Comparative Transcriptome-Based Analysis of the Regulation of Leaf Senescence in the Upper and Middle Canopy of Different Soybean Cultivars
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials and Growth Conditions
2.2. Determination of Samples, Location and Period of Sampling
2.3. Determination of Chlorophyll and Leaf SPAD
2.4. Determination of Antioxidant Reductase
2.5. Leaf gas Exchange and Chlorophyll Fluorescence Analysis
2.6. RNA-Seq Analysis
2.7. Quantitative Real-Time PCR (qRT-PCR) Analysis
2.8. Data Analysis
3. Results
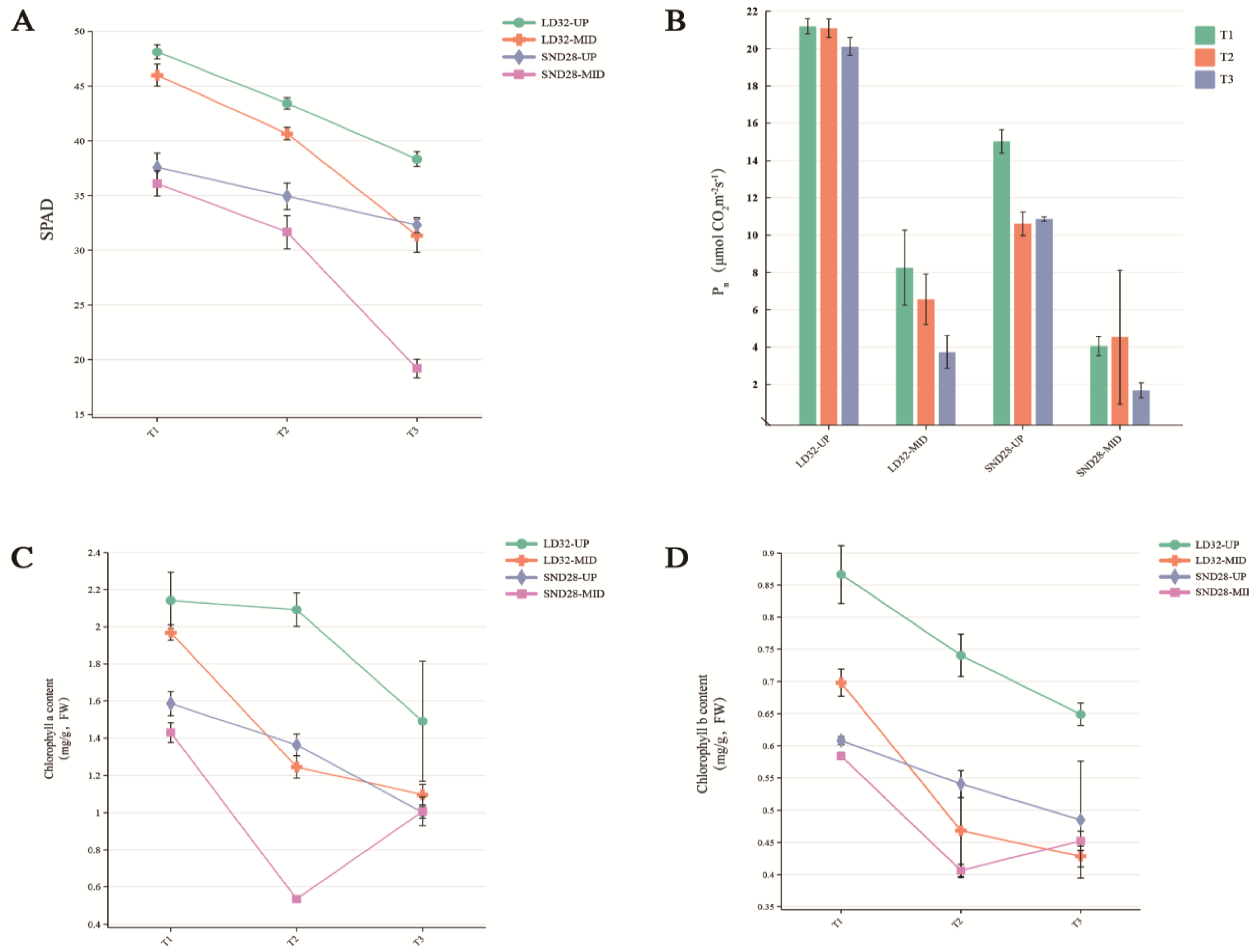
3.1. Leaf Phenotypes and Physiological Indices of Soybean
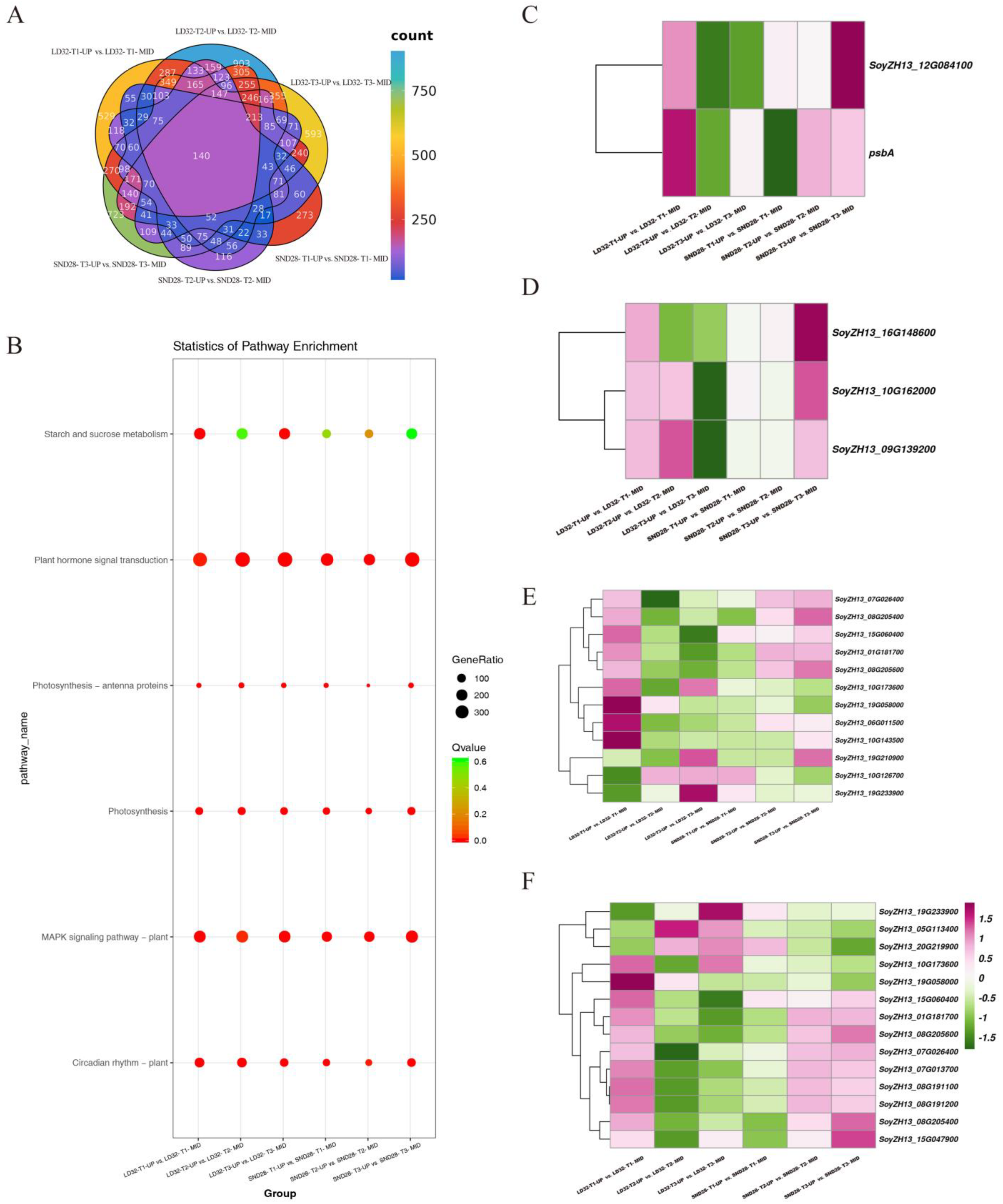
3.2. Transcriptome Differences and Enrichment Analysis
3.3. Transcriptional Analysis Reveals Enrichment Pathways Involved in Upper and Middle Leaf Senescence in the Soybean Canopy at Soybean Grain-Filling Stage
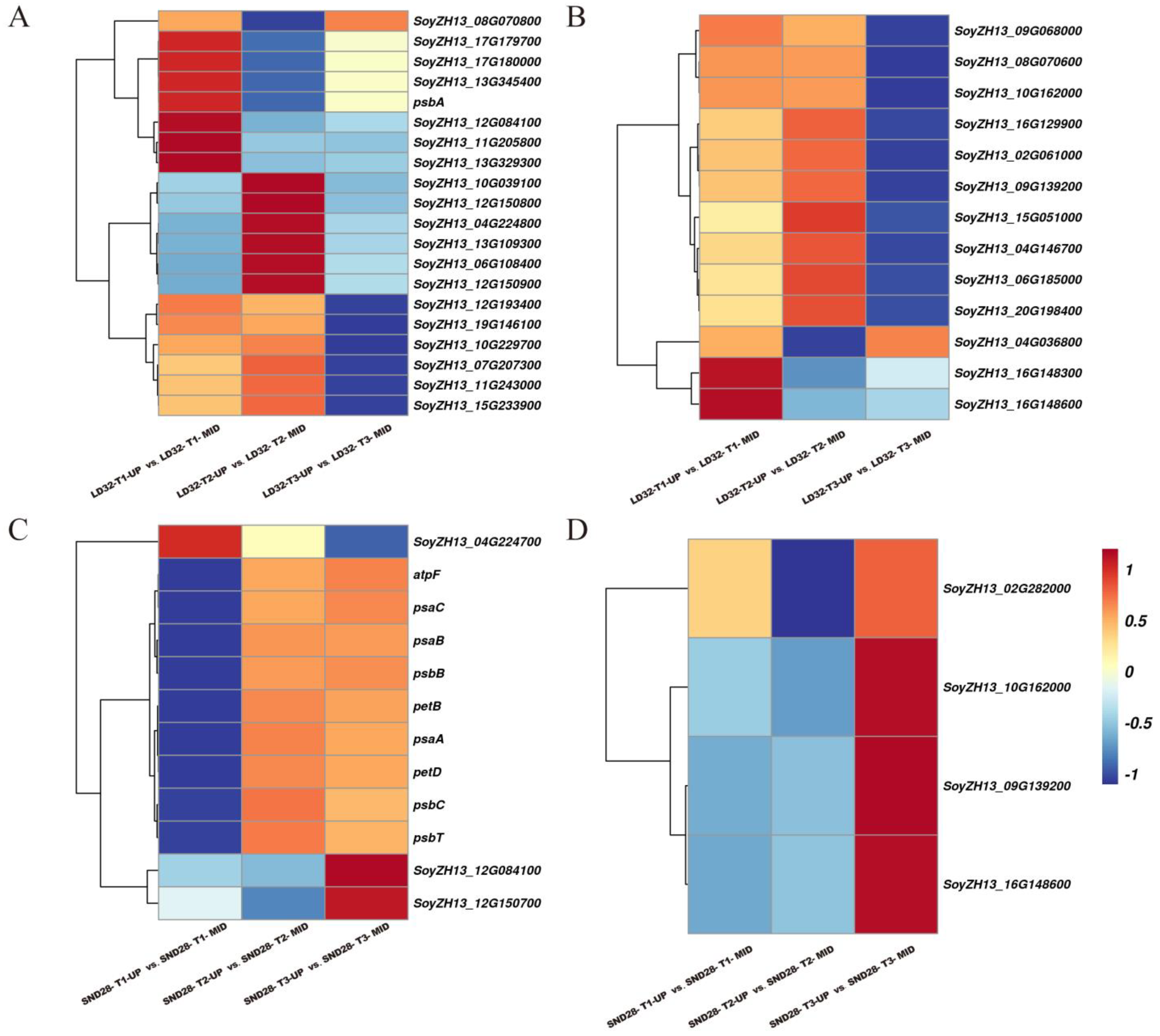
3.4. Analysis of Senescence Regulatory Pathways in the Upper and Middle Leaves of Soybean Canopy at Soybean Grain-Filling Stage
3.5. Differentially Expressed Genes in Photosynthesis-Related Pathways Involved in the Regulation of Senescence of Upper and Middle Leaves in the Soybean Canopy at Soybean Grain-Filling Stage
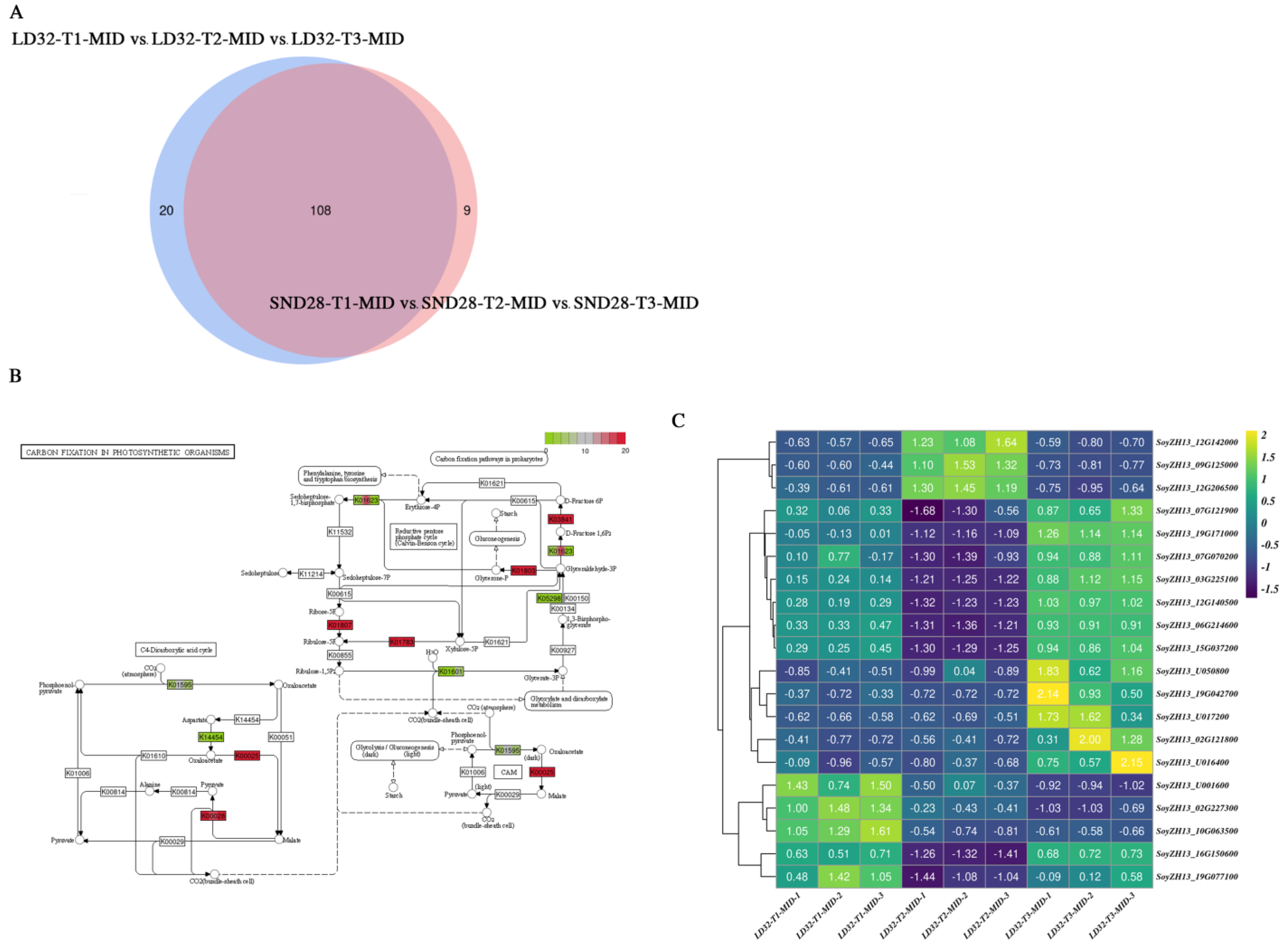
3.6. Transcriptional Analysis Reveals Differentially Expressed Genes Involved in Leaf Senescence in the Middle of the Soybean Canopy at Soybean Grain-Filling Stage
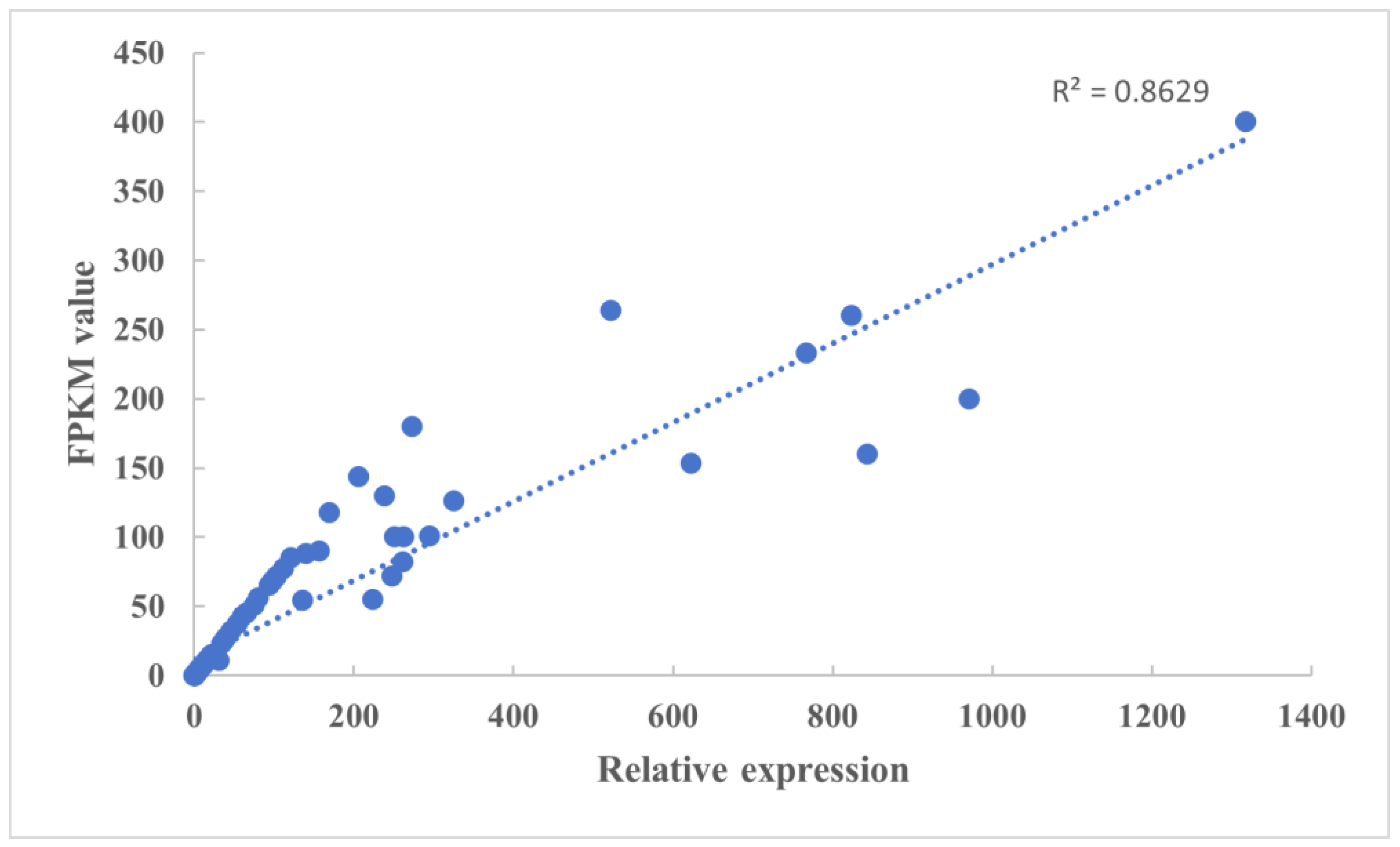
3.7. Validation of DEGs by qRT-PCR Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Leng, Y.; Ye, G.; Zeng, D. Genetic Dissection of Leaf Senescence in Rice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Lyu, X.; Li, H.; Tu, Q.; Zhao, T.; Liu, J.; Liu, B. Author Correction: The mechanism of low blue light-induced leaf senescence mediated by GmCRY1s in soybean. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Board, J.E.; Harville, B.G. Soybean Yield Component Responses to a Light Interception Gradient during the Reproductive Period. Crop Sci. 1993, 33, 772–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tranbarger, T.J.; Tucker, M.L.; Roberts, J.A.; Meir, S. Editorial: Plant Organ Abscission: From Models to Crops. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouyang, X.; Zhong, X.; Chang, S.; Qian, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, X. Partially functional NARROW LEAF1 balances leaf photosynthesis and plant architecture for greater rice yield. Plant Physiol. 2022, 189, 772–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burkey, K.O.; Wells, R. Response of soybean photosynthesis and chloroplast membrane function to canopy development and mutual shading. Plant Physiol. 1991, 97, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jumrani, K.; Bhatia, V.S.; Pandey, G.P. Impact of elevated temperatures on specific leaf weight, stomatal density, photosynthesis and chlorophyll fluorescence in soybean. Photosynth. Res. 2017, 131, 333–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Yang, J.; Yang, R.; Sicher, R.C.; Chang, C.; Tucker, M.L. Transcriptome Analysis of Soybean Leaf Abscission Identifies Transcriptional Regulators of Organ Polarity and Cell Fate. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Zhao, Y.; Tan, S.; Li, Z. Non-coding RNAs and leaf senescence: Small molecules with important roles. Plant Physiol. Bioch 2024, 207, 108399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, A.J.; Hesketh, J.D.; Peters, D.B. Soybean leaf photosynthesis in relation to maturity classification and stage of growth. Photosynth. Res. 1982, 3, 81–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Favero, B.T.; Nardy, R.; He, J.; de Godoy Maia, I.; Liu, F.; Lütken, H. Rhizobium rhizogenes rolC gene promotes leaf senescence and enhances osmotic stress resistance in Arabidopsis: The positive role of abscisic acid. Physiol. Plant. 