Nodules of Medicago spp. Host a Diverse Community of Rhizobial Species in Natural Ecosystems
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Nodule Collection and Isolation of Bacteria
2.2. Phenotypic Characterization of Rhizobia
2.3. Nodulation Test
2.4. DNA Extraction, Amplification and Sequencing
2.5. Genetic Analyses
2.6. Nucleotide Sequence Data
3. Results
3.1. Phenotypic Characterization and Nodulation of the Rhizobial Isolates
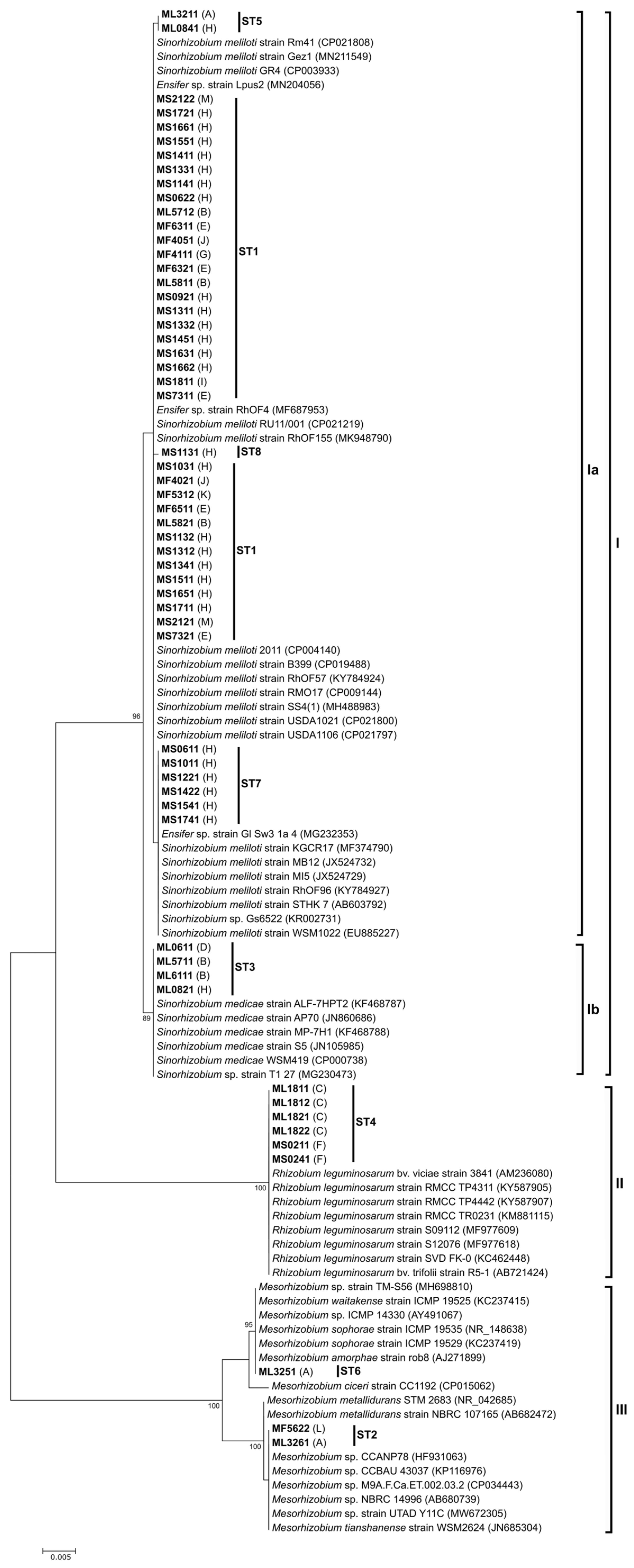
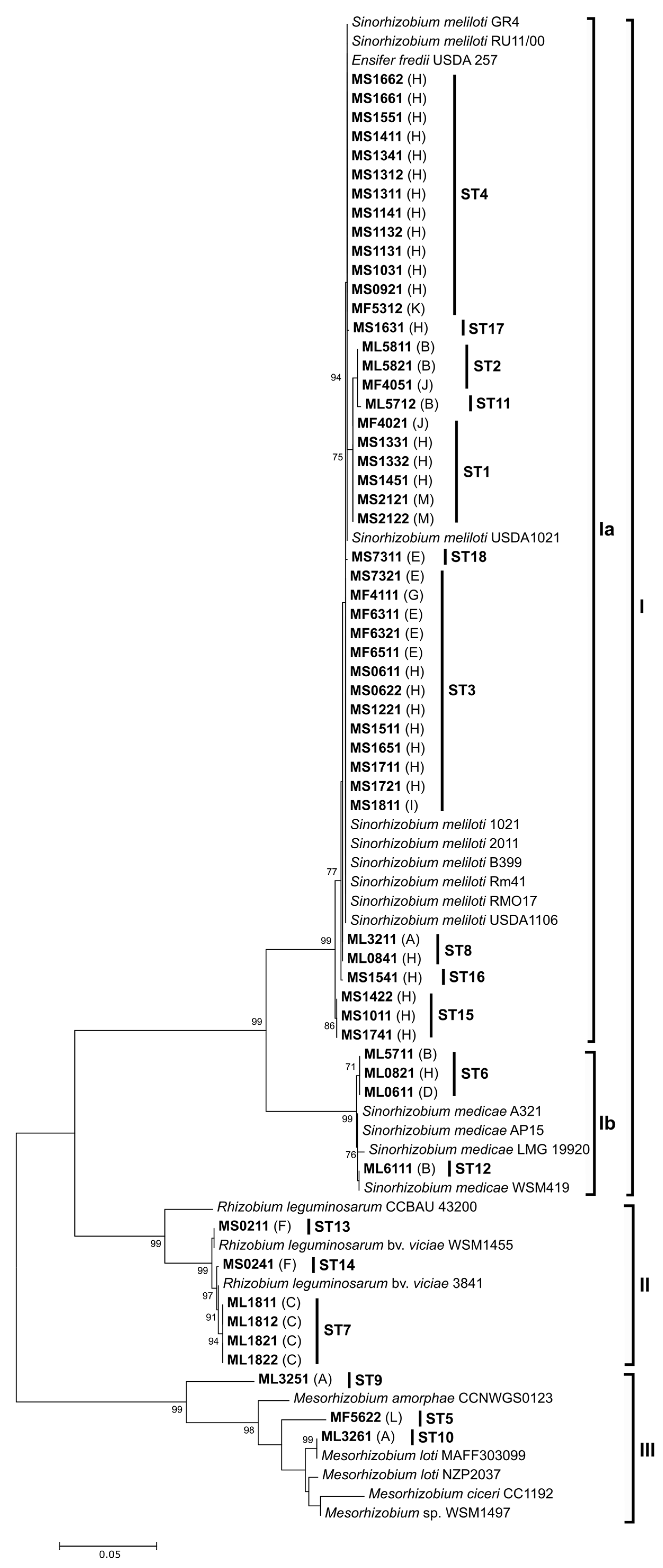
3.2. Molecular Characterization of Rhizobia
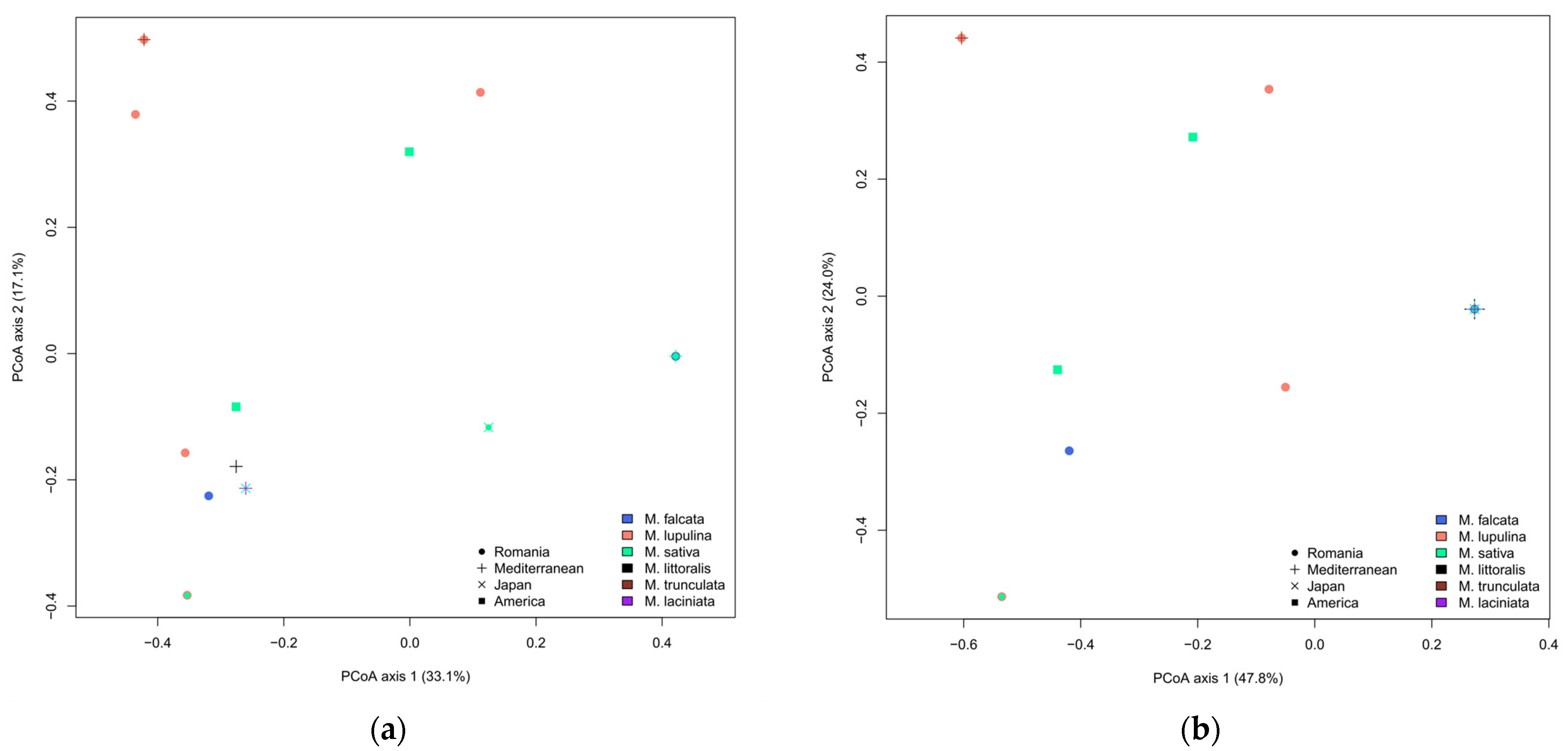
3.3. Diversity of Rhizobia Associated with Medicago: Comparative Analyses
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Masson-Boivin, C.; Giraud, E.; Perret, X.; Batut, J. Establishing nitrogen-fixing symbiosis with legumes: How many rhizobium recipes? Trends Microbiol. 2009, 17, 458–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Yang, S.; Tang, F.; Zhu, H. Symbiosis Specificity in the Legume: Rhizobial Mutualism. Cell. Microbiol. 2012, 14, 334–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Liu, J.; Zhu, H. Genetic and Molecular Mechanisms Underlying Symbiotic Specificity in Legume-Rhizobium Interactions. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindström, K.; Mousavi, S.A. Effectiveness of nitrogen fixation in rhizobia. Microb. Biotechnol. 2019, 13, 1314–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulte, C.C.M.; Borah, K.; Wheatley, R.M.; Terpolilli, J.J.; Saalbach, G.; Crang, N.; de Groot, D.H.; Ratcliffe, R.G.; Kruger, N.J.; Papachristodoulou, A.; et al. Metabolic control of nitrogen fixation in rhizobium-legume symbioses. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabh2433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masson-Boivin, C.; Sachs, J.L. Symbiotic nitrogen fixation by rhizobia—The roots of a success story. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2018, 44, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herridge, D.F.; Peoples, M.B.; Boddey, R.M. Global inputs of biological nitrogen fixation in agricultural systems. Plant Soil 2008, 311, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hénault, C.; Barbier, E.; Hartmann, A.; Revellin, C. New Insights into the Use of Rhizobia to Mitigate Soil N2O Emissions. Agriculture 2022, 12, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, J.; Liu, H.; Macdonald, C.A.; Singh, B.K. Application of microbial inoculants significantly enhances crop productivity: A meta-analysis of studies from 2010 to 2020. J. Sustain. Agric. Environ. 