Patterns and Relationships of Pesticide Use in Agricultural Crops of Latin America: Review and Analysis of Statistical Data
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Databases of Agricultural Pesticides Used in Mexico and Central and South America
2.2. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- United Nations. The Sustainable Development Goals Report 2023; Department of Economic and Social Affairs, United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2023; 80p. [Google Scholar]
- Tostado, L.; Bollmohr, S. (Eds.) Pesticide Atlas 2022; Heinrich-Böll-Stiftung, Friends of the Earth Europe, Bund für Umwelt und Naturschutz, and PAN Europe: Berlin, Germany, 2022; 58p. [Google Scholar]
- United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP). Synthesis Report on the Environmental and Health Impacts of Pesticides and Fertilizers and Ways to Minimize Them; United Nations Environment Programme, Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- FAO. FAOSTAT: The Pesticides Use Database; Food and Agricultural Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2023; Available online: https://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#data/RP (accessed on 10 March 2024).
- Riches, C.R.; Valverde, B.E. Agricultural and biological diversity in Latin America: Implications for development, testing, and commercialization of herbicide-resistant crops. Weed Technol. 2002, 16, 200–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van den Berg, H.; Gu, B.; Grenier, B.; Kohlschmid, E.; Al-Eryani, S.; da Silva-Bezerra, H.S.; Nagpal, B.N.; Chanda, E.; Gasimov, E.; Velayudhan, R.; et al. Pesticide lifecycle management in agriculture and public health: Where are the gaps? Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 742, 140598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subramanian, K.S.; Pazhanivelan, S.; Srinivasan, G.; Santhi, R.; Sathiah, N. Drones in insect pest management. Front. Agron. 2021, 3, 640885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasco, C.; Torres, B.; Jacome, E.; Torres, A.; Eche, D.; Velasco, C. Use of chemical fertilizers and pesticides in frontier areas: A case study in the Northern Ecuadorian Amazon. Land Use Pol. 2021, 107, 105490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez-Morales, D.; Pérez-Villanueva, M.E.; Chin-Pampillo, J.S.; Aguilar-Mora, P.; Víctor Arias-Mora, V.; Masís-Mora, M. Pesticide occurrence and water quality assessment from an agriculturally influenced Latin-American tropical region. Chemosphere 2021, 262, 