Genome-Wide Association Study Reveals Marker–Trait Associations for Heat-Stress Tolerance in Sweet Corn
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials and Growth Conditions
2.2. Phenotyping and Data Analysis
2.3. DNA Extraction and Genotyping
2.4. GWAS and the Prediction of Candidate Genes
3. Results
3.1. Phenotypic Variation of Target Traits
3.2. SNP Quality Control
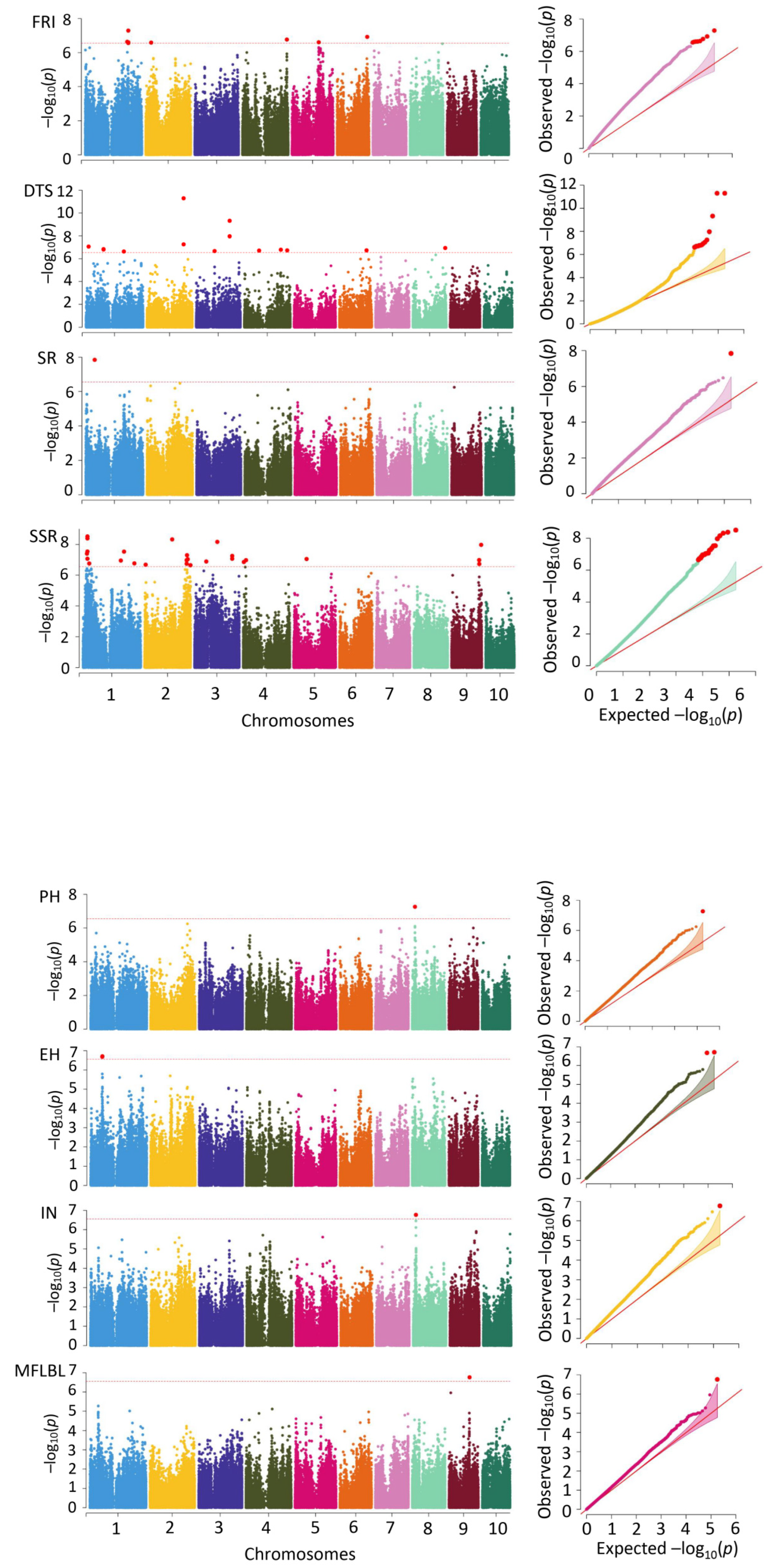
3.3. GWAS on the Eight Traits
3.4. Candidate Genes Associated with Heat-Stress Tolerance
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Luo, N.; Mueller, N.; Zhang, Y.; Feng, P.; Huang, S.; Liu, D.L.; Yu, Y.; Wang, X.; Wang, P.; Meng, Q. Short-term extreme heat at flowering amplifies the impacts of climate change on maize production. Environ. Res. Lett. 2023, 18, 084021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos Santos, T.B.; Ribas, A.F.; de Souza, S.G.H.; Budzinski, I.G.F.; Domingues, D.S. Physiological responses to drought, salinity, and heat stress in plants: A review. Stresses 2022, 2, 113–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xu, J.; Li, R.; Ge, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, R. Plants’ response to abiotic stress: Mechanisms and strategies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 10915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Praveen, A.; Dubey, S.; Singh, S.; Sharma, V.K. Abiotic stress tolerance in plants: A fascinating action of defense mechanisms. 3 Biotech 2023, 13, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siebert, S.; Ewert, F. Future crop production threatened by extreme heat. Environ. Res. Lett. 2014, 9, 041001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djalovic, I.; Kundu, S.; Bahuguna, R.N.; Pareek, A.; Raza, A.; Singla-Pareek, S.L.; Prasad, P.V.V.; Varshney, R.K. Maize and heat stress: Physiological, genetic, and molecular insights. Plant Genome 2024, 17, e20378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Du, T.; Zhang, J.; Chen, S.K.; Fu, J.; Li, H.H.; Yang, Q. Genes and pathways correlated with heat stress responses and heat tolerance in maize kernels. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1228213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabagh, A.E.L.; Hossain, A.; Iqbal, M.A.; Barutçular, C.; Islam, M.S.; Çiğ, F.; Erman, M.; Sytar, O.; Brestic, M.; Wasaya, A.; et al. Maize adaptability to heat stress under changing climate. In Plant Stress physiology; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2020; Volume 9. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Howell, S.H. Heat stress responses and thermotolerance in Maize. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, W.; Oubounyt, M.; Baumbach, J.; Dresselhaus, T. Heat-stress-induced ROS in maize silks cause late pollen tube growth arrest and sterility. iScience. 2024, 27, 110081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Tao, H.; Tian, B.; Sheng, D.; Xu, C.; Zhou, H.; Huang, S.; Wang, P. Flowering dynamics, pollen, and pistil contribution to grain yield in response to high temperature during maize flowering. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2019, 158, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, X.; Hou, X.; Sheng, D.; Dong, X.; Gao, Y.; Wang, P.; Huang, S. Maximum lethal temperature for flowering and seed set in maize with contrasting male and female flower sensitivities. J. Agron. Crop Sci. 2021, 207, 679–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, L.; Gu, X.; Li, J.; Guo, J.; Lu, D. Leaf photosynthetic characteristics of waxy maize in response to different degrees of heat stress during grain filling. BMC Plant Biol. 2023, 23, 469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karim, M.D.A.; Fracheboud, Y.; Stamp, P. Photosynthetic activity of developing leaves of Zea mays is less affected by heat stress than that of developed leaves. Physiol. Plant. 1999, 105, 685–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elashtokhy, M.M.A.; Soaud, N.; Koul, M.; Mir, R.R.; Yan, K.; Li, J.; El-Tarabily, K.A.; Abbas, M. Heat stress-mediated constraints in maize (Zea mays) production: Challenges and solutions. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 879366. [Google Scholar]