2022, 1, 216–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maitra, S.; Brestic, M.; Bhadra, P.; Shankar, T.; Praharaj, S.; Palai, J.B.; Shah, M.M.R.; Barek, V.; Ondrisik, P.; Skalický, M.; et al. Bioinoculants—Natural Biological Resources for Sustainable Plant Production. Microorganisms 2021, 10, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamkhi, I.; Cheto, S.; Geistlinger, J.; Zeroual, Y.; Kouisni, L.; Bargaz, A.; Ghoulam, C. Legume-based intercropping systems promote beneficial rhizobacterial community and crop yield under stressing conditions. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2022, 183, 114958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kebede, E. Contribution, Utilization, and Improvement of Legumes-Driven Biological Nitrogen Fixation in Agricultural Systems. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2021, 5, 767998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Layek, J.; Das, A.; Mitran, T.; Nath, C.; Meena, R.S.; Yadav, G.S.; Shivakumar, B.G.; Kumar, S.; Lal, R. Cereal+Legume Intercropping: An Option for Improving Productivity and Sustaining Soil Health. In Legumes for Soil Health and Sustainable Management; Meena, R.S., Das, A., Yadav, G.S., Lal, R., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2018; pp. 347–386. ISBN 9789811302534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fageria, N.K. Green Manuring in Crop Production. J. Plant Nutr. 2007, 30, 691–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatsios, A.; Ntatsi, G.; Celi, L.; Said-Pullicino, D.; Tampakaki, A.; Savvas, D. Legume-Based Mobile Green Manure Can Increase Soil Nitrogen Availability and Yield of Organic Greenhouse Tomatoes. Plants 2021, 10, 2419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meena, B.L.; Fagodiya, R.K.; Prajapat, K.; Dotaniya, M.L.; Kaledhonkar, M.J.; Sharma, P.C.; Meena, R.S.; Mitran, T.; Kumar, S. Legume Green Manuring: An Option for Soil Sustainability. In Legumes for Soil Health and Sustainable Management; Meena, R.S., Das, A., Yadav, G.S., Lal, R., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2018; pp. 387–408. ISBN 9789811302534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindström, K.; Murwira, M.; Willems, A.; Altier, N. The biodiversity of beneficial microbe-host mutualism: The case of rhizobia. Res. Microbiol. 