Optimizing Phosphatic Fertilizer Drip Timing to Improve Cotton Yield in Saline–Alkali Soil and Mitigate Phosphorus–Calcium Binding Risks
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Site Conditions
2.2. Field Management
2.3. Sample Measurements
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Result
3.1. Plant Height and SPAD
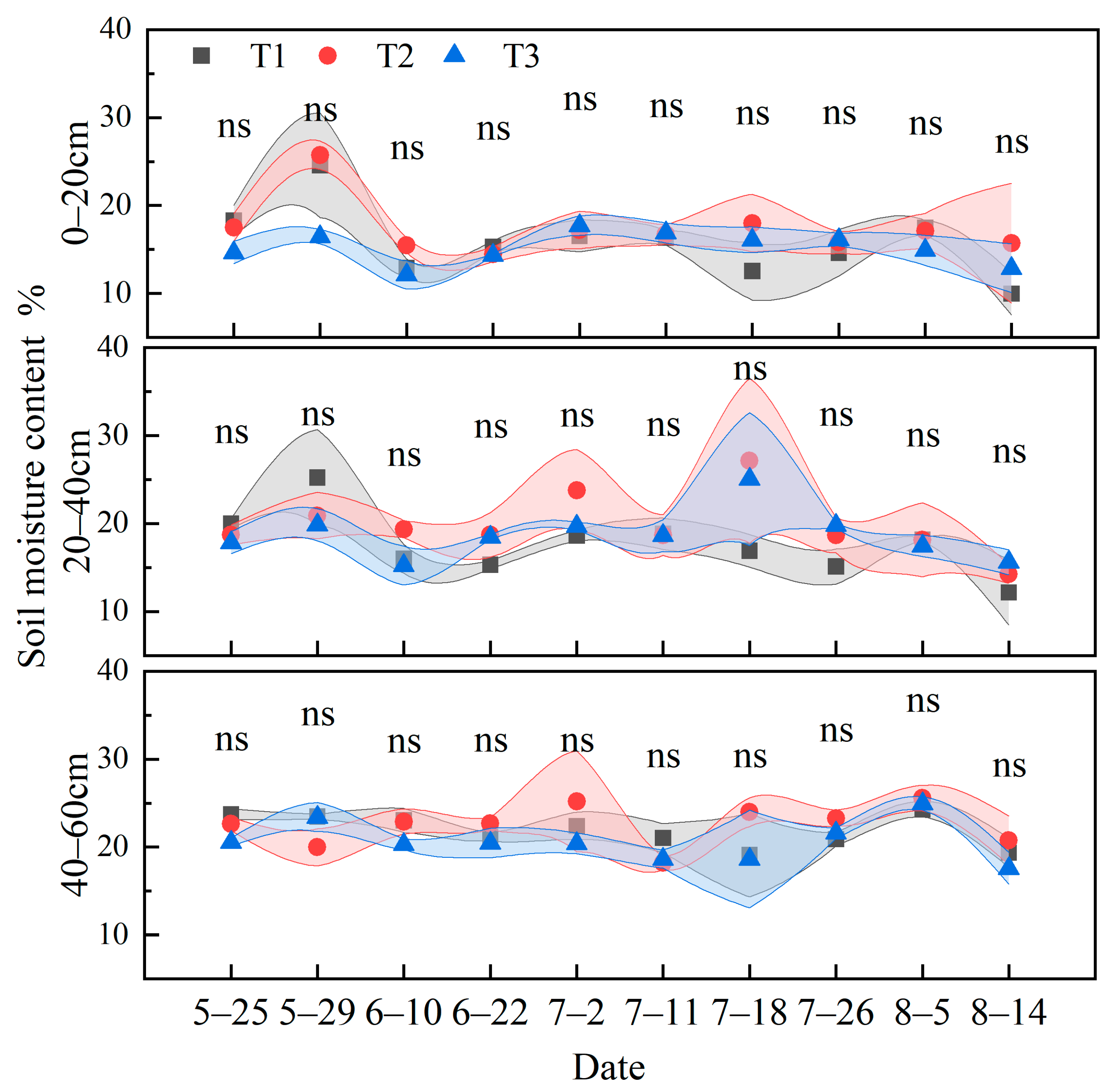
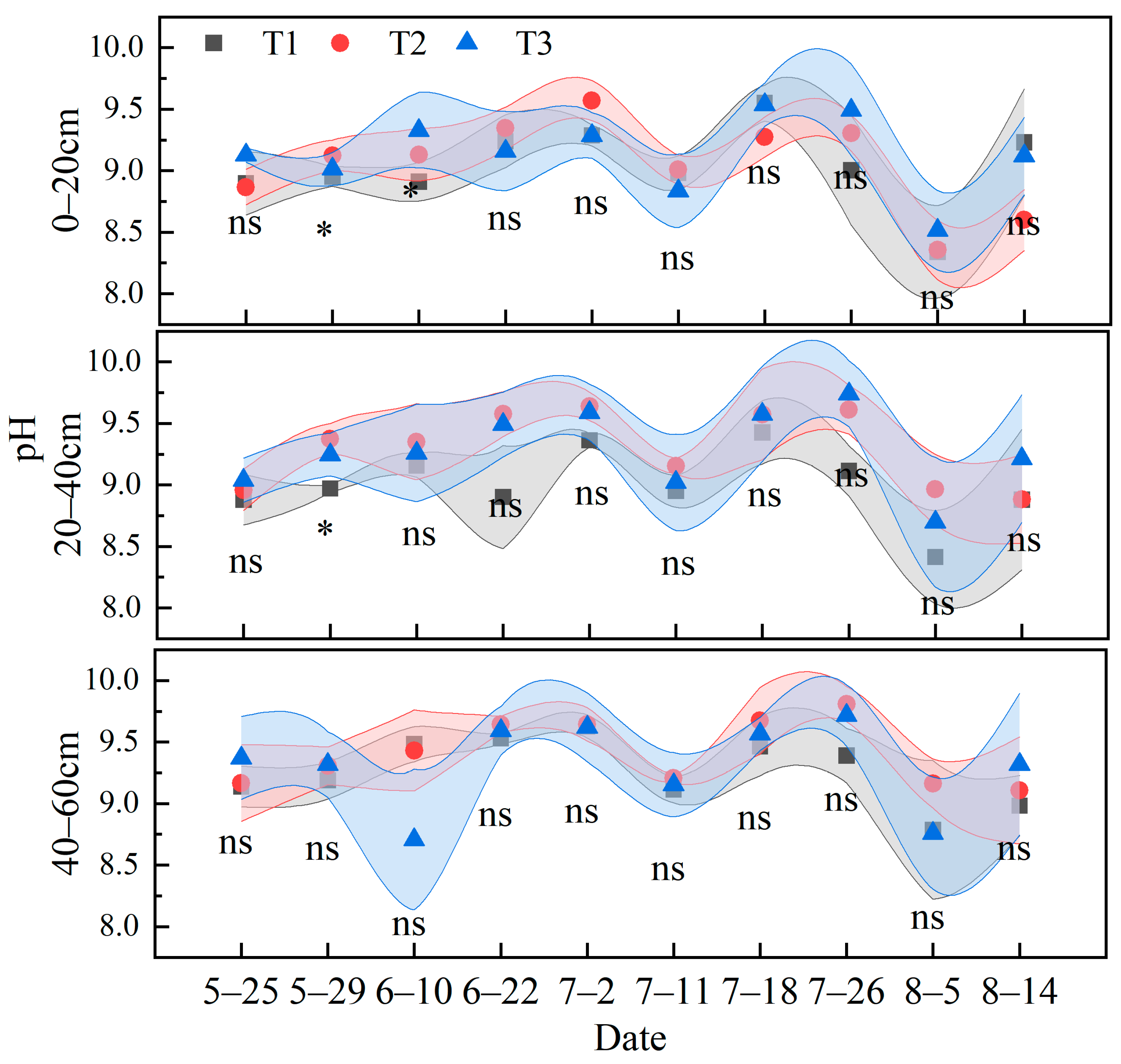
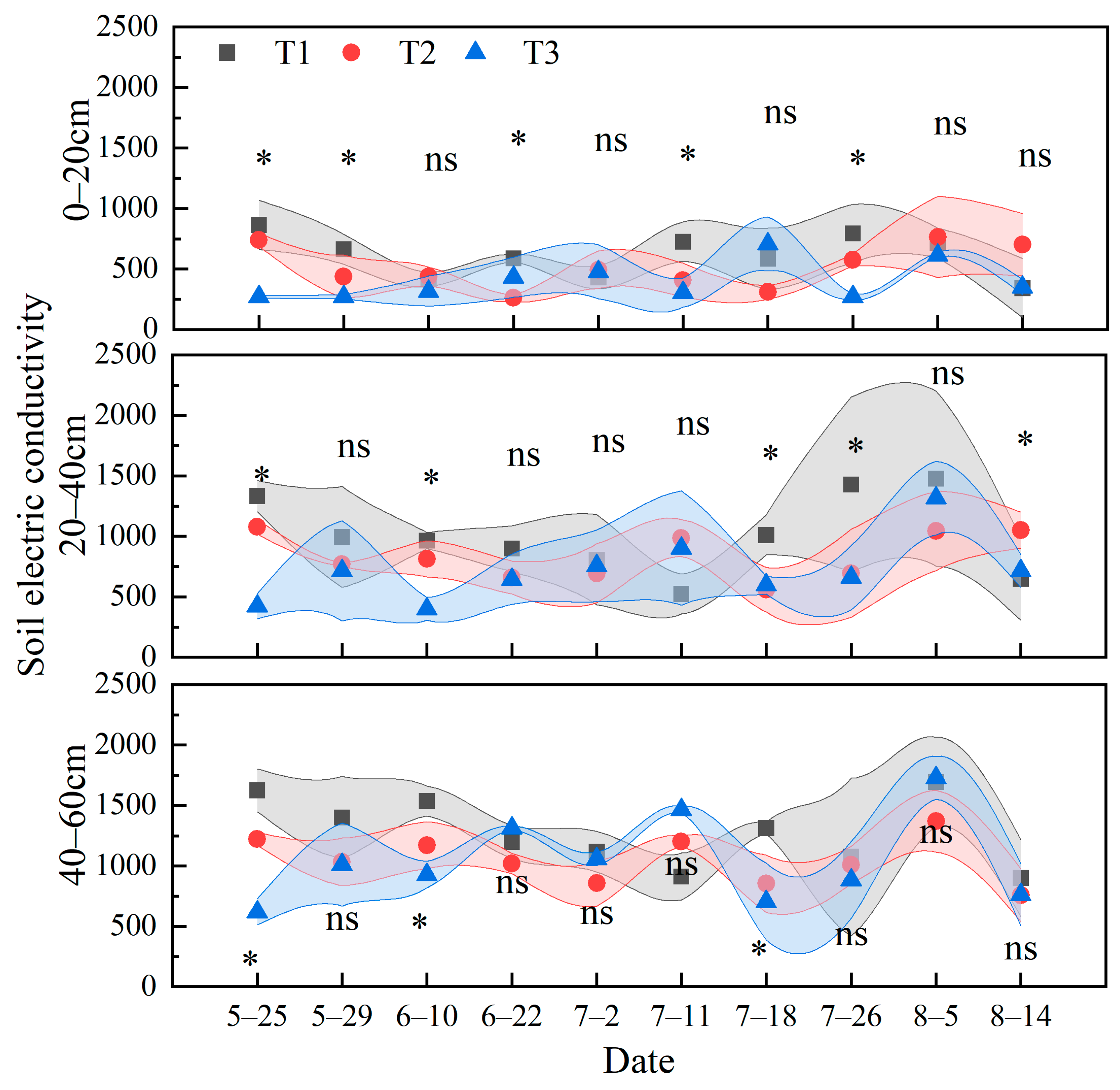
3.2. Soil Moisture Content, pH, and Electrical Conductivity
3.3. Soil Total Salt Content
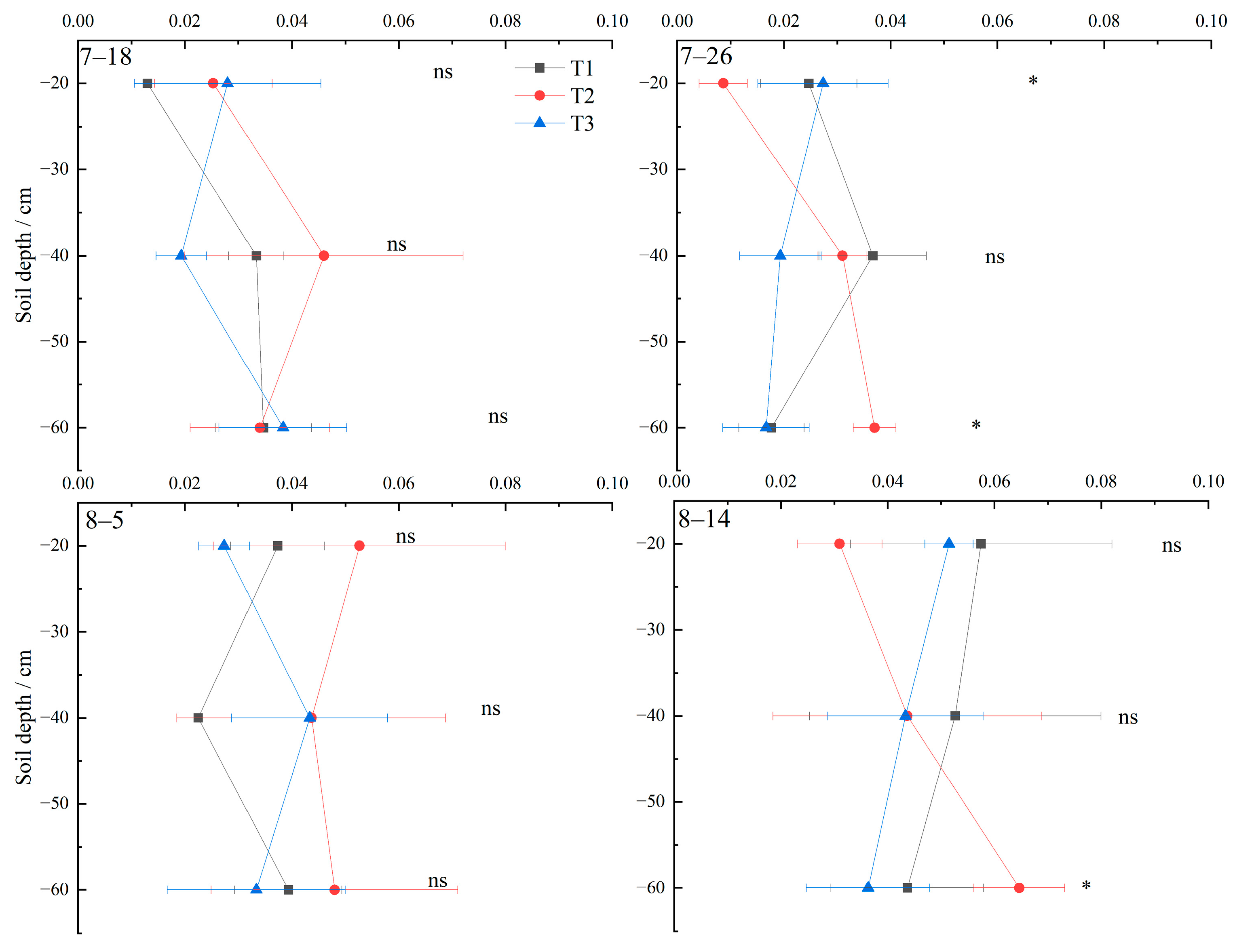
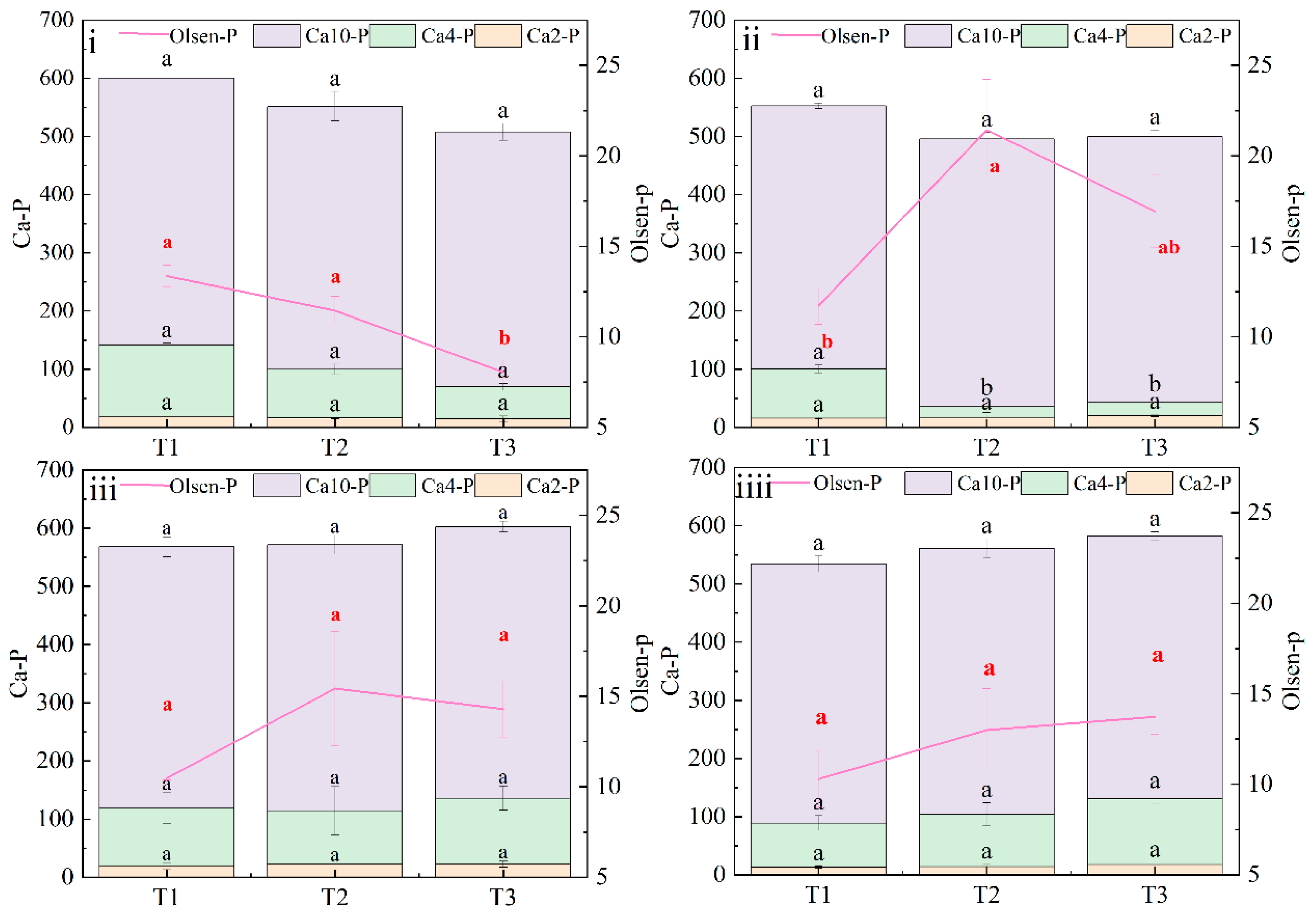
3.4. Soil Olsen-P and Calcium–Phosphorus Component
3.5. Yield
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yu, X.; Lei, J.; Gao, X. An over review of desertification in Xinjiang, Northwest China. J. Arid. Land. 2022, 14, 1181–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, Q.; Shao, Z.; Huang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, W.; Feng, X.; Altan, O. Evolution of soil salinization under the background of landscape patterns in the irrigated northern slopes of Tianshan Mountains, Xinjiang, China. Catena 2021, 206, 105561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tessema, N.; Yadeta, D.; Kebede, A.; Ayele, G.T. Soil and irrigation water salinity, and its consequences for agriculture in Ethiopia: A systematic review. Agriculture. 2022, 13, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, G.; Banerjee, P.; Sharma, R.K.; Maity, J.P.; Etesami, H.; Shaw, A.K.; Chen, C.Y. Management of phosphorus in salinity-stressed agriculture for sustainable crop production by salt-tolerant phosphate-solubilizing bacteria—A review. Agronomy 2021, 11, 1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adnan, M.; Fahad, S.; Zamin, M.; Shah, S.; Mian, I.A.; Danish, S.; Datta, R. Coupling phosphate-solubilizing