- Gagliardi, D.; Breton, C.; Chaboud, A.; Vergne, P.; Dumas, C. Expression of heat shock factor and heat shock protein 70 genes during maize pollen development. Plant Mol. Biol. 1995, 29, 841–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.X.; Jiang, H.-Y.; Chu, Z.X.; Tang, X.L.; Zhu, S.W.; Cheng, B.J. Genome-wide identification, classification and analysis of heat shock transcription factor family in maize. BMC Genom. 2011, 12, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Z.; Zheng, Z.; Qi, F.; Wang, J.; Wang, M.; Zhao, R.; Liu, H.; Xu, J.; Qin, L.; Dong, W.; et al. Development and evaluation of the utility of GenoBaits Peanut 40K for a peanut MAGIC population. Mol. Breed. 2023, 43, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adak, A.; Conrad, C.; Chen, Y.; Wilde, S.C.; Murray, S.C.; Anderson, I.S.L.; Subramanian, N.K. Validation of functional polymorphisms affecting maize plant height by unoccupied aerial systems discovers novel temporal phenotypes. G3 (Bethesda) 2021, 11, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Zhang, M.; Chen, J.; Qing, C.; He, S.; Zou, C.; Yuan, G.; Yang, C.; Peng, H.; Pan, G.; et al. GWAS and WGCNA uncover hub genes controlling salt tolerance in maize (Zea mays L.) seedlings. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2021, 134, 3305–3318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beló, A.; Zheng, P.; Luck, S.; Shen, B.; Meyer, D.J.; Li, B.; Tingey, S.; Rafalski, A. Whole genome scan detects an allelic variant of fad2 associated with increased oleic acid levels in maize. Mol. Genet. Genom. 2008, 279, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnable, P.S.; Ware, D.; Fulton, R.S.; Stein, J.C.; Wei, F.; Pasternak, S.; Liang, C.; Zhang, J.; Fulton, L.; Graves, T.A.; et al. The B73 maize genome: Complexity, diversity, and dynamics. Science 2009, 326, 1112–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahito, J.H.; Zhang, H.; Gishkori, Z.G.; Ma, C.; Wang, Z.; Ding, D.; Zhang, X.; Tang, J. Advancements and prospects of genome-wide association studies (GWAS) in maize. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, H.; Xue, Z.; Ju, X.; Yang, L.; Gao, J.; Sun, L.; Xu, S.; Li, J.; Xiong, X.; Sun, Y.; et al. The genetic architecture of prolificacy in maize revealed by association mapping and bulk segregant analysis. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2023, 136, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Y.; Zhang, M.; Liu, Y.; Liu, J.; Li, W.; Chen, G.; Peng, Y.; Jin, M.; Wei, W.; Jian, L.; et al. Genetic variation in YIGE1 contributes to ear length and grain yield in maize. New Phytol. 2022, 23, 513–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, F.; Jing, J.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, S.; Sang, Z.; Li, W. GWAS and Meta-QTL analysis of yield-related ear traits in maize. Plants 2023, 12, 3806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, T.; Meng, Z.; Yue, R.; Lu, S.; Li, W.; Li, W.; Meng, H.; Sun, Q. Genome wide association analysis for yield related traits in maize. BMC Plant Biol. 2022, 22, 449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, P.; Du, Q.; Chen, H.; Guo, Z.; Wang, Z.; Tang, J.; Li, W.X. Biofortification of iron content by regulating a NAC transcription factor in maize. Science 2023, 382, 1159–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, H.; Liu, S.; Ferjani, A.; Li, J.; Yan, J.; Yang, X.; Qin, F. Genetic variation in ZmVPP1 contributes to drought tolerance in maize seedlings. Nat. Genet. 