The Application of Straw Return with Nitrogen Fertilizer Increases Rice Yield in Saline–Sodic Soils by Regulating Rice Organ Ion Concentrations and Soil Leaching Parameters
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
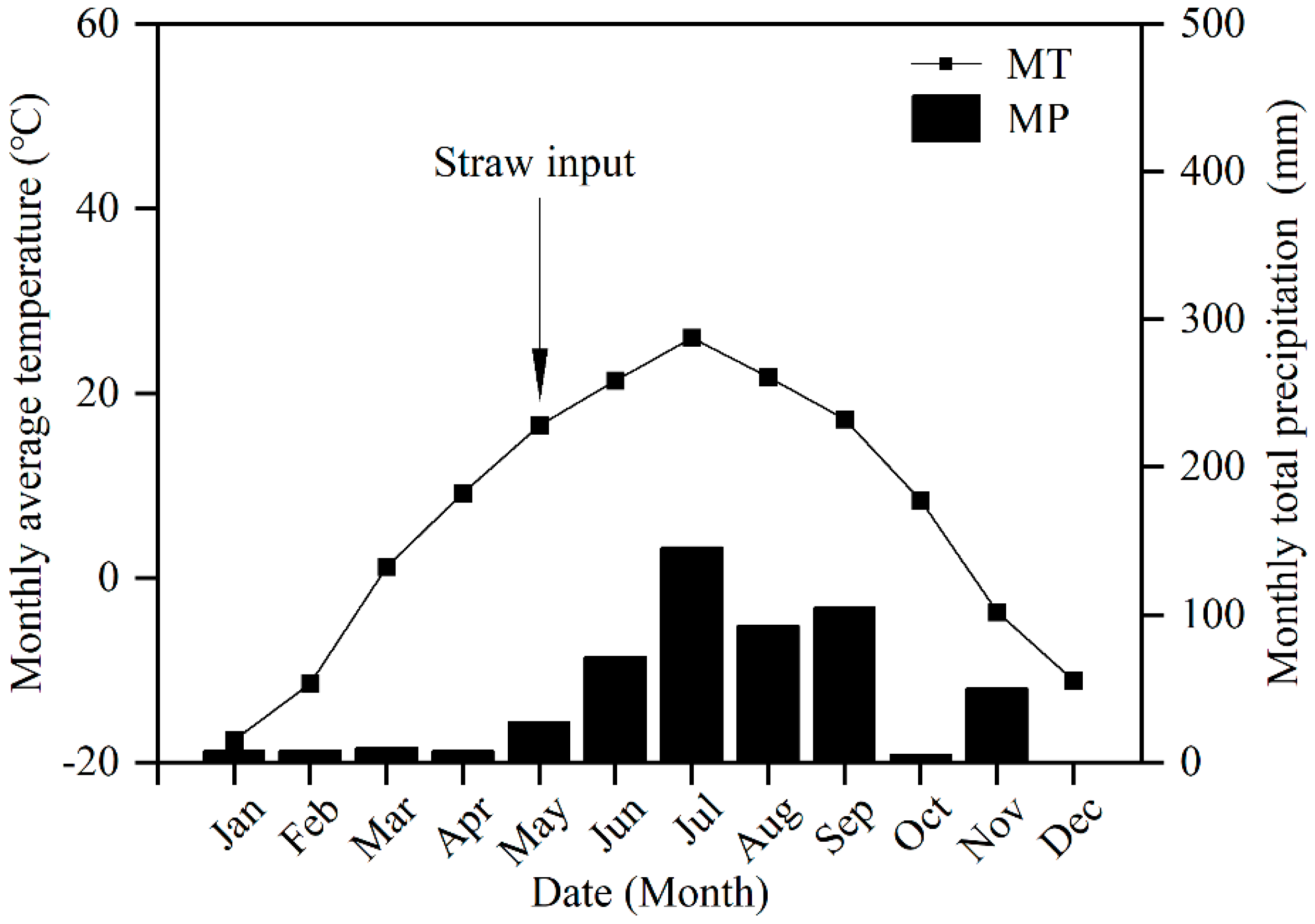
2.1. Experimental Site
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Preparation of Soil Columns
2.4. Planting Rice
2.5. Leaching Soil Columns
2.6. Leachate Analysis
2.7. Determination of Na+ and K+ in Different Rice Organs
2.8. Rice Yield Analysis
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Leachate Volume
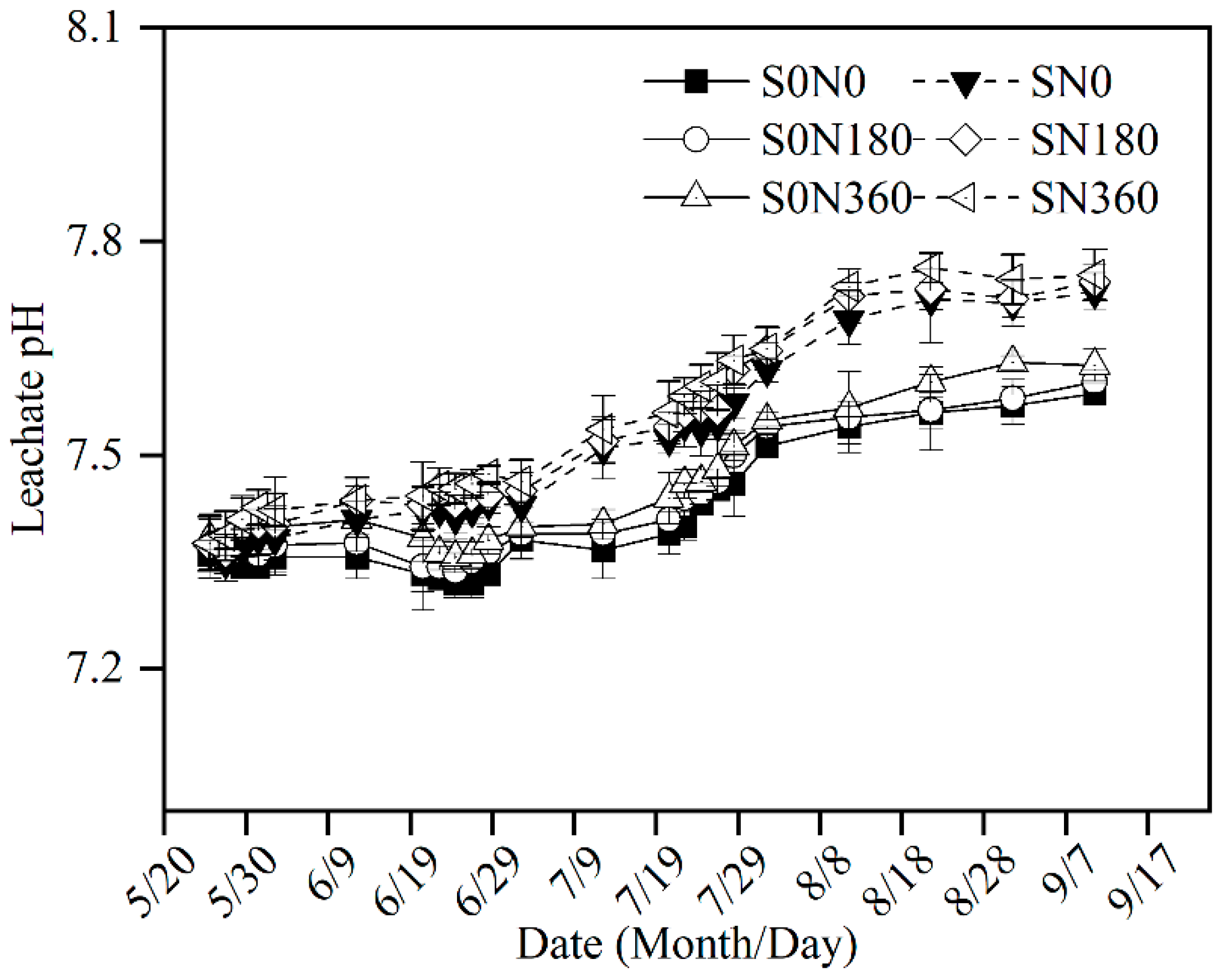
3.2. Leachate pH
3.3. Na+ and K+ Concentrations and Na+/K+ Ratio in the Leachate
3.4. NO3−-N and NH4+-N Concentrations in the Leachate
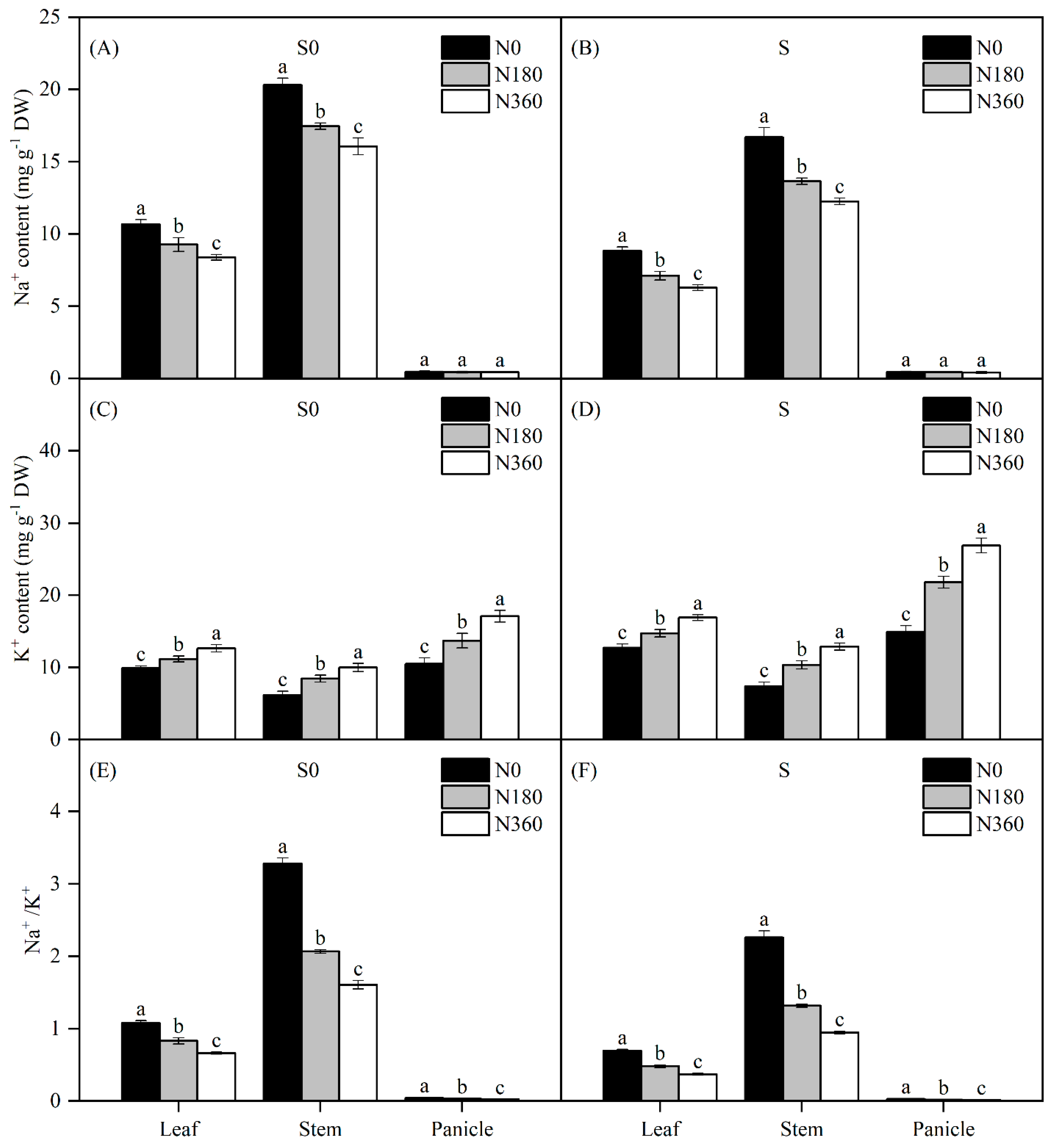
3.5. Na+ and K+ Contents and Na+/K+ Ratio in Different Organs
3.6. Rice Biomass Yield (BY), Grain Yield (GY), and Harvest Index (HI)
4. Discussion
4.1. Effect of Straw Return with Nitrogen Fertilizer on the Leachate Volume in Saline–Sodic Soils
4.2. Effect of Straw Return with Nitrogen Fertilizer on Chemical Properties of Soil Leachate in Saline–Sodic Soils
4.3. Effect of Straw Return with Nitrogen Fertilizer on Ion Content in Different Rice Organs at Maturity in Saline–Sodic Soil
4.4. Effect of Straw Return with Nitrogen Fertilizer on Rice Yield in Saline–Sodic Soil
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kong, T.; Zhang, D.S.; Xu, H.; Wang, L.H. Microbial Ecological Characteristics of Alkaline-saline Lands and Its Amelioration Process: A Review. Soils 2014, 46, 581–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Sun, L.; Ling, N.; Zhu, C.; Chi, F.Q.; Li, W.Q.; Hao, X.Y.; Zhang, W.; Bian, J.Y.; Chen, L.; et al. Exploring soil factors determining composition and structure of the bacterial communities in saline-alkali soils of songnen plain. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 2902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.P.; Yang, J.S.; Yao, R.J.; Zhang, X.; Chen, X.B.; Wang, X.P.; Xie, W.P. Effects of Biochar and Chemical Fertilizer Application on Soil Properties in Farmland Reclaimed from Salinity Tidal Flat. Chin. J. Soil Sci. 2017, 48, 454–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, C.H.; Yang, Y.; Yang, Y.Q.; Hou, Y.C. Effects of Two Amendments on Soil Properties and Quinoa Yield in Saline-alkaline Soil in South Shanxi. Acta Agric. Boreali-Occident. Sin. 2022, 31, 1185–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, H.Y.; Li, Y.F.; Li, S.J. Effects of the interaction between biochar and nutrients on soil organic carbon sequestration in soda saline-alkali grassland: A review. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2021, 26, e1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darwish, T.; Atallah, T.; Moujabber, M.E.; Khatib, N. Salinity evolution and crop response to secondary soil salinity in two agroclimatic zones in Lebanon. Agric. Water Manag. 