Asynchronous Synergetic Remediation Strategy for Cd-Contaminated Soil via Passivation and Phytoremediation Technology
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Medicines
2.2. Soil Sample Preparation
2.3. Experimental Design
2.3.1. Plant Screening Experiment
2.3.2. Passivator Screening Experiment and Dosage Conditions Experiment
2.3.3. Impact of Passivators on Plant Growth in Cd-Contaminated Soil
2.3.4. Synergetic Remediation Experiment
2.3.5. Field Remediation
2.4. Analysis of Soil Samples
2.4.1. Determination of Bioavailable Cd
2.4.2. Determination of Cd Forms in Soil
2.4.3. Soil Humus Content Measurement
2.4.4. Soil Electrical Conductivity Measurement
2.4.5. Soil X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS)
2.4.6. Analysis of Microbial Diversity in Soil
2.4.7. Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Screening of Optimized Plants for Synergetic Remediation
3.2. Screening of Optimized Passivators for Combined Remediation
3.2.1. Effect of SDD Dosage on Passivation Effect
3.2.2. Effect of SDD Dosage on the Fraction of Cd in Soil
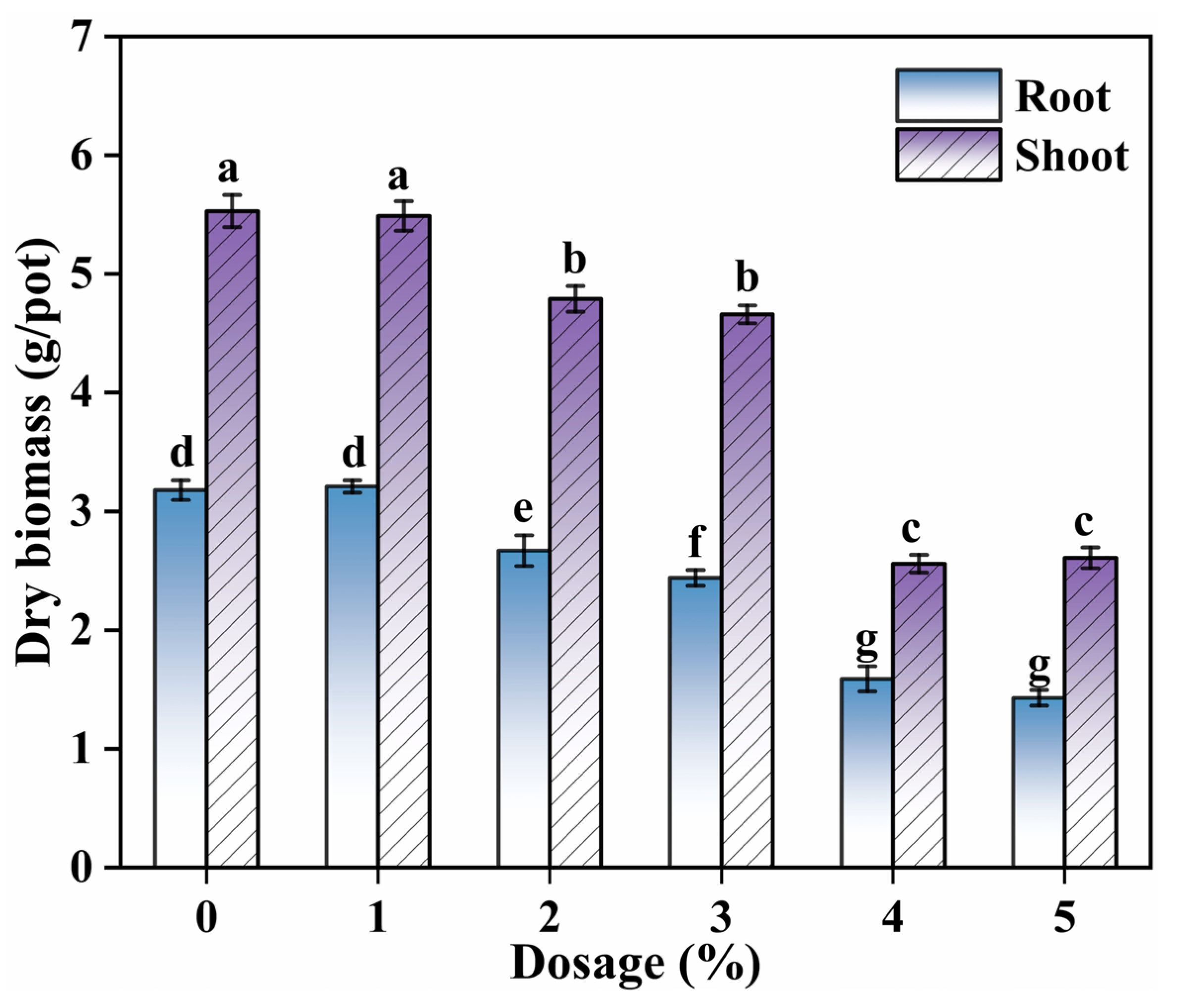
3.2.3. The Effect of SDD Dosage on Plant Biomass
3.3. Comparison of Passivation Effects in Synergetic Remediation Strategies
3.4. Remediation Mechanism
3.4.1. Effect of SDD Dosage on Soil Humus Content
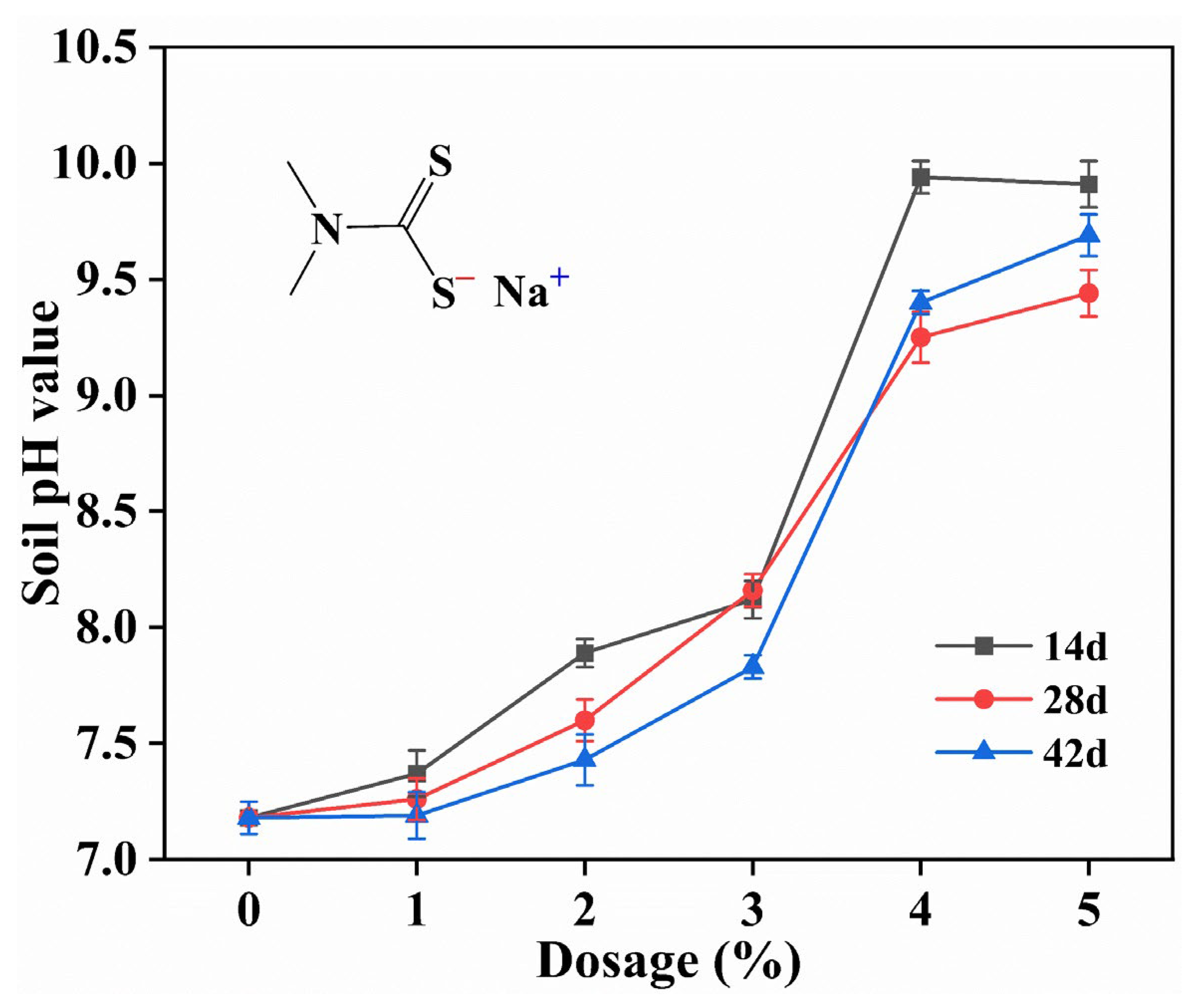
3.4.2. Effect of SDD on Soil pH Value
3.4.3. Impact of SDD Dosage on Soil Electrical Conductivity and Moisture Content
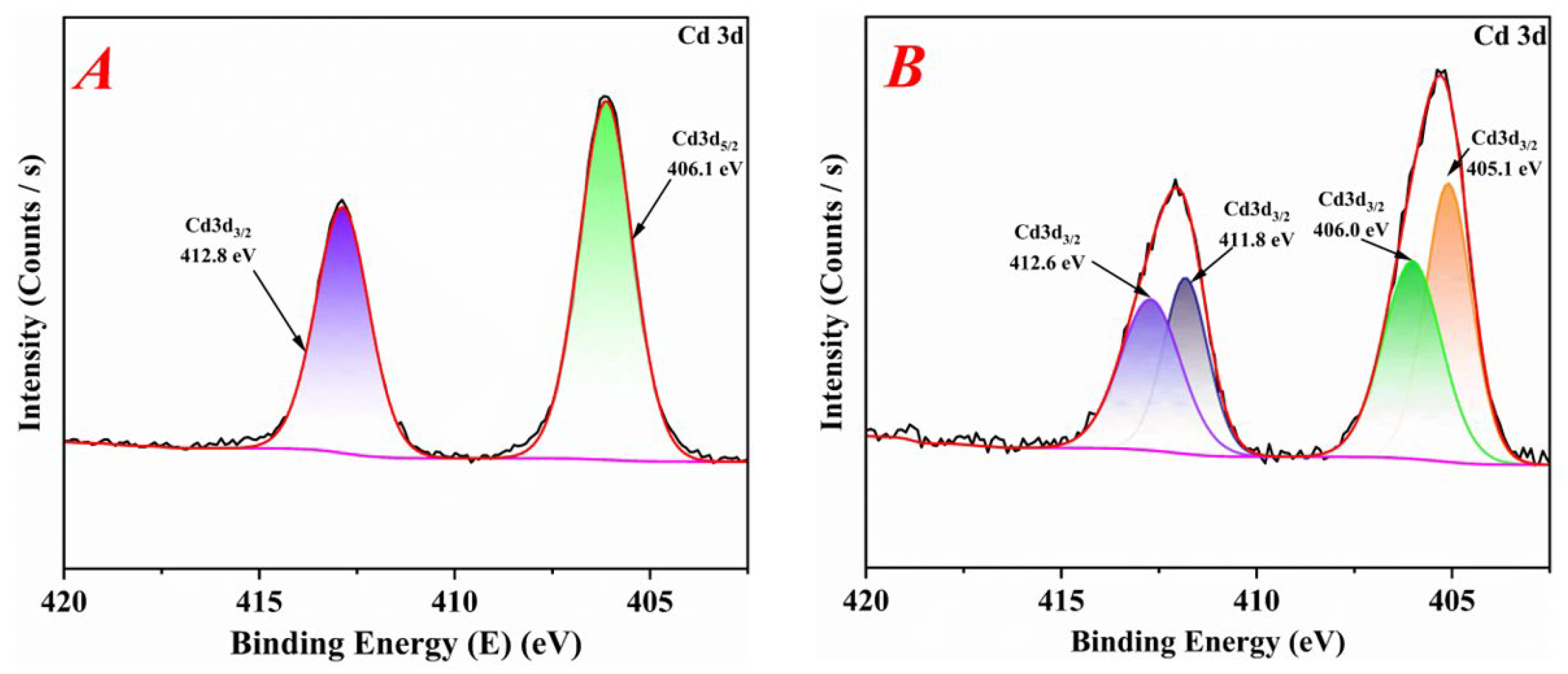
3.4.4. X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS) Analysis
3.4.5. Microbial Diversity Analysis in Soil
4. Application of Two Remediation Strategies in the Field
5. Conclusions
- Screening experiments on enrichment plants and six passivators revealed that SDD and Tagetes patula L. exhibited the most effective remediation results.