2016, 48, 1233–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, J.; Xu, Q.; Wang, D.; Di, H.; Huang, J.; Yang, X.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Dong, L.; et al. Identification of candidate tolerance genes to low-temperature during maize germination by GWAS and RNA-seqapproaches. BMC Plant Biol. 2020, 20, 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Li, C.; Zhang, X.; Li, Y.; Zhang, D.; Shi, Y.; Song, Y.; Li, Y.; Yang, D.; Wang, T. Transcriptome and GWAS analyses reveal candidate gene for seminal root length of maize seedlings under drought stress. Plant Sci. 2020, 292, 110380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Guo, J.; Wang, D.; Chen, X.; Guan, H.; Li, Y.; Zhang, D.; Liu, X.; He, G.; Wang, T.; et al. Genomic insight into changes of root architecture under drought stress in maize. Plant Cell Environ. 2023, 46, 1860–1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, N.; Wang, S.; Zhao, S.; Chen, D.; Tian, H.; Li, J.; Zhang, L.; Li, S.; Liu, L.; Shi, C.; et al. Global crotonylatome and GWAS revealed a TaSRT1-TaPGK model regulating wheat cold tolerance through mediating pyruvate. Sci. Adv. 2023, 9, 1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Z.; Zou, C.; Liu, X.; Wang, S.; Li, W.X.; Jeffers, D.; Fan, X.; Xu, M.; Xu, Y. Complex genetic system involved in fusarium ear rot resistance in maize as revealed by GWAS, bulked sample analysis, and genomic prediction. Plant Dis. 2020, 10, 1725–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, M.; Liu, S.; Pei, Y.; Jiang, X.; Jaqueth, J.S.; Li, B.; Han, J.; Jeffers, D.; Wang, J.; Song, X. Identification of genetic loci associated with rough dwarf disease resistance in maize by integrating GWAS and linkage mapping. Plant Sci. 2022, 315, 111100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shu, G.; Wang, A.; Wang, X.; Ding, J.; Chen, R.; Gao, F.; Wang, A.; Li, T.; Wang, Y. Identification of southern corn rust resistance QTNs in Chinese summer maize germplasm via multi-locus GWAS and post-GWAS analysis. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1221395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warburton, M.L.; Womack, E.D.; Tang, J.D.; Thrash, A.; Smith, J.S.; Xu, W.; Murray, S.C.; Williams, W.P. Genome-wide association and metabolic pathway analysis of corn earworm resistance in maize. Plant Genome 2018, 11, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamiru, A.; Paliwal, R.; Manthi, S.J.; Odeny, D.A.; Midega, C.A.O.; Khan, Z.R.; Pickett, J.A.; Bruce, T.J.A. Genome wide association analysis of a stemborer egg induced “call-for-help” defence trait in maize. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 11205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Washburn, J.D.; LaFond, H.F.; Lapadatescu, M.C.; Pereira, A.E.; Erb, M.; Hibbard, B.E. GWAS analysis of maize host plant resistance to western corn rootworm (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae) reveals candidate small effect loci for resistance breeding. J. Econ. Entomol. 2023, 116, 2184–2192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, Z.; Khalid, M.; Ghafoor, A.; Shah, M.K.N.; Raja, G.K.; Rana, R.M.; Mahmood, T.; Thompson, A.M. SNP-based genome-wide association mapping of pollen viability under heat stress in tropical Zea mays L. Inbred Lines. Front. Genet. 2022, 13, 819849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longmei, N.; Gill, G.K.; Zaidi, P.H.; Kumar, R.; Nair, S.K.; Hindu, V.; Vinayan, M.T.; Vikal, Y. Genome wide association mapping for heat tolerance in sub-tropical maize. BMC Genom. 2021, 22, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NY/T 2232-2012; Guidelines for the Conduct of Tests for Distinctness, Uniformity and Stability. Maize (Zea mays L.). National public Service Platform for Standards Information. Ministry of Agriculture of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2012.
