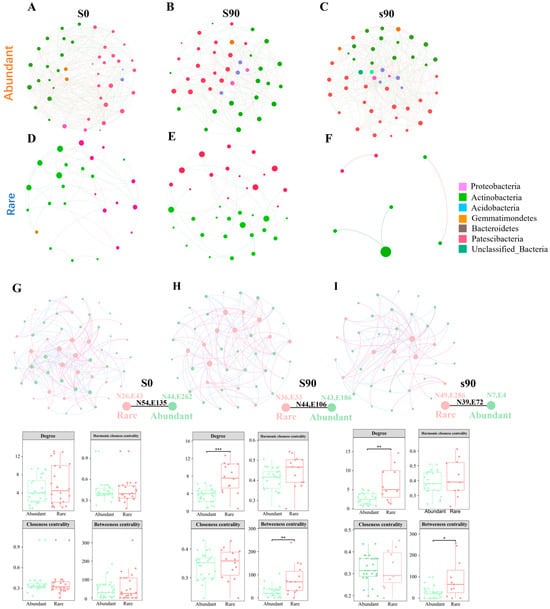
Figure 3.
Co-occurrence network of different S application. (A–F): Co-occurrence network colored by phylum under different S application treatments. (G–I): Properties of the co-occurrence network colored for abundant or rare species and composition of each co-occurrence network. The external and internal (black numbers) connections among each subcommunity are shown on the bottom right. In the results of the analysis of variance. The two numbers separated by a comma represent the number of edges (E) and nodes (N), respectively. *, **, and *** indicate significant differences between the treatments at the levels of p = 0.05, p = 0.01, and p = 0.001.
A bacterial community co-occurrence network was constructed to evaluate the patterns of co-occurrence among abundant and rare taxa under different treatments (Figure 3G–I). Comparative analysis of network-level topological features revealed that the S0 network had a significantly higher average degree than the S application networks, suggesting more intimate relationships within the former. S application, however, increased network modularity, with the ammonium sulfate treatment exhibiting the highest modularity (0.413). At the node level, topological features such as degree, harmonic closeness, closeness, and betweenness centrality we investigated. The abundant taxa treated with S fertilizer displayed lower topological characteristic parameters compared to the S0 treatment, with communities treated with elemental sulfur having lower values than those treated with ammonium sulfate. The rare taxa showed higher degree and betweenness centrality indices, with these values being more pronounced for rare taxa compared to abundant taxa across all treatments (Figure 3G–I).
3.5. Driving Factors of Rare and Abundant Taxa
Significant differences were observed in the contributions of different S treatments and soil properties to the community structure of rare and abundant taxa (Figure 4). In black soil, soil properties contributed 8.12% to the community structure of abundant taxa, surpassing the contribution of different S applications. Soil properties contributed 2.92% to the community structure of rare taxa, which was less than the contribution of different S applications. In sandy soil, soil properties contributed 24.68% to the community structure of abundant taxa, exceeding the contribution of different S applications. Soil properties contributed 6.87% to the community structure of rare taxa, which was less than the contribution of different S applications.
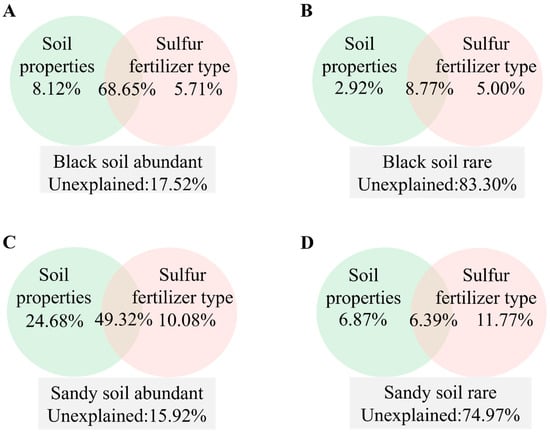
Figure 4.
VPA (A–D) for the contributions of soil properties, S variables to abundant and rare taxa communities’ variations in black and sandy soils.
