Molecular Mechanisms Regulating Lamina Joint Development in Rice
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Structure and Development Process of Rice LJ
3. Regulation of PC Development in LJ
3.1. Regulation by Brassinosteroids (BRs)
3.2. Regulation by Auxin
3.3. Crosstalk between the Phytohormones
3.3.1. BR and Auxin
3.3.2. BR and GA
3.3.3. Synergism between the Other Phytohormones
3.4. Regulation by TFs
4. Regulation of SC Development in LJ
4.1. Regulation of SC Proliferation
4.2. Regulation of Secondary Wall Synthesis
5. Regulation by Environmental Factors
6. Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sakamoto, T.; Morinaka, Y.; Ohnishi, T.; Sunohara, H.; Fujioka, S.; Ueguchi-Tanaka, M.; Mizutani, M.; Sakata, K.; Takatsuto, S.; Yoshida, S.; et al. Erect leaves caused by brassinosteroid deficiency increase biomass production and grain yield in rice. Nat. Biotechnol. 2006, 24, 105–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Wu, P.; Lu, Y.; Guo, S.; Zhong, Z.; Shen, R.; Xie, Q. Synergistic interaction of phytohormones in determining leaf angle in crops. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Wang, J.J.; Xue, H.W.; Zhang, G.H. Leaf direction: Lamina joint development and environmental responses. Plant Cell Environ. 2021, 44, 2441–2454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Y.; Zhong, Z.; Wang, H.; Shen, R. Leaf angle: A target of genetic improvement in cereal crops tailored for high-density planting. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2022, 20, 426–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Liu, C.; Li, Q.; Chen, Z.; Sun, S.; Wang, X. Spatiotemporal resolved leaf angle establishment improves rice grain yield via controlling population density. iScience 2020, 23, 101489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.-J.; Xiao, L.-T.; Xue, H.-W. Dynamic cytology and transcriptional regulation of rice lamina joint development. Plant Physiol. 2017, 174, 1728–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Méchin, V.; Argillier, O.; Rocher, F.; Hébert, Y.; Mila, I.; Pollet, B.; Barrière, Y.; Lapierre, C. In search of a maize ideotype for cell wall enzymatic degradability using histological and biochemical lignin characterization. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 5872–5881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choe, S. Brassinosteroid biosynthesis and inactivation. Physiol. Plant. 2006, 126, 539–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, K.; Ou, X.; Tang, H.; Wang, R.; Wu, P.; Jia, Y.; Wei, X.; Xu, X.; Kang, S.H.; Kim, S.K.; et al. Rice microRNA osa-miR1848 targets the obtusifoliol 14α-demethylase gene OsCYP51G3 and mediates the biosynthesis of phytosterols and brassinosteroids during development and in response to stress. New Phytol. 2015, 208, 790–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Wu, C.; Wang, C.; Roh, J.; Zhang, L.; Chen, J.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, H.; Yang, C.; Hu, J.; et al. SLG controls grain size and leaf angle by modulating brassinosteroid homeostasis in rice. J. Exp. Bot. 2016, 67, 4241–4253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Z.; Ueguchi-Tanaka, M.; Fujioka, S.; Takatsuto, S.; Yoshida, S.; Hasegawa, Y.; Ashikari, M.; Kitano, H.; Matsuoka, M. The rice brassinosteroid-deficient dwarf2 mutant, defective in the rice homolog of arabidopsis DIMINUTO/DWARF1, is rescued by the endogenously accumulated alternative bioactive brassinosteroid, dolichosterone. Plant Cell. 2005, 17, 2243–2254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsukagoshi, Y.; Suzuki, H.; Seki, H.; Muranaka, T.; Ohyama, K.; Fujimoto, Y. Ajuga δ24-sterol reductase catalyzes the direct reductive conversion of 24-methylenecholesterol to campesterol. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 8189–8198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, R.; Zeng, D.; Yang, C.; Akhter, D.; Alamin, M.; Jin, X.; Shi, C. LTBSG1, a new allele of BRD2, regulates panicle and grain development in rice by brassinosteroid biosynthetic pathway. Genes 2018, 9, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanabe, S.; Ashikari, M.; Fujioka, S.; Takatsuto, S.; Yoshida, S.; Yano, M.; Yoshimura, A.; Kitano, H.; Matsuoka, M.; Fujisawa, Y.; et al. Novel cytochrome P450 is implicated in brassinosteroid biosynthesis via the characterization of a rice dwarf mutant, dwarf11, with reduced seed length. Plant Cell. 2005, 17, 776–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Jiang, L.; Youn, J.H.; Sun, W.; Cheng, Z.; Jin, T.; Ma, X.; Guo, X.; Wang, J.; Zhang, X.; et al. A comprehensive genetic study reveals a crucial role of CYP90D2/D2 in regulating plant architecture in rice (Oryza sativa). New Phytol. 2013, 200, 1076–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mori, M.; Nomura, T.; Ooka, H.; Ishizaka, M.; Yokota, T.; Sugimoto, K.; Okabe, K.; Kajiwara, H.; Satoh, K.; Yamamoto, K.; et al. Isolation and characterization of a rice dwarf mutant with a defect in brassinosteroid biosynthesis. Plant Physiol. 