bacteria with phosphorus supplements improve maize phosphorus acquisition and growth under lime induced salinity stress. Plants 2020, 9, 900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hallama, M.; Pekrun, C.; Lambers, H.; Kandeler, E. Hidden miners—The roles of cover crops and soil microorganisms in phosphorus cycling through agroecosystems. Plant Soil 2019, 434, 7–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.L.; Li, H.; Huang, Y.R.; Yao, Q.Z.; Huang, Y.; Zhou, G.T. Microbial mineralization of struvite: Salinity effect and its implication for phosphorus removal and recovery. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 358, 1324–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado RM, A.; Serralheiro, R.P. Soil salinity: Effect on vegetable crop growth. Management practices to prevent and mitigate soil salinization. Horticulturae 2017, 3, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, F.; Siddique, A.B.; Shabala, S.; Zhou, M.; Zhao, C. Phosphorus plays key roles in regulating plants’ physiological responses to abiotic stresses. Plants 2023, 12, 2861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frazier, R.M.; Vivas, K.A.; Azuaje, I.; Vera, R.; Pifano, A.; Forfora, N.; Gonzalez, R. Beyond Cotton and Polyester: An Evaluation of Emerging Feedstocks and Conversion Methods for the Future of Fashion Industry. J. Bioresour. Bioprod. 2024, 9, 130–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Ayoubi, S.; Mousavi, S.R.; Mireei, S.A.; Shahpouri, F.; Wu, S.X.; Tian, C.Y. Integrating proximal soil sensing data and environmental variables to enhance the prediction accuracy for soil salinity and sodicity in a region of Xinjiang Province, China. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 364, 121311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, Q.; Xia, G.; Wu, Q.; Chi, D. Continuous regulated deficit irrigation enhances peanut water use efficiency and drought resistance. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 255, 106997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, X.; Wu, Q.; Qiu, Y.; Chi, D.; Xia, G.; Arthur, E. Mulched drip irrigation and maize straw biochar increase peanut yield by regulating soil nitrogen, photosynthesis and root in arid regions. Agric. Water Manag. 2023, 289, 108565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Xu, H.; Xiang, Y.; Wu, J. Effects of microplastics pollution on plant and soil phosphorus: A meta-analysis. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 461, 132705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.X.; Liu, S.; Zhang, S.; Li, H.; Maimaitiaili, B.; Feng, G.; Rengel, Z. Localized ammonium and phosphorus fertilization can improve cotton lint yield by decreasing rhizosphere soil pH and salinity. Field Crop Res. 2018, 217, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Luo, M.; Zhang, T.; Yan, S.; Wang, C.; Feng, H.; Kisekka, I. Organic substitution improves soil structure and water and nitrogen status to promote sunflower (Helianthus annuus L.) growth in an arid saline area. Agric. Water Manag. 2023, 283, 108320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Li, F.Y.; Liu, J.; Wang, S.; Liu, H.; Ding, Y.; Ji, L. Grazing promotes soil phosphorus cycling by enhancing soil microbial functional genes for phosphorus transformation in plant rhizosphere in a semi-arid natural grassland. Geoderma 2023, 430, 116303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Z.; Chen, Q.; Yin, S.; Feng, H.; Liu, Y.; Li, C. Effects of drip irrigation coupled with controlled release potassium fertilizer on maize growth and soil properties. Agric. Water Manag. 