2024, 176, e14142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, N.; Nagar, P.; Rawat, A.; Mustafiz, A. Phytosulfokine receptor 1 (AtPSKR1) acts as a positive regulator of leaf senescence by mediating ROS signaling in Arabidopsis thaliana. Env. Exp. Bot. 2024, 220, 105674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Chen, C.; Guo, R.; Zhu, X.; Tao, X.; He, M.; Li, Z.; Shen, L.; Li, Q.; Ren, D.; et al. Plasma membrane-localized hexose transporter OsSWEET1b, affects sugar metabolism and leaf senescence. Plant Cell Rep. 2024, 43, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tice, M.M.; Lowe, D.R. Hydrogen-based carbon fixation in the earliest known photosynthetic organisms. Geology 2006, 34, 37–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Chen, J.; Wang, Z.; Tan, T.; Li, S.; Li, J.; Wang, B.; Zhang, J.; Cheng, Y.; Wu, X.; et al. Soybean (Glycine max L. Merr.) seedlings response to shading: Leaf structure, photosynthesis and proteomic analysis. Bmc Plant Biol. 2019, 19, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chen, G.; Li, X.; Fu, X.; Li, S.; Tao, X.; Chen, Z.; Xu, S. Transcriptome and Metabolome Analysis of a Late-Senescent Vegetable Soybean during Seed Development Provides New Insights into Degradation of Chlorophyll. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 2480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, R.; Tanaka, A. Chlorophyll cycle regulates the construction and destruction of the light-harvesting complexes. Acta (BBA) Bioenerg. 2011, 1807, 968–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Y.N.; Zhong, R.H.; Wei, J.B.; Luo, H.H.; Eyal, Y.; Jin, H.L.; Wu, L.; Liang, K.; Li, Y.; Chen, S.; et al. Arabidopsis CHLOROPHYLLASE 1 protects young leaves from long-term photodamage by facilitating FtsH-mediated D1 degradation in photosystem II repair. Mol. Plant 2021, 14, 1149–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hörtensteiner, S.; Kräutler, B. Chlorophyll breakdown in higher plants. Acta (BBA) Bioenerg. 2010, 1807, 977–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martyna, Z.; Zbigniew, T. Biochemical and physiological aspects of chlorophyll breakdown. Postep. Biochem. 2019, 65, 128–134. [Google Scholar]