2002, 130, 1152–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vriet, C.; Russinova, E.; Reuzeau, C. From squalene to brassinolide: The steroid metabolic and signaling pathways across the plant kingdom. Mol. Plant. 2013, 6, 1738–1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Hu, B.; Chu, C. Nitrogen use efficiency in crops: Lessons from Arabidopsis and rice. J. Exp. Bot. 2017, 68, 2477–2488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, W.K.H.B.; Kim, W.T.; Park, P.B.; An, G.; Choe, S. Rice bending lamina 2 (bla2) mutants are defective in a cytochrome P450 (CYP734A6) gene predicted to mediate brassinosteroid catabolism. J. Plant Biol. 2006, 49, 469–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakamoto, T.; Kawabe, A.; Tokida-Segawa, A.; Shimizu, B.; Takatsuto, S.; Shimada, Y.; Fujioka, S.; Mizutani, M. Rice CYP734As function as multisubstrate and multifunctional enzymes in brassinosteroid catabolism. Plant J. 2011, 67, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Je, B.I.; Piao, H.L.; Park, S.J.; Park, S.H.; Kim, C.M.; Xuan, Y.H.; Park, S.H.; Huang, J.; Do Choi, Y.; An, G.; et al. RAV-Like1 maintains brassinosteroid homeostasis via the coordinated activation of BRI1 and biosynthetic genes in rice. Plant Cell. 2010, 22, 1777–1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xuan, Y.H.; Duan, F.Y.; Je, B.I.; Kim, C.M.; Li, T.Y.; Liu, J.M.; Park, S.J.; Cho, J.H.; Kim, T.H.; von Wiren, N.; et al. Related to ABI3/VP1-Like 1 (RAVL1) regulates brassinosteroid-mediated activation of AMT1;2 in rice (Oryza sativa). J. Exp. Bot. 2016, 68, 727–737. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, R.; Xing, Y.; Xu, Y.; Xiong, D.; Wang, Y.; Yao, S. Separable regulation of POW1 in grain size and leaf angle development in rice. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2021, 19, 2517–2531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Fan, X.-Y.; Cao, D.-M.; Tang, W.; He, K.; Zhu, J.-Y.; He, J.-X.; Bai, M.-Y.; Zhu, S.; Oh, E.; et al. Integration of brassinosteroid signal transduction with the transcription network for plant growth regulation in Arabidopsis. Dev. Cell. 2010, 19, 765–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.; Liu, Y.; Xie, Q.; Tong, H.; Chu, C. Crosstalk between brassinosteroid signaling and variable nutrient environments. Sci. China Life Sci. 2023, 66, 1231–11244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamuro, C.I.Y.; Wu, X.; Noguchi, T.; Fujioka, S.; Takatsuto, S.; Ashikari, M.; Kitano, H.; Matsuoka, M. Loss of function of a rice brassinosteroid insensitive1 homolog prevents internode elongation and bending of the lamina joint. Plant Cell. 2000, 12, 1591–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Wang, L.; Wang, M.; Xu, Y.Y.; Luo, W.; Liu, Y.J.; Xu, Z.H.; Li, J.; Chong, K. Engineering OsBAK1 gene as a molecular tool to improve rice architecture for high yield. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2009, 7, 791–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Niu, R.; Yu, H.; Guo, J.; Du, C.; Zhang, Z.; Wei, Y.; Li, J.; Zhang, S. OsSLA1 functions in leaf angle regulation by enhancing the interaction between OsBRI1 and OsBAK1 in rice. Plant J. 2022, 110, 1111–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.; Song, X.; Guo, H.; Wu, Y.; Chen, X.; Fang, R. A small G protein as a novel component of the rice brassinosteroid signal transduction. Mol. Plant. 2016, 9, 1260–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.-J.; Lin, W.-H.; Fu, F.-F.; Xu, Z.-H.; Xue, H.-W. Receptor-like protein ELT1 promotes brassinosteroid signaling through interacting with and suppressing the endocytosis-mediated degradation of receptor BRI1. Cell Res. 2017, 27, 1182–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Yu, Z.; Zhang, G.; Yin, W.; Li, L.; Niu, M.; Meng, W.; Zhang, X.; Dong, N.; Liu, J.; et al. Diversification of plant agronomic traits by genome editing of brassinosteroid signaling family genes in rice. Plant Physiol. 2021, 187, 2563–2576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, X.; Zhang, J.-Q.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, J.; Jiang, Z.; Huang, P.; Tang, Z.; Bao, Y.; Cheng, J.; Tang, H.; et al. Rice qGL3/OsPPKL1 functions with the GSK3/SHAGGY-Like Kinase OsGSK3 to modulate brassinosteroid signaling. Plant Cell. 2019, 31, 1077–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koh, S.; Lee, S.-C.; Kim, M.-K.; Koh, J.H.; Lee, S.; An, G.; Choe, S.; Kim, S.-R. T-DNA tagged knockout mutation of rice OsGSK1, an orthologue of Arabidopsis BIN2, with enhanced tolerance to various abiotic stresses. Plant Mol. Biol. 2007, 65, 453–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirano, K.; Yoshida, H.; Aya, K.; Kawamura, M.; Hayashi, M.; Hobo, T.; Sato-Izawa, K.; Kitano, H.; Ueguchi-Tanaka, M.; Matsuoka, M. SMALL ORGAN SIZE 1 and SMALL ORGAN SIZE 2/DWARF AND LOW-TILLERING form a complex to integrate auxin and brassinosteroid signaling in rice. Mol. Plant. 