Electric Discharge-Generating Devices Developed for Pathogen, Insect Pest, and Weed Management: Current Status and Future Directions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Electric Discharge Generation
3. Ozone-Generative Spore Precipitator
4. Portable Device for Eliminating Fungal Pustules on Leaves Using Plasma Stream
5. Corona Discharge Devices for Trapping Sidestream Smoke and Droplet-Enclosed Viruses via Negative Ion Adhesion
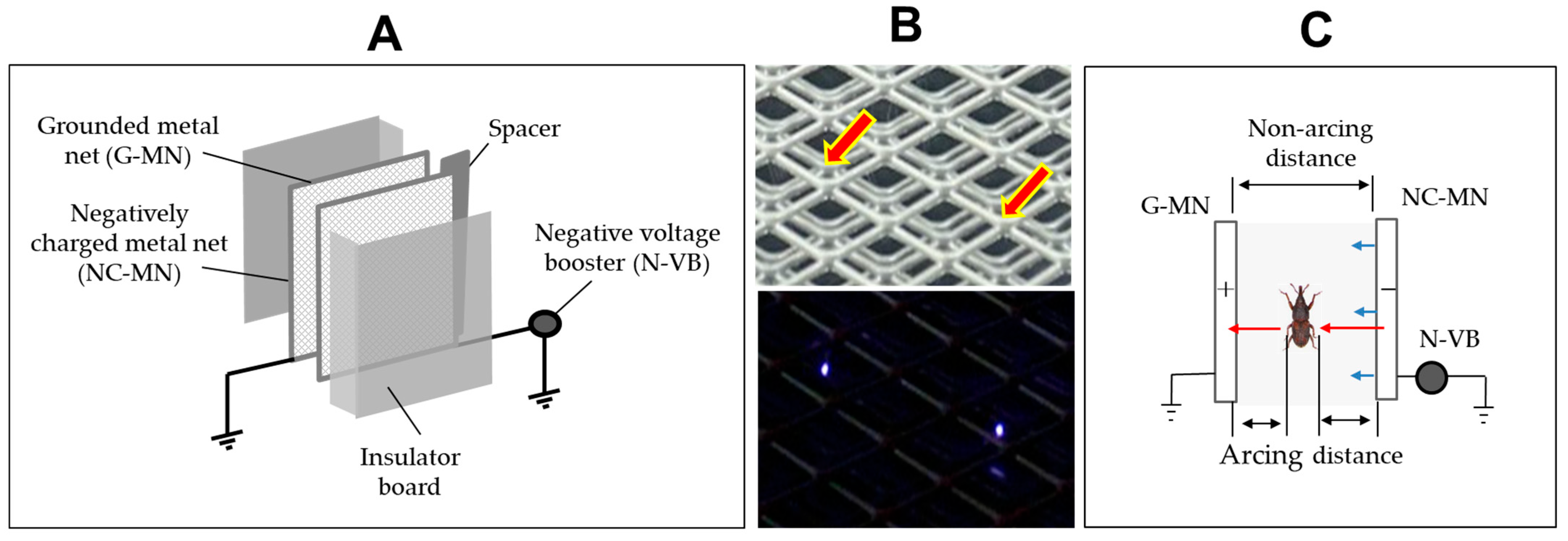
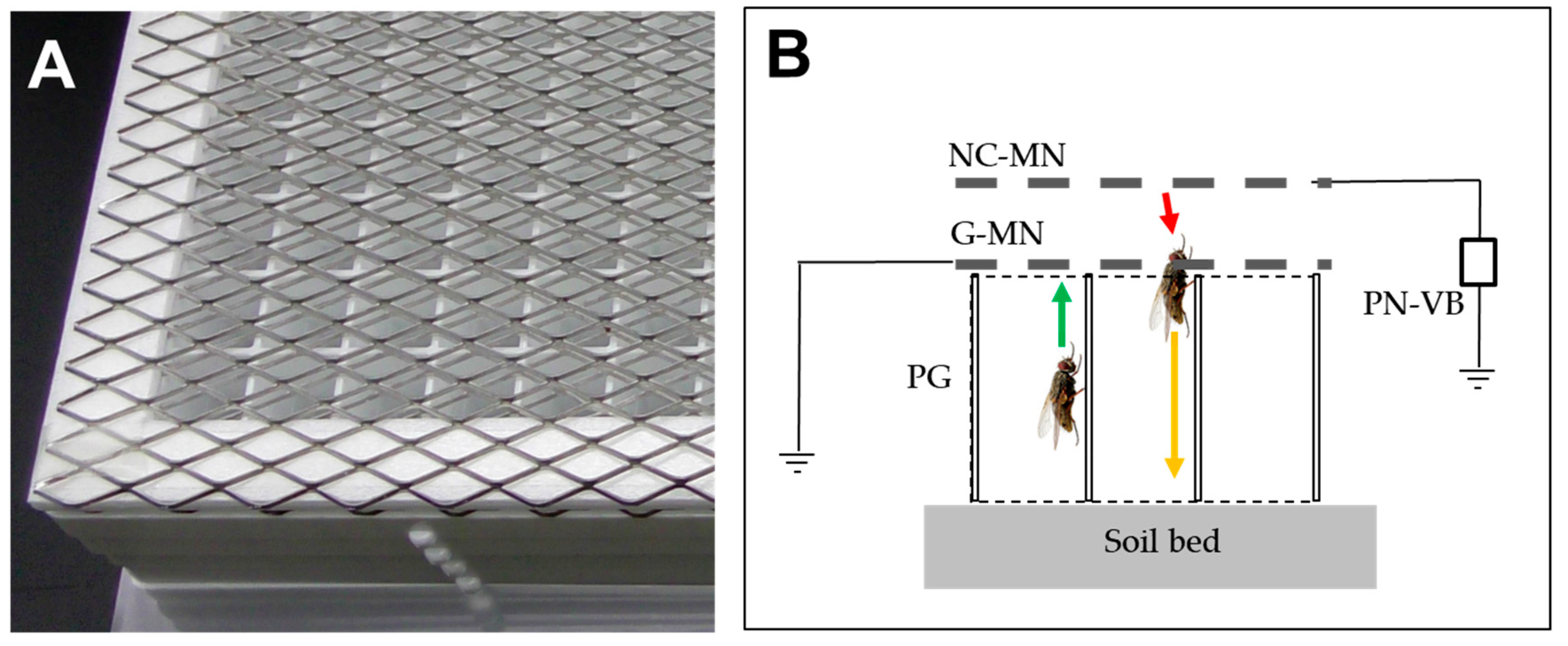
6. Insect and Weed Seedling Control with Corona Discharge Devices
6.1. Pest Control
6.2. Weed Control
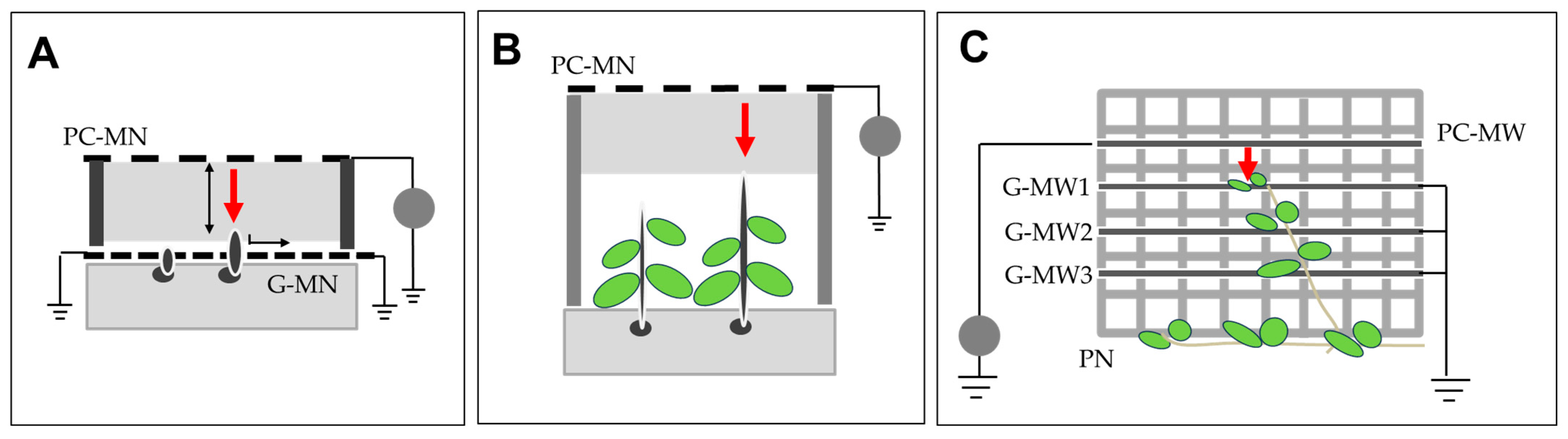

7. Challenges and Future Directions in Electrostatic Pest Control
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Toyoda, H.; Kusakari, S.; Matsuda, Y.; Kakutani, K.; Xu, L.; Nonomura, T.; Takikawa, Y. Electric field screen structures. In An Illustrated Manual of Electric Field Screens: Their Structures and Functions; Toyoda, H., Ed.; RAEFSS Publishing Department: Nara, Japan, 2019; pp. 9–15. [Google Scholar]
- Griffith, W.T. Electrostatic phenomena. In The Physics of Everyday Phenomena, a Conceptual Introduction to Physics; Bruflodt, D., Loehr, B.S., Eds.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2004; pp. 232–252. [Google Scholar]
- Kaiser, K.L. Air breakdown. In Electrostatic Discharge; Kaiser, K.L., Ed.; Taylor & Francis: New York, NY, USA, 2006; pp. 1–93. [Google Scholar]
- Kusakari, S.; Matsuda, Y.; Toyoda, H. Electrostatic insect repulsion, capture, and arc-discharge techniques for physical pest management in greenhouses. Agronomy 2023, 13, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, J.; Zeng, M.; Zhang, D.; Yang, D.; Wu, X.; Ren, Q.; Zhang, J. A review on recent advances and challenges of ionic wind produced by corona discharges with practical applications. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2022, 55, 153002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakutani, K.; Matsuda, Y.; Nonomura, T.; Takikawa, Y.; Takami, T.; Toyoda, H. A simple electrostatic precipitator for trapping virus particles spread via droplet transmission. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 4934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuda, Y.; Takikawa, Y.; Nonomura, T.; Kakutani, K.; Okada, K.; Shibao, M.; Kusakari, S.; Miyama, K.; Toyoda, H. A simple electrostatic device for eliminating tobacco sidestream to prevent passive smoking. Instruments 2018, 2, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kettleson, E.M.; Schriewer, J.M.; Buller, R.M.L.; Biswas, P. Soft X-ray enhanced electrostatic precipitation for protection against inhalable allergens, ultrafine particles, and microbial infections. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 1333–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogan, C.J.; Lee, M.H.; Biswas, P. Capture of viral particles in soft X-ray-enhanced corona systems: Charge distribution and transport characteristics. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 475–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kettleson, E.M.; Ramaswami, B.; Hogan, C.J.; Lee, M.-H.; Statyukha, G.A.; Biswas, P.; Angenent, L.T. Airborne virus capture and inactivation by an electrostatic particle collector. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 5940–5946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.S.; Wen, Y.M. Control effectiveness of electrostatic precipitation on airborne microorganisms. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2003, 37, 933–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-A.; Willeke, K.; Mainelis, G.; Adhikari, A.; Wang, H.; Reponen, T.; Grinshpun, S.A. Assessment of electrical charge on airborne microorganisms by a new bioaerosol sampling method. J. Occup. Environ. Hyg. 2004, 1, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Davidson, J.H. Ozone production in the positive DC corona discharge: Model and comparison to experiments. Plasma Chem. Plasma Process. 2002, 22, 495–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, K.; Matsuda, Y.; Nonomura, T.; Ikeda, H.; Tamura, N.; Kusakari, S.; Kimbara, J.; Toyoda, H. Dual protection of hydroponic tomatoes from rhizosphere pathogens Ralstonia solanacearum and Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. radicis-lycopersici and airborne conidia of Oidium neolycopersici with an ozone-generative electrostatic spore precipitator. Plant Pathol. 2007, 56, 987–997. [Google Scholar]
- Burleson, G.R.; Murray, T.M.; Pollard, M. Inactivation of viruses and bacteria by ozone, with and without sonication. Appl. Microbiol. 1975, 29, 340–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuda, Y.; Takikawa, Y.; Nonomura, T.; Kakutani, K.; Okada, K.; Shibao, M.; Kusakari, S.; Miyama, K.; Toyoda, H. Selective electrostatic eradication of Sitopholus oryzae nesting in stored rice. J. Food Technol. Pres. 2018, 2, 15–20. [Google Scholar]