3.6. Effect of Different Types S Fertilization-Driven Soil Properties on Maize Yields
SEM was conducted to examine the direct and indirect effects of soil properties, diversity, and community structure of rare and abundant taxa on maize yield. The SEM analysis produced a chi-square (χ2) value of 0.708 (df = 5), a p-value of 0.4, and a goodness-of-fit index (GFI) of 0.997 for maize yield (Figure 5). According to the SEM analysis, different S applications significantly influenced soil properties, including pH, AS, and SAR, all of which had direct and indirect effects on maize yield by affecting the diversity and community structure of rare taxa (Figure 5). Among these indicators, the diversity of rare taxa (path coefficient = 0.635) was identified as the most crucial factor influencing maize yield due to its individual effect. AS had an indirect effect on maize yield by regulating the diversity of rare taxa (path coefficient = 0.474). pH indirectly influenced maize yield by regulating the diversity and community structure of rare taxa (path coefficients = 0.783, 0.462). However, AS (path coefficient = 0.389) and SAR (path coefficient = 0.257) both exerted direct positive effects on maize yield (Figure 5).

Figure 5.
SEM between yield, soil properties, and rare and rich bacterial communities. S types are represented as different S types. The red line represents positive correlation, the blue line represents negative correlation, and the gray line indicates irrelevance. “*” indicates significance between root morphology or crops p index and maize yield (*, p < 0.05; ***, p < 0.001).
3.7. Predictive Functional Analysis of Abundant and Rare Taxa under Different S Applications
Based on PICRUSt2, we predicted the potential functions of abundant and rare taxa, finding that metabolism (Level 1) is the primary KEGG pathway (Figure S1). Linear discriminant analysis effect size (LEfSe) was applied to evaluate the differences across various S applications (Figure 6). For both abundant and rare taxa, four functions were significantly enriched in the rare taxa: metabolism, cellular processes, human diseases, and organismal systems (Level 1). Additionally, environmental information processing and genetic information processing (Level 1) were significantly enriched in the abundant taxa. Specifically, in abundant taxa, metabolism (e.g., other amino acid metabolism, carbohydrate metabolism) played a more significant role in the S90 treatment (Figure 6), while metabolism (e.g., lipid metabolism, xenobiotic biodegradation, and metabolism) played a larger role in the s90 treatment. Similarly, for rare taxa, metabolism (e.g., xenobiotic biodegradation and metabolism, amino acid metabolism, and energy metabolism) contributed the most under different S treatments (Figure 6). Furthermore, abundant taxa (S90 = 30, s90 = 17) were significantly (p < 0.05) enriched with more functions (Level 3) compared to rare taxa (S90 = 6, s90 = 6). These results suggest that the main bacterial functions differ between various S treatments and that different functions were enriched in abundant and rare taxa.
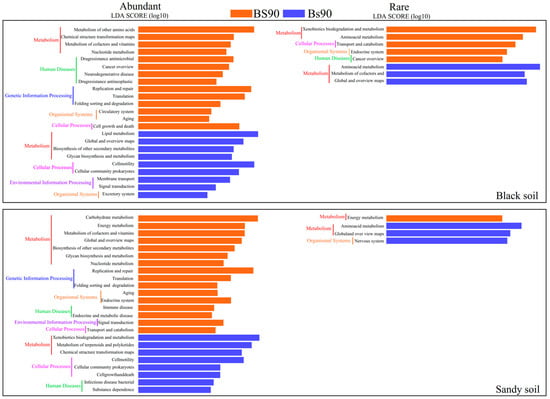
Figure 6.
Linear discriminant analysis effect size (LEfSe) analysis of functions of abundant and rare taxa in different S types. The potential function of bacteria was based on PICRUSt2. LDA score determined the differentiation size of abundant and rare bacterial sub-communities in S90 and s90 systems with a threshold value of 2.0.
4. Discussion
4.1. The Effect of Different S Fertilizer Applications on Maize Yield
The results of this experiment indicate that the application of S fertilizer can significantly increase maize yield, with the highest yields reaching 8.9 t ha−1 and 11.1 t ha−1 in both soils under the S90 treatment. Comparing the effects of different types of S on maize yield at the same application rates, it was found that ammonium sulfate resulted in higher yields than elemental sulfur. Previous research has demonstrated that ammonium sulfate has a more significant effect on yield [33,34]. Jiang [35] demonstrated that the application of ammonium sulfate on meadow soil improved maize growth traits, such as grain number per ear, resulting in a yield increase of 26.6–31.2 kg ha−1. The variability in the impact of S on maize yield may be related to the type of soil tested and the level of macronutrient fertilizer application. The diverse effects of S fertilizer on maize yield and its underlying mechanisms require further in-depth research.
4.2. The Effect of Different S Fertilizer Applications on Soil Properties
Following the application of S fertilizer, most of the S is stored in the soil through adsorption and fixation, undergoing a series of migrations and transformations that directly or indirectly influence soil properties [36]. Du [34] demonstrated that applying S fertilizer can lower the pH of mildly alkaline soil, with a more pronounced pH reduction as the S fertilizer content increases. Skwierawska [33] found that applying varying amounts of desulfurized gypsum to saline-alkaline land effectively reduces soil pH. Research by Bolan [12] and Khan [36] confirmed that when S powder is applied to soil, it is converted into sulfuric acid by soil bacteria, reducing pH and leading to soil acidification.
