Analysis of Phenotypic Trait Variation in Germplasm Resources of Lycium ruthenicum Murr.
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Site Overview
2.2. Source of Planting Resources
2.3. Experimental Survey and Trait Value Assignment Based on Distinctness
- (1)
- Plant traits: plant height, crown width.
- (2)
- Branch traits: one-year-old branch length, one-year-old branch internode length, thorn density, number of fruiting branches on one-year-old branches, and maximum number of flowers in short branch clusters on one-year-old branches. The middle-upper sections of one-year-old branches from each plant (3 to 4 branches per plant) were used as test materials.
- (3)
- Leaf traits: leaf thickness, leaf length, leaf width, leaf length-to-width ratio, leaf area, leaf perimeter, and leaf shape factor. The leaves from the middle and upper parts of the current year’s branches were used as the test material (3–4 branches per plant, with 3–4 single leaves or terminal leaflets of compound leaves per branch). The measurements were taken using a multifunctional leaf area analyzer (WanShen LA-S, Hangzhou, China).
- (4)
- Fruit traits: fruit vertical diameter, fruit horizontal diameter, fruit skin thickness, number of seeds, pedicel length, fruit weight, and number of seeds. The fruits from the middle and upper parts of the current year’s branches were used as the test material (3–4 branches per plant, with 3–4 fruits per branch), and the measurements were taken using a vernier caliper and an electronic balance.
2.4. Data Processing
3. Results
3.1. Analysis of Pseudo-Qualitative Traits
3.2. Analysis of Quantitative Trait Diversity
3.3. PCA of Phenotypic Traits
3.4. Correlation Analysis of Phenotypic Traits
3.5. Q-Type Cluster Analysis of Phenotypic Traits
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mo, S.; Biao, A.; Wang, Z.; Lin, S.; Yang, T.; Pan, L.; Wang, Y.; Zeng, S. Spatio transcriptome uncover novel insight into the Lycium ruthenicum seedling tolerant to salt stress. Ind. Crops Prod. 2022, 177, 114502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, M.; Waheed, A.; Wahab, A.; Majeed, M.; Nazim, M.; Liu, Y.-H.; Li, L.; Li, W.-J. Soil salinity and drought tolerance: An evaluation of plant growth, productivity, microbial diversity, and amelioration strategies. Plant Stress 2024, 11, 100319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Chen, S.; Zhou, W.; Meng, J.; Deng, K.; Zhou, H.; Hu, N.; Suo, Y. Anthocyanin composition of fruit extracts from Lycium ruthenicum and their protective effect for gouty arthritis. Ind. Crops Prod. 2019, 129, 414–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, D.; Yan, Y.; Liu, J. Isolation, structure and biological activity of polysaccharides from the fruits of Lycium ruthenicum Murr: A review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 291, 119618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ninomiya, S.; Baret, F.; Cheng, Z.-M. Plant Phenomics: Emerging Transdisciplinary Science. Plant Phenomics 2019, 2019, 2765120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, J.; Qiao, G.; Wen, X.; Gao, G.; Liu, T.; Peng, Z.; Cai, Y.; Chen, N.; Yan, F.; Zhang, B. Characterization of genetic relationship of dragon fruit accessions (Hylocereus spp.) by morphological traits and ISSR markers. Sci. Hortic. 2014, 170, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Kirk, C.; Deng, C.; Wiedow, C.; Knaebel, M.; Brewer, L. Genotyping-by-sequencing of pear (Pyrus spp.) accessions unravels novel patterns of genetic diversity and selection footprints. Hortic. Res. 2017, 4, 17015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, M.; Gao, F.; Wuyun, T. High-level genetic diversity of Siberian apricot (Armeniaca sibirica (L.) Lam) in Inner Mongolia as revealed by phenotypic traiting. J. Plant Genet. Resour. 2017, 18, 242–252. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ai, P.; Zhen, Z.; Jin, Z. Genetic diversity and relationships within sweet kernel apricot and related Armeniaca species based on sequence-related amplified polymorphism markers. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2011, 39, 694–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Li, J.; Tao, W.; Zhang, X.; Gao, X.; Yong, J.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, L.; Li, Y.; Duan, J.-A. Lycium ruthenicum studies: Molecular biology, Phytochemistry and pharmacology. Food Chem. 2018, 240, 759–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Yang, M.K.; Zhu, J.; Li, X.J.; Feng, R.; Xu, R.; Chen, J. Study on phenotypic diversity and cluster analysis of Cistanche Herba in different populations in Xinjiang. China J. Chin. Mater. Medica 2018, 43, 3841–3847. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Zeng, S.; Wu, X.; Lei, H.; Wang, Y.; Tang, H. Interspecies Developmental Differences in Metabonomic Phenotypes of Lycium ruthenicum and L. barbarum Fruits. J. Proteome Res. 2018, 17, 3223–3236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, Y.; Zhu, C.; Chen, J.; Liu, G.; Yang, Z.; Chen, W. Comparative analysis of the quality and health-promoting compounds of two-shaped fruits of wild Lycium ruthenicum Murr. from the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau. Acta Physiol. Plant. 2019, 41, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, M.; Tao, L.; Zhang, B.; He, X.; Mi, J.; Xu, W. Study on the Genetic Diversity of Phenotypic and Quality Traits of 48 Germplasm Resources of Lycium ruthenicum Murr. J. Henan Agric. Sci. 2023, 52, 78–90. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- GB/T 19557.1–2004; General Directives for the Conduct of Tests of Distinctness, Uniformity and Stability for New Varieties of Plants. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2004.
