Invasive Characteristics and Impacts of Ambrosia trifida
Abstract
1. Introduction
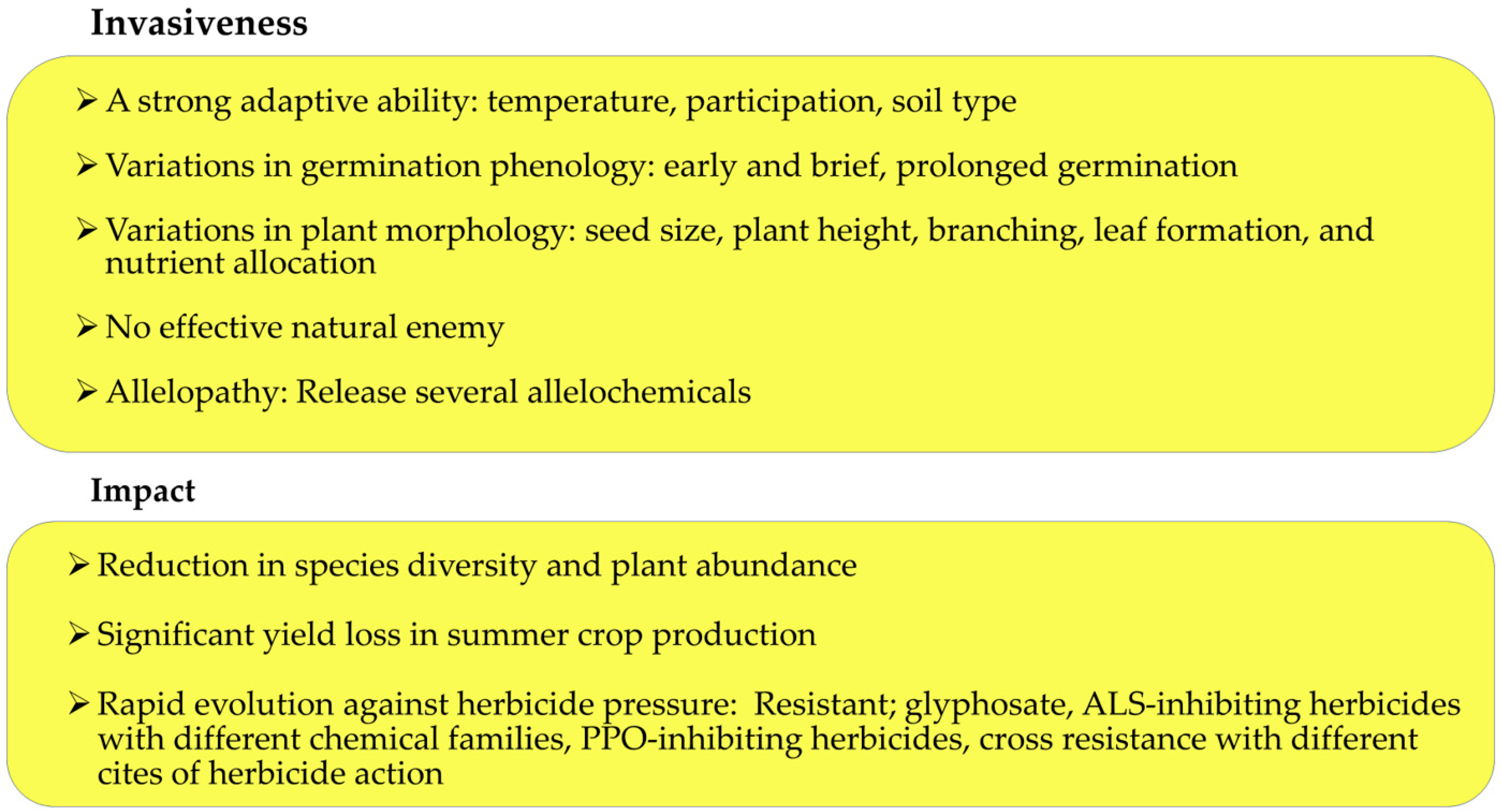
2. Invasive Characteristics
2.1. Habitat and Climate
2.2. Seed and Germination
2.3. Growth
2.4. Natural Enemy
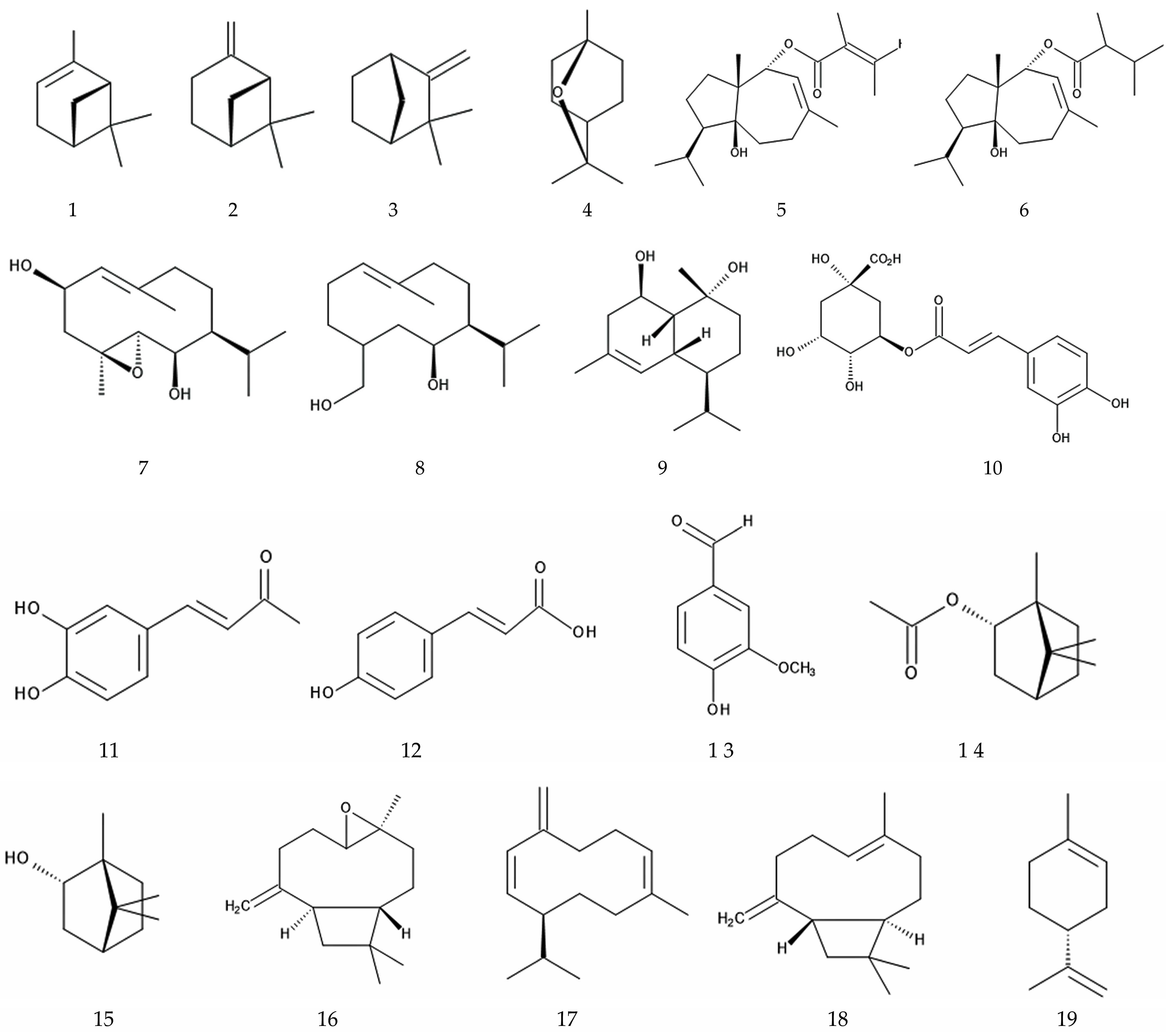
2.5. Allelopathy
3. Impacts of Ambrosia trifida Infestation
3.1. Impact on Agricultural Production and Control
3.2. Impact on Natural Environments
4. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Royal Botanical Gardens, Kew, Ambrosia trifida. Available online: https://powo.science.kew.org/taxon/urn:lsid:ipni.org:names:315739-2 (accessed on 12 September 2024).
- Bassett, I.J.; Crompton, C.W. The biology of Canada weeds. 55. Ambrosia trifida L. Can. J. Plant Sci. 1982, 62, 1003–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauvel, B.; Fried, G.; Follak, S.; Chapman, D.; Kulakova, Y.; Le Bourgeois, T.; Marisavljevic, D.; Monty, A.; Rossi, J.P.; Starfinger, U.; et al. Monographs on invasive plants in Europe N° 5: Ambrosia trifida L. Bot. Lett. 2021, 168, 167–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savić, A. Ambrosia trifida L. (giant ragweed). Matica Srp. J. Nat. Sci. 2021, 141, 35–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, L.; Zhang, G.; Zhou, C.; Ou, Z.; Qu, B.; Zhao, H.; Zuo, E.; Liu, B.; Wan, F.; Qian, W. Chromosome-level genome of Ambrosia trifida provides insights into adaptation and the evolution of pollen allergens. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 259, 129232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- CABI Copmpendium. Ambrosia trifida. Available online: https://www.cabidigitallibrary.org/doi/full/10.1079/cabicompendium.4693 (accessed on 12 September 2024).
- EPPO Global Database. Ambrosia trifida. Available online: https://gd.eppo.int/taxon/AMBTR/documents (accessed on 12 September 2024).