In an experiment where S fertilizer was applied in paddy fields, Masuda [37] found that the concentration of thiosulfate and sulfides in pot plants treated with CaSO4 was slightly higher than in the control and in pot plants treated with CaCO3 fertilizer. The likely reason is that the oxidation of S in soil primarily occurs with the participation of soil microorganisms. The addition of S fertilizer primarily influences the relative abundance of sulfate-reducing bacteria, which, in turn, affects the content of AS [38]. However, the AS in soils treated with elemental sulfur was lower than in those treated with ammonium sulfate. The possible reason is that ammonium sulfate is a fast-acting fertilizer, and the SO42− it contains can be directly absorbed by plants, thereby immediately increasing the AS in the soil. Elemental sulfur must be oxidized by soil microorganisms into SO42− before it can be absorbed by plants. This conversion process is typically slow. Therefore, in the short term after application, the contribution of S to the AS content in soil may not be as pronounced as that of ammonium sulfate [39,40].
SAR is a key soil enzyme that decomposes organic S compounds present in the soil, such as aryl sulfates, into SO42− forms that are directly available to plants and soil microorganisms. This enzyme plays an important role in the “mineralization” process of converting organic S into inorganic S. SAR effectively increases the S available to plants in the soil by converting organic S into inorganic sulfate, thereby promoting plant growth and development, particularly when S is an important nutrient element [41]. In this study, the application of S fertilizer increased the activity of SAR in the soil compared to S0, and the increase was more significant in the ammonium sulfate treatment than in the S treatment. This is because ammonium sulfate application immediately raises the concentration of SO42− in the soil, and the increased S supply stimulates soil microbial activity, thereby indirectly enhancing arylsulfatase activity. Ammonium sulfate application increases AS and provides nitrogen, which further stimulates the growth and metabolic activity of soil microorganisms [42,43].
4.3. The Effect of Different S Application on Rare and Abundant Bacterial Communities
Our research found that the diversity of rare taxa is higher than that of abundant taxa (Figure 2A–D). This finding is consistent with previous studies [32,44,45,46,47]. These studies primarily focused on farmland and wetland environments, and in these studies, the diversity of rare taxa surpassed that of abundant taxa. In our study, the diversity of enriched bacteria under elemental sulfur treatment was significantly lower than under ammonium sulfate treatment. Although rare taxa did not show significant differences, they exhibited a decreasing trend, suggesting that the long-term effects of ammonium sulfate application on soil microbial community structure may be relatively mild, while long-term S application may lead to a significant decrease in microbial diversity and richness. This decline could be attributed to prolonged S oxidation, which exerts greater pressure on microorganisms, affecting their survival and reproduction [48]. Therefore, from the perspective of microbial diversity and richness, soils with long-term application of elemental sulfur may experience lower levels of microbial diversity and richness, particularly in abundant taxonomic groups.
Discovered that fertilization influences the abundance of specific microbial populations in the context of tillage systems and farmland ecosystem management. Studies by Schmalenberger [49] and Lu [50] have also shown that sulfate treatments can significantly alter bacterial communities in soil, particularly those involved in S cycling. Chronic application of elemental sulfur as a fertilizer has been observed to decrease soil pH, which in turn can lead to a reduction in microbial biomass. These findings suggest that while S fertilization may enhance certain soil attributes, it can also have adverse effects on microbial health [51]. The literature on the effects of elemental sulfur and ammonium sulfate application on soil microbial community structure presents contradictory statements. While some studies document beneficial outcomes for plant growth and soil properties, others emphasize the potential for negative impacts on microbial health and diversity. These discrepancies underscore the need for further research to clarify the mechanisms driving these diverse responses.
4.4. The Mechanism of Rare and Abundant Taxa Regulating Maize Yield
In this study, we found that S fertilizer application increased the diversity index of rare groups more than that of abundant groups. Compared to S, ammonium sulfate resulted in greater bacterial richness and a more stable network structure. Variations in S fertilizer types affected rare groups more, whereas changes in soil properties explained the abundant groups.