- Ferreira, N.G.; Yoshimitsu, M.S.; Naomi, K.K.; Giraldo, M.S.; Damião, C.C.; Valadares, d.S.W. Genetic diversity of Syagrus coronata and principal component analysis of phenotypic traits: A palm from the brazilian semiarid biome. Biodivers. Conserv. 2023, 32, 4275–4293. [Google Scholar]
- Karim, H.; Ahmed, D.; Jamal, C.; Lahcen, H.; Mohamed, E.F.; Abdelghani, N. Appropriate statistical methods for analysis of safflower genetic diversity using agglomerative hierarchical cluster analysis through combination of phenotypic traits and molecular markers. Crop Sci. 2021, 61, 4164–4180. [Google Scholar]
- Ana, U.; Marina, Ć.; Dalibor, Ž.; Radu, G.; Leif, S.; Ellen, S.; David, L. Phenotypic and Genotypic Characterization and Correlation Analysis of Pea (Pisum sativum L.) Diversity Panel. Plants 2022, 11, 1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santhy, V.; Rathinavel, K.; Saravanan, M.; Meshram, M.; Priyadharshini, C. Genetic diversity assessment of extant cotton varieties based on Principal Component Analysis (PCA) and cluster analysis of enlisted DUS traits. Electron. J. Plant Breed. 2020, 11, 430–438. [Google Scholar]
- Koskela, J.; Vinceti, B.; Dvorak, W.; Bush, D.; Dawson, I.K.; Loo, J.; Kjaer, E.D.; Navarro, C.; Padolina, C.; Bordács, S.; et al. Utilization and transfer of forest genetic resources: A global review. For. Ecol. Manag. 2014, 333, 22–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upadhyaya, H.; Gowda, C.; Sastry, D. Plant genetic resources management: Collection, characterization, conservation and utilization. J. SAT Agric. Res. 2008, 6, 16pp. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, L.; Ru, M.; Wang, B.; Wang, Y.; Li, B.; Yu, J.; Liang, Z. Genetic diversity assessment of a germplasm collection of Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge. based on morphology, ISSR and SRAP markers. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2014, 55, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, A.; Osman, N. Utilizing genetic diversity to select tomato lines tolerant of tomato yellow leaf curl virus based on genotypic coefficient of variation, heritability, genotypic correlation, and multivariate analyses. Braz. J. Bot. 2023, 46, 609–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.; Wang, Z.; Fan, G. Morphological variation of Lycium ruthenicum under artificial cultivation conditions. Nonwood For. Res. 2014, 32, 171–174. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Salem, N.; Hussein, S. Data dimensional reduction and principal components analysis. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2019, 163, 292–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, O.; Park, H. Assessment of genetic diversity in cultivated radishes (Raphanus sativus) by agronomic traits and SSR markers. Sci. Hortic. 2017, 223, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Zhang, Z.; Tang, W.; Li, Q. Reproductive allocation characteristics of Lycium barbarum population in different habitats. J. Northwest For. Univ. 2021, 36, 144–149. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Lin, L.; Zhang, M.; Du, Z.; Zhu, T.; Sun, S.; Jin, L. Analysis on genetic diversity of 16 populations of Lycium ruthenicum Murr. in middle and lower reaches of Heihe River basin based on ISSR molecular markers. Chin. J. Inf. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2019, 26, 62–67. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Chen, J.; Chen, W.; Zhou, X.; Xu, D.; Li, J.; Qi, X. Population genetic diversity of wild Lycium ruthenicum in Qaidam inferred from AFLP markers. Chin. J. Plant Ecol. 2015, 39, 1003–1011. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Gong, H.; Rehman, F.; Ma, Y.; Zeng, S.; Yang, T.; Huang, J.; Wang, Y. Germplasm resources and strategy for genetic breeding of Lycium species: A Review. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 802936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Yang, H.; Liu, F.; Li, H. Research Progress of Chemical Constituents Pharmacological Activity and Cultivation Techniques of Lycium ruthenicum Murr. J. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2018, 37, 673–678. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, W.; Huang, W.; Biao, A.; Lin, S.; Wang, Y.; Yan, S.; Zeng, S. Salt stress affects the fruit quality of Lycium ruthenicum Murr. Ind. Crops Prod. 2023, 193, 116240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
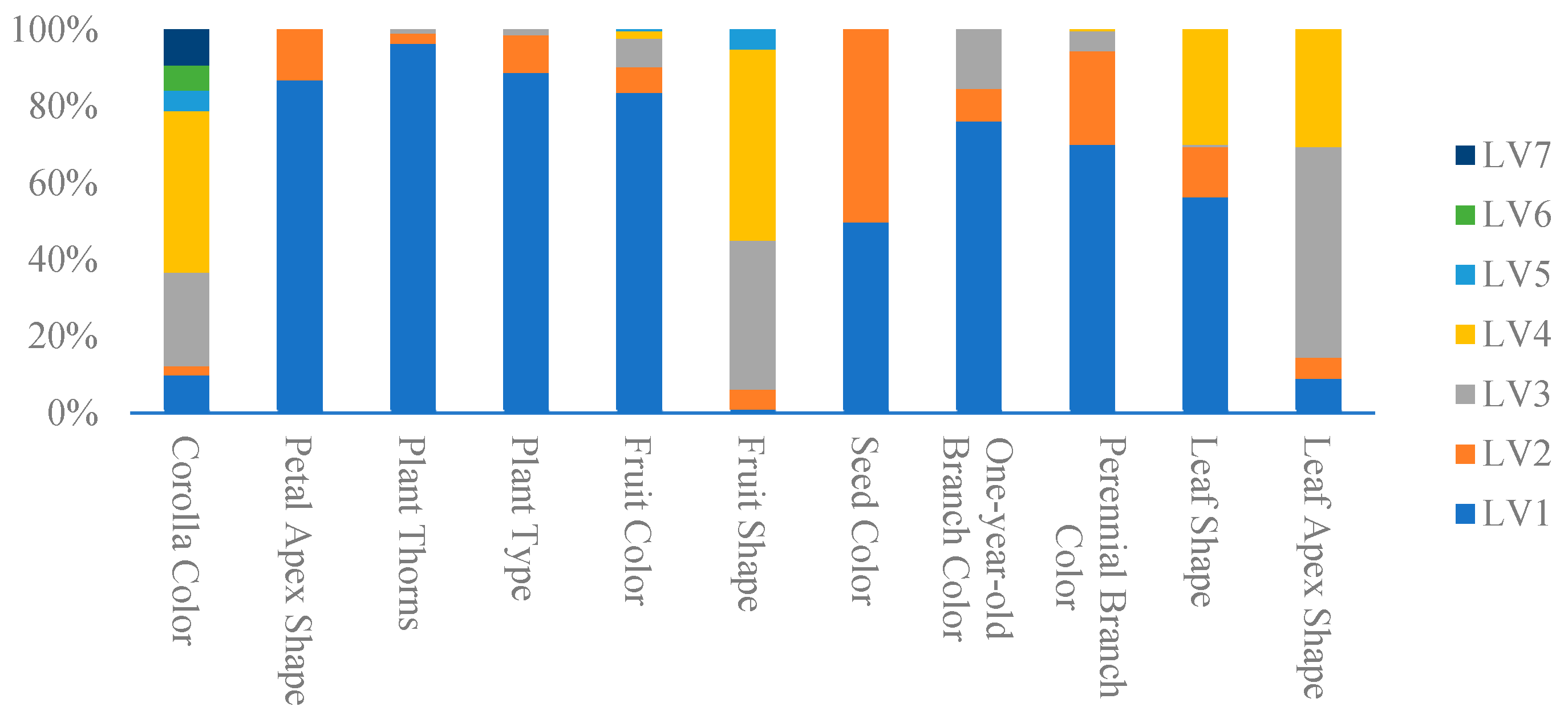

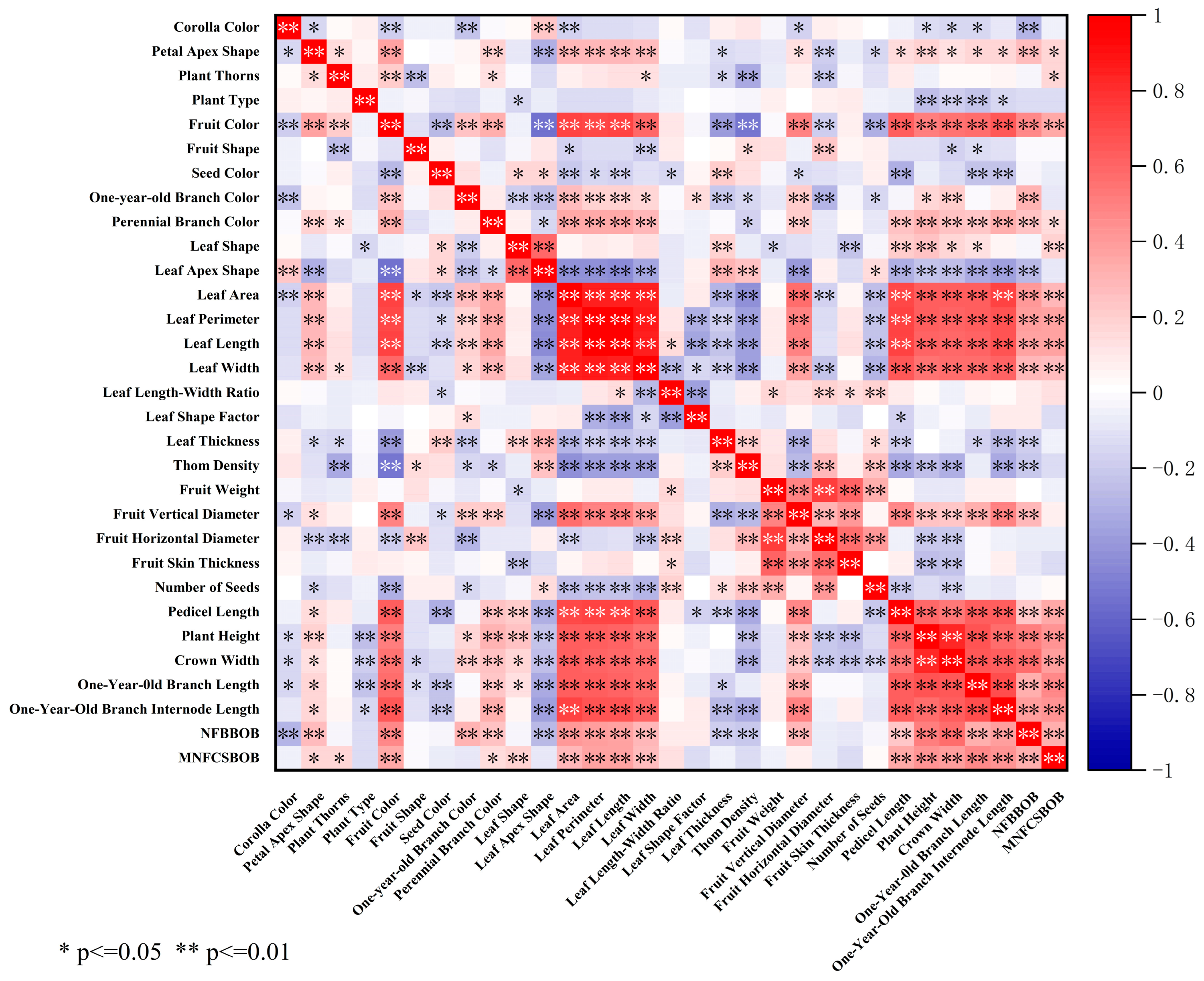
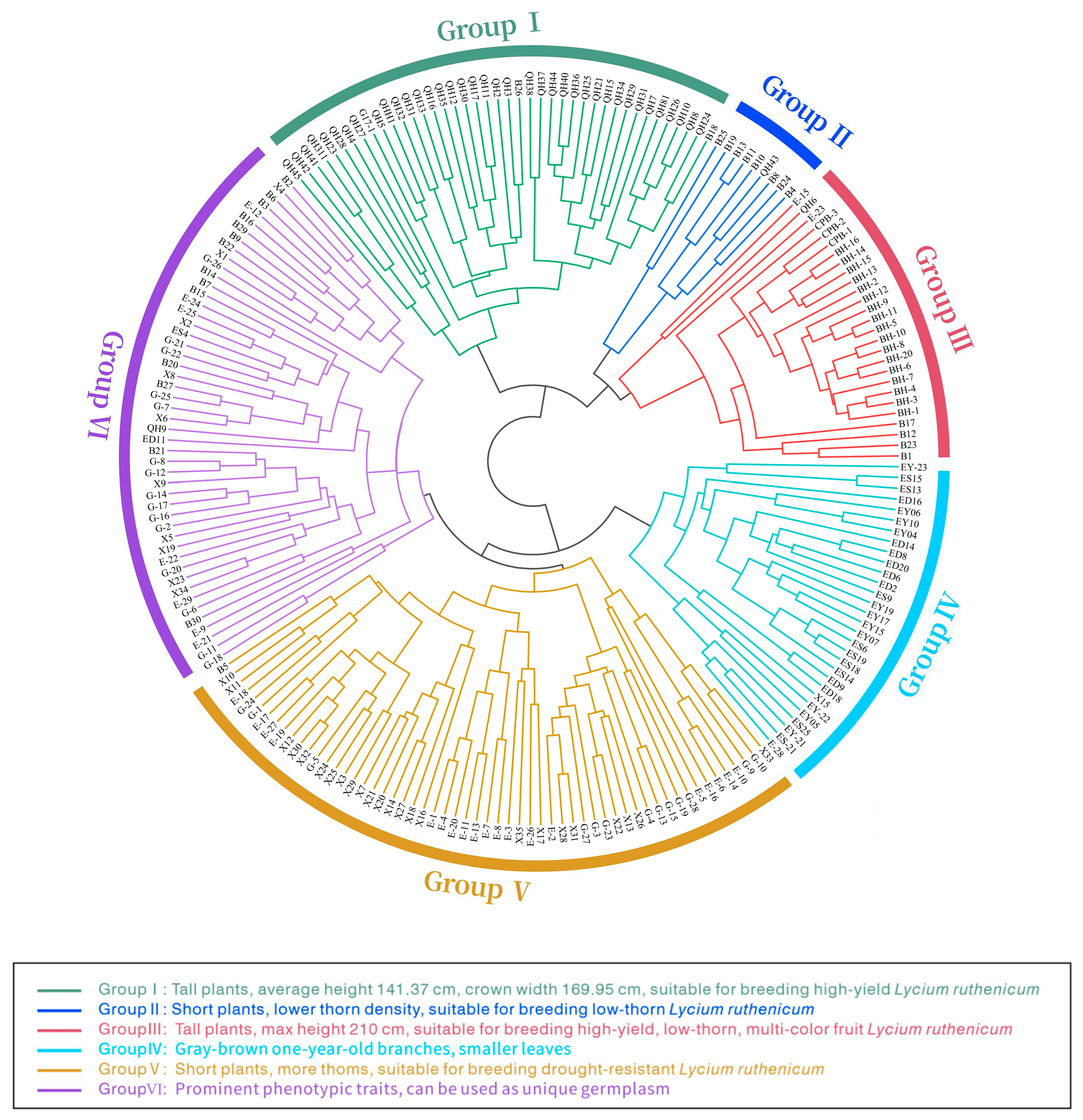
| Number | Provenance | Province | Provenance Number | Latitude and Longitude | Elevation (m) | Field Number | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Urad Rear Banner | Inner Mongolia | B | E:106.56; N:40.80 | 996 | B1~B30 | 29 |
| 2 | Dalaihubuzhen | Inner Mongolia | E | E:100.97; N:41.858 | 900 | E1~E29 | 29 |
| 3 | Subonao’er Sumu | Inner Mongolia | ES | E:101.04; N:42.12 | 869 | ES4, ES6, ES9, ES13~ES15, ES18~19, ES21, ES25 | 10 |
| 4 | Dongfengzhen | Inner Mongolia | ED | E:101.07; N:42.01 | 873 | ED2, ED6, ED8~ED9, ED11, ED14, ED16, ED18, ED20 | 9 |
| 5 | Saihantaolai Sumu | Inner Mongolia | EY | E:100.59; N:41.88 | 911 | EY04~EY07, EY10, EY15, EY17, EY19, EY21~EY23 | 11 |
| 6 | Guazhou County | Gansu | G | E:94.99; N:40.26 | 1274 | G1~G17, G17-1, G18~G28 | 29 |
| 7 | Uqturpan County | Xinjiang | X | E:78.53; N:41.3 | 1379 | X1~X25 | 35 |
| 8 | Nuomuhong | Qinghai | Q | E:96.19; N:36.25 | 2712 | QH1~QH12, QH15~QH17, QH21, QH23, QH24~QH38, QH40~QH45, QH3-1, QH8-1, QH21, QH31-1, BH1~BH16, BH20, CPB1~CPB3 | 61 |
| Traits | Grading and Assignment of Values |
|---|---|
| Corolla Color | Full Color = 1, White = 2, Light Purple = 3, Medium Purple = 4, White and Light Purple = 5, White and Medium Purple = 6, Light Purple and Medium Purple = 7 |