- Chauvel, B.; Rodriguez, A.; Moreau, C.; Martinez, Q.; Bilon, R.; Fried, G. Spread of Ambrosia trifida L. in France: Historical and ecological knowledge for the eradication of the species. J. Bot. 2015, 71, 2538. [Google Scholar]
- Stoyanov, S.; Vladimirov, V.; Milanova, S. Ambrosia trifida (Asteraceae), a new non-native species for the Bulgarian flora. C. R. Acad. Bulg. Sci. 2014, 67, 1653–1656. [Google Scholar]
- Elton, C.S. The Ecology of Invasions by Animals and Plants; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1958; pp. 1–261. [Google Scholar]
- Byun, C.; Lee, E.J. Giant ragweed invasion is not well controlled by biotic resistance. J. Plant Biol. 2018, 61, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Song, Z.; Liu, T.; Liu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Chen, B.; Ma, Q.; Li, Z. Causes of differences in the distribution of the invasive plants Ambrosia artemisiifolia and Ambrosia trifida in the Yili Valley, China. Ecol. Evol. 2020, 10, 13122–13133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, M.; Fu, D.; Wang, X.; Liu, Z.; Qu, B. Genetic diversity of Ambrosia trifida L. as revealed by AFLP markers. Biotechnol. J. Int. 2018, 21, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, H.; Hyvonen, J.; Poczai, P. Development of chloroplast microsatellite markers for giant ragweed (Ambrosia trifida). Appl. Plant Sci. 2020, 8, e11313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Gschwend, A.R.; Hovick, S.M.; Gutek, A.; McHale, L.; Harrison, S.K.; Regnier, E.E. Evolution of weedy giant ragweed (Ambrosia trifida): Multiple origins and gene expression variability facilitates weediness. Ecol. Evol. 2022, 12, e9590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leck, M.; Simpson, R.L. Tidal freshwater wetland zonation: Seed and seedling dynamics. Aquat. Bot. 1994, 47, 61–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sosnoskie, L.M.; Luschei, E.C.; Fanning, M.A. Field margin and weed-species diversity in relation to landscape attributes adjacent land use. Weed Sci. 2007, 55, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.S.; Cho, Y.C.; Shin, H.C.; Kim, G.S.; Pi, J.H. Control of an invasive alien species, Ambrosia trifida with restoration by introducing willows as a typical riparian vegetation. J. Ecol. Field Biol. 2010, 33, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korres, N.E.; Norsworthy, J.K.; Bagavathiannan, M.V.; Mauromoustakos, A. Distribution of arable weed populations along eastern Arkansas Mississippi delta roadsides: Occurrence, distribution, favored growth habitats. Weed Technol. 2015, 29, 587–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, T.M.; Loux, M.M.; Regnier, E.E.; Harrison, S.K. Giant ragweed (Ambrosia trifida) canopy architecture and interference studies in soybean (Glycine max). Weed Technol. 1994, 8, 559–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, S.K.; Regnier, E.E.; Schmoll, J.T.; Webb, J.E. Competition fecundity of giant ragweed in corn. Weed Sci. 2001, 49, 224–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnett, K.A.; Steckel, L.E. Giant ragweed (Ambrosia trifida) competition in cotton. Weed Sci. 2013, 61, 543–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, K.D.; Johnson, W.G.; Hillger, D.E. Farmer perceptions of weed problems in corn and soybean rotation systems. Weed Technol. 2006, 20, 751–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soltani, N.; Geddes, C.; Laforest, M.; Dille, J.A.; Sikkema, P.H. Economic impact of glyphosate-resistant weeds on major field crops grown in Ontario. Weed Technol. 2022, 36, 629–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wortman, S.E.; Davis, A.S.; Schutte, B.J.; Lindqusit, J.L.; Cardina, J.; Felix, J.; Sprague, C.L.; Dille, J.A.; Ramirez, A.H.M.; Reicks, G.; et al. Local conditions, not regional gradients, drive demographic variation of giant ragweed Ambrosia trifida common sunflower Helianthus annuus across Northern U. S. maize belt. Weed Sci. 2012, 60, 440–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Follak, S.; Dullinger, S.; Kleinbauer, I.; Moser, D.; Essl, F. Invasion dynamics of three allergenic invasive Asteraceae Ambrosia trifida, Artemisia annua, Iva xanthiifolia in central Eastern Europe. Preslia 2013, 85, 41–61. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, K. Response of Giant Ragweed (Ambrosia trifida) Source Populations to Varying Soil Moisture Conditions. Undergraduate Research Thesis, Ohio State University, Columbus, OH, USA, 2024; pp. 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- Regnier, E.E.; Harrison, S.K.; Loux, M.M.; Holloman, C.; Venkatesh, R.; Diekmann, F.; Taylor, R.; Ford, R.A.; Stoltenberg, D.E.; Hartzler, R.G.; et al. Certified crop advisors’ perceptions of giant ragweed (Ambrosia trifida) distribution, herbicide resistance, and management in the Corn Belt. Weed Sci. 2016, 64, 361–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.J.; Hong, M.G.; Kim, J.G. Effects of soil fertility and flooding regime on the growth of Ambrosia trifida. Landsc. Ecol. Eng. 2020, 16, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mun, S.; Lee, E.J. Litter decomposition rate and nutrient dynamics of giant ragweed (Ambrosia trifida L.) in the non-native habitat of South Korea. Plant Soil 2020, 449, 373–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savić, A.; Matzrafi, M.; Durović, S.; Gentili, R.; Citterio, S. Is Ambrosia trifida L. preparing for a wider invasion? Changes in the plant morpho-functional traits over a decade. Agronomy 2024, 14, 1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, S.; Yamamura, Y.; Yasuda, T.; Nakano, T.; Ikeguchi, H. The effects of human-induced disturbance and environmental conditions on the growth and developments of an exotic annual, Ambrosia trifida L. in riverside vegetation. Jpn. J. Conserv. Ecol. 2007, 12, 36–44. [Google Scholar]
