The Regulatory Effect of Se-Cd Interaction on Tea Plants (Camellia sinensis (L.) O. Kuntze) Under Cadmium Stress
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Experimental Design
2.2.2. Determining the Indicators
- Physiological indicators
- Antioxidant-related indicators
- Photosynthesis-related indicators
- Accumulative distribution of cadmium ions
2.2.3. Data Processing
3. Results
3.1. Effects of Se-Cd Interaction on the Electrolyte Permeability, Malondialdehyde, and Proline Content in Tea Plants Under Cadmium Stress
3.2. Effects of Se-Cd Interaction on the Regulation of Antioxidant System in Tea Plants Under Cadmium Stress
3.2.1. Effects of Se-Cd Interaction on the Content of H2O2 and Superoxide Anion (O2•−) in Tea Plants Under Cadmium Stress
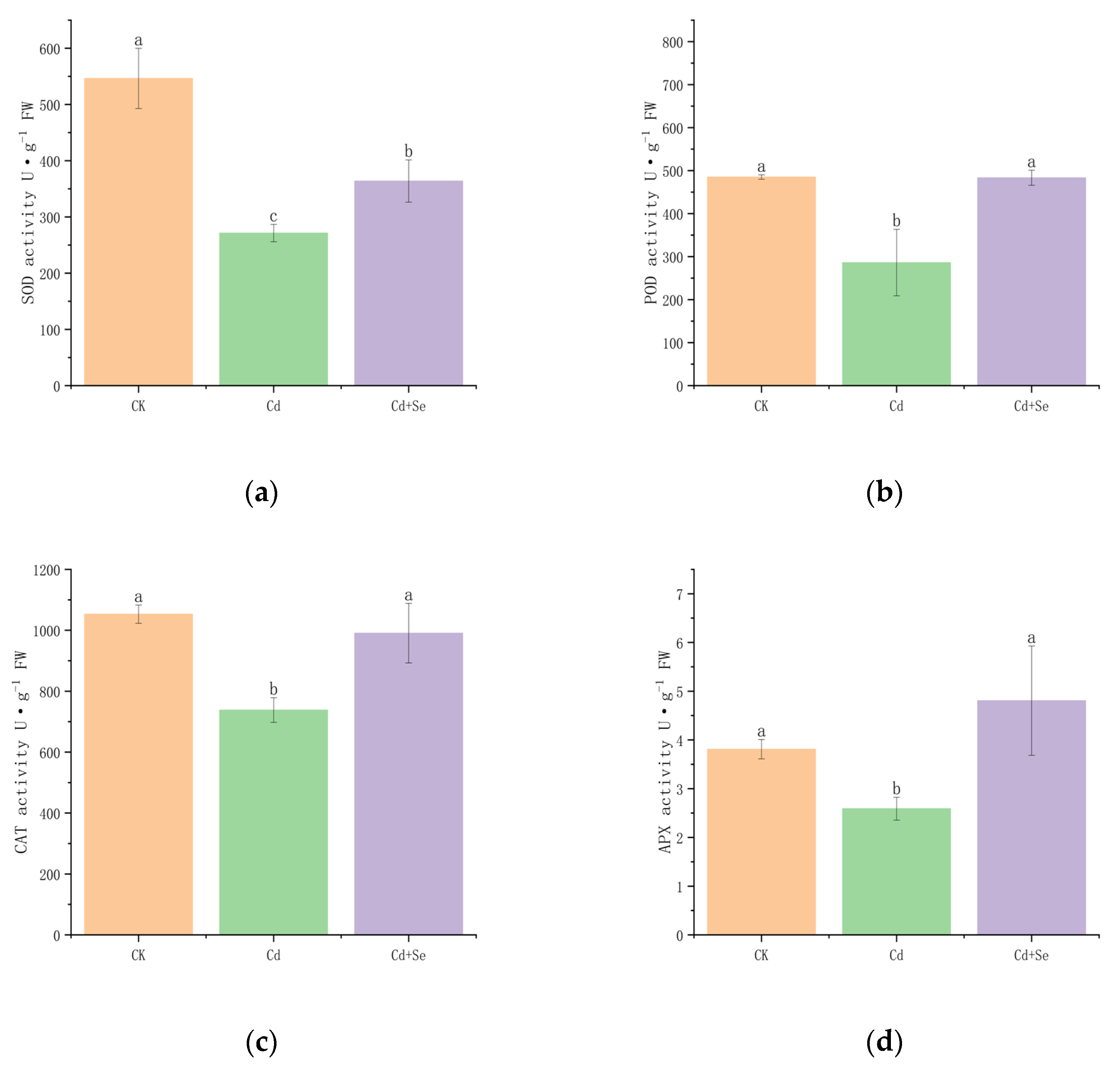
3.2.2. Effects of Se-Cd Interaction on the Activity of Antioxidant Enzymes in Tea Plants Under Cadmium Stress
3.3. The Regulatory Effect of Se-Cd Interaction on the Photosynthetic System of Tea Plants Under Cadmium Stress
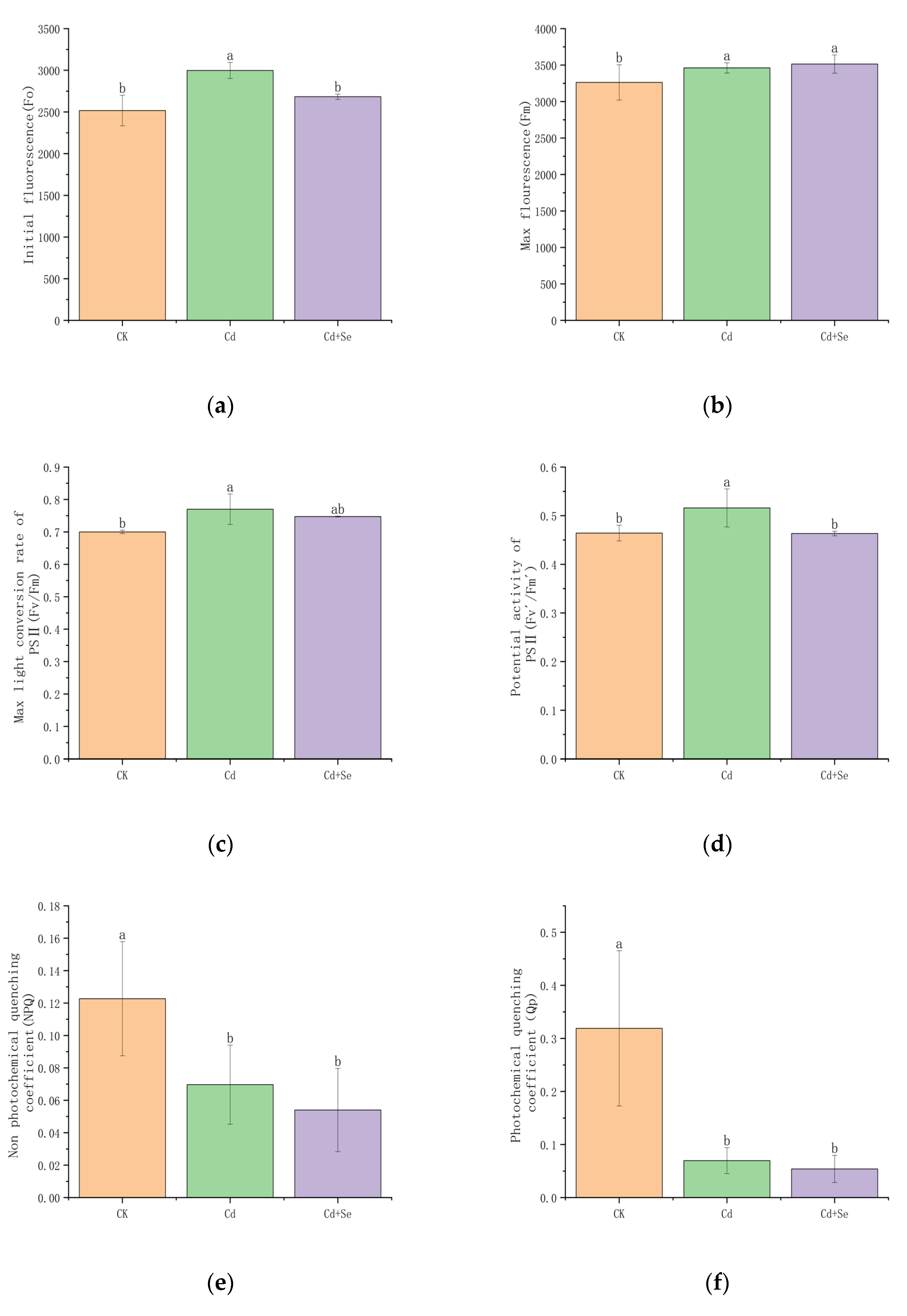
3.3.1. Effects of Se-Cd Interaction on Chlorophyll Fluorescence Parameters in Tea Leaves Under Cadmium Stress
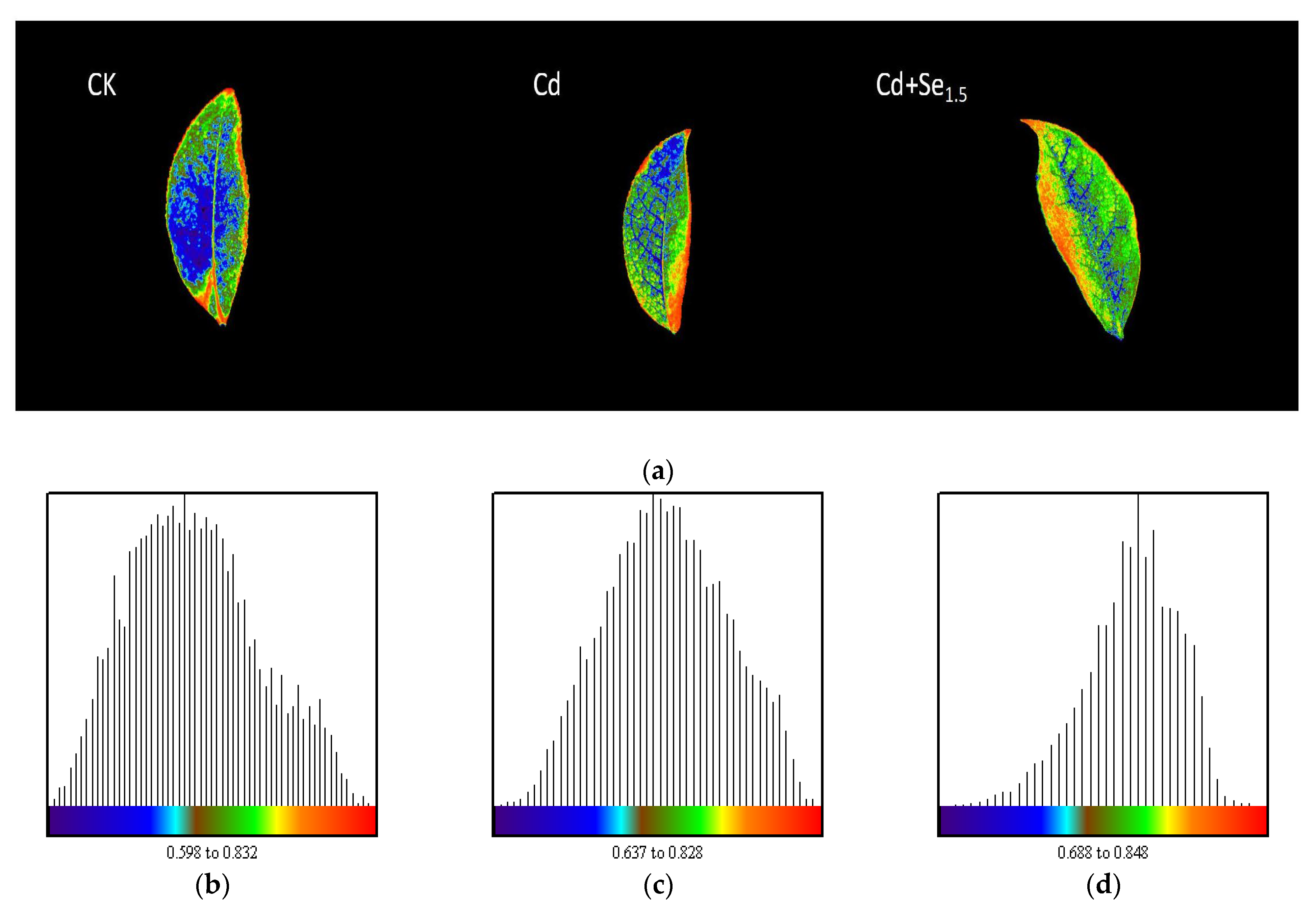
3.3.2. Effects of Se-Cd Interactions on the Fv/Fm Fluorescence Imaging of Tea Leaves Under Cadmium Stress
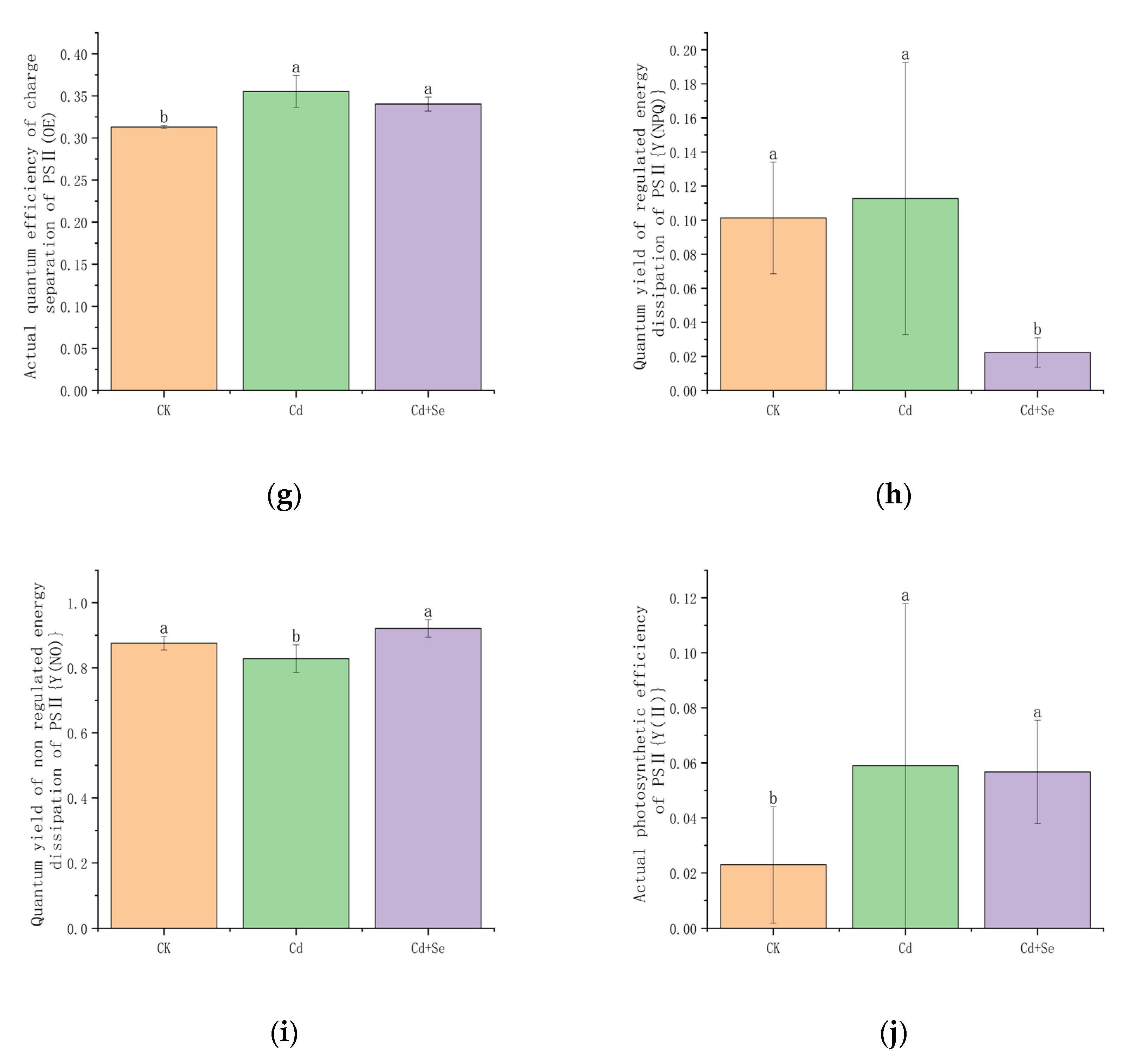
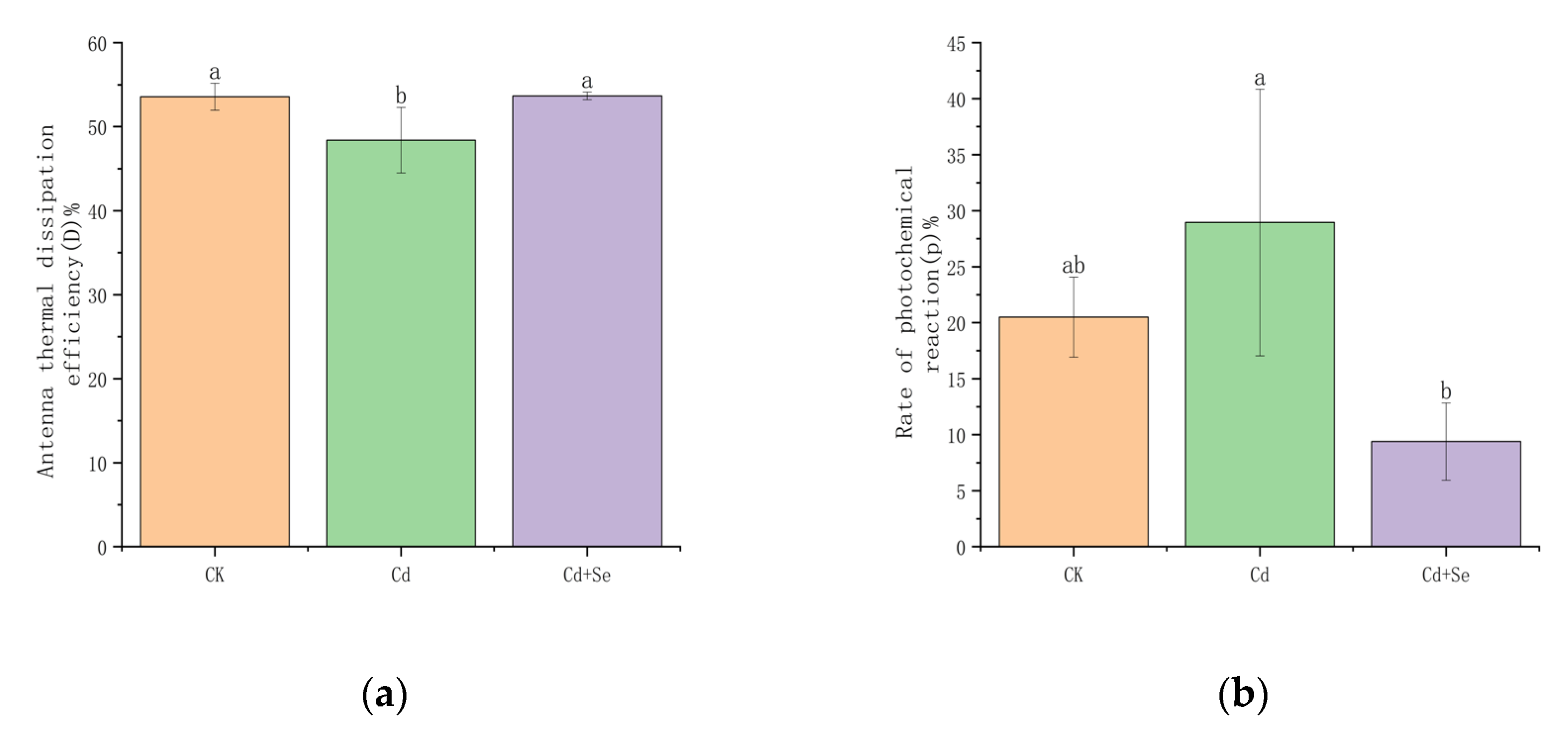
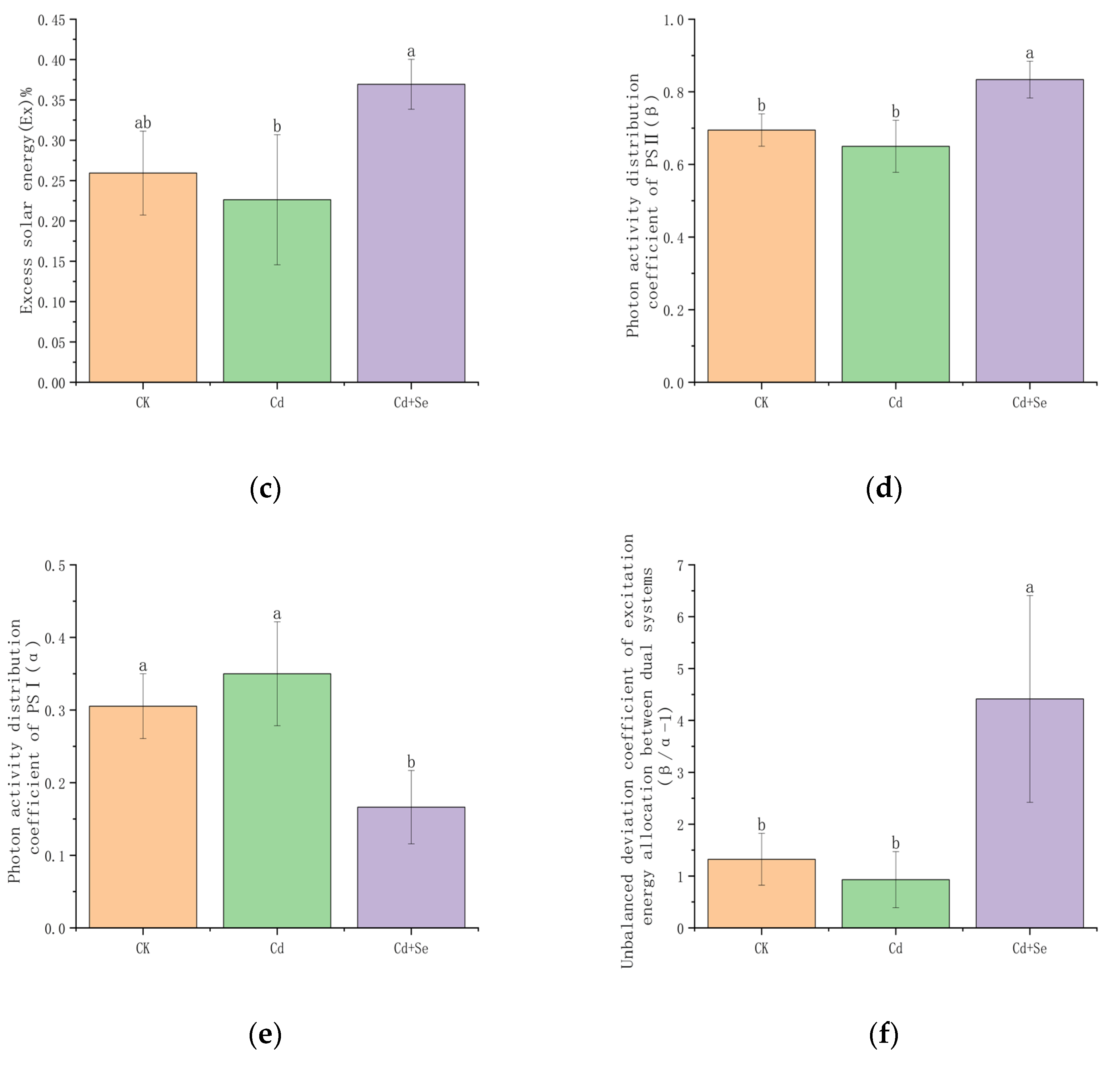
3.3.3. The Effect of Se-Cd on the Distribution of Light Energy Absorption in Tea Leaves Under Cadmium Stress
3.4. Effects of Se-Cd Interaction on the Accumulation and Micro-Distribution Characteristics of Cadmium in Different Organs of Tea Plants
3.4.1. Effects of Se-Cd Interaction on the Contents of Cadmium in Different Organs of Tea Plants
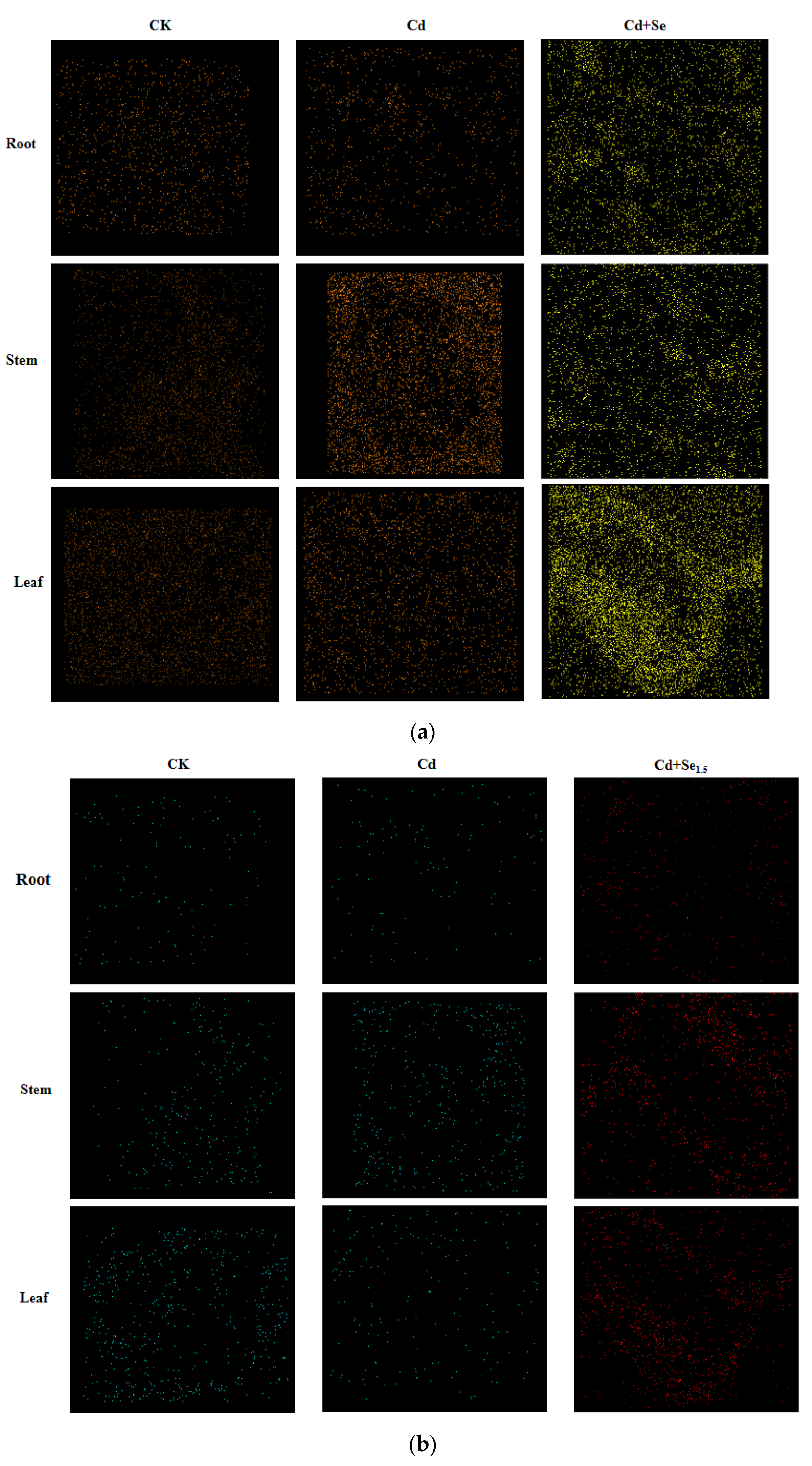
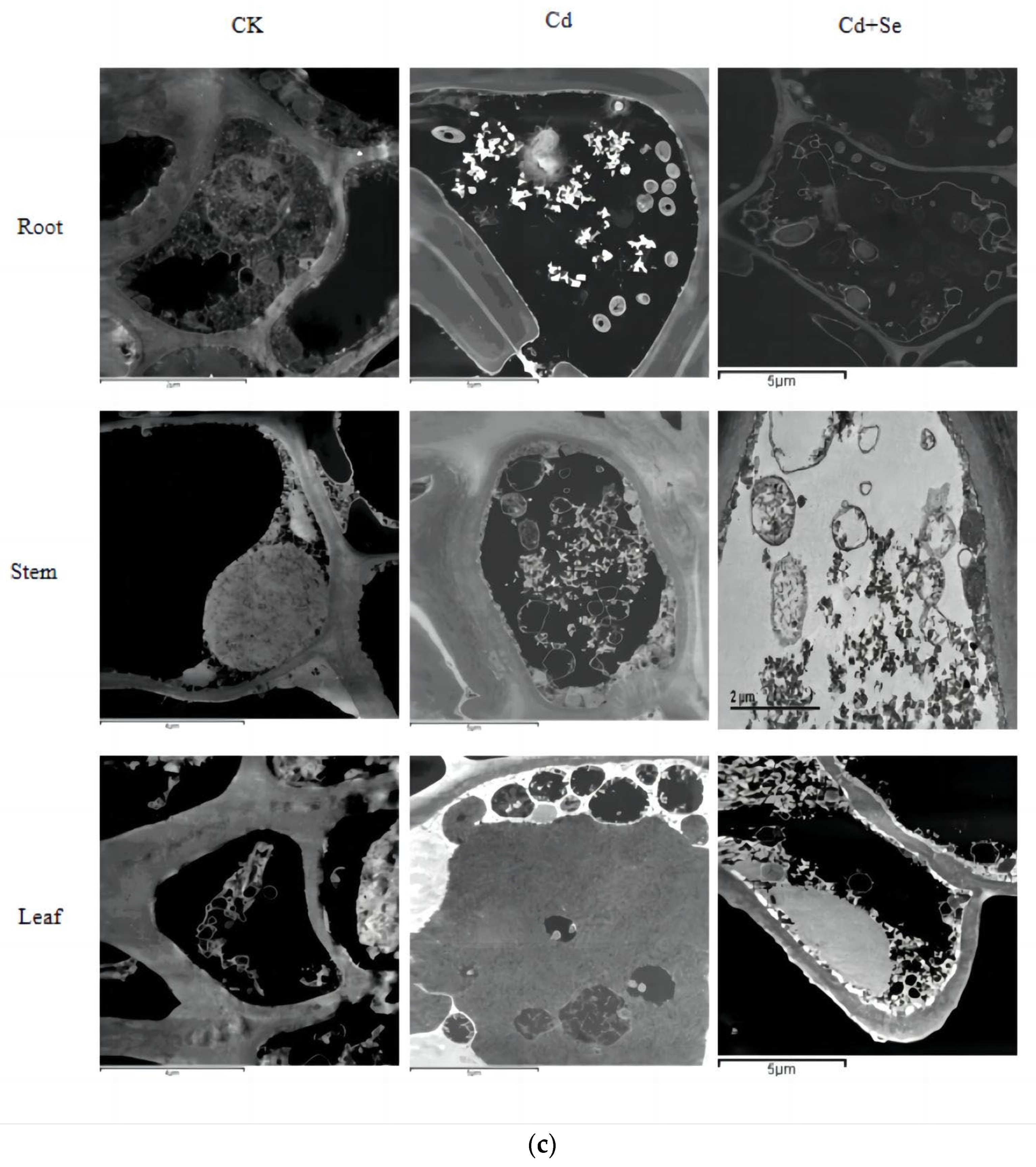
