Iodine Accumulation and Distribution in Carrots (Daucus carota L.)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Carrot Cultivation
2.2. Sample Processing
2.3. Iodine Determination
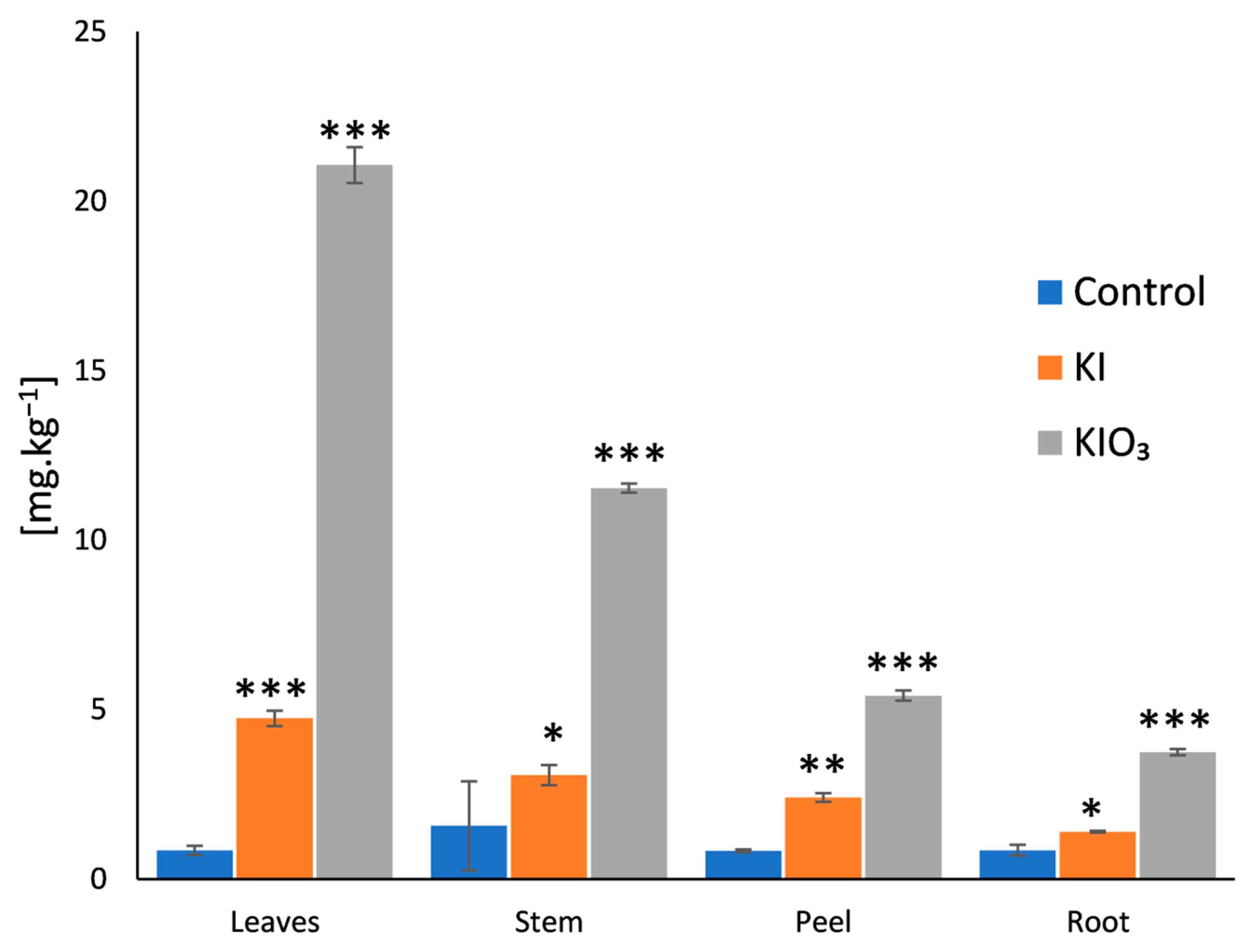
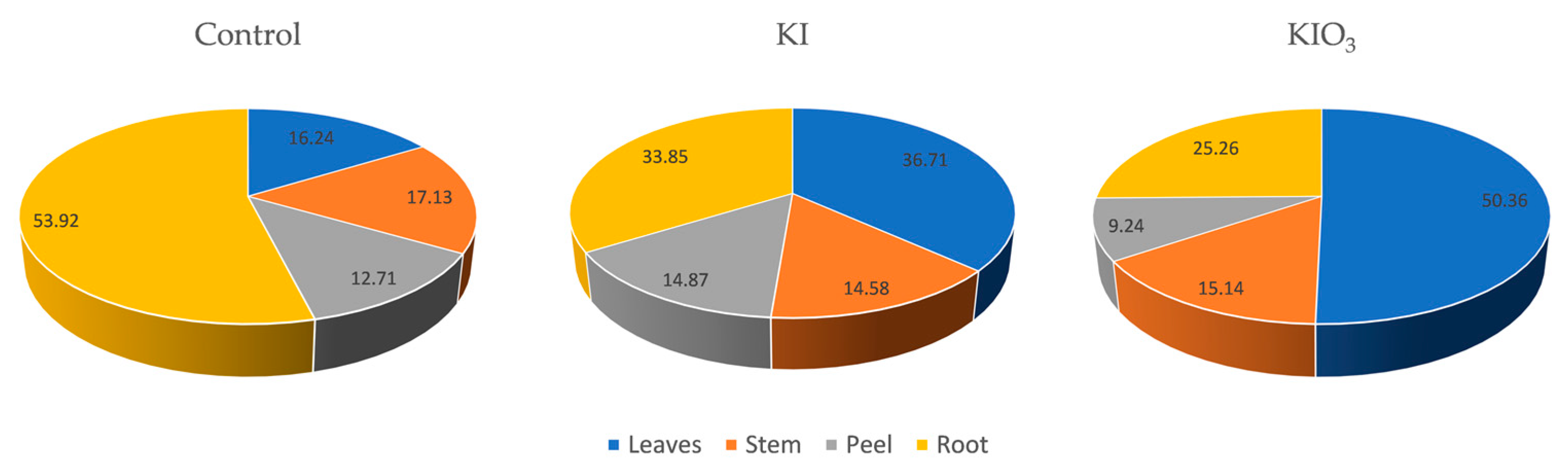
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sorrenti, S.; Baldini, E.; Pironi, D.; Lauro, A.; D’Orazi, V.; Tartaglia, F.; Tripodi, D.; Lori, E.; Gagliardi, F.; Praticò, M.; et al. Iodine: Its Role in Thyroid Hormone Biosynthesis and Beyond. Nutrients 2021, 13, 4469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, M.; Braegger, C.P. The Role of Iodine for Thyroid Function in Lactating Women and Infants. Endocr. Rev. 2021, 43, 469–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mégier, C.; Dumery, G.; Luton, D. Iodine and Thyroid Maternal and Fetal Metabolism during Pregnancy. Metabolites 2023, 13, 633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.; Meng, F.; Gao, Y.; Liu, P. Insufficient iodine nutrition may affect the thyroid cancer incidence in China. Br. J. Nutr. 2021, 126, 1852–1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malya, F.U.; Kadioglu, H.; Hasbahceci, M.; Dolay, K.; Guzel, M.; Ersoy, Y.E. The correlation between breast cancer and urinary iodine excretion levels. J. Int. Med. Res. 2017, 46, 687–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gołkowski, F.; Szybiński, Z.; Rachtan, J.; Sokołowski, A.; Buziak-Bereza, M.; Trofimiuk, M.; Hubalewska-Dydejczyk, A.; Przybylik-Mazurek, E.; Huszno, B. Iodine prophylaxis—The protective factor against stomach cancer in iodine deficient areas. Eur. J. Nutr. 2007, 46, 251–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Recommended Iodine Levels in Salt and Guidelines for Monitoring Their Adequacy and Effectiveness; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- He, F.J.; Burnier, M.; MacGregor, G.A. Nutrition in cardiovascular disease: Salt in hypertension and heart failure. Eur. Heart J. 2011, 32, 3073–3080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Global Strategy on Diet, Physical Activity and Health; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Smoleń, S.; Kowalska, I.; Halka, M.; Ledwożyw-Smoleń, I.; Grzanka, M.; Skoczylas, Ł.; Czernicka, M.; Pitala, J. Selected Aspects of Iodate and Iodosalicylate Metabolism in Lettuce Including the Activity of Vanadium Dependent Haloperoxidases as Affected by Exogenous Vanadium. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koronowicz, A.A.; Kopeć, A.; Master, A.; Smoleń, S.; Piątkowska, E.; Bieżanowska-Kopeć, R.; Ledwożyw-Smoleń, I.; Skoczylas, Ł.; Rakoczy, R.; Leszczyńska, T.; et al. Transcriptome Profiling of Caco-2 Cancer Cell Line following Treatment with Extracts from Iodine-Biofortified Lettuce (Lactuca sativa L.). PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0147336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piątkowska, E.; Kopeć, A.; Bieżanowska-Kopeć, R.; Pysz, M.; Kapusta-Duch, J.; Koronowicz, A.A.; Smoleń, S.; Skoczylas, Ł.; Ledwożyw-Smoleń, I.; Rakoczy, R.; et al. The Impact of Carrot Enriched in Iodine through Soil Fertilization on Iodine Concentration and Selected Biochemical Parameters in Wistar Rats. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0152680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, J.L.; Zhu, Y.G.; Zhang, M.; Huang, Y.Z. Selecting iodine-enriched vegetables and the residual effect of iodate application to soil. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2004, 101, 265–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, J.L.; Zhu, Y.G.; Huang, Y.Z.; Zhang, M.; Song, J.L. Availability of iodide and iodate to spinach (Spinacia oleracea L.) in relation to total iodine in soil solution. Plant Soil 2006, 289, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duborská, E.; Urík, M.; Kubová, J. Interaction with soil enhances the toxic effect of iodide and iodate on barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) compared to artificial culture media during initial growth stage. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2018, 64, 46–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiferle, C.; Martinelli, M.; Salzano, A.M.; Gonzali, S.; Beltrami, S.; Salvadori, P.A.; Hora, K.; Holwerda, H.T.; Scaloni, A.; Perata, P. Evidences for a Nutritional Role of Iodine in Plants. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 616868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cakmak, I.; Prom-u-thai, C.; Guilherme, L.R.G.; Rashid, A.; Hora, K.H.; Yazici, A.; Savasli, E.; Kalayci, M.; Tutus, Y.; Phuphong, P.; et al. Iodine biofortification of wheat, rice and maize through fertilizer strategy. Plant Soil 2017, 418, 319–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duborská, E.; Urík, M.; Bujdoš, M.; Kubová, J. Aging and Substrate Type Effects on Iodide and Iodate Accumulation by Barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). Water Air Soil Pollut. 2016, 227, 407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrett, R.A.; Hatfield, H.H., Jr.; Crosby, D.G.; Vlitos, A.J. Leaf abscission induced by the iodide ion. Plant Physiol. 1962, 37, 358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackowiak, C.L.; Grossl, P.R.; Cook, K.L. Iodine toxicity in a plant-solution system with and without humic acid. Plant Soil 2005, 269, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonacchera, M.; Dimida, A.; De Servi, M.; Frigeri, M.; Ferrarini, E.; De Marco, G.; Grasso, L.; Agretti, P.; Piaggi, P.; Aghini-Lombardi, F.; et al. Iodine Fortification of Vegetables Improves Human Iodine Nutrition: In Vivo Evidence for a New Model of Iodine Prophylaxis. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 98, E694–E697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augšpole, I.; Kince, T.; Dukalska, L. Content of sugars, dietary fibre and vitamin C in hybrids of “Nante” carrots cultivated in Latvia. Res. Rural Dev. 2012, 1, 137–142. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, T.; Cawood, M.; Iqbal, Q.; Ariño, A.; Batool, A.; Tariq, R.M.S.; Azam, M.; Akhtar, S. Phytochemicals in Daucus carota and Their Health Benefits-Review Article. Foods 2019, 8, 424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, C.L.; Weng, H.X.; Qin, Y.C.; Yan, A.L.; Xie, L.L. Transfer of iodine from soil to vegetables by applying exogenous iodine. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2008, 28, 575–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, C.-L.; Weng, H.-X.; Yan, A.L.; Xie, L.-L. Characteristics of iodine uptake and accumulation by vegetables. Yingyong Shengtai Xuebao 2007, 18, 2313–2318. [Google Scholar]
- Kato, S.; Wachi, T.; Yoshihira, K.; Nakagawa, T.; Ishikawa, A.; Takagi, D.; Tezuka, A.; Yoshida, H.; Yoshida, S.; Sekimoto, H.; et al. Rice (Oryza sativa L.) roots have iodate reduction activity in response to iodine. Front. Plant Sci. 2013, 4, 47204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiller, P.; Mercier-Bion, F.; Gimenez, N.; Barré, N.; Miserque, F. Iodination of humic acid samples from different origins. Radiochim. Acta 2006, 94, 739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawson, P.G.; Daum, D.; Czauderna, R.; Meuser, H.; Hartling, J.W. Soil versus foliar iodine fertilization as a biofortification strategy for field-grown vegetables. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smolen, S.; Sady, W. Influence of iodine form and application method on the effectiveness of iodine biofortification, nitrogen metabolism as well as the content of mineral nutrients and heavy metals in spinach plants (Spinacia oleracea L.). Sci. Hortic. 2012, 143, 176–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzali, S.; Kiferle, C.; Perata, P. Iodine biofortification of crops: Agronomic biofortification, metabolic engineering and iodine bioavailability. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2017, 44, 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smoleń, S.; Baranski, R.; Ledwożyw-Smoleń, I.; Skoczylas, Ł.; Sady, W. Combined biofortification of carrot with iodine and selenium. Food Chem. 2019, 300, 125202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobosy, P.; Endrédi, A.; Sandil, S.; Vetési, V.; Rékási, M.; Takács, T.; Záray, G. Biofortification of Potato and Carrot With Iodine by Applying Different Soils and Irrigation With Iodine-Containing Water. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 593047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapusta-Duch, J.; Bieżanowska-Kopeć, R.; Smoleń, S.; Pysz, M.; Kopeć, A.; Piątkowska, E.; Rakoczy, R.; Koronowicz, A.; Skoczylas, Ł.; Leszczyńska, T. The effect of preliminary processing and different methods of cooking on the iodine content and selected antioxidative properties of carrot (L.) biofortified with (potassium) iodine. Folia Hortic. 