- Synergetic remediation experiments showed that both sequential combined methods significantly reduced the effective Cd content in the soil. The remediation effectiveness was ranked as asynchronous application > synchronous application.
- Mechanistic studies fully confirmed that the strong chelation of the dithiocarbamate group (S=C-S-) in SDD with Cd2+ in the soil, coupled with the increase in soil pH, were the primary factors contributing to the observed excellent remediation effects in the two sequential synergetic remediation strategies. Furthermore, variations in microbial populations, specifically Proteobacteria and Chloroflexi, were identified as crucial factors influencing the effectiveness of the two sequential remediation approaches.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zulkernain, N.H.; Uvarajan, T.; Ng, C.C. Roles and significance of chelating agents for potentially toxic elements (PTEs) phytoremediation in soil: A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 341, 117926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cristaldi, A.; Conti, G.O.; Jho, E.H.; Zuccarello, P.; Ferrante, M. Phytoremediation of contaminated soils by heavy metals and PAHs. A brief review. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2017, 8, 309–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, W.; Mao, K.; Zhang, H.; Junaid, M.; Xu, N.; Rasool, A.; Feng, X.; Yang, Z. Comprehensive review of the basic chemical behaviours, sources, processes, and endpoints of trace element contamination in paddy soil-rice systems in rice-growing countries. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 397, 122720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Li, H.; Wang, C.; Yuan, X. Heavy metal contamination risk assessment of commercial fish in China’s Dongting Lake. Ecohydrol. Hydrobiol. 2023, 1642–3593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Luo, K.; Su, Z.; Wu, Y.; Wang, X. Impact Imposed by Urbanization on Soil Heavy Metal Content of Lake Wetland and Evaluation of Ecological Risks in East Dongting Lake in China. Urban Clim. 2021, 42, 101117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.; Tian, Y.; Yao, Y.; Jiang, W.; Dong, J.; Huang, X.; Wu, X.; Farooq, T.H.; Yan, W. Ecological restoration research progress and prospects: A bibliometric analysis. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 155, 110968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarwar, N.; Imran, M.; Shaheen, M.R.; Ishaque, W.; Kamran, M.A.; Matloob, A.; Rehim, A.; Hussain, S. Phytoremediation strategies for soils contaminated with heavy metals: Modifications and future perspectives. Chemosphere 2017, 171, 710–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Aghajani Delavar, M. Techno-economic analysis of phytoremediation: A strategic rethinking. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 902, 165949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Wu, S.; Sui, X.; Cheng, S. Phytoremediation of contaminated sediment combined with biochar: Feasibility, challenges and perspectives. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 465, 133135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mai, X.; Tang, J.; Tang, J.; Zhu, X.; Yang, Z.; Liu, X.; Zhuang, X.; Feng, G.; Tang, L. Research progress on the environmental risk assessment and remediation technologies of heavy metal pollution in agricultural soil. J. Environ. Sci. 2024, 149, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Liu, H.; Li, J.; Chen, S.; uz Zaman, Q.; Sultan, K.; Rehman, M.; Saud, S.; El-Kahtany, K.; Fahad, S.; et al. Combined passivators regulate physiological, antioxidant potential and metals accumulation in potato grown in metals contaminated soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 912, 168956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gasco, G.; Alvarez, M.L.; Paz-Ferreiro, J.; Mendez, A. Combining phytoextraction by Brassica napus and biochar amendment for the remediation of a mining soil in Riotinto (Spain). Chemosphere 2019, 231, 562–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Sun, G.; Liang, X.; Sun, Y.; Wang, L.; Huang, Q. Comparative effects of Tagetes patula L. extraction, mercapto-palygorskite immobilisation, and the combination thereof on Cd accumulation by wheat in Cd-contaminated soil. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 224, 112639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno-Maroto, J.M.; Alonso-Azcarate, J. Evaluation of the USDA soil texture triangle through Atterberg limits and an alternative classification system. Appl. Clay Sci. 2022, 229, 106689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HJ 804-2016; Soil—Determination of Bioavailable Form of Eight Elements—Extraction with Buffered DTPA Solution/Inductively Coupled Plasma Optical Emission Spectrometry. China Environmental Press: Beijing, China, 2016. Available online: https://www.mee.gov.cn/ywgz/fgbz/bz/bzwb/jcffbz/201606/W020160701540428540945.pdf (accessed on 10 August 2024).
- GB/T 25282-2010; Soil and Sediment-Sequential Extraction Procedure of Speciation of 13 Trace Elements. Standardization Administration of China: Beijing, China, 2016. Available online: http://c.gb688.cn/bzgk/gb/showGb?type=online&hcno=3CD527C889212919CFEC80932D514455 (accessed on 10 August 2024).
- Khan, I.; Awan, S.A.; Rizwan, M.; Ali, S.; Huang, L. Effects of silicon on heavy metal uptake at the soil-plant interphase: A review. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 222, 112510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.; Ma, J.; Chen, F.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Bian, Z. Effective remediation of electronic waste contaminated soil by the combination of metal immobilization and phytoremediation. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 107410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- F-HZ-DZ-TR-0046; Soil—Determination of Organic Matter—Potassium Dichromate Oxidation External Heating Method. Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2011. Available online: http://www.sczhjc.com/u/site/a2/201806/nfcms_20180611093026ZWO2VP.pdf (accessed on 10 August 2024).
