Understanding the Leaching Dynamics of Lead (Pb+2) in Artificial Soils under Different Conditions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Artificial Soil Preparation and Characterization
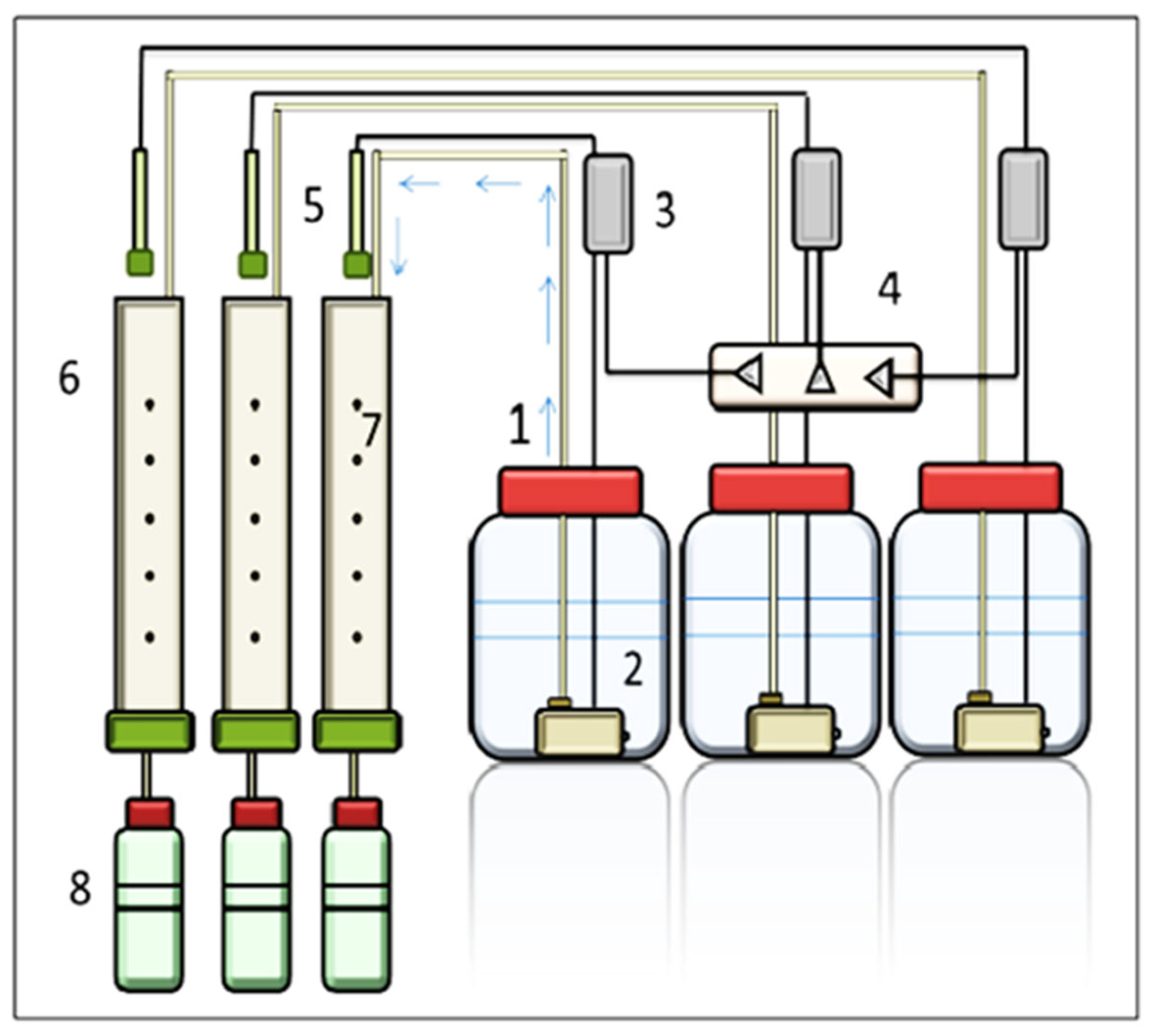
2.2. Leaching System
2.3. Determination of the Ionic Strength in the Pb (II) Leaching
2.4. Determination of pH in the Pb (II) Leaching
2.5. Determination of pH and Organic Matter in the Spatiotemporal Distribution of Pb(II) Leaching
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
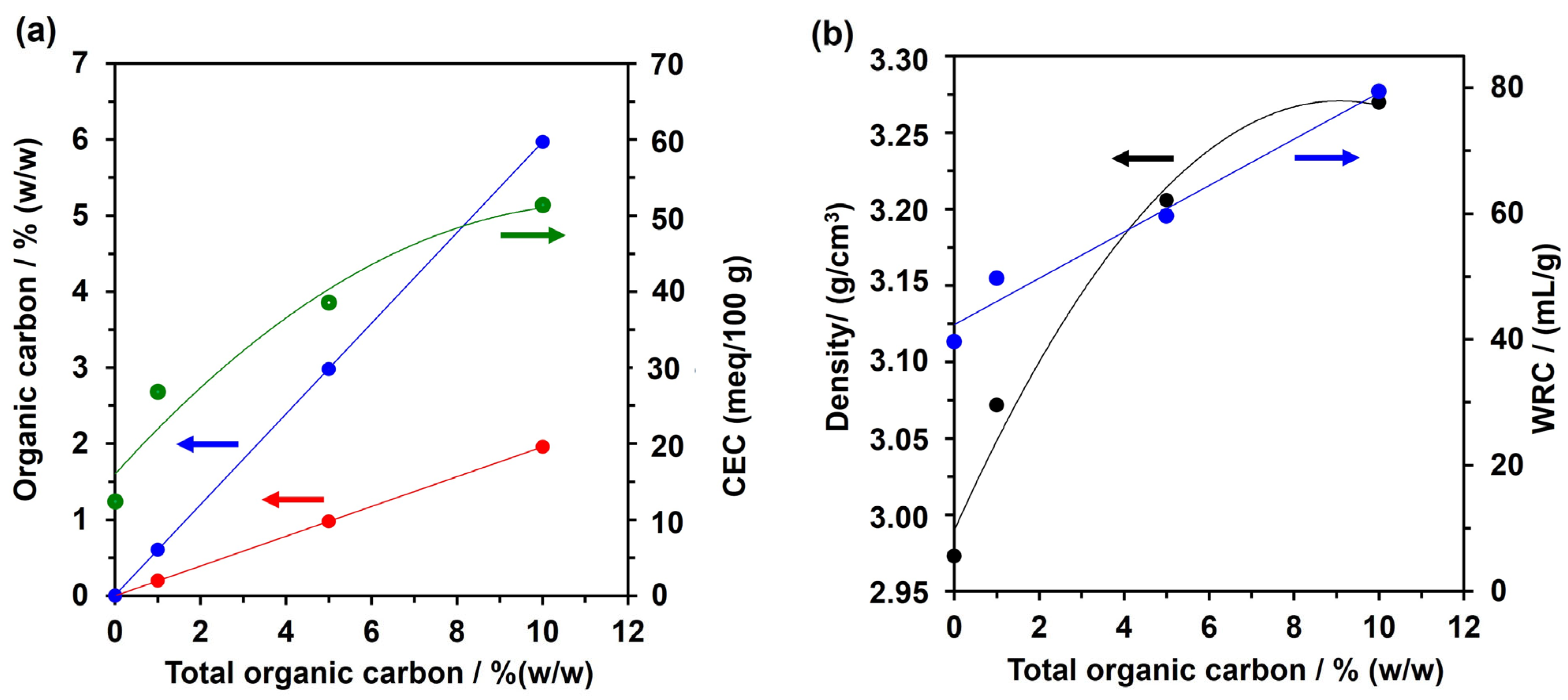
3.1. AS Characterization
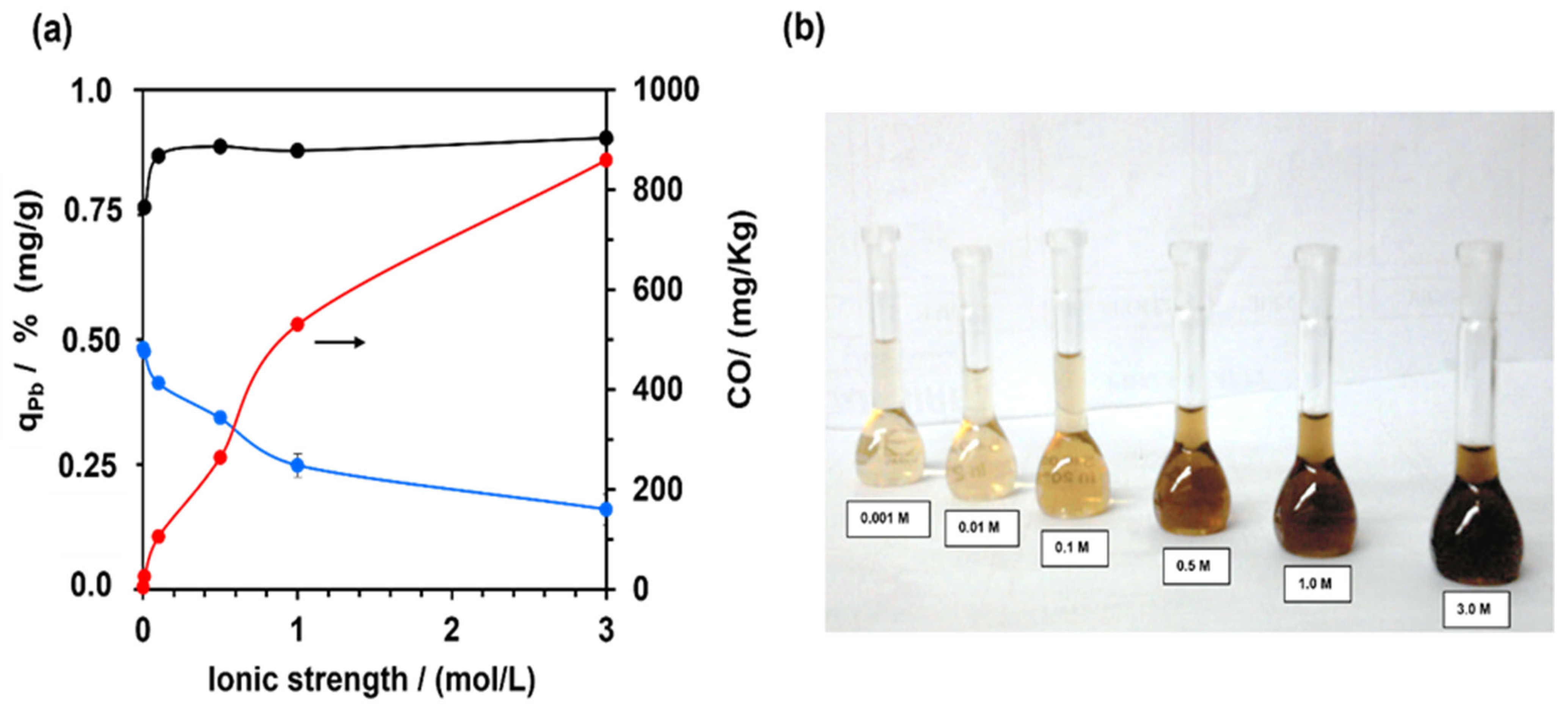
3.2. Pb (II) Leaching—Effect of the Ionic Strength
3.3. Spatiotemporal Distribution of Pb(II) in Soils
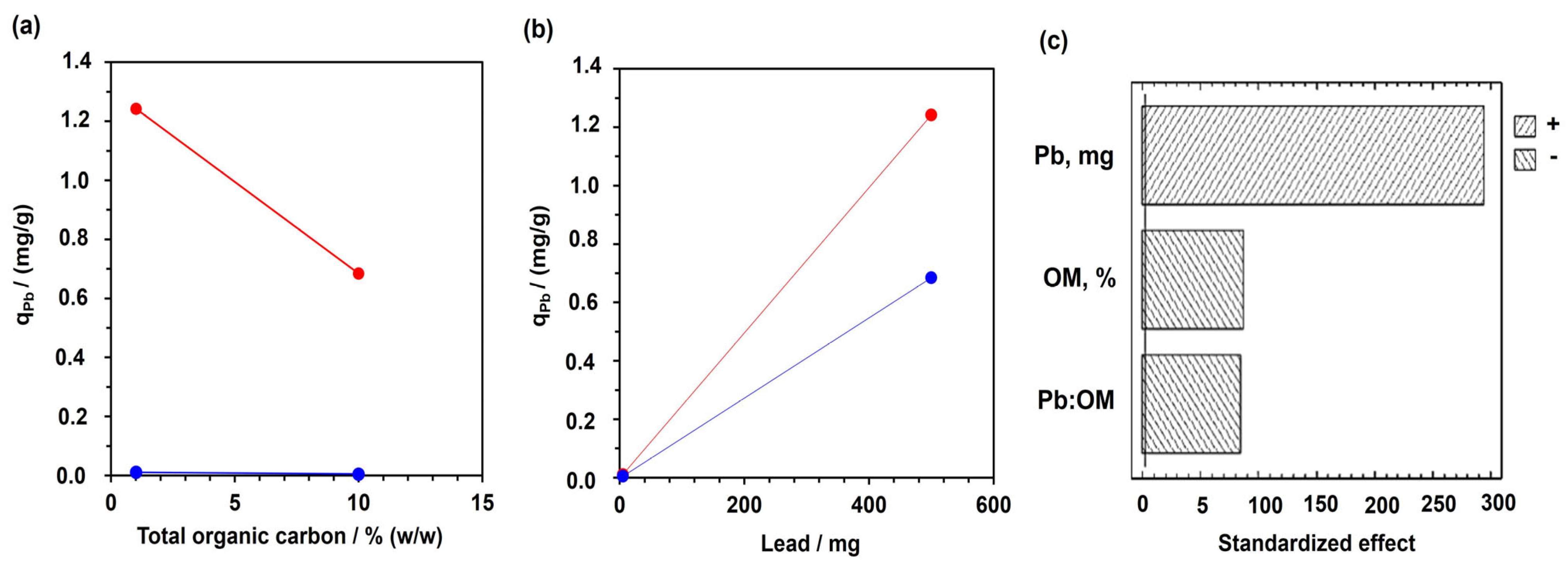
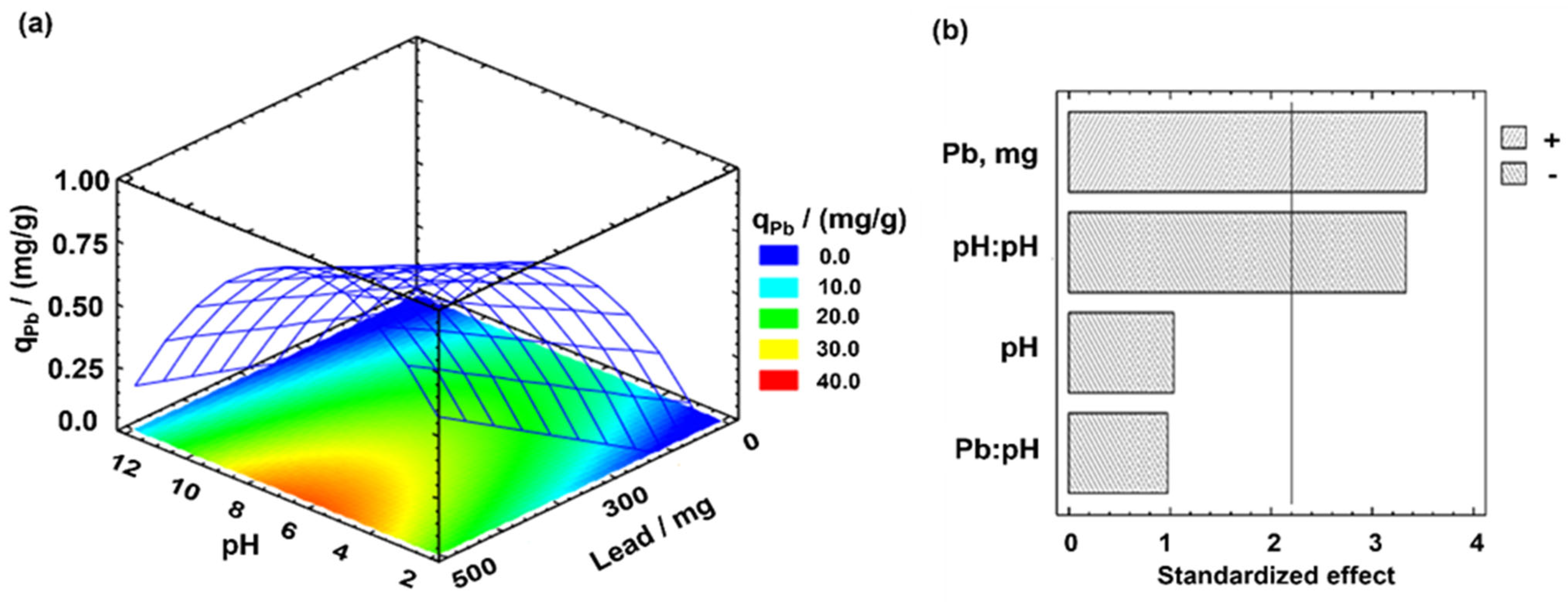
3.4. Pb (II) Leaching—Effect the Organic Matter and pH
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rashid, A.; Schutte, B.J.; Ulery, A.; Deyholos, M.K.; Sanogo, S.; Lehnhoff, E.A.; Beck, L. Heavy Metal Contamination in Agricultural Soil: Environmental Pollutants Affecting Crop Health. Agronomy 2023, 13, 1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gimeno-Garcíaa, E.; Andreua, V.; Boluda, R. Heavy metals incidence in the application of inorganic fertilizers and pesticides to rice farming soils. Environ. Pollut. 