127851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adil, M.; Abbas, G.; Khan, R.N.; Abbas, F. Impact of climate change on environmental fate and ecological effects of pesticides. In Strategizing Agricultural Management for Climate Change Mitigation and Adaptation; Bandh, S.A., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 247–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaka, H.; Opute, P.A.; Maboeta, M.S. Potential impacts of climate change on the toxicity of pesticides towards earthworms. J. Toxicol. 2021, 2021, 8527991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, H.S.; Vidal-Luna, F. The growth of the soybean frontier in South America: The case of Brazil and Argentina. J. Iber. Lat. Am. Hist. 2021, 39, 427–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soutullo, A.; Ríos, M.; Zaldúa, N.; Teixeira-de-Mello, F. Soybean expansion and the challenge of the coexistence of agribusiness with local production and conservation initiatives: Pesticides in a Ramsar site in Uruguay. Environ. Conserv. 2020, 47, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wesz-Junior, V.J. Soybean production in Paraguay: Agribusiness, economic change and agrarian transformations. J. Agrar. Chang. 2021, 22, 317–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutter, H.-P.; Poteser, M.; Lemmerer, K.; Wallner, P.; Kundi, M.; Moshammer, H.; Weitensfelder, L. Health symptoms related to pesticide use in farmers and laborers of ecological and conventional banana plantations in Ecuador. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, C.A.; Pritts, A.A.; Zwetsloot, M.J.; Jansen, K.; Pulleman, M.M.; Armbrecht, I.; Avelino, J.; Barrera, J.F.; Bunn, C.; Hoyos-García, J.; et al. Transformation of coffee-growing landscapes across Latin America. A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2021, 41, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schreinemachers, P.; Tipraqsa, P. Agricultural pesticides and land use intensification in high, middle and low income countries. Food Policy 2012, 37, 616–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sierra-Diaz, E.; Celis-de la Rosa, A.; Lozano-Kasten, F.; Trasande, L.; Peregrina-Lucano, A.; Sandoval-Pinto, E.; Gonzalez-Chavez, H. Urinary pesticide levels in children and adolescents residing in two agricultural communities in Mexico. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avila-Vazquez, M.; Difilippo, F.S.; Lean, B.M.; Maturano, E.; Etchegoyen, A. Environmental Exposure to glyphosate and reproductive health impacts in agricultural population of Argentina. J. Environ. Prot. 2018, 9, 241–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Siqueira, M.T.; Braga, C.; Cabral-Filho, J.E.; Augusto, L.G.D.S.; Figueiroa, J.N.; Souza, A.I. Correlation between pesticide use in agriculture and adverse birth outcomes in Brazil: An ecological study. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2010, 84, 647–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, R.A.; Wichern, D.W. Applied Multivariate Satatistical Analysis, 6th ed.; Pearson: Prentice Hall, NJ, USA, 2007; pp. 430–480. [Google Scholar]
- SAS Institute Inc. Base SAS® 9.1.3 Procedures Guide, 2nd ed.; SAS Institute Inc.: Cary, NC, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Ryberg, K.R.; Gilliom, R.J. Trends in pesticide concentrations and use for major rivers of the United Sates. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 538, 431–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassaan, M.A.; Nemr, A.E. Pesticides pollution: Classification, human health impact, extraction and treatment techniques. Egypt. J. Aquat. Res. 2020, 46, 207–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aye, T.S.; Jirapongsuwan, A.; Siri, S. Pesticide safety behaviours among agricultural workers and farmers: A cross-sectional study. Int. J. Nurs. Pract. 2023, 30, e13222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panis, C.; Bufalo-Kawassaki, A.C.; Crestani, A.P.J.; Risso-Pascotto, C.; Schiavoni-Bortoloti, D.; Vicentini, G.E.; Lucio, L.C.; Ferreira, M.O.; Cunha-Prates, R.T.; Vieira, V.K.; et al. Evidence on human exposure to pesticides and the occurrence of health in the Brazilian population: A systematic review. Front. Public Health 2022, 9, 787438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippi, I.; Bravo, N.; Grimalt, J.O.; Butinof, M.; Lerda, D.; Fernández, R.A.; Muñoz, S.E.; Amé, M.V. Pilot study of exposure of the male populations to organophosphate and pyrethroid pesticides in a region of high agricultural activity (Córdoba, Argentina). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 53908–53916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mas, L.I.; Aparicio, V.C.; De Gerónimo, E. Pesticides in water sources used for human consumption in the semiarid region of Argentina. SN Appl. Sci. 2020, 2, 691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verzeñassi, D.; Vallini, A.; Fernández, F.; Ferrazini, L.; Lasagna, M.; Sosa, A.J.; Hough, G.E. Cancer incidence and death rates in Argentine rural towns surrounded by pesticide-treated agricultural land. Clin. Epidemiol. Glob. Health 2023, 20, 101239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, L.; Camacho, R.; López, J.E.; Saldarriaga, J.F. Assessment