- Xian, X.; Zhao, H.; Wang, R.; Huang, H.; Chen, B.; Zhang, G.; Liu, W.; Wan, F. Climate change has increased the global threats posed by three ragweeds (Ambrosia L.) in the Anthropocene. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 859, 160252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Bai, X.; Ye, J.; Chen, W.; Xu, G. Prediction of suitable habitat of alien invasive plant Ambrosia trifida in Northeast China under various climatic scenarios. Diversity 2024, 16, 322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazzaz, F.A.; Carlson, R.W. Photosynthetic contribution of flowers and seeds to reproductive effort of an annual colonizer. New Phytol. 1979, 82, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goplen, J.J.; Sheaffer, C.C.; Becker, R.L.; Coulter, J.A.; Breitenbach, F.R.; Behnken, L.M.; Johnson, J.A.; Gunsolus, J.L. Giant ragweed (Ambrosia trifida) seed production and retention in soybean and field margins. Weed Technol. 2016, 30, 246–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abul-Fatih, H.A.; Bazzaz, F.A. The biology of Ambrosia trifida L. II. Germination, emergence, growth survival. New Phytol. 1979, 83, 817–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, A.S.; Clay, S.; Cardina, J.; Dille, A.; Forcella, F.; Lindquist, J.; Sprague, C. Seed burial physical environment explains departures from regional hydrothermal model of giant ragweed (Ambrosia trifida) seedling emergence in U.S. Midwest. Weed Sci. 2013, 61, 415–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Washitani, I.; Nishiyama, S. Effects of seed size seedling emergence time on the fitness components of Ambrosia trifida and A. artemisiaefolia var. elatior in competition with grass perennials. Plant Species Biol. 1992, 7, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Royer, F.; Dickinson, R. Weeds of Canada and the Northern United States: A Guide for Identification; University of Alberta: Edmonton, AB, Canada, 1999; pp. 1–470. [Google Scholar]
- Sako, Y.; Regnier, E.E.; Daoust, T.; Fujimura, K.; Harrison, S.K.; McDonald, M.B. Computer image analysis and classification of giant ragweed seeds. Weed Sci. 2001, 49, 738–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regnier, E.; Harrison, S.K.; Liu, J.; Schmoll, J.T.; Edwards, C.A.; Arancon, N.; Holloman, C. Impact of an exotic earthworm on seed dispersal of an indigenous US weed. J. Appl. Ecol. 2008, 45, 1621–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, S.K.; Regnier, E.E.; Schmoll, J.T. Postdispersal predation of giant ragweed (Ambrosia trifida) seed in no-tillage corn. Weed Sci. 2003, 51, 955–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willson, M.F.; Harmeson, J.C. Seed preferences and digestive efficiency of cardinals and song sparrows. Condor 1973, 75, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, A.S.; Raghu, S. Weighing abiotic and biotic influences on weed seed predation. Weed Res. 2010, 50, 402–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, S.K.; Regnier, E.E.; Schmoll, J.T.; Harrison, J.M. Seed size and burial effects on giant ragweed (Ambrosia trifida) emergence and seed demise. Weed Sci. 2007, 55, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schutte, B.J.; Liu, J.; Davis, A.S.; Harrison, S.K.; Regnier, E.E. Environmental factors that influence the association of an earthworm (Lumbricus terrestris L.) and an annual weed (Ambrosia trifida L.) in no-till agricultural fields across the eastern US Corn Belt. Agric. Ecosys. Environ. 2010, 138, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Liu, T.; Liu, Z.; Song, Z. Fate of the soil seed bank of giant ragweed and its significance in preventing and controlling its invasion in grasslands. Ecol. Evol. 2020, 10, 4854–4866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballard, T.O.; Foley, M.E.; Bauman, T.T. Germination, viability, and protein changes during cold stratification of giant ragweed (Ambrosia trifida L.) seed. J. Plant Physiol. 1996, 149, 229–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, W.E. Primary dormancy, after-ripening, the development of secondary dormancy in embryos of Ambrosia trifida. Am. J. Bot. 1930, 171, 58–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schutte, B.J.; Regnier, E.E.; Harrison, S.K. The association between seed size seed longevity among maternal families in Ambrosia trifida L. populations. Seed Sci. Res. 2008, 18, 201–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schutte, B.J.; Regnier, E.E.; Harrison, S.K. Seed dormancy adaptive seedling emergence timing in giant ragweed Ambrosia trifida. Weed Sci. 2012, 60, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruziev, F.; Park, I.K.; Umurzokov, M.; Khaitov, B.; Bo, A.B.; Jia, W.Q.; Hien, L.T.; Choi, J.S.; Park, K.W. Seed germination ecology of giant ragweed (Ambrosia trifida) in Korea. Weed Turf. Sci. 2020, 9, 21–28. [Google Scholar]