- Murray, M.G.; Thompson, W.F. Rapid isolation of high molecular weight plant DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980, 8, 4321–4325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Z.; Yang, Q.; Huang, F.; Zheng, H.; Sang, Z.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, C.; Wu, K.; Tao, J.; Prasanna, B.M.; et al. Development of high-resolution multiple-SNP arrays for genetic analyses and molecular breeding through genotyping by target sequencing and liquid chip. Plant Commun. 2021, 2, 100230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Y.; Gu, J. fastp: An ultra-fast all-in-one FASTQ preprocessor. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, i884–i890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Durbin, R. Fast and accurate short read alignment with Burrows-Wheeler transform. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1754–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, C.; Wang, L.; Zeng, W.; Han, G.; Qiu, C.; Wang, T.; Tao, Z.; Wang, K.; et al. Linkage mapping combined with GWAS revealed the genetic structural relationship and candidate genes of maize flowering time-related traits. BMC Plant Biol. 2022, 22, 328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipka, A.E.; Tian, F.; Wang, Q.; Peiffer, J.; Li, M.; Bradbury, P.J.; Gore, M.A.; Buckler, E.S.; Zhang, Z. GAPIT: Genome association and prediction integrated tool. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 2397–2399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoper, J.B.; Lambert, R.J.; Vasilas, B.L. Maize pollen viability and ear receptivity under water and high-temperature stress. Crop Sci. 1986, 26, 1029–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Guan, Z.; Li, Z.; Liu, P.; Ma, L.; Zhang, Y.; Pan, L.; He, S.; Zhang, Y.; Li, P.; et al. A combination of linkage mapping and GWAS brings new elements on the genetic basis of yield-related traits in maize across multiple environments. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2020, 133, 2881–2895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edreira, J.I.R.; Otegui, M.E. Heat stress in temperate and tropical maize hybrids: A novel approach for assessing sources of kernel loss in field conditions. Field Crop. Res. 2013, 142, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhaliwal, D.S.; Williams, M.M. Evidence of sweet corn yield losses from rising temperatures. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 18218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.-Y.; Chen, Z.H.; Tang, B.; Zeng, Q.; Guo, H.L.; Huang, W.H.; Luo, Y.; Shen, S.; Zhou, S.L. The effects of sowing date on maize: Phenology, morphology, and yield formation in a hot subtropical monsoon region. Field Crop. Res. 2024, 309, 109309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peet, M.M.; Sato, S.; Gardner, R.G. Comparing heat stress effects on male-fertile and male-sterile tomatoes. Plant Cell Environ. 1998, 21, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, S.; Kamiyama, M.; Iwata, T.; Makita, N.; Furukawa, H.; Ikeda, H. Moderate increase of mean daily temperature adversely affects fruit set of Lycopersicon esculentum by disrupting specific physiological processes in male reproductive development. Ann. Bot. 2006, 97, 731–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Guo, W.; Le, L.; Yu, J.; Wu, Y.; Li, D.