3.4.2. The Effect of Se-Cd Interaction on the Microdistribution of Se and Cd Elements in Different Organs of Tea Plant Cells
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, J.; Lu, W.; Zhang, N.; Su, D.; Zeer, L.; Du, H.; Hu, K. Collaborative Assessment and Health Risk of Heavy Metals in Soils and Tea Leaves in the Southwest Region of China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Yang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Sui, X.; Gong, Z.; Liu, S.; Chen, X.; Li, X.; Wang, Y. Ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in tea plantation soil around Tai Lake region in Suzhou, China. Stress Biol. 2024, 4, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Peng, X.; Wang, X.; Zhuang, W. Transcriptome Analysis Reveals Differentially Expressed Genes Involved in Cadmium and Arsenic Accumulation in Tea Plant (Camellia sinensis). Plants 2023, 12, 1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, H.; Tan, L.; Li, S.; Wang, Q.; Xu, Z.; Ryan, P.R. Effects of Cadmium Stress on Tartary Buckwheat Seedlings. Plants 2024, 13, 1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.; Huang, J.; Lin, L.; Tang, Q.X. Exogenous Melatonin Attenuates Cd Toxicity in Tea (Camellia sinensis). Agronomy 2022, 12, 2485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, J.; Zhu, F.; Chen, X.; Liang, H.; Wang, R.; Wang, X.; Huang, X. Effects of cadmium on photosynthesis of Schima superba young plant detected by chlorophyll fluorescence. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 10679–10687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Wei, S.; Dai, H.; Jia, G. The alleviating effects of selenium on cadmium-induced toxicity in tea leaves. J. Nanjing For. Univ. 2020, 44, 200–204. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, S.; Bai, Y.; Jin, Z.; Long, L.; Diao, W.; Chen, W.; Tan, L.; Tang, Q.; Tang, D. Effects of the Combined Application of Nitrogen and Selenium on Tea Quality and the Expression of Genes Involved in Nitrogen Uptake and Utilization in Tea Cultivar ‘Chuancha No.2’. Agronomy 2023, 12, 2997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Du, B.; Wu, Q.; Zhang, H.; Deng, Y.; Tang, X.; Zhu, J. Selenium Decreases the Cadmium Content in Brown Rice: Foliar Se Application to Plants Grown in Cd-contaminated Soil. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2022, 22, 1033–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.M.; Luo, S.G.; Liu, Y.Y. Effects of Se on Cd content and distribution in rice plant under Cd stress in cold climate. J. Plant Natrition Fertil. 2015, 21, 190–199. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, H.; Dai, H.; Wang, X.; Wang, G. Physiological and proteomic analysis of selenium-mediated tolerance to Cd stress in cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2016, 11, 114–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, S.; Sun, S.; Zhao, W.; Yang, X.; Mao, H.; Sheng, L.; Chen, Z. Utilizing transcriptomics and proteomics to unravel key genes and proteins of Oryza sativa seedlings mediated by selenium in response to cadmium stress. BMC Plant Biol. 2024, 360, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.; Zhang, S.; Li, J. Impact of three exogenous phosphorus-solubilizing bacteria on zinc and selenium contents and rhizosphere soil nutrients of Longjing and Huangjinya tea plants. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1413538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Li, Y.; Ma, J.; Wu, F.; Wang, L.; Sun, L.; Zhang, P.; Wang, W.; Xu, J. Comparative physiological and soil microbial community structural analysis revealed that selenium alleviates cadmium stress in Perilla frutescens. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 1022935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, H.; Zhan, K.; Xu, W.; Peng, C.; Hou, C.; Li, Y.; Hou, R.; Wan, X.; Cai, H. Selenium treatment modulates fluoride distribution and mitigates fluoride stress in tea plant (Camellia sinensis (L.) O. Kuntze). Environ. Pollut. 2020, 267, 115603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, X.; Luo, F.; Tang, X.; Wang, X.; Li, C.; Wang, Y.; Du, X. Construction of a characteristic model of potassium accumulation utilization in tea tree seedlings. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2017, 28, 2597. [Google Scholar]
- Heath, R.L.; Packer, L. Photoperoxidation in isolated chloroplasts. I. Kinetics and stoichiometry of fatty acid peroxidation. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1968, 125, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, P.S.; nia Quartin, V.; chicho Ramalho, J.; Nunes, M.A. Electrolyte leakage and lipid degradation account for cold sensitivity in leaves of Coffea sp. plants. J. Plant Physiol. 2003, 160, 283–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Wang, W. A Rapid Colorimetric Method for Determination of γ-Aminobutyric Acid. Food Res. Dev. 2015, 10, 85–89. [Google Scholar]
- Grace, S.C.; Logan, B.A. Acclimation of foliar antioxidant systems to growth irra-diance in three broad-leaved evergreen species. Plant Physiol. 1996, 112, 1631–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elstner, E.F.; Heupel, A. Inhibition of nitrite formation from hydroxylammoni-umchloride: A simple assay for superoxide dismutase. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 70, 616–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Meng, Q.; Jiang, G.; Zou, Q. The susceptibility of cucumber and sweet pepper to chilling under low irradiance is related to energy dissipation and water-water cy-cle. Photosynthetica 2003, 41, 259–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, X.; Jing, R.; Qin, X.; Liang, X.; Wang, L.; Xu, Y.; Sun, Y.; Huang, Q. The role and transcriptomic mechanism of cell wall in the mutual antagonized effects between selenium nanoparticles and cadmium in wheat. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 472, 134549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di, X.; Jing, R.; Qin, X.; Liang, X.; Wang, L.; Xu, Y.; Sun, Y.; Huang, Q. Regulatory effects and mechanism of different selenium species on cadmium accumulation in Triticum aestivum L. (microbial response, gene expression and element accumulation). Env. Res 2024, 264, 120374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MirR, R.; Zaman-Allah, M.; Sreenivasulu, N. Integrated genomics, physiology and breeding approaches for improving drought tolerance in crops. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2012, 125, 625–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.; Zhan, M.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, X. Insight into the transcriptional regulation of key genes involved in proline metabolism in plants under osmotic stress. Biochimie 2024, 8, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseinifard, M.; Stefaniak, S.; Ghorbani Javid, M.; Soltani, E.; Wojtyla, Ł.; Garnczarska, M. Contribution of Exogenous Proline to Abiotic Stresses Tolerance in Plants: A Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 5186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goncharuk, E.A.; Zagoskina, N.V. Heavy Metals, Their Phytotoxicity, and the Role of Phenolic Antioxidants in Plant Stress Responses with Focus on Cadmium: Review. Molecules 2023, 28, 3921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.B.; Liu, Y.Q.; Chen, L.L.; Li, X.Q.; Ha, N.H.; Hoang, T.X.; Chen, X. The impact of cadmium stress on the ascorbate-glutathione pathway and ascorbate regeneration in tea plants. Biol. Plant. 