Multiple Nitrogen Sources Application Inhibits Increasing Ammonia Volatilization Under Reducing Irrigation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Soil Column Incubation Experiment
2.2. Soil NH3 Volatilization Measurement
2.3. Soil Sampling and Measurement
2.4. Metagenomic Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Soil NH3 Volatilization
3.2. Soil Properties Characteristics
3.3. Core Microorganisms and N Functional Genes
4. Discussion
4.1. NH3 Volatilization Character Under Different Irrigation Levels
4.2. Effects of Soil Mineral Nitrogen on NH3 Volatilization
4.3. Effects of Microorganism and N Functional Genes on NH3 Volatilization
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Galloway, J.N.; Townsend, A.R.; Erisman, J.W.; Bekunda, M.; Cai, Z.; Freney, J.R.; Martinelli, L.A.; Seitzinger, S.P.; Sutton, M.A. Transformation of the nitrogen cycle: Recent trends, questions, and potential solutions. Science 2008, 320, 889–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouwman, A.F.; Boumans, L.J.M.; Batjes, N.H. Estimation of global NH3 volatilization loss from synthetic fertilizers and animal manure applied to arable lands and grasslands. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2002, 16, 8-1–8-14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.; Tian, H.; Pan, S.; Prior, S.A.; Feng, Y.; Batchelor, W.D.; Chen, J.; Yang, J. Global ammonia emissions from synthetic nitrogen fertilizer applications in agricultural systems: Empirical and process-based estimates and uncertainty. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2019, 25, 314–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, R.; Zou, J.; Han, Z.; Yu, K.; Wu, S.; Li, Z.; Liu, S.; Niu, S.; Horwath, W.R.; Zhu Barker, X. Global soil-derived ammonia emissions from agricultural nitrogen fertilizer application: A refinement based on regional and crop-specific emission factors. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2021, 27, 855–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gazola, B.; Mariano, E.; Mota Neto, L.V.; Rosolem, C.A. Greenhouse gas and ammonia emissions from a maize-soybean rotation under no-till as affected by intercropping with forage grass and nitrogen fertilization. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2024, 345, 109855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Feng, Y.; Xu, X.; Zhang, X.; Liu, H.; Xu, J.; Gu, B. Hierarchical driving factors of ammonia emissions from cropland in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 451, 142127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powlson, D.S.; Dawson, C.J. Use of ammonium sulphate as a sulphur fertilizer: Implications for ammonia volatilization. Soil Use Manag. 2022, 38, 622–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sha, Z.; Ma, X.; Liu, H.; Wang, J.; Lv, T.; Goulding, K.; Liu, X. Crop-specific ammonia volatilization rates and key influencing factors in the upland of China—A data synthesis. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 336, 117676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holcomb III, J.C.; Sullivan, D.M.; Horneck, D.A.; Clough, G.H. Effect of irrigation rate on ammonia volatilization. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2011, 75, 2341–2347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, T.; Xie, N.; Chen, C.; He, X.; Deng, O.; Zhou, W.; Chen, G.; Ling, J.; Yuan, S.; Huang, R.; et al. Effects of biological nitrification inhibitor in regulating NH3 volatilization and fertilizer nitrogen recovery efficiency in soils under rice cropping. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 838, 155857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Tan, L.; Liu, W.; Li, X.; Zhang, D.; Xu, Y. Unraveling the effect of added microbial inoculants on ammonia emissions during co-composting of kitchen waste and sawdust: Core microorganisms and functional genes. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 874, 162522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Yu, Q.; Su, W.; Wang, S.; Wang, X.; Han, Q.; Qu, J.; Li, H. Metagenomics reveals elevated temperature causes nitrogen accumulation mainly by inhibiting nitrate reduction process in polluted water. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 882, 163631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, P.; Li, G.; Zheng, Y.; Fung, J.C.H.; Chen, A.; Zeng, Z.; Shen, H.; Hu, M.; Mao, J.; Zheng, Y.; et al. Fertilizer management for global ammonia emission reduction. Nature 2024, 626, 792–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Gu, B.; van Grinsven, H.; Lam, S.K.; Liang, X.; Bai, M.; Chen, D. Societal benefits of halving agricultural ammonia emissions in China far exceed the abatement costs. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 4357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Li, Z.; Gao, W.; Ding, W.; Xu, Q.; Song, X. Diurnal, seasonal, and spatial variation of PM2.5 in Beijing. Sci. Bull. 2015, 60, 387–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, B.; Zhang, L.; Van Dingenen, R.; Vieno, M.; Van Grinsven, H.J.M.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, S.; Chen, Y.; Wang, S.; Ren, C.; et al. Abating ammonia is more cost-effective than nitrogen oxides for mitigating PM2.5 air pollution. Science 2021, 374, 758–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, B.; Pathak, H.; Aggarwal, P.K. Effects of dicyandiamide, farmyard manure and irrigation on crop yields and ammonia volatilization from an alluvial soil under a rice (Oryza sativa L.)-wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) cropping system. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2002, 36, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verdi, L.; Kuikman, P.J.; Orlandini, S.; Mancini, M.; Napoli, M.; Dalla Marta, A. Does the use of digestate to replace mineral fertilizers have less emissions of N2O and NH3? Agric. For. Meteorol. 