Our results indicate significant differences in the contributions of different S treatments and soil properties to the community structure of rare and abundant taxa, which vary between black and sandy soil. In black soil, soil properties contributed significantly to the community structure of abundant taxa (8.12%), while for rare taxa, although soil properties also played a role (2.92%), S application had a more pronounced effect. This suggests that rare taxa are more sensitive to environmental changes, particularly to nutrient elements like S [19,52]. In sandy soil, the contribution of soil properties to the community structure of abundant taxa was even more pronounced (24.68%), overshadowing the contributions from varying S applications. This indicates that the physical and chemical characteristics of this soil type may be the dominant factors influencing the distribution of abundant taxa. Overall, these results illustrate that soil type and properties play distinct roles in the ecological distribution of different microbial groups. In black soil, abundant taxa are primarily influenced by soil properties, while rare taxa are more sensitive to S; conversely, in sandy soil, although soil properties significantly affect abundant taxa, rare taxa are predominantly influenced by S application. This underscores the importance of tailored management strategies for microbial communities, taking into account the specific soil types and microbial groups to optimize microbial diversity and ecological functions [53,54].
SEM analysis showed that different S fertilizers regulate maize yield by influencing soil properties, which, in turn, alter the community structure of rare groups. Research on the microbial mechanisms by which different S fertilizers regulate maize yield is limited. Thus, the potential reason for the above results is that ammonium sulfate supplies not only sulfate ions (SO42−) but also ammonium nitrogen (NH4+). The application of ammonium sulfate may change the soil pH, with rare bacteria, often more sensitive to environmental changes, potentially gaining a growth advantage as the drop in pH suppresses some abundant bacteria [55,56]. Nitrogen in ammonium sulfate can change soil nitrogen dynamics by influencing key nitrogen cycle microorganisms, such as ammonia-oxidizing bacteria and nitrifying bacteria. This shift in nitrogen dynamics may better suit certain rare bacteria, allowing them to gain a competitive advantage [57,58]. Although rare bacteria are less abundant in soil, they usually possess specialized metabolic pathways, which might include utilizing specific organic S compounds, producing stress-resistance substances, or participating in complex biogeochemical cycles [59]. Certain rare bacteria might more effectively mineralize organic S through sulfur-nitrogen interactions, releasing nutrients that benefit crops. Within soil microbial communities, there is a complex interplay of competition and symbiosis between abundant and rare bacteria. Ammonium sulfate application might disrupt the original microbial balance, enabling certain rare bacteria to rapidly proliferate due to their unique physiological traits (e.g., more efficient S oxidation or greater resilience), which could significantly impact the soil environment and crops. Abundant bacteria often show functional redundancy in soil, meaning that multiple species can carry out similar ecological roles. However, rare bacteria often occupy specific ecological niches, and their metabolic activities may compensate for the functional gaps of abundant bacteria, thus playing a critical role in crop production [1,60]. Based on the above results and discussion, considering the effects of different sulfur fertilizers on soil microbial communities and maize yield, ammonium sulfate favors stable maize yields and soil microbial communities.
4.5. The Effects of Different S Applications on the Functions of Rare and Abundant Taxa
The findings from our study using PICRUSt2 highlight the significant functional differences between abundant and rare bacterial taxa under various S treatments. The prediction of potential functions revealed that metabolism is the primary KEGG pathway, with distinct roles being played by both abundant and rare taxa (Figure 6) [61].
For abundant taxa, the data showed a significant enrichment in metabolic functions such as amino acid and carbohydrate metabolism, particularly under the S90 treatment. This suggests that these bacteria might be crucial in driving key metabolic processes in environments with higher S fertilizer inputs. The significant enrichment of genetic and environmental information processing in abundant taxa further underscores their role in maintaining critical ecosystem functions, likely due to their higher presence and activity levels [62,63]. On the other hand, rare taxa exhibited a distinct functional profile, with significant enrichments in metabolism, cellular processes, human diseases, and organismal systems. These functions suggest that rare taxa might be involved in more specialized or less dominant ecological roles, possibly acting as a functional reservoir that can be crucial under specific environmental conditions or perturbations [64,65]. Xenobiotics biodegradation and metabolism is associated with the degradation and metabolism of foreign compounds in the environment. The function of Xenobiotics biodegradation and metabolism genes is to eliminate harmful substances from the soil, improve soil health, and indirectly enhance maize growth and yield [66]. Amino acid metabolism is closely associated with protein synthesis and metabolic regulation in plants and microorganisms. Amino acid metabolism genes in rare taxa can regulate the synthesis and degradation of amino acids, facilitating effective nitrogen utilization in the soil and nutrient acquisition by plants, which, in turn, directly enhances maize growth and yield. Liu [67] found through their study on nitrogen-sulfur interaction that sulfur fertilizer can promote amino acid balance in grains, thereby enhancing maize grain quality and yield. These genes directly participate in the nutritional metabolism of plants, thus promoting plant growth and yield.