| Petal Apex Shape | Blunt = 1, Sharp = 2 |
| Plant Thorns | Present = 1, Very Few = 2, None = 3 |
| Plant Type | Upright = 1, Upright to Semi-Upright = 2, Semi-Upright = 3, Prostrate = 4 |
| Fruit Color | Black = 1, Red = 2, Yellow = 3, Brownish Red = 4, Multicolored = 5 |
| Fruit Shape | Long Elliptical = 1, Medium Elliptical = 2, Round = 3, Flattened Spherical = 4, Ovoid = 5 |
| Seed Color | Yellow = 1, Brown = 2 |
| One-year-old Branch Color | White = 1, Yellow = 2, Gray-Brown = 3 |
| Perennial Branch Color | Gray-Brown = 1, Yellow-Brown = 2, Brown = 3, Dark Brown = 4 |
| Leaf Shape | Linear = 1, Narrow Lanceolate = 2, Broad Lanceolate = 3, Ovoid = 4, Linear and Narrow Lanceolate = 5 |
| Leaf Apex Shape | Acute = 1, Acuminate = 2, Obtuse and Rounded = 3, Acuminate and Obtuse = 4 |
| Estimated Value of Traits | Level |
|---|---|
| 1 | |
| 2 | |
| 3 | |
| 4 | |
| 5 |
| Quantitative Traits | Mean | Maximum | Minimum | CV (%) | H | D | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Leaf Area (mm2) | 34.40 | 182.60 | 10.20 | 25.70 | 74.70 | 0.54 | 0.25 |
| Leaf Perimeter (mm) | 41.17 | 84.56 | 18.25 | 12.68 | 30.79 | 1.20 | 0.62 |
| Leaf Length (mm) | 21.19 | 42.49 | 9.97 | 6.25 | 29.52 | 1.23 | 0.63 |
| Leaf Width (mm) | 3.11 | 7.37 | 1.00 | 1.01 | 32.39 | 1.12 | 0.61 |
| Leaf Length–Width Ratio | 7.39 | 14.70 | 4.20 | 1.30 | 17.60 | 1.30 | 0.68 |
| Leaf Shape Factor | 0.25 | 0.42 | 0.10 | 0.06 | 23.99 | 1.49 | 0.75 |
| Leaf Thickness (mm) | 1.02 | 1.59 | 0.19 | 0.22 | 21.12 | 1.44 | 0.73 |
| Thorn Density | 14.77 | 43.00 | 0.00 | 8.20 | 55.50 | 1.41 | 0.73 |
| Fruit Weight (g) | 0.22 | 0.60 | 0.06 | 0.09 | 40.34 | 1.27 | 0.66 |
| Fruit Vertical Diameter (mm) | 6.54 | 12.25 | 4.51 | 1.13 | 17.26 | 1.04 | 0.57 |
| Fruit Horizontal Diameter (mm) | 7.90 | 12.96 | 5.01 | 1.43 | 18.10 | 1.28 | 0.69 |