2017, 10, 590–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, S.; Sun, S.; Wang, L.; Wu, Z.; Li, C.; Li, X.; Wang, T.; Leng, L.; Tian, W.; Lu, T.; et al. The RLA1/SMOS1 transcription factor functions with OsBZR1 to regulate brassinosteroid signaling and rice architecture. Plant Cell. 2017, 29, 292–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, H.; Liu, L.; Jin, Y.; Du, L.; Yin, Y.; Qian, Q.; Zhu, L.; Chu, C. DWARF AND LOW-TILLERING acts as a direct downstream target of a GSK3/SHAGGY-Like kinase to mediate brassinosteroid responses in rice. Plant Cell. 2012, 24, 2562–2577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, F.; Zheng, X.; Wang, J.; Qiu, T.; Yang, Q.; Fang, K.; Bhadauria, V.; Peng, Y.L.; Zhao, W. The GRAS protein OsDLA involves in brassinosteroid signalling and positively regulates blast resistance by forming a module with GSK2 and OsWRKY53 in rice. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2023, 22, 363–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, M.-Y.; Zhang, L.-Y.; Gampala, S.S.; Zhu, S.-W.; Song, W.-Y.; Chong, K.; Wang, Z.-Y. Functions of OsBZR1 and 14-3-3 proteins in brassinosteroid signaling in rice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 13839–13844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, H.J.; Cui, L.H.; Oh, T.R.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, T.W.; Kim, W.T. OsBZR1 turnover mediated by OsSK22-regulated U-box E3 ligase OsPUB24 in rice BR response. Plant J. 2019, 99, 426–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Diao, Z.; Yang, D.; Wang, X.; Zheng, X.; Xiang, X.; Xiao, Y.; Chen, Z.; Wang, W.; Wu, Y.; et al. The 14-3-3 protein GF14c positively regulates immunity by modulating the protein homoeostasis of the GRAS protein OsSCL7 in rice. Plant Cell Environ. 2022, 45, 1065–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Xu, Y.; Guo, S.; Zhu, J.; Huan, Q.; Liu, H.; Wang, L.; Luo, G.; Wang, X.; Chong, K. Dynamics of brassinosteroid response modulated by negative regulator LIC in rice. PLoS Genet. 2012, 8, e1002686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, K.; Li, L.; Hu, P.; Xu, S.P.; Xu, Z.H.; Xue, H.W. A brassinolide-suppressed rice MADS-box transcription factor, OsMDP1, has a negative regulatory role in BR signaling. Plant J. 2006, 47, 519–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, S.-Q.; Hu, J.; Guo, L.-B.; Qian, Q.; Xue, H.-W. Rice leaf inclination2, a VIN3-like protein, regulates leaf angle through modulating cell division of the collar. Cell Res. 2010, 20, 935–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, H.-P.; Chen, S.-K. Brassinosteroid-induced rice lamina joint inclination and its relation to indole-3-acetic acid and ethylene. Plant Growth Regul. 1995, 16, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Han, S.; Lin, Y.; Qiao, J.; Han, N.; Li, Y.; Feng, Y.; Li, D.; Qi, Y. Auxin transporter OsPIN1b, a novel regulator of leaf inclination in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plants 2023, 12, 409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sazuka, T.; Kamiya, N.; Nishimura, T.; Ohmae, K.; Sato, Y.; Imamura, K.; Nagato, Y.; Koshiba, T.; Nagamura, Y.; Ashikari, M.; et al. A rice tryptophan deficient dwarf mutant, tdd1, contains a reduced level of indole acetic acid and develops abnormal flowers and organless embryos. Plant J. 2009, 60, 227–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshikawa, T.; Ito, M.; Sumikura, T.; Nakayama, A.; Nishimura, T.; Kitano, H.; Yamaguchi, I.; Koshiba, T.; Hibara, K.I.; Nagato, Y.; et al. The rice FISH BONE gene encodes a tryptophan aminotransferase, which affects pleiotropic auxin-related processes. Plant J. 2014, 78, 927–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, H.; Wu, N.; Fu, J.; Wang, S.; Li, X.; Xiao, J.; Xiong, L. A GH3 family member, OsGH3-2, modulates auxin and abscisic acid levels and differentially affects drought and cold tolerance in rice. J. Exp. Bot. 2012, 63, 6467–6480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Wang, S.; Xu, Y.; Yu, C.; Shen, C.; Qian, Q.; Geisler, M.; Jiang, D.A.; Qi, Y. The auxin response factor, OsARF19, controls rice leaf angles through positively regulating OsGH3-5 and OsBRI1. Plant Cell Environ. 2015, 38, 638–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, S.-Q.; Xiang, J.-J.; Xue, H.-W. Studies on the rice LEAF INCLINATION1 (LC1), an IAA-amido synthetase, reveal the effects of auxin in leaf inclination control. Mol. Plant. 2013, 6, 174–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.-W.; Li, C.-H.; Cao, J.; Zhang, Y.-C.; Zhang, S.-Q.; Xia, Y.-F.; Sun, D.-Y.; Sun, Y. Altered architecture and enhanced drought tolerance in rice via the down-regulation of indole-3-acetic acid by TLD1/OsGH3.13 activation. Plant Physiol. 2009, 151, 1889–1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, N.; Zhu, A.; Tao, X.; Ding, Z.J.; Chang, S.; Ye, F.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, C.; Chen, Q.; Wang, J.; et al. Structures and mechanisms of the Arabidopsis auxin transporter PIN3. Nature 2022, 609, 616–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, K.; Wang, R.; Ou, X.; Fang, Z.; Tian, C.; Duan, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, M. OsTIR1 and OsAFB2 downregulation via OsmiR393 overexpression leads to more tillers, early flowering and less tolerance to salt and drought in rice. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e30039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bian, H.; Xie, Y.; Guo, F.; Han, N.; Ma, S.; Zeng, Z.; Wang, J.; Yang, Y.; Zhu, M. Distinctive expression patterns and roles of the miRNA393/TIR1 homolog module in regulating flag leaf inclination and primary and crown root growth in rice (Oryza sativa). New Phytol. 2012, 196, 149–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; You, J.; Xiong, L. Characterization of OsIAA1 gene, a member of rice Aux/IAA family involved in auxin and brassinosteroid hormone responses and plant morphogenesis. Plant Mol. Biol. 2009, 70, 297–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, F.; Huang, Y.; Qi, P.; Lian, G.; Hu, X.; Han, N.; Wang, J.; Zhu, M.; Qian, Q.; Bian, H. Functional analysis of auxin receptor OsTIR1/OsAFB family members in rice grain yield, tillering, plant height, root system, germination, and auxinic herbicide resistance. New Phytol. 2021, 229, 2676–2692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, L.; Lin, L.B.; Xue, H.W. Rice miR394 suppresses leaf inclination through targeting an F-box gene, LEAF INCLINATION 4. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2019, 61, 406–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.M.; Park, S.J.; Huang, J.; Lee, E.J.; Xuan, Y.H.; Je, B.I.; Kumar, V.; Priatama, R.A.; Raj, K.V.; Kim, S.H.; et al. Loose Plant Architecture1(LPA1) determines lamina joint bending by suppressing auxin signalling that interacts with C-22-hydroxylated and 6-deoxo brassinosteroids in rice. J. Exp. Bot. 2016, 67, 1883–1895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Yang, C.Y.; Miao, R.; Zhou, C.L.; Cao, P.H.; Lan, J.; Zhu, X.J.; Mou, C.L.; Huang, Y.S.; Liu, S.J.; et al. DS1/OsEMF1 interacts with OsARF11 to control rice architecture by regulation of brassinosteroid signaling. Rice 2018, 11, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, A.; Fujioka, S.; Takatsuto, S.; Tsujimoto, M.; Kitano, H.; Yoshida, S.; Asami, T.; Nakano, T. Involvement of C-22-Hydroxylated brassinosteroids in auxin-Induced lamina joint bending in rice. Plant Cell Physiol. 2009, 50, 1627–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakamoto, T.; Morinaka, Y.; Inukai, Y.; Kitano, H.; Fujioka, S. Auxin signal transcription factor regulates expression of the brassinosteroid receptor gene in rice. Plant J. 2013, 73, 676–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Q.; Li, T.Y.; Li, D.D.; Wang, Z.Y.; Li, S.; Li, D.P.; Han, X.; Liu, J.M.; Xuan, Y.H. Overexpression of Loose Plant Architecture 1 increases planting density and resistance to sheath blight disease via activation of PIN-FORMED 1a in rice. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2019, 17, 855–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, H.; Xiao, Y.; Liu, D.; Gao, S.; Liu, L.; Yin, Y.; Jin, Y.; Qian, Q.; Chu, C. Brassinosteroid regulates cell elongation by modulating gibberellin metabolism in rice. Plant Cell 2014, 26, 4376–4393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Unterholzner, S.J.; Rozhon, W.; Papacek, M.; Ciomas, J.; Lange, T.; Kugler, K.G.; Mayer, K.F.; Sieberer, T.; Poppenberger, B. Brassinosteroids are master regulators of gibberellin biosynthesis in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2015, 27, 2261–2672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Liu, H.; Guo, S.; Wang, B.; Li, Z.; Chong, K.; Xu, Y. OsmiR396d affects gibberellin and brassinosteroid signaling to regulate plant architecture in rice. Plant Physiol. 2018, 176, 946–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimada, A.; Ueguchi-Tanaka, M.; Sakamoto, T.; Fujioka, S.; Takatsuto, S.; Yoshida, S.; Sazuka, T.; Ashikari, M.; Matsuoka, M. The rice SPINDLY gene functions as a negative regulator of gibberellin signaling by controlling the suppressive function of the DELLA protein, SLR1, and modulating brassinosteroid synthesis. Plant J. 2006, 48, 390–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yano, K.; Morinaka, Y.; Wang, F.; Huang, P.; Takehara, S.; Hirai, T.; Ito, A.; Koketsu, E.; Kawamura, M.; Kotake, K.; et al. GWAS with principal component analysis identifies a gene comprehensively controlling rice architecture. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 21262–21267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Wang, Z.; Xu, Y.; Joo, S.H.; Kim, S.K.; Xue, Z.; Xu, Z.; Wang, Z.; Chong, K. OsGSR1 is involved in crosstalk between gibberellins and brassinosteroids in rice. Plant J. 2009, 57, 498–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.; Qian, Q.; Xu, T.; Zhang, Y.; Dong, G.; Gao, T.; Xie, Q.; Xue, Y. The U-Box E3 Ubiquitin Ligase TUD1 functions with a heterotrimeric G α subunit to regulate brassinosteroid-mediated growth in rice. PLoS Genet. 2013, 9, e1003391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Dan, Z.; Gao, F.; Chen, P.; Fan, F.; Li, S. Rice GROWTH-REGULATING FACTOR7 modulates plant architecture through regulating GA and indole-3-acetic acid metabolism. Plant Physiol. 