2024, 301, 108948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Miao, Q.; Shi, H.; Li, X.; Yan, J.; Gonçalves, J.M.; Feng, W. Irrigation scheduling in sand-layered farmland: Evaluation of water and salinity dynamics in the soil by SALTMED-1D model under mulched maize production in Hetao Irrigation District, China. Eur. J. Agron. 2024, 157, 127177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamalimoghadam, M.; Vakili, A.H.; Keskin, I.; Totonchi, A.; Bahmyari, H. Solidification and utilization of municipal solid waste incineration ashes: Advancements in alkali-activated materials and stabilization techniques, a review. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 367, 122014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.; Chen, D.; Duan, X.; Chen, Y.; Li, C.; Li, S.; Pan, X. Collaboratively removal of phosphate and glyphosate from wastewater by a macroscopic Zr-SA/Ce-UIO-66 adsorbent: Performance, mechanisms and applicability. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 136786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santoro, V.; Schiavon, M.; Celi, L. Role of soil abiotic processes on phosphorus availability and plant responses with a focus on strigolactones in tomato plants. Plant Soil 2024, 494, 1–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakami, R.A.; Naser, R.S.; El-Bakkali, M.; Othman MD, M.; Yahya, M.S.; Raweh, S.; Belghyti, D. Groundwater quality deterioration evaluation for irrigation using several indices and geographic information systems: A case study. Desalin Water Treat. 2024, 320, 100645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouras, H.; Mamassi, A.; Devkota, K.P.; Choukr-Allah, R.; Bouazzama, B. Integrated effect of saline water irrigation and phosphorus fertilization practices on wheat (Triticum aestivum) growth, productivity, nutrient content and soil proprieties under dryland farming. Plant Stress 2023, 10, 100295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riseh, R.S.; Vatankhah, M.; Hassanisaadi, M.; Varma, R.S. A review of chitosan nanoparticles: Nature’s gift for transforming agriculture through smart and effective delivery mechanisms. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 129522. [Google Scholar]