- Page, E.R.; Nurse, R.E. Cropping systems and the prevalence of giant ragweed (Ambrosia trifida): From the 1950’s to present. Field Crops Res. 2015, 184, 104–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abul-Fatih, H.A.; Bazzaz, F.A.; Hunt, R. The biology of Ambrosia trifida L. III. Growth biomass allocation. New Phytol. 1979, 83, 829–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Liu, T.; Liu, Y.; Wang, H.; Wang, R.; Ma, Q.; Dong, J.; Bi, X. The significance of biomass allocation to population growth of the invasive species Ambrosia artemisiifolia and Ambrosia trifida with different densities. BMC Ecol. Evol. 2021, 21, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurik, T.W. Population distributions of plant size and light environment of giant ragweed (Ambrosia trifida L.) at three densities. Oecologia 1991, 87, 539–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abul-Fatih, H.A.; Bazzaz, F.A. The biology of Ambrosia trifida L. IV. Demography of plant leaves. New Phytol. 1980, 84, 107–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Sun, B.; Li, J.D.; Wang, G.J.; Sun, J.N.; Wang, X.R.; Zhong, R.T. Effects of light intensity on the phenotypic plasticity of invasive species Ambrosia trifida. Ying Yong Sheng Tai Xue Bao = J. Appl. Ecol. 2012, 23, 1797–1802. [Google Scholar]
- Chu, C.J.; Maestre, F.T.; Xiao, S.; Weiner, J.; Wang, Y.S.; Duan, Z.H.; Wang, G. Balance between facilitation and resource competition determines biomass-density relationships in plant populations. Ecol. Lett. 2008, 11, 1189–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bo, Q.; Xue, C.Y.; Xu, Y.F.; Gao, Y.M.; Xian, C.X.; Wang, W.J. Effects of Ambrosia trifida on the early spring plant community in abandoned farmland. J. Shenyang Agric. Univ. 2019, 50, 358–364. [Google Scholar]
- Hovick, S.M.; McArdle, A.; Harrison, S.K.; Regnier, E.E. A mosaic of phenotypic variation in giant ragweed (Ambrosia trifida): Local-and continental-scale patterns in a range-expanding agricultural weed. Evol. Appl. 2018, 11, 995–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lockwood, J.L.; Cassey, P.; Blackburn, T. The role of propagule pressure in explaining species invasions. Trend Ecol. Evol. 2005, 20, 223–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simberloff, D. The role of propagule pressure in biological invasions. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2009, 40, 81–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, C.E.; Power, A.G. Release of invasive plants from fungal and viral pathogens. Nature 2003, 421, 625–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyatake, T.; Ohno, T. Seasonal abundance of exotic leaf beetle Ophraella communa LeSage (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae) on two different host plants. Appl. Entomol. Zool. 2010, 45, 283–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukano, Y.; Doi, H. Population abundance host use pattern of Ophraella communa (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae) in its native and introduced range. Biocontrol Sci. Technol. 2013, 23, 595–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernays, E.A.; Funk, D.J. Specialists make faster decisions than generalists: Experiments with aphids. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B. Biol. Sci. 1999, 266, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitolo, D.B.; Stiles, E.W. The effect of density of Ambrosia trifida L. on seed predation Euaresta festiva (Loew) (Diptera: Tephritidae). J. N. Y. Entomol Soc. 1987, 95, 491–494. [Google Scholar]
- Kato-Noguchi, H. Involvement of allelopathy in the invasive potential of Tithonia diversifolia. Plants 2020, 9, 766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato-Noguchi, H.; Kurniadie, D. Allelopathy and allelochemicals of Leucaena leucocephala as an invasive plant species. Plants 2022, 11, 1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato-Noguchi, H.; Kurniadie, D. Allelopathy of Lantana camara as an invasive plant. Plants 2021, 10, 1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato-Noguchi, H. Allelopathy of knotweeds as invasive plants. Plants 2022, 11, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, E.L. Allelopathy, 2nd ed.; Academic Press: Orlando, FL, USA, 1984; pp. 1–422. [Google Scholar]
- Bonanomi, G.; Sicurezza, M.G.; Caporaso, S.; Esposito, A.; Mazzoleni, S. Phytotoxicity dynamics of decaying plant materials. New Phytol. 2006, 169, 571–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belz, R.G. Allelopathy in crop/weed interactions—An update. Pest Manag. Sci. 2007, 63, 308–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato-Noguchi, H. Defensive molecules momilactones A and B: Function, biosynthesis, induction and occurrence. Toxins 2023, 15, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bais, H.P.; Weir, T.L.; Perry, L.G.; Gilroy, S.; Vivanco, J.M. The role of root exudates in rhizosphere interactions with plants and other organisms. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2006, 57, 233–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato-Noguchi, H. Allelopathy and allelochemicals of Imperata cylindrica as an invasive plant species. Plants 2022, 11, 2551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato-Noguchi, H. The impact and invasive mechanisms of Pueraria montana var. lobata, one of the world’s worst alien species. Plants 2023, 12, 3066. [Google Scholar]