The LEfSe analysis provided additional insights, indicating that the S application significantly influenced the functional capacity of both abundant and rare taxa. The higher enrichment of various metabolic pathways, especially those related to xenobiotic biodegradation and energy metabolism in rare taxa, points to their potential role in detoxifying environments and contributing to energy flow under sulfur-rich conditions [68]. In conclusion, our study demonstrates that S fertilizer applications can distinctly alter the functional roles of abundant and rare taxa, with significant implications for nutrient cycling, environmental health, and agricultural sustainability. These findings contribute to our understanding of how microbial communities respond to nutrient inputs and the potential consequences for ecosystem functions.
5. Conclusions
This study provides new insights into the responses of complex soil microbial communities, particularly abundant and rare taxa, to different sulfur (S) applications in two typical soil types from the black soil region of Northeast China. Our findings revealed that different S applications distinctly impacted soil microbial communities, with effects that may vary depending on soil type, climate, and agricultural practices. Elemental sulfur significantly decreased the diversity and network complexity of abundant taxa compared to ammonium sulfate. Both S treatments simplified the networks of rare taxa, with elemental sulfur having a more pronounced effect. Networks without S application were more interconnected, while S treatments increased communication frequency within microbial communities. Rare taxa exhibited higher topological attributes, underscoring their key role in microbial diversity, functional uniqueness, and ecological stability, which had a more substantial impact on maize yield. In terms of maize yield, higher soil microbial diversity, and more stable community structures, ammonium sulfate proves to be more advantageous in agricultural production for these soils. It is essential to investigate abundant and rare taxa separately to further analyze the changes in microbial communities caused by different S sources and to understand the mechanisms driving maize yield. Our research offers a theoretical basis for understanding how S application affects shifts in soil microbial populations and enhances maize yield in specific soil types. Future research should focus on how ammonium sulfate regulates N and S cycling processes under varying soil and environmental conditions to better understand its broader impacts.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/agronomy14102251/s1, Figure S1: Functional prediction KEGG pathways (level 1) of soil abundant and rare bacterial community samples; Table S1: Network-level topological features of the bacterial networks.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.D. and X.Z.; Data curation, S.D. and X.Z.; Formal analysis, S.D. and B.Z.; Investigation, S.D. and W.H.; Methodology, S.D., W.H. and Q.G.; Software, S.D. and B.Z.; Validation, W.H., X.Z. and Q.G.; Writing—original draft, S.D.; Writing—review and editing, W.H. and X.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the technology innovation and demonstration of efficient management of rice fertilizer and water in Northeast China (NK2022180804) and National Key Research and Development Program (2022YFD1500703).
Data Availability Statement
16S rRNA sequencing data are stored in NCBI database (BioProject: PRJNA893081).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Chaudhary, S.; Sindhu, S.S.; Dhanker, R.; Kumari, A. Microbes-mediated sulphur cycling in soil: Impact on soil fertility, crop production and environmental sustainability. Microbiol. Res. 2023, 271, 127340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maruyama Nakashita, A. Metabolic changes sustain the plant life in low-sulfur environments. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2017, 39, 144–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutar, R.K.; Pujar, A.M.; Kumar, B.N.A.; Hebsur, N.S. Sulphur nutrition in maize a critical review. Int. J. Pure Appl. Biosci. 2018, 5, 1582–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulczycki, G. The effect of elemental sulfur fertilization on plant yields and soil properties. Adv. Agron. 2021, 167, 105–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carciochi, W.D.; Wyngaard, N.; Divito, G.A.; Calvo, N.I.R.; Cabrera, M.L.; Echeverría, H.E. Diagnosis of sulfur availability for corn based on soil analysis. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2016, 52, 917–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutradhar, A.K.; Kaiser, D.E.; Fernández, F.G. Does total nitrogen/sulfur ratio predict nitrogen or sulfur requirement for corn? Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2017, 81, 564–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, A.A.; Puissant, J.; Buckeridge, K.M.; Goodall, T.; Jehmlich, N.; Chowdhury, S.; Gweon, H.S.; Peyton, J.M.; Mason, K.E.; van Agtmaal, M.; et al. Land use driven change in soil pH affects microbial carbon cycling processes. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 3591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zenda, T.; Liu, S.; Dong, A.; Duan, H. Revisiting Sulphur—The Once Neglected Nutrient: It’s Roles in Plant Growth, Metabolism, Stress Tolerance and Crop Production. Agriculture 2021, 11, 626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fageria, N.K.; dos Santos, A.B.; Moraes, M.F. Influence of Urea and Ammonium Sulfate on Soil Acidity Indices in Lowland Rice Production. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2010, 41, 1565–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anwari, G.; Tianxu, Y.; Alio Moussa, A.; Wentao, Z.; Mandozai, A.; Gamal, M.; Feng, J. Influence of biochar and aluminum sulfate on rice growth and production in saline soil. J. Crop Improv. 2022, 37, 776–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eriksen, J. Gross sulphur mineralization-immobilization turnover in soil amended with plant residues. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2005, 37, 2216–2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolan, N.S.; Hedley, M.J. Role of carbon, nitrogen, and sulfur cycles in soil acidification. Acidification of soils. In Handbook of Soil Acidity, 1st ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2003; pp. 29–56. [Google Scholar]
- Scherer, H.W. Sulfur in soils. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2009, 172, 326–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Wang, L.; Shi, H.; Liu, Y.; Chen, S. Soil bacteria, genes, and metabolites stimulated during sulfur cycling and cadmium mobilization under sodium sulfate stress. Environ. Res. 2021, 201, 111599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedrós-Alió, C. The rare bacterial biosphere. Annu. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2012, 4, 449–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parvathi, A.; Catena, M.; Jasna, V.; Phadke, N.; Gogate, N. Influence of hydrological factors on bacterial community structure in a tropical monsoonal estuary in India. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 50579–50592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lauber, C.; Ramirez, K.; Aanderud, Z.; Jay, L.; Noah, F. Temporal variability in soil microbial communities across land-use types. ISME J. 2013, 7, 1641–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jousset, A.; Bienhold, C.; Chatzinotas, A.; Gallien, L.; Gobet, A.; Kurm, V.; Hol, W.H. Where less may be more: How the rare biosphere pulls ecosystems strings. ISME J. 2017, 11, 853–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lynch, M.; Neufeld, J. Ecology and exploration of the rare biosphere. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2015, 13, 217–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pester, M.; Bittner, N.; Deevong, P.; Wagner, M.; Loy, A. A ‘rare biosphere’ microorganism contributes to sulfate reduction in a peatland. ISME J. 2010, 4, 1591–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauret, C.; Séverin, T.; Vétion, G.; Guigue, C.; Goutx, M.; Pujo-Pay, M.; Conan, P.; Fagervold, S.K.; Ghiglione, J.F. Rare biosphere’ bacteria as key phenanthrene degraders in coastal seawaters. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 194, 246–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pennekamp, F.; Pontarp, M.; Tabi, A.; Altermatt, F.; Alther, R.; Choffat, Y.; Fronhofer, E.A.; Ganesanandamoorthy, P.; Garnier, A.; Griffiths, J.I.; et al. Biodiversity increases and decreases ecosystem stability. Nature 2018, 563, 109–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, P.; Li, G.X.; Sun, G.X.; Xu, Y.Y.; Meharg, A.A.; Zhu, Y.G. The role of sulfate-reducing prokaryotes in the coupling of element biogeochemical cycling. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 613, 398–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.; Ling, N.; Wang, T.; Zhu, C.; Wang, Y.; Wang, S.; Gao, Q. Responses of soil biological traits and bacterial communities to nitrogen fertilization mediate maize yields across three soil types. Soil Tillage Res. 2019, 185, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, S.R.; Pop, M.; DeBoy, R.T.; Eckburg, P.B.; Turnbaugh, P.J.; Samuel, B.S.; Gordon, J.I.; Relman, D.A.; Fraser-Liggett, C.M.; Nelson, K.E. Metagenomic analysis of the human distal gut microbiome. Science 2006, 312, 1355–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Jiang, W. Application of high-throughput sequencing in understanding human oral microbiome related with health and disease. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Kuczynski, J.; Stombaugh, J.; Bittinger, K.; Bushman, F.D.; Costellz, E.K.; Fierer, N.; Pena, A.G.; Goodrich, J.K.; Gordon, J.I.; et al. QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat. Methods 2010, 7, 335–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolyen, E.; Rideout, J.R.; Dillon, M.R.; Bokulich, N.A.; Abnet, C.C.; Al-Ghalith, G.A.; Alexander, H.; Alm, E.J.; Arumugam, M.; Asnicar, F.; et al. Reproducible, interactive, scalable and extensible microbiome data science using QIIME 2. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 852–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.; Zhang, B.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, X.; Gao, Q. Responses of soil bacterial communities and maize yields to sulfur application across four soil types. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 13, 1329938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Liu, D.; Shi, Y.; Wu, X.; Dai, Y.; Shang, Y.; Peng, J.; Cui, Z. Broader environmental adaptation of rare rather than abundant bacteria in reforestation succession soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 828, 154364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, C.; Feng, Q.; Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Liu, L.; Yu, X.; Ren, S. Rare soil bacteria are more responsive in desertification restoration than abundant bacteria. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 33323–33334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, F. Abundant and rare bacteria possess different diversity and function in crop monoculture and rotation systems across regional farmland. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2022, 171, 108742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skwierawska, M.; Zawartka, L.; Zawadski, B. The effect of different rates and forms of sulphur applied on changes of soil agrochemical properties. Plant Soil Environ. 2008, 54, 171–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Liu, G.; Pu, P.; Liu, J.; Li, W.; Xu, X. Effects of SO42−-S and S0-S on the Sultur Nutrition in Pakchoi. J. Nucl. Agric. Sci. 2020, 34, 0635–0641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.; Dong, C.; Bian, W.; Zhang, W.; Wang, Y. Effects ofdifferent fertilization practices on maize yield, soil nutrients, soil moisture, and water use efficiency in northern China based on a meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 6480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, K.S.; Joergensen, R.G. Microbial C, N, and P relationships in moisture–stressed soils of a semiarid subtropical forest after nitrogen and sulfur amendments. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2006, 38, 2902–2911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masuda, S.; Bao, Z.; Okubo, T.; Sasaki, K.; Ikeda, S.; Shinoda, R.; Anda, M.; Kondo, R.; Mori, Y.; Minamisawa, K. Sulfur Fertilization Changes the Community Structure of Rice Root-, and Soil- Associated Bacteria. Microbes Environ. 2016, 31, 70–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGrath, S.P.; Zhao, F.J.; Blake-Kalff, M.M.A. History and outlook for sulfur fertilizers in Europe. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2002, 33, 421–425. [Google Scholar]
- Eriksen, J.; Mortensen, J.V. Effects of timing of sulphur application on yield, S-uptake and quality of barley. Agron. J. 2002, 94, 493–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.J.; McGrath, S.P. Biofortification and phytoremediation. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2009, 12, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klose, S.; Bilen, S.; Ali Tabatabai, M.; Dick, W.A. Sulfur Cycle Enzymes. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2011, 9, 125–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunito, T.; Kurita, H.; Kumori, M.; Sakaguchi, K.; Nishizawa, S.; Fujita, K.; Moro, H.; Sawada, K.; Miyabara, Y.; Toda, H.; et al. Microbial synthesis of arylsulfatase depends on the soluble and adsorbed sulfate concentration in soils. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2022, 111, 103418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Yang, L.; Wen, L.; Luo, P.; Liu, L.; Yang, Y.; Wang, K.; Li, D. Effects of nitrogen deposition on soil sulfur cycling, Global Biogeochem. Cycles 2016, 30, 1568–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Liu, J.; Li, D.; Xiao, K.; Wang, K. Controls on soil arylsulfatase activity at a regional scale. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2019, 90, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Cheng, K.; Li, K.; Jin, Y.; He, X. Deciphering the diversity patterns and community assembly of rare and abundant bacterial communities in a wetland system. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 838, 156334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.L.; Meng, W.U.; Li, P.F.; Wei, S.P.; Jia, L.I.U.; Jiang, C.Y.; Ming, L.I.U.; Li, Z.P. Assembly and co-occurrence patterns of rare and abundant bacterial sub-communities in rice rhizosphere soil under short-term nitrogen deep placement. J. Integr. Agric. 2021, 20, 3299–3311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Oliveira, R.S.; Nai, F.; Rajkumar, M.; Luo, Y.; Rocha, I.; Freitas, H. The hyperaccumulator Sedum plumbizincicola harbors metal-resistant endophytic bacteria that improve its phytoextraction capacity in multi-metal contaminated soil. J. Environ. Manag. 2015, 156, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, E.D.B.; Stone, L.F.; Martin-Didonet, C.C.G. Populacao e atividade microbiana do solo em sistema agroecologico de producao. Rev. Cienc. Agron. 2017, 48, 3–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Schmalenberger, A.; Telford, A.; Kertesz, M. Sulfate treatment affects desulfonating bacterial community structures in Agrostis rhizospheres as revealed by functional geneanalysis based on asfA. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2010, 46, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Cong, P.; Kuang, S.; Tang, L.; Li, Y.; Dong, J.; Song, W. Long-term excessive application of K2SO4 fertilizer alters bacterial community and functional pathway of tobacco-planting soil. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 1005303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deltedesco, E.; Keiblinger, K.M.; Piepho, H.P.; Antonielli, L.; Pötsch, E.M.; Zechmeister-Boltenstern, S.; Gorfer, M. Soil microbial community structure and function mainly respond to indirect effects in a multifactorial climate manipulation experiment. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2020, 142, 107704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhalnina, K.; Dias, R.; de Quadros, P.D.; Davis-Richardson, A.; Camargo, F.A.; Clark, I.M.; McGrath, S.P.; Hirsch, P.R.; Triplett, E.W. Soil pH determines microbial diversity and composition in the Park Grass Experiment. Nat. Microbiol. 2015, 69, 395–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Lao, Y.-M.; Song, J.-T.; Jin, H.; Zhu, J.-M.; Cai, Z.-H. Temporal heterogeneity of microbial communities and metabolic activities during a natural algal bloom. Water Res. 2020, 183, 116020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, V.; Lawrence, J.; Germida, J. Impact of elemental sulfur fertilization on agricultural soils. i. effects on microbial biomass and enzyme activities. Can. J. Soil Sci. 1988, 68, 463–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, B.M.; Kim, M.; Lai-Hoe, A.; Shukor, N.A.; Rahim, R.A.; Go, R.; Adams, J.M. pH dominates variation in tropical soil archaeal diversity and community structure. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2013, 86, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tripathi, B.M.; Kim, M.; Tateno, R.; Kim, W.; Wang, J.J.; Lai-Hoe, A.; Ab Shukor, N.A.; Rahim, R.A.; Go, R.; Adams, J.M. Soil pH and biome are both key determinants of soil archaeal community structure. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2015, 88, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, L.; Yu, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, Z.; Pan, Y.; Larssen, T.; Tang, J.; Mulder, J. Acid deposition in Asia: Emissions, deposition, and ecosystem effects. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 146, 55–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Dai, Z.; Wang, Y.; Ma, X.; Shi, Z.; Wang, R.; Xu, Z.; Li, H.; Han, X.; Jiang, Y. Interacting effects of water and nitrogen addition on soil–plant sulfur dynamics in a semi-arid grassland. Geoderma 2024, 442, 116796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, S.; Wang, J.; Wei, G.; Chen, W.; Lu, Y. Dominant role ofabundant rather than rare bacterial taxa in maintaining agro-soil microbiomes under environmental disturbances. Chemosphere 2019, 235, 248–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagg, C.; Bender, S.F.; Widmer, F.; van der Heijden, M.G. Soil biodiversity and soil community composition determine ecosystem multifunctionality. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 5266–5270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; Liu, J.; Feng, J.; Li, X.; Li, B. Microbial community composition and metabolic functions in landfill leachate from different landfills of China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 767, 144861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Yang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Tang, J.; Zeng, L.; Cong, P.; Chen, L.; Wang, J. Unlocking soil revival: The role of sulfate-reducing bacteria in mitigating heavy metal contamination. Environ. Geochem. Health 2024, 46, 417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Gao, W.; Wang, C.; Gao, M. Distinct distribution patterns and functional potentials of rare and abundant microorganisms between plastisphere and soils. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 873, 162413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.W.; Bai, D.S.; Yang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Luo, X.G. Soil sulfur cycle bacteria and metabolites affected by soil depth and afforestation conditions in high-sulfur coal mining areas. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2023, 185, 104802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhou, Z.; Zijing, L.; Xia, L.; Song, S.; Meza, J.V.G.; Montes, M.L.; Li, J. Surge of native rare taxa in tailings soil induced by peat bacterial invasion. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 908, 168596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marzec-Grządziel, A.; Gałązka, A. Sequencing of the Whole Genome of a Bacterium of the Genus Achromobacter Reveals Its Potential for Xenobiotics Biodegradation. Agriculture 2023, 13, 1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Cui, S.; Ying, F.; Nasar, J.; Wang, Y.; Gao, Q. Simultaneous improvement of protein concentration and amino acid balance in maize grains by coordination application of nitrogen and sulfur. J. Cereal Sci. 2021, 99, 103189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, Y.; Ji, L.; Wang, Z.; Li, K.; Xu, X.; Guo, D. Functional Diversity and CO2 Emission Characteristics of Soil Bacteria during the Succession of Halophyte Vegetation in the Yellow River Delta. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 12919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).