2023, 67, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Wang, X.; Yang, N.; Zhou, H.; Gao, Y.; Yu, J.; Wang, X. Effect of Exogenous Selenium on Mineral Nutrition and Antioxidative Capacity in Cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.) Seedlings under Cadmium Stress. Plant Soil Environ. 2022, 68, 580–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaid, A.; Mohammad, F.; Fariduddin, Q. Plant growth regulators improve growth, photosynthesis, mineral nutrient and antioxidant system under cadmium stress in menthol mint (Mentha arvensis L.). Physiol. Mol. Biol. Plants 2019, 26, 25–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammadzadeh, A.; Tavakoli, M.; Motesharezadeh, B.; Chaichi, M.R. Effects of plant growth-promoting bacteria on the phytoremediation of cadmium-contaminated soil by sunflower. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2017, 63, 807–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, L.; Luo, Y.; Dai, Z.; Wang, L.Q.; Huang, Y.P. Responses of Distylium chinense to Cd Stress in Cd Accumulation, Growth and Chlorophyll Fluorescence Dynamics. J. Ecol. Rural Environ. 2017, 33, 665–672. [Google Scholar]
- Kupper, H.; Mijovilovich, A.; Meyer-Klaucke, W. Tissue- and age-dependent differences in the complexation of cadmiumand zinc in the cadmium/zinc hyperaccumulator Thlaspi caerulescens (Ganges ecotype) revealed by x-ray absorption spectroscopy. Plant Physiol. 2004, 134, 748–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhopadyay, M.; Bantawn, P.; Das, A. Changes of growth, photosynthesis and alteration of leaf antioxidative defence system of tea [Camellia sinensis (L.) O. Kuntze] seedlings under aluminum stress. Biometals 2012, 25, 1141–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, C.N.; Jarrell-Hurtado, S.; Haag, M.V.; Ye, Y.S.; Simenc, M.; Alvarez-Maldonado, P.; Behnami, S.; Zhang, L.; Swift, J.; Papikian, A.; et al. A single-nuclei transcriptome census of the Arabidopsis maturing root identifies that MYB67 controls phellem cell maturation. Dev. Cell 2025. [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.H.; Khan, A.L.; Kim, D.H.; Lee, S.Y.; Kim, K.M.; Waqas, M.; Jung, H.