- Kato-Noguchi, H. Isolation and identification of allelochemicals and their activities and functions. J. Pestic. Sci. 2024, 49, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappuccino, N.; Arnason, J.T. Novel chemistry of invasive exotic plants. Biol. Lett. 2006, 2, 189–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato-Noguchi, H.; Kato, M. Allelopathy and allelochemicals of Solidago canadensis L. and S. altissima L. for their naturalization. Plants 2022, 11, 3235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato-Noguchi, H. Invasive mechanisms of one of the world’s worst alien plant species Mimosa pigra and its management. Plants 2023, 12, 1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato-Noguchi, H.; Kurniadie, D. The invasive mechanisms of the noxious alien plant species Bidens pilosa. Plants 2024, 13, 356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kil, J.H.; Shim, K.C.; Park, K.A.; Kim, K. Inhibitory effects of Ambrosia trifida L. on the development of root hairs and protein patterns of radicles. World Acad. Sci. Eng. Technol. Int. J. Environ. Ecol. Eng. 2014, 8, 608–611. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.I.; Zhu, X.Z. Allelopathic research of Ambrosia trifida. Acta Phytoecol. Sinica 1996, 20, 330–337. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, C.H.; Wang, P.; Xu, X.H. Allelopathic interference of Ambrosia trifida with wheat (Triticum aestivum). Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2007, 119, 416–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Kang, Z.; Hua, J.; Feng, Y.; Luo, S. Root exudate sesquiterpenoids from the invasive weed Ambrosia trifida regulate rhizospheric Proteobacteria. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 834, 155263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalton, B.R. The occurrence and behavior of plant phenolic acids in soil environments and their potential involvement in allelochemical interference interactions: Methodological limitations in establishing conclusive proof of allelopathy. In Principals and Practices in Plant Ecology: Allelochemical Interactions; Inderjit, Dakshini, K.M.M., Foy, C.L., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1999; pp. 57–74. [Google Scholar]
- Inderjit. Plant phenolics in allelopathy. Bot. Rev. 1996, 62, 186–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Einhellig, F.A. Mode of action of allelochemical action of phenolic compounds. In Chemistry and Mode of Action of Allelochemicals; Macías, F.A., Galindo, J.C.G., Molino, J.M.G., Cutler, H.G., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2004; pp. 217–238. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.H.; Wang, Q.; Ruan, X.; Pan, C.D.; Jiang, D.A. Phenolics and plant allelopathy. Molecules 2010, 15, 8933–8952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato-Noguchi, H.; Kato, M. Evolution of the secondary metabolites in invasive plant species Chromolaena odorata for the defense and allelopathic functions. Plants 2023, 12, 521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, P.; Liu, X.; Wang, R.; Liu, T.; Zhao, W.; Sun, M.; Wang, H.; Liu, Y.; Wu, Q. Autotoxicity of Ambrosia artemisiifolia and Ambrosia trifida and its significance for the regulation of intraspecific populations density. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 17424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Liang, W.; Kong, C.; Jiang, Y. Allelopathic potential of volatile allelochemicals of Ambrosia trifida L. on other plants. Allelopathy J. 2005, 15, 131–136. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, P.; Kong, C.H.; Zhang, C.X. Chemical composition and antimicrobial activity of the essential oil from Ambrosia trifida L. Molecules 2007, 11, 549–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarić-Krsmanović, M.; Umiljendić, J.G.; Radivojević, L.; Rajković, M.; Šantrić, L.; Đurović-Pejčev, R. Chemical composition of Ambrosia trifida essential oil and phytotoxic effect on other plants. Chem. Biodivers. 2000, 17, e1900508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.; Liu, X.; Zhao, C.; Pan, Q.; Chen, X.; Jiang, N.; Du, C.; Xu, Y.; Shao, M.; Qu, B. Nitrogen deposition further increases Ambrosia trifida root exudate invasiveness under global warming. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2023, 195, 759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, M.; Munné-Bosch, S. Malondialdehyde: Facts and artifacts. Plant Physiol. 2019, 180, 1246–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perry, J.J.P.; Shin, D.S.; Getzoff, E.D.; Tainer, J.A. The structural biochemistry of the superoxide dismutases. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2010, 1804, 245–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, L.; Clair, D.K.S. Regulation of superoxide dismutase genes: Implications in disease. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2009, 47, 344–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heck, D.E.; Shakarjian, M.; Kim, H.D.; Laskin, J.D.; Vetrano, A.M. Mechanisms of oxidant generation by catalase. Ann N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2010, 1203, 120–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arora, A.; Sairam, R.K.; Srivastava, G.C. Oxidative stress and antioxidative system in plants. Curr. Sci. 2002, 82, 1227–1238. [Google Scholar]
- Demidchik, V. Mechanisms of oxidative stress in plants: From classical chemistry to cell biology. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2015, 109, 212–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gniazdowska, A.; Krasuska, U.; Andrzejczak, O.; Soltys, D. Allelopathic compounds as oxidative stress agents: YES or NO. In Reactive Oxygen and Nitrogen Species Signaling and Communication in Plants; Gupta, K.J., Igamberdiev, A.U., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2015; pp. 155–176. [Google Scholar]