2010, 161, 453–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argaw, A.; Tsigie, A. Indigenous rhizobia population influences the effectiveness of Rhizobium inoculation and need of inorganic N for common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) production in eastern Ethiopia. Chem. Biol. Technol. Agric. 2015, 2, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athul, P.P.; Patra, R.K.; Sethi, D.; Panda, N.; Mukhi, S.K.; Padhan, K.; Sahoo, S.K.; Sahoo, T.R.; Mangaraj, S.; Pradhan, S.R.; et al. Efficient native strains of rhizobia improved nodulation and productivity of French bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) under rainfed condition. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 1048696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellano-Hinojosa, A.; Mora, C.; Strauss, S.L. Native Rhizobia Improve Plant Growth, Fix N2, and Reduce Greenhouse Emissions of Sunnhemp More than Commercial Rhizobia Inoculants in Florida Citrus Orchards. Plants 2022, 11, 3011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koskey, G.; Mburu, S.W.; Njeru, E.M.; Kimiti, J.M.; Ombori, O.; Maingi, J.M. Potential of Native Rhizobia in Enhancing Nitrogen Fixation and Yields of Climbing Beans (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) in Contrasting Environments of Eastern Kenya. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.T.; Atieno, M.; Herrmann, L.; Nakasathien, S.; Sarobol, E.; Wongkaew, A.; Nguyen, K.T.; Lesueur, D. Does inoculation with native rhizobia enhance nitrogen fixation and yield of cowpea through legume-based intercropping in the northern mountainous areas of Vietnam? Exp. Agric. 2020, 56, 825–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, W.; Shi, S.; Xu, L. Diversity and symbiotic divergence of endophytic and non-endophytic rhizobia of Medicago sativa. Ann. Microbiol. 2018, 68, 247–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Berkum, P.; Elia, P.; Eardly, B.D. Multilocus Sequence Typing as an Approach for Population Analysis of Medicago-Nodulating Rhizobia. J. Bacteriol. 2006, 188, 5570–5577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- van Berkum, P.; Badri, Y.; Elia, P.; Aouani, M.E.; Eardly, B.D. Chromosomal and Symbiotic Relationships of Rhizobia Nodulating Medicago truncatula and M. laciniata. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 7597–7604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lemaire, B.; Dlodlo, O.; Chimphango, S.; Stirton, C.; Schrire, B.; Boatwright, J.S.; Honnay, O.; Smets, E.; Sprent, J.; James, E.K.; et al. Symbiotic diversity, specificity and distribution of rhizobia in native legumes of the Core Cape Subregion (South Africa). FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2015, 91, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Cauwenberghe, J.; Verstraete, B.; Lemaire, B.; Lievens, B.; Michiels, J.; Honnay, O. Population structure of root nodulating Rhizobium leguminosarum in Vicia cracca populations at local to regional geographic scales. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2014, 37, 613–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozieł, M.; Kalita, M.; Janczarek, M. Genetic diversity of microsymbionts nodulating Trifolium pratense in subpolar and temperate climate regions. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 12144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bessadok, K.; Navarro-Torre, S.; Fterich, A.; Caviedes, M.A.; Pajuelo, E.; Rodríguez-Llorente, I.D.; Mars, M. Diversity of rhizobia isolated from Tunisian arid soils capable of forming nitrogen-fixing symbiosis with Anthyllis henoniana. J. Arid. Environ. 2021, 188, 104467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efstathiadou, E.; Ntatsi, G.; Savvas, D.; Tampakaki, A.P. Genetic characterization at the species and symbiovar level of indigenous rhizobial isolates nodulating Phaseolus vulgaris in Greece. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 8674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tampakaki, A.P.; Fotiadis, C.T.; Ntatsi, G.; Savvas, D. Phylogenetic multilocus sequence analysis of indigenous slow-growing rhizobia nodulating cowpea (Vigna unguiculata L.) in Greece. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2017, 40, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simbine, M.G.; Mohammed, M.; Jaiswal, S.K.; Dakora, F.D. Functional and genetic diversity of native rhizobial isolates nodulating cowpea (Vigna unguiculata L. Walp.) in Mozambican soils. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 12747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steele, K.P.; Ickert-Bond, S.M.; Zarre, S.; Wojciechowski, M.F. Phylogeny and character evolution in Medicago (Leguminosae): Evidence from analyses of plastid trnK/matK and nuclear GA3ox1 sequences. Am. J. Bot. 2010, 97, 1142–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.; Han, Y.; Torres-Jerez, I.; Wang, M.; Tang, Y.; Monteros, M.; Udvardi, M. System responses to long-term drought and re-watering of two contrasting alfalfa varieties. Plant J. 2011, 68, 871–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.-L.; Zhao, M.-G.; Tian, Q.-Y.; Zhang, W.-H. Comparative studies on tolerance of Medicago truncatula and Medicago falcata to freezing. Planta 2011, 234, 445–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Coulman, B.; Bai, Y.; Tar’an, B.; Biligetu, B. Genetic diversity and local adaption of alfalfa populations (Medicago sativa L.) under long-term grazing. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epstein, B.; Branca, A.; Mudge, J.; Bharti, A.K.; Briskine, R.; Farmer, A.D.; Sugawara, M.; Young, N.D.; Sadowsky, M.J.; Tiffin, P. Population Genomics of the Facultatively Mutualistic Bacteria Sinorhizobium meliloti and S. medicae. PLoS Genet. 2012, 8, e1002868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rome, S.; Brunel, B.; Normand, P.; Fernandez, M.; Cleyet-Marel, J.C. Evidence that two genomic species of Rhizobium are associated with Medicago truncatula. Arch. Microbiol. 1996, 165, 285–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bromfield, E.S.P.; Tambong, J.T.; Cloutier, S.; Prévost, D.; Laguerre, G.; van Berkum, P.; Thi, T.V.T.; Assabgui, R.; Barran, L.R. Ensifer, Phyllobacterium and Rhizobium species occupy nodules of Medicago sativa (alfalfa) and Melilotus alba (sweet clover) grown at a Canadian site without a history of cultivation. Microbiology 2010, 156, 505–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Meyer, S.E.; Van Hoorde, K.; Vekeman, B.; Braeckman, T.; Willems, A. Genetic diversity of rhizobia associated with indigenous legumes in different regions of Flanders (Belgium). Soil Biol. Biochem. 2011, 43, 2384–2396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciocârlan, V. Flora Ilustrată a României: Pteridophyta et Spermatophyta (The Illustrated Flora of Romania), 2nd ed.; Ceres: Bucharest, Romania, 2000; ISBN 973-40-0495-6. (In Romanian) [Google Scholar]
- Vîrdol, D.C. (Ed.) The Romanian Statistical Yearbook 2022; National Institute of Statistics (NIS): Bucharest, Romania, 2023; pp. 476–477. ISBN 1220-3246. Available online: https://insse.ro/cms/en/content/romanian-statistical-yearbook-book-format-5 (accessed on 11 October 2023).