2017, 29, 11–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bieżanowska-Kopeć, R.; Pysz, M.; Kapusta-Duch, J.; Kopeć, A.; Smoleń, S.; Koronowicz, A.; Piątkowska, E.; Rakoczy, R.; Skoczylas, Ł.; Leszczyńska, T. The effects of peeling and cooking on the mineral content and antioxidant properties in carrots enriched with potassium iodate and/or selenite (SeIV) and selenite (SeVI). Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2016, 67, 919–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerretani, L.; Comandini, P.; Fumanelli, D.; Scazzina, F.; Chiavaro, E. Evaluation of iodine content and stability in recipes prepared with biofortified potatoes. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2014, 65, 797–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhandari, S.R.; Choi, C.S.; Rhee, J.; Shin, Y.K.; Song, J.W.; Kim, S.H.; Kang, S.; Lee, J.G. Influence of Root Color and Tissue on Phytochemical Contents and Antioxidant Activities in Carrot Genotypes. Foods 2022, 12, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Signore, A.; Renna, M.; D’Imperio, M.; Serio, F.; Santamaria, P. Preliminary Evidences of Biofortification with Iodine of “Carota di Polignano”, An Italian Carrot Landrace. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smoleń, S.; Sady, W.; Ledwożyw-Smoleń, I.; Strzetelski, P.; Liszka-Skoczylas, M.; Rożek, S. Quality of fresh and stored carrots depending on iodine and nitrogen fertilization. Food Chem. 2014, 159, 316–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skoczylas, Ł.; Tabaszewska, M.; Smoleń, S.; Słupski, J.; Liszka-Skoczylas, M.; Barański, R. Carrots (Daucus carota L.) Biofortified with Iodine and Selenium as a Raw Material for the Production of Juice with Additional Nutritional Functions. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smoleń, S.; Kowalska, I.; Kováčik, P.; Halka, M.; Sady, W. Biofortification of Six Varieties of Lettuce (Lactuca sativa L.) with Iodine and Selenium in Combination with the Application of Salicylic Acid. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goindi, G.; Karmarkar, M.G.; Kapil, U.; Jagannathan, J. Estimation of losses of iodine during different cooking procedures. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Nutr. 1995, 4, 225–227. [Google Scholar]