1996, 92, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mar, S.S.; Okazaki, M.; Motobayashi, T. The influence of phosphate fertilizer application levels and cultivars on cadmium uptake by Komatsuna (Brassica rapa L. var. perviridis). Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2012, 58, 492–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, B.; Yu, J.; Cao, Z.; Meng, M.; Yang, L.; Chen, Q. The Availability and Accumulation of Heavy Metals in Greenhouse Soils Associated with Intensive Fertilizer Application. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 5359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Kumar, A.; Cabral-Pinto, M.M.S.; Chaturvedi, A.K.; Shabnam, A.A.; Subrahmanyam, G.; Mondal, R.; Gupta, D.K.; Malyan, S.K.; Kumar, S.S.; et al. Lead toxicity: Health hazards, influence on food chain, and sustainable remediation approaches. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.; Wang, L.; Li, B.; He, S.; Li, Y.; He, Y.; Liang, X.; Zhan, F. Remediation of Cadmium and Lead in Mine Soil by Ameliorants and Its Impact on Maize (Zea mays L.) Cultivation. Agronomy 2024, 14, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Kim, H. Impacts of road salts on leaching behavior of lead contaminated soil. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 324, 291–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charter, R.A.; Tabatabai, M.A.; Schafer, J.W. Metal contents of fertilizers marketed in Iowa. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 1993, 24, 961–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dijkstra, J.J.; Meeussen, J.C.; Comans, R.N. Leaching of heavy metals from contaminated soils: An experimental and modeling study. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 4390–4395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elnajdi, A.; Berland, A.; Haeft, J.; Dowling, C. Influence of Soil pH, Organic Matter, and Clay Content on Environmentally Available Lead in Soils: A Case Study in Muncie, Indiana, USA. Open J. Soil Sci. 2023, 13, 414–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Costa, J.J.; Reigosa, M.J.; Matías, J.M.; Fernandez-Covelo, E. Analysis of the importance of oxides and clays in Cd, Cr, Cu, Ni, Pb and Zn adsorption and retention with regression trees. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0168523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semenov, V.M.; Tulina, A.S.; Semenova, N.A.; Ivannikova, L.A. Humification and nonhumification pathways of the organic matter stabilization in soil: A review. Eurasian Soil Sci. 2013, 46, 355–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, B.; Ullah, H.; Khan, S.; Aamir, M.; Khan, A.; Khan, W. Sources and contamination of heavy metals in sediments of Kabul River: The role of organic matter in metals retention and accumulation. Soil Sediment Contam. Int. J. 2016, 25, 891–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wang, C.X.; Wang, Z.J.; Cao, Z.H. Fractionation of heavy metals in surface sediments of Taihu Lake, East China. Environ. Geochem. Health 2004, 26, 303–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nawab, J.; Khan, S.; Aamir, M.; Shamshad, I.; Qamar, Z.; Din, I.; Huang, Q. Organic amendments impact the availability of heavy metal (loid) s in mine-impacted soil and their phytoremediation by Penisitum americanum and Sorghum bicolor. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 2381–2390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parvin, A.; Moniruzzaman, M.; Hossain, M.K.; Saha, B.; Parvin, A.; Suchi, P.D.; Hoque, S. Chemical speciation and potential mobility of heavy metals in organic matter amended soil. Appl. Environ. Soil Sci. 2022, 2022, 2028860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Andica, R.A.; Chamorro-Rengifo, A.F.; Páez-Melo, M.I. Assessment of the effect of organic matter on the retention of Pb+2 in artificial soils. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2021, 232, 426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Molinari, S.; Dalconi, M.C.; Valentini, L.; Ricci, G.; Carrer, C.; Ferrari, G.; Artioli, G. The leaching behaviors of lead, zinc, and sulfate in pyrite ash contaminated soil: Mineralogical assessments and environmental implications. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 109687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauvé, S.; McBride, M.; Hendershot, W. Soil Solution Speciation of Lead(II): Effects of Organic Matter and pH. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1998, 62, 618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, X.; Sun, J.; Shaghaleh, H.; Jiang, X.; Yu, H.; Zhai, S.; Hamoud, Y.A. Environmental assessment of soils and crops based on heavy metal risk analysis in Southeastern China. Agronomy 2023, 13, 1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhu, C.; Liu, F.; Yuan, Y.; Wu, H.; Li, A. Effects of ionic strength on removal of toxic pollutants from aqueous media with multifarious adsorbents: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 646, 265–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Li, W.; Yin, X.; Wang, N.; Yuan, S.; Yan, T.; Qu, S.; Yang, X.; Chen, D. Cd (II) adsorption on different modified rice straws under FTIR spectroscopy as influenced by Initial pH, Cd (II) concentration, and Ionic strength. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 4129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, Y.J.; Wei, M.L.; Reddy, K.R.; Liu, Z.P.; Jin, F. Effect of acid rain pH on leaching behavior of cement stabilized lead-contaminated soil. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 271, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Instituto Colombiano de Normas Técnicas, ICONTEC. 2011. Agricultural Industry Products. Organic Products Used as Fertilizers and Soil Amendments. (NTC 5167). Available online: https://tienda.icontec.org/gp-ntc-productos-para-la-industria-agricola-productos-organicos-usados-como-abonos-o-fertilizantes-y-enmiendas-o-acondicionadores-de-suelo-ntc5167-2022.html (accessed on 18 June 2024).