- Kakutani, K.; Matsuda, Y.; Takikawa, Y.; Nonomura, T.; Okada, K.; Shibao, M.; Kusakari, S.; Miyama, K.; Toyoda, H. Electrocution of mosquitoes by a novel electrostatic window screen to minimize mosquito transmission of Japanese encephalitis viruses. Int. J. Sci. Res. 2018, 7, 47–50. [Google Scholar]
- Matsuda, Y.; Shimizu, K.; Sonoda, T.; Takikawa, Y. Use of electric discharge for simultaneous control of weeds and houseflies emerging from soil. Insects 2020, 11, 861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakutani, K.; Takikawa, Y.; Matsuda, Y. Selective arcing electrostatically eradicates rice weevils in rice grains. Insects 2021, 12, 522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakutani, K.; Matsuda, Y.; Toyoda, H. A simple and safe electrostatic method for managing houseflies emerging from underground pupae. Agronomy 2023, 13, 310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuda, Y.; Takikawa, Y.; Shimizu, K.; Kusakari, S.; Toyoda, H. Use of a pair of pulse-charged grounded metal nets as an electrostatic soil cover for eradicating weed seedlings. Agronomy 2023, 13, 1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuda, Y.; Kakutani, K.; Toyoda, H. A simple electrostatic apparatus for controlling weeds on slopes without causing soil erosion. Am. J. Civil Eng. Archit. 2024, 12, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halliday, D.; Resnick, R.; Walker, J. Electric discharge and electric fields. In Fundamentals of Physics; Johnson, S., Ford, E., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2005; pp. 561–604. [Google Scholar]
- Matsuda, Y.; Ikeda, H.; Moriura, N.; Tanaka, N.; Shimizu, K.; Oichi, W.; Nonomura, T.; Kakutani, K.; Kusakari, S.; Higashi, K.; et al. A new spore precipitator with polarized dielectric insulators for physical control of tomato powdery mildew. Phytopathology 2006, 96, 967–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cross, J.A. Dielectrophoresis. In Electrostatics: Principles, Problems and Applications; De Barr, A.E., Ed.; Adam Hilger: Bristol, UK; Ada, MI, USA, 1987; pp. 269–276. [Google Scholar]