- He, Z.; Cao, H.; Xing, X.; Hu, Q.; Li, Z. Optimization of leaching level and alternating drip irrigation start time improved water saving, yield enhancement, and salt leaching. Ind. Crop Prod. 2024, 222, 119537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, A.K.; Das, R.; George Kerry, R.; Biswal, B.; Sinha, T.; Sharma, S.; Kumar, M. Promising management strategies to improve crop sustainability and to amend soil salinity. Front. Environ. Sci. 2023, 10, 962581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shekhar, S.; Mailapalli, D.R.; Raghuwanshi, N.S.; Pohshna, C. Hydrus-1D model for simulating phosphorus transport in paddy crop irrigated with alternate wetting and drying practice. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2024, 55, 57–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Chen, M.; Fu, J.; Zhang, X.; Li, Y.; Shao, Y.; Wang, X. Coupling effects of irrigation amount and fertilization rate on yield, quality, water and fertilizer use efficiency of different potato varieties in Northwest China. Agric. Water Manag. 2023, 287, 108446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.L.; Wu, M.C.; Tiyip, T. Study on soil salinization information in arid region using remote sensing technique. Agric. Sci. China 2011, 10, 404–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shenoy, M.; Raju PV, S.; Prasad, J. Optimization of physical schemes in WRF model on cyclone simulations over Bay of Bengal using one-way ANOVA and Tukey’s test. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 24412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigua, G.C.; Stone, K.C.; Bauer, P.J.; Szogi, A.A.; Shumaker, P.D. Impacts of irrigation scheduling on pore water nitrate and phosphate in coastal plain region of the United States. Agric. Water Manag. 2017, 186, 75–85. [Google Scholar]
