Influence of Lateral Length and Residual Chlorine Concentration on Soil Nitrogen and Soil Enzyme Activities under Drip Irrigation with Secondary Sewage Effluent
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Field
2.2. Experimental Arrangement
2.3. Irrigation and Fertigation
2.4. Water Physical and Biochemical Characteristics
2.5. Soil, Plant, and Chlorine Sample Collection and Measurements
2.5.1. Soil Collection
2.5.2. Plant Measurements
2.5.3. Chlorine Measurements
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
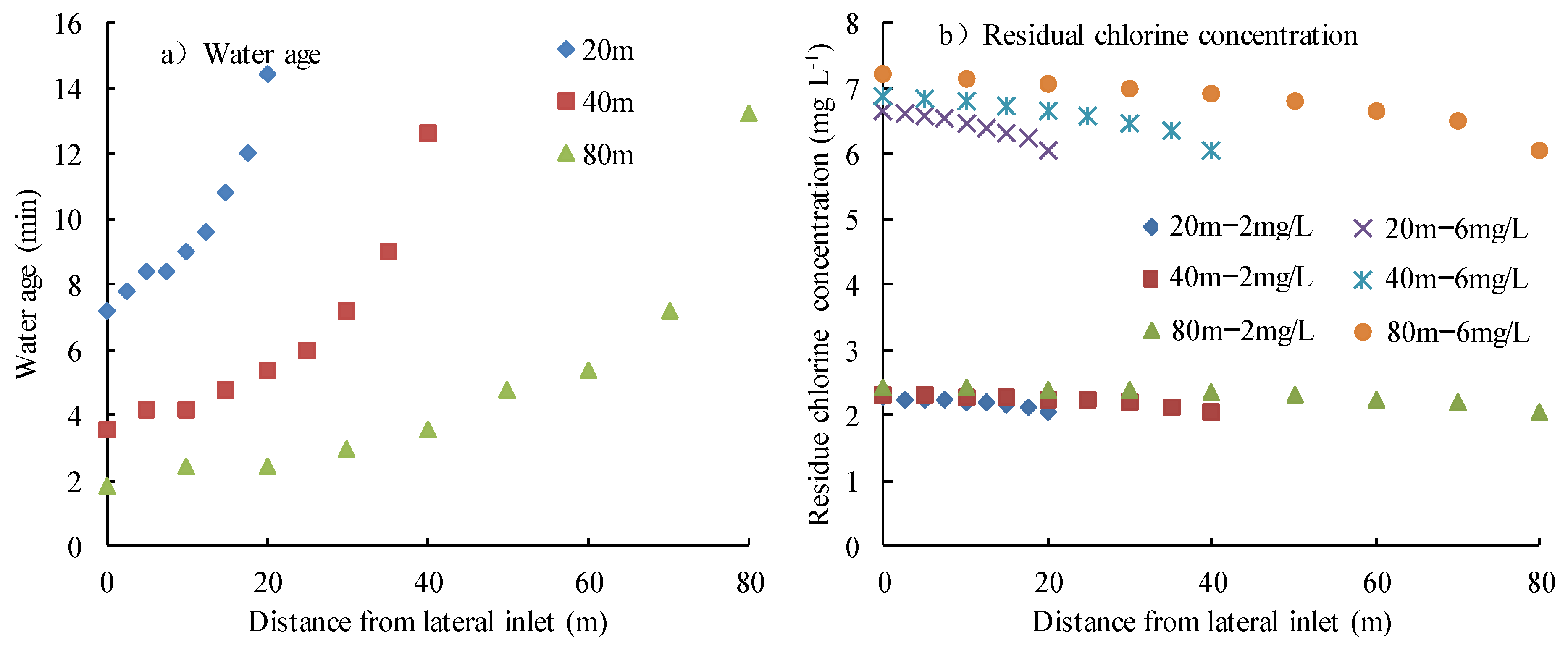
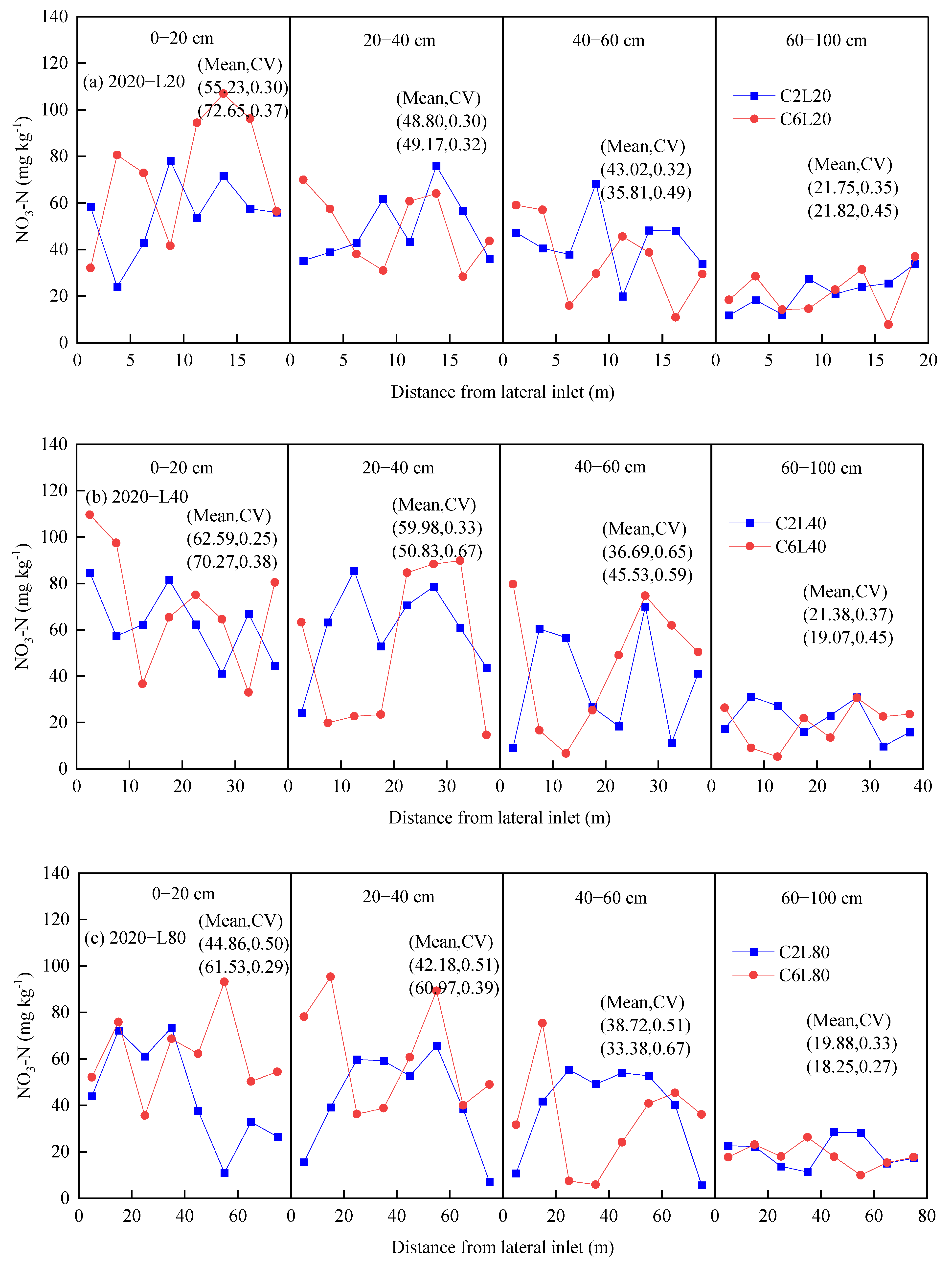
3.1. Distribution of Chlorine along Laterals
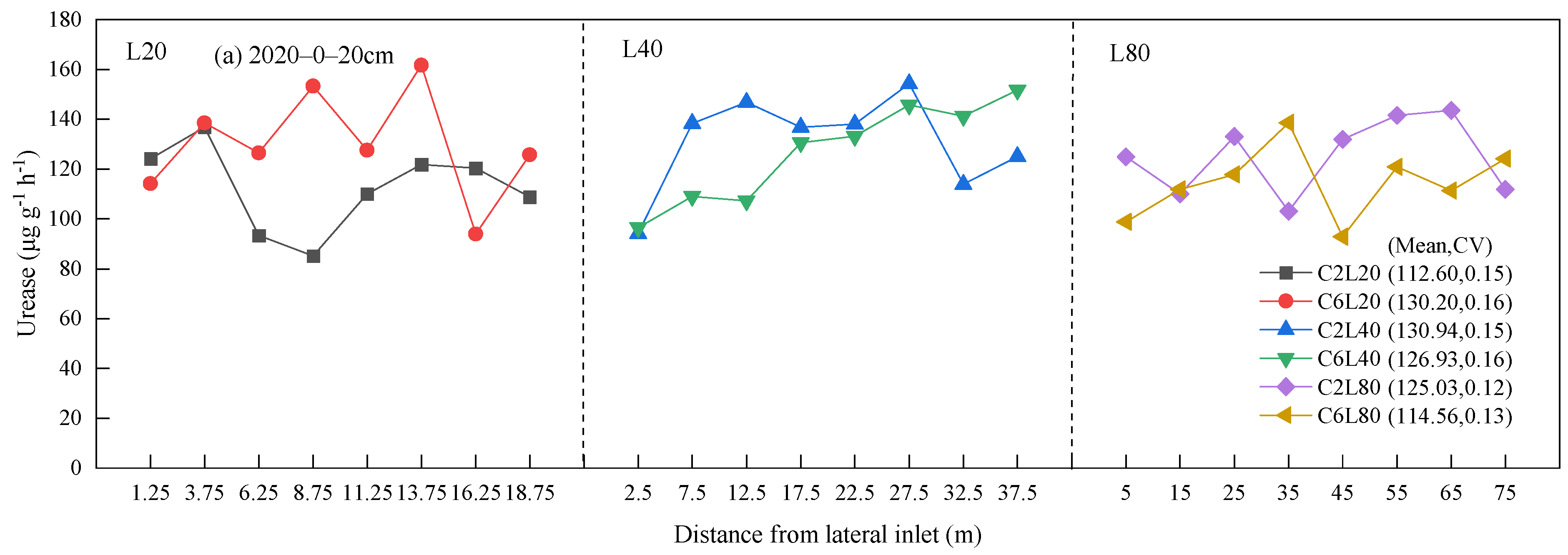
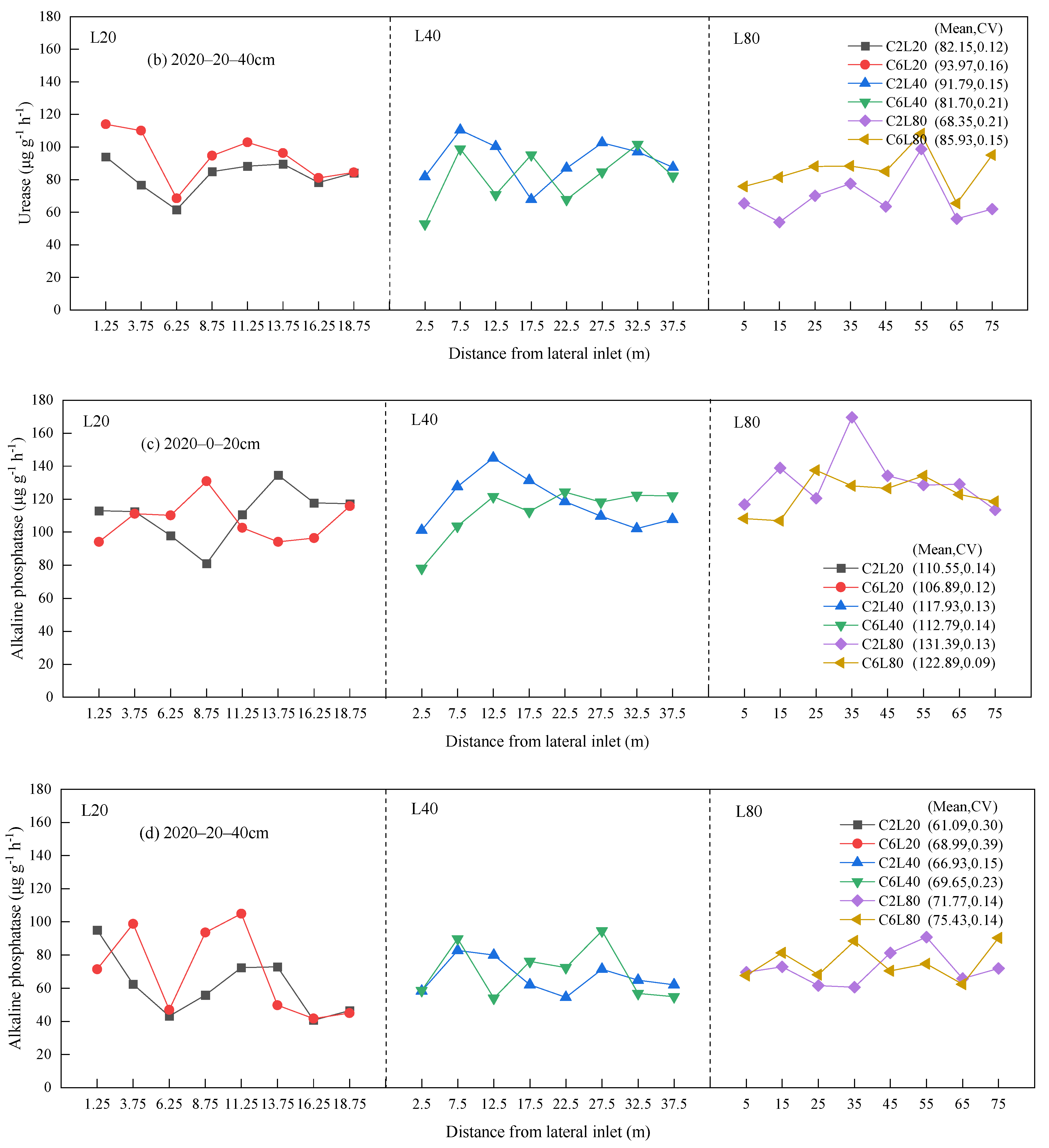
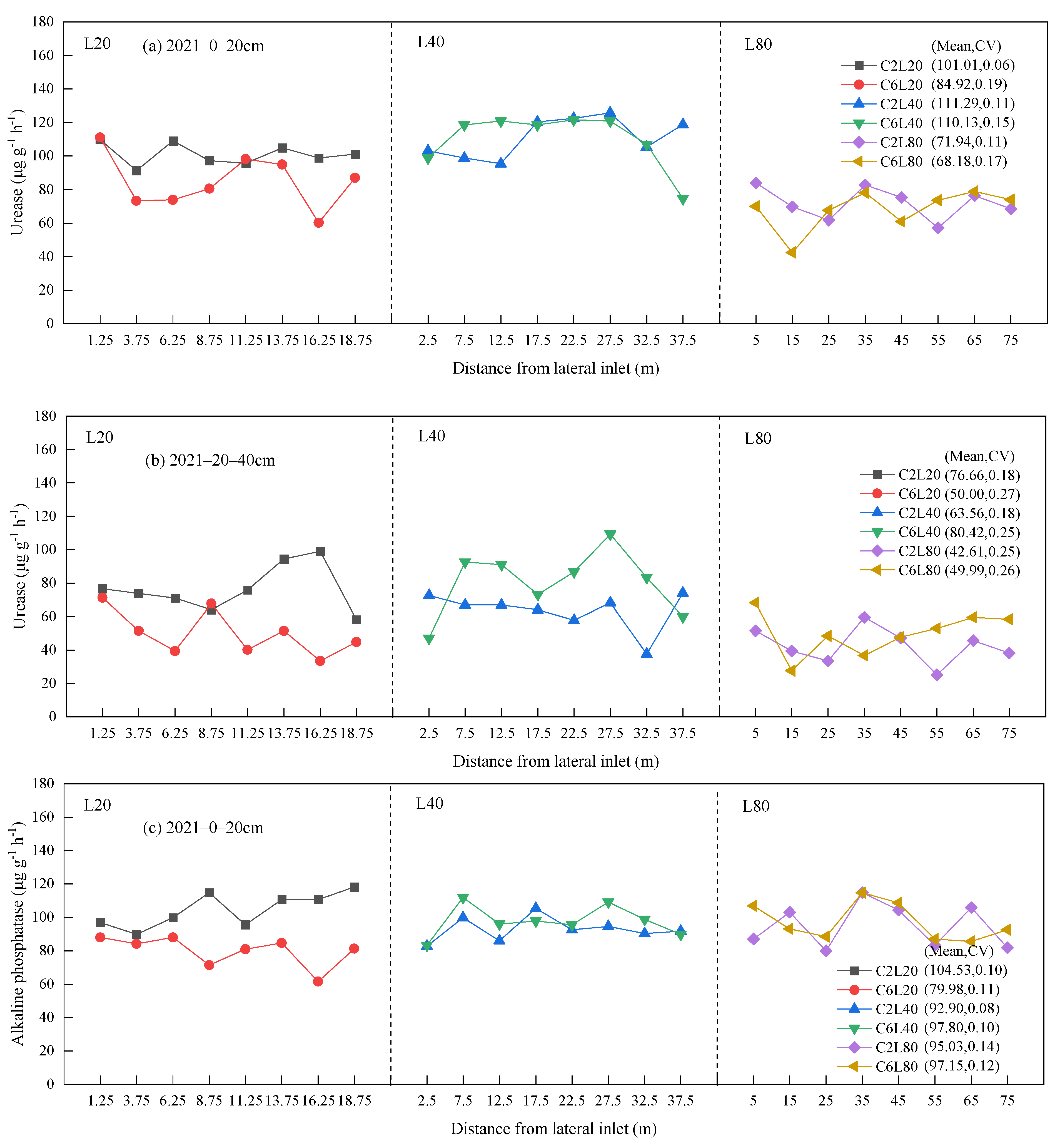
3.2. Distribution of Soil Urease and Alkaline Phosphatase Activities
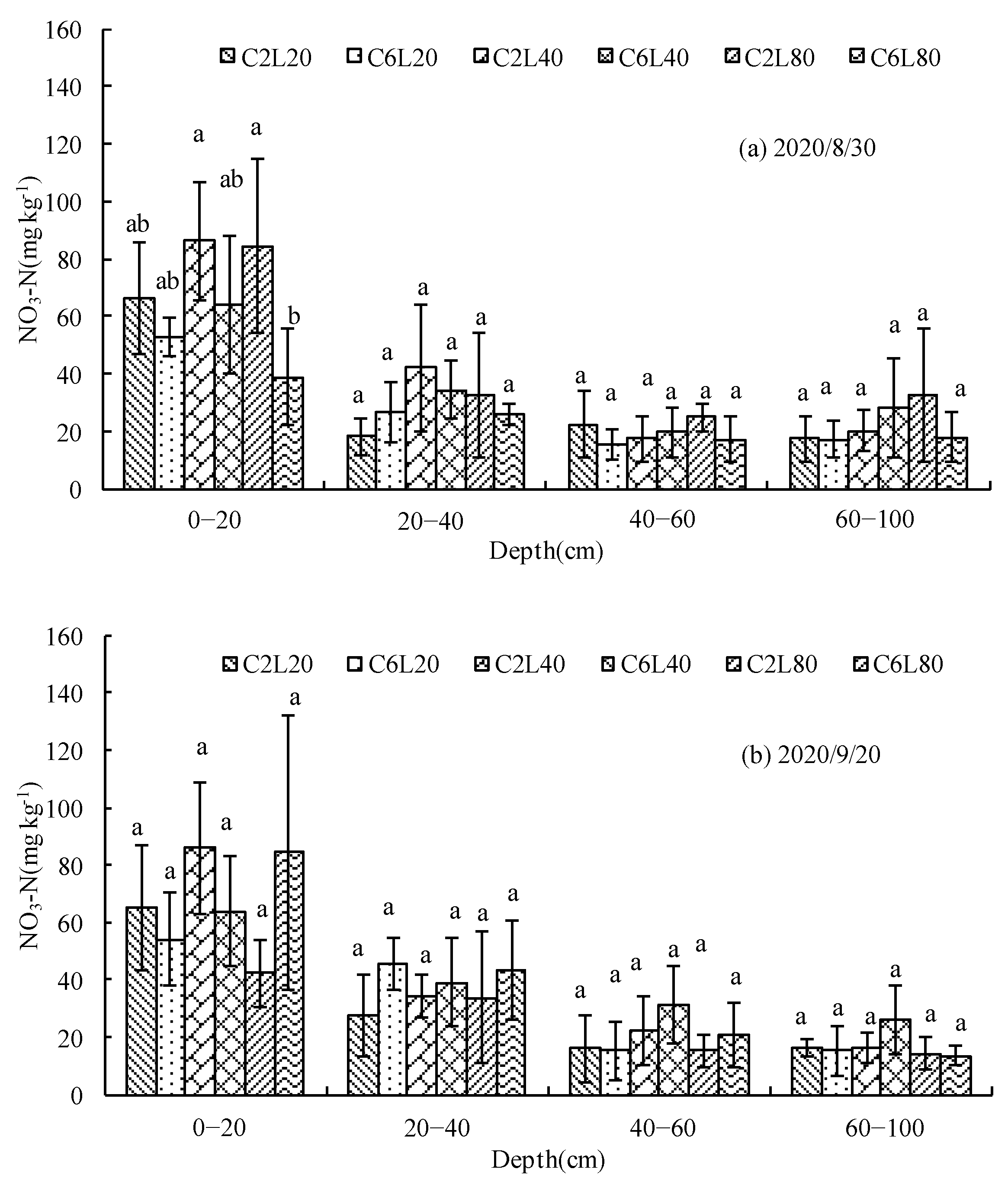
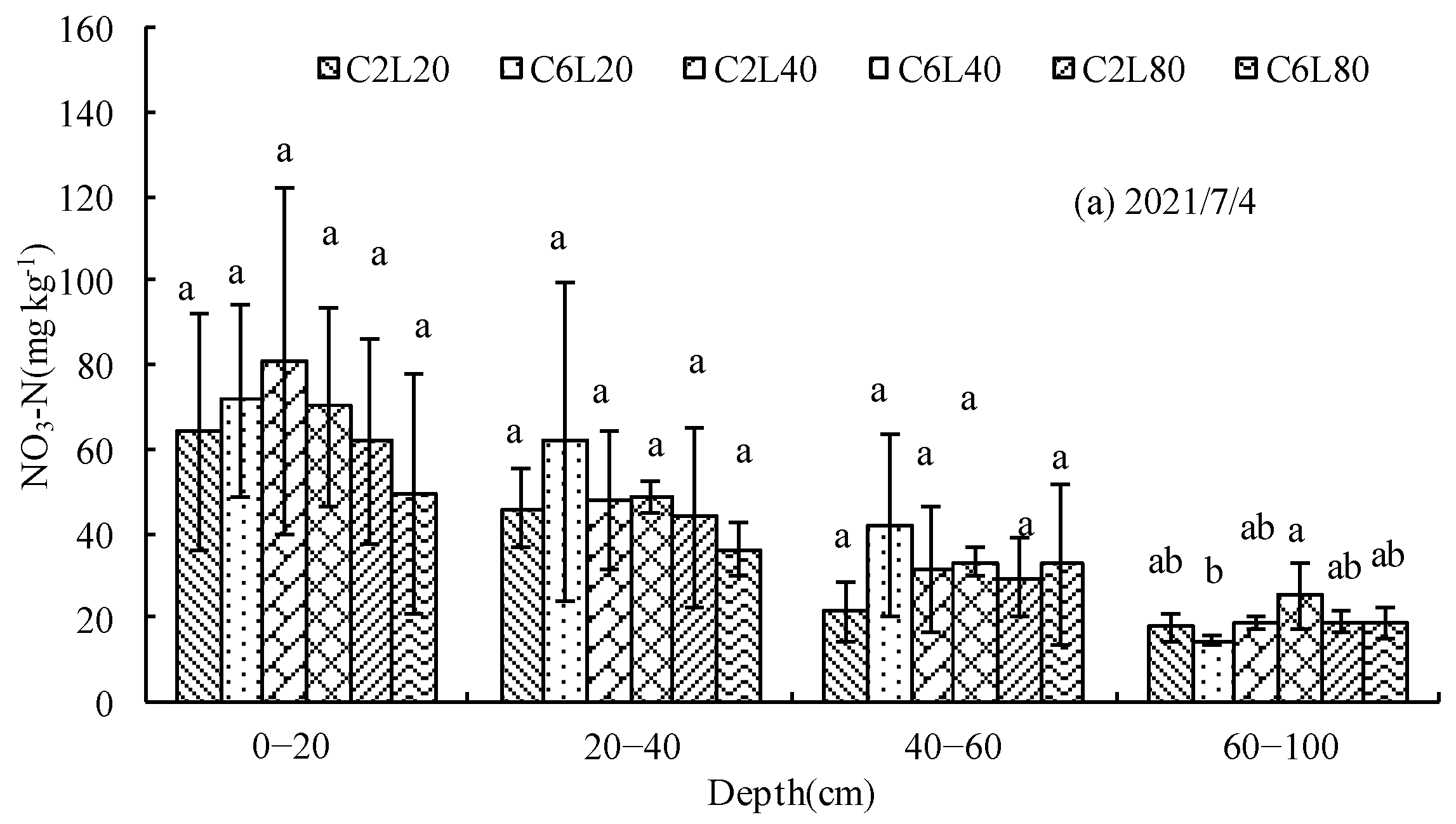
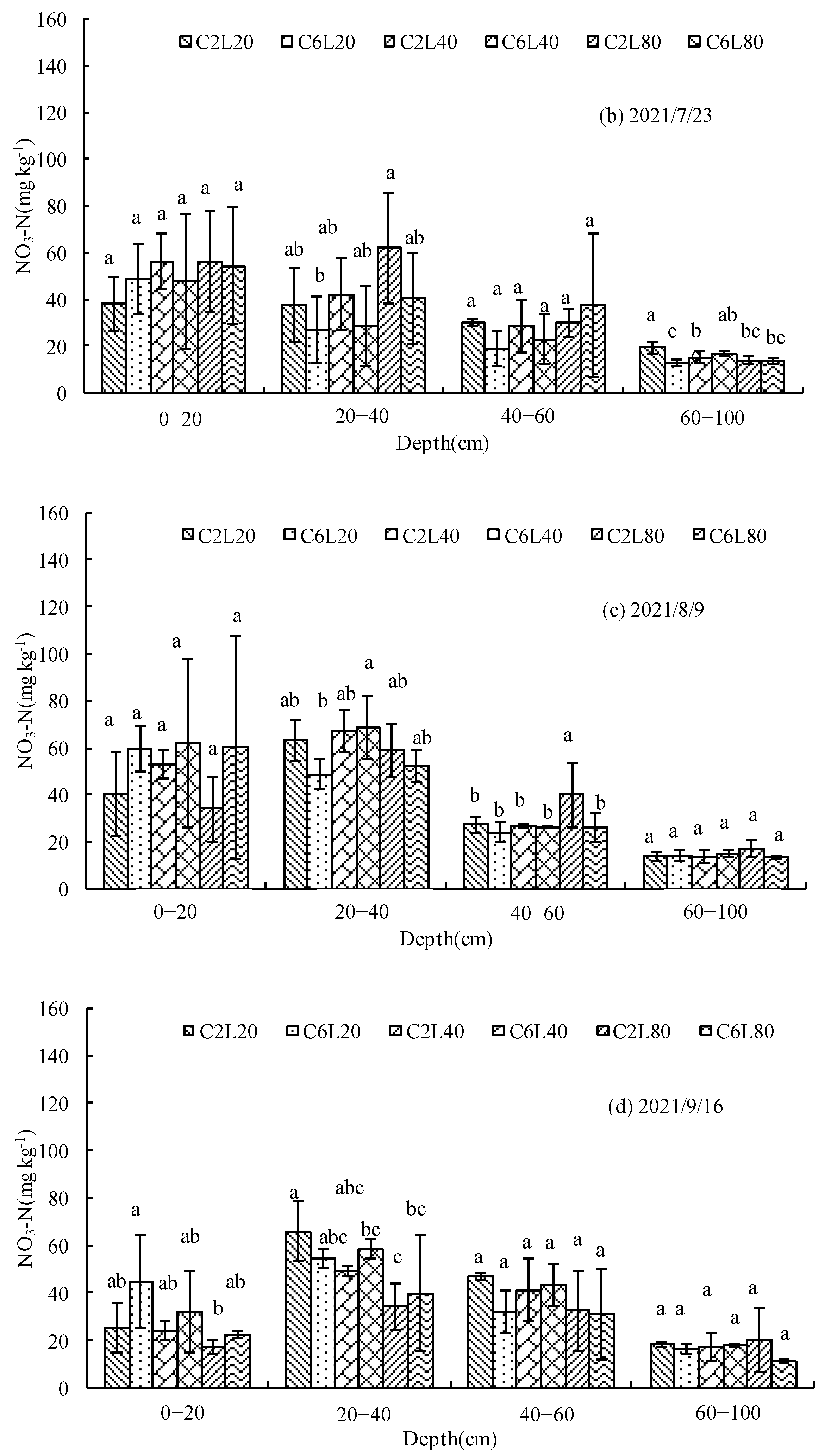
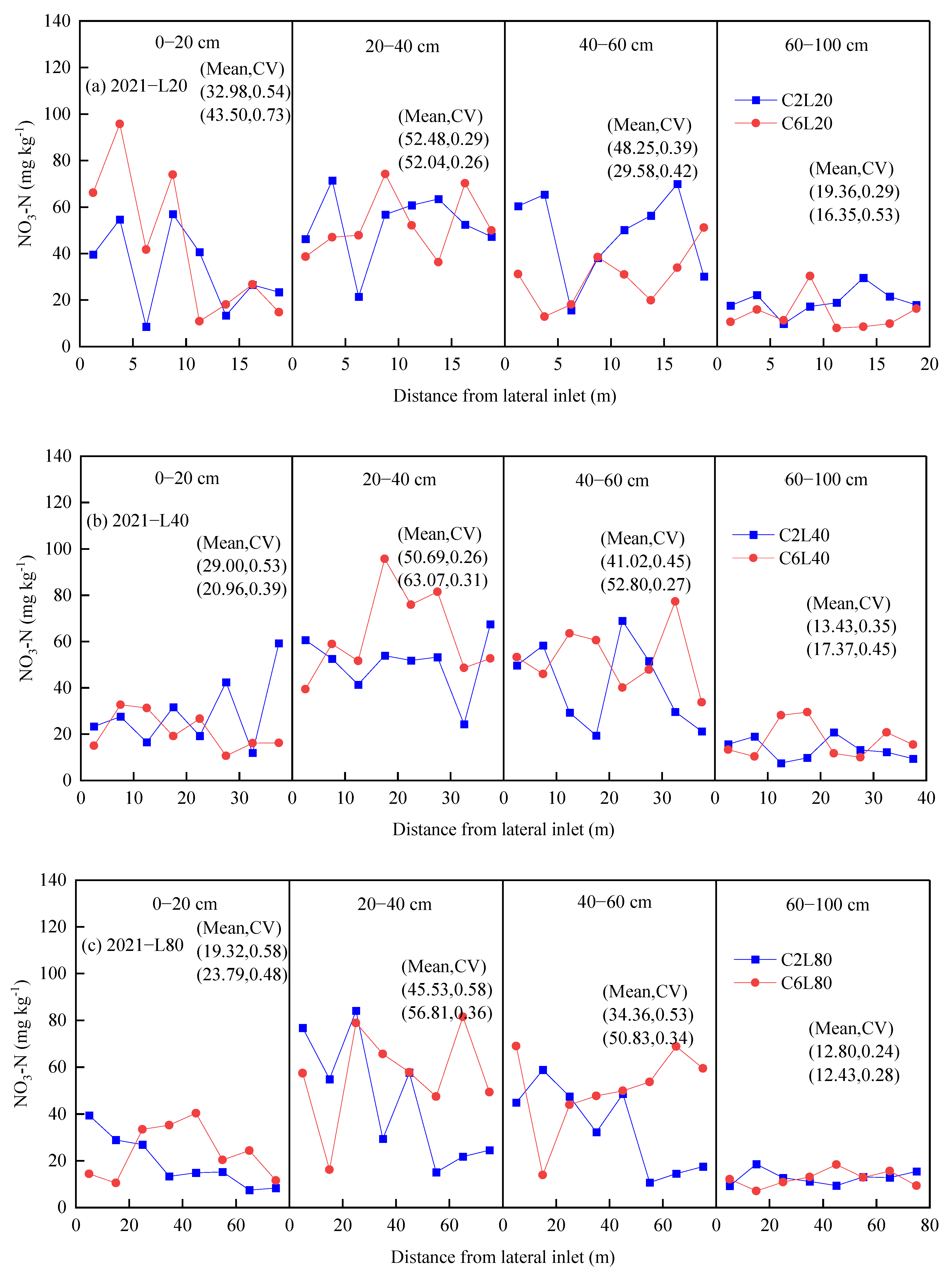
3.3. Distribution of NO3-N in Soil
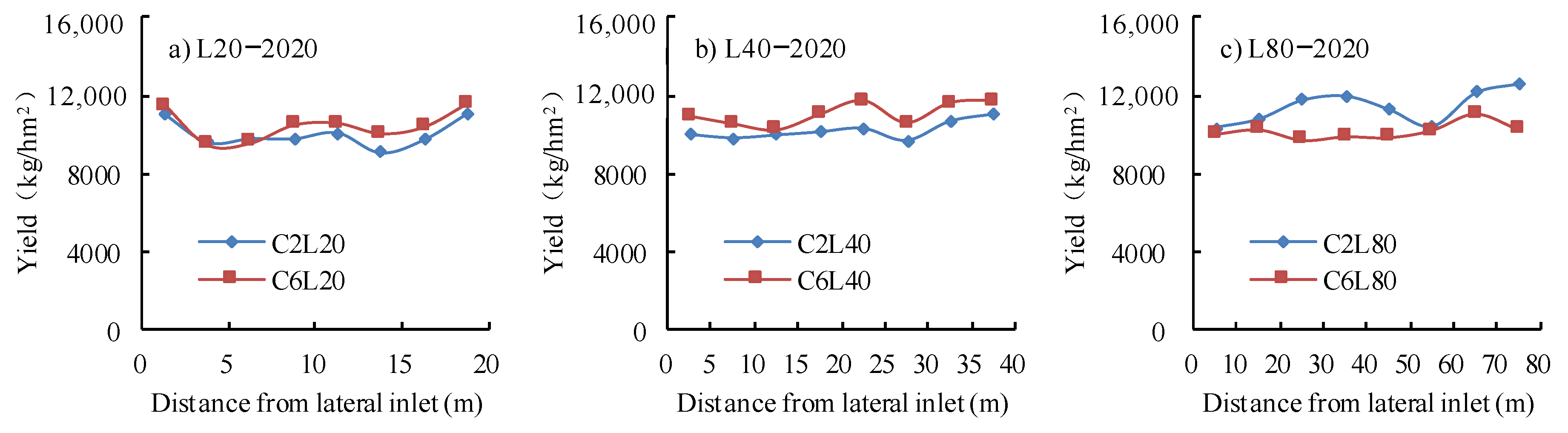
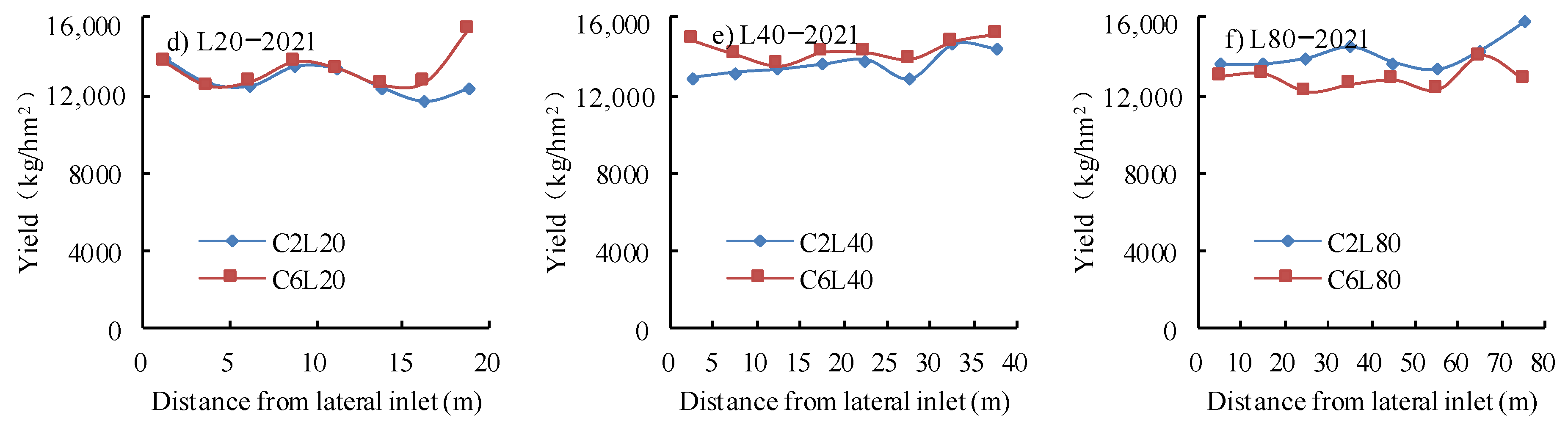
3.4. Nitrogen Uptake and Yield
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Seleiman, M.F.; Alotaibi, M.A.; Alhammad, B.A.; Alharbi, B.M.; Refay, Y.; Badawy, S.A. Effects of ZnO nanoparticles and biochar of rice straw and cow manure on characteristics of contaminated soil and sunflower productivity, oil quality, and heavy metals uptake. Agronomy 2020, 10, 790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A. Soil salinization management for sustainable development: A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 277, 111383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Chen, S.B.; Chen, L.; Wang, D.; Zhao, C.M. The responses of a soil bacterial community under saline stress are associated with Cd availability in long-term wastewater-irrigated field soil. Chemosphere 2019, 236, 124372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lequette, K.; Ait-Mouheb, N.; Adam, N.; Muffat-Jeandet, M.; Bru-Adan, A.; Wéry, N. Effects of the chlorination and pressure flushing of drippers fed by reclaimed wastewater on biofouling. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 758, 143598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.S.; Chen, L.; Li, Y.F.; Yin, J.F.; Zhang, H. Effects of chlorination schemes on clogging in drip emitters during applications of sewage effluent. Appl. Eng. Agric. 2010, 26, 565–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehghanisanij, H.; Yamamoto, T.; Ahmad, B.O.; Fujiyama, H.; Miyamoto, K. The effects of chlorine on emitter clogging induced by algae and protozoa and the performance of drip irrigation. Trans. ASAE 2005, 48, 519–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, F.Z.; Li, J.S.; Wang, Z.; Li, Y.F. Influence of chlorine injection on soil enzyme activities and maize growth under drip irrigation with secondary sewage effluent. Irrig. Sci. 2018, 36, 363–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.F.; Li, J.S.; Zhang, H. Effects of chlorination on soil chemical properties and nitrogen uptake for tomato drip irrigated with secondary sewage effluent. J. Integr. Agr. 2014, 13, 2049–2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.F.; Li, J.S. Effect of chlorination on yield and nitrogen uptake of tomato and emitter clogging in a drip irrigation system with sewage effluent. Trans. CSAE 2010, 26, 18–24, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Ebrahimizadeh, M.A.; Amiri, M.J.; Eslamian, S.S. The effects of different water qualities and irrigation methods on soil chemical properties. Res. J. Environ. Sci. 2009, 3, 497–503. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, J.; Guo, J. Disinfection spreads antimicrobial resistance. Science 2021, 371, 474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agnelo, L.; Leonel, L.P.; Silva, N.B.; Candello, F.P.; Schneider, J.; Tonetti, A.L. Effects of wastewater disinfectants on the soil: Implications for soil microbial and chemical attributes. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 706, 136007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adetunji, A.T.; Lewu, F.B.; Mulidzi, R.; Ncube, B. The biological activities of β-glucosidase, phosphatase and urease as soil quality indicators: A review. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nut. 2017, 17, 794–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrow, R.N.; Duncan, R.R.; Huck, M.T. Turfgrass and Landscape Irrigation Water Quality: Assessment and Management; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, Z.J.; Li, J.S.; Zhao, W.X. Effect of applying sewage effluent with subsurface drip irrigation on soil enzyme activities during the maize growing season. Irrig. Drain. 2017, 66, 723–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.M.; Zhu, L.S.; Wang, J.; Xie, H.; Wang, J.H.; Wang, F.H.; Sun, F.X. Effects of fomesafen on soil enzyme activity, microbial population, and bacterial community composition. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2014, 186, 2801–2812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, W.; Fang, C.; Deng, Y.; Xu, Z. Intensified disinfection amid COVID-19 pandemic poses potential risks to water quality and safety. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 4084–4086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.Y.; Zhang, Q.; Lu, T.; Zhang, J.Y.; Sun, L.W.; Hu, B.L.; Hu, J.; Peñuelas, J.; Zhu, L.Z.; Qian, H.F. Residual chlorine disrupts the microbial communities and spreads antibiotic resistance in freshwater. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 423, 127152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, G.R.; Chen, M.C.; Li, C.J.; Shi, W.Y.; Feng, Q.B. Effects of Cl- on transformation of nitrogenous fertilizers, microbes and enzyme activities in soil. J. Zhejiang Agric. Univ. 1993, 19, 437–440. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.S.; Zhang, Y.T.; Huang, X.C.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Zhao, Y.N.; Shi, X.J. Effects of long-term application of chloride containing fertilizers on the biological fertility of purple soil under a rice-wheat rotation system. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2016, 49, 686–694. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.S.; Li, Y.F.; Zhang, H. Tomato yield and quality and emitter clogging as effected by chlorination schemes of drip irrigation systems applying sewage effluent. J. Integr. Agric. 2012, 11, 1744–1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truchado, P.; Gil, M.I.; Suslow, T.; Allende, A. Impact of chlorine dioxide disinfection of irrigation water on the epiphytic bacterial community of baby spinach and underlying soil. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0199291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, X.M.; Wang, Z.; Li, J.S. Identifying the factors dominating the spatial distribution of water and salt in soil and cotton yield under arid environments of drip irrigation with different lateral lengths. Agr. Water Manag. 2021, 250, 106834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirazi, M.A.; Boersma, L. A unifying quantitative analysis of soil texture. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1984, 48, 142–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, S.Y. Soil enzyme and Its Research Methods; Beijing Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 1986. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Hao, F.Z.; Li, J.S.; Li, Y.F. Modeling of the residual chlorine distribution in drip irrigation system applying reclaimed water based on EPANET. T. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2020, 36, 99–106, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Hua, F.; West, J.R.; Barker, R.A.; Forster, C.F. Modelling of chlorine decay in municipal water supplies. Water Res. 1999, 33, 2735–2746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, P.; Feng, G.; Brooks, J.; Zhou, B.; Zhou, H.X.; Zhao, Z.R.; Li, Y.K. Environmental risk of chlorine-controlled clogging in drip irrigation system using reclaimed water: The perspective of soil health. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 232, 1452–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Donk, S.J.; Petersen, J.L.; Davison, D.R. Effect of amount and timing of subsurface drip irrigation on corn yield. Irrig. Sci. 2013, 31, 599–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Li, J.S.; Li, Y.F. Effect of drip irrigation system uniformity and nitrogen applied on deep percolation and nitrate leaching during growing seasons of spring maize in semi-humid region. Irrig. Sci. 2014, 32, 221–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.R.; He, Z.L.; Yang, X.E.; Mishra, S.; Stoffella, P.J. Chlorine nutrition of higher plants: Progress and perspectives. J. Plant Nutr. 2010, 33, 943–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lonigro, A.; Montemurro, N.; Laera, G. Effects of residual disinfectant on soil and lettuce crop irrigated with chlorinated water. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 584–585, 595–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, F.Z. Effects of Chemical Injection on Emitter Clogging and Soil-Plant System under Drip Irrigation Applying Sewage Effluent; China Institute of Water Resources and Hydropower Research: Beijing, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
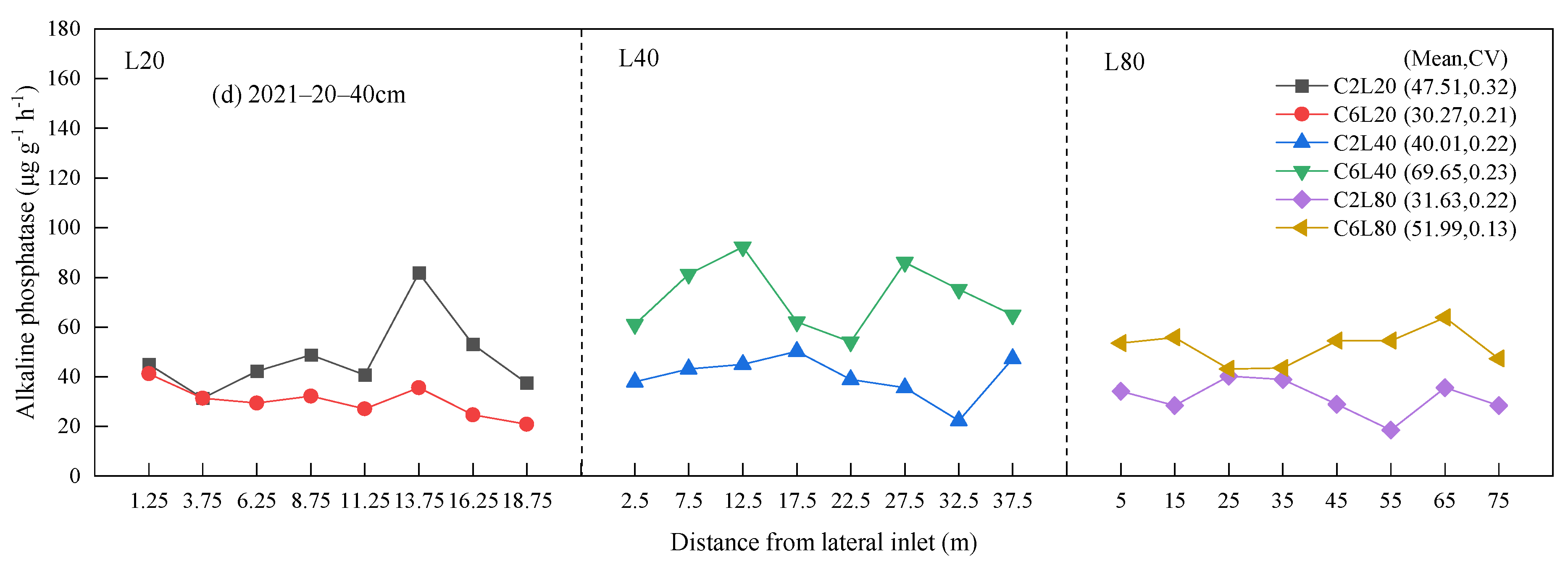
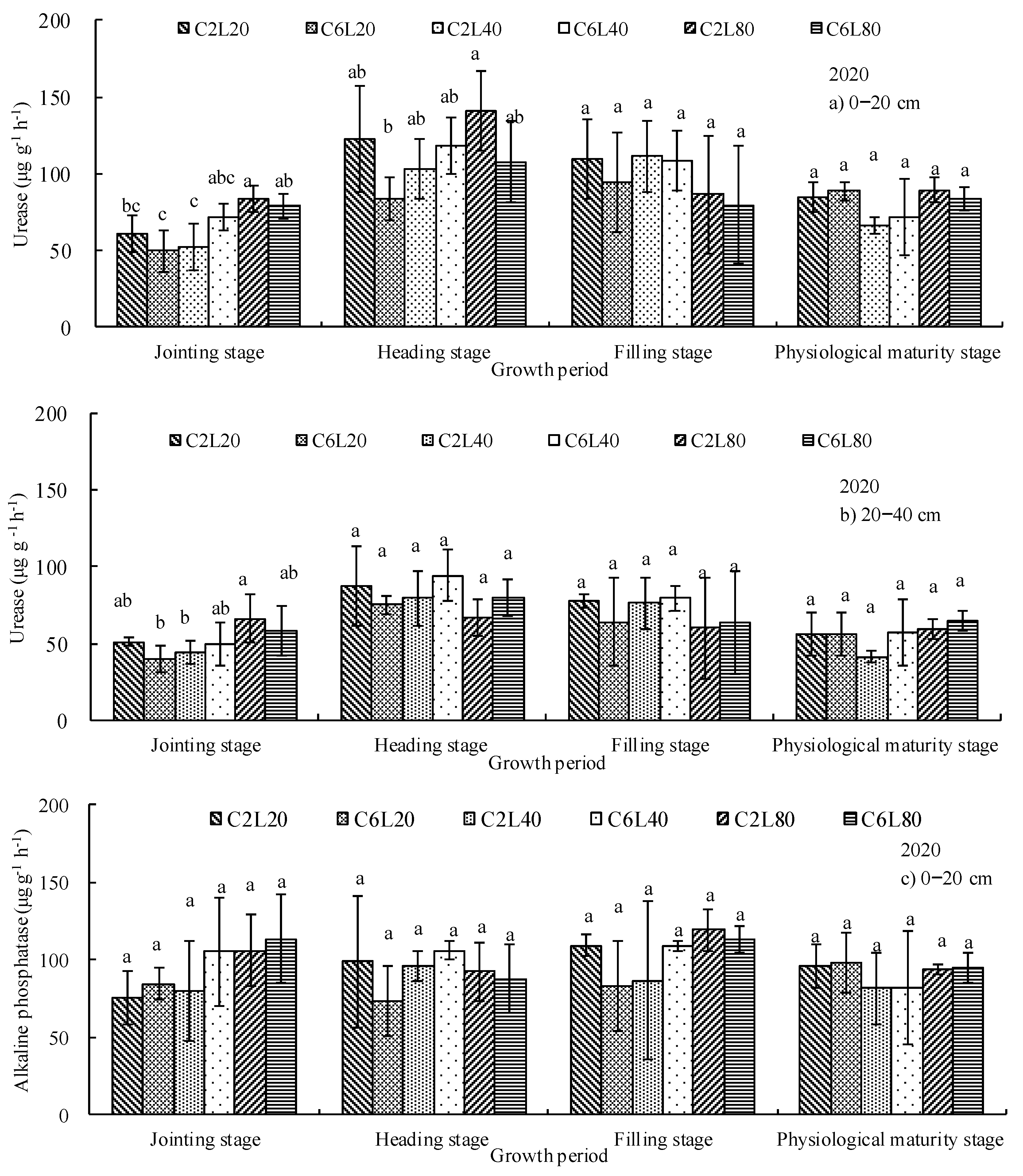

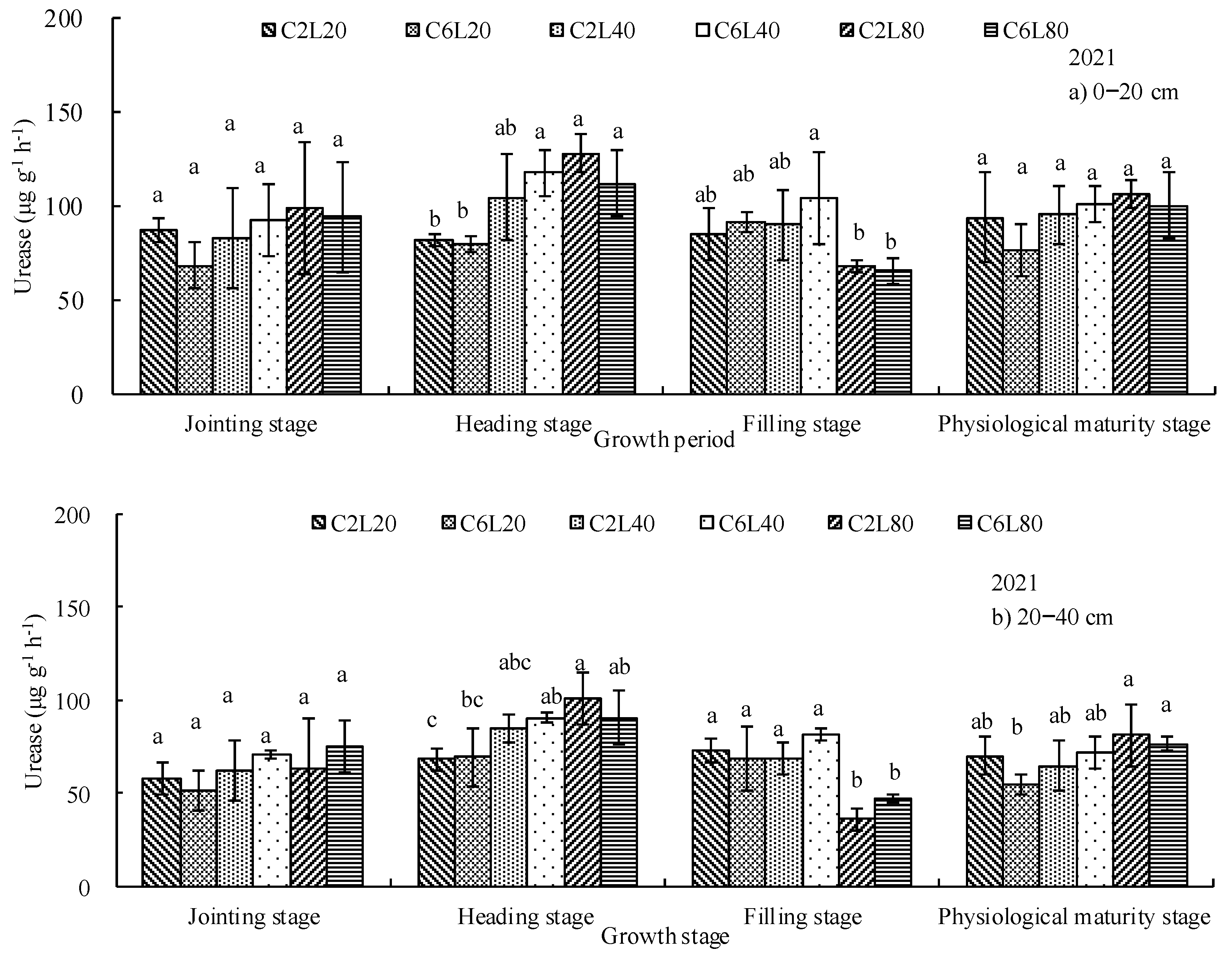
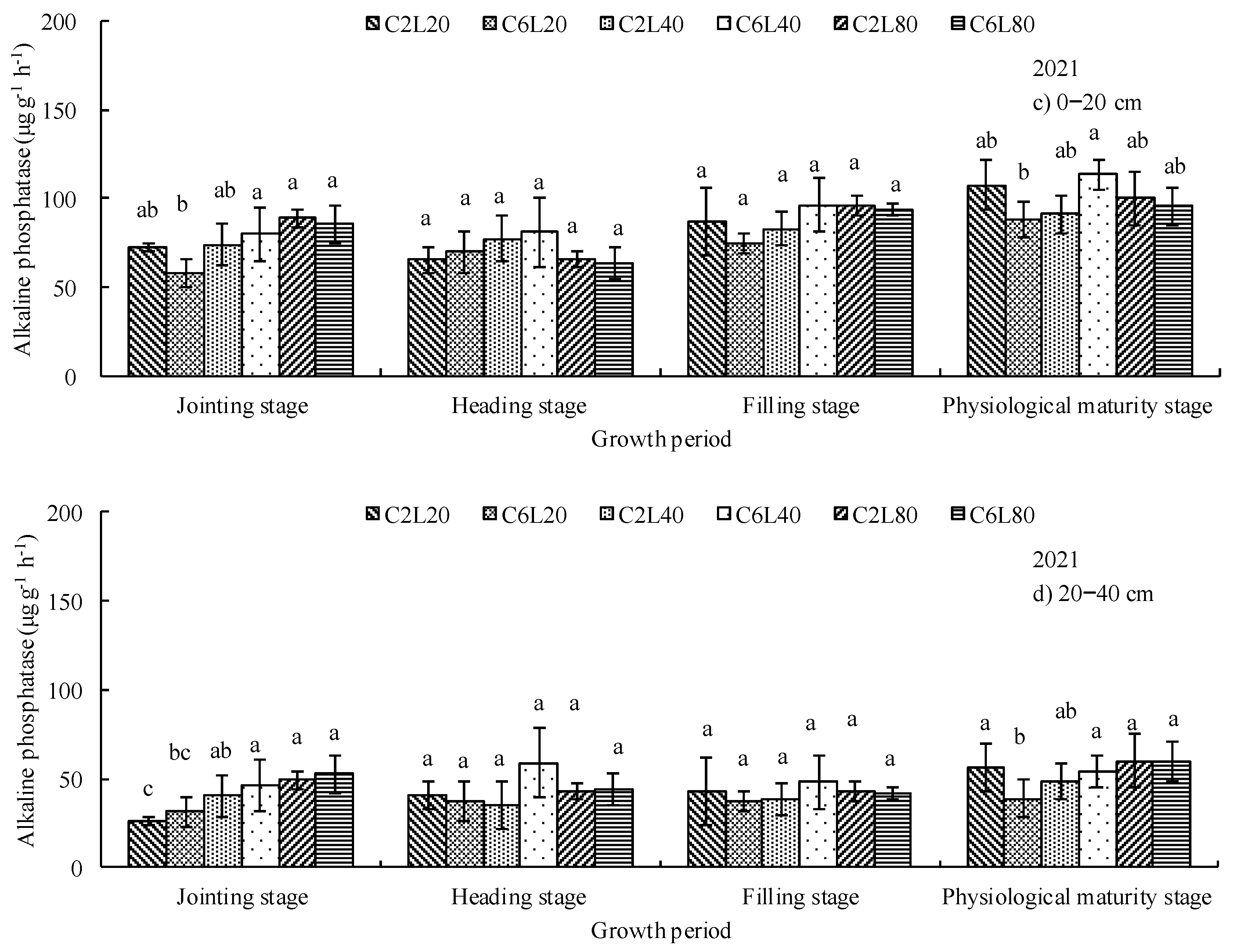

| Number of Irrigation, Fertigation and Chlorination | 2020 | 2021 | Fertilizer Applied (kg ha−1) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Date | Irrigation (mm) | Chlorination | Date | Irrigation (mm) | Chlorination | N | |
| 1 | 28-Aug. | 16.5 | √ | 1-Jul. | 30 | √ | 60 |
| 2 | 17-Sep. | 30 | √ | 19-Jul. | 30 | √ | 60 |
| 3 | 8-Oct. | 23.8 | √ | 7-Aug. | 30 | √ | 60 |
| Total | 70.3 | 90 | 180 |
| Parameter | Unit | During Irrigation Season of 2020 | During Irrigation Season of 2021 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average | Standard Deviation | Average | Standard Deviation | ||
| Chemical oxygen demand | mg L−1 | 449.1 | 317.8 | 592.9 | 704.6 |
| Total nitrogen | mg L−1 | 22.2 | 5.0 | 18.2 | 2.2 |
| Total phosphorous | mg L−1 | 0.33 | 0.1 | 0.32 | 0.04 |
| NO3-N | mg L−1 | 5.1 | 2.7 | 5.7 | 2.8 |
| NH4-N | mg L−1 | 4.9 | 3.9 | 9.6 | 1.8 |
| Layer | Source | 2020 | 2021 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 30 Aug. | 20 Sep. | 11 Oct. | 31 Oct. | 4 Jul. | 23 Jul. | 9 Aug. | 16 Sep. | ||
| Urease | |||||||||
| 0–20 cm | Chlorine concentration | NS (p = 0.851) | NS (p = 0.088) | NS (p = 0.606) | NS (p = 0.816) | NS (p = 0.691) | NS (p = 0.807) | NS (p = 0.398) | NS (p = 0.419) |
| Lateral length | ** (p = 0.006) | NS (p = 0.263) | NS (p = 0.378) | * (p = 0.046) | NS (p = 0.408) | ** (p = 0.001) | ** (p = 0.009) | NS (p = 0.156) | |
| C×L | NS (p = 0.097) | NS (p = 0.096) | NS (p = 0.948) | NS (p = 0.691) | NS (p = 0.609) | NS (p = 0.229) | NS (p = 0.599) | NS (p = 0.455) | |
| 20–40 cm | Chlorine concentration | NS (p = 0.407) | NS (p = 0.580) | NS (p = 0.837) | NS (p = 0.388) | NS (p = 0.527) | NS (p = 0.817) | NS (p = 0.120) | NS (p = 0.441) |