-Y.; Shin, J.H.; Kim, G.K.; Lee, I.-J. Silicon mitigates heavy metal stress by regulating P-type heavy metal ATPases, Oryza sativa low silicon genes, and endogenous phytohormones. BMC Plant Biol. 2014, 13, 14. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Heal, K.; Zhu, X.; Tigabu, M.; Xue, Y.; Zhou, C. Tolerance and detoxification mechanisms to cadmium stress by hyperaccumulator Erigeron annuus include molecule synthesis in root exudate. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 219, 112359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, F.; Chen, H.; Wei, G.; Tang, D.; Quan, C.; Xu, M. Physiological and metabolic responses of Sophora tonkinensis to cadmium stress. Physiol. Mol. Biol. Plants 2023, 7, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, K.; Zhan, Z.; Wang, B.; Wang, W.; Wei, W.; Li, D. Exogenous Selenium Enhances Cadmium Stress Tolerance by Improving Physiological Characteristics of Cabbage (Brassica oleracea L. var. capitata) Seedlings. Horticulturae 2023, 9, 1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Parameters of Chlorophyll Fluorescence | |
|---|---|
| Fo [measuring beam (<0.05 μ mol m−2 s−1)] | Initial fluorescence |
| Fm [saturating pulse (12,000 μ mol m−2 s−1)] | Maximum fluorescence |
| Fv/Fm | Maximum photochemical efficiency of PSII |
| qP = (Fm′ − Fs)/(Fm′ − Fo′) | Photochemical quenching coefficient |
| NPQ = (Fm − Fm′)/Fm′ | Non-photochemical quenching coefficient |
| Y(NPQ) = (Fs/Fm′) − (Fs/Fm) | Quantum yield of regulated energy dissipation in photosystem II |
| Y(NO) = Fs/Fm | Quantum yield of non-regulated energy dissipation in PSII |