- Azam, H.M.; Alam, S.T.; Hasan, M.; Yameogo DD, S.; Kannan, A.D.; Rahman, A.; Kwon, M.J. Phosphorous in the environment: Characteristics with distribution and effects, removal mechanisms, treatment technologies, and factors affecting recovery as minerals in natural and engineered systems. Environ. Sci. Pollut. 2019, 26, 20183–20207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bindraban, P.S.; Dimkpa, C.O.; Pandey, R. Exploring phosphorus fertilizers and fertilization strategies for improved human and environmental health. Biol. Fert. Soils. 2020, 56, 299–317. [Google Scholar]
- McDowell, R.W.; Gray, C.W.; Cameron, K.C.; Di, H.J.; Pellow, R. The efficacy of good practice to prevent long-term leaching losses of phosphorus from an irrigated dairy farm. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2019, 273, 86–94. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Che, W.; Piao, J.; Song, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Xi, F. Biochar Increases Rice Yield in Soda Saline-Alkali Paddy Fields by Improving Saline-Alkali Stress and Phosphorus Use Efficiency. Agronomy 2024, 14, 2159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minhas, P.S.; Sharma, O.P. Management of soil salinity and alkalinity problems in India. J. Crop Prod. 2003, 7, 181–230. [Google Scholar]
- Andersson, K.O.; Tighe, M.K.; Guppy, C.N.; Milham, P.J.; McLaren, T.I. The release of phosphorus in alkaline vertic soils as influenced by pH and by anion and cation sinks. Geoderma 2016, 264, 17–27. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Guo, S.; Zhai, L.; Hua, L.; Khoshnevisan, B.; Wang, H.; Liu, H. Comprehensive effects of integrated management on reducing nitrogen and phosphorus loss under legume-rice rotations. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 361, 132031. [Google Scholar]