- Nonomura, T.; Matsuda, Y.; Kakutani, K.; Takikawa, Y.; Toyoda, H. Physical control of powdery mildew (Oidium neolycopersici) on tomato leaves by exposure to corona discharge. Can. J. Plant Pathol. 2008, 30, 517–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polčic, P.; Machala, Z. Effects of non-thermal plasma on yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindahl, J.F.; Chirico, J.; Boqvist, S.; Thu, H.T.V.; Magnusson, U. Occurrence of Japanese encephalitis virus mosquito vectors in relation to urban pig holdings. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2012, 87, 1076–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burke, M.; Odell, M.; Bouwer, H.; Murdoch, A. Electric fences and accidental death. Forensic Sci. Med. Pathol. 2017, 13, 196–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.J.; Zurek, L. Association of Escherichia coli O157:H7 with houseflies on a cattle farm. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 70, 7578–7580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, A.; Nagaraja, T.G.; Zurek, L. Transmission of Escherichia coli O157:H7 to cattle by house flies. Prev. Vet. Med. 2007, 80, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, A.; Cho, S.; Scheftel, J.; Jawahir, S.; Smith, K.; Diez-Gonzalez, F. Soil survival of Escherichia coli O157:H7 acquired by a child from garden soil recently fertilized with cattle manure. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2006, 101, 429–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandl, M.T. Plant lesions promote the rapid multiplication of Escherichia coli O157:H7 on postharvest lettuce. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 74, 5285–5289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibekwe, A.M.; Grieve, C.M.; Papiernik, S.K.; Yang, C.-H. Persistence of Escherichia coli O157:H7 on the rhizosphere and phyllosphere of lettuce. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2009, 49, 784–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; He, Q.; McEvoy, J.L. Effect of storage temperature and duration on the behavior of Escherichia coli O157:H7 on packaged fresh-cut salad containing romaine and Iceberg lettuce. J. Food Sci. 2010, 75, M390–M397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, R.G.; Anderson, F.N. Control of three weed species in sugar beets (Betavulgaris) with an electrical discharge system. Weed Sci. 1981, 29, 93–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diprose, M.F.; Benson, F.A. Electrical methods of killing plants. J. Agric. Eng. Res. 1984, 30, 197–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagura, A.; Tenma, T.; Sakaguchi, Y.; Yamano, N.; Mizuno, A. Destruction of weeds by pulsed high voltage discharges. J. Inst. Electrostat. Jpn. 1992, 16, 59–66. [Google Scholar]