- Ulrich, E.; Bernhard, G.; Stefan, H. Recent advances in chlorophyll biosynthesis and breakdown in higher plants. Plant Mol. Biol. 2004, 56, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira, D.O.; Fraga, O.T.; Pimenta, M.R.; Caetano, H.D.N.; Machado, J.P.B.; Carpinetti, P.A.; Brustolini, O.J.B.; Quadros, I.P.S.; Reis, P.A.B.; Fontes, E.P.B. GmNAC81 Inversely Modulates Leaf Senescence and Drought Tolerance. Front. Genet. 2020, 11, 601876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, H.; Zhang, C.; Zhou, A.; Huang, H.; Tang, Y.; Li, H.; Huang, Z.; Zhang, F.; Sun, B. Transcriptome Analysis Reveals the Mechanism by Which Exogenous Melatonin Treatment Delays Leaf Senescence of Postharvest Chinese Kale (Brassica oleracea var. alboglabra). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 2250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, A.; Allu, A.D.; Garapati, P.; Siddiqui, H.; Dortay, H.; Zanor, M.I.; Asensi-Fabado, M.A.; Munné-Bosch, S.; Antonio, C.; Tohge, T.; et al. JUNGBRUNNEN1, a reactive oxygen species-responsive NAC transcription factor, regulates longevity in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2012, 24, 482–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Woo, H.R.; Kim, J.; Lim, P.O.; Lee, I.C.; Choi, S.H.; Hwang, D.; Gil Nam, H. Trifurcate Feed-Forward Regulation of Age-Dependent Cell Death Involving miR164 in Arabidopsis. Science 2009, 323, 1053–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.S.; Sakuraba, Y.; Han, S.H.; Yoo, S.C.; Paek, N.C. Mutation of the Arabidopsis NAC016 transcription factor delays leaf senescence. Plant Cell Physiol. 2013, 54, 1660–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Tang, J.; Hu, B.; Liu, L.; Ou, S.; Wu, H.; Sun, X.; Chu, J.; et al. OsNAP connects abscisic acid and leaf senescence by fine-tuning abscisic acid biosynthesis and directly targeting senescence-associated genes in rice. Prac. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 10013–10018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendes, G.C.; Reis, P.A.; Calil, I.P.; Carvalho, H.H.; Aragão, F.J.; Fontes, E.P. GmNAC30 and GmNAC81 integrate the endoplasmic reticulum stress- and osmotic stress-induced cell death responses through a vacuolar processing enzyme. Prac. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 19627–19632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, F.O.; de Melo, B.P.; Silva, Q.I.P.; Reis, P.A.B.; Fontes, E.P.B. Senescence-Associated Glycine max (Gm)NAC Genes: Integration of Natural and Stress-Induced Leaf Senescence. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8287. [Google Scholar]
- Sartory, D.P.; Grobbelaar, J.U. Extraction of Chlorophyll a from Freshwater Phytoplankton for Spectrophotometric Analysis. Hydrobiologia 1984, 114, 177–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wu, Z.; Zhou, Q.; Wang, X.; Song, S.; Dong, S. Physiological Response of Soybean Plants to Water Deficit. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 12, 809692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Kooten, O.; Snel, J.F. The Use of Chlorophyll Fluorescence Nomenclature in Plant Stress Physiology. Photosynth. Res. 1990, 25, 147–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krause, G.H.; Weis, E. Chlorophyll Fluorescence and Photosynthesis: The Basics. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 1991, 42, 313–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahim, S.S.M.; Marghoob, M.; Robert, S.; Tilgner, H.; Afshar, P.T.; Au, K.F.; Bani Asadi, N.; Gerstein, M.B.; Wong, W.H.; Snyder, M.P.; et al. Gaining comprehensive biological insight into the transcriptome by performing a broad-spectrum RNA-seq analysis. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 59. [Google Scholar]
- Yi, L.; Pimentel, H.; Bray, N.L.; Pachter, L. Gene-level differential analysis at transcript-level resolution. Genome Biol. 2018, 19, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.; Lu, D.; Wang, S.; Lu, Z.; Liu, W.; Wang, X.; Fang, Z.; He, X. Integrated transcriptomic and metabolomic analysis provides insight into the regulation of leaf senescence in rice. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- de Bianchi, S.; Dall’Osto, L.; Tognon, G.; Morosinotto, T.; Bassi, R. Minor antenna proteins CP24 and CP26 affect the interactions between photosystem II subunits and the electron transport rate in grana membranes of Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Online 2008, 20, 1012–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullet, J.E.; Burke, J.J.; Arntzen, C.J. A Developmental Study of Photosystem I Peripheral Chlorophyll Proteins. Plant Physiol. 1980, 65, 823–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, J.; Walters, R.G.; Jansson, H.S. Antisense Inhibition of the Photosynthetic Antenna Proteins CP29 and CP26: Implications for the Mechanism of Protective Energy Dissipation. Plant Cell Online 2001, 13, 1193–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zienkiewicz, M.; Ferenc, A.; Wasilewska, W.; Romanowska, E. High light stimulates Deg1-dependent cleavage of the minor LHCII antenna proteins CP26 and CP29 and the PsbS protein in Arabidopsis thaliana. Planta 2012, 235, 279–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Huang, L.; Feng, N.; Zheng, D.; Zhao, J. Exogenous Uniconazole Enhances Tolerance to Chilling Stress in Mung Beans (Vigna Radiata L.) through Cross Talk among Photosynthesis, Antioxidant System, Sucrose Metabolism, and Hormones. J. Plant Physiol. 2022, 276, 153772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, L.; Zheng, Y.; Nie, L.; Zhang, L.; Wu, Y.; Zhu, S.; Hou, J.; Shan, G.L.; Liu, T.K.; Chen, G.; et al. Transcriptional Profiling Reveals Changes in Gene Regulation and Signaling Transduction Pathways during Temperature Stress in Wucai (Brassica Campestris L.). BMC Genom. 2021, 22, 687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wu, H.; Zhang, W.; Mu, W. Ribose-5-phosphate isomerases: Characteristics, structural features, and applications. Appl. Microbiol. Biot. 2020, 104, 6429–6441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, E.; Wang, H.; Han, L.; Li, J.; Li, S.; Wang, B. Cloning and Functional Analysis of GmABCG1 Gene in Glycine max. Mol. Plant Breed. 2018, 24, 7925–7932. [Google Scholar]