2005, 78, 152–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Q.; Li, J.D.; Zheng, H.Y. A dynamic landscape simulation model for the alkaline grasslands on Songnen Plain in northeast China. Landsc. Ecol. 1996, 11, 339–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, C.M.; Zhao, C.W.; Sun, X.J.; Wang, Z.C. Reclamation of saline-sodic soil properties and improvement of rice (Oriza sativa L.) growth and yield using desulfurized gypsum in the west of Songnen Plain, northeast China. Geoderma 2012, 187, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.H.; Liu, Y.; Ferreira, J.F.S.; Wang, M.M.; Na, J.; Huang, J.X.; Liang, Z.W. Long-term combined effects of tillage and rice cultivation with phosphogypsum or farmyard manure on the concentration of salts, minerals, and heavy metals of saline-sodic paddy fields in Northeast China. Soil Tillage Res. 2022, 215, 105222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.D.; Wang, Z.C.; Yang, F.; Zhu, W.D.; An, F.H.; Ma, H.Y.; Tóth, T.; Liao, X.; Yang, H.T.; Zhang, L. Amendments to saline-sodic soils showed long-term effects on improving growth and yield of rice (Oryza sativa L.). PeerJ 2020, 8, e8726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.H.; Lan, Y.C.; Xu, L.Q.; Yin, D.W.; Li, H.Y.; Qian, Y.D.; Zheng, G.P.; Lv, Y.D. Effects of nitrogen application rate and hill density on rice yield and nitrogen utilization in sodic saline-alkaline paddy fields. J. Integr. Agric. 2021, 20, 540–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.Y.; Ran, C.; Liu, B.L.; Zhao, Z.X.; Bai, T.Q.; Zhao, M.M.; Cheng, Z.W.; Chen, G.; Geng, Y.Q. Effect of straw return with nitrogen fertilizer on photosynthetic characteristics and yield of rice in soda saline-alkali rice paddy fields. Cereal Res. Commun. 2023, 51, 509–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Feng, C.; Guo, W.; Shi, D.; Yang, C. Comparative effects of osmotic-, salt- and alkali stress on growth, photosynthesis, and osmotic adjustment of cotton plants. Photosynthetica 2011, 49, 417–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piao, J.L.; Che, W.K.; Li, X.; Li, X.B.; Zhang, C.B.; Wang, Q.S.; Jin, F.; Hua, S. Application of peanut shell biochar increases rice yield in saline-alkali paddy fields by regulating leaf ion concentrations and photosynthesis rate. Plant Soil 2023, 483, 589–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.J.; Negrao, S.; Tester, M. Salt resistant crop plants. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2014, 26, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.B.; Kang, Y.H.; Wan, S.Q.; Chen, X.L.; Chu, L.L.; Xu, J.C. First and second-year assessments of the rapid reconstruction and re-vegetation method for reclaiming two saline-sodic, coastal soils with drip-irrigation. Ecol. Eng. 2015, 84, 496–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prichard, T.L.; Hoffman, G.J.; Oster, J.D. Reclamation of saline organic soil. Irrig. Sci. 1985, 6, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerozi, B.D.S.; Fitzsimmons, K. The effect of pH on phosphorus availability and speciation in an aquaponics nutrient solution. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 219, 778–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Ahan, J.; Wu, Z.H.; Shi, D.C.; Liu, B.; Yang, C.W. Alteration of nitrogen metabolism in rice variety ‘Nipponbare’ induced by alkali stress. Plant Soil 2012, 355, 131–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jutras, P.V.; Goulet, M.; Lavoie, P.; D’Aoust, M.; Sainsbury, F.; Michaud, D. Recombinant protein susceptibility to proteolysis in the plant cell secretory pathway is pH-dependent. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2018, 16, 1928–1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamran, M.; Wang, D.; Xie, K.; Lu, Y.; Shi, C.; Sabagh, A.E.; Gu, W.; Xu, P. Pre-sowing seed treatment with kinetin and calcium mitigates salt induced inhibition of seed germination and seedling growth of choysum (Brassica rapa var. parachinensis). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 227, 112921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fridovich, I. Biological effects of the superoxide radical. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1986, 247, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaganti, V.N.; Crohn, D.M. Evaluating the relative contribution of physiochemical and biological factors in ameliorating a saline-sodic soil amended with composts and biochar and leached with reclaimed water. Geoderma 2015, 259–260, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.M.; Zhu, M.L.; Guo, X.X.; Wang, H.B.; Sui, B.; Zhao, L.P. Organic carbon content and humus composition after application aluminum sulfate and rice straw to soda saline-alkaline soil. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2019, 26, 13746–13754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.J.; He, H.S.; Zu, Y.G.; Guan, Y.; Liu, Z.G.; Zhang, Z.H.; Xu, H.N.; Yu, X.Y. Addition of HPMA affects seed germination, plant growth and properties of heavy saline-alkali soil in northeastern China: Comparison with other agents and determination of the mechanism. Plant Soil 2011, 339, 177–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; An, F.H.; Ma, H.Y.; Wang, Z.C.; Zhou, X.; Liu, Z.J. Variations on Soil Salinity and Sodicity and Its Driving Factors Analysis under Microtopography in Different Hydrological Conditions. Water 2016, 8, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.G.; Wang, S.J.; Li, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhuo, Y.Q.; Chen, H.X.; Wang, J.; Xu, L.Z.; Sun, Z.T. Extensive reclamation of saline-sodic soils with flue gas desulfurization gypsum on the Songnen Plain, Northeast China. Geoderma 2018, 321, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garbowski, T.; Bar-Michalczyk, D.; Charazińska, S.; Grabowska-Polanowska, B.; Kowalczyk, A.; Lochyński, P. An overview of natural soil amendments in agriculture. Soil Tillage Res. 2023, 225, 105462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.F.; Meng, J.; Wang, Q.X.; Zhang, W.M.; Cheng, X.Y.; Chen, W.F. Effects of straw and biochar addition on soil nitrogen, carbon, and super rice yield in cold waterlogged paddy soils of North China. J. Integr. Agric. 2017, 16, 1064–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.S.; Liu, C.M.; Zhang, W.J.; Guo, Y.L. Effect of integrating straw into agricultural soils on soil infiltration and evaporation. Water Sci. Technol. 2012, 65, 2213–2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.G.; Pang, H.C.; Wang, J.; Huo, L.; Li, Y.Y. Effects of straw mulch and buried straw on soil moisture and salinity in relation to sunflower growth and yield. Field Crops Res. 2014, 161, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Wang, Z.C.; Guo, X.P.; Liu, M.H.; Hamoud, Y.A.; Zheng, J.C.; Qiu, R.J. Effects of uneven vertical distribution of soil salinity under a buried straw layer on the growth, fruit yield, and fruit quality of tomato plants. Sci. Hortic. 