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H.; Lu, X.; Qiao, H.; et al. Integration of high-throughput phenotyping, GWAS, and predictive models reveals the genetic architecture of plant height in maize. Mol. Plant. 2023, 1, 354–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, X.; Bi, Y.; Jiang, F.; Guo, R.; Zhang, Y.; Fan, J.; Kang, M.S.; Fan, X. Fine mapping of candidate quantitative trait loci for plant and ear height in a maize nested-association mapping population. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 963985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, G.; Wang, A.; Wang, X.; Chen, R.; Gao, F.; Wang, A.; Li, T.; Wang, Y. Identification of QTNs, QTN-by-environment interactions for plant height and ear height in maize multi-environment GWAS. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1284403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, L.; Zhang, H.; Xin, W.; Ma, K.; Du, D.; Yu, C.; Liu, Y. Dissecting the genetic basis of flowering time and height related-traits using two doubled haploid populations in maize. Plants 2021, 10, 1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNellie, J.P.; Chen, J.; Li, X.; Yu, J. Genetic mapping of foliar and tassel heat stress tolerance in maize. Crop Sci. 2018, 58, 2484–2493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Pastor, R.; Burchfiel, E.T.; Thiele, D.J. Regulation of heat shock transcription factors and their roles in physiology and disease. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Bio. 2018, 19, 4–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, K.; Fujimoto, M.; Takii, R.; Takaki, E.; Hayashida, N.; Nakai, A. Mitochondrial SSBP1 protects cells from proteotoxic stresses by potentiating stress-induced Hsf1 transcriptional activity. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Chen, L.; Si, W.; Jiang, H. A maize heat shock factor ZmHsf11 negatively regulates heat stress tolerance in transgenic plants. BMC Plant Biol. 2022, 22, 406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.C.; Zhang, H.N.; Li, G.L.; Liu, Z.H.; Zhang, Y.M.; Zhang, H.M.; Guo, X.L. Expression of maize heat shock transcription factor gene ZmHsf06 enhances the thermotolerance and drought-stress tolerance of transgenic Arabidopsis. Funct. Plant Biol. 2015, 42, 1080–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, L.; Hu, W.; Qian, Y.; Ren, Q.; Zhang, J. Genome-wide identification, classification and expression analysis of the Hsf and Hsp70 gene families in maize. Gene 2021, 770, 145348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Huang, Y.; Sun, H.; Wang, T.; Ru, W.; Pan, L.; Zhao, X.; Dong, Z.; Huang, W.; Jin, W. Heat shock protein 101 contributes to the thermotolerance of male meiosis in maize. Plant Cell 2022, 34, 3702–3717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
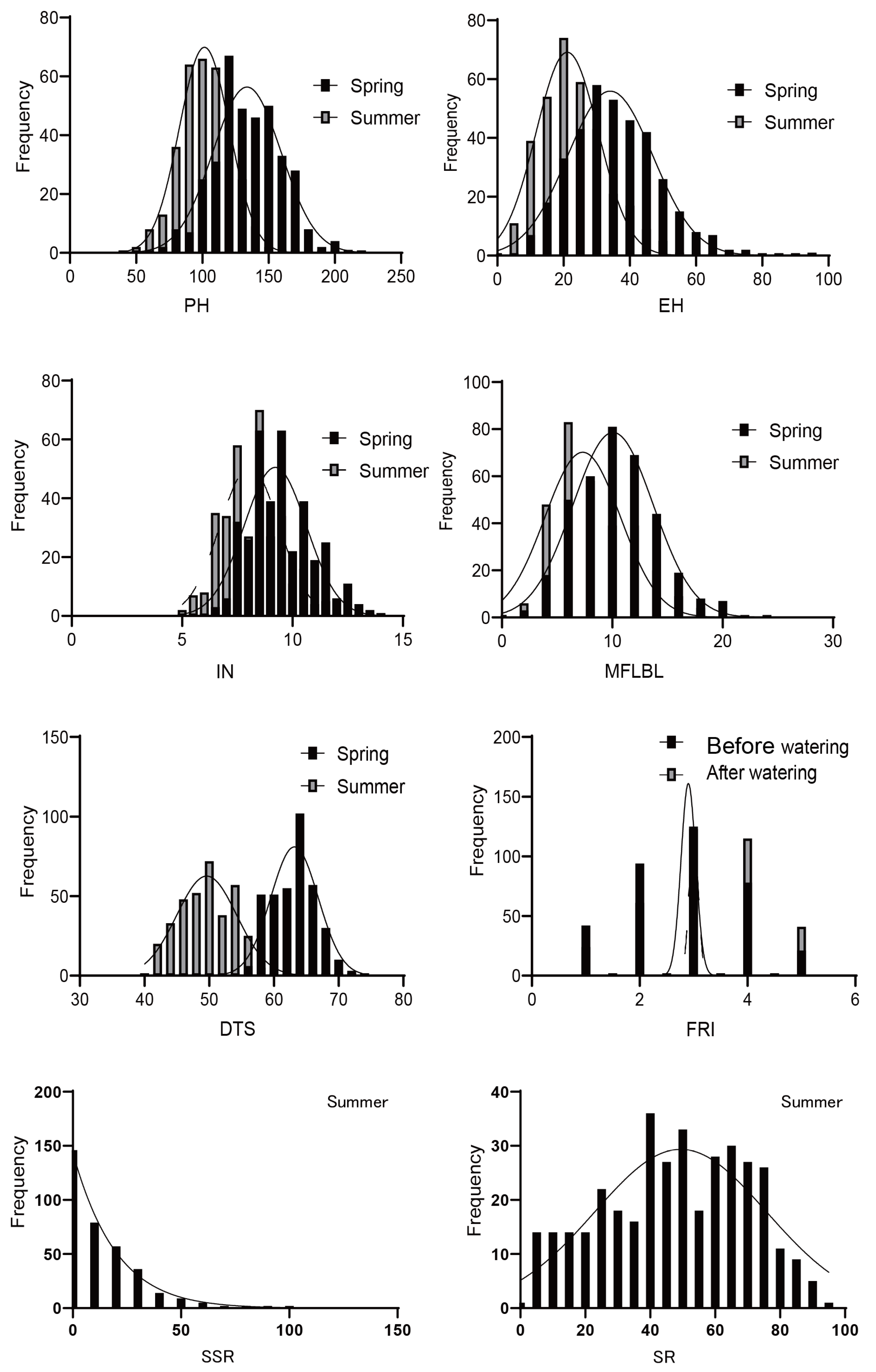
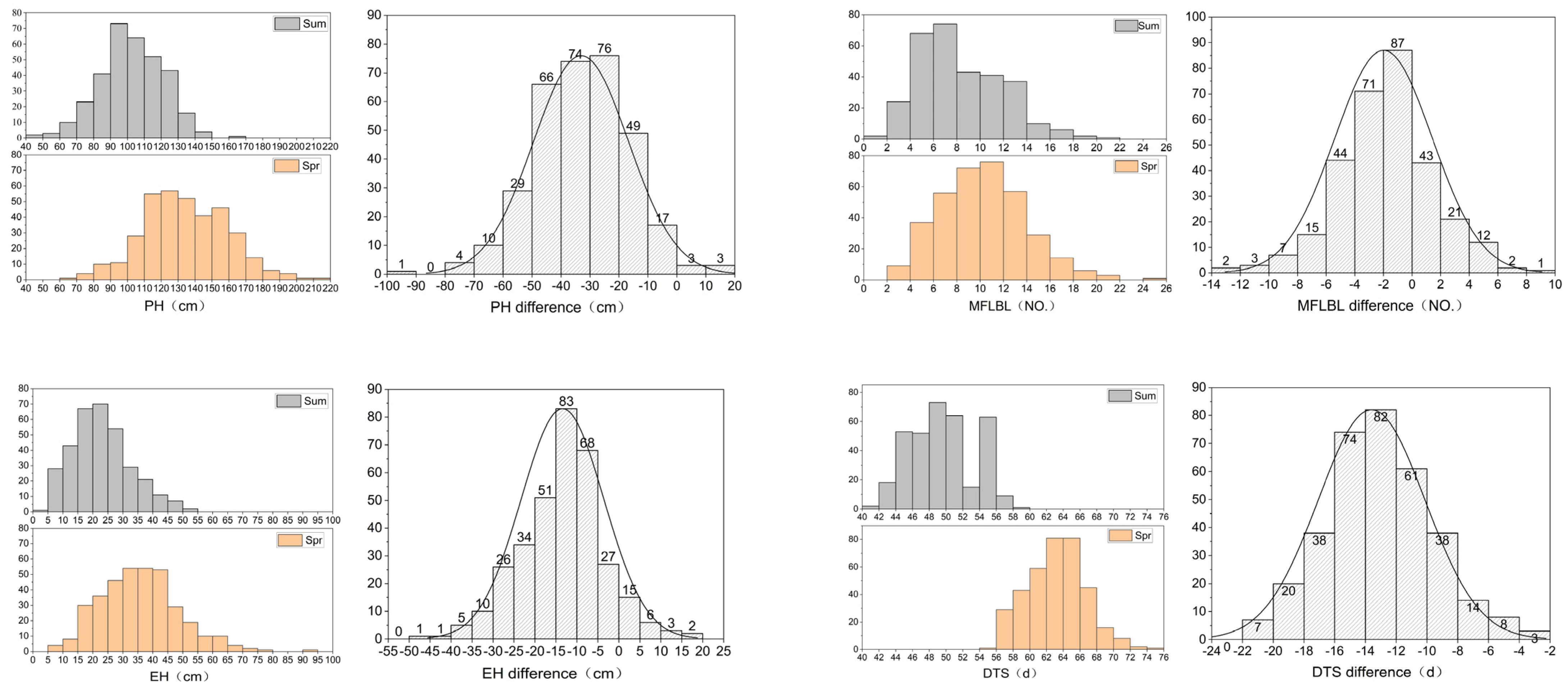
| Trait | Treatment | Number | Average | CV | Skew | Kurt | H2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PH | spring | 361.00 | 134.11 | 18.57 | 0.16 | −0.08 | 99.03 |