2019, 269–270, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Fang, Q.; Zhang, T.; Ma, W.; Velthof, G.L.; Hou, Y.; Oenema, O.; Zhang, F. Benefits and trade-offs of replacing synthetic fertilizers by animal manures in crop production in China: A meta-analysis. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2020, 26, 888–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Li, K.; Chen, S.; Fu, X.; Feng, S.; Zhuang, Z. A sustainable agricultural supply chain considering substituting organic manure for chemical fertilizer. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2022, 29, 432–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhuang, M.; Shan, N.; Zhao, Q.; Li, H.; Wang, L. Substituting organic manure for compound fertilizer increases yield and decreases NH3 and N2O emissions in an intensive vegetable production systems. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 670, 1184–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, P.; Li, G.; Houlton, B.Z.; Ma, L.; Ai, D.; Zhu, L.; Luan, B.; Zhai, S.; Hu, S.; Chen, A.; et al. Role of organic and conservation agriculture in ammonia emissions and crop productivity in China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 2977–2989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mooshammer, M.; Wanek, W.; Hämmerle, I.; Fuchslueger, L.; Hofhansl, F.; Knoltsch, A.; Schnecker, J.; Takriti, M.; Watzka, M.; Wild, B.; et al. Adjustment of microbial nitrogen use efficiency to carbon:nitrogen imbalances regulates soil nitrogen cycling. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, G.; Chang, D.; Gao, S.; Liang, T.; Liu, R.; Cao, W. Co-incorporating leguminous green manure and rice straw drives the synergistic release of carbon and nitrogen, increases hydrolase activities, and changes the composition of main microbial groups. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2021, 57, 547–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Sui, X.; Li, B.; Su, B.; Li, J.; Zhou, D. An improved water-use efficiency for winter wheat grown under reduced irrigation. Field Crops Res. 1998, 59, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, R.; Li, J.; Zhang, M.; Zhou, S.; Wang, Z. Reduced irrigation increases the water use efficiency and productivity of winter wheat-summer maize rotation on the North China Plain. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 618, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, C.; Liu, Y.; Guo, J.; Zhang, W.; Xu, R.; Zhou, B.; Xiao, X.; Zhang, Z.; Gao, Z.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Novel annual nitrogen management strategy improves crop yield and reduces greenhouse gas emissions in wheat-maize rotation systems under limited irrigation. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 353, 120236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateos, L.; Araus, J.L. Hydrological, engineering, agronomical, breeding and physiological pathways for the effective and efficient use of water in agriculture. Agric. Water Manag. 2016, 164, 190–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Zhang, P.; Wei, Z.; Liu, J.; Hu, X.; Liu, F. Effects of CO2 fertilization on tomato fruit quality under reduced irrigation. Agric. Water Manag. 2020, 230, 105985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavado, N.; Prieto, M.H.; Mancha, L.A.; Moreno, D.; Valdés, M.E.; Uriarte, D. Combined effect of crop forcing and reduced irrigation as techniques to delay the ripening and improve the quality of cv. Tempranillo (Vitis vinifera L.) berries in semi-arid climate conditions. Agric. Water Manag. 2023, 288, 108469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamran, M.; Yan, Z.; Chang, S.; Ning, J.; Lou, S.; Ahmad, I.; Ghani, M.U.; Arif, M.; El Sabagh, A.; Hou, F. Interactive effects of reduced irrigation and nitrogen fertilization on resource use efficiency, forage nutritive quality, yield, and economic benefits of spring wheat in the arid region of Northwest China. Agric. Water Manag. 2023, 275, 108000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chilundo, M.; Joel, A.; Wesström, I.; Brito, R.; Messing, I. Effects of reduced irrigation dose and slow release fertiliser on nitrogen use efficiency and crop yield in a semi-arid loamy sand. Agric. Water Manag. 2016, 168, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Lin, M.; Du, C.; Hao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z. The use of manure shifts the response of α-diversity and network while not β-diversity of soil microbes to altered irrigation regimes. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2022, 174, 104423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastida, F.; Torres, I.F.; Romero-Trigueros, C.; Baldrian, P.; Větrovský, T.; Bayona, J.M.; Alarcón, J.J.; Hernández, T.; García, C.; Nicolás, E. Combined effects of reduced irrigation and water quality on the soil microbial community of a citrus orchard under semi-arid conditions. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2017, 104, 226–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, A.; Huang, J.; Han, T.; Khan, M.N.; Tadesse, K.A.; Daba, N.A.; Khan, S.; Ullah, S.; Sardar, M.F.; Fahad, S.; et al. Impact of soil moisture regimes on greenhouse gas emissions, soil microbial biomass, and enzymatic activity in long-term fertilized paddy soil. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2024, 36, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abadía, J.; Bastida, F.; Romero-Trigueros, C.; Bayona, J.M.; Vera, A.; García, C.; Alarcón, J.J.; Nicolás, E. Interactions between soil microbial communities and agronomic behavior in a mandarin crop subjected to water deficit and irrigated with reclaimed water. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 247, 106749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Ramos, J.C.; Turini, T.; Wang, D.; Hale, L. Impacts of deficit irrigation and organic amendments on soil microbial populations and yield of processing tomatoes. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2022, 180, 104625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDermid, S.; Nocco, M.; Lawston-Parker, P.; Keune, J.; Pokhrel, Y.; Jain, M.; Jägermeyr, J.; Brocca, L.; Massari, C.; Jones, A.D.; et al. Irrigation in the Earth system. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2023, 4, 435–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamran, M.; Yan, Z.; Ahmad, I.; Jia, Q.; Ghani, M.U.; Chen, X.; Chang, S.; Li, T.; Siddique, K.H.M.; Fahad, S.; et al. Assessment of greenhouse gases emissions, global warming potential and net ecosystem economic benefits from wheat field with reduced irrigation and nitrogen management in an arid region of China. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2023, 341, 108197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, M.; Zeng, L.; Qin, W.; Feng, J. Measures for reducing nitrate leaching in orchards: A review. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 263, 114553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Yang, X.; Hu, Z.; Liu, F.; Xie, Z.; Li, S.; Wang, G.; Li, M.; Sun, Z.; Bol, R. Biochar effects on soil nitrogen retention, leaching and yield of perennial citron daylily under three irrigation regimes. Agric. Water Manag. 2024, 296, 108788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, B.; Lam, S.K.; Mosier, A.; Luo, Y.; Chen, D. Ammonia volatilization from synthetic fertilizers and its mitigation strategies: A global synthesis. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2016, 232, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Xiao, G.; Bol, R.; Wang, L.; Zhuge, Y.; Wu, W.; Li, H.; Meng, F. Influences of irrigation and fertilization on soil N cycle and losses from wheat–maize cropping system in northern China. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 278, 116852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno-Maroto, J.M.; Alonso-Azcárate, J. Evaluation of the USDA soil texture triangle through Atterberg limits and an alternative classification system. Appl. Clay Sci. 2022, 229, 106689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghirian, A.; Fall, M. Coupled thermo-hydro-mechanical–chemical behaviour of cemented paste backfill in column experiments. Part I: Physical, hydraulic and thermal processes and characteristics. Eng. Geol. 2013, 164, 195–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, X.; Ju, X.; Zhang, F.; Malhi, S.S. Ammonia volatilization loss from surface-broadcast urea: Comparison of vented- and closed-chamber methods and loss in winter wheat-summer maize rotation in North China Plain. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2004, 35, 2917–2939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Xu, X.; Li, Z.; Wang, T.; Wang, C. Detection methods of ammonia nitrogen in water: A review. TrAC-Trends Anal. Chem. 2020, 127, 115890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raza, S.T.; Zhu, B.; Yao, Z.; Wu, J.; Chen, Z.; Ali, Z.; Tang, J.L. Impacts of vermicompost application on crop yield, ammonia volatilization and greenhouse gases emission on upland in Southwest China. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 860, 160479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohira, Y.; Fentie, D.; Lewoyehu, M.; Wutisirirattanachai, T.; Gezahegn, A.; Addisu, S.; Sato, S. Mitigation of ammonia volatilization from organic and inorganic nitrogen sources applied to soil using water hyacinth biochars. Chemosphere 2024, 363, 142872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schofield, R.K.; Wormald Taylor, A. The measurement of soil pH. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1955, 19, 164–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S. Ultrafast one-pass FASTQ data preprocessing, quality control, and deduplication using fastp. iMeta 2023, 2, e107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Fuhrman, J.A.; Sun, F.; Zhu, S. Assessment of metagenomic assemblers based on hybrid reads of real and simulated metagenomic sequences. Briefings Bioinf. 2020, 21, 777–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durrant, M.G.; Bhatt, A.S. Automated prediction and annotation of small open reading frames in microbial genomes. Cell Host Microbe 2021, 29, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinegger, M.; Soding, J. MMseqs2 enables sensitive protein sequence searching for the analysis of massive data sets. Nat. Biotechnol. 2017, 35, 1026–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalikar, S.; Jain, C.; Vasimuddin, M.; Misra, S. Accelerating minimap2 for long-read sequencing applications on modern CPUs. Nat. Comput. Sci. 2022, 2, 78–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, F.; Hong, C.; Wang, W.; Lyu, H.; Zhu, W.; Xv, H.; Yao, Y. A microbial agent effectively reduces ammonia volatilization and ensures good maggot yield from pig manure composted via housefly larvae cultivation. J. Clean Prod. 2020, 270, 122373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roguet, A.; Eren, A.M.; Newton, R.J.; McLellan, S.L. Fecal source identification using random forest. Microbiome 2018, 6, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, J.; Ma, S.; He, X.; Han, L.; Huang, G. Nitrogen transformation and dynamic changes in related functional genes during functional-membrane covered aerobic composting. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 332, 125087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Sun, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, X.; Lu, L.; Shi, L.; Zhou, S. Effects of different fertilization methods on ammonia volatilization from rice paddies. J. Clean Prod. 2021, 295, 126299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, F.; Fan, B.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, H.; Wang, Z.; Bashir, M.A.; Ezzati, G.; Zhai, L.; Di, H.J.; et al. Fate of 15N-labelled urea as affected by long-term manure substitution. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 893, 164924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Xie, B.; Khan, R.; Yan, H.; Shen, G. The changes in functional marker genes associated with nitrogen biological transformation during organic-inorganic co-composting. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 295, 122197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, L.; Gu, J.; Wang, X.; Song, Z.; Yu, J.; Wang, J.; Dai, X.; Zhao, W. Effects of phosphogypsum and medical stone on nitrogen transformation, nitrogen functional genes, and bacterial community during aerobic composting. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 753, 141746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Wang, Z.; Wang, C.; Huang, J.; Feng, Y.; Shen, W.; Zhou, M.; Yang, L. Ammonia volatilization mitigation in crop farming: A review of fertilizer amendment technologies and mechanisms. Chemosphere 2022, 303, 134944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, L.; Sun, B.; Yang, Y.; Jin, B.; Zhuang, G.; Bai, Z.; Zhuang, X. Efficiency and mechanism of reducing ammonia volatilization in alkaline farmland soil using Bacillus amyloliquefaciens biofertilizer. Environ. Res. 2021, 202, 111672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Li, C.; Liu, M.; Xiong, T.; Wu, X.; Tang, Y. Balancing grain yield and environmental performance by optimizing planting patterns of rice-wheat cropping systems. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 906, 167813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martines, A.M.; Nogueira, M.A.; Santos, C.A.; Nakatani, A.S.; Andrade, C.A.; Coscione, A.R.; Cantarella, H.; Sousa, J.P.; Cardoso, E.J.B.N. Ammonia volatilization in soil treated with tannery sludge. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 4690–4696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, N.; Wang, Y.; Ye, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Huang, Y.; Fu, W.; Chu, X. Effects of continuous nitrogen fertilizer application on the diversity and composition of rhizosphere soil bacteria. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wang, L.; Peng, Y.; Zhang, S.; Lv, S.; Li, J.; Abdo, A.I.; Zhou, C.; Wang, L. Film mulching, residue retention and N fertilization affect ammonia volatilization through soil labile N and C pools. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2021, 308, 107272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, S.; Ding, J.; Yang, S.; Jiang, Z.; Xu, Y. Impact of biochar application on ammonia volatilization from paddy fields under controlled irrigation. Sustainability 2022, 14, 1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assémien, F.L.; Cantarel, A.A.M.; Florio, A.; Lerondelle, C.; Pommier, T.; Gonnety, J.T.; Le Roux, X. Different groups of nitrite-reducers and N2O-reducers have distinct ecological niches and functional roles in West African cultivated soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2019, 129, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, T.; Fang, X.; Liu, Y.; Zang, H.; Zeng, Z.; Yang, Y. Irrigation rather than fertilization drives the abundance, community structure and assembly process of soil denitrifiers. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2023, 357, 108688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

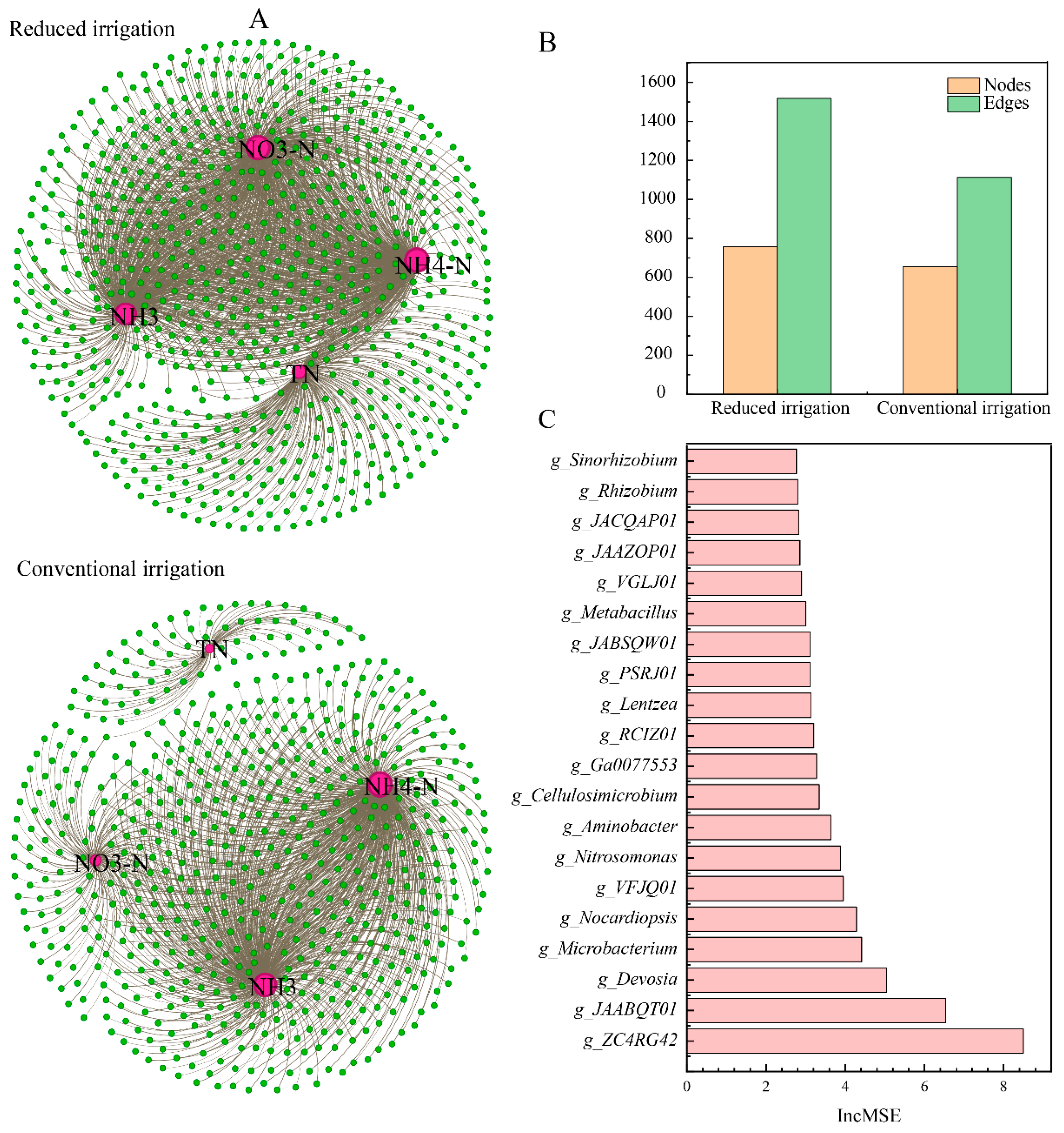
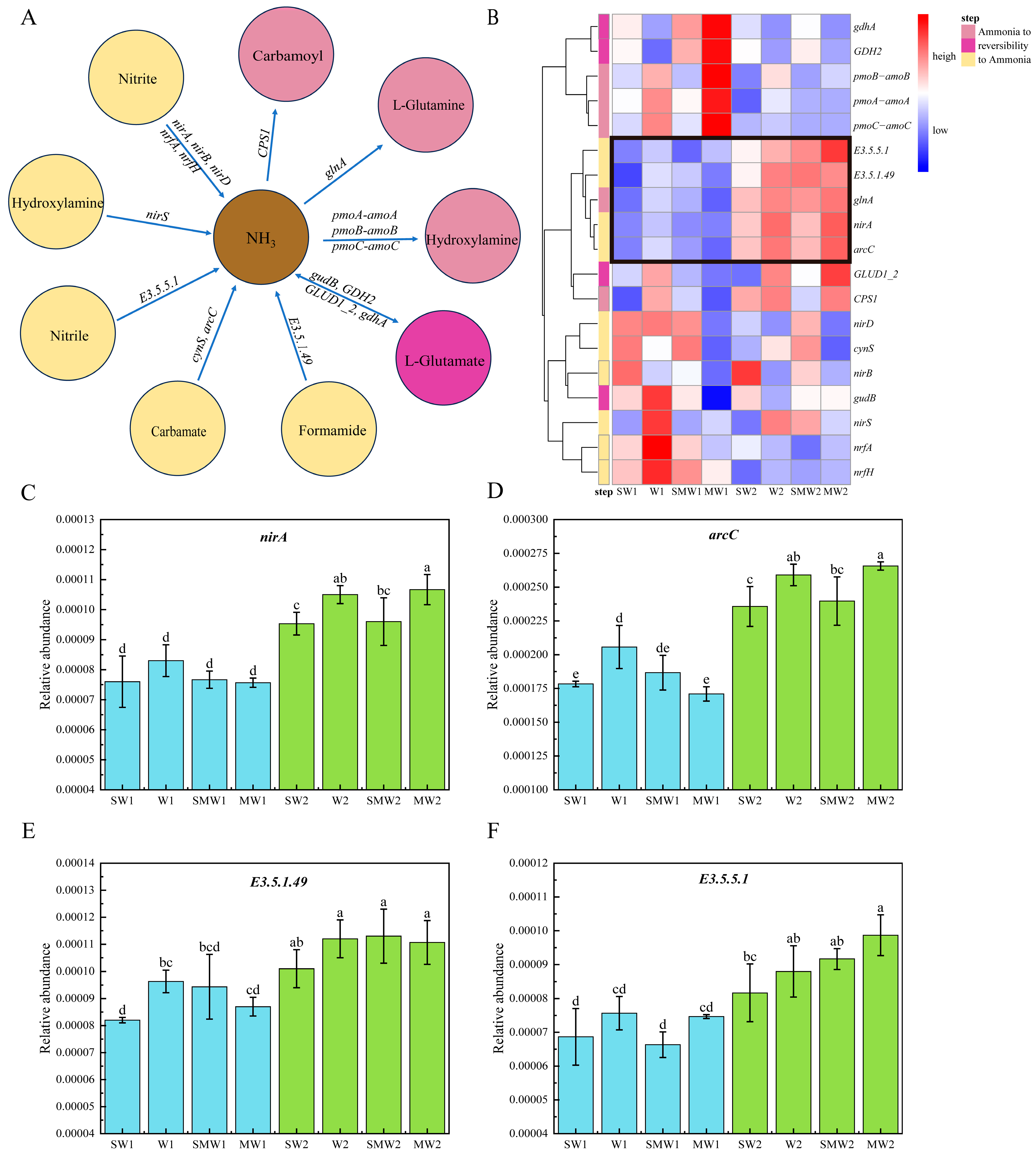
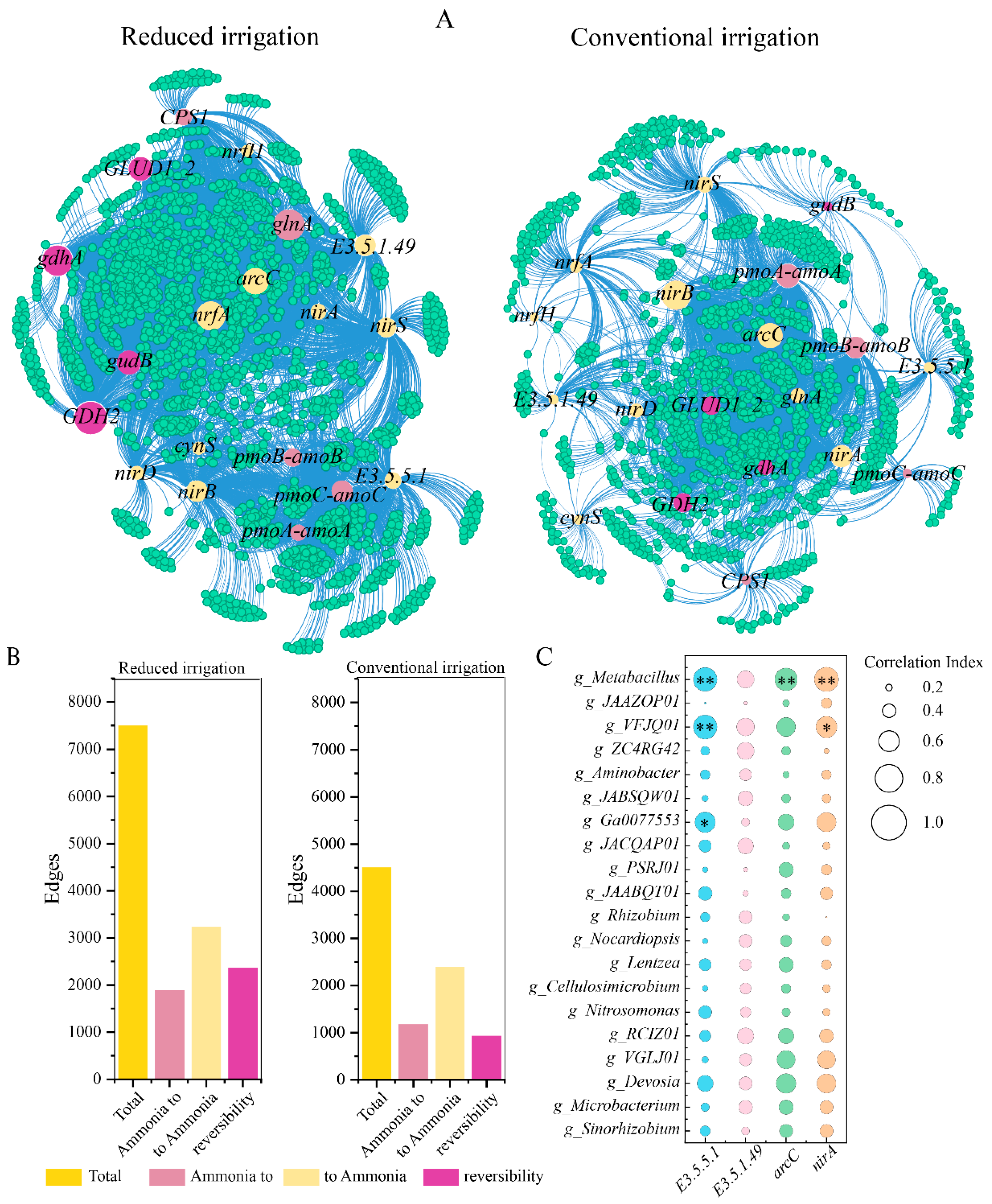
| Treatment | SW1 | W1 | SMW1 | MW1 | SW2 | W2 | SMW2 | MW2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NH4+-N (mg kg−1) | 2.82 ± 0.36 c | 7.06 ± 0.47 a | 1.55 ± 0.15 d | 5.49 ± 0.10 b | 1.03 ± 0.09 e | 2.72 ± 0.29 c | 0.83 ± 0.04 e | 1.51 ± 0.17 d |
| NO3−-N (mg kg−1) | 53.55 ± 1.54 cd | 69.08 ± 2.35 b | 43.90 ± 1.47 e | 64.78 ± 1.02 b | 55.50 ± 2.27 c | 87.45 ± 4.87 a | 45.81 ± 2.44 e | 50.87 ± 1.92 d |
| TN (mg g−1) | 0.81 ± 0.04 abc | 0.77 ± 0.05 abc | 0.76 ± 0.01 bc | 0.74 ± 0.01 c | 0.83 ± 0.02 ab | 0.80 ± 0.08 abc | 0.84 ± 0.02 a | 0.82 ± 0.01 ab |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, T.; Cui, E.; Sun, K.; Hu, C.; Li, S.; Li, P.; Zhao, Z.; Liu, C.; Cui, B.; Fan, X. Multiple Nitrogen Sources Application Inhibits Increasing Ammonia Volatilization Under Reducing Irrigation. Agronomy 2024, 14, 2927. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14122927
Chen T, Cui E, Sun K, Hu C, Li S, Li P, Zhao Z, Liu C, Cui B, Fan X. Multiple Nitrogen Sources Application Inhibits Increasing Ammonia Volatilization Under Reducing Irrigation. Agronomy. 2024; 14(12):2927. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14122927
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Taotao, Erping Cui, Ke Sun, Chao Hu, Siyi Li, Ping Li, Zhijuan Zhao, Chuncheng Liu, Bingjian Cui, and Xiangyang Fan. 2024. "Multiple Nitrogen Sources Application Inhibits Increasing Ammonia Volatilization Under Reducing Irrigation" Agronomy 14, no. 12: 2927. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14122927
APA StyleChen, T., Cui, E., Sun, K., Hu, C., Li, S., Li, P., Zhao, Z., Liu, C., Cui, B., & Fan, X. (2024). Multiple Nitrogen Sources Application Inhibits Increasing Ammonia Volatilization Under Reducing Irrigation. Agronomy, 14(12), 2927. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14122927