2016, 203, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, W.Q.; Wang, Y.N.; Sun, Y.Y.; Liu, Z.F.; Wang, W.J.; Wu, D.; Zhang, Y.X.; Sun, W.; Wang, X.; Feng, Z.B.; et al. Assessing the formation and stability of paddy soil aggregate driven by organic carbon and Fe/Al oxides in rice straw cyclic utilization strategies: Insight from a six-year field trial. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 951, 175607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Guo, Q.; Li, X.; Li, X.; Yu, Z.X.; Li, X.Y.; Yang, T.T.; Su, Z.C.; Zhang, H.W.; Zhang, C.G. Effects of long-term no-tillage with different straw mulching frequencies on soil microbial community and the abundances of two soil-borne pathogens. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2020, 148, 103488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.C.; Samo, N.; Zhao, C.K.; Wang, H.N.; Yang, G.T.; Hu, Y.G.; Peng, Y.L.; Rasul, F. Negative and Positive Impacts of Rape Straw Returning on the Roots Growth of Hybrid Rice in the Sichuan Basin Area. Agronomy 2019, 9, 690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.S.; Xu, M.M.; Koide, R.T.; Liu, Q.; Dai, Y.J.; Liu, L.; Bian, X.M. Effects of ditch-buried straw return on water percolation, nitrogen leaching and crop yields in a rice-wheat rotation system. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2016, 96, 1141–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IUSS Working Group. World Reference Base for Soil Resources 2014 International Soil Classification System for Naming Soils and Creating Legends for Soil Maps; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.H.; Li, T.X.; Liu, H.; Zhang, Z.W.; Yang, A.Z.; Li, H.Y. Combined Effect of Freeze–Thaw Cycles and Biochar Addition on Soil Nitrogen Leaching Characteristics in Seasonally Frozen Farmland in Northeast China. Agronomy 2024, 14, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamada, K.; Nakamura, S.; Kuniyoshi, D. Pipe experiment elucidates biochar application depth affects nitrogen leaching under crop present condition. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 22823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramsay, J.A.; Brown, R.H.J.; Falloon, S.W.H.W. Simultaneous Determination of Sodium and Potassium in Small Volumes of Fluid by Flame Photometry. J. Exp. Biol. 1953, 30, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stavi, I.; Thevs, N.; Priori, S. Soil Salinity and Sodicity in Drylands: A Review of Causes, Effects, Monitoring, and Restoration Measures. Front. Environ. Sci. 2021, 9, 712831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmeknassi, M.; Elghali, A.; Carvalho, H.W.P.; Laamrani, A.; Benzaazoua, M. A review of organic and inorganic amendments to treat saline-sodic soils: Emphasis on waste valorization for a circular economy approach. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 921, 171087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Lu, M.; Cui, J.; Li, B.; Fang, C.M. Effects of straw carbon input on carbon dynamics in agricultural soils: A meta-analysis. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2014, 20, 1366–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amini, S.; Ghadiri, H.; Chen, C.R.; Marschner, P. Salt-affected soils, reclamation, carbon dynamics, and biochar: A review. J. Soils Sediments 2016, 16, 939–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghimire, R.; Lamichhane, S.; Acharya, B.S.; Bista, P.; Sainju, U.M. Tillage, crop residue, and nutrient management effects on soil organic carbon in rice-based cropping systems: A review. J. Integr. Agric. 2017, 16, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambus, J.V.; Awe, G.O.; Carvalho, P.C.D.; Reichert, J.M. Integrated crop-livestock systems in lowlands with rice cultivation improve root environment and maintain soil structure and functioning. Soil Tillage Res. 2023, 227, 105592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aller, D.; Rathke, S.; Laird, D.; Cruse, R.; Hatfield, J. Impacts of fresh and aged biochars on plant available water and water use efficiency. Geoderma 2017, 307, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouattara, K.; Ouattara, B.; Assa, A.; Sédogo, P.M. Long-term effect of ploughing, and organic matter input on soil moisture characteristics of a Ferric Lixisol in Burkina Faso. Soil Tillage Res. 2005, 88, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.F.; Zhong, F.F. Nitrogen release and re-adsorption dynamics on crop straw residue during straw decomposition in an Alfisol. J. Integr. Agric. 2021, 20, 248–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelrhman, A.A.; Gao, L.L.; Li, S.P.; Lu, J.J.; Song, X.J.; Zhang, M.N.; Zheng, F.J.; Wu, H.J.; Wu, X.P. Long-Term Application of Organic Wastes Improves Soil Carbon and Structural Properties in Dryland Affected by Coal Mining Activity. Sustainability 2021, 13, 5686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.D.; Ran, C.; Gao, D.P.; Zhao, Z.X.; Meng, X.Y.; Geng, Y.Q.; Shao, X.W.; Chen, G. Changes in soil characteristics and rice yield under straw returning in saline sodic soils. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2022, 68, 563–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drake, J.A.; Cavagnaro, T.R.; Cunningham, S.C.; Jackson, W.R.; Patti, A.F. Does Biochar Improve Establishment of Tree Seedlings in Saline Sodic Soils? Land Degrad. Dev. 2016, 27, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saifullah; Dahlawi, S.; Naeem, A.; Rengel, Z.; Naidu, R. Biochar application for the remediation of salt-affected soils: Challenges and opportunities. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 625, 320–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.Y.; Ran, C.; Hou, H.M.; Guo, L.Y.; Zhang, Q.; Geng, Y.Q.; Shao, X.W. Synergistic improvement of straw decomposition and rice yield in saline sodic paddy soils by rational nitrogen application. Plant Soil 2024, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Yang, S.H.; Jiang, Z.W.; Ding, J.; Sun, X. Biochar as a tool to reduce environmental impacts of nitrogen loss in water-saving irrigation paddy field. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 290, 125811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.G.; Han, Y.; Liu, G.; Zhang, Y.L.; Shao, X.H. Nitrogen in percolation water in paddy fields with a rice/wheat rotation. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2000, 57, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, X.T.; Xing, G.X.; Chen, X.P.; Zhang, S.L.; Zhang, L.J.; Liu, X.J.; Cui, Z.L.; Yin, B.; Christie, P.; Zhu, Z.L.; et al. Reducing environmental risk by improving N management in intensive Chinese agricultural systems. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 3041–3046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, L.; Juan, Y.H.; Wang, J.H.; Liu, Y.; Sun, W.T. Study on the Variations of Nitrogen and Phosphorus in Surface Water Body of Paddy Field. Chin. Agric. Sci. Bull. 2014, 30, 168–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galloway, J.N.; Townsend, A.R.; Erisman, J.W.; Bekunda, M.; Cai, Z.C.; Freney, J.R.; Martinelli, L.A.; Seitzinger, S.P.; Sutton, M.A. Transformation of the Nitrogen Cycle: Recent Trends, Questions, and Potential Solutions. Science 2008, 320, 889–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.X.; Wang, D.; Shen, X.B.; Li, C.C.; Liu, J.; Lan, T.; Wang, W.Y.; Xie, H.T.; Zhang, Y.L. Effects of biochar, compost and straw input on root exudation of maize (Zea mays L.): From function to morphology. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2020, 297, 106952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.Q.; Guo, Y. Elucidating the molecular mechanisms mediating plant salt-stress responses. New Phytol. 2018, 217, 523–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamran, M.; Xie, K.Z.; Sun, J.; Wang, D.; Shi, C.H.; Lu, Y.S.; Gu, W.J.; Xu, P.Z. Modulation of growth performance and coordinated induction of ascorbate-glutathione and methylglyoxal detoxification systems by salicylic acid mitigates salt toxicity in choysum (Brassica parachinensis L.). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 188, 109877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakraborty, K.; Bhaduri, D.; Meena, H.N.; Kalariya, K. External potassium (K+) application improves salinity tolerance by promoting Na+-exclusion, K+-accumulation and osmotic adjustment in contrasting peanut cultivars. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2016, 103, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, R.; Nishio, T.; Ichizen, N.; Takano, T. Cloning and functional analysis of the K+ transporter, PhaHAK2, from salt-sensitive and salt-tolerant reed plants. Biotechnol. Lett. 2007, 29, 501–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.J.; Jia, Z.K.; Liang, L.Y.; Zhao, Y.F.; Yang, B.P.; Ding, R.X.; Wang, J.P.; Nie, J.F. Changes in soil characteristics and maize yield under straw returning system in dryland farming. Field Crops Res. 2018, 218, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sofy, M.R.; Elhawat, N.; Alshaal, T. Glycine betaine counters salinity stress by maintaining high K+/Na+ ratio and antioxidant defense via limiting Na+ uptake in common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 200, 110732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Yao, T.X.; Huang, X.X.; Li, X.B.; Li, P.Y.; Du, S.; Wang, W.; Miao, S.H.; Wang, D.; Jin, F.; et al. Biochar increases rice yield by improving root morphological and root physiological functions in heavily saline-sodic paddy soil of northeast China. BioResources 2022, 1, 1421–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, C.; Gao, D.P.; Bai, T.Q.; Geng, Y.Q.; Shao, X.W.; Guo, L.Y. Straw return alleviates the negative effects of saline sodic stress on rice by improving soil chemistry and reducing the accumulation of sodium ions in rice leaves. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2023, 342, 108253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, I.N.B.L.; Kim, B.K.; Yoon, I.S.; Kim, K.H.; Kwon, T.R. Salt Tolerance in Rice: Focus on Mechanisms and Approaches. Rice Sci. 2017, 24, 123–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganie, S.A.; Molla, K.A.; Henry, R.J.; Bhat, K.V.; Mondal, T.K. Advances in understanding salt tolerance in rice. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2019, 132, 851–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qadir, M.; Schubert, S. Degradation processes and nutrient constraints in sodic soils. Land Degrad. Dev. 2002, 13, 275–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palansooriya, K.N.; Wong, J.T.F.; Hashimoto, Y.; Huang, L.B.; Rinklebe, J.; Chang, S.X.; Bolan, N.; Wang, H.L.; Ok, Y.S. Response of microbial communities to biochar-amended soils: A critical review. Biochar 2019, 1, 3–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Jin, Z.Y.; Wang, S.H.; Gong, B.; Wen, D.; Wang, X.F.; Wei, M.; Shi, Q.H. Sodic alkaline stress mitigation with exogenous melatonin involves reactive oxygen metabolism and ion homeostasis in tomato. Sci. Hortic. 2015, 181, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabokrow Foomani, K.; Valad Abadi, S.A.; Kavoosi, M.; Zakerin, H.; Yazdani, M. The Effect of Periodic Irrigation and Different Amounts of Nitrogen Fertilizer on Yield and Yield Components of Rice. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2020, 52, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.K.; Teng, Z.N.; Yuan, Y.Q.; Yi, Z.X.; Zheng, Q.; Yu, H.H.; Lv, J.H.; Wang, Y.X.; Duan, M.J.; Zhang, J.H.; et al. Excessive nitrogen in field-grown rice suppresses grain filling of inferior spikelets by reducing the accumulation of cytokinin and auxin. Field Crops Res. 2022, 283, 108542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| pH | EC | Cation | Anion | ESP | Bulk Density | Texture (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (dS·m−1) | (mmole·L−1) | (mmole·L−1) | (%) | (g·cm−3) | |||||
| 9.44 | 0.978 | K+ | 0.35 | CO32− | 2.41 | 48.80 | 1.48 | Sand | 23.18 |
| Na+ | 17.64 | HCO3− | 15.51 | Silt | 44.51 | ||||
| Ca2+ | 1.40 | Cl− | 1.28 | Clay | 32.31 | ||||
| Mg2+ | 1.30 | SO42− | 1.49 | ||||||
| Composition Properties | Value |
|---|---|
| Total C (mg g−1) | 357.2 |
| Total N (mg g−1) | 4.85 |
| Total P (mg g−1) | 1.47 |
| Total K (mg g−1) | 8.51 |
| C/N ratio | 73.65 |
| Cellulose (mg g−1) | 356.4 |
| Hemicellulose (mg g−1) | 167.4 |
| Lignin (mg g−1) | 56.84 |
| pH | ECe | Cation | Anion | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (dS·m−1) | (mmole·L−1) | (mmole·L−1) | |||
| 7.40 | 0.21 | K+ | 0.15 | CO32− | 0.30 |
| Na+ | 0.29 | HCO3− | 0.39 | ||
| Ca2+ | 0.40 | Cl− | 0.25 | ||