- Hamada, K.; Ago, H.; Sugahara, M.; Nodake, Y.; Kuramitsu, S.; Miyano, M. Oxyanion hole-stabilized stereospecific isomerization in ribose-5-phosphate isomerase (Rpi). J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 49183–49190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruth, A.H. Chloroplast Alkaline Fructose 1,6-Bisphosphatase Exists in a Membrane-Bound Form. Plant Physiol. 1982, 3, 728–734. [Google Scholar]
- Slovacek, R.E.; Monahan, B.C. Reductive activation of fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase and the peroxide effect on chloroplast photosynthesis. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1983, 224, 310–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.-F.; Wang, T.-H.; Feng, C.-Y.; Guo, H.-F.; Guan, X.-X.; Zhang, T.-L.; Li, W.-Z.; Xing, G.-M.; Sun, S.; Tan, G.-F. Multigene manipulation of photosynthetic carbon metabolism enhances the photosynthetic capacity and biomass yield of cucumber under low-CO(2) environment. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 1005261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simkin, A.J.; McAusland, L.; Headland, L.R.; Lawson, T.; Raines, C.A. Multigene manipulation of photosynthetic carbon assimilation increases CO2 fixation and biomass yield in tobacco. J. Exp. Bot. 2015, 66, 4075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
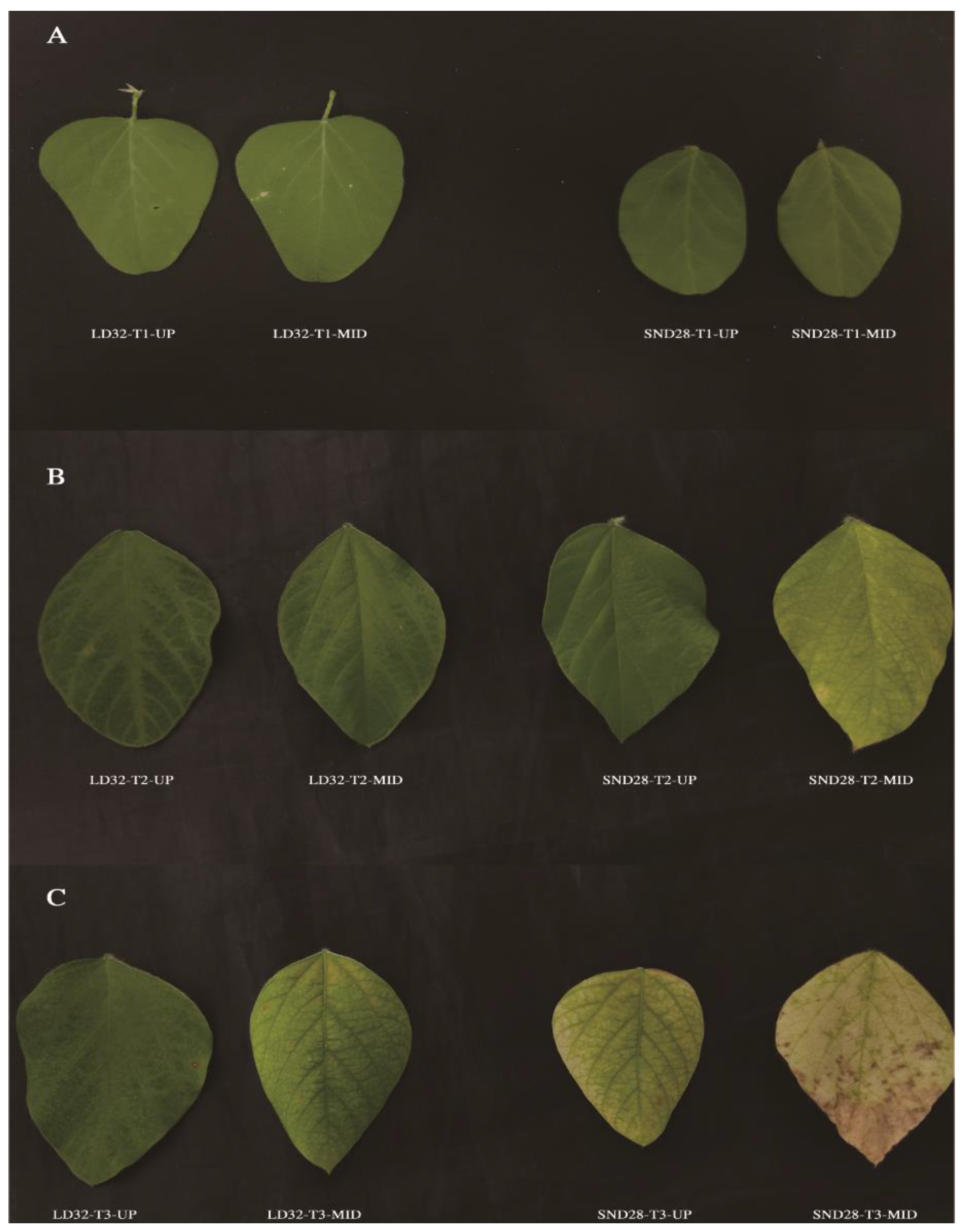




| Sample Code | Representative Meaning |
|---|---|
| LD32-T1-UP (S1) | LD32 upper canopy leaves sampled for the first time during the seed filling |
| LD32-T1-MID (S2) | LD32 middle canopy leaves sampled for the first time during the seed filling |
| LD32-T2-UP (S3) | LD32 upper canopy leaves sampled for the second time during the grain filling |
| LD32-T2-MID (S4) | LD32 middle canopy leaves sampled for the second time during the grain filling |
| LD32-T3-UP (S5) | LD32 upper canopy leaves sampled for the third time during the grain filling |