| Lateral length | * (p = 0.039) | NS (p = 0.481) | NS (p = 0.471) | NS (p = 0.478) | NS (p = 0.241) | ** (p = 0.004) | ** (p = 0.000) | NS (p = 0.055) | |
| C×L | NS (p = 0.422) | NS (p = 0.405) | NS (p = 0.753) | NS (p = 0.729) | NS (p = 0.559) | NS (p = 0.492) | NS (p = 0.212) | NS (p = 0.230) | |
| Alkaline phosphatase | |||||||||
| 0–20 cm | Chlorine concentration | NS (p = 0.278) | NS (p = 0.554) | NS (p = 0.780) | NS (p = 0.912) | NS (p = 0.407) | NS (p = 0.717) | NS (p = 0.945) | NS (p = 0.924) |
| Lateral length | NS (p = 0.182) | NS (p = 0.538) | NS (p = 0.344) | NS (p = 0.440) | NS (p = 0.007) | NS (p = 0.120) | NS (p = 0.139) | NS (p = 0.739) | |
| C×L | NS (p = 0.797) | NS (p = 0.445) | NS (p = 0.282) | NS (p = 0.999) | NS (p = 0.240) | NS (p = 0.859) | NS (p = 0.176) | NS (p = 0.030) | |
| 20–40 cm | Chlorine concentration | NS (p = 0.071) | NS (p = 0.295) | NS (p = 0.629) | NS (p = 0.711) | NS (p = 0.174) | NS (p = 0.357) | NS (p = 0.829) | NS (p = 0.275) |
| Lateral length | NS (p = 0.222) | NS (p = 0.987) | * (p = 0.019) | NS (p = 0.207) | ** (p = 0.000) | NS (p = 0.698) | NS (p = 0.876) | * (p = 0.046) | |
| C×L | NS (p = 0.626) | NS (p = 0.265) | NS (p = 0.285) | NS (p = 0.941) | NS (p = 0.941) | NS (p = 0.349) | NS (p = 0.440) | NS (p = 0.053) | |
| Layer | Source | 2020 | 2021 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 30 Aug. | 20 Sep. | 11 Oct. | 31 Oct. | 4 Jul. | 23 Jul. | 9 Aug. | 16 Sep. | ||
| 0–20 cm | Chlorine concentration | * (p = 0.017) | NS (p = 0.818) | NS (p = 0.100) | NS (p = 0.908) | NS (p = 0.709) | NS (p = 0.994) | NS (p = 0.168) | NS (p = 0.073) |
| Lateral length | NS (p = 0.402) | NS (p = 0.586) | NS (p = 0.649) | NS (p = 0.289) | NS (p = 0.506) | NS (p = 0.584) | NS (p = 0.781) | NS (p = 0.116) | |
| C×L | NS (p = 0.412) | NS (p = 0.115) | NS (p = 0.677) | NS (p = 0.942) | NS (p = 0.804) | NS (p = 0.715) | NS (p = 0.847) | NS (p = 0.553) | |
| 20–40 cm | Chlorine concentration | NS (p = 0.769) | NS (p = 0.159) | NS (p = 0.523) | NS (p = 0.754) | NS (p = 0.734) | NS (p = 0.093) | NS (p = 0.170) | NS (p = 0.851) |
| Lateral length | NS (p = 0.194) | NS (p = 0.966) | NS (p = 0.126) | NS (p = 0.761) | NS (p = 0.495) | NS (p = 0.181) | NS (p = 0.080) | * (p = 0.015) | |