- Rana, R.; Raghuvanshi, R.S. Effect of different cooking methods on iodine losses. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2013, 50, 1212–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Comandini, P.; Cerretani, L.; Rinaldi, M.; Cichelli, A.; Chiavaro, E. Stability of iodine during cooking: Investigation on biofortified and not fortified vegetables. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2013, 64, 857–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Houtman, C.; Atalla, R.H. The complex of amylose and iodine. Carbohydr. Res. 1996, 292, 129–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, C.-C.; Wong, G.; Dunstan, W. Iodate Reduction Activity in Nitrate Reductase Extracts from Marine Phytoplankton. Bull. Mar. Sci. 2005, 76, 61–72. [Google Scholar]
- Smoleń, S.; Skoczylas, Ł.; Ledwożyw-Smoleń, I.; Rakoczy, R.; Liszka-Skoczylas, M.; Kopeć, A.; Piątkowska, E.; Bieżanowska-Kopeć, R.; Koronowicz, A.; Kapusta-Duch, J.; et al. The quality of carrot (L.) cultivated in the field depending on iodine and selenium fertilization. Folia Hortic. 2016, 28, 151–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smoleń, S.; Skoczylas, Ł.; Ledwożyw-Smoleń, I.; Rakoczy, R.; Kopeć, A.; Piątkowska, E.; Bieżanowska-Kopeć, R.; Koronowicz, A.; Kapusta-Duch, J. Biofortification of Carrot (Daucus carota L.) with Iodine and Selenium in a Field Experiment. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capriello, S.; Stramazzo, I.; Bagaglini, M.F.; Brusca, N.; Virili, C.; Centanni, M. The relationship between thyroid disorders and vitamin A: A narrative minireview. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 968215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carazo, A.; Macáková, K.; Matoušová, K.; Krčmová, L.K.; Protti, M.; Mladěnka, P. Vitamin A Update: Forms, Sources, Kinetics, Detection, Function, Deficiency, Therapeutic Use and Toxicity. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Sample Introduction | |
| Sample uptake | 0.40 mL·min−1 |
| Nebulizer type | Concentric PFA µFlow |
| Spray chamber | Cyclonic Quartz |
| Internal standard | 126Te 30 µg·L−1 |
| Sample background | 0.5% TMAH |
| ICP | |
| RF power | 1550 W |
| Plasma gas | Argon, 14 L·min−1 |
| Auxiliary gas | Argon, 0.8 L·min−1 |
| Cones | Nickel |
| Data Acquisition | |
| Acquisition mode | Peak hopping |
| Dwell time | 50 ms |
| Integration time | 1000 ms |
| Limit of detection | 0.01 µg·L−1 |
| Measurement uncertainty | ±1.5% |
| Type | Name | I [mg∙kg−1] | Reference Value [mg∙kg−1] |
|---|---|---|---|
| Soil | GBW07401 | 2 ± 0.2 | 1.8 ± 0.3 |
| GBW07405 | 3.8 ± 0.1 | 3.8 ± 0.5 | |
| NCS DC73325 | 19.25 ± 0.2 | 19.3 | |
| Hay powder | BCR—129 | 0.136 ± 0.02 | 0.167 ± 0.024 |
| Treatment | Background Iodine Content | Before Cultivation | After Harvest |
|---|---|---|---|
| KI | 0.63 ± 0.12 | 10.4 ± 0.15 | 8.6 ± 0.4 |
| KIO3 | 9.9 ± 0.35 | 9.0 ± 0.4 |
| Organ | Treatment | Fresh Weight [g] | Dry Weight [g] | Change [%] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Leaves | Control | 2.27 ± 1.40 | 0.53 ± 0.31 | 76.75 ± 3.21 |
| KI | 2.35 ± 0.88 | 0.55 ± 0.22 | 76.70 ± 1.00 | |
| KIO3 | 2.37 ± 0.96 | 0.55 ± 0.23 | 76.86 ± 2.06 | |
| Stem | Control | 2.40 ± 1.31 | 0.30 ± 0.15 | 87.05 ± 1.12 |