of the potential risk of leaching pesticides in agricultural soils: Study case Tibasosa, Boyacá, Colombia. Heliyon 2021, 7, e08301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzmán-Barragán, B.L.; Gonzalez-Rivillas, M.A.; Cuero-Villegas, M.S.; Olivar-Medina, J.D. Presence of pesticides, mercury and trihalomethanes in the water supply systems of Ibagué, Colombia: Threats to human health. Rev. Ambient. Água 2020, 15, e2477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yáñez-Estrada, L.; Ramírez-Jiménez, M.R.; Rodríguez-Agudelo, Y.; Calderón-Hernández, J.; Ramos-Ruiz, E. Evaluación de las alteraciones en el desempeño cognitivo de niños mexicanos expuestos a plaguicidas organofosforados. Rev. Int. Contam. Ambient. 2018, 34, 9–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Herrera, N.; Vera-Avilés, M.; Castillo-Burguete, T.; Perera-Rios, J.; Esperón-Hernández, R.; Rojas-García, A.E.; Medina-Díaz, I.M.; Quintanilla-Vega, B. Pesticide exposure index: Practices among women from an agricultural community in Southeast Mexico. Rev. Int. Contam. Ambient. 2018, 34, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuñiga-Venegas, L.A.; Hyland, C.; Muñoz-Quezada, M.T.; Quirós-Alcalá, L.; Butinof, M.; Buralli, R.; Cardenas, A.; Fernandez, R.A.; Foerster, C.; Gouveia, N.; et al. Health effects of pesticide exposure in Latin America and the Caribbean populations: A scoping review. Environ. Health Perspect. 2022, 130, 096002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larsen, A.E.; Quandt, A.; Foxfoot, I.; Parker, N.; Sousa, D. The effect of agricultural land retirement on pesticide use. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 896, 165224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merotto, A., Jr.; Gazziero, D.L.P.; Oliveira, M.C.; Scursoni, J.; Garcia, M.A.; Figueroa, R.; Turra, G.M. Herbicide use history and perspective in South America. Adv. Weed Sci. 2022, 40, e020220050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Kumar, V.; Shahzad, B.; Tanveer, M.; Sidhu, G.P.S.; Handa, N.; Kohli, S.K.; Yadav, P.; Bali, A.S.; Parihar, R.D.; et al. Worldwide pesticide usage and its impacts on ecosystem. SN Appl. Sci. 2019, 1, 1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casallanovo, F.; Mejias-Simone, D.; Souza-Santos, G.; de Oliverira-Kaminski, T.S.; Cione, A.P.; Peranginangin, N. Estimating pesticide environmental concentrations in Latin America: The importance of developing local scenarios. Integr. Environ. Assess. Manag. 