2020, 184, 393–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Xu, F.; Chen, Z.; Teng, Z.; Sun, K.; Li, X.; Yu, J.; Zhang, G.; Liang, Y.; Huang, X.; et al. Synergistic interplay of ABA and BR signal in regulating plant growth and adaptation. Nat. Plants 2021, 7, 1108–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, F.; Yang, D.-C.; Meng, Y.-Q.; Jin, J.; Gao, G. PlantRegMap: Charting functional regulatory maps in plants. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 48, D1104–D1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.-Y.; Nakano, T.; Gendron, J.; He, J.; Chen, M.; Vafeados, D.; Yang, Y.; Fujioka, S.; Yoshida, S.; Asami, T.; et al. Nuclear-localized BZR1 mediates brassinosteroid-induced growth and feedback suppression of brassinosteroid biosynthesis. Dev. Cell. 2002, 2, 505–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.-H.; Zhou, L.-J.; Xu, P.; Xue, H.-W. SPOC domain-containing protein Leaf inclination3 interacts with LIP1 to regulate rice leaf inclination through auxin signaling. PLoS Genet. 2018, 14, e1007829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, S.; An, G.; Li, H.-Y. Rice leaf angle and grain size are affected by the OsBUL1 transcriptional activator complex. Plant Physiol. 2017, 173, 688–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.-Y.; Bai, M.-Y.; Wu, J.; Zhu, J.-Y.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, W.; Sun, Y.; Zhao, J.; Sun, X.; et al. Antagonistic HLH/bHLH transcription factors mediate brassinosteroid regulation of cell elongation and plant development in rice and Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2009, 21, 3767–3780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Li, M.-Q.; Chang, Y.-P.; Zhang, B.; Zhao, Q.-Z.; Zhao, W.-L. The basic helix-loop-helix transcription factor OsBLR1 regulates leaf angle in rice via brassinosteroid signalling. Plant Mol. Biol. 2020, 102, 589–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, H.; Kim, S.-H.; Lee, B.-D.; Lim, J.-H.; Lee, S.-J.; An, G.; Paek, N.-C. The Rice Basic Helix–Loop–Helix 79 (OsbHLH079) determines leaf angle and grain shape. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Long, Q.; Huang, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, K.; Zheng, M.; Sun, J.; Chen, H.; Chen, S.; et al. Overexpression of OsZHD1, a zinc finger homeodomain class homeobox transcription factor, induces abaxially curled and drooping leaf in rice. Planta 2014, 239, 803–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; Li, X.; Zhou, W.; Ren, Y.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Z.; Tang, J.; Tong, H.; Fang, J.; Bu, Q. Transcription factor OsWRKY53 positively regulates brassinosteroid signaling and plant architecture. Plant Physiol. 2017, 175, 1337–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.; Ke, Y.; Cao, J.; Wang, S.; Yuan, M. Knock out of transcription factor WRKY53 thickens sclerenchyma cell walls, confers bacterial blight resistance. Plant Physiol. 2021, 187, 1746–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, A.; Nakagawa, H.; Tomita, C.; Shimatani, Z.; Ohtake, M.; Nomura, T.; Jiang, C.-J.; Dubouzet, J.G.; Kikuchi, S.; Sekimoto, H.; et al. BRASSINOSTEROID UPREGULATED1, encoding a Helix-Loop-Helix protein, is a novel gene involved in brassinosteroid signaling and controls bending of the lamina joint in rice. Plant Physiol. 2009, 151, 669–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, S.; Chen, D.; Li, X.; Qiao, S.; Shi, C.; Li, C.; Shen, H.; Wang, X. Brassinosteroid signaling regulates leaf erectness in Oryza sativa via the control of a specific U-Type cyclin and cell proliferation. Dev. Cell 2015, 34, 220–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, P.; Zhao, J.; Hong, J.; Zhu, B.; Xia, S.; Zhu, E.; Han, P.; Zhang, K. Cytokinins regulate rice lamina joint development and leaf angle. Plant Physiol. 2023, 191, 56–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ning, J.; Zhang, B.; Wang, N.; Zhou, Y.; Xiong, L. Increased Leaf Angle1, a Raf-Like MAPKKK that interacts with a nuclear protein family, regulates mechanical tissue formation in the lamina joint of rice. Plant Cell 2011, 23, 4334–4347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Xu, Z.; Cao, S.; Chen, K.; Li, S.; Liu, X.; Gao, C.; Zhang, B.; Zhou, Y. An uncanonical CCCH-Tandem Zinc-Finger protein represses secondary wall synthesis and controls mechanical strength in rice. Mol. Plant. 2018, 11, 163–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, G.; Hu, H.; van de Meene, A.; Zhang, J.; Dong, L.; Zheng, S.; Zhang, F.; Betts, N.S.; Liang, W.; Bennett, M.J.; et al. AUXIN RESPONSE FACTORS 6 and 17 control the flag leaf angle in rice by regulating secondary cell wall biosynthesis of lamina joints. Plant Cell 2021, 33, 3120–3133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Ma, Y.; Yang, C.; Li, J. Rice OVATE family protein 6 regulates leaf angle by modulating secondary cell wall biosynthesis. Plant Mol. Biol. 2020, 104, 249–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, X.; He, M.; Mei, E.; Zhang, B.; Tang, J.; Xu, M.; Liu, J.; Li, X.; Wang, Z.; Tang, W.; et al. WRKY53 integrates classic brassinosteroid signaling and the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway to regulate rice architecture and seed size. Plant Cell 2021, 33, 2753–2775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Mei, E.; Tian, X.; He, M.; Tang, J.; Xu, M.; Liu, J.; Song, L.; Li, X.; Wang, Z.; et al. OsMKKK70 regulates grain size and leaf angle in rice through the OsMKK4-OsMAPK6-OsWRKY53 signaling pathway. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2021, 63, 2043–2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, W.; Guo, M.; Xu, L.; Wang, X.; Zhao, H.; Wang, J.; Yi, K. An SPX-RLI1 module regulates leaf inclination in response to phosphate availability in rice. Plant Cell 2018, 30, 853–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, M.; Zhang, Y.; Jia, X.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, J.; Yang, Q.; Ruan, W.; Yi, K. Alternative splicing of REGULATOR OF LEAF INCLINATION 1 modulates phosphate starvation signaling and growth in plants. Plant Cell 2022, 34, 3319–3338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, Z.-L.; Liu, N.; Deng, Z.-P.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, Z.-M.; Zhao, J.-L.; Sun, Y.; Wang, Z.-Y.; Zhang, S.-W. The receptor kinase OsWAK11 monitors cell wall pectin changes to fine-tune brassinosteroid signaling and regulate cell elongation in rice. Curr. Biol. 2022, 32, 2454–2466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Lu, M.; Zhao, Z.; Luo, Q.; Liu, F.; Zhao, J.; He, Y.; Tian, Y.; Zhan, H. Rice ILI atypical bHLH transcription factors antagonize OsbHLH157/OsbHLH158 during brassinosteroid signaling. Plant Physiol. 2024, 194, 1545–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rong, C.; Liu, Y.; Chang, Z.; Liu, Z.; Ding, Y.; Ding, C.; Zhang, J. Cytokinin oxidase/dehydrogenase family genes exhibit functional divergence and overlap in rice growth and development, especially in control of tillering. J. Exp. Bot. 2022, 73, 3552–3568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiao, X.; Wang, H.; Yan, J.; Kong, X.; Liu, Y.; Chu, J.; Chen, X.; Fang, R.; Yan, Y. Promotion of BR biosynthesis by miR444 is required for ammonium-triggered inhibition of root growth. Plant Physiol. 2020, 182, 1454–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shindo, M.; Yamamoto, S.; Shimomura, K.; Umehara, M. Strigolactones decrease leaf angle in response to nutrient deficiencies in rice. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, C.; Wang, X.; Li, Z.; He, Y.; Li, Y. Effects and mechanism of enhanced UV-B radiation on the flag leaf angle of rice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 12776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, J.-G.; Wang, C.-L.; Chen, F.-Y.; Qin, W.-C.; Yang, H.; Zhao, S.-H.; Xia, J.-L.; Du, X.; Zhu, Y.-F.; Wu, L.-S.; et al. Maize smart-canopy architecture enhances yield at high densities. Nature 2024. ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.-Y.; Zheng, J.-S.; Huang, R.-Y.; Huang, Y.-M.; Wang, H.-C.; Jiang, L.-R.; Fang, X.-J. Phytohormones signaling and crosstalk regulating leaf angle in rice. Plant Cell Rep. 2016, 35, 2423–2433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
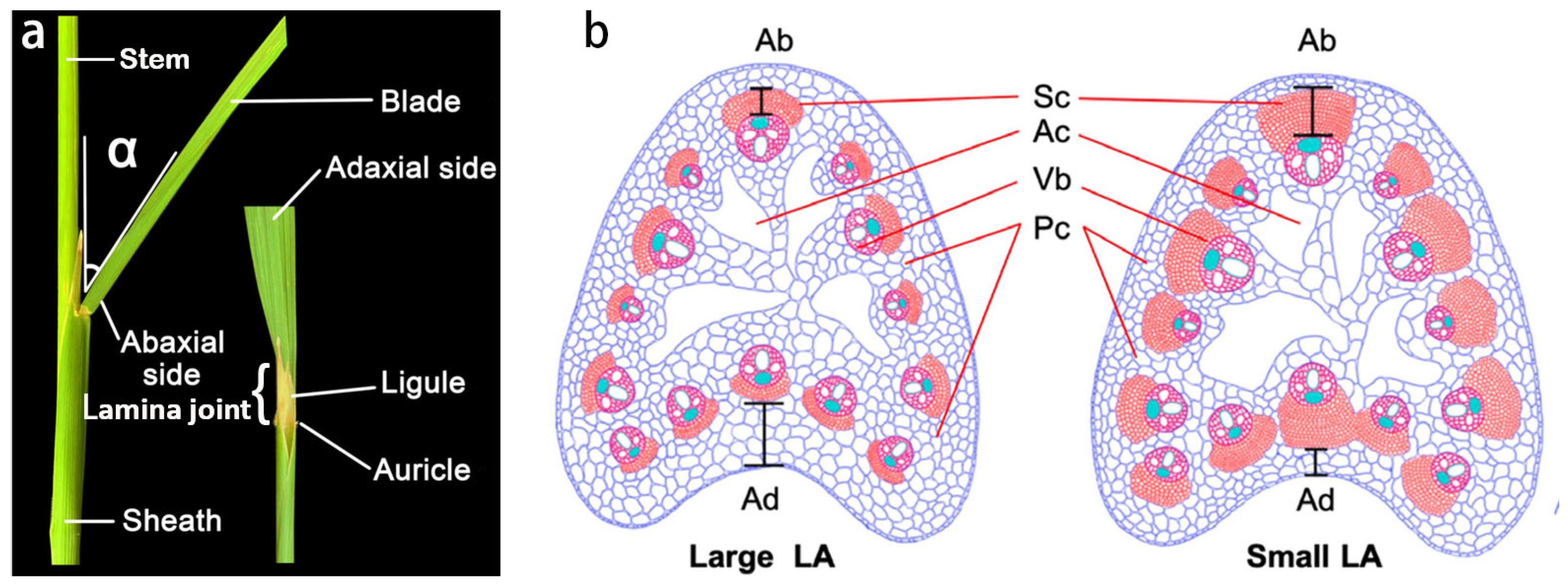
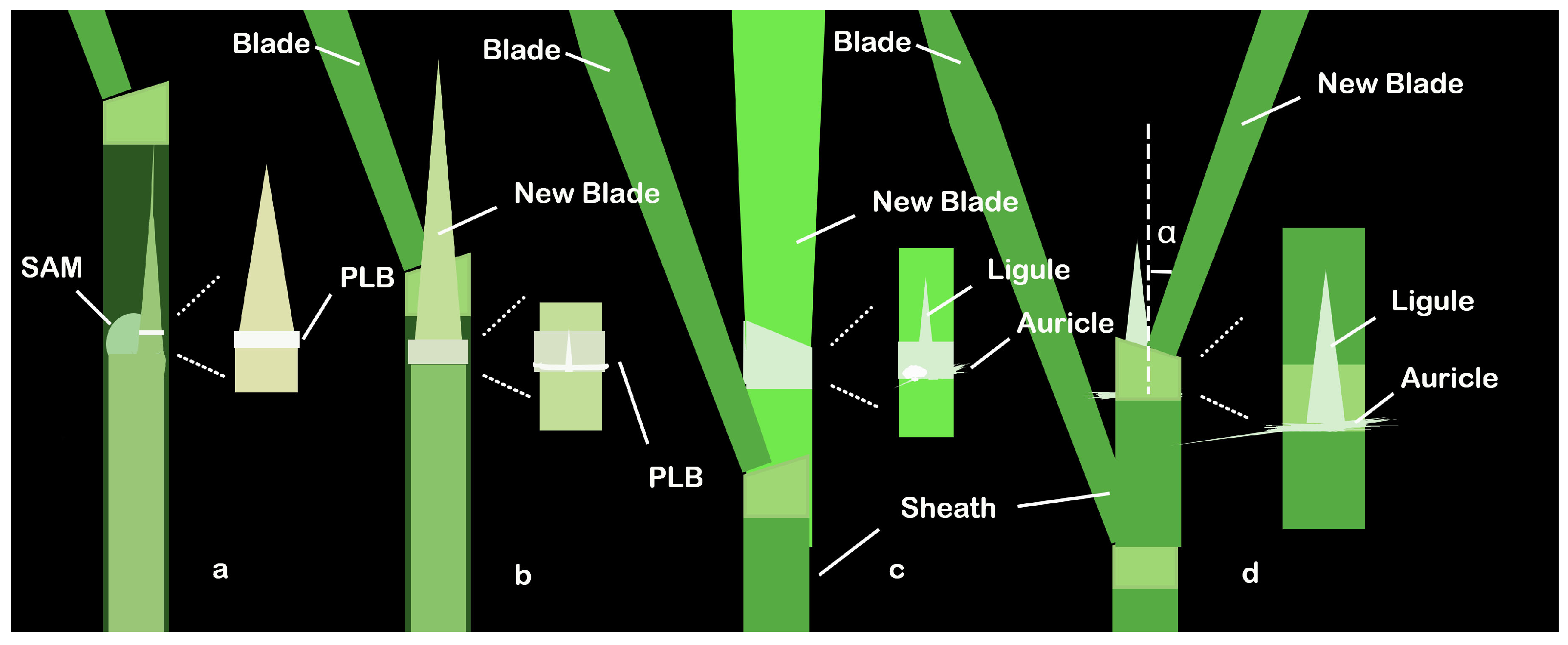

| Gene | MSU Locus | The Encoded Protein | Leaf Inclination Regulation | Regulatory Mechanism | References | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BR | CYP51G3 | LOC_Os05g12040 | A obtusifoliol 14 -demethylase | Promotes the expansion of parenchyma cells on the adaxial side of the lamina joint; positive | BR biosynthesis | [9] |
| SLG | LOC_Os08g44840 | a BAHD acyltransferase-like protein | Adaxial parenchyma cell length; positive | BR biosynthesis | [10] | |
| DWARF2 BRD2 DIM/DWF1 | LOC_Os10g25780 | A (24)-sterolreductase | Positive | BR biosynthesis | [11,12,13] | |
| D11 | LOC_Os04g39430 | A cytochrome P450 protein, CYP724B1 | Adaxial parenchyma cell length; positive | BR biosynthesis | [14] | |
| DWARF4 | LOC_Os03g12660 | A cytochrome P450 protein, CYP90B2 | Positive | BR biosynthesis | [1] | |
| CYP90D2/D2 | LOC_Os01g10040 | A cytochrome P450 protein, CYP90D2 | Positive | BR biosynthesis | [15] | |
| BRD1 OsDWARF | LOC_Os03g40540 | BR C-6 oxidase | Positive | BR biosynthesis | [16] | |
| BLA2 | LOC_Os01g29150 | A cytochrome P450 monooxygenase, CYP734As | Positive | BR biosynthesis | [19,20] | |
| RAVL1 | LOC_Os04g49230 | Related to ABI3/VP1-Like 1 | Positive | BR biosynthesis and BR signaling | [21,22] | |
| POW1 | LOC_Os07g07880 | Contains a putative helix-turn-helix DNA binding domain | Negative | Affects BR homeostasis | [23] | |
| OsBRI1 | LOC_Os01g52050 | Brassinolide receptor kinase | Positive | BR signaling | [26] | |
| OsBAK1 | LOC_Os08g07760 | BRI1-ASSOCIATED RECEPTOR KINASE | Adaxial parenchyma cell elongation; positive | BR signaling | [27] | |
| OsBZR1 | LOC_Os07g39220 | BR-signaling factor | Adaxial parenchyma cell elongation; positive | BR signaling | [38,73] | |
| OsSLA1 | LOC_Os04g41030 | Immunity-associated leucine-rich repeat receptor-like protein kinase | Positive | BR signaling | [28] | |