| Mg2+ | 0.30 | SO42− | 0.20 | ||
| Treatment | NH4+-N Concentration (mg L−1) | NO3−-N Concentration (mg L−1) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BF-MF | MF-PF | After PF | BF-MF | MF-PF | After PF | |
| S0N0 | 0.37 ± 0.08 b | 0.32 ± 0.03 b | 0.19 ± 0.05 a | 1.47 ± 0.15 b | 1.03 ± 0.05 b | 0.90 ± 0.05 b |
| S0N180 | 1.22 ± 0.68 a | 0.55 ± 0.19 a | 0.29 ± 0.16 a | 3.66 ± 1.77 ab | 2.75 ± 1.03 a | 1.51 ± 0.57 ab |
| S0N360 | 2.02 ± 1.28 a | 0.74 ± 0.26 a | 0.39 ± 0.24 a | 5.10 ± 2.58 a | 3.72 ± 1.33 a | 1.93 ± 0.97 a |
| SN0 | 0.34 ± 0.07 b | 0.28 ± 0.04 b | 0.17 ± 0.04 a | 1.30 ± 0.15 b | 0.88 ± 0.05 b | 0.77 ± 0.04 b |
| SN180 | 0.93 ± 0.46 a | 0.45 ± 0.12 a | 0.24 ± 0.12 a | 2.55 ± 1.35 ab | 2.00 ± 0.71 a | 1.00 ± 0.26 ab |
| SN360 | 1.29 ± 0.57 a | 0.60 ± 0.16 a | 0.33 ± 0.16 a | 3.20 ± 1.55 a | 2.63 ± 0.69 a | 1.27 ± 0.39 a |
| Index | ANOVA | Leaf | Stem | Panicle |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Na+ | S | ** | ** | ns |
| N | * | * | ns | |
| S × N | * | ns | ns | |
| K+ | S | ** | ** | ** |
| N | * | * | * | |
| S × N | ** | ** | ** | |
| Na+/K+ | S | ** | ** | ** |
| N | ** | ** | ** | |
| S × N | ** | ** | ns |
| Treatment | Grain Yield (g pot−1) | Biomass Yield (g pot−1) | Harvest Index |
|---|---|---|---|
| S0N0 | 17.27 ± 0.29 c | 50.24 ± 1.50 c | 0.34 ± 0.01 b |
| S0N180 | 30.15 ± 0.68 b | 63.63 ± 1.78 b | 0.47 ± 0.01 a |
| S0N360 | 33.00 ± 1.32 a | 73.32 ± 1.62 a | 0.45 ± 0.02 a |
| SN0 | 16.09 ± 0.25 c | 50.41 ± 1.21 c | 0.32 ± 0.00 b |
| SN180 | 32.19 ± 0.81 b | 69.22 ± 1.66 b | 0.47 ± 0.01 a |
| SN360 | 35.28 ± 1.02 a | 76.54 ± 1.41 a | 0.46 ± 0.01 a |
| S | * | ** | ns |
| N | ** | ** | ** |
| S × N | ** | * | ns |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bai, T.; Ran, C.; Ma, Q.; Miao, Y.; Li, S.; Lan, H.; Li, X.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Shao, X. The Application of Straw Return with Nitrogen Fertilizer Increases Rice Yield in Saline–Sodic Soils by Regulating Rice Organ Ion Concentrations and Soil Leaching Parameters. Agronomy 2024, 14, 2807. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14122807
Bai T, Ran C, Ma Q, Miao Y, Li S, Lan H, Li X, Chen Q, Zhang Q, Shao X. The Application of Straw Return with Nitrogen Fertilizer Increases Rice Yield in Saline–Sodic Soils by Regulating Rice Organ Ion Concentrations and Soil Leaching Parameters. Agronomy. 2024; 14(12):2807. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14122807
Chicago/Turabian StyleBai, Tianqi, Cheng Ran, Qiyue Ma, Yue Miao, Shangze Li, Heng Lan, Xinru Li, Qinlian Chen, Qiang Zhang, and Xiwen Shao. 2024. "The Application of Straw Return with Nitrogen Fertilizer Increases Rice Yield in Saline–Sodic Soils by Regulating Rice Organ Ion Concentrations and Soil Leaching Parameters" Agronomy 14, no. 12: 2807. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14122807
APA StyleBai, T., Ran, C., Ma, Q., Miao, Y., Li, S., Lan, H., Li, X., Chen, Q., Zhang, Q., & Shao, X. (2024). The Application of Straw Return with Nitrogen Fertilizer Increases Rice Yield in Saline–Sodic Soils by Regulating Rice Organ Ion Concentrations and Soil Leaching Parameters. Agronomy, 14(12), 2807. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14122807