| summer | 332.00 | 101.90 | 18.37 | −0.03 | 0.05 | 96.86 | |
| difference | 330.00 | 32.78 | 48.72 | 0.06 | −0.10 | ||
| EH | spring | 361.00 | 35.55 | 36.86 | 0.65 | 0.99 | 95.5 |
| summer | 333.00 | 22.61 | 43.64 | 0.55 | 0.09 | 92.89 | |
| difference | 326.00 | 13.42 | 67.93 | −0.15 | 0.01 | ||
| IN | spring | 361.00 | 9.47 | 15.18 | 0.56 | 0.01 | 89.1 |
| summer | 338.00 | 8.15 | 15.99 | 0.25 | −0.28 | 92.66 | |
| difference | 332.00 | 1.38 | 82.18 | −0.06 | −0.32 | ||
| MFLBL | spring | 360.00 | 10.12 | 36.16 | 0.40 | 0.21 | 92.53 |
| summer | 308.00 | 8.11 | 45.18 | 0.69 | 0.11 | 98.57 | |
| difference | 303.00 | 1.83 | 173.42 | 0.20 | 0.33 | ||
| DTS | spring | 366.00 | 62.62 | 5.49 | 0.15 | −0.26 | 98.47 |
| summer | 350.00 | 49.07 | 7.95 | 0.04 | −0.87 | 98.83 | |
| difference | 15.69 | 10.81 | 68.90 | −3.52 | 12.78 | ||
| FRI | Before watering | 362.00 | 2.84 | 37.79 | 0.05 | −0.62 | 99.06 |
| After watering | 364.00 | 3.24 | 32.97 | −0.26 | −0.49 | 99.07 | |
| difference | 366.00 | 15.69 | 68.90 | −3.52 | 12.78 | ||
| SSR | summer | 348.00 | 12.71 | 119.29 | 0.87 | 0.07 | 95.31 |
| difference | 342.00 | 88.26 | 15.02 | −1.14 | 0.56 | ||
| SR | summer | 364.00 | 47.36 | 46.83 | 0.18 | −1.07 | 96.24 |
| difference | 359.00 | 53.01 | 40.96 | 0.22 | −0.89 |
| SNP | Chr | Pos | p | Data | Traits | r2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1_14846985 | 1 | 14846985 | 8.53 × 10−8 | Difference value | DTS | 0.102 |
| 1_92816129 | 1 | 92816129 | 1.46 × 10−7 | Difference value | DTS | 0.090 |
| 1_92816142 | 1 | 92816142 | 1.57 × 10−7 | Difference value | DTS | 0.089 |
| 1_196372063 | 1 | 196372063 | 7.73 × 10−8 | Spring | DTS | 0.055 |
| 1_264934721 | 1 | 264934721 | 1.15 × 10−7 | Spring | DTS | 0.053 |
| 2_192568550 | 2 | 192568550 | 5.44 × 10−8 | Difference value | DTS | 0.104 |
| 2_192568593 | 2 | 192568593 | 5.08 × 10−12 | Difference value | DTS | 0.153 |
| 2_192568599 | 2 | 192568599 | 5.09 × 10−12 | Difference value | DTS | 0.153 |
| 3_97340159 | 3 | 97340159 | 2.10 × 10−7 | Difference value | DTS | 0.097 |
| 3_176087879 | 3 | 176087879 | 4.82 × 10−10 | Difference value | DTS | 0.130 |
| 3_176087909 | 3 | 176087909 | 1.09 × 10−8 | Difference value | DTS | 0.113 |
| 3_194075434 | 3 | 194075434 | 1.87 × 10−8 | Summer | DTS | 0.091 |
| 4_78346322 | 4 | 78346322 | 1.93 × 10−7 | Difference value | DTS | 0.097 |
| 4_191942157 | 4 | 191942157 | 1.64 × 10−7 | Difference value | DTS | 0.089 |
| 4_225417694 | 4 | 225417694 | 1.85 × 10−7 | Difference value | DTS | 0.112 |
| 4_81277097 | 4 | 81277097 | 5.22 × 10−8 | Spring | DTS | 0.056 |
| 4_81277111 | 4 | 81277111 | 5.22 × 10−8 | Spring | DTS | 0.056 |
| 6_142837202 | 6 | 142837202 | 1.83 × 10−7 | Difference value | DTS | 0.089 |
| 6_104922285 | 6 | 104922285 | 2.06 × 10−7 | Spring | DTS | 0.051 |
| 6_104922330 | 6 | 104922330 | 5.32 × 10−8 | Spring | DTS | 0.056 |
| 8_169772992 | 8 | 169772992 | 1.13 × 10−7 | Difference value | DTS | 0.100 |
| 8_8194215 | 8 | 8194215 | 8.15 × 10−8 | Spring | DTS | 0.060 |
| 8_22985423 | 8 | 22985423 | 1.30 × 10−8 | Summer | DTS | 0.093 |
| 8_22985494 | 8 | 22985494 | 2.30 × 10−7 | Summer | DTS | 0.079 |
| 8_23774018 | 8 | 23774018 | 1.71 × 10−8 | Summer | DTS | 0.092 |
| 9_31570524 | 9 | 31570524 | 1.84 × 10−7 | Spring | DTS | 0.052 |