| C×L | NS (p = 0.561) | NS (p = 0.748) | NS (p = 0.371) | NS (p = 0.169) | NS (p = 0.596) | NS (p = 0.856) | NS (p = 0.399) | NS (p = 0.313) | |
| 40–60 cm | Chlorine concentration | NS (p = 0.306) | NS (p = 0.362) | NS (p = 0.301) | NS (p = 0.463) | NS (p = 0.231) | NS (p = 0.644) | NS (p = 0.090) | NS (p = 0.438) |
| Lateral length | NS (p = 0.840) | NS (p = 0.231) | NS (p = 0.405) | NS (p = 0.883) | NS (p = 0.986) | NS (p = 0.499) | NS (p = 0.137) | NS (p = 0.374) | |
| C×L | NS (p = 0.508) | NS (p = 0.741) | NS (p = 0.984) | NS (p = 0.611) | NS (p = 0.465) | NS (p = 0.534) | NS (p = 0.227) | NS (p = 0.533) | |
| 60–100 cm | Chlorine concentration | NS (p = 0.714) | NS (p = 0.439) | NS (p = 0.353) | NS (p = 0.794) | NS (p = 0.635) | NS (p = 0.065) | NS (p = 0.441) | NS (p = 0.307) |
| Lateral length | NS (p = 0.535) | NS (p = 0.228) | NS (p = 0.307) | NS (p = 0.494) | NS (p = 0.077) | NS (p = 0.065) | NS (p = 0.655) | NS (p = 0.793) | |
| C×L | NS (p = 0.344) | NS (p = 0.342) | NS (p = 0.286) | NS (p = 0.688) | NS (p = 0.151) | ** (p = 0.010) | NS (p = 0.169) | NS (p = 0.372) | |
| Treatment | Ear Length (cm) | Ear Barren Tip (cm) | Kernal Number per Cob | 100-Seed Weight (g) | Aboveground Plant Biomass (kg ha−1) | Nitrogen Uptake (kg ha−1) | Yield (kg ha−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C2L20 | 18.9 a | 5.7 ab | 417 a | 22.3 b | 17,929.1 a | 181.0 a | 10,020.8 b |
| C6L20 | 18.6 a | 5.9 a | 404 a | 21.1 b | 16,739.0 a | 165.9 a | 10,445.6 ab |
| C2L40 | 19.4 a | 5.3 ab | 471 a | 22.5 ab | 16,968.9 a | 183.0 a | 10,193.7 ab |
| C6L40 | 19.6 a | 4.8 b | 484 a | 23.4 a | 17,632.6 a | 187.5 a | 11,040.6 ab |
| C2L80 | 19.6 a | 4.8 b | 492 a | 23.7 a | 18,212.6 a | 182.7 a | 11,406.2 a |
| C6L80 | 19.1 a | 4.6 b | 476 a | 22.8 ab | 17,628.3 a | 173.4 a | 10,144.8 b |
| ANOVA | |||||||
| Chlorine concentration | NS (p = 0.421) | NS (p = 0.590) | NS (p = 0.823) | NS (p = 0.513) | NS (p = 0.685) | NS (p = 0.444) | NS (p = 0.991) |
| Lateral length | NS (p = 0.087) | * (p = 0.014) | * (p = 0.032) | * (p = 0.035) | NS (p = 0.818) | NS (p = 0.529) | NS (p = 0.346) |
| C×L | NS (p = 0.569) | NS (p = 0.519) | NS (p = 0.839) | NS (p = 0.232) | NS (p = 0.694) | NS (p = 0.629) | * (p = 0.032) |