- Šoln, K.; Klemenčič, M.; Koce, J.D. Plant cell responses to allelopathy: From oxidative stress to programmed cell death. Protoplasma 2022, 259, 1111–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato-Noguchi, H.; Kato, M. Defense molecules of the invasive plant species Ageratum conyzoides. Molecules 2024, 29, 4673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šućur, J.; Konstantinović, B.; Crnković, M.; Bursić, V.; Samardžić, N.; Malenćić, Ð.; Prvulović, D.; Popov, M.; Vuković, G. Chemical composition of Ambrosia trifida L. and its allelopathic influence on crops. Plants 2021, 10, 2222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halsted, B.D. Our worst weeds. Bot. Gaz. 1889, 14, 69–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, M.M. Biological significance of low weed population densities on sweet corn. Agron. J. 2010, 102, 464–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baysinger, J.A.; Sims, B.D. Giant ragweed (Ambrosia trifida) interference in soybeans (Glycine max). Weed Sci. 1991, 39, 358–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werle, R.; Sandell, L.D.; Buhler, D.D.; Hartzler, R.G.; Lindquist, J. Predicting emergence of 23 summer annual weed species. Weed Sci. 2014, 62, 267–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, S.; Sandell, L.D.; Lindquist, J.L.; Jhala, A.J. Glyphosateresistant giant ragweed (Ambrosia trifida) control in glufosinate-resistant soybean. Weed Technol. 2014, 28, 569–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.B.; Gao, F.F.; Feng, W.W.; Wu, Q.Y.; Feng, Y.L. The native stem holoparasitic Cuscuta japonica suppresses the invasive plant Ambrosia trifida and related mechanisms in different light conditions in northeast China. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 904326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batra, S.W.T. Puccinia xanthii forma specialis ambrosid-trifidae. A microcyclic rust for the biological control of giant ragweed, Ambrosia trifida (Compositae). Mycopathologia 1981, 72, 61–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goplen, J.J.; Sheaffer, C.C.; Becker, R.L.; Coulter, J.A.; Breitenbach, F.R.; Behnken, L.M.; Johnson, G.A.; Gunsolus, J.L. Giant ragweed emergence pattern influenced by spring tillage timing in Minnesota. Crop Forage Turfgrass Manag. 2018, 4, 1800025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byun, C.; Choi, H.; Kang, H. Effects of cutting and sowing seeds of native species on giant ragweed invasion and plant diversity in a field experiment. J. Ecol. Environ. 2020, 44, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byun, C. Role of priority effects in invasive plant species management: Early arrival of native seeds guarantees the containment of invasion by Giant ragweed. Ecol. Evol. 2023, 13, e9940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byun, C.; Singh, K.; Hong, S.H.; Lee, J.; Yoon, T.K.; Kang, H. Uprooting is a promising tool to control invasive giant ragweed and recover native diversity. NeoBiota 2024, 94, 311–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liebman, M.; Nichols, V.A. Cropping system redesign for improved weed management: A modeling approach illustrated with giant ragweed (Ambrosia trifida). Agronomy 2020, 10, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goplen, J.J.; Sheaffer, C.C.; Becker, R.L.; Moon, R.D.; Coulter, J.A.; Breitenbach, F.R.; Behnken, L.M.; Gunsolus, J.L. Giant ragweed (Ambrosia trifida) emergence model performance evaluated in diverse cropping systems. Weed Sci. 2018, 66, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patzoldt, W.L.; Tranel, P.J. Molecular analysis of cloransulam resistance in a population of giant ragweed. Weed Sci. 2002, 50, 299–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brabham, C.B.; Gerber, C.K.; Johnson, W.G. Fate of glyphosate-resistant giant ragweed (Ambrosia trifida) in the presence absence of glyphosate. Weed Sci. 2011, 59, 506–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Herbicide Resistant Weed Database. Available online: https://www.weedscience.org/Pages/Species.aspx (accessed on 12 September 2024).
- Sikkema, P.; Soltani, N.; Shropshire, C.; Smith, P.; Lawton, M.; Tardif, F. Suspected glyphosate-resistant giant ragweed in Ontario. Proc. North Cent. Weed Sci. Soc. 2009, 64, 167. [Google Scholar]
- Van Horn, C.R.; Moretti, M.L.; Robertson, R.R.; Segobye, K.; Weller, S.C.; Young, B.G.; Johnson, W.G.; Schulz, B.; Green, A.C.; Jeffery, T.; et al. Glyphosate resistance in Ambrosia trifida: Part 1. Novel rapid cell death response to glyphosate. Pest Manag. Sci. 2018, 74, 1071–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moretti, M.L.; Van Horn, C.R.; Robertson, R.; Segobye, K.; Weller, S.C.; Young, B.G.; Johnson, W.G.; Sammons, R.D.; Wang, D.; Ge, X.; et al. Glyphosate resistance in Ambrosia trifida: Part 2. Rapid response physiology and non-target-site resistance. Pest Manag. Sci. 2018, 74, 1079–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, C.E.; Takano, H.K.; Van Horn, C.R.; Yerka, M.K.; Westra, P.; Stoltenberg, D.E. Physiological and molecular analysis of glyphosate resistance in non-rapid response Ambrosia trifida from Wisconsin. Pest Manag. Sci. 2020, 76, 150–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, E.R.; Martin, S.; Meloche, S.; Thibodeau, A.; Nurse, R.E.; Sikkema, P.H.; Tardif, F.J.; Cowbrough, M.J.; Laforest, M. Revisiting the origins of glyphosate-resistant giant ragweed (Ambrosia trifida L.) in Canada. Can. J. Plant Sci. 2024, 104, 124–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faleco, F.A.; Machado, F.M.; Bobadilla, L.K.; Tranel, P.J.; Stoltenberg, D.; Werle, R. Resistance to protoporphyrinogen oxidase inhibitors in giant ragweed (Ambrosia trifida). Pest Manag. Sci. 2024, 80, 6211–6221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johal, G.S. Effect of soilborne plant-pathogenic fungi on the herbicidal action of glyphosate on bean seedlings. Phytopathology 1984, 74, 950–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lévesque, A.C.; Rahe, J.E. Herbicide interaction with fungal root pathogens, with special reference to glyphosate. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 1992, 30, 579–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schafer, J.R.; Hallett, S.G.; Johnson, W.G. Response of giant ragweed (Ambrosia trifida), horseweed (Conyza canadensis), and common lambsquarters (Chenopodium album) biotypes to glyphosate in the presence and absence of soil microorganisms. Weed Sci. 2012, 60, 641–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schafer, J.R.; Hallett, S.G.; Johnson, W.G. Soil microbial root colonization of glyphosate-treated giant ragweed (Ambrosia trifida), horseweed (Conyza canadensis), and common lambsquarters (Chenopodium album) biotypes. Weed Sci. 2013, 61, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schafer, J.R.; Hallett, S.G.; Johnson, W.G. Rhizosphere microbial community dynamics in glyphosate-treated susceptible and resistant biotypes of giant ragweed (Ambrosia trifida). Weed Sci. 2014, 62, 370–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, J.B.; Loux, M.M.; Harrison, S.K.; Regnier, E. Response of ALS-resistant common ragweed (Ambrosia artemisiifolia) and giant ragweed (Ambrosia trifida) to ALS-inhibiting and alternative herbicides. Weed Techn. 2002, 16, 815–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marion, S.M.; Davis, V.M.; Stoltenberg, D.E. Characterization of Wisconsin giant ragweed (Ambrosia trifida) resistant to cloransulam. Weed Sci. 2017, 65, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordan, T.N. Weed survey of the north central weed control conference. North Cent. Weed Control Conf. Res. Rep. 1985, 42, 344–355. [Google Scholar]
- Loux, M.M.; Berry, M.A. Use of a grower survey for estimating weed problems. Weed Technol. 1991, 5, 460–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fickett, N.D.; Boerboom, C.M.; Stoltenberg, D.E. Predicted corn yield loss due to weed competition prior to postemergence herbicide application on Wisconsin farms. Weed Technol. 2013, 27, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fickett, N.D.; Boerboom, C.M.; Stoltenberg, D. E Soybean yield loss potential associated with early-season weed competition across 64 site-years. Weed Sci. 2013, 61, 500–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposito, M.; Crimaldi, M.; Cirillo, V.; Sarghini, F.; Maggio, A. Drone and sensor technology for sustainable weed management: A review. Chem. Biol. Technol. Agric. 2021, 8, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerhards, R.; Sanchez, D.A.; Hamouz, P.; Peteinatos, G.G.; Christensen, S.; Fernandez-Quintanilla, C. Advances in site-specific weed management in agriculture: A review. Weed Res. 2022, 62, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korres, N.E.; Burgos, N.R.; Travlos, I.; Vurro, M.; Gitsopoulos, T.K.; Varanasi, V.K.; Duke, S.O.; Kudsk, P.; Brabham, C.; Rouse, C.E.; et al. Chapter six—New directions for integrated weed management: Modern technologies, tools, and knowledge discovery. Adv. Agron. 2019, 155, 243–319. [Google Scholar]
- Monteiro, A.; Santos, S. Sustainable approach to weed management: The role of precision weed management. Agronomy 2022, 12, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norsworthy, J.K.; Ward, S.M.; Shaw, D.R.; Llewellyn, R.S.; Nichols, R.L.; Webster, T.M.; Bradley, K.W.; Frisvold, G.; Powles, S.P.; Burgos, N.R.; et al. Reducing the risks of herbicide resistance: Best management practices and recommendations. Weed Sci. 2012, 60, 31–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, G.; Shrestha, S.; Kunwar, S.; Tseng, T. Crop diversification for improved weed management: A review. Agriculture 2021, 11, 461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westwood, J.H.; Charudattan, R.; Duke, S.O.; Fennimore, S.A.; Marrone, P.; Slaughter, D.C.; Swanton, C.; Zollinger, R. Weed management in 2050: Perspectives on the future of weed science. Weed Sci. 2018, 66, 275–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Miao, Z.; Li, N.; He, C.; Sun, T. Review of current robotic approaches for precision weed management. Curr. Robot. Rep. 2022, 3, 139–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Feng, Y.L.; Liu, M.C.; Qu, B. Effects of Ambrosia trifida invasion on vegetation succession and soil nutrients in the enclosed riparian ecosystems-a case study of Liaohe River main stream. J. Shenyang Agric. Univ. 2022, 53, 520–531. [Google Scholar]
- Washitani, I. Plant conservation ecology for management and restoration of riparian habitats of lowland Japan. Popul. Ecol. 2001, 433, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Liu, T.; Dong, H.; Zhao, W.; Liu, X.; Wang, R.; Xu, W. Changes in the composition of the soil seed bank of grassland after giant ragweed (Ambrosia trifida L.) invasion. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 317, 115468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kato-Noguchi, H.; Kato, M. Invasive Characteristics and Impacts of Ambrosia trifida. Agronomy 2024, 14, 2868. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14122868
Kato-Noguchi H, Kato M. Invasive Characteristics and Impacts of Ambrosia trifida. Agronomy. 2024; 14(12):2868. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14122868
Chicago/Turabian StyleKato-Noguchi, Hisashi, and Midori Kato. 2024. "Invasive Characteristics and Impacts of Ambrosia trifida" Agronomy 14, no. 12: 2868. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14122868
APA StyleKato-Noguchi, H., & Kato, M. (2024). Invasive Characteristics and Impacts of Ambrosia trifida. Agronomy, 14(12), 2868. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14122868