| KI | 2.69 ± 1.01 | 0.34 ± 0.12 | 87.18 ± 1.05 | |
| KIO3 | 2.15 ± 1.28 | 0.30 ± 0.17 | 86.80 ± 0.36 | |
| Peel | Control | 3.34 ± 0.84 | 0.42 ± 0.13 | 87.47 ± 1.67 |
| KI | 3.30 ± 0.47 | 0.44 ± 0.12 | 86.22 ± 5.25 | |
| KIO3 | 3.08 ± 0.93 | 0.39 ± 0.10 | 87.09 ± 1.87 | |
| Root | Control | 12.47 ± 3.87 | 1.76 ± 0.56 | 85.99 ± 1.05 |
| KI | 12.07 ± 1.60 | 1.73 ± 0.44 | 85.18 ± 5.48 | |
| KIO3 | 11.32 ± 4.26 | 1.55 ± 0.46 | 85.87 ± 2.34 |
| Plant Part | Iodine Concentration in Dry Weight Biomass [mg∙kg−1] | Iodine Species | Application Form | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Leaves | 21.06 ± 0.53 | KIO3 | 10 mg∙kg−1 pre-sowing (pot) | This study |
| 4.74 ± 0.23 | KI | |||
| 2.26–6.52 * | KI | 4 kg∙ha−1 pre-sowing (field) | [31] | |
| 83–90 | KI | 0.5 mg∙L−1 in irrigation water (greenhouse) | [32] | |
| Stem without leaves | 11.54 ± 0.13 | KIO3 | 10 mg∙kg−1 pre-sowing (pot) | This study |
| 3.07 ± 0.30 | KI | |||
| Root peel | 5.42 ± 0.15 | KIO3 | 10 mg∙kg−1 pre-sowing (pot) | This study |
| 2.41 ± 0.13 | KI | |||
| Root | 3.75 ± 0.09 | KIO3 | 10 mg∙kg−1 pre-sowing (pot) | This study |
| 1.4 ± 0.03 | KI | |||
| 2.26–2.93 * | KI | 4 kg∙ha−1 pre-sowing (field) | [31] | |
| 10–17 | KI | 0.5 mg∙L−1 in irrigation water (greenhouse) | [32] |
| Group | Soil Iodine Content [mg∙kg−1] | TF | Iodine Content in One Plant [µg] | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Leaves | Stem | Peel | Root | Leaves | Stem | Peel | Root | ||
| Control | 0.63 ± 0.11 | 1.35 ± 0.21 | 2.49 ± 2.08 | 1.32 ± 0.04 | 1.35 ± 0.25 | 0.45 ± 1 × 10−5 | 0.48 ± 4 × 10−4 | 0.35 ± 2 × 10−5 | 1.51 ± 3 × 10−4 |
| KI | 10.4 ± 1.2 | 0.46 ± 0.02 | 0.29 ± 0.02 | 0.23 ± 0.01 | 0.13 ± 0.01 | 2.62 ± 1 × 10−4 | 1.04 ± 8 × 10−5 | 1.06 ± 5 × 10−5 | 2.42 ± 4 × 10−5 |
| KIO3− | 9.90 ± 0.75 | 2.13 ± 0.05 | 1.17 ± 0.01 | 0.54 ± 0.01 | 0.37 ± 0.1 | 11.55 ± 1 × 10−4 | 3.47 ± 9 × 10−5 | 2.12 ± 6 × 10−5 | 5.79 ± 6 × 10−5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Duborská, E.; Bujdoš, M.; Matúš, P.; Diviš, P.; Urík, M. Iodine Accumulation and Distribution in Carrots (Daucus carota L.). Agronomy 2024, 14, 3015. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14123015
Duborská E, Bujdoš M, Matúš P, Diviš P, Urík M. Iodine Accumulation and Distribution in Carrots (Daucus carota L.). Agronomy. 2024; 14(12):3015. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14123015
Chicago/Turabian StyleDuborská, Eva, Marek Bujdoš, Peter Matúš, Pavel Diviš, and Martin Urík. 2024. "Iodine Accumulation and Distribution in Carrots (Daucus carota L.)" Agronomy 14, no. 12: 3015. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14123015
APA StyleDuborská, E., Bujdoš, M., Matúš, P., Diviš, P., & Urík, M. (2024). Iodine Accumulation and Distribution in Carrots (Daucus carota L.). Agronomy, 14(12), 3015. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14123015