| Fruit Skin Thickness (mm) | 1.24 | 7.19 | 0.59 | 0.47 | 37.63 | 1.11 | 0.60 |
| Number of Seeds | 13.48 | 30.00 | 3.33 | 5.00 | 37.07 | 1.34 | 0.70 |
| Pedicel Length (mm) | 7.98 | 19.41 | 2.81 | 2.95 | 36.95 | 1.30 | 0.68 |
| Plant Height (cm) | 107.34 | 210.00 | 30.00 | 37.27 | 34.72 | 1.27 | 0.66 |
| Crown Width (cm) | 126.54 | 482.50 | 42.50 | 68.93 | 54.47 | 1.04 | 0.60 |
| One-Year-Old Branch Length (cm) | 17.62 | 45.88 | 0.00 | 7.84 | 44.52 | 1.19 | 0.63 |
| One-Year-Old Branch Internode Length (mm) | 7.13 | 17.39 | 2.17 | 2.55 | 35.69 | 1.33 | 0.69 |
| Number of Fruit-Bearing Branches on One-Year-Old Branches | 69.48 | 410.00 | 0.00 | 73.25 | 105.41 | 0.91 | 0.47 |
| Maximum Number of Flowers in Clusters on Short Branches of One-Year-Old Branches | 2.41 | 6.60 | 0.00 | 1.20 | 49.65 | 1.31 | 0.69 |
| Traits | Principal Component Eigenvectors | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PC1 | PC2 | PC3 | PC4 | PC5 | PC6 | PC7 | PC8 | PC9 | PC10 | |
| Corolla Color | −0.215 | 0.042 | 0.197 | −0.493 | 0.104 | −0.110 | −0.045 | −0.137 | −0.136 | 0.163 |
| Petal Apex Shape | 0.345 | −0.140 | −0.236 | −0.008 | −0.278 | 0.129 | 0.161 | 0.566 | 0.073 | −0.194 |
| Plant Thorns | 0.158 | −0.242 | −0.207 | −0.403 | 0.014 | 0.296 | 0.577 | −0.104 | 0.068 | 0.046 |
| Plant Type | −0.155 | 0.058 | −0.332 | −0.360 | 0.165 | −0.032 | 0.081 | 0.405 | 0.101 | 0.158 |
| Fruit Color | 0.845 | −0.021 | −0.230 | −0.051 | −0.049 | −0.079 | 0.076 | −0.029 | 0.155 | −0.011 |
| Fruit Shape | −0.184 | 0.237 | 0.031 | 0.266 | −0.160 | −0.036 | −0.247 | 0.227 | 0.556 | −0.306 |
| Seed Color | −0.238 | −0.227 | 0.140 | 0.282 | −0.069 | 0.650 | 0.105 | 0.003 | −0.032 | −0.208 |
| One-year-old Branch Color | 0.245 | −0.234 | −0.393 | 0.448 | −0.128 | 0.279 | −0.210 | −0.345 | −0.022 | 0.144 |
| Perennial Branch Color | 0.405 | −0.055 | 0.052 | −0.043 | 0.032 | 0.219 | 0.188 | 0.080 | −0.153 | 0.117 |