2021, 17, 901–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopes-Ferreira, M.; Almeida-Maleski, A.L.A.; Balan-Lima, L.; Goncalves-Bernardo, J.T.; Marques-Hipolito, L.; Seni-Silva, A.; Batista-Filho, J.; Pimentel-Falcao, M.A.; Lima, C. Impact of pesticides on human health in the las six years in Brazil. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 3198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Hernández, J.; Leyva-Morales, J.B.; Martínez-Rodríguez, I.E.; Hernández-Ochoa, M.I.; Aldana-Madrid, M.L.; Rojas-García, A.E.; Betancourt-Lozano, M.; Perez-Herrera, N.E.; Perera-Rios, J.H. Estado actual de la investigación sobre plaguicidas naturales. Rev. Int. Contam. Ambient. 2018, 34, 29–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, H.O.; Menezes, J.M.C.; da Costa, J.G.M.; Coutinho, H.D.M.; Teixeira, R.M.P.; do Nascimento, R.F. A socio-environmental perspective on pesticide use and food production. Ecotox. Environ. Safe 2020, 197, 110627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chowdhury, S.K.; Banerjee, M.; Basnett, D.; Mazumdar, T. Natural pesticides for pest control in agricultural crops: An alternative and eco-friendly method. Plant Sci. Today 2024, 11, 433–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willer, H.; Trávníček, J.; Schlatter, B. The World of Organic Agriculture Statistics and Emerging Trends 2024; Research Institute of Organic Agriculture (FiBL), Frick, and IFOAM—Organics International: Hachenburg, Germany, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Kudsk, P.; Mathiassen, S.K. Pesticide regulation in the European Union and the glyphosate controversy. Weed Sci. 2020, 68, 214–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

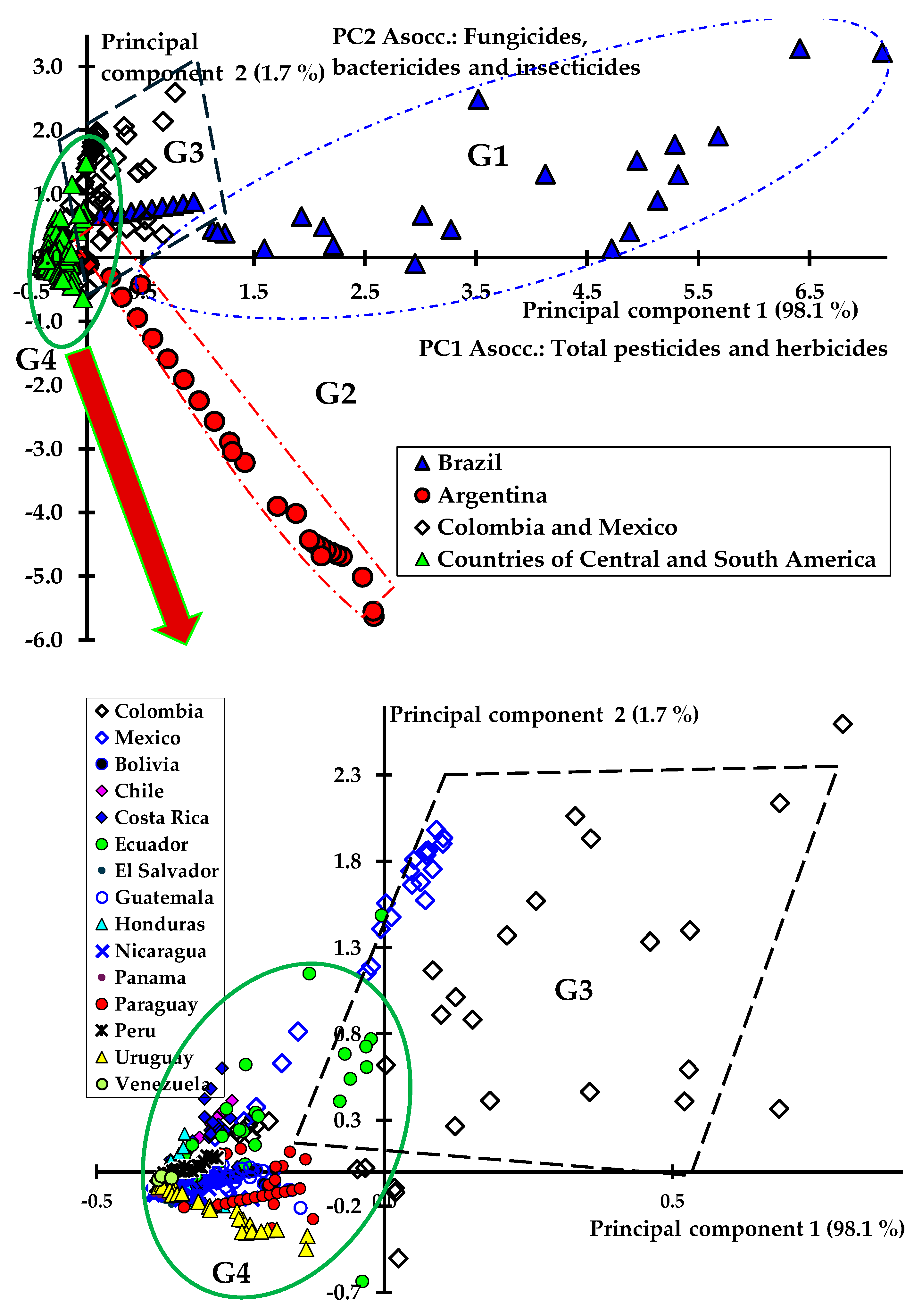
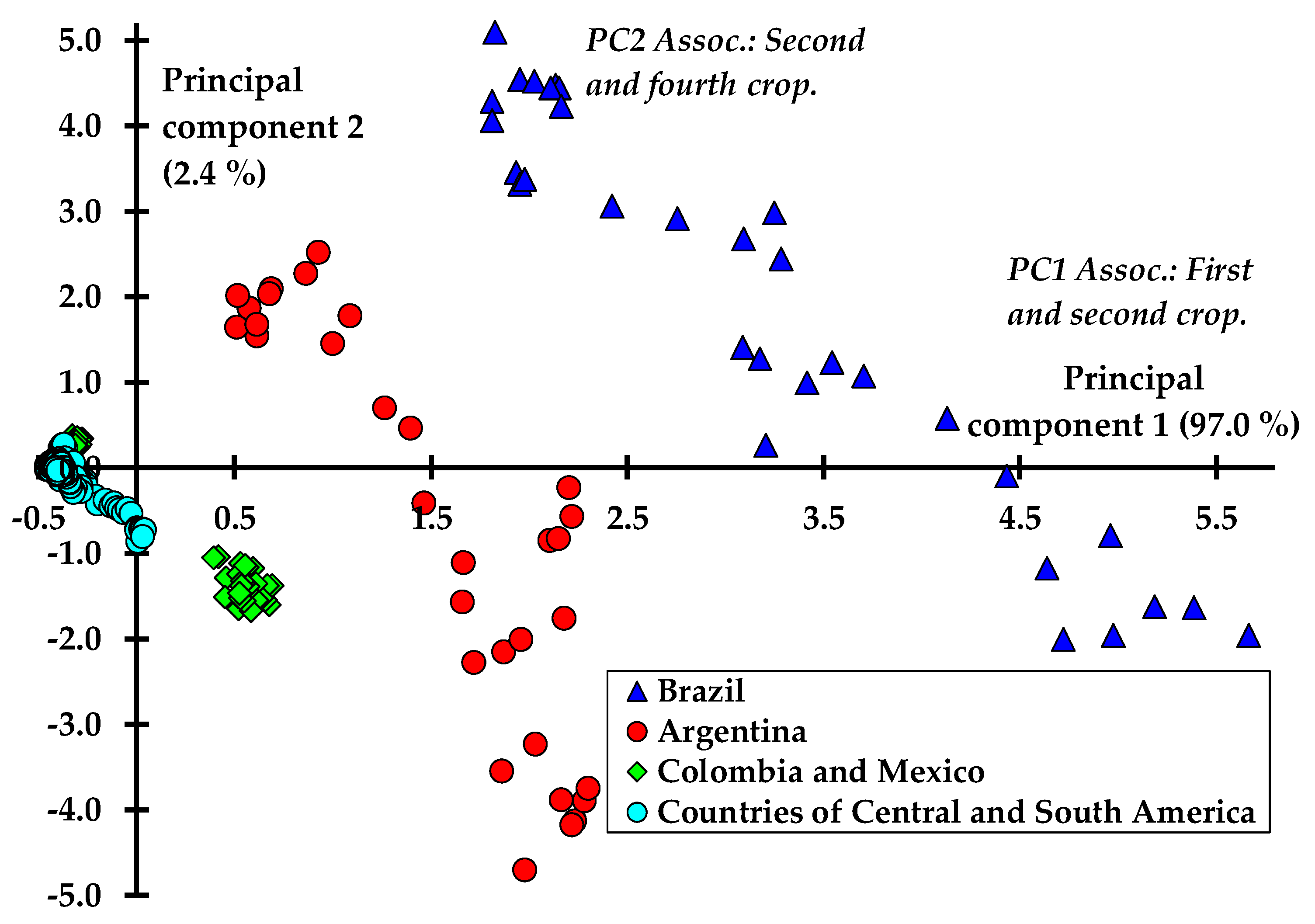
| Quinquennial or Sexennial Averages | Brazil (G1) | Argentina (G2) | Colombia and Mexico (G3) | Countries of Central and South America 1 (G4) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average harvested area (×100,000 ha) | ||||
| 1990–1995 | 510.8 | 190.9 | 102.6 | 12.7 |
| 1996–2000 | 488.0 | 239.4 | 102.8 | 13.9 |
| 2001–2005 | 581.9 | 268.5 | 100.7 | 15.4 |
| 2006–2010 | 644.2 | 301.5 | 99.3 | 17.8 |
| 2011–2015 | 724.9 | 344.8 | 100.5 | 20.0 |
| 2016–2021 | 809.1 | 367.3 | 102.2 | 20.1 |
| Average total pesticides applied (×1000 tons) | ||||
| 1990–1995 | 71.9 | 28.8 | 21.8 | 3.6 |
| 1996–2000 | 120.4 | 70.4 | 37.0 | 5.7 |
| 2001–2005 | 186.2 | 116.9 | 59.1 | 7.0 |
| 2006–2010 | 311.5 | 183.1 | 57.1 | 9.4 |
| 2011–2015 | 464.1 | 212.1 | 50.6 | 11.2 |
| 2016–2021 | 600.8 | 209.4 | 44.9 | 12.4 |
| Average herbicides applied (×1000 tons) | ||||