| 9_34673256 | 9 | 34673256 | 1.27 × 10−7 | Spring | DTS | 0.058 |
| 9_37933184 | 9 | 37933184 | 3.56 × 10−8 | Spring | DTS | 0.057 |
| 9_37933680 | 9 | 37933680 | 5.52 × 10−9 | Spring | DTS | 0.063 |
| 10_102968054 | 10 | 102968054 | 9.32 × 10−9 | Spring | DTS | 0.061 |
| 10_108429070 | 10 | 108429070 | 3.90 × 10−8 | Spring | DTS | 0.062 |
| 10_122251098 | 10 | 122251098 | 1.7657 × 10−7 | Spring | DTS | 0.052 |
| 1_62928393 | 1 | 62928393 | 2.09 × 10−7 | Difference value | EH | 0.093 |
| 1_63354731 | 1 | 63354731 | 1.94 × 10−7 | Difference value | EH | 0.094 |
| 1_228645147 | 1 | 228645147 | 7.5638 × 10−8 | Summer | EH | 0.092 |
| 1_229066598 | 1 | 229066598 | 5.11 × 10−8 | Difference value | FRI | 0.071 |
| 1_2084505 | 1 | 2084505 | 1.38 × 10−7 | Summer | FRI | 0.058 |
| 4_234654189 | 4 | 234654189 | 1.72 × 10−7 | Difference value | FRI | 0.066 |
| 6_159207149 | 6 | 159207149 | 1.19 × 10−7 | Difference value | FRI | 0.068 |
| 7_6583867 | 7 | 6583867 | 1.44 × 10−7 | Summer | FRI | 0.058 |
| 7_6583868 | 7 | 6583868 | 1.79 × 10−7 | Summer | FRI | 0.063 |
| 10_136501826 | 10 | 136501826 | 7.6151 × 10−8 | Summer | FRI | 0.054 |
| 5_199785132 | 5 | 199785132 | 9.97 × 10−8 | Spring | IN | 0.056 |
| 8_14849637 | 8 | 14849637 | 1.7124 × 10−7 | Difference value | IN | 0.095 |
| 3_230712563 | 3 | 230712563 | 8.24 × 10−8 | Summer | MFLBL | 0.086 |
| 3_230712604 | 3 | 230712604 | 2.13 × 10−7 | Summer | MFLBL | 0.081 |
| 3_230712621 | 3 | 230712621 | 8.10 × 10−9 | Summer | MFLBL | 0.097 |
| 4_172221873 | 4 | 172221873 | 3.18 × 10−7 | Spring | MFLBL | 0.076 |
| 4_172221887 | 4 | 172221887 | 3.18 × 10−7 | Spring | MFLBL | 0.076 |
| 8_162585121 | 8 | 162585121 | 9.94 × 10−8 | Summer | MFLBL | 0.085 |
| 9_109659921 | 9 | 109659921 | 1.73 × 10−7 | Difference value | MFLBL | 0.105 |
| 9_108369429 | 9 | 108369429 | 8.9924 × 10−8 | Summer | MFLBL | 0.085 |
| 2_184209311 | 2 | 184209311 | 2.96 × 10−7 | Spring | PH | 0.065 |
| 2_196310471 | 2 | 196310471 | 1.76 × 10−7 | Spring | PH | 0.067 |
| 5_92656266 | 5 | 92656266 | 2.03 × 10−7 | Spring | PH | 0.073 |
| 8_14839247 | 8 | 14839247 | 5.45 × 10−8 | Difference value | PH | 0.099 |
| 9_143187014 | 9 | 143187014 | 7.81 × 10−9 | Spring | PH | 0.087 |
| 9_143174798 | 9 | 143174798 | 1.4325 × 10−7 | Summer | PH | 0.082 |
| 1_47423640 | 1 | 47423640 | 1.4443 × 10−8 | Difference value | SR | 0.096 |
| 1_21601434 | 1 | 21601434 | 4.02 × 10−8 | Difference value | SSR | 0.101 |
| 1_24042490 | 1 | 24042490 | 2.91 × 10−8 | Difference value | SSR | 0.103 |
| 1_24042491 | 1 | 24042491 | 3.08 × 10−9 | Difference value | SSR | 0.115 |
| 1_24189637 | 1 | 24189637 | 8.55 × 10−8 | Difference value | SSR | 0.097 |
| 1_24189700 | 1 | 24189700 | 4.12 × 10−9 | Difference value | SSR | 0.114 |
| 1_33530079 | 1 | 33530079 | 1.76 × 10−7 | Difference value | SSR | 0.102 |
| 1_197446396 | 1 | 197446396 | 1.12 × 10−7 | Difference value | SSR | 0.120 |
| 1_214371187 | 1 | 214371187 | 2.96 × 10−8 | Difference value | SSR | 0.112 |
| 1_267637610 | 1 | 267637610 | 1.72 × 10−7 | Difference value | SSR | 0.102 |
| 2_5010101 | 2 | 5010101 | 2.10 × 10−7 | Difference value | SSR | 0.109 |
| 2_143022981 | 2 | 143022981 | 4.718 × 10−9 | Difference value | SSR | 0.113 |