| OsPRA2 | LOC_Os06g50060 | Small GTP-binding protein; small G protein | Negative | BR signaling | [29] | |
| ELT1 | LOC_Os02g58390 | Receptor-like protein that has enhanced leaf inclination and tiller number | Positive | BR signaling | [30] | |
| OsGSK1 | LOC_Os01g10840 | Glycogen synthase kinase3-like | Negative | BR signaling | [33] | |
| OsGSK2 | LOC_Os05g11730 | GSK3/SHAGGY-like kinase | Negative | BR signaling | [35,36] | |
| OsGSK3 | LOC_Os02g14130 | GSK3/SHAGGY-like kinase | Negative | BR signaling | [32] | |
| OsGSK4 | LOC_Os06g35530 | GSK3/SHAGGY-like kinase | Negative | BR signaling | [31] | |
| DLT | LOC_Os06g03710 | GRAS protein | Positive | BR signaling | [36] | |
| OsDLA | LOC_Os01g71970 | GRAS protein | Positive | BR signaling | [37] | |
| RLA1/SMOS1 | LOC_Os05g32270 | GRAS protein | Positive | BR signaling | [34,35] | |
| 14-3-3 (GF14c) | LOC_Os08g33370 | G-box factor 14-3-3 homologs | — | BR signaling | [38,40] | |
| OsLIC1 OsLIC | LOC_Os06g49080 | CCCH-Type Zinc Finger Protein | Negative | BR signaling | [41] | |
| OsMDP1 | LOC_Os03g08754 | Rice MADS-box transcription factor | Adaxial parenchyma cell elongation; negative | BR signaling | [42] | |
| OsXTR1 | LOC_Os11g33270 | Xyloglucan endotransglycosylase-related gene 1 | Adaxial parenchyma cell elongation; positive | BR signaling | [42] | |
| OsLC2 | LOC_Os02g05840 | Vernalization insensitive 3-like protein | Adaxial parenchyma cell division; negative | BR signaling | [43] | |
| AUXIN | OsTDD1 | LOC_Os04g38950 | Rice Anthranilate Synthase -Subunit | Negative | IAA biosynthesis | [46] |
| FIB/OsTAR2 OsTAA1 | LOC_Os01g07500 | Tryptophan aminotransferase | Negative | IAA biosynthesis | [47] | |
| LC1/OsGH3-1 | LOC_Os01g57610 | Indole-3-acetic acid-amido synthetase | Adaxial parenchyma cell length and division; positive | Auxin signaling | [50] | |
| OsGH3-2 | LOC_Os01g55940 | Indole-3-acetic acid-amido synthetase gene | Negative | Auxin signaling | [48] | |
| OsGH3-5 | LOC_Os05g50890 | JA-amino acid synthetase | Negative | Auxin signaling | [49] | |
| OsGH3-13/TLD1 | LOC_Os11g32510 | Auxin-responsive GH3 gene family member | Positive | Auxin signaling | [51] | |
| OsARF19 | LOC_Os06g48950 | Auxin response factor | Adaxial parenchyma cell division; positive | BR and IAA interactions | [49] | |
| OsPIN1b | LOC_Os02g50960 | Auxin efflux transporter | The increase in the adaxial cell division; positive | Auxin signaling | [45] | |
| OsTIR1 | LOC_Os05g05800 | Auxin receptor | Negative | Auxin signaling and interaction with N | [53,54] | |
| OsAFB2 | LOC_Os04g32460 | Auxin receptor | Negative | Auxin signaling interaction with N | [53] | |
| OsIAA1 | LOC_Os01g08320 | Aux/IAA protein | Positive | Auxin signaling | [55] | |
| OsLC4 | LOC_Os01g69940 | F-box protein | Adaxial parenchyma cell length; positive | Auxin signaling | [57] | |
| OsMIR394 | miRBase Library Accession Number:MI0001027 | MicroRNA | Adaxial parenchyma cell length; positive | Auxin signaling | [57] | |
| OsIAA12 | LOC_Os03g43410 | Aux/IAA protein | Negative | Auxin signaling | [74] | |
| Crosstalk between the phytohormones | DS1 | LOC_Os01g12890 | EMF1-like protein | Positive | BR and IAA interactions | [59] |
| OsARF11 | LOC_Os04g56850 | Auxin response factor | Positive | BR and IAA interactions | [59] | |
| LPA1 | LOC_Os03g13400 | NDETERMINATE DOMAIN Protein | Adaxial parenchyma cell length; positive | BR and IAA interactions | [59] | |
| OsSLR1 | LOC_Os03g49990 | DELLA protein | Negative | BR and GA interactions | [63] | |
| OsMIR396 | LOC_Os04g57830 | MicroRNA | Adaxial cell size; positive | BR and GA interactions | [65] | |
| OsGRF4/GS2 GL2/LGS1 GLW2 | LOC_Os02g47280 | Growth-regulating factor | Negative | BR and GA interactions | [65] | |
| OsSPY | LOC_Os08g44510 | O-linked N-acetylglucosamine transferase | Negative | BR and GA interactions | [66,67] | |
| OsGSR1 | LOC_Os06g15620 | GA-stimulated transcript gene | Positive | BR and GA interactions | [68] | |
| D1/RGA1 | LOC_Os05g26890 | G protein subunit | Positive | BR and GA interactions | [61,69] | |
| TUD1 | LOC_Os03g13010 | U-box E3 ubiquitin ligase | Positive | BR signaling | [69] | |
| OsGRF7 | LOC_Os12g29980 | Growth-regulating factor | Increased parenchymal cell layers in the adaxial side of the lamina joints | IAA and GA signaling | [70] | |
| ARF12 | LOC_Os04g57610 | Auxin response factor | Negative | Auxin signaling | [70] | |
| ABI3 | LOC_Os01g68370 | B3 domain transcription factor | Positive | IAA and ABA signaling | [71] | |
| Trans- cription factors | OsBUL1 | LOC_Os02g51320 | Atypical bHLH protein | Adaxial parenchyma cell length; positive | BR signaling | [75] |
| OsBC1 | LOC_Os09g33580 | bHLH protein | Adaxial parenchyma cell length; positive | BR signaling | [75] | |
| LO9-177 | LOC_Os03g43910 | OsBUL1-interacting protein; kxDL motif-containing protein | Adaxial parenchyma cell length; positive | BR signaling | [75] | |
| OsILI1 | LOC_Os04g54900 | bHLH transcription factor | Adaxial parenchyma cell elongation; positive | BR signaling | [76] | |