- Beattie, G.A.; Handelsman, J. A rapid method for the isolation and identification of Rhizobium from root nodules. J. Microbiol. Methods 1989, 9, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincent, J.M. A Manual for the Practical Study of the Root-Nodule Bacteria (IBP Handbuch No. 15 des International Biology Program, London); Blackwell Scientific Publishing: Oxford, UK; Edinburgh, UK, 1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somasegaran, P.; Hoben, H.J. Quantifying the Growth of Rhizobia. In Handbook for Rhizobia: Methods in Legume-Rhizobium Technology; Somasegaran, P., Hoben, H.J., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1994; pp. 47–57. ISBN 978-1-4613-8375-8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frioni, L.; Rodríguez, A.; Meerhoff, M. Differentiation of rhizobia isolated from native legume trees in Uruguay. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2001, 16, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.-L.; Turner, S.L.; Kan, F.L.; Wang, E.T.; Tan, Z.Y.; Qiu, Y.H.; Gu, J.; Terefework, Z.; Young, J.P.W.; Lindström, K.; et al. Mesorhizobium septentrionale sp. nov. and Mesorhizobium temperatum sp. nov., isolated from Astragalus adsurgens growing in the northern regions of China. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2004, 54, 2003–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Josey, D.P.; Beynon, J.L.; Johnston, A.W.B.; Beringer, J.E. Strain Identification in Rhizobium Using Intrinsic Antibiotic Resistance. J. Appl. Bacteriol. 1979, 46, 343–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mpepereki, S.; Makonese, F.; Wollum, A.G. Physiological characterization of indigenous rhizobia nodulating Vigna unguiculata in Zimbabwean soils. Symbiosis 1997, 22, 275–292. [Google Scholar]
- Sneath, P.H.A.; Sokal, R.R. Numerical Taxonomy: The Principles and Practice of Numerical Classification; W. H. Freeman: New York, NY, USA, 1973; ISBN 978-0-7167-0697-7. [Google Scholar]
- Efrose, R.C.; Rosu, C.M.; Stedel, C.; Stefan, A.; Sirbu, C.; Gorgan, L.D.; Labrou, N.E.; Flemetakis, E. Molecular diversity and phylogeny of indigenous Rhizobium leguminosarum strains associated with Trifolium repens plants in Romania. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2017, 111, 135–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefan, A.; Van Cauwenberghe, J.; Rosu, C.M.; Stedel, C.; Labrou, N.E.; Flemetakis, E.; Efrose, R.C. Genetic diversity and structure of Rhizobium leguminosarum populations associated with clover plants are influenced by local environmental variables. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2018, 41, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozas, J.; Ferrer-Mata, A.; Sánchez-DelBarrio, J.C.; Guirao-Rico, S.; Librado, P.; Ramos-Onsins, S.E.; Sánchez-Gracia, A. DnaSP 6: DNA Sequence Polymorphism Analysis of Large Data Sets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2017, 34, 3299–3302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sayers, E.W.; Cavanaugh, M.; Clark, K.; Pruitt, K.D.; Schoch, C.L.; Sherry, S.T.; Karsch-Mizrachi, I. GenBank. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 49, D92–D96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altschul, S.F.; Gish, W.; Miller, W.; Myers, E.W.; Lipman, D.J. Basic Local Alignment Search Tool. J. Mol. Biol. 1990, 215, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Li, M.; Knyaz, C.; Tamura, K. MEGA X: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis across Computing Platforms. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 1547–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goslee, S.C.; Urban, D.L. The ecodist Package for Dissimilarity-based Analysis of Ecological Data. J. Stat. Softw. 2007, 22, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oksanen, J.; Simpson, G.L.; Blanchet, F.G.; Kindt, R.; Legendre, P.; Minchin, P.R.; O’Hara, R.B.; Solymos, P.; Stevens, M.H.H.; Szoecs, E.; et al. Vegan: Community Ecology Package 2022. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/vegan/index.html (accessed on 11 October 2023).