| 1990–1995 | 35.5 | 19.1 | 6.7 | 1.2 |
| 1996–2000 | 64.8 | 53.8 | 12.3 | 2.0 |
| 2001–2005 | 108.7 | 103.5 | 26.6 | 3.3 |
| 2006–2010 | 185.5 | 169.2 | 22.3 | 4.9 |
| 2011–2015 | 292.7 | 197.0 | 17.5 | 6.0 |
| 2016–2021 | 361.3 | 197.2 | 18.5 | 6.2 |
| Average insecticides applied (×1000 tons) | ||||
| 1990–1995 | 21.3 | 4.2 | 4.5 | 0.9 |
| 1996–2000 | 27.4 | 9.1 | 6.9 | 1.3 |
| 2001–2005 | 36.0 | 7.6 | 10.8 | 1.4 |
| 2006–2010 | 61.4 | 8.2 | 8.7 | 1.8 |
| 2011–2015 | 92.1 | 8.1 | 9.0 | 1.7 |
| 2016–2021 | 99.2 | 4.5 | 8.0 | 1.6 |
| Average fungicides and bactericides applied (×1000 tons) | ||||
| 1990–1995 | 11.7 | 5.2 | 10.4 | 1.1 |
| 1996–2000 | 18.4 | 6.3 | 17.8 | 1.4 |
| 2001–2005 | 21.6 | 3.4 | 21.6 | 1.7 |
| 2006–2010 | 38.6 | 2.5 | 26.1 | 2.3 |
| 2011–2015 | 68.8 | 3.9 | 23.9 | 2.8 |
| 2016–2021 | 123.3 | 4.0 | 18.4 | 3.7 |
| Applied Pesticides and Harvested Area | Brazil (G1) | Argentina (G2) | Colombia and Mexico (G3) | Countries of Central and South America 1 (G4) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total applied pesticides (ton) | 719,507.4 | 241,520.0 | 82,902.1 | 162,958.5 |
| Herbicides (ton) | 407,462.7 | 228,429.2 | 28,053.0 | 82,477.0 |
| Insecticides (ton) | 122,182.4 | 6076.9 | 15,297.4 | 18,921.4 |
| Fungicides and bactericides (ton) | 168,169.4 | 3756.5 | 39,089.8 | 48,465.3 |
| Total harvested area (ha) | 86,549,711.0 | 38,099,766.0 | 20,557,313.0 | 26,694,095.0 |
| First main crop (ha) | 39,168,068.0 | 16,466,714.0 | 7,979,733.0 | 9,675,569.0 |
| Second main crop (ha) | 19,024,538.0 | 8,146,596.0 | 2,214,137.0 | 4,133,578.0 |
| Third main crop (ha) | 9,970,958.0 | 6,394,102.0 | 1,796,902.0 | 2,890,867.0 |
| Fourth main crop (ha) | 2,750,264.0 | 1,666,843.0 | 1,238,910.0 | 1,798,826.0 |
| Fifth main crop (ha) | 2,613,086.0 | 1,006,503.0 | 1,044,366.0 | 1,369,553.0 |
| Total Harvested Area and Areas of the Five Main Crops | Brazil (G1, n = 32) | Argentina (G2, n = 32) | Colombia and Mexico (G3, n = 64) | Countries of Central and South America 1 (G4, n = 416) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total pesticides applied | ||||
| Total harvested area | 0.98 ** | 0.96 ** | −0.36 ** | 0.51 ** |
| First main crop | 0.98 ** | 0.96 ** | −0.36 ** | 0.49 ** |
| Second main crop | 0.95 ** | 0.22 ns | −0.41 ** | 0.54 ** |
| Third main crop | 0.94 ** | 0.57 ** | −0.34 * | 0.52 ** |
| Fourth main crop | −0.89 ** | −0.55 ** | −0.32 * | 0.40 ** |
| Fifth main crop | −0.84 ** | 0.47 * | −0.27 * | 0.41 ** |
| Herbicides applied | ||||
| Total harvested area | 0.97 ** | 0.96 ** | −0.63 ** | 0.56 ** |