| Leaf Shape | 0.063 | −0.197 | 0.736 | −0.052 | 0.200 | 0.150 | 0.078 | −0.136 | 0.330 | −0.168 |
| Acute Leaf Apex Shape | −0.523 | −0.112 | 0.596 | −0.003 | 0.214 | 0.061 | 0.041 | −0.156 | 0.264 | −0.030 |
| Leaf Area (mm2) | 0.909 | −0.013 | −0.055 | 0.044 | 0.212 | 0.026 | −0.117 | −0.009 | −0.040 | −0.100 |
| Leaf Perimeter (mm) | 0.909 | 0.099 | 0.069 | −0.157 | −0.086 | 0.182 | −0.168 | −0.011 | −0.047 | −0.098 |
| Leaf Length (mm) | 0.905 | 0.122 | 0.037 | −0.179 | −0.107 | 0.176 | −0.165 | −0.040 | −0.031 | −0.098 |
| Leaf Width (mm) | 0.827 | −0.118 | 0.068 | −0.146 | 0.198 | 0.193 | −0.209 | 0.115 | −0.102 | −0.113 |
| Leaf Length–Width Ratio | 0.041 | 0.435 | −0.007 | −0.101 | −0.638 | −0.141 | 0.086 | −0.368 | 0.099 | −0.003 |
| Leaf Shape Factor | −0.100 | −0.231 | −0.197 | 0.511 | 0.587 | −0.266 | 0.184 | 0.056 | 0.079 | 0.047 |
| Leaf Thickness (mm) | −0.312 | 0.056 | 0.497 | 0.037 | −0.016 | 0.308 | −0.090 | 0.282 | −0.238 | 0.252 |
| Thorn Density | −0.468 | 0.263 | 0.231 | 0.190 | −0.185 | −0.107 | −0.174 | 0.239 | −0.328 | −0.113 |
| Fruit Weight (g) | 0.004 | 0.828 | −0.073 | 0.075 | 0.221 | 0.281 | 0.084 | 0.017 | −0.034 | 0.013 |
| Fruit Vertical Diameter (mm) | 0.549 | 0.488 | −0.313 | 0.094 | 0.283 | 0.168 | 0.076 | −0.166 | 0.050 | −0.136 |
| Fruit Horizontal Diameter (mm) | −0.199 | 0.866 | 0.046 | 0.052 | 0.190 | 0.032 | 0.057 | 0.066 | 0.020 | −0.012 |
| Fruit Skin Thickness (mm) | 0.047 | 0.403 | 0.044 | −0.129 | 0.048 | 0.202 | −0.223 | 0.063 | 0.357 | 0.567 |
| Number of Seeds | −0.269 | 0.471 | 0.160 | 0.257 | −0.040 | 0.006 | 0.416 | −0.098 | −0.258 | −0.128 |
| Pedicel Length (mm) | 0.783 | 0.128 | 0.176 | −0.227 | 0.112 | −0.133 | −0.085 | −0.035 | 0.054 | −0.134 |
| Plant Height (cm) | 0.752 | −0.081 | 0.386 | 0.236 | −0.086 | −0.049 | −0.029 | 0.027 | −0.073 | 0.155 |
| Crown Width (cm) | 0.756 | −0.133 | 0.283 | 0.238 | −0.006 | −0.087 | 0.008 | 0.017 | −0.085 | 0.250 |