- Mizuno, A. Destruction of weeds by high voltage discharge. J. Plasma Fusion Res. 1999, 75, 666–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minoda, A. A basic study on weeding method by using high voltage. Jpn. J. Ind. Appl. Eng. 2021, 9, 21–24. [Google Scholar]
- Rodrigues, L.B.; Oliveira, R.; Abe, F.R.; Brito, L.B.; Moura, D.S.; Valadares, M.C.; Grisolia, C.K.; Oliveira, D.P.; Oliveira, G.A.R. Ecotoxicological assessment of glyphosate-based herbicides: Effects on different organisms. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2017, 36, 1755–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; Riley, S.; Fischer, E.; Khan, S. Greening roadway infrastructure with vetiver grass to support transportation resilience. CivilEng 2022, 3, 147–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, J.H. Kudzu eradication and management. In The Vine to Love or Hate Kudzu; Hoots, D., Baldwin, J., Eds.; Suntop Press: Kodak, TN, USA, 1996; pp. 137–149. [Google Scholar]
- Matsuda, Y.; Takikawa, Y.; Kakutani, K.; Nonomura, T.; Okada, K.; Kusakari, S.; Toyoda, H. Use of pulsed arc discharge exposure to impede expansion of the invasive vine Pueraria montana. Agriculture 2020, 10, 600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuda, Y.; Kakutani, K.; Toyoda, H. Unattended electric weeder (UEW): A novel approach to control floor weeds in orchard nurseries. Agronomy 2023, 13, 1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kusakari, S.-i.; Toyoda, H. Electric Discharge-Generating Devices Developed for Pathogen, Insect Pest, and Weed Management: Current Status and Future Directions. Agronomy 2025, 15, 123. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15010123
Kusakari S-i, Toyoda H. Electric Discharge-Generating Devices Developed for Pathogen, Insect Pest, and Weed Management: Current Status and Future Directions. Agronomy. 2025; 15(1):123. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15010123
Chicago/Turabian StyleKusakari, Shin-ichi, and Hideyoshi Toyoda. 2025. "Electric Discharge-Generating Devices Developed for Pathogen, Insect Pest, and Weed Management: Current Status and Future Directions" Agronomy 15, no. 1: 123. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15010123
APA StyleKusakari, S.-i., & Toyoda, H. (2025). Electric Discharge-Generating Devices Developed for Pathogen, Insect Pest, and Weed Management: Current Status and Future Directions. Agronomy, 15(1), 123. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15010123