| Y(II) + Y(NPQ) + Y(NO) = 1 | Actual photosynthetic efficiency of PSII |
| OE = Fq′/Fm′ | Actual quantum efficiency of charge separation in the PSII reaction center with initial fluorescence |
| Distribution of Energy Score Points | |
|---|---|
| D = (1 − Fv′/Fm′) × 100% | Share of antenna thermal dissipation |
| P = Fv′/Fm′ × qP × 100% | Part that absorbs photon energy for photosynthetic electron transport in PSII |
| Ex = Fv′/Fm′ × (1 − qP) PSII | PSII reaction center of excess excitation energy |
| Β = 1/(1 + f) and α = f/(1 + f) f = (Fm′ − Fs)/(Fm′ − Fo′) | β and α represent the photon yield distribution coefficients for PSII and PSI, respectively |
| β/α − 1 = (1 − f)/f | Excitation energy distribution imbalance deviation coefficient between dual-light systems |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Zhou, H.; Li, F.; Wang, Y.; Du, X. The Regulatory Effect of Se-Cd Interaction on Tea Plants (Camellia sinensis (L.) O. Kuntze) Under Cadmium Stress. Agronomy 2025, 15, 246. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15010246
Sun Y, Zhao Y, Zhou H, Li F, Wang Y, Du X. The Regulatory Effect of Se-Cd Interaction on Tea Plants (Camellia sinensis (L.) O. Kuntze) Under Cadmium Stress. Agronomy. 2025; 15(1):246. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15010246
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Yanyun, Yueling Zhao, Hongyu Zhou, Faxing Li, Yuanyuan Wang, and Xiao Du. 2025. "The Regulatory Effect of Se-Cd Interaction on Tea Plants (Camellia sinensis (L.) O. Kuntze) Under Cadmium Stress" Agronomy 15, no. 1: 246. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15010246
APA StyleSun, Y., Zhao, Y., Zhou, H., Li, F., Wang, Y., & Du, X. (2025). The Regulatory Effect of Se-Cd Interaction on Tea Plants (Camellia sinensis (L.) O. Kuntze) Under Cadmium Stress. Agronomy, 15(1), 246. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15010246