- HJ802-2016; Soil Quality-Determination of Conductivity-Electrode Method. China Environmental Press: Beijing, China, 2016. Available online: https://www.mee.gov.cn/ywgz/fgbz/bz/bzwb/jcffbz/201606/W020160701538833535834.pdf (accessed on 10 August 2024).
- Parajuli, P.B.; Duffy, S. Evaluation of Soil Organic Carbon and Soil Moisture Content from Agricultural Fields in Mississippi. Open J. Soil Sci. 2013, 3, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, X.; Kang, X.; Zhang, J.; Sun, M.; Yu, J.; Wang, H.; Pan, H.; Yang, Q.; Lou, Y.; et al. Effects of a novel Cd passivation approach on soil Cd availability, plant uptake, and microbial activity in weakly alkaline soils. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 253, 114631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NY/T 1377-20; Determination of pH in Soil. The Ministry of Agriculture of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2007. Available online: https://qccdata.qichacha.com/Standard/StandardIndus/5a0bcc145f45d903949f1e15f03a098f.pdf (accessed on 10 August 2024).
- Fan, J.-X.; Wang, Y.-J.; Liu, C.; Wang, L.-H.; Yang, K.; Zhou, D.-M.; Li, W.; Sparks, D.L. Effect of iron oxide reductive dissolution on the transformation and immobilization of arsenic in soils: New insights from X-ray photoelectron and X-ray absorption spectroscopy. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 279, 212–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Wang, D.; Tang, W.; Wang, L.; Guo, S. Phytoremediation of cadmium-polluted soil assisted by D-gluconate- enhanced Enterobacter cloacae colonization in the Solanum nigrum L. rhizosphere. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 732, 139265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Y.; Sun, J.; Ren, L.; Gao, Y.; Wu, X.; Lian, G. Enhanced microbial remediation of uranium tailings through red soil utilization. J. Environ. Radioact. 2024, 277, 107463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswal, B.; Singh, S.; Patra, A.; Mohapatra, K. Evaluation of phytoremediation capability of French marigold (Tagetes patula) and African marigold (Tagetes erecta) under heavy metals contaminated soils. Int. J. Phytoremediat. 2021, 24, 954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, L.; Zhong, X.; Liao, J.; Zheng, L.; Huang, X. Efficient phytoremediation of Cd-contaminated soils by Tagetes patula L.: Greenhouse experiment, field study and meta-analysis. Curr. Res. Biotechnol. 2024, 7, 100212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrington, J.M.; Jones, S.B.; Vanderveer, D.J.; Bartolotti, L.J.; Hancock, R.D. Structural, molecular mechanics, and DFT study of cadmium(II) in its crown ether complexes with axially coordinated ligands, and of the binding of thiocyanate to cadmium(II). Inorg. Chim. Acta 2009, 362, 1122–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Liu, B.; Lu, Y.; Lu, F.; Wu, X.; You, W.; Huang, B. Bioavailability of cadmium to celery (Apium graveolens L.) grown in acidic and Cd-contaminated greenhouse soil as affected by the application of hydroxyapatite with different particle sizes. Chemosphere 2020, 240, 124916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Gong, H.; He, F.; Repo, E.; Yang, W.; Liao, Q.; Zhao, F. Iron-doped hydroxyapatite for the simultaneous remediation of lead-, cadmium-and arsenic-co-contaminated soil. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 312, 119953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Xi, D.; Li, C.; Yang, Z.; Lin, Z.; Si, M. “In-situ synthesized” iron-based bimetal promotes efficient removal of Cr(VI) in by zero-valent iron-loaded hydroxyapatite. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 420, 126540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Song, X.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H.; Ge, S. The sorption and short-term immobilization of lead and cadmium by nano-hydroxyapatite/biochar in aqueous solution and soil. Chemosphere 2022, 286, 131810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, O.Y. Effects of Aqueous Al, Cd, Cu, Fe (II), Ni, and Zn on Pb Immobllization by Hydroxyapatite. Environ. Technol. 1994, 28, 1219–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramer, E.R.; Morey, A.M.; Staruch, M.; Suib, S.L.; Jain, M.; Budnick, J.I.; Wei, M. Synthesis and characterization of iron-substituted hydroxyapatite via a simple ion-exchange procedure. J. Mater. Sci. 2013, 48, 665–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Chen, D.; Pan, M.; Gu, T.; Zhong, L.; Chen, G.; Yan, B.; Cheng, Z. Performance of chemical chelating agent stabilization and cement solidification on heavy metals in MSWI fly ash: A comparative study. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 247, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.H.; Ji, Y.X.; Wang, J.J. Synthesis of heavy metal chelating agent with four chelating groups of N~1,N~2,N~4,N~5-tetrakis(2-mercaptoethyl)benzene-1,2,4,5-tetracarboxamide (TMBTCA) and its application for Cu-containing wastewater. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 241–242, 427–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-El-Halawa, R.; Zabin, S.A. Removal efficiency of Pb, Cd, Cu and Zn from polluted water using dithiocarbamate ligands. J. Taibah Univ. Sci. 2015, 11, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shotonwa, I.O.; Osifeko, O.L.; Amos, S.F.; Akande, E.O.; Adejare, A.A.; Olaoye, T.R.; Akinwande, B.B.; Adeoluwa, Z.A.; Benjamin, N.F.; Lambo, M.O. Structural diversity, computational outputs, and supramolecular solid-state assemblies in sustaining the coordination chemistry of zinc, cadmium, and mercury dithiocarbamates. J. Mol. Struct. 2024, 1310, 138242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Li, D.; Yang, J.; Ye, Y.; Luo, J.; Zhou, X.; Yang, L.; Liu, Z. A combined passivator of zeolite and calcium magnesium phosphate fertilizer: Passivation behavior and mechanism for Cd (II) in composting. Environ. Res. 2023, 231, 116306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, M.; Sun, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, Q.; Chen, Q.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, B.; Chen, T.; Jin, J.; Yang, T. The potential of ferrihydrite-synthetic humic-like acid composite as a soil amendment for metal-contaminated agricultural soil: Immobilization mechanisms by combining abiotic and biotic perspectives. Environ. Res. 2024, 250, 118470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, M.; Ha, Z.; Xu, X.; Lv, C.; Li, C.; Du, D.; Chi, R. Simultaneous immobilization of multiple heavy metals in polluted soils amended with mechanical activation waste slag. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 894, 164730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, L.; Tang, M.; Hu, W.; Chen, L.; Ai, S. Speciation of heavy metals in soils and their immobilization at micro-scale interfaces among diverse soil components. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 825, 153862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yan, Y.; He, C.; Feng, Y.; Darma, A.; Yang, J. The immobilization of cadmium by rape straw derived biochar in alkaline conditions: Sorption isotherm, molecular binding mechanism, and in-situ remediation of Cd-contaminated soil. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 351, 123969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odularu, A.T.; Ajibade, P.A. Dithiocarbamates: Challenges, Control, and Approaches to Excellent Yield, Characterization, and Their Biological Applications. Bioinorg. Chem. Appl. 2019, 2019, 8260496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Jia, J.; Zhang, H.; Sun, S. Enhanced Cr (VI) stabilization in soil by chitosan/bentonite composites. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 238, 113573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, H.; Qu, C.C.; Liu, J.; Chen, W.; Cai, P.; Shi, Z.; Yu, X.Y.; Huang, Q. Molecular investigation on the binding of Cd(II) by the binary mixtures of montmorillonite with two bacterial species. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 229, 871–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, C.; Qian, S.; Chen, L.; Guan, Y.; Zheng, L.; Liu, S.; Chen, W.; Cai, P.; Huang, Q. Size-dependent bacterial toxicity of hematite particles. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 8147–8156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almeida, E.M.F.; De Souza, D. Current electroanalytical approaches in the carbamates and dithiocarbamates determination. Food Chem. 2023, 417, 135900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Xiao, X.; Wei, W.; Li, L.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, N.; Wang, M. Soil rare microorganisms mediated the plant cadmium uptake: The central role of protists. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 908, 168505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farinati, S.; DalCorso, G.; Panigati, M.; Furini, A. Interaction between selected bacterial strains and Arabidopsis halleri modulates shoot proteome and cadmium and zinc accumulation. J. Exp. Bot. 2011, 62, 3433–3447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dakora, F.D.; Phillips, D.A. Root exudates as mediators of mineral acquisition in low-nutrient environments. Plant Soil 2002, 245, 35–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harmsen, K. Behaviour of Heavy Metals in Soils; Wageningen University and Research: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 1977. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, X.; Zhang, J.; Liu, G.; Kong, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, G.; Luo, Y.; Wang, G.; Yuan, J. Enhancing the transformation of carbon and nitrogen organics to humus in composting: Biotic and abiotic synergy mediated by mineral material. Bioresour. Technol. 2024, 393, 130126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Six, J.; Conant, R.T.; Paul, E.A.; Paustian, K. Stabilization mechanisms of soil organic matter: Implications for C-saturation of soils. Plant Soil 2002, 241, 155–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q.; He, Y.; Wu, Y.; Dian, B.; Zhang, J.; Li, T.; Jiang, M. Solidification/stabilization of soil heavy metals by alkaline industrial wastes: A critical review. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 312, 120094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zha, F.; Wang, H.; Xu, L.; Yang, C.; Kang, B.; Chu, C.; Deng, Y.; Tan, X. Initial feasibility study in adsorption capacity and mechanism of soda residue on lead (II)-contaminated soil in solidification/stabilization technology. Environ. Earth Sci. 2020, 79, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Huang, Y.; Huang, L.; Huang, Q.; Li, Y.; Li, X.; Yang, S.; Liu, C.; Liu, Z. Combined biochar and soda residues increases maize yields and decreases grain Cd/Pb in a highly Cd/Pb-polluted acid Udults soil. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2021, 306, 107198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Zhang, N.; Tan, F.; He, J.; Li, J.; Bao, L. The influence of passivating agent on soil pollution. MethodsX 2021, 8, 101321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pomiès, M.-P.; Lequeux, N.; Boch, P. Speciation of cadmium in cement: Part I. Cd2+ uptake by CSH. Cem. Concr. Res. 2001, 31, 563–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Siddique, M.S.; Liu, M.; Graham, N.; Yu, W. The migration and microbiological degradation of dissolved organic matter in riparian soils. Water Res. 2022, 224, 119080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, T.; Zhang, B.; Gao, X.; Cui, S.; Guan, C.-Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, B.; Peng, Y. Recent progresses, challenges, and opportunities of carbon-based materials applied in heavy metal polluted soil remediation. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 856, 158810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Li, J.; Zeng, X.; Zhang, N.; Wen, J.; Liu, J.; Jiku, M.A.S.; Wu, C.; Su, S. The performance and mechanism of cadmium availability mitigation by biochars differ among soils with different pH: Hints for the reasonable choice of passivators. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 312, 114903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, C.; Yuan, X.; Xiong, T.; Tan, Y.Z.; Wang, H. Physicochemical properties, metal availability and bacterial community structure in heavy metal-polluted soil remediated by montmorillonite-based amendments. Chemosphere 2020, 261, 128010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mtioui-Sghaier, O.; Mendoza-Meroño, R.; Fernández-Zapico, E.; García-Granda, S.; Fernández-González, A.; Ktari, L.; Dammak, M. Synthesis of a new Cd (II)–Ni (II) hetero-metallic coordination polymer base on citric acid ligand. X-ray structure, thermal stability, XPS and fluorescence studies. J. Mol. Struct. 