| OsIBH1 | LOC_Os04g56500 | bHLH protein | Adaxial parenchyma cell elongation; negative | BR signaling | [76] | |
| OsBLR1 OsbHLH079 | LOC_Os02g47660 | bHLH transcription factor | The expansion of cell size in the adaxial side; positive | BR signaling | [77,78] | |
| OsZHD1 | LOC_Os09g29130 | Zn-finger transcription factor | Positive | Other | [79] | |
| OsLC3 | LOC_Os06g39480 | SPOC domain-containing transcription suppressor | Adaxial parenchyma cell length; negative | Auxin signaling | [74] | |
| LIP1 | LOC_Os10g37640 | HIT zinc finger domain-containing protein | Adaxial parenchyma cell length; negative | Auxin signaling | [74] | |
| OsWRKY53 | LOC_Os05g27730 | WRKY transcription factor | Adaxial parenchyma cell elongation; positive | BR homeostasis | [80,81] | |
| OsBU1 | LOC_Os06g12210 | bHLH protein | Adaxial parenchyma cell length; positive | BR signaling | [82] | |
| Sclere- nchyma cells development | CYC U4;1 | LOC_Os10g41430 | Cyclin-like gene | Abaxial sclerenchyma cell proliferation; negative | BR signaling | [83] |
| OsCKX3 | LOC_Os10g34230 | Cytokinin oxidase/dehydrogenase | Asymmetric proliferation of the cells and vascular bundles; negative | CK signaling | [84] | |
| OsILA1 | LOC_Os06g50920 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase | Abnormal vascular bundle formation and cell wall composition; negative | Other | [85] | |
| IIP4 | LOC_Os04g38520 | ILA1-interacting protein 4 | The secondary cell wall biosynthesis; negative | The secondary cell wall biosynthesis | [85,86] | |
| NAC29 | LOC_Os08g02300 | NAC Transcription Factor | The cellulose biosynthesis; positive | The secondary cell wall biosynthesis | [86] | |
| NAC31 | LOC_Os08g01330 | NAC Transcription Factor | The cellulose biosynthesis; positive | The secondary cell wall biosynthesis | [86] | |
| MYB61 | LOC_Os01g18240 | MYB family transcription factor | the cellulose biosynthesis; positive | The secondary cell wall biosynthesis | [86] | |
| CesA4 | LOC_Os01g54620 | Cellulose synthase catalytic subunit 4 | The cellulose biosynthesis; positive | The secondary cell wall biosynthesis | [86] | |
| CesA7 | LOC_Os10g32980 | Cellulose synthase catalytic subunit 7 | The cellulose biosynthesis; positive | The secondary cell wall biosynthesis | [86] | |
| CesA9 | LOC_Os09g25490 | Cellulose synthase catalytic subunit 9 | The cellulose biosynthesis; positive | The secondary cell wall biosynthesis | [86] | |
| CESA6 | LOC_Os07g14850 | Cellulose synthase catalytic subunit 6 | The cellulose biosynthesis; positive | The secondary cell wall biosynthesis | [86] | |
| OsARF6 | LOC_Os02g06910 | Auxin response factor | negative | Auxin signaling | [87] | |
| OsARF17 | LOC_Os06g46410 | Auxin response factor | negative | Auxin signaling | [87] | |
| OSH15 (KNOX) | LOC_Os07g03770 | KNOX family class 1 homeobox gene of rice | The secondary cell wall biosynthesis; negative | The secondary cell wall biosynthesis | [88] | |
| OsIRX9 | LOC_Os07g49370 | glycosyltransferase family 43 protein | Xylan; negative | Xylan | [88] | |
| OsOFP6 | LOC_Os01g60810 | OVATE family protein 6 | The secondary cell wall biosynthesis; negative | The secondary cell wall biosynthesis | [88] | |
| OsMYB63 | LOC_Os04g50770 | R2R3-type MYB family transcription factor | Positive | The cell wall biosynthesis | [81] | |
| MKKK10 SMG2 | LOC_Os04g47240 | Mitogen activated protein Kinase Kinase Kinase 10 | Positive | BR homeostasis | [89] | |
| MAPKK4 | LOC_Os02g54600 | Mitogen activated protein Kinase Kinase 4 | Positive | BR homeostasis | [80,89] | |
| MAPK6 | LOC_Os06g06090 | Mitogen activated protein Kinase 6 | Positive | BR homeostasis | [80,89] | |
| MKKK70 | LOC_Os01g50410 | Mitogen activated protein Kinase Kinase Kinase 70 | Positive | BR homeostasis | [90] | |
| Other | SPX1 | LOC_Os06g40120 | SPX family protein | Cell elongation of Lamin joint; negative | Involved in Pi and BR interactions | [91] |
| SPX2 | LOC_Os02g10780 | SPX family protein | Cell elongation of Lamin joint; negative | Involved in Pi and BR interactions | [91] | |
| RLI1 | LOC_Os04g56990 | GARP family transcription factor | Cell elongation of Lamin joint; positive | Involved in Pi and BR interactions | [91,92] | |
| OsWAK11 | LOC_Os02g02120 | Wall-associated receptor kinase 11 | Negative | The cell wall biosynthesis | [93] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, F.; Fang, C.; Liang, W. Molecular Mechanisms Regulating Lamina Joint Development in Rice. Agronomy 2024, 14, 1562. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14071562
Zhang F, Fang C, Liang W. Molecular Mechanisms Regulating Lamina Joint Development in Rice. Agronomy. 2024; 14(7):1562. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14071562
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Fan, Chaowei Fang, and Weihong Liang. 2024. "Molecular Mechanisms Regulating Lamina Joint Development in Rice" Agronomy 14, no. 7: 1562. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14071562
APA StyleZhang, F., Fang, C., & Liang, W. (2024). Molecular Mechanisms Regulating Lamina Joint Development in Rice. Agronomy, 14(7), 1562. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14071562