- Instituto Colombiano de Normas Técnicas, ICONTEC. 2011. Soil Quality. Determination of Organic Carbon. NTC 5403. Available online: https://tienda.icontec.org/gp-calidad-del-suelo-determinacion-del-carbono-organico-ntc5403-2021.html (accessed on 18 June 2024).
- Gutiérrez, P.H.; De la Vara, S.R. Análisis y Diseño de Experimentos, 3rd ed.; McGrawHill: Mexico City, Mexico, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Ukalska-jaruga, A.; Bejger, R.; Debaene, G.; Smreczak, B. Characterization of soil organic matter individual fractions (fulvic acids, humic acids, and humins) by spectroscopic and electrochemical techniques in agricultural soils. Agronomy 2021, 11, 1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, M.; Kumar, D. Parameters of Soil Chemistry. In Applied Soil Chemistry; Ahamed, M.I., Ed.; Wiley: Beverly, MA, USA, 2021; pp. 197–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Liu, M.; Peng, S.; Li, J.; Liang, Y.; Shi, Z. Binding characteristics of heavy metals to humic acid before and after fractionation by ferrihydrite. Chemosphere 2019, 226, 140–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islam, M.A.; Morton, D.W.; Johnson, B.B.; Angove, M.J. Adsorption of humic and fulvic acids onto a range of adsorbents in aqueous systems, and their effect on the adsorption of other species: A review. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 247, 116949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Yang, S.; Yang, S.; Hu, J.; Tan, X.; Wang, X. Effect of pH, ionic strength and temperature on sorption of Pb (II) on NKF-6 zeolite studied by batch technique. J. Chem. Eng. 2011, 168, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamar, R.T.; Olk, D.C.; Mayhew, L.; Bloom, P.R. A new standardized method for quantification of humic and fulvic acids in humic ores and commercial products. J. AOAC Int. 2014, 97, 721–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappuyns, V.; Swennen, R. The use of leaching tests to study the potential mobilization of heavy metals from soils and sediments: A comparison. Wat. Air Soil Poll. 2008, 191, 95–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amini, M.; Younesi, H.; Bahramifar, N.; Lorestani, A.A.Z.; Ghorbani, F.; Daneshi, A.; Sharifzadeh, M. Application of response surface methodology for optimization of lead biosorption in an aqueous solution by Aspergillus niger. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 154, 694–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, K.; Liu, K.; Peng, Q.; Zhou, M. Adsorption of Pb (II) and Zn (II) ions on humus-like substances modified montmorillonite. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2021, 631, 127706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| OM 0% | OM 1% | OM 5% | OM 10% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Humus (%) | 0.00 | 12.44 | 37.50 | 78.55 |
| Bentonite (%) | 10.54 | 10.65 | 10.52 | 10.71 |
| Kaolin (%) | 10.54 | 10.64 | 10.52 | 10.71 |
| PVC (%) | 78.92 | 66.26 | 41.46 | 0.00 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chamorro, A.F.; Sánchez-Andica, R.A. Understanding the Leaching Dynamics of Lead (Pb+2) in Artificial Soils under Different Conditions. Agronomy 2024, 14, 1520. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14071520
Chamorro AF, Sánchez-Andica RA. Understanding the Leaching Dynamics of Lead (Pb+2) in Artificial Soils under Different Conditions. Agronomy. 2024; 14(7):1520. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14071520
Chicago/Turabian StyleChamorro, Andrés Felipe, and Rubén Albeiro Sánchez-Andica. 2024. "Understanding the Leaching Dynamics of Lead (Pb+2) in Artificial Soils under Different Conditions" Agronomy 14, no. 7: 1520. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14071520
APA StyleChamorro, A. F., & Sánchez-Andica, R. A. (2024). Understanding the Leaching Dynamics of Lead (Pb+2) in Artificial Soils under Different Conditions. Agronomy, 14(7), 1520. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14071520