| Treatment | Ear Length (cm) | Ear Barren Tip (cm) | Kernal Number per Cob | 100-Seed Weight (g) | Aboveground Plant Biomass (kg ha−1) | Nitrogen Uptake (kg ha−1) | Yield (kg ha−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C2L20 | 20.8 ab | 3.1 a | 591 a | 31.5 a | 20,547.8 a | 210.9 a | 12,733.7 a |
| C6L20 | 21.4 ab | 3.1 a | 603 a | 32.0 a | 20,368.9 a | 209.6 a | 13,343.6 a |
| C2L40 | 20.9 ab | 2.9 a | 600 a | 32.7 a | 21,836.9 a | 242.6 a | 13,543.9 a |
| C6L40 | 21.7 a | 2.7 a | 632 a | 32.5 a | 22,063.7 a | 244.7 a | 14,353.7 a |
| C2L80 | 21.5 ab | 2.7 a | 633 a | 32.1 a | 21,355.9 a | 218.4 a | 14,057.5 a |
| C6L80 | 20.6 b | 2.9 a | 587 a | 31.7 a | 20,855.0 a | 211.9 a | 12,849.5 a |
| ANOVA | |||||||
| Chlorine concentration | NS (p = 0.538) | NS (p = 0.910) | NS (p = 0.942) | NS (p = 0.939) | NS (p = 0.825) | NS (p = 0.859) | NS (p = 0.889) |
| Lateral length | NS (p = 0.732) | NS (p = 0.153) | NS (p = 0.489) | NS (p = 0.459) | NS (p = 0.229) | NS (p = 0.051) | NS (p = 0.358) |
| C×L | * (p = 0.026) | NS (p = 0.510) | NS (p = 0.064) | NS (p = 0.772) | NS (p = 0.906) | NS (p = 0.947) | NS (p = 0.230) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hao, F.; Wang, Z.; Zhen, Z. Influence of Lateral Length and Residual Chlorine Concentration on Soil Nitrogen and Soil Enzyme Activities under Drip Irrigation with Secondary Sewage Effluent. Agronomy 2024, 14, 1538. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14071538
Hao F, Wang Z, Zhen Z. Influence of Lateral Length and Residual Chlorine Concentration on Soil Nitrogen and Soil Enzyme Activities under Drip Irrigation with Secondary Sewage Effluent. Agronomy. 2024; 14(7):1538. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14071538
Chicago/Turabian StyleHao, Fengzhen, Zhen Wang, and Zhilei Zhen. 2024. "Influence of Lateral Length and Residual Chlorine Concentration on Soil Nitrogen and Soil Enzyme Activities under Drip Irrigation with Secondary Sewage Effluent" Agronomy 14, no. 7: 1538. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14071538
APA StyleHao, F., Wang, Z., & Zhen, Z. (2024). Influence of Lateral Length and Residual Chlorine Concentration on Soil Nitrogen and Soil Enzyme Activities under Drip Irrigation with Secondary Sewage Effluent. Agronomy, 14(7), 1538. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14071538