| LD32-T3-MID (S6) | LD32 middle canopy leaves sampled for the third time during the grain filling |
| SND28-T1-UP (S7) | SND28 upper canopy leaves sampled for the first time during the seed filling |
| SND28-T1-MID (S8) | SND28 middle canopy leaves sampled for the first time during the seed filling |
| SND28-T2-UP (S9) | SND28 upper canopy leaves sampled for the second time during the grain filling |
| SND28-T2-MID (S10) | SND28 middle canopy leaves sampled for the second time during the grain filling |
| SND28-T3-UP (S11 | SND28 upper canopy leaves sampled for the third time during the grain filling |
| SND28-T3-MID (S12) | SND28 middle canopy leaves sampled for the third time during the grain filling |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, N.; Zhang, Z.; Li, J.; Li, R.; Zhang, X.; Yao, X.; Xie, F. Comparative Transcriptome-Based Analysis of the Regulation of Leaf Senescence in the Upper and Middle Canopy of Different Soybean Cultivars. Agronomy 2024, 14, 1250. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14061250
Wang N, Zhang Z, Li J, Li R, Zhang X, Yao X, Xie F. Comparative Transcriptome-Based Analysis of the Regulation of Leaf Senescence in the Upper and Middle Canopy of Different Soybean Cultivars. Agronomy. 2024; 14(6):1250. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14061250
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Nan, Zhenghao Zhang, Jiayi Li, Ruoning Li, Xuejing Zhang, Xingdong Yao, and Futi Xie. 2024. "Comparative Transcriptome-Based Analysis of the Regulation of Leaf Senescence in the Upper and Middle Canopy of Different Soybean Cultivars" Agronomy 14, no. 6: 1250. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14061250
APA StyleWang, N., Zhang, Z., Li, J., Li, R., Zhang, X., Yao, X., & Xie, F. (2024). Comparative Transcriptome-Based Analysis of the Regulation of Leaf Senescence in the Upper and Middle Canopy of Different Soybean Cultivars. Agronomy, 14(6), 1250. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14061250