2016, 1105, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhadian, M.; Vachelard, C.; Duchez, D.; Larroche, C. In situ bioremediation of monoaromatic pollutants in groundwater: A review. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 5296–5308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chanclud, E.; Morel, J.B. Plant hormones: A fungal point of view. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2016, 17, 1289–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Fang, L.; Beiyuan, J.; Cui, Y.; Peng, Q.; Zhu, S.; Wang, M.; Zhang, X. Improvement of alfalfa resistance against Cd stress through rhizobia and arbuscular mycorrhiza fungi co-inoculation in Cd-contaminated soil. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 277, 116758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ablimit, R.; Li, W.; Zhang, J.; Gao, H.; Zhao, Y.; Cheng, M.; Meng, X.; An, L.; Chen, Y. Altering microbial community for improving soil properties and agricultural sustainability during a 10-year maize-green manure intercropping in Northwest China. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 321, 115859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


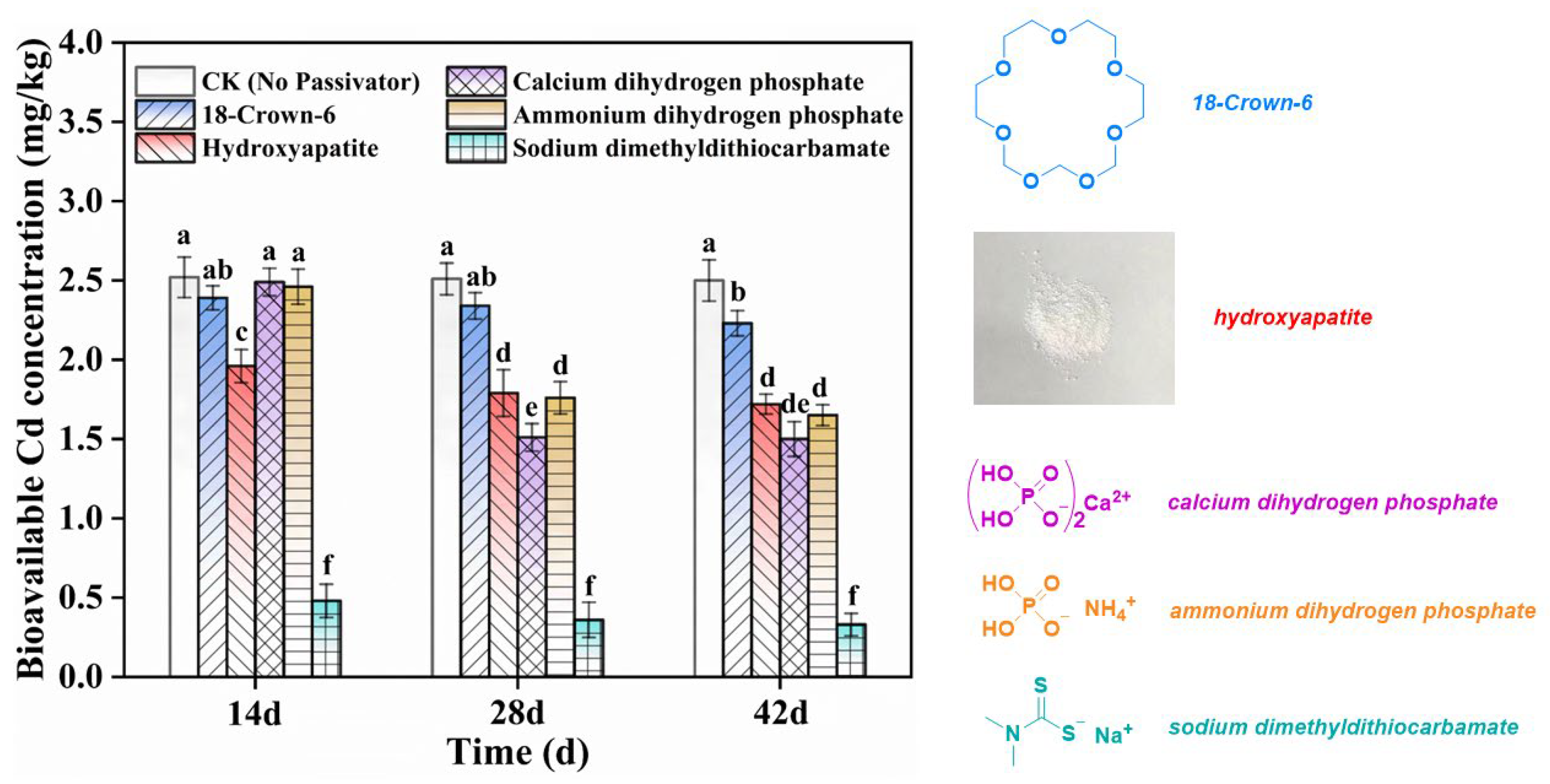
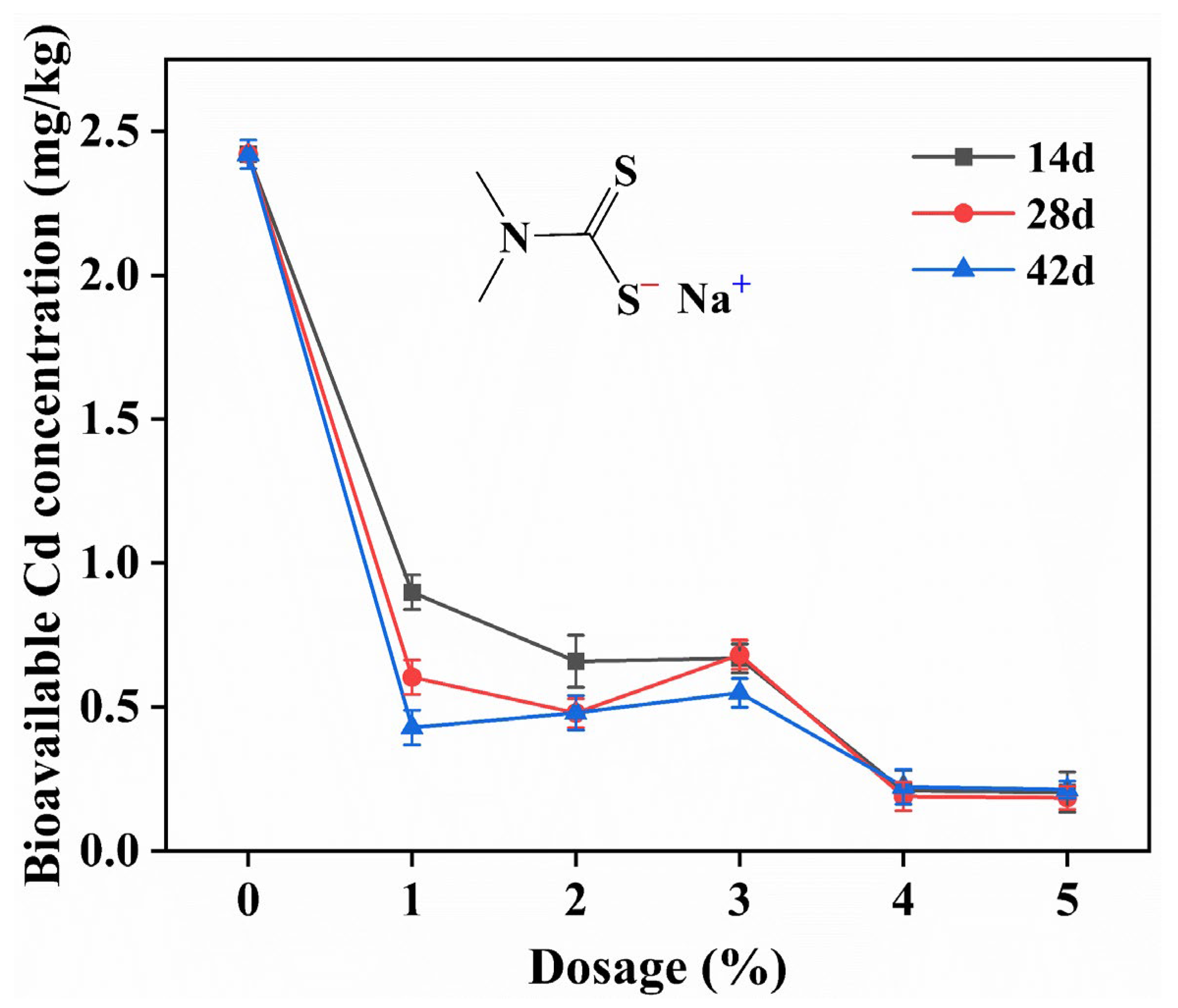
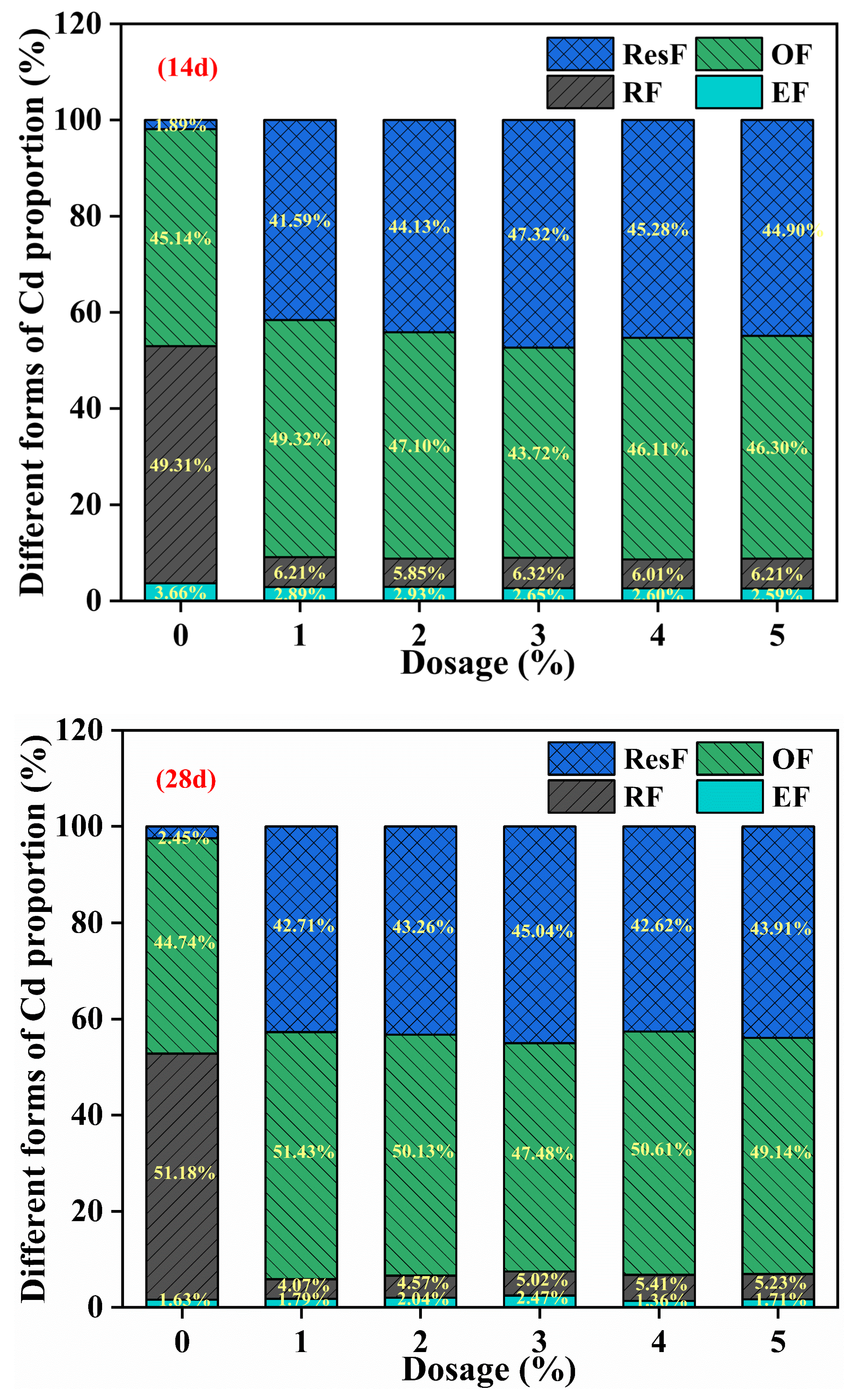
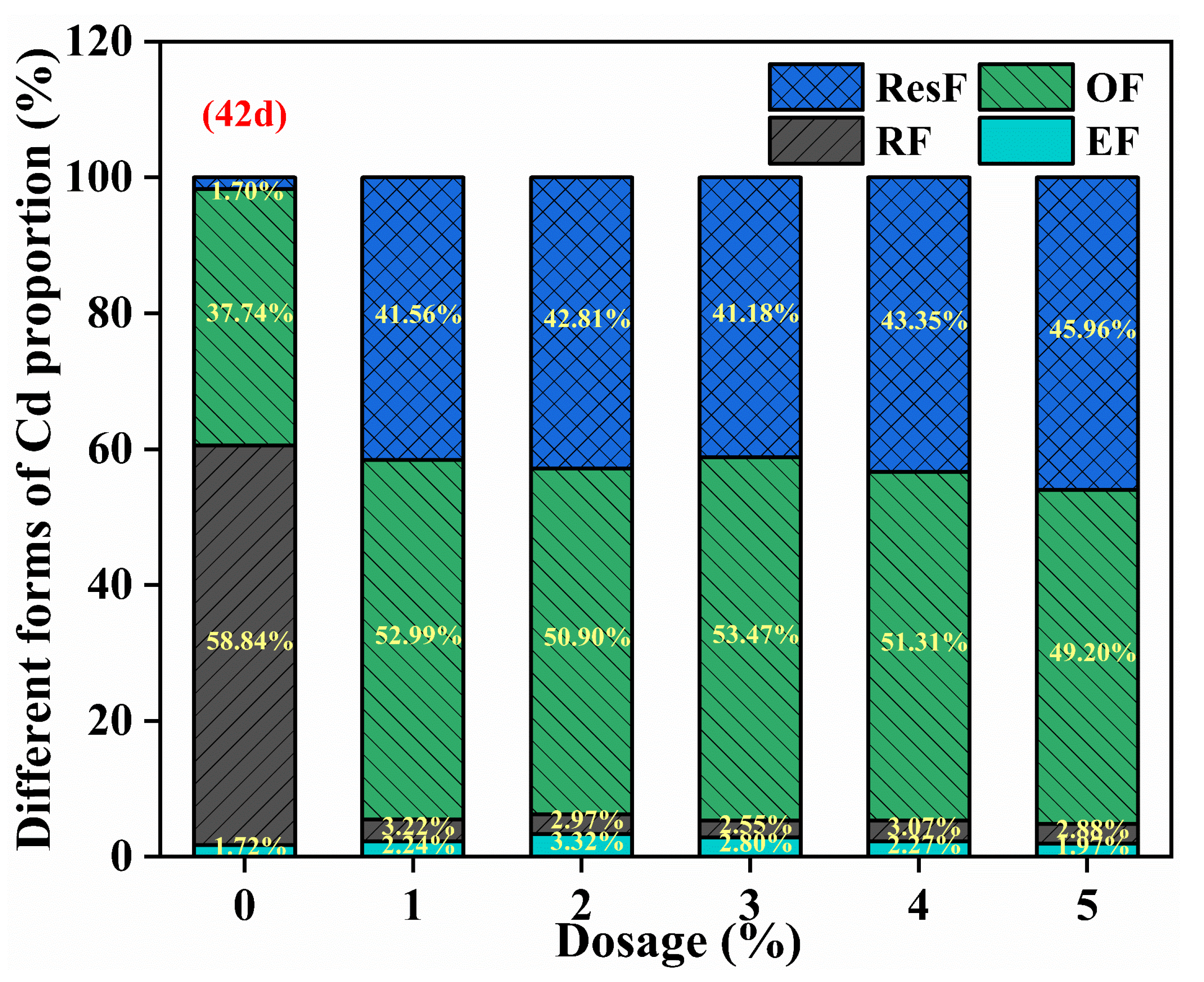




| Properties | pH | Soil Organic Matter (g/kg) | Available Nitrogen (mg/kg) | Bioavailable Cd (mg/kg) | Available Phosphorus (mg/kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Soil | 7.70 | 46.8 | 341.9 | 0.08 | 109 |
| The Physical Properties of the Soil Sample | |||||
| Composition (%) | Sand | 45.5 | |||
| Silt | 35.4 | ||||
| Clay | 19.1 | ||||
| Texture [14] | Loam | ||||
| Time/day | Bioavailable Cd Concentration (mg/kg) | |
|---|---|---|
| Scheme 1 | Scheme 2 | |
| 0 | 2.56 | 2.56 |
| 14 | 0.39 | 0.65 |
| 28 | 0.36 | 0.60 |
| 42 | 0.29 | 0.90 |
| 56 | 0.23 | 0.93 |
| 70 | 0.22 | 0.94 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cao, J.; Lv, C.; Zhang, C.; Yin, F.; Gao, Z.; Wei, L.; Wang, L. Asynchronous Synergetic Remediation Strategy for Cd-Contaminated Soil via Passivation and Phytoremediation Technology. Agronomy 2024, 14, 1913. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14091913
Cao J, Lv C, Zhang C, Yin F, Gao Z, Wei L, Wang L. Asynchronous Synergetic Remediation Strategy for Cd-Contaminated Soil via Passivation and Phytoremediation Technology. Agronomy. 2024; 14(9):1913. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14091913
Chicago/Turabian StyleCao, Jian, Chenyang Lv, Chenxu Zhang, Fengxiang Yin, Zhengbo Gao, Long Wei, and Lichang Wang. 2024. "Asynchronous Synergetic Remediation Strategy for Cd-Contaminated Soil via Passivation and Phytoremediation Technology" Agronomy 14, no. 9: 1913. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14091913
APA StyleCao, J., Lv, C., Zhang, C., Yin, F., Gao, Z., Wei, L., & Wang, L. (2024). Asynchronous Synergetic Remediation Strategy for Cd-Contaminated Soil via Passivation and Phytoremediation Technology. Agronomy, 14(9), 1913. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14091913