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2020; Available online: https://www.r-project.org/ (accessed on 15 May 2023).
- Dray, S.; Dufour, A.-B. The ade4 Package: Implementing the Duality Diagram for Ecologists. J. Stat. Softw. 2007, 22, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siberchicot, A.; Julien-Laferrière, A.; Dufour, A.-B.; Thioulouse, J.; Dray, S. adegraphics: An S4 Lattice-Based Package for the Representation of Multivariate Data. R J. 2017, 9, 198–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- QGIS Development Team. 2023. Available online: https://www.qgis.org/ (accessed on 15 May 2023).
- Inkscape Project, 2020. Available online: https://inkscape.org/ (accessed on 15 May 2023).
- Silva, C.; Kan, F.L.; Martínez-Romero, E. Population genetic structure of Sinorhizobium meliloti and S. medicae isolated from nodules of Medicago spp. in Mexico. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2007, 60, 477–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, R.; Jackson, R.W.; Mauchline, T.H.; Hirsch, P.R.; Shaw, L.J.; Döring, T.F.; Jones, H.E. Is there sufficient Ensifer and Rhizobium species diversity in UK farmland soils to support red clover (Trifolium pratense), white clover (T. repens), lucerne (Medicago sativa) and black medic (M. lupulina)? Appl. Soil Ecol. 2017, 120, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, B.C.; Wang, E.T.; Li, Y.; Jia, R.Z.; Chen, W.F.; Man, C.X.; Sui, X.H.; Chen, W.X. Rhizobial Resource Associated with Epidemic Legumes in Tibet. Microb. Ecol. 2009, 57, 69–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muntyan, V.S.; Baturina, O.A.; Afonin, A.M.; Cherkasova, M.E.; Laktionov, Y.V.; Saksaganskaya, A.S.; Kabilov, M.R.; Roumiantseva, M.L. Draft Genome Sequence of Sinorhizobium meliloti AK555. Microbiol. Resour. Announc. 2019, 8, e01567-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, T.L.; Wood, C.W.; Heath, K.D.; Stinchcombe, J.R. Geographically Structured Genetic Variation in the Medicago lupulina-Ensifer Mutualism. Evolution 2017, 71, 1787–1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Meyer, S.E.; Tan, H.W.; Andrews, M.; Heenan, P.B.; Willems, A. Mesorhizobium calcicola sp. nov., Mesorhizobium waitakense sp. nov., Mesorhizobium sophorae sp. nov., Mesorhizobium newzealandense sp. nov. and Mesorhizobium kowhaii sp. nov. isolated from Sophora root nodules. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2016, 66, 786–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, Y.F.; Grogan, P.; Walker, V.K.; diCenzo, G.C. Whole genome sequencing of mesorhizobia isolated from northern Canada. Can. J. Microbiol. 2022, 68, 661–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.W.; Song, J.; Doty, S.L.; Lee, D.K. Diversity of Rhizobia Associated with Leguminous Trees Growing in South Korea. J. Basic Microbiol. 2013, 53, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulrich, A.; Zaspel, I. Phylogenetic diversity of rhizobial strains nodulating Robinia pseudoacacia L. Microbiology 2000, 146 Pt 11, 2997–3005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greenlon, A.; Chang, P.L.; Damtew, Z.M.; Muleta, A.; Carrasquilla-Garcia, N.; Kim, D.; Nguyen, H.P.; Suryawanshi, V.; Krieg, C.P.; Yadav, S.K.; et al. Global-level population genomics reveals differential effects of geography and phylogeny on horizontal gene transfer in soil bacteria. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 15200–15209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armas-Capote, N.; Pérez-Yépez, J.; Martínez-Hidalgo, P.; Garzón-Machado, V.; Del Arco-Aguilar, M.; Velázquez, E.; León-Barrios, M. Core and symbiotic genes reveal nine Mesorhizobium genospecies and three symbiotic lineages among the rhizobia nodulating Cicer canariense in its natural habitat (La Palma, Canary Islands). Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2014, 37, 140–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardley, J.K.; Reeve, W.G.; O’Hara, G.W.; Yates, R.J.; Dilworth, M.J.; Howieson, J.G. Nodule morphology, symbiotic specificity and association with unusual rhizobia are distinguishing features of the genus Listia within the Southern African crotalarioid clade Lotononis s.l. Ann. Bot. 2013, 112, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, J.; Parker, M.A. Contrasting nifD and Ribosomal Gene Relationships Among Mesorhizobium from Lotus oroboides in Northern Mexico. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2002, 25, 68–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, Q.; Wei, X.; Wei, X.; Ou, E.; Ji, Y.; Shu, J.; Long, Z. Research on Resource Exploration, Nitrogen Fixation Characteristics and Diversity of Rhizobia of Medicago lupulina in Karst Mountainous Area of Guizhou. Acta Agrestia Sin. 2022, 30, 1891–1899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, M.; De Meyer, S.; James, E.K.; Stępkowski, T.; Hodge, S.; Simon, M.F.; Young, J.P.W. Horizontal Transfer of Symbiosis Genes within and between Rhizobial Genera: Occurrence and Importance. Genes 2018, 9, 321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerding, M.; O’Hara, G.W.; Bräu, L.; Nandasena, K.; Howieson, J.G. Diverse Mesorhizobium spp. with unique nodA nodulating the South African legume species of the genus Lessertia. Plant Soil 2012, 358, 385–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fterich, A.; Mahdhi, M.; Caviedes, M.A.; Pajuelo, E.; Rivas, R.; Rodriguez-Llorente, I.D.; Mars, M. Characterization of root-nodulating bacteria associated to Prosopis farcta growing in the arid regions of Tunisia. Arch. Microbiol. 2011, 193, 385–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epstein, B.; Tiffin, P. Comparative genomics reveals high rates of horizontal transfer and strong purifying selection on rhizobial symbiosis genes. Proc. Biol. Sci. 2021, 288, 20201804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| GM | L | ST (sST) | VarS/ParI | π | GC | Fu & Li’s D* | Fu & Li’s F* | Tajima’s D |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 16S rDNA | 1345 | 8 (2) | 99/95 | 0.012 | 55.1 | 1.465 * | 0.738 | −0.752 |
| atpD | 435 | 9 (3) | 97/88 | 0.044 | 63.8 | 0.547 | 0.261 | −0.311 |
| glnII | 588 | 16 (8) | 162/151 | 0.053 | 62.4 | 0.798 | 0.426 | −0.344 |
| recA | 330 | 10 (7) | 75/69 | 0.047 | 62.3 | 0.198 | 0.077 | −0.153 |
| nifH | 168 | 6 (1) | 47/46 | 0.055 | 60.7 | 1.806 ** | 1.231 | −0.278 |
| nodA | 580 | 13 (5) | 171/170 | 0.078 | 56.9 | 2.066 ** | 1.888 * | 0.803 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stefan, A.; Van Cauwenberghe, J.; Rosu, C.M.; Stedel, C.; Chan, C.; Simms, E.L.; Iticescu, C.; Tsikou, D.; Flemetakis, E.; Efrose, R.C. Nodules of Medicago spp. Host a Diverse Community of Rhizobial Species in Natural Ecosystems. Agronomy 2024, 14, 2156. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14092156
Stefan A, Van Cauwenberghe J, Rosu CM, Stedel C, Chan C, Simms EL, Iticescu C, Tsikou D, Flemetakis E, Efrose RC. Nodules of Medicago spp. Host a Diverse Community of Rhizobial Species in Natural Ecosystems. Agronomy. 2024; 14(9):2156. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14092156
Chicago/Turabian StyleStefan, Andrei, Jannick Van Cauwenberghe, Craita Maria Rosu, Catalina Stedel, Crystal Chan, Ellen L. Simms, Catalina Iticescu, Daniela Tsikou, Emmanouil Flemetakis, and Rodica Catalina Efrose. 2024. "Nodules of Medicago spp. Host a Diverse Community of Rhizobial Species in Natural Ecosystems" Agronomy 14, no. 9: 2156. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14092156
APA StyleStefan, A., Van Cauwenberghe, J., Rosu, C. M., Stedel, C., Chan, C., Simms, E. L., Iticescu, C., Tsikou, D., Flemetakis, E., & Efrose, R. C. (2024). Nodules of Medicago spp. Host a Diverse Community of Rhizobial Species in Natural Ecosystems. Agronomy, 14(9), 2156. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14092156