| First main crop | 0.97 ** | 0.96 ** | −0.63 ** | 0.64 ** |
| Second main crop | 0.95 ** | 0.23 ns | −0.64 ** | 0.61 ** |
| Third main crop | 0.95 ** | 0.58 ** | −0.58 ** | 0.52 ** |
| Fourth main crop | −0.89 ** | −0.57 ** | −0.57 ** | 0.35 ** |
| Fifth main crop | −0.86 ** | 0.46 * | −0.56 ** | 0.36 ** |
| Insecticides applied | ||||
| Total harvested area | 0.96 ** | 0.06 ns | −0.08 ns | 0.43 ** |
| First main crop | 0.95 ** | 0.15 ns | −0.09 ns | 0.37 ** |
| Second main crop | 0.92 ** | −0.16 ns | −0.13 ns | 0.45 ** |
| Third main crop | 0.96 ** | −0.27 ns | −0.09 ns | 0.49 ** |
| Fourth main crop | −0.86 ** | 0.33 ns | −0.07 ns | 0.34 ** |
| Fifth main crop | −0.82 ** | −0.02 ns | −0.05 ns | 0.43 ** |
| Fungicides and bactericides applied | ||||
| Total harvested area | 0.91 ** | −0.45 * | 0.05 ns | 0.19 ** |
| First main crop | 0.93 ** | −0.63 ** | 0.04 ns | 0.10 ns |
| Second main crop | 0.91 ** | 0.02 ns | −0.03 ns | 0.17 ** |
| Third main crop | 0.84 ** | 0.03 ns | 0.01 ns | 0.24 ** |
| Fourth main crop | −0.84 ** | 0.48 * | 0.05 ns | 0.22 ** |
| Fifth main crop | −0.75 ** | 0.17 ns | 0.14 ns | 0.21 ** |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Olguín-Hernández, L.; Carrillo-Rodríguez, J.C.; Mayek-Pérez, N.; Aquino-Bolaños, T.; Vera-Guzmán, A.M.; Chávez-Servia, J.L. Patterns and Relationships of Pesticide Use in Agricultural Crops of Latin America: Review and Analysis of Statistical Data. Agronomy 2024, 14, 2889. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14122889
Olguín-Hernández L, Carrillo-Rodríguez JC, Mayek-Pérez N, Aquino-Bolaños T, Vera-Guzmán AM, Chávez-Servia JL. Patterns and Relationships of Pesticide Use in Agricultural Crops of Latin America: Review and Analysis of Statistical Data. Agronomy. 2024; 14(12):2889. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14122889
Chicago/Turabian StyleOlguín-Hernández, Licet, José Cruz Carrillo-Rodríguez, Netzahualcóyotl Mayek-Pérez, Teodulfo Aquino-Bolaños, Araceli Minerva Vera-Guzmán, and José Luis Chávez-Servia. 2024. "Patterns and Relationships of Pesticide Use in Agricultural Crops of Latin America: Review and Analysis of Statistical Data" Agronomy 14, no. 12: 2889. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14122889
APA StyleOlguín-Hernández, L., Carrillo-Rodríguez, J. C., Mayek-Pérez, N., Aquino-Bolaños, T., Vera-Guzmán, A. M., & Chávez-Servia, J. L. (2024). Patterns and Relationships of Pesticide Use in Agricultural Crops of Latin America: Review and Analysis of Statistical Data. Agronomy, 14(12), 2889. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14122889