- Fetzer, J.; Moiseev, P.; Frossard, E.; Kaiser, K.; Mayer, M.; Gavazov, K.; Hagedorn, F. Plant–soil interactions alter nitrogen and phosphorus dynamics in an advancing subarctic treeline. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2024, 30, e17200. [Google Scholar]
- Guelfi, D.; Nunes AP, P.; Sarkis, L.F.; Oliveira, D.P. Innovative phosphate fertilizer technologies to improve phosphorus use efficiency in agriculture. Sustainability 2022, 14, 14266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, L.; Dai, J.; Dong, H. Mitigating salinity stress and improving cotton productivity with agronomic practices. Agronomy 2023, 13, 2486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, F.; Yang, G.; Li, W.; He, X.; Gao, Y.; Tian, L.; Liu, S. Yield-compatible salinity level for growing cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) under mulched drip irrigation using saline water. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 250, 106859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, Z.; Wang, J.; Li, J. Modeling strategies to balance salt leaching and nitrogen loss for drip irrigation with saline water in arid regions. Agric. Water Manag. 2022, 274, 107943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menezes-Blackburn, D.; Giles, C.; Darch, T.; George, T.S.; Blackwell, M.; Stutter, M.; Haygarth, P.M. Opportunities for mobilizing recalcitrant phosphorus from agricultural soils: A review. Plant Soil 2018, 427, 5–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, Z.; Khattak, R.A.; Fareed, I.; Irshad, M.; Mahmood, Q. Interaction of phosphorus and potassium on maize (Zea mays L.) in saline-sodic soil. J. Agric. Sci. 2015, 7, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Singh, V. Nutrient management in salt affected soils for sustainable crop production. Ann. Plant Soil Res. 2022, 24, 182–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Treatments | Fertilization Timing (One Irrigation Cycle Is t) |