| 2_218126982 | 2 | 218126982 | 1.82 × 10−7 | Difference value | SSR | 0.093 |
| 2_218126997 | 2 | 218126997 | 1.06 × 10−7 | Difference value | SSR | 0.096 |
| 2_219685733 | 2 | 219685733 | 5.09 × 10−8 | Difference value | SSR | 0.100 |
| 2_223957129 | 2 | 223957129 | 9.16 × 10−8 | Difference value | SSR | 0.096 |
| 2_237697475 | 2 | 237697475 | 2.23 × 10−7 | Difference value | SSR | 0.091 |
| 3_61338215 | 3 | 61338215 | 1.29 × 10−7 | Difference value | SSR | 0.104 |
| 3_119048837 | 3 | 119048837 | 6.92 × 10−9 | Difference value | SSR | 0.120 |
| 3_195758031 | 3 | 195758031 | 8.62 × 10−8 | Difference value | SSR | 0.106 |
| 3_195758034 | 3 | 195758034 | 5.65 × 10−8 | Difference value | SSR | 0.108 |
| 4_3486651 | 4 | 3486651 | 1.40 × 10−7 | Difference value | SSR | 0.103 |
| 4_14386124 | 4 | 14386124 | 1.07 × 10−7 | Difference value | SSR | 0.096 |
| 5_67269559 | 5 | 67269559 | 9.00 × 10−8 | Difference value | SSR | 0.106 |
| 9_143432848 | 9 | 143432848 | 1.04 × 10−7 | Difference value | SSR | 0.096 |
| 9_143611049 | 9 | 143611049 | 1.89 × 10−7 | Difference value | SSR | 0.092 |
| 9_154009472 | 9 | 154009472 | 1.07 × 10−8 | Difference value | SSR | 0.118 |
| Maize | Best-Hit- Arabidopsis -Name | Arabi-Defline | Best-Hit-Rice-Name | Rice-Defline |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GRMZM2G149647 | AT4G27670.1 | Heat shock protein 21 | Os10g07200.1 | Hsp20/alpha crystallin family protein, putative, expressed |
| GRMZM2G065355 | AT4G15802.1 | Heat shock factor binding protein | Os09g20830.5 | Heat shock factor-binding protein 1, putative, expressed |
| AC216247.3_FG001 | AT1G46264.1 | Heat shock transcription factor B4 | Os07g44690.1 | HSF-type DNA-binding domain containing protein, expressed |
| GRMZM2G016734 | AT1G56300.1 | Chaperone DnaJ-domain superfamily protein | Os03g18870.1 | Heat shock protein DnaJ, putative, expressed |
| GRMZM2G042133 | AT5G22060.1 | DNAJ homologue 2 | Os03g57340.1 | Chaperone protein DnaJ, putative, expressed |
| GRMZM2G448368 | AT2G17880.1 | Chaperone DnaJ-domain superfamily protein | Os08g43490.1 | Heat shock protein DnaJ, putative, expressed |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, Q.; Guo, Z.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Nian, H. Genome-Wide Association Study Reveals Marker–Trait Associations for Heat-Stress Tolerance in Sweet Corn. Agronomy 2024, 14, 2171. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14092171
Yang Q, Guo Z, Zhang J, Wang Y, Xu Y, Nian H. Genome-Wide Association Study Reveals Marker–Trait Associations for Heat-Stress Tolerance in Sweet Corn. Agronomy. 2024; 14(9):2171. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14092171
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Quannv, Zifeng Guo, Jianan Zhang, Yunbo Wang, Yunbi Xu, and Hai Nian. 2024. "Genome-Wide Association Study Reveals Marker–Trait Associations for Heat-Stress Tolerance in Sweet Corn" Agronomy 14, no. 9: 2171. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14092171
APA StyleYang, Q., Guo, Z., Zhang, J., Wang, Y., Xu, Y., & Nian, H. (2024). Genome-Wide Association Study Reveals Marker–Trait Associations for Heat-Stress Tolerance in Sweet Corn. Agronomy, 14(9), 2171. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14092171