| One-Year-Old Branch Length (cm) | 0.746 | 0.148 | 0.275 | 0.078 | −0.001 | −0.253 | 0.051 | 0.087 | −0.154 | −0.056 |
| One-Year-Old Branch Internode Length (mm) | 0.803 | 0.115 | 0.078 | 0.066 | 0.183 | −0.206 | 0.115 | −0.031 | −0.029 | −0.039 |
| Number of Fruit-Bearing Branches on One-Year-Old Branches | 0.541 | 0.010 | −0.052 | 0.484 | −0.211 | 0.013 | 0.174 | 0.079 | 0.159 | 0.347 |
| Maximum Number of Flowers in Clusters on Short Branches of One-Year-Old Branches | 0.454 | 0.036 | 0.357 | −0.011 | −0.254 | −0.141 | 0.440 | 0.148 | 0.186 | 0.052 |
| Eigenvalues | 8.868 | 2.791 | 2.333 | 1.791 | 1.472 | 1.302 | 1.212 | 1.11 | 1.069 | 1.001 |
| Contribution Rates% | 28.61 | 9.00 | 7.53 | 5.78 | 4.75 | 4.20 | 3.91 | 3.58 | 3.45 | 3.23 |
| Total Contribution Rates% | 28.61 | 37.61 | 45.14 | 50.91 | 55.66 | 59.86 | 63.77 | 67.35 | 70.80 | 74.03 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, R.; Li, J.; Huang, H.; Wu, X.; Wu, R.; Bai, Y. Analysis of Phenotypic Trait Variation in Germplasm Resources of Lycium ruthenicum Murr. Agronomy 2024, 14, 1930. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14091930
Yang R, Li J, Huang H, Wu X, Wu R, Bai Y. Analysis of Phenotypic Trait Variation in Germplasm Resources of Lycium ruthenicum Murr. Agronomy. 2024; 14(9):1930. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14091930
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Rong, Jinpu Li, Haiguang Huang, Xiuhua Wu, Riheng Wu, and Yu’e Bai. 2024. "Analysis of Phenotypic Trait Variation in Germplasm Resources of Lycium ruthenicum Murr." Agronomy 14, no. 9: 1930. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14091930
APA StyleYang, R., Li, J., Huang, H., Wu, X., Wu, R., & Bai, Y. (2024). Analysis of Phenotypic Trait Variation in Germplasm Resources of Lycium ruthenicum Murr. Agronomy, 14(9), 1930. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14091930