|---|---|
| T1 | 1 h |
| T2 | 1 h + 1/3 t h |
| T3 | 1 h + 2/3 t h |
| CK | Local fertilization pattern, 1/3 t h. |
| Treatments | Yield kg/hm2 | Single Boll Weight g | Number of Bolls Per Plant |
|---|---|---|---|
| T1 | 4938.24 ± 270.80 b | 5.61 ± 0.15 a | 8.43 ± 1.42 a |
| T2 | 6492.09 ± 173.85 a | 5.39 ± 0.30 ab | 9.98 ± 1.73 a |
| T3 | 4935.79 ± 278.08 b | 5.58 ± 0.22 a | 8.50 ± 1.42 a |
| CK | 6316.80 ± 278.43 a | 4.89 ± 0.46 b | 7.99 ± 0.42 a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bu, X.; Xie, X.; Wu, C.; Liu, M.; Xu, Y. Optimizing Phosphatic Fertilizer Drip Timing to Improve Cotton Yield in Saline–Alkali Soil and Mitigate Phosphorus–Calcium Binding Risks. Agronomy 2025, 15, 138. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15010138
Bu X, Xie X, Wu C, Liu M, Xu Y. Optimizing Phosphatic Fertilizer Drip Timing to Improve Cotton Yield in Saline–Alkali Soil and Mitigate Phosphorus–Calcium Binding Risks. Agronomy. 2025; 15(1):138. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15010138
Chicago/Turabian StyleBu, Xiangxi, Xiangwen Xie, Changxue Wu, Manqi Liu, and Yongmei Xu. 2025. "Optimizing Phosphatic Fertilizer Drip Timing to Improve Cotton Yield in Saline–Alkali Soil and Mitigate Phosphorus–Calcium Binding Risks" Agronomy 15, no. 1: 138. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15010138
APA StyleBu, X., Xie, X., Wu, C., Liu, M., & Xu, Y. (2025). Optimizing Phosphatic Fertilizer Drip Timing to Improve Cotton Yield in Saline–Alkali Soil and Mitigate Phosphorus–Calcium Binding Risks. Agronomy